urinalysis 1.5
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
clean all spills with
10% bleach or approved disinfectant
reagent labeling requirements
received date, opened date, expiration date
parallel check the lot number
reagent QC requirements and storage
QC each shift, at least 1x per day
oldest reagent should be used first
how often does proficiency testing happen (external QC)
3x per year
refractometer QC
daily
do cleaning and documentation
semiannual correlation with dipstick specific gravity method
how often should instrument QC be?
every shift/day/week/month/year
when are specimens processed?
ASAP
QC Centrifuge
check RPM and record 2x each year
check timer 2x each year
QC room temp and humidity
measured daily
take corrective action if outside of acceptable range
QC refrigerator/freezer
record temps daily and in specified ranges
how long is reporting/documentation saved?
at least 2 yrs unless electronic
anisotropic definition
directional dependent
light, wood, metal, etc.
birefringent definition (pos/neg)
ability to bend light
Positive: rotates plane of light clockwise
negative: rotates plane of light counterclockwise
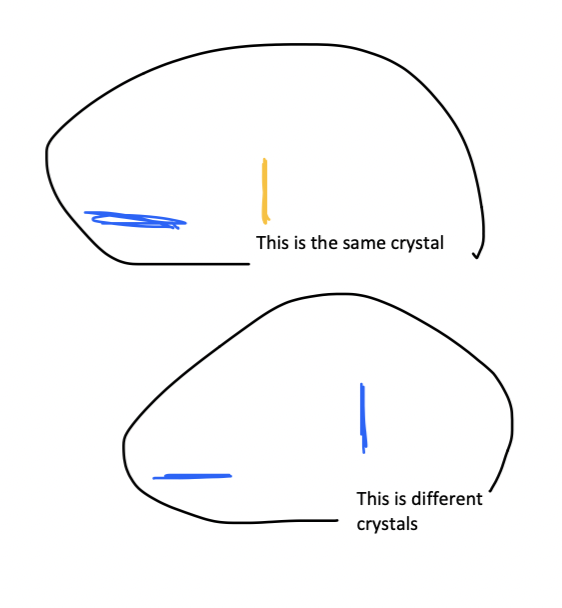
how does a polarizing microscope compensator work?
allows differentiation of
Ca pyrophosphate (+)
monosodium urate (=)
how does polarized light work?
it vibrates in only 1 direction/plane. substances that aren’t optically active allow light to pass through unchanged.
type I, II, III water
purified, reagent grade, distilled
polarizing filter used for what
allows light vibrating in east-west direction perpendicular to light path to pass to specimen
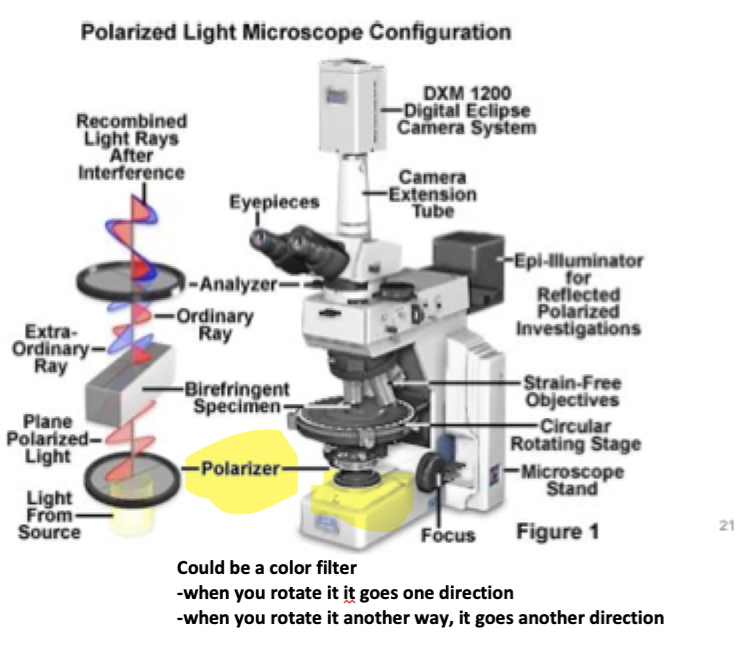
analyzer filter which light vibirates
only N-S direction can pass through
2 different QC materials (=,+)
=: can’t use distilled water
+: good QC has minimum RBC, WBC, etc
CLIA standard for QC material
test QC 1x per day
with new lot of QC, what to do with it?
parallel test each, recording lot #, expiration date, DAT, etc
QC how stable for how long?
little stability, 3-5 days
where is QC stored?
brown bottle because of bilirubin
if there are 2 instruments/methods, they must be corrected how often?
