College Bio Midterm Review
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
electronegativity
the tendency for atoms to draw electrons toward themselves
electronegativity and covalent bonds
some atoms will "grab" the electron more in a covalent bond, some share it equally
polar molecule
have an uneven charge distribution while being electrically neutral, formed when atoms show strong electronegativity differences
non polar molecules
have even charge distributions, formed when atoms have similar electronegativity
ion
a charged atom or molecule
nucleus in an atom
contains protons and neutrons
atomic number
number of protons in an atom
atomic weight
protons plus neutrons
chemical bonding
process by which atoms becomes physically attached through electron exchange or sharing (involves valence electrons)
ionic bonding
transfer of electrons
covalent bonding
sharing of electrons
hydrogen bonding
a weak charge attraction between positive and negative charges
solute
a substance that is dissolved in a solute
solvent
the substance in which the solute is dissolved
reference solvent for polar molecules
water (H20)
reference solvent for non polar molecules
liquid fats (oils)
hydrophilic
loves water (polar)
hydrophobic
hates water (non polar)
acid
any molecule that releases a proton (H+) in water solution
base
any molecule that absorbs a proton in water solution
pH
a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a water solution
pH 7
neutral
pH < 7
acidic
pH > 7
basic
buffer
any molecule that can act as an acid or base, minimizes pH shifts in solutions
definition of organic chemistry
the chemistry of carbon, hydrogen, and any atom that can replace a hydrogen around a carbon
number of bonds in a carbon containing molecule
four
hydrocarbons
nonpolar, consist entirely of C and H, building blocks of all other organic molecules
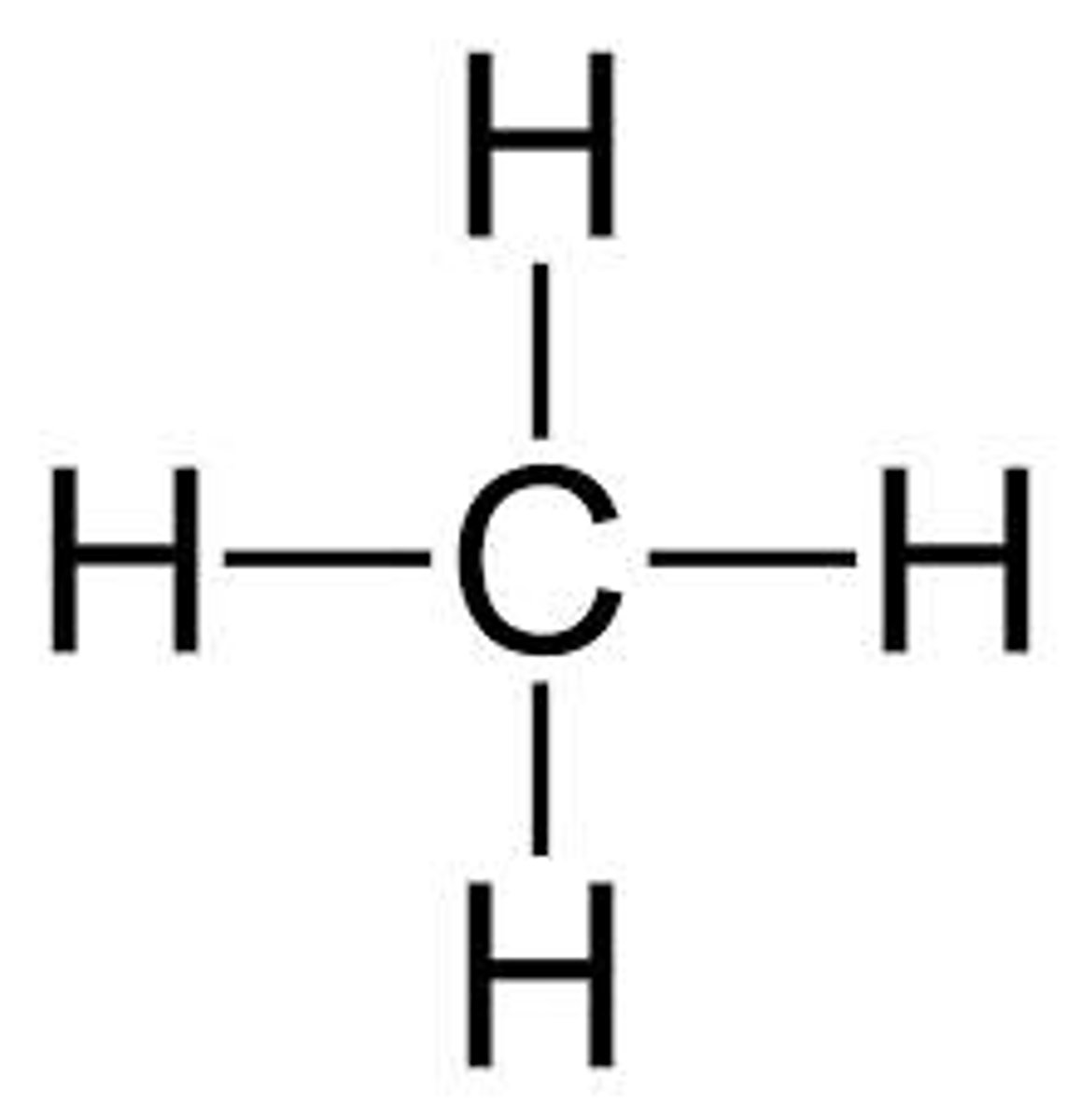
hydrocarbons functional group
methane
alcohols
polar, modified water molecules
alcohols functional group
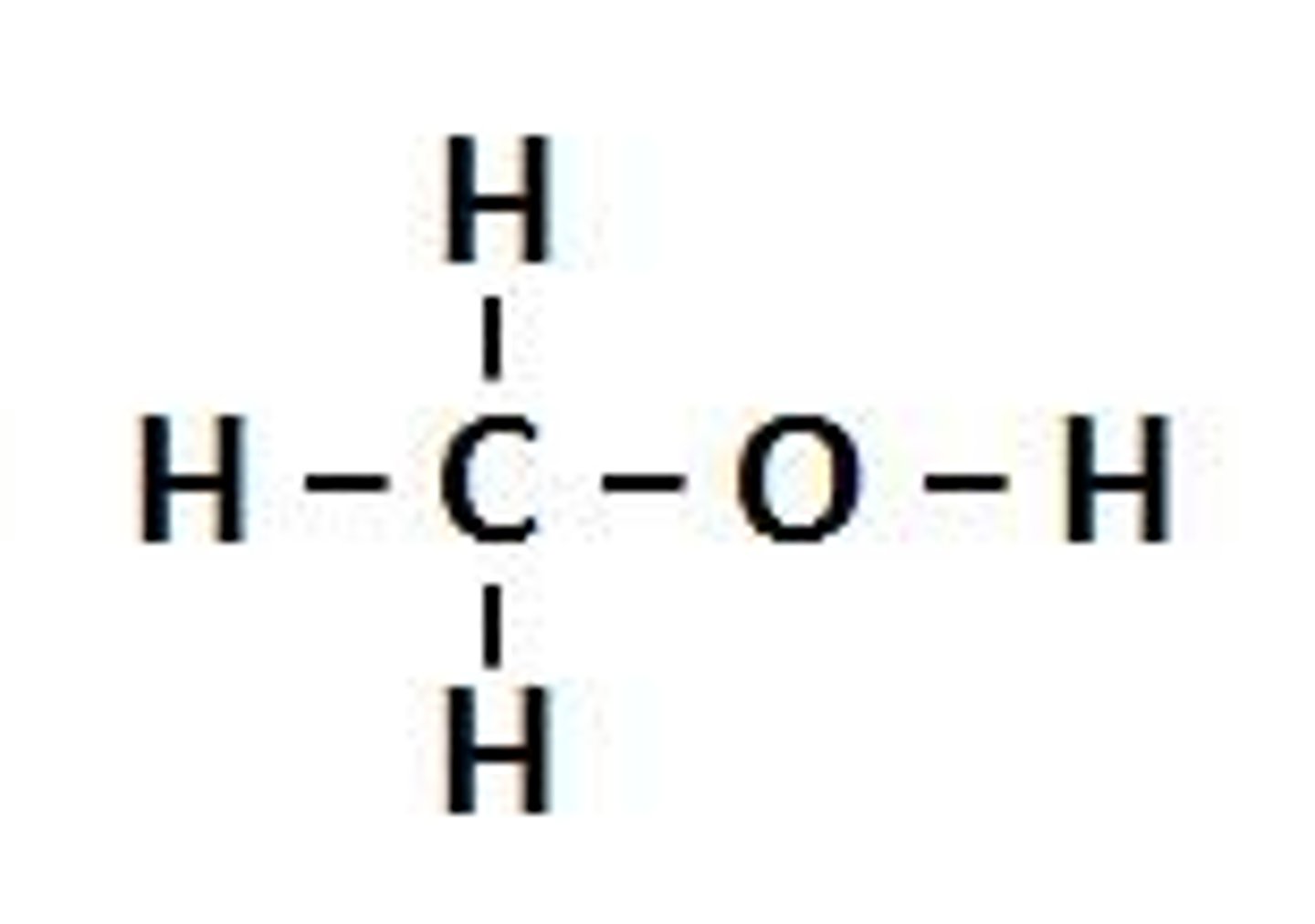
special case of alcohols
waxes are large multicarbon alcohols that do not dissolve in water because they have large hydrocarbon tails
