2014 Biology and Physics College Entrance Exam Guide
1/543
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
544 Terms
What is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms according to cell theory?
The cell.
What are the two distinct types of cells?
Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
What is a key feature of eukaryotic cells?
They contain a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
What are examples of eukaryotic cells?
Fungi, protists, plant cells, and animal cells.
What is a key feature of prokaryotic cells?
They lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
What are examples of prokaryotic cells?
Bacteria and Rickettsiae.
What is the genetic material in prokaryotic cells?
One continuous, circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid.
What is the function of light microscopes?
To study stained or living cells, magnifying up to 1,000 times.
What is the function of electron microscopes?
To study detailed structures of a cell, magnifying up to 250,000 times, but only for killed specimens.

What are organelles?
Tiny structures within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, often referred to as 'little organs'.
What is the composition of the cell wall in most prokaryotes?
Peptidoglycan.
What is the significance of the development of the electron microscope in cell biology?
It allowed scientists to discover the functions and structures of cells.
What is the role of ATP in cellular energetics?
ATP serves as the primary energy currency of the cell.
What is photosynthesis?
The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
What is cellular respiration?
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
To enable cell division for growth, repair, and reproduction.
What are haploids and diploids?
Haploids have one set of chromosomes, while diploids have two sets.
Who is Gregor Mendel?
The father of genetics, known for his work on inheritance patterns in pea plants.
What is natural selection?
The process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
What is taxonomy?
The science of classification of organisms.
What are gymnosperms and angiosperms?
Gymnosperms are seed-producing plants that do not form flowers, while angiosperms are flowering plants.
What are the main systems studied in animal structure and function?
Digestive, respiratory, circulatory, lymphatic and immune, excretory, nervous, musculoskeletal, endocrine, and reproductive systems.
What is the biosphere?
The global sum of all ecosystems, where life exists.
What is human impact on the environment?
The effects of human activities on ecosystems and natural resources.
What is the primary function of ribosomes in a cell?
To manufacture all the proteins required by the cell or secreted by the cell.
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and their functions?
Rough ER (RER) is studded with ribosomes and synthesizes proteins for export, while Smooth ER (SER) lacks ribosomes and makes lipids, hormones, and steroids, and breaks down toxic chemicals.

What is the role of the Golgi bodies in a cell?
To modify, process, and sort proteins synthesized by ribosomes and package them into vesicles for distribution.
What is the function of mitochondria in a cell?
To convert energy from organic molecules into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy molecule of the cell.
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
A complex double-layered structure made up of phospholipids and proteins, with hydrophobic fatty acid tails facing inward and hydrophilic phosphate heads facing outward.
What is the significance of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
It is the control center of the cell, directing cellular activities and housing hereditary information (DNA) organized into chromosomes.
What is the nucleolus and its function?
The most visible structure within the nucleus, responsible for making ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assembling ribosomes.
What is the role of lysosomes in a cell?
To carry digestive enzymes that break down old organelles, debris, or large ingested particles.
What distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells regarding ribosomes?
Prokaryotic cells have smaller ribosomes compared to those found in eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of flagella in prokaryotic cells?
To help them move.
What is the composition of the plasma membrane?
It is composed of phospholipids and proteins.
What is the shape and characteristic feature of mitochondria?
Mitochondria have a unique oblong shape and a double membrane with inner folds known as cristae.
What do microfilaments and microtubules contribute to in a cell?
They are part of the cytoskeleton, providing structure and support to the cell.
What is the primary function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
To synthesize proteins that are earmarked for export out of the cell.
What is the primary function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
To synthesize lipids, hormones, and steroids, and to detoxify chemicals.
How do vesicles function in relation to the Golgi bodies?
Vesicles carry the final products packaged by the Golgi bodies to the plasma membrane.
What is the function of chromatin in the nucleus?
To package DNA into a more compact, dense shape, allowing for efficient storage and regulation of gene expression.
What type of cells are likely to have a high number of mitochondria?
Cells that require a lot of energy, such as muscle cells.
What is the role of the plasma membrane in a cell?
To regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell, acting as a semi-permeable barrier.
What are the components of a prokaryotic cell?
Ribosomes, plasma membrane, nucleoid, cell wall, capsule, and bacterial chromosome.
What is the general function of organelles in a eukaryotic cell?
Each organelle has its own special tasks, contributing to the overall function of the cell.
What is the importance of the cristae in mitochondria?
Cristae are the sites where most ATP production occurs.
How do lysosomes contribute to cellular health?
By breaking down and recycling old or damaged organelles and debris.
What is the function of lysosomes in a cell?
Lysosomes act as the cell's cleanup crew, helping to keep the cytoplasm clear of unwanted materials.
What are centrioles and their role during cellular division?
Centrioles are small, paired cylindrical structures that produce microtubules to pull replicated chromosomes apart during cellular division.
In which type of cells are centrioles commonly found?
Centrioles are commonly found in animal cells but are not present in plant cells.
What is the definition of a vacuole?
A vacuole is a fluid-filled sac that stores water, food, wastes, salts, or pigments.
What do peroxisomes do?
Peroxisomes detoxify various substances and produce hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct, which they then break down into oxygen and water.
Where are peroxisomes commonly found in animals?
Peroxisomes are commonly found in liver and kidney cells.
What is the cytoskeleton and its importance in a cell?
The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that holds the cell together and helps maintain its shape.
What are microtubules made of and what is their role?
Microtubules are made of the protein tubulin and are involved in cellular division and movement.
What structures are microtubules an integral part of?
Microtubules are integral parts of centrioles, cilia, and flagella.
How do cilia and flagella assist single-celled organisms?
Cilia and flagella are threadlike structures that propel single-celled organisms through watery environments.
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts are involved in photosynthesis and contain chlorophyll, which captures light energy.
What is the composition of the cell wall in plant cells?
The cell wall in plant cells is made of cellulose.
What is the difference between plant and animal cells regarding vacuoles?
Plant cells typically have a large vacuole that occupies most of the cytoplasm, while animal cells have smaller vacuoles.
What is endocytosis?
Endocytosis is the process by which a cell engulfs large particles by forming a pocket in the cell membrane that eventually becomes a vacuole or vesicle.