1x every 6 months to make sure both analyzers give the same/similar results
collection technique for random void
24-32 oz water 2 hrs before, random “clean catch”
usually need daily collection for 3-5 days
may not be accurate
midstream clean catch technique and purpose
clean external genitals, void at first and then collect the middle of the pee
purpose: eliminate contamination
catheterized urine technique
inserted into urethra and in bladder, gather in sterile bag, may causei infection
suprapubic aspiration technique
collect directly from the bladder with needle + syringe for bacterial cultures
pediatric urine collection technique
“wee bag,” check every 15 min
timed collection technique
used for quantitative assays, usually 12 or 24 hr gap due to exercise, circadian rhythm, hormones, proteins, GFR
urine kept in fridge/ice
benefits of first morning urine specimen
Immediately after sleep, urine is collected for metabolic analysis
optimal detection (nitrites, proteins)
RBC/WBC/Casts stable in urine
cytology studies: usually more epithelial cells
cell components and casts due to high osmotic environemnt
timed urine 9 collection errors
improper timing
2 first morning urine specimen
filled to the brim
discarded part of specimen
improper measurement
transcription error in volume
mixing up specimens
inadequate preservative
discarded all of urine
most common urine preservatives (when you don’t measure right away)
refrigeration 4-6°C
boric acid preservatives in urine tubes
***organic things in urine
Hyaline Cast (Tamm Horsfall), Creatinine, Urea
****inorganic things in urine
some ions? maybe some sodium
***components present in urine and blood
RBCs, albumin, creatinine, glucose, hemoglobin, myoglobin, protein?
yellow (colorless, straw, yellow, dark yellow, amber)
normal urine color
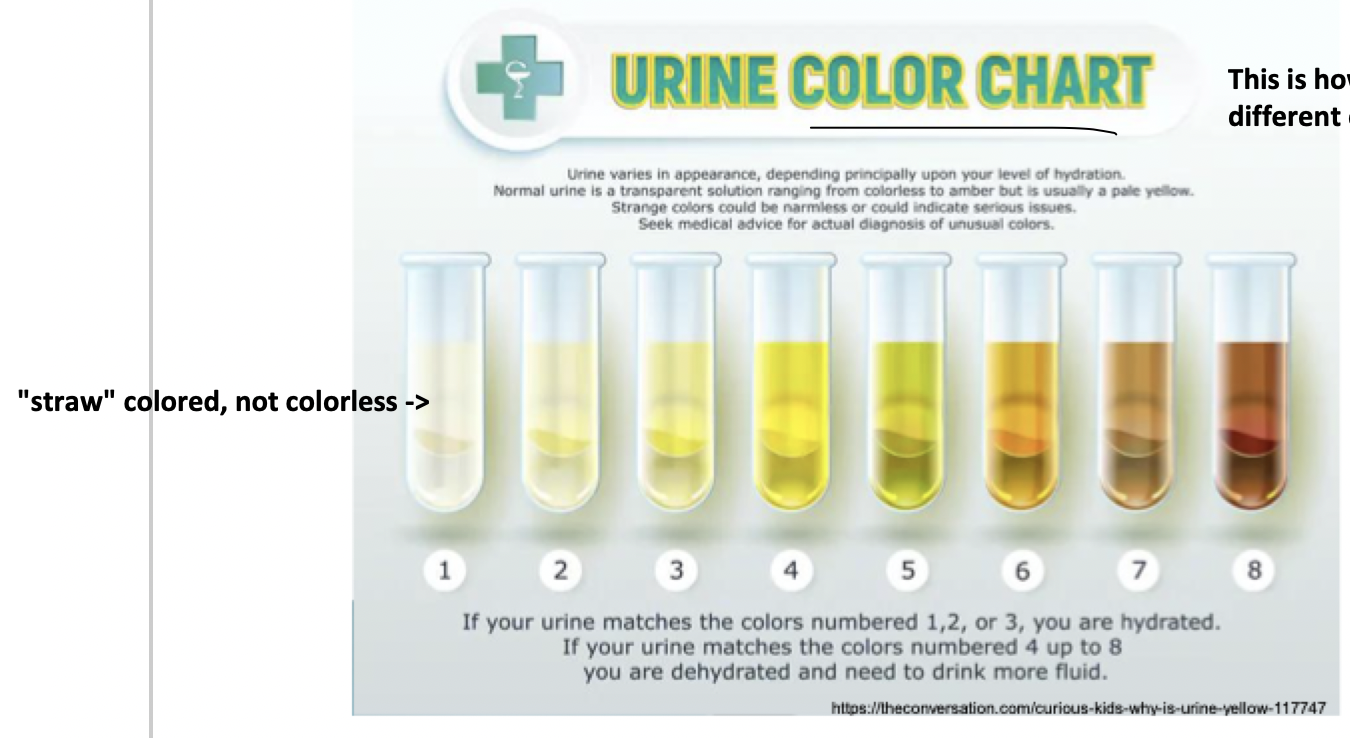
abnormal urine clarity
hazy, cloudy, turbid
should be well-mixed and uncentrifuged to view
yellow color of urine from
urochrome
urobillin
uroerythrin
epithelial cells, mucus, and fecal material can ____ normal urine if not collected properly
Cloud
cloudy specimens may contain what?