amines
polar, modified ammonia molecules, can be powerful bases
amines functional group
C-NH2

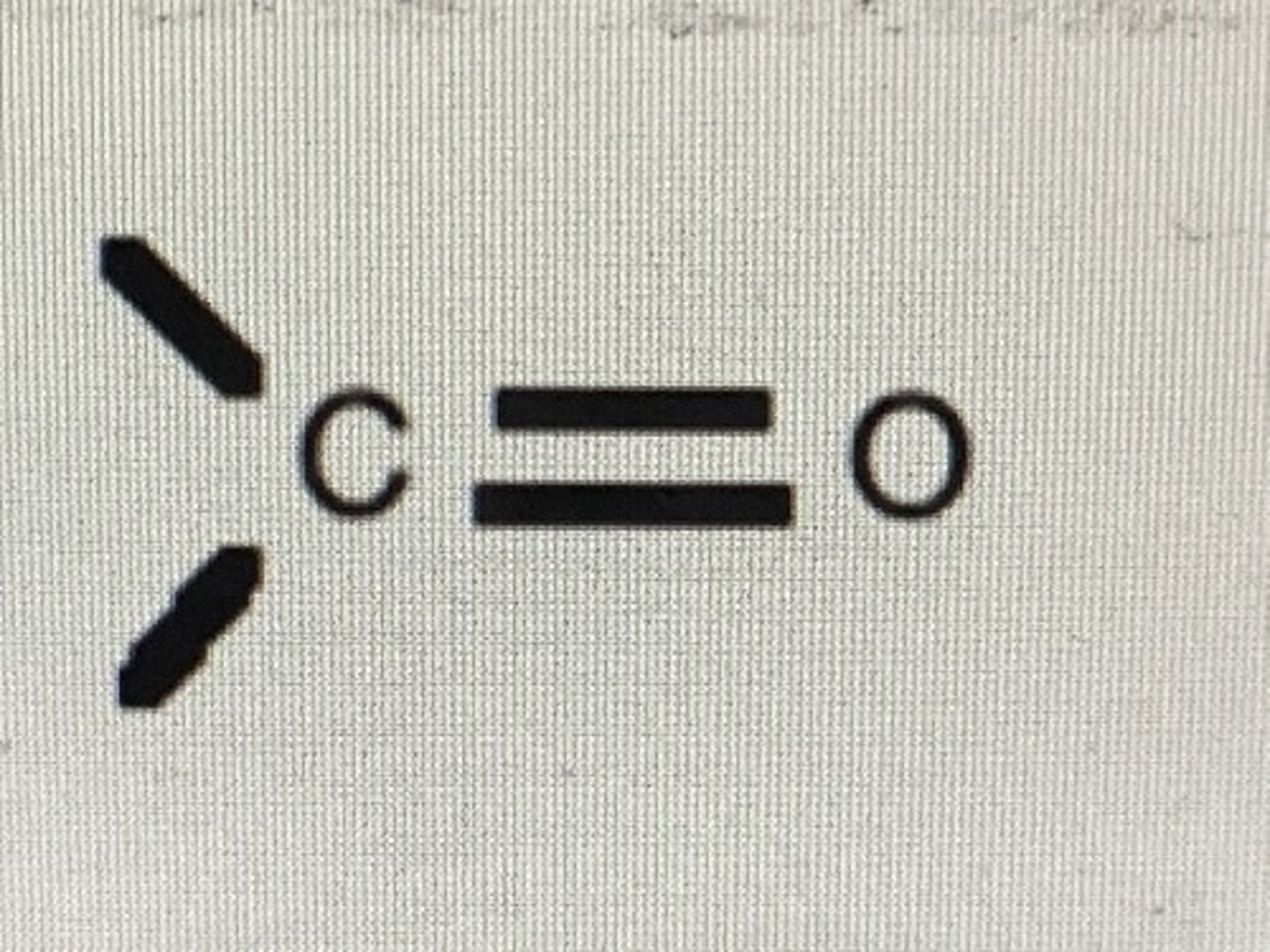
aldehydes and ketones
polar
aldehydes and ketones functional group
carbonyl
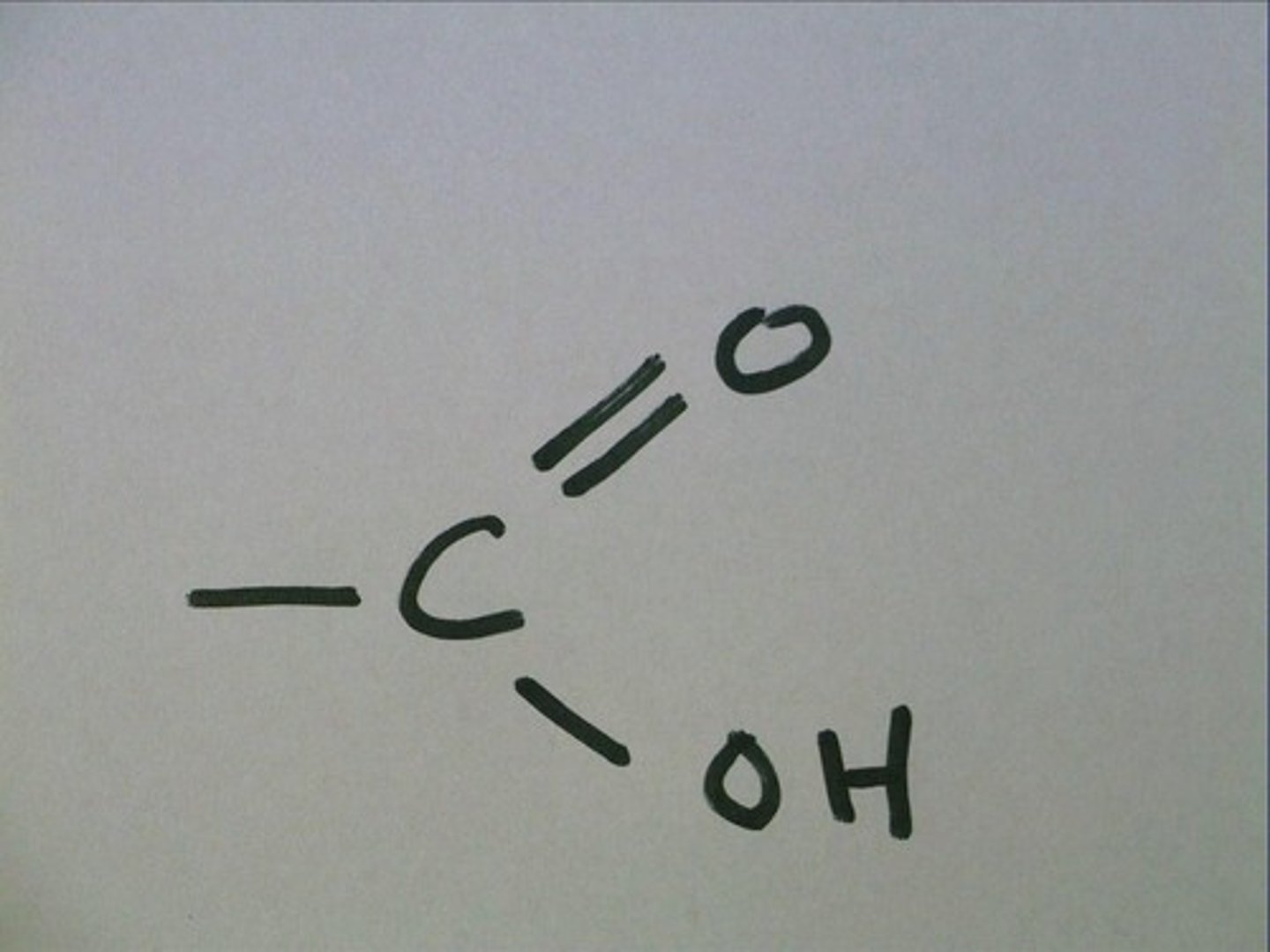
carboxylic acids
polar, weak acids
carboxylic acids functional group
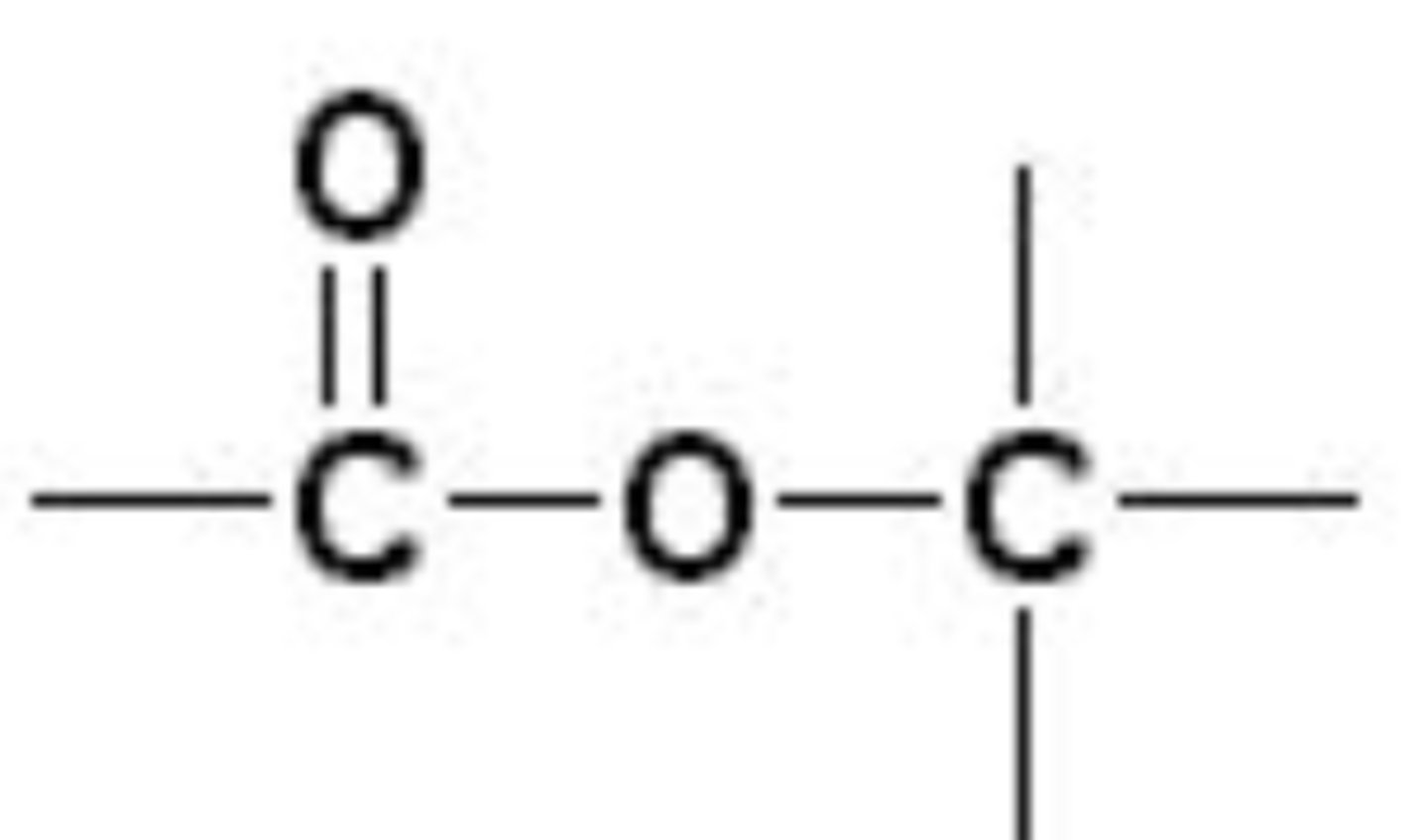
esters
non polar, combination of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, fats are special cases, formed by dehydration, responsible for scents and flavors
esters functional group
carbohydrates definition
polyhyrdoxy aldehyde or ketone, aka sugars
biologically important carbohydrates
have 3-7 Cs (triose, tetrose, pentose, hexose)
monosaccharides definition
single hexose units
disaccharides definition
two conjoined monosaccharides
glucose
monosaccharide
-universal cell food
-found in honey and maple syrup
fructose
monosaccharide
-found in all sweet fruit and corn
galactose
monosaccharide
-found in milk only
sucrose
disaccharide
