ER Med - Pa
Resuscitation
Non shockable :
pulseless electrical activity
asystole
Shockable :
pulseless ventricle tachycardia
VFib (can’t have pulse)
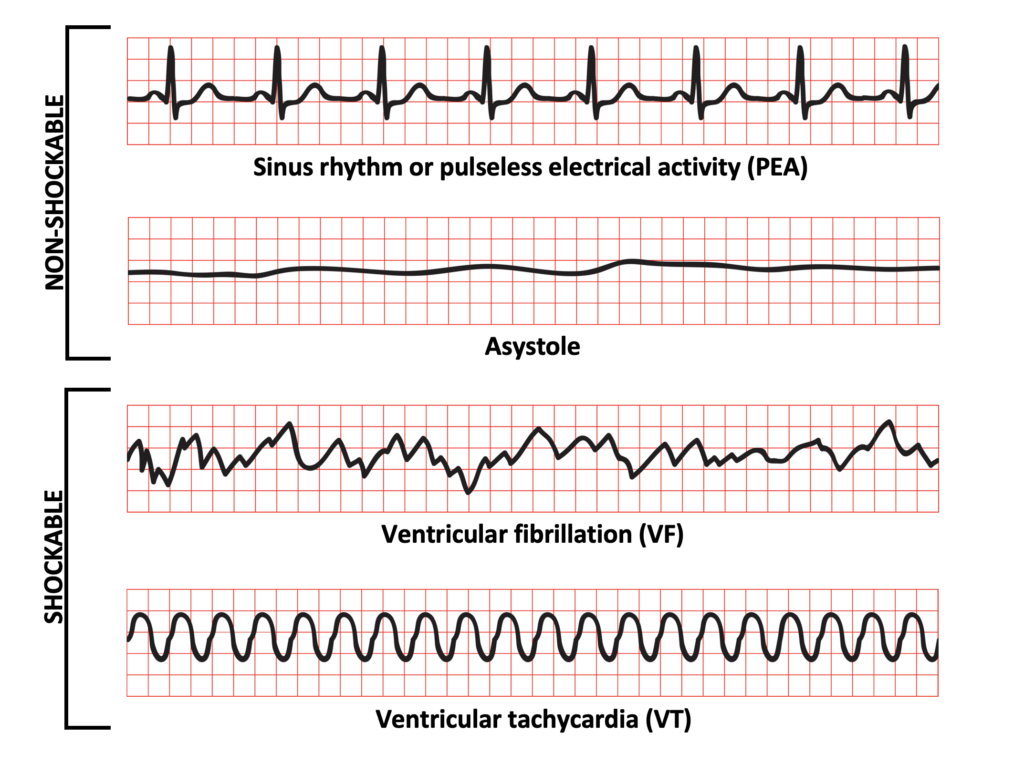
Pulse VT - cardioversion → 70-120J, sedate patient, up to 3 shocks, shocks must be synchronous w/ r wave
Supraventricular tachycardia → try Valsava first (blow into syringe), adenosine
CPR:
Check for breathing - for 10s (look, listen, feel)
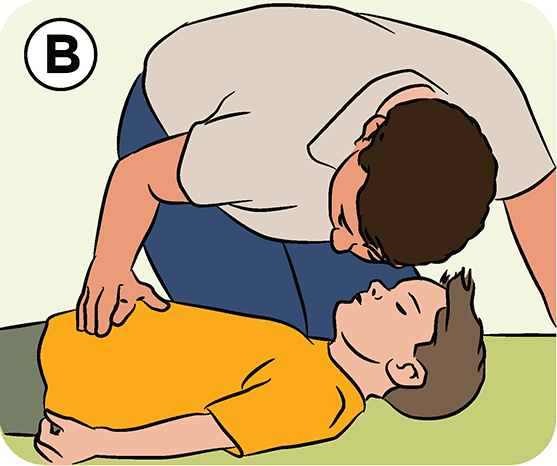
30 compressions
- depth 1/3 of thorax
- let thorax refill
- lift fingers of other hand so pressure is on palms
- lower half of sternum

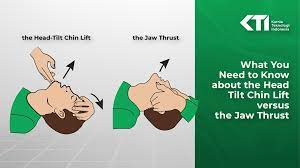
2 ventilations - head lift, chin lift IF NO TRAUMA
- 2 fingers on chin, 1 palm on forehead
- if cervical spine lesion -> jaw thrust, 3 fingers behind mandible, palms on face, thumbs on mandible, lift it forwards and push chin down
<2s to stop compressions when checking rhythm during defib
Pacemaker - 8cm from device (@ scapula)
Pulse - use central pulse (femoral, carotid)
Resus Protocol
If shockable : 1mg ADRENALINE + 300 → 150mg AMIODARONE every 4m, after 3rd + 5th shocks, bag mask then intubate
