ecology (copy)
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
population
a group of organisms of the same species populating a given area -species make up populations which then make up communities -studied by examining geographic range, growth rate, density/distribution, & age structure
population distribution
describe the way individuals are spaced out across their range
clumped population distribution
-packed closely together -can help animals avoid predators -school fish, flocking birds

uniform population distribution
-individuals are evenly spaced -individuals compete w/ one another for space or resources -orchard, penguins
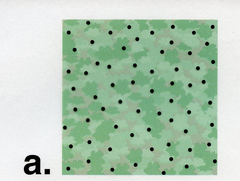
random population distribution
-individuals spaced out unevenly -when the location of an individual in a population is independent of others -trees, dandelions

limiting factor
anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing
density dependent factors
limiting factor that depends on population size -competition -predation -parasitism and disease -food/resource availability
density independent factors
limiting factor that affects all populations, regardless of population size -unusual weather (affects food chains and food webs) -natural disasters (tornadoes, hurricanes, etc.) -human activity (destruction of habitat, introduction to non-native species)
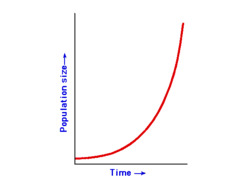
exponential growth
occurs when population size increases dramatically over time
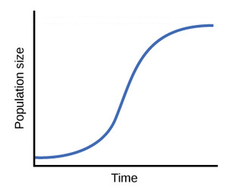
logistic growth
begins with period of slow growth followed by a brief exponential growth before leveling off at a stable size
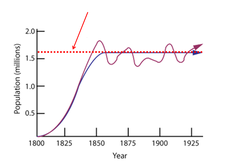
carrying capacity
the largest population that an area can support -when a population goes over carrying capacity, density-dependent factors affect it greatly.
population growth
determined by the birth rate, death rate, immigration rate, and emigration rate.
population +/- equation
birth+immigration - death+emigration
birth/death rate
-more deaths = population decrease -more births = population increases
immigration
movement of individuals into an area w/ an existing population -more immigration = population increase -speed of immigration/emigration depends on species' speed, travel distance, & if human activity moves them around/ (squirrels immigrating in search of food, population +)
emigration
movement of individuals out of a population -more emigration + population decrease -speed of immigration/emigration depends on species' speed, travel distance, & if human activity moves them around/ (local food shortage causing emigration, population -)
biotic factors
are living factors in an ecosystem (plants, animals, insects, fungi, bacteria, etc.) -predation -parasites
abiotic factors
nonliving factors in an ecosystem (terrain, temperature, humidity, precipitation, etc.) -weather
niche
range of physical and biological conditions under which a species lives (its role in the community) -how it uses all its resources
neutral relationship
neither species directly affects the other (fox on grass)
interspecific competition
competition between members of different species for limited supply of resources (food, shelters, mates, etc.)
resource partioning
two species divide a niche to avoid competition -interspecific competition -negative effect on both species (anteaters)
competitive exclusion
two species in the same community cannot share the exact same niche -interspecific competition -negative effect on both species (lion vs hyena)
predator-prey relationship
the interaction between 2 different species where one hunts and feeds on the other -predator stops the prey from overpopulating
(hunted is prey, hunter is predator)
predation and herbivory
an interaction in which one organism kills another for food -good for predator, bad for prey (shark/seal, cat/mouse, panda/bamboo)
symbiosis
species living closely together (interactive relationship)
commenalism
-symbiotic relationship -good for one species, neutral for the other (whale/barnacle, bird nesting in a tree)
mutualism
-symbiotic relationship -good for both species (bee/flower)
parasitism
-symbiotic relationship -good for one species, bad for the other (dog/flea)
succession
a series of predictable events that occur overtime -an ecosystem is destroyed but comes back
primary succession
ecological succession that begins in an area where no community previously existed -total destruction
examples of succession not occuring as it normally should
-deforestation -animal endangerment (hunting) -maintaining a lawn -climate change
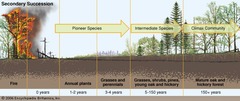
pioneer species
first species to populate an area during primary succession
secondary succession
type of succession that occurs in an area that was only partially destroyed -partial destruction
climax community
final stage of succession, in which the community is stable -collection of most stable organisms (resembling goal of succession)
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem -ecosystem diversity, species diversity, and genetic diversity
why is biodiversity important?
-maintains healthy biosphere -provides natural resources (food, water, etc.) -natural services (water purification, pest control, etc.) -ecosystem resilience (ability to recover after a disturbance
human population growth
exponential growth
keystone species
species that exert strong effects on the community (wolves in yellowstone, coral)
tolerance
range of conditions an organism can survive & reproduce in (can be true for animals, plants, etc.)