-cane or table sugar
-composed of a glucose and a fructose
maltose
disaccharide
-found in dark grains
-composed of two glucoses
lactose
disaccharide
-found in mammal milk
-composed of a glucose and a galactose
hexose polymers
fructose: fructans
galactose: galactans
the 2 glucose polymers
two glucose polymers
starches and celluloses
starches
-animals (glycogen)
-plants (starch)
-purpose: glucose storage
-amylase: enzyme that breaks up glucose for use
celluloses
-purpose: structural material
-used by plants to build bark, wood, leaves, etc
cellulase
enzyme that breaks down cellulose into glucose, made by bacteria
lipids definition
esters that are made of an alcohol called glycerol and 1-3 large carboxylic acids (aka fatty acids)
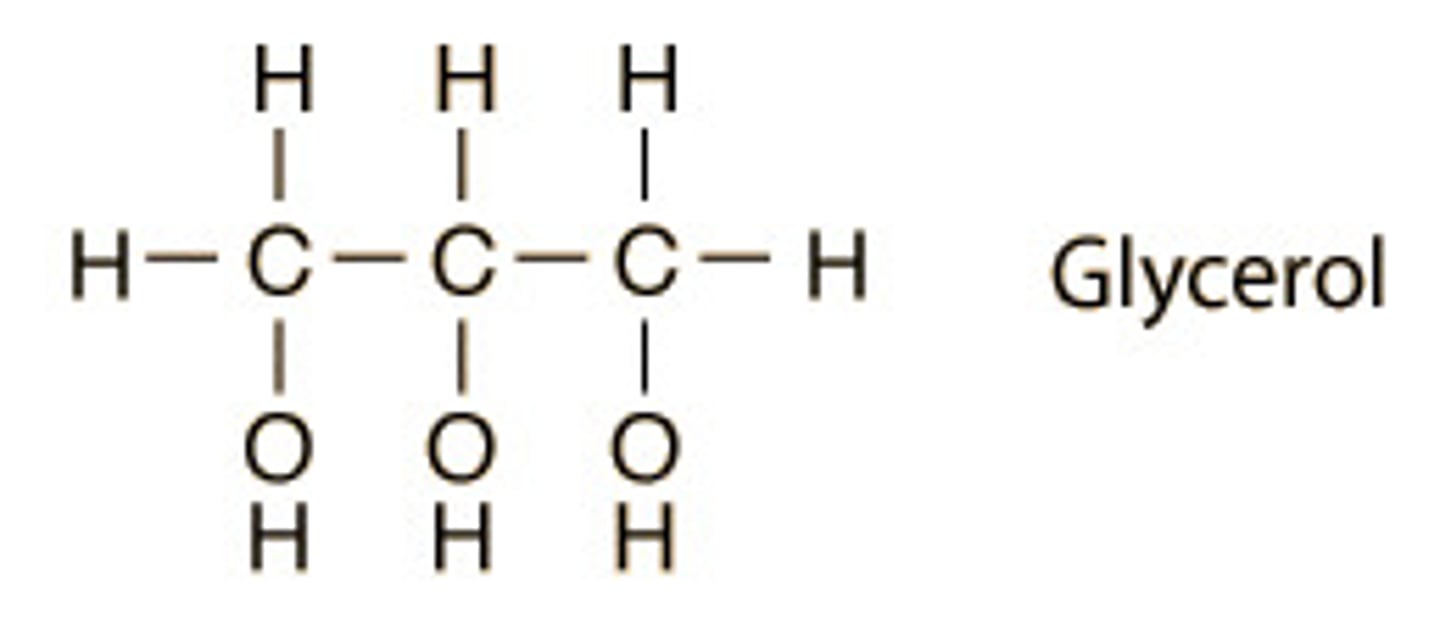
glycerol
3 carbon alcohol
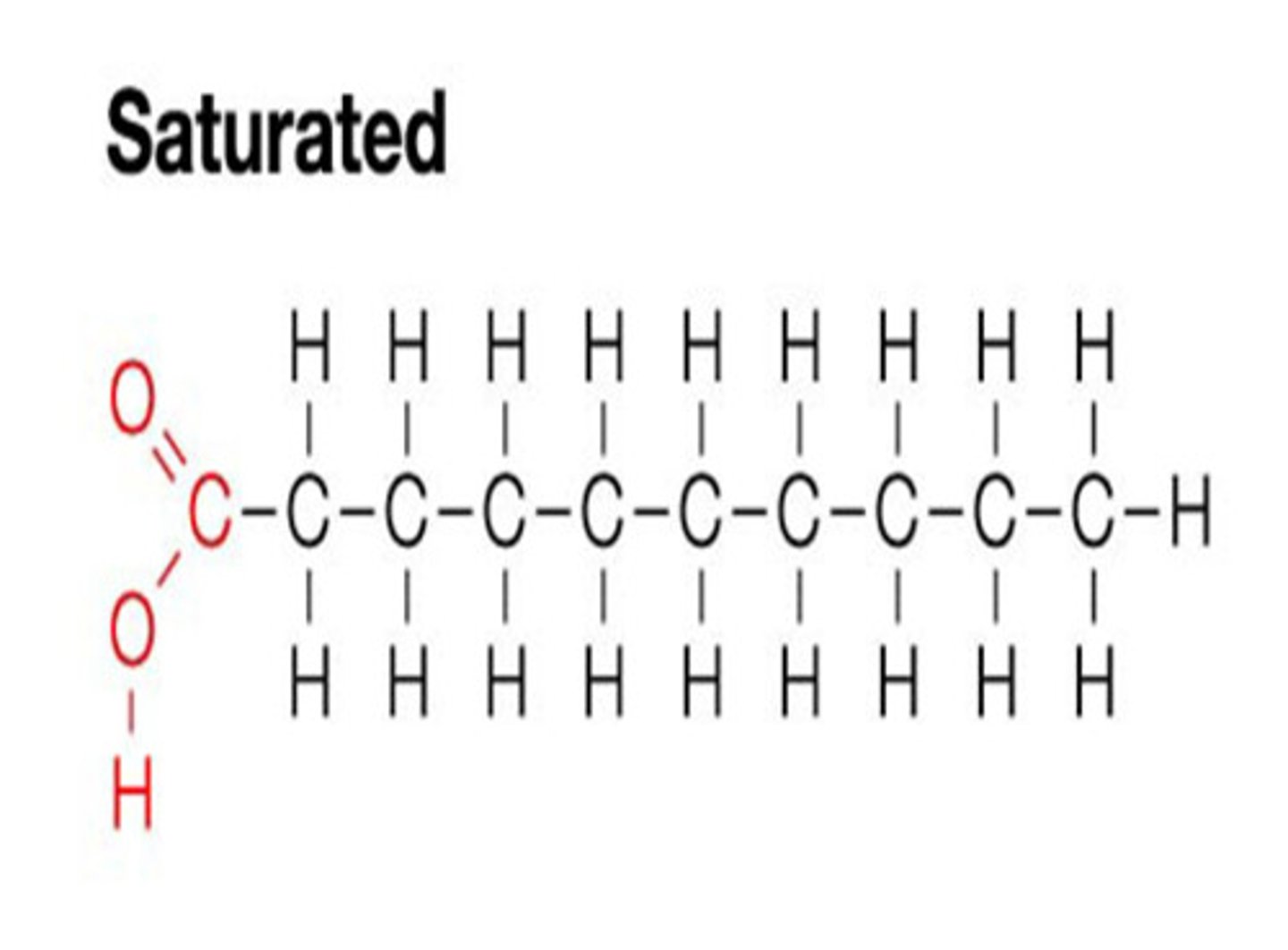
fatty acids
large 10-28 C carboxylic acids
basic lipid
mono acyl glyceride
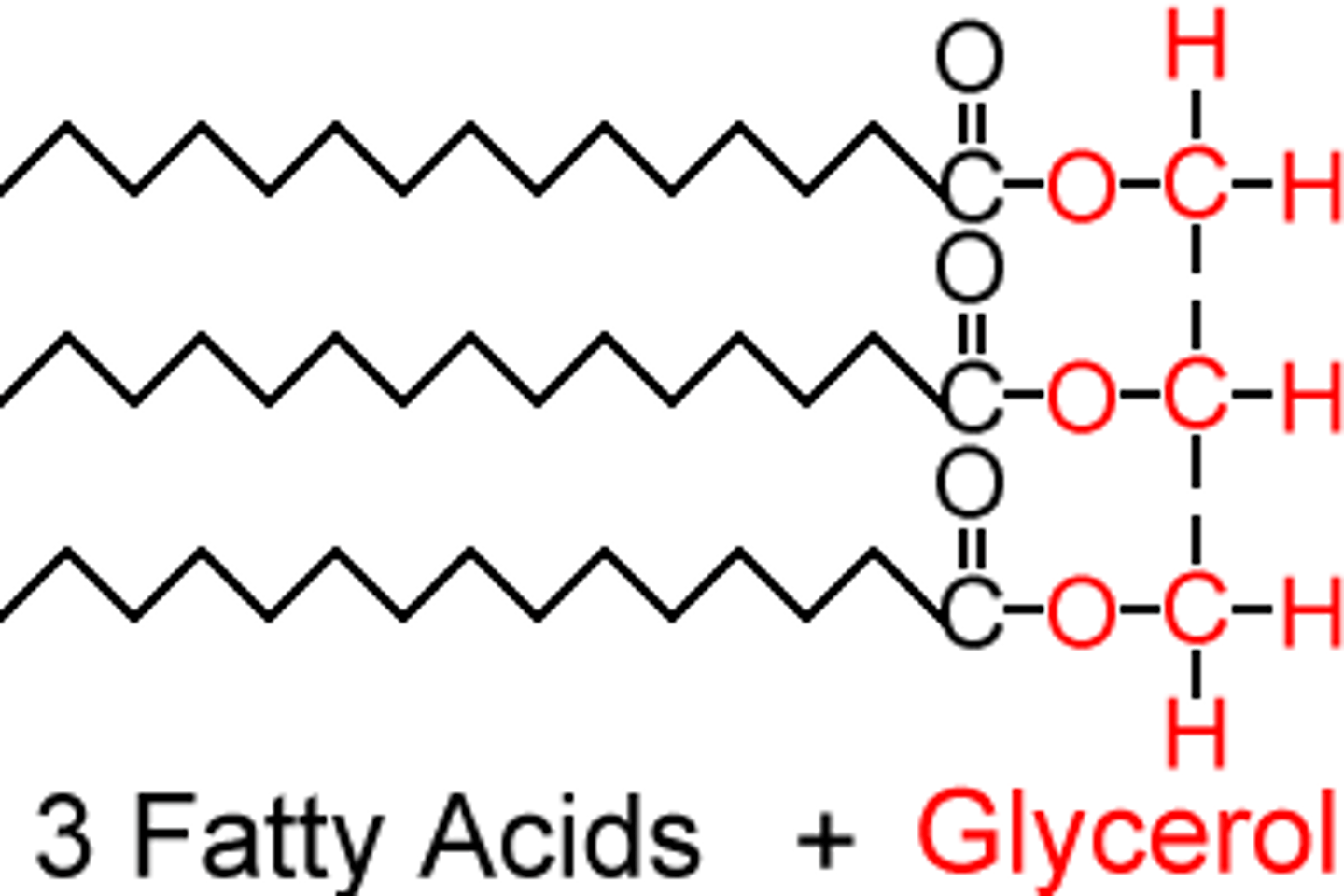
saturated vs unsaturated lipids
saturated: no double bonds, solid
unsaturated: has double bonds, liquid