If non-shockable : 1mg ADRENALINE (to bring back to shockable rhythm), then every 4m (even if it becomes shockable), immediate intubation
20-30m → stop maneuvers
If shockable → continue Resus
* after switching to advanced ventilation - 10 breaths/m
If pulse back → check breathing
If <6 breaths/min continue ventilating, until 12breaths/min
Check abnormal lung sounds
How to check if ventilation works - check co2
sudden increases ETCO2 (>45mmHg) after initiation CPR → sign of ROSC
If cant get IV access - IO (tibia or humeral head)
Airway Desobstruction:
Partial : encourage cough
Severe (silent) : 5 back blows, 5 abd thrusts - repeat until unconscious -> cardiac arrest → Resus
* McGill forceps for solid removal
stridor - inspiratory, by obstruction at laryngeal level or above
wheeze - expiratory, by obstruction of lower airways
gurgling - by l or semisolid foreign material
snoring - pharynx occluded by soft palate or epiglottis
crowing - sound of laryngeal spasm
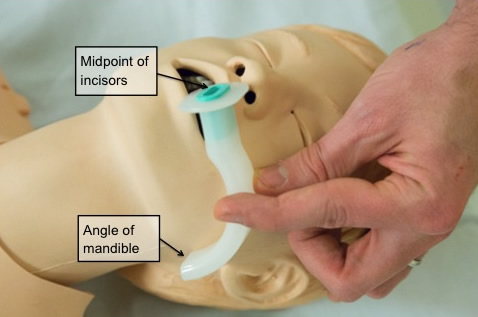
In conscious patients - nasopharyngeal Wendel → hold like pen, into nostrils
CO in trauma
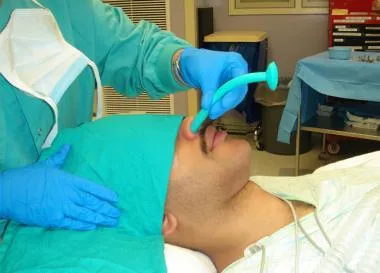
In unconscious patients - oropharyngeal Guedel pipe