crystals, amorphous urates/phosphates
phosphates and carbonates
acidic urines (amorphous urates
RBC, WBC, bacteria
Fat- milky
Sperm
infection (bacteria/yeast/trichomonas)
what abnormal things can urine have?
glucose, protein, ketones, lysed cells
bacterial infection with WBC and [casts/no casts]
casts: upper UTI (kidney)
no casts: lower UTI (bladder/urethra)
normal urine smells like
faintly aromatic
ammoniacal odor of urine happens because
urea sits too long and breaks down ammonia
Pus, protein decay, bacteria
fruity urine smell
diabetes (ketones)
“mousy” urine smell
asparagus
foul urine smell
infection
bleach urine smell
FAKE specimen
what happens if you shake a urine specimen containing bilirubin or albumin protein?
bili: yellow foam forms, it dissipates when standing
albumin: white foam forms, not dissipating
cloudy red urine vs clear red urine
cloudy: Acidic urines - amorphous urates (uroerythrin on urates)
clear: blood in urine
what happens if phenazopyridine (AKA____) is in a specimen?
pyridium, azo dyes, azo gantrisin, axo, gantanol
turns a specimen orange, causing false positives
black/brown urine caused by
disease/drugs/diet
bilirubin, hematin, methemoglobin, melanin, homogentisic acid (tyrosine metabolite
amorphous phosphates vs urates
urates: pink precipitate, acidic
phosphates: white precipitate
***how to test amorphous phosphates and urates
test within 2 hrs, crystals precipitate out in the cold temps
osmolality determines what?
solutes present in water volume, shown as specific gravity/osmolality
osmolality gives more information
proper storage of reagent strips
once opened, expiration date changes
keep out of sun
write received and opened date on container, monitor contamination comparing colors
DON”T MIX STRIPS from different containers
no bleach
reagent strip technique
horizontal position
timing
adequate light
hold strip close to container chart
preventing reagent strip discrepancy
read at correct time, don’t touch test areas, do confirmatory tests
premature reagent strip deterioration caused by
protect against heat, light, moisture
reagent strip image

purpose of confirmation tests
they’re more sensitive than the dipstick test for whatever you’re trying to get more info from
specific gravity vs refractive index
SG: includes all the solutes, both ionic and nonionic
reagent strip: only measures SGionic
Refractive index: shows everything
how to calibrate a refractometer
use water to calibrate at 1.000
Refractometer correction Glucose
Corrected specific gravity = SG – (0.004)(glucose g/dL)
Refractometer correction Protein
Corrected SG = SG – (0.003) (protein g/dL)
osmolality formula
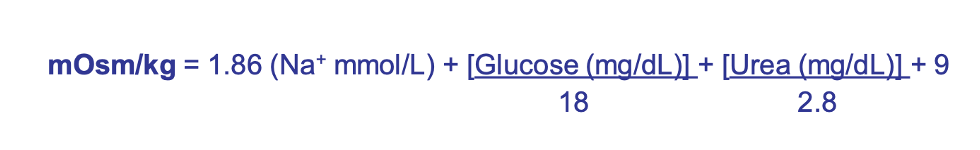
isothenuria urine specific gravity
1.010
you lost the ability to concentrate
what 3 things can cause wrong results for pH?
improper storage with bacterial growth
container contamination
improper technique
what can cause a false positive SG?
moderate protein and ketones
what can cause a false = SG?