double bond in saturation
double bond has the potential to absorb hydrogen, double bonds create kinks that make it harder for molecules to stick together (liquids)
lipids biological significance
building blocks of cell membranes, used for long term energy storage, high energy density
carbs vs fats energy storage
carbs are used for short term energy short falls, fat is used longterm to prevent starvation
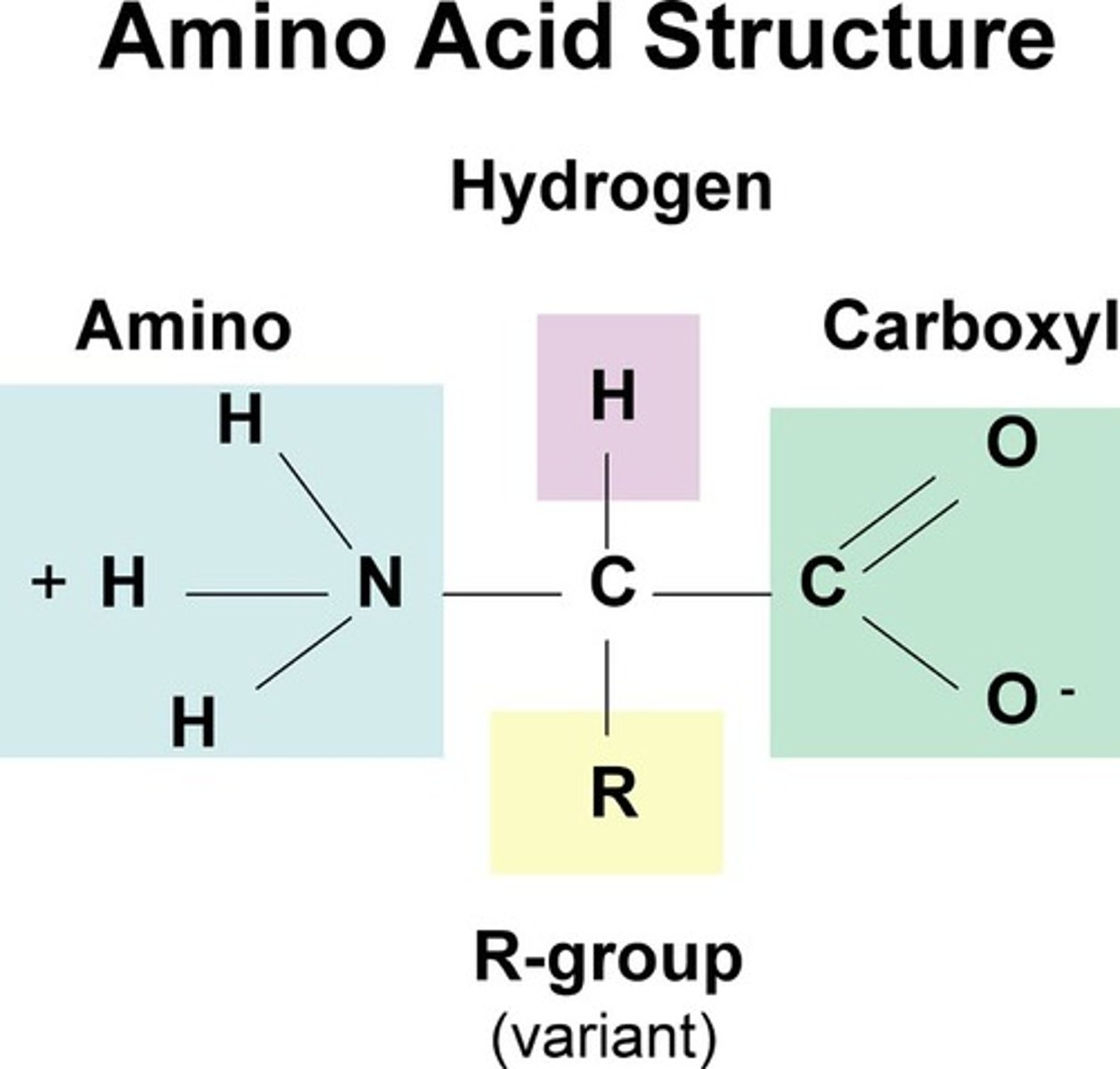
amino acid definition
monomers of proteins, all have the same generic structure
amino acid structure
R group can be anything
number of amino acids used by living things
20
three R group categories
nonpolar, polar uncharged, charged
charged R groups
can be negative or positive, can switch between neg and pos from pH shifts
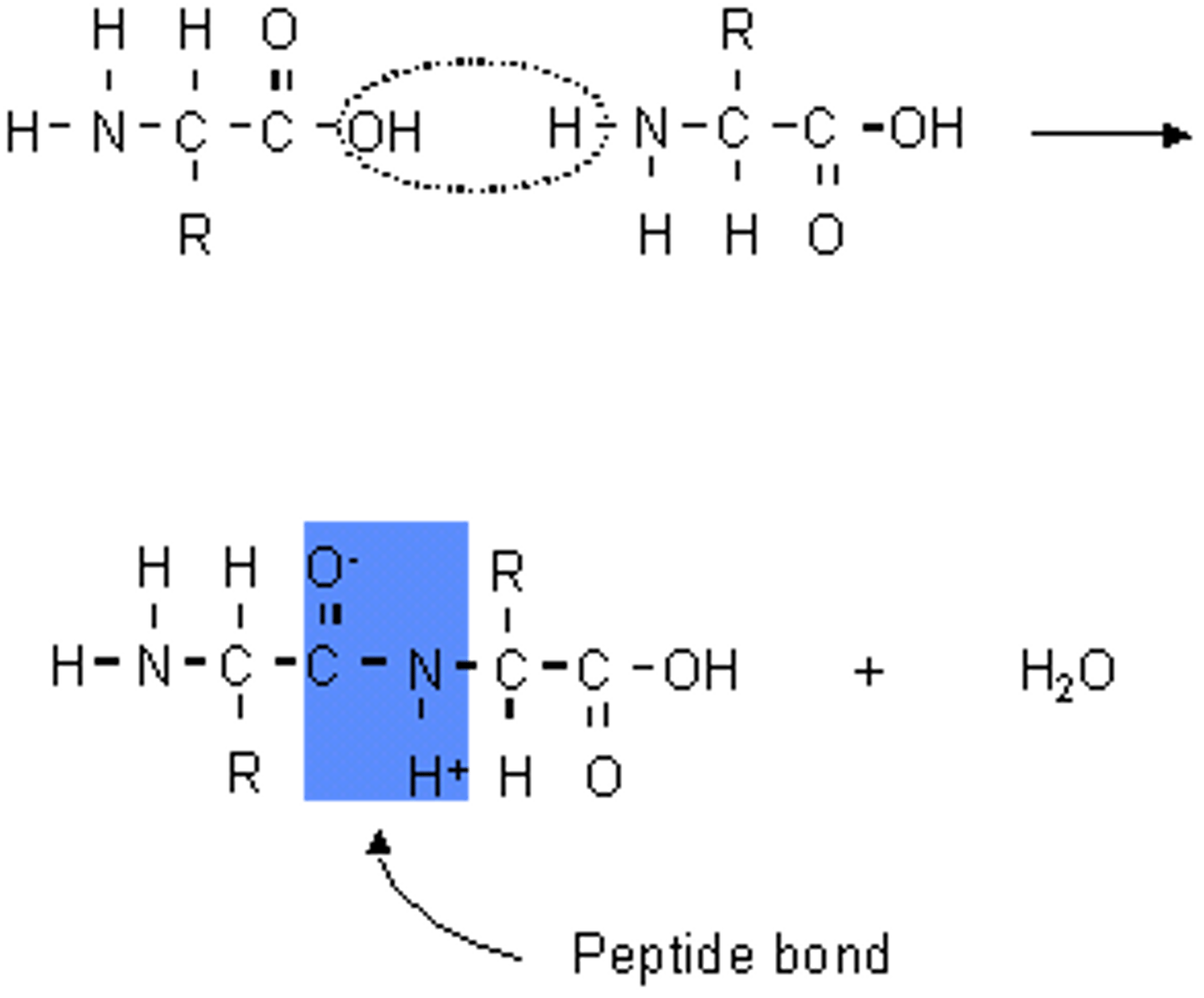
dipeptides
two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond
peptide bond
proteins definition
amino acid polymers
three structural levels of proteins
primary, secondary, tertiary
primary structure
amino acid sequence
secondary structure