measure it
insert other way then rotate

Venturi mask (w/ colourful valves) - constant o2
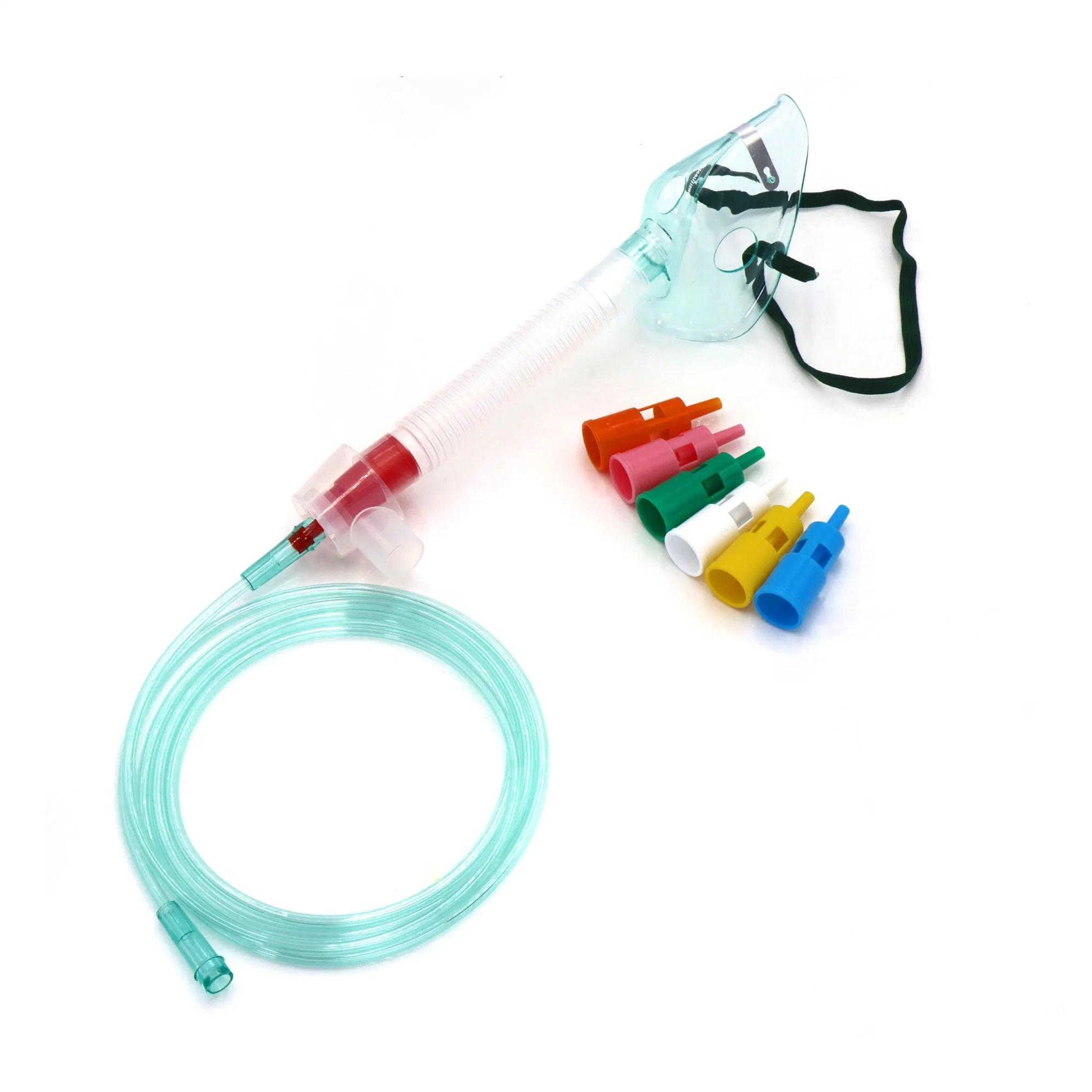
Mask w/ bag
CO - copd
Ampi bag (yellow band around neck)
Wendel pipe (nasopharyngeal) - palliative

Laryngeal mask (brown), i-Gel (green) - preferred to bag-mask
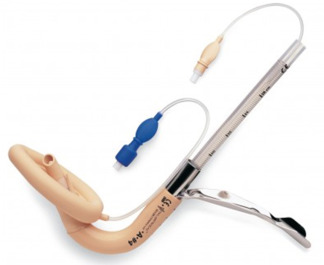

Combitube (tube 1 blue, tube 2 smaller)
Make letter C w/ fingers to push mask on face, letter e lifts chin
Pregnant woman: Patient in left lat decubitus (15-20d) to remove p from IVC
belly @ umbilicus - 20w
fundus of uterus bw umbilicus + sternum - 25w
fundus to diaphragm, belly occupying abd - 30-34w
Intubate asap (big risk aspiration reflux)
Same drugs + shocks
If after 5 min of advanced resuscitation -> peri-mortem c-section if after 20w (call neonatologist and obgyn)
Drowning: 5 rescue breaths asap
Same maneuver for cardiac arrest (dry chest first)
Intubate asap (high risk aspiration)
Immobilize c spine with c-collar if suspect trauma
Hypothermia:
32-35 - rewarm, rewarmed saline in 2+ big IVs (urinary catheter, nasogastric tube, infuse normal saline). blankets
28-32 - mild, warming, cardiac arrest (?)