buffered alkaline urine
non-ionizable substances (comparing to refractometer)
what can cause false + nitrites
in vitro conversion: bacterial contamination, bad storage, delayed testing
medication: phenazopyridine/azo dyes
what causes false + leukocyte esterase
substances that color urine: nitrofurantoin, bilirubin, phenazopyridine
vaginal contamination
strong oxidizing agents
elevated glucose (>3 g/dL)
high specific gravity
oxalic acid
high albumin/protein (>500 mg/dL)
antibiotics: cephalexin, cephalothin, tetracycline, gentamicin
ascorbic acid
CAUSES what??
what causes false = leukocyte esterase
menstrual/hemorrhoidal contamination
strong oxidizing agents (sodium hypochlorite, H2O2)
soaps and detergents
microbial peroxidases
CAUSES what??
what causes false + blood
high SG
high glucose/protein
antibiotics
unmixed specimen
high nitrites
ascorbic acid
CAUSES what?
what causes false = blood
what causes false + protein
buffered/alkaline urine
phenazopyridine, bleach
what causes false = protein
non-albumin protein
what causes false + ketone
free sulfhydral group (amino acid cystine, mecaptoethane sulfonic acid used in cancers, N-acetyl-cysteine used for acetaminophen overdose)
high pigmented urine
ketone false =
improper handling of urine
heat, moisture, light
what can cause hypostenuria (low SG) readings?
<1.010
diabetes insipidus causes impaired antidiuretic hromone (ADH) function
can’t concentrate urine
high water intake
what can cause hyperstenuria (high SG) readings?
>1.010
adrenal gland insufficiency
hepatic disease
CHF
why measure urine pH?
to modify diet/manage disease
emphysema/respiratory disease
diabetes mellitus
starvation
dehydration
diarrhea
acid-producing bacteria
high protein diet
cranberry juice
medication (methionine)
CAUSES what?
acidic urine can reveal what?
hyperventilation
vomiting
renal tubular acidosis
urease-producing bacteria
vegetarian diet
old specimen
CAUSES what?
alkaline urine can cause
what’s alkaline tide?
after eating a meal, urine is more alkaline
pH urine strip reaction
Methyl red and bromthymol blue double-indicator system
Methyl red: pH 4.4-6.2. -red-> yellow
Bromthymol blue: pH 6-7.6 -yellow-> blue
what’s paradoxical aciduria?
metabolic alkalosis where the distal tubule secretes potassium in exchange for sodium
pH confirmatory test
pH meter if needed
SG reagent reaction
pKa of polyelectrode decreases proportionally to urine ionic concentration
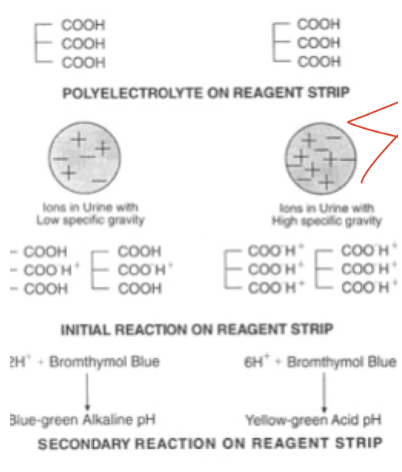
SG confirmatory test
refractometer
nitrite reaction
Lower urinary tract infection
Fecal contamination from intestinal bacteria E. coli
G+ enteric pathogens causing UTI have this.
nitrite confirmatory test
urine culture
Leukocyte Esterase reaction
reacts with neutrophils responding to bacterial infections (Trichomonas, Chlamydia, yeast)
Esterases catalyze hydrolysis of derivatized pyrrole amino acid ester to liberate 3-hydroxy-5-phenyl pyrrole (5-member ring)
Pyrrole + diazonium salt= purple product
leukocyte esterase confirmatory test
Microscopic analysis of sediment
Gram stain
Urine culture
bilirubin reagent reaction
Diazonium salt coupling in the reagent pad with bilirubin in an acid medium
Forms azo dye azobilirubin
Light tan → beige/pink
(0.5 mg/dL)
protein reagent reaction
Tetrabromphenol blue changes to blue-green if a proten is present
Reagent pad has a buffer to keep pad at pH 3.0
protein confirmatory tests
Electrophoresis, IFX, nephelometry, turbidimetry, radial immunodiffusion
blood reagent reaction
Tetramethylbenzidine and a peroxide in the strip. Peroxide is reduced, and the chromogen is oxidized to test the heme pseudoperoxidase activity
Yellow -> green dots from RBC
blood confirmatory test
Correlate with macroscopic, plasma color
80% ammonium sulfate
- Hgb precipitates OUT, = for blood
- Myoglobin soluble, still + for blood