hydrogen bond interactions between amino acids in the protein chain, leads to simple 2D or 3D shapes
types of hydrogen bond interactions
alpha helices and pleated sheets, polar parts stick together with h bonds
tertiary structure
complex 3D structures produced by R group interactions, determines a proteins functional properties
quaternary structure
two or more proteins joined to form a superstructure, Ex: hemoglobins
protein denaturation
process by which external physical factors disturb the 3D structures of a protein, protein is not broken
important denaturing factors
excessively high temperatures (cause vibrations), excessive pH (alkaline or acidic), excessive salinity
biological significance of denaturation
denatured proteins are usually altered for the worse, can be reversible or irreversible
common example of denaturation
cooking
nucleotide generic structure
phosphate-pentose-nitrogenous base
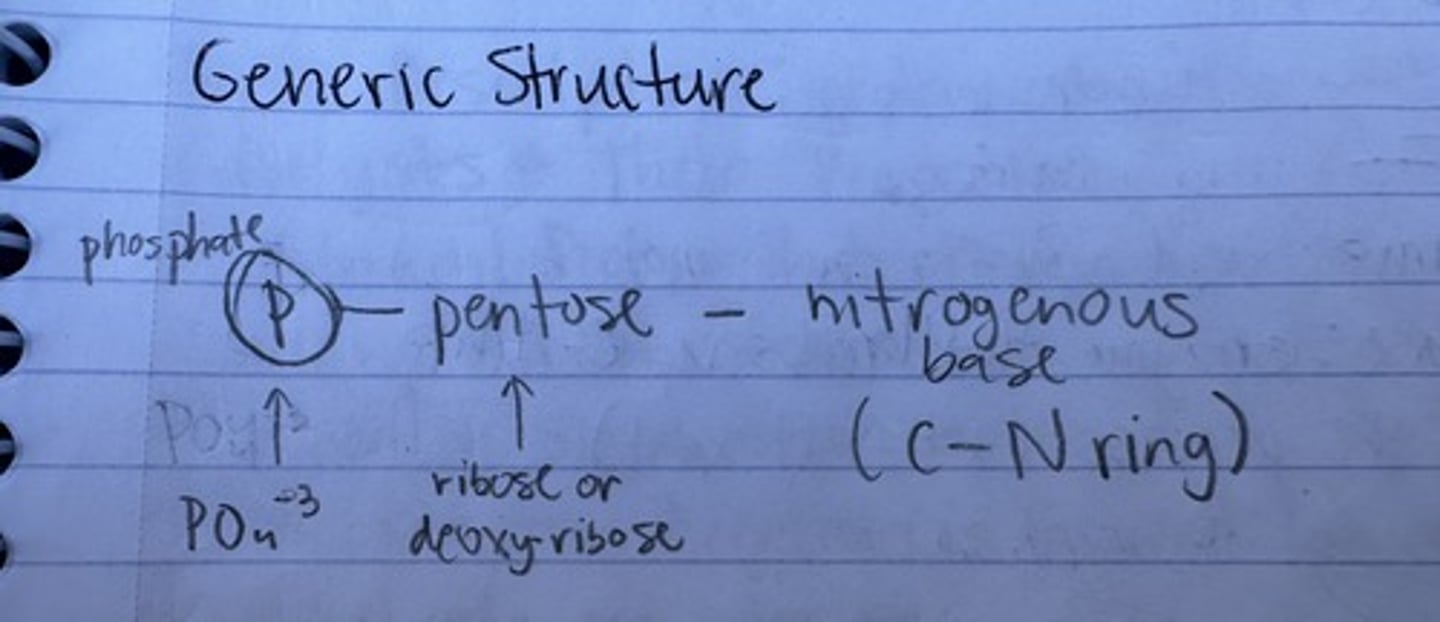
two pentose variations
ribose or deoxyribose
ribose vs deoxyribose structure
deoxy is missing an OH