<28 - severe, chest drains, wash pleural space with saline, peritoneal wash
Gold standard - ECMO (hemodialysis for hypothermia)
Move patient carefully (can cause arrhythmias), remove clothing
Try 3 shocks without break bw, and if it doesn't work then don't shock until 30° → Double dose and double time - 2mg adrenaline 6 @ 10m
Can't give drugs or shocks under 30°
Osborne sign on ecg - sinus bradycardia
No resus if patient under snow for hrs
Electrocution: Lesion like burn (on hand), lesions of heart, m, n, bones
Risk arrhythmias
Cardiac arrest - monitor -> defib, intubate (drugs + dose the same)
C-spine collar
Protocol - liquids (crystalloids), atb
Toxins: no mouth-mouth, don’t go in facility, certain ppl take patients out
Alcohol - metabolic acidosis, hepatic + renal failure -> ER dialysis
CO - give O2 high flow, get ABG (carboxyhb), dizziness, vomit, red face, coma, seizure, arrythmias
Pills - if <1.5h do gastric lavage
- gastric lavage within an hour, activated charcoal 1g/kilo
- nasogastric tube if altered mental status, charcoal nasogastric
Antidotes:
Paracetamol - acetyl cysteine
Opioids - nalaxone
Benzos - flumazenil
Organophosphates (farmers w/ salivation, lacrimation, big urinary output, wet, diarrhea) -> atropine, repeated until dry
Ca+ channel blockers - give Ca+
Tricyclic antidepressants - sodium bicarb
Dialysis for substances
Burns: Immediate intubation, Parkland fluid amount (first 5h give half, 18h second half)
Check int bleed trauma (signs - shock, pain, tenderness, swelling around area)
Moist covers + gels
Infection:
Check procalcitonin (sepsis), lactate >4mmol (sign of hypoxia and low perfusion)
Stable - antipyretics if temp
Unstable - 30ml crystalloids/kg bolus
Atb - ceftriaxone in first hr
Sepsis - fluids, vasopressors, NOR, atb, 2 hemocultures (within golden hour)
Anaphylactic shock:
Remove agent, ABCDE protocol, IV lines big caliber, meds (IM adrenaline every 10-15m until response→ hydrocortisone), cricotracheostomy if can’t intubate
Cardiogenic shock:
Due to MI, valve or m. rupture - heart can't pump
Treat infarction → PTCA (percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty), antiplatelets (aspirin, clopidogrel), O2 (<85), morphine until no pain, nitrates (not in inferior wall MI)
Treat dysfxn heart contractility→ inotropes (dobutamine), NOR
Neurogenic shock:
Hypotension, bradycardia due to spine injury
Treatment - surgery, inotropes, vasopressors
Obstructive shock: tension pneumothorax, tamponade, PE (→ give thrombolytics then prolonged cpr 90m)
Treat cause
Trauma:
First 5 s : check for
1. major bleed - press with hands, use tourniquet when it doesn’t work (5-7cm above bleeding point)
2. airway obstruction - take out, suction (Yankauer), Guedel pipe if under GCS 8, jaw thrust, O2
3. check if alive -> CPR
First evaluation: find all traumatic lesions that can kill patient in 30-40m
(ABCDE approach also done if ROSC)
Airway - look, hear (stridor in upper obstruction -> remove obstruction, snoring if tongue relaxed -> jaw thrust, wheezing in lower obstruction, gurgling if fluids -> suction, apply gurgle tube), cervical collar
Breathing - look, listen (10s), percussion, hands on thorax (rib fractures), auscultate, subcutaneous emphysema
- tension pneumothorax -> no sounds or movements on one side, jugular v distention, trachea deviated, bp decreasing, not responding to restoration v. or airway opening, hypersonority on other side, subcutaneous emphysema -> puncture 2nd intercostal on midclavicular line above lower rib THEN resuscitative thoracotomy midaxillary line 4th or 5th intercostal space, on upper margin of lower rib, atb
- massive hemothorax -> check w/ US (also eFAST), self saver kit, give blood from the hemothorax (massive transfusion protocol)
>1500ml drained - thoracotomy
*eFAST : pericardial tamponade + pneumothorax
* Chest tube insertion - bubbling is sign of air draining from pleura, persistent bubbling → broncho-pleural fistula
- open pneumothorax (penetrating wounds) -> seal it, 3 sided occlusive dressing, Asherman chest seal, intercostal catheter insertion