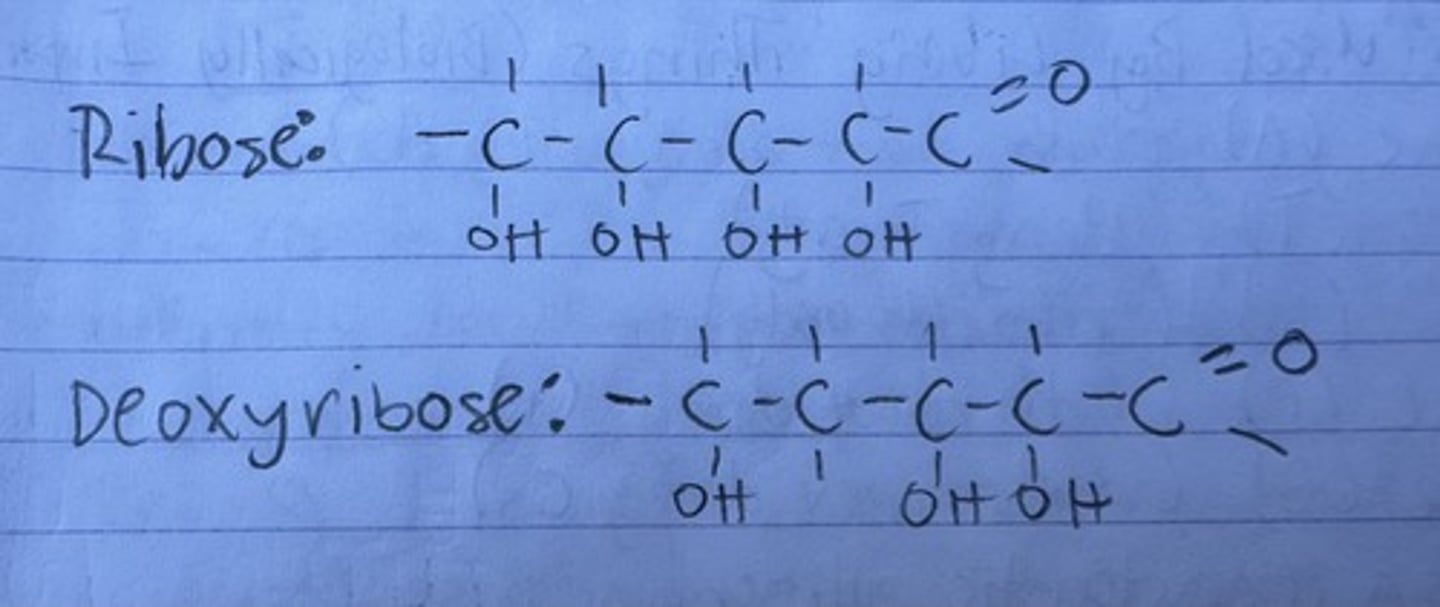
two nucleotide base types
purines and pyrimidines
five biologically important types of nucleotides
adenine (A)- both
thymine (T)- deoxy
uracil (U)- ribo
cytosine (C)- both
guanine (G)- both
hydrogen bond nucleotide combos
nucleotides can selectively h-bond thru their bases
A-T, A-U, C-G
important single nucleotides
ATP and C-AMP
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
P-P-P-pentose-base
second bond is loaded with energy and wants to break to form energy

C-AMP (cyclic AMP)
C-AMP diesterase- enzyme that breaks up C-AMP
caffeine stops the process (anti relaxant)
enzymes definition
protein catalysts
catalysts and their properties
chemical factors that change reaction rates without being used up in the process, usually speed them up, no reaction direction is favored, they are selective
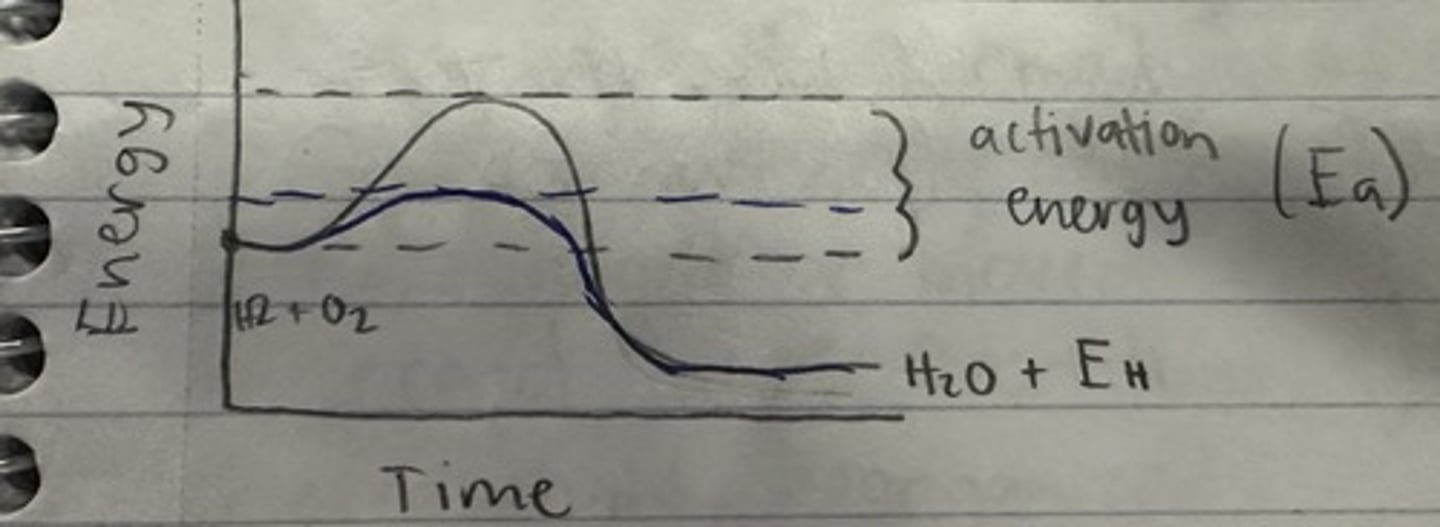
energy model of catalyst
less activation energy is needed with catalyst
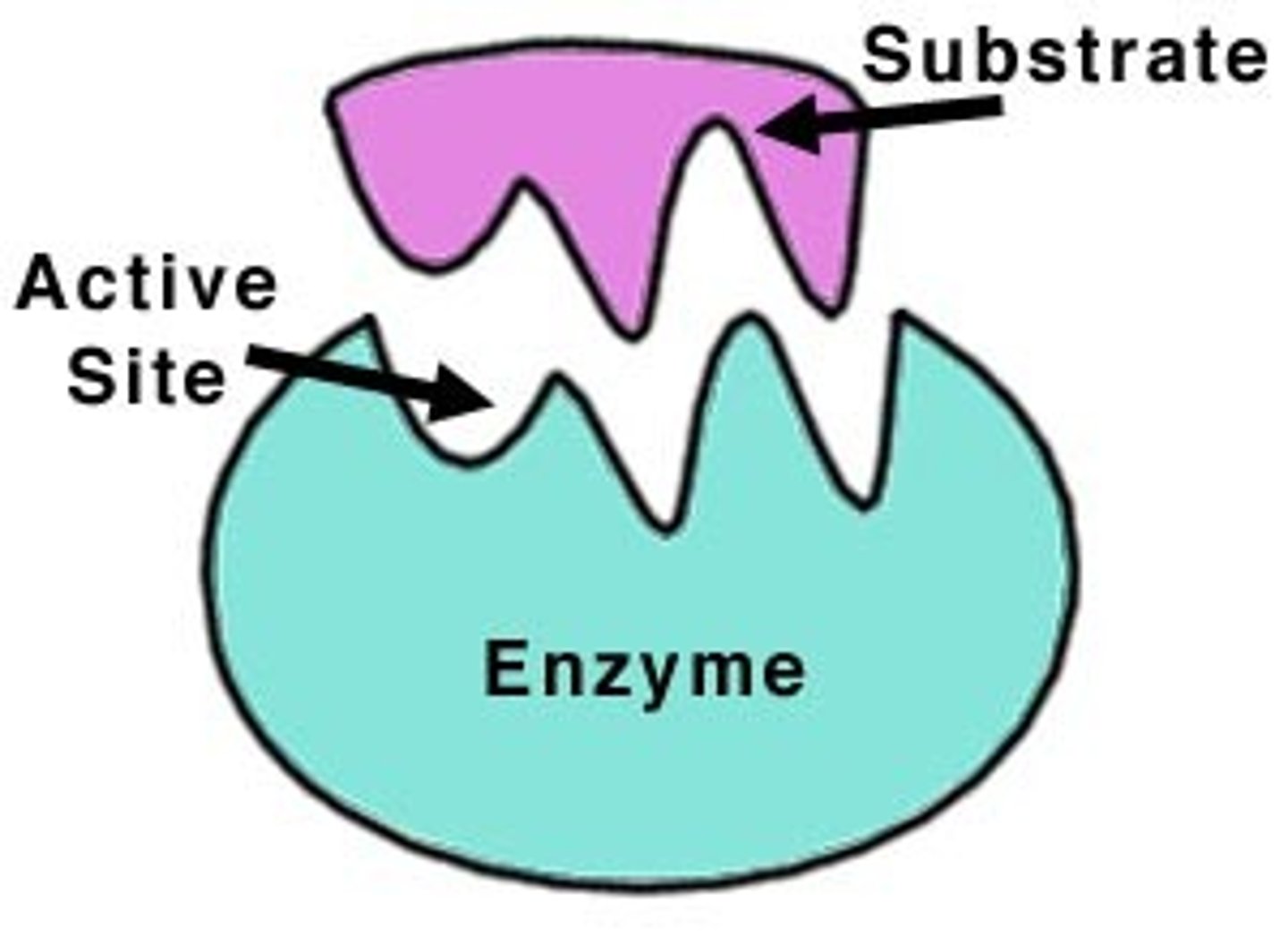
lock and key model of enzymes
substrate is shape compatible with the binding site
substrate imitators
agonists-trigger at least a partial enzyme response
antagonists- bind to binding site, but trigger no enzyme response
substrate binding
authentic substrates, agonists, and sometimes antagonists weakly bind to binding site and may release and reattach repeatedly
competitive competition mechanism
overwhelming amount of antagonists surrounds and outcompetes the substrates, enzyme is activated by dramatic increase of substrates
allosteric regulation mechanism
allosteric site is a secondary binding site that influences the primary binding site, secondary substrate binds to secondary binding site and activates the primary binding site
substrate cleavage mechanism
chops the substrate to stop an enzyme response, ex: pesticide sprays shut down acetylcholinesterase to make muscles constantly contract, acetylcholine doesn't get chopped so reaction never stops
substrate negative feedback mechanism
an enzyme produces its own competitor to limit itself and slow down reaction, reaction continues once competitor is absorbed by cells