- flail chest - 3+ ribs broken bilaterally -> paradoxical chest movements, hypoxia, hypercapnia (>45mmHg) -> put tape around flailing parts
- tamponade -> US, muffled heart sounds, distended jugular veins -> syringe from epigastrium to left shoulder, aspirate epicardium
do pericardiocentesis if patient in peri-arrest or cardiac arrest w/ tamponade - 18-22g needle inserted to subxiphoid space, directed to left shoulder, once aspirated cannula is advanced to pericardial space
Beck’s triad - hypotension, increased JVP, muffled heart sounds
- airway rupture -> check w/ US, bilateral pneumothorax sign, drain
- major tracheo-bronchial injuries - careful intubation, 2 intercostal catheters to allow lung to fully inflate
- trachea midline? - deviated in tension pneumothorax
* Jugular vein distention = tamponade and tension pneumothorax
* don't remove c spine until final evaluation done (CT scan, imaging, conscious and says no pain)
Circulation - Bp, heart frequency, look for bleeding (by FAST), capillary refill on sternum (>3s), ECG, blood test
- give transfusion + tranexamic acid 1g in 10m then continuous on automatic syringe, O2, permissive hypotension, limited fluids/saline but 1:1:1 frozen plasma, thrombocytes, rbc, vasoconstrictors, BP no more than 80/90, x2 large bore IV access
IF hypovolemia (as source of cardiac arrest): initial fluid bolus 20ml/kg of crystalloid fluid
- massive hemothorax - needs the same, chest tube
- amputation -> traction splint
- pelvic - traction splint, pelvic binder, tranexamic acid, blood products, hypotension
Disability - pupils (reactive, intermediate size, bilateral), maintain sedation
- Glasgow under 8 → intubation
- verbal tactile and pain stimulus -> open eyes, how are movements
- if rxn only to pain -> GCS <8 (coma)
- glycemia
- cap refill (hold 5 sec, >3s too long)
Environment - temperature, toxins, modifications of skin, devices or foreign bodies, look for sites of possible hemorrhages
* HYPOTENSION : blood loss + tension pneumothorax
Secondary evaluation: see, touch, hear ; take history
1. Head - look, feel, palpate (for bone integrity, not if patient says they have face pain), pupils + eyes, small bleedings
2. Chest - look, palpate, percuss, auscultate
- modifications - integrity, crepitus, movements symmetrical/not
3. Upper limbs - keep alignment, splint, look at ability and colour
4. Abdomen - bruises, open wounds, liver or spleen rupture
5. Pelvic ring -> press front to back at iliac crest, lateral movements -> pelvic binder @ big trochanters level, controls abd bleeding, DRE
- bladder -> blood at urethral meatus, rupture urethra (CO for catheter), hematoma, high riding prostate -> post. urethral rupture
6. Lower limbs - look for sensation in feet, palpate pulse (femoral, popliteal, dorsal pedis), colour , bony palpation
- fracture → hemorrhagic shock, patient cry from severe pain, leg abnormally rotated, leg shortened -> immobilize
7. Roll-over - 3+ ppl, 1 person for head + commands, 2 others roll (1 on shoulder opposite to side, other hand on pelvic ring, other 1 on extremities and crossing over to pelvic ring)
- check back of skull (after temporarily removing collar) sensitivity of spine, palpation of spine, observing
C- collar - tell patient
- with right hand, measure with fingers on neck
Signs of head trauma - otorrhagia, retroorbital bruise, Battle’s sign (ecchymosis over mastoid)
Mobilizing
Scoop stretcher
- separate stretcher in 2 pieces, roll under back
- if patient on belly or lat -> mobilize head, put arm over head, stretch feet, place stretcher laterally, roll patient onto it
Vacuum splints - for fxs
- suction air out to mold onto limb
Closed fx - reduce before splint (grab proximal and distal joints and pull), give pain meds, check colour + pulse below splint, look for paleness, cyanosis, numbness
- never put bone back in
- give atb asap

4Hs 4Ts
Hypoxemia (hypoxia), hypovolemia, hyper/hypokalemia, hypothermia
Tamponade, tension pneumothorax, thrombosis, toxins
 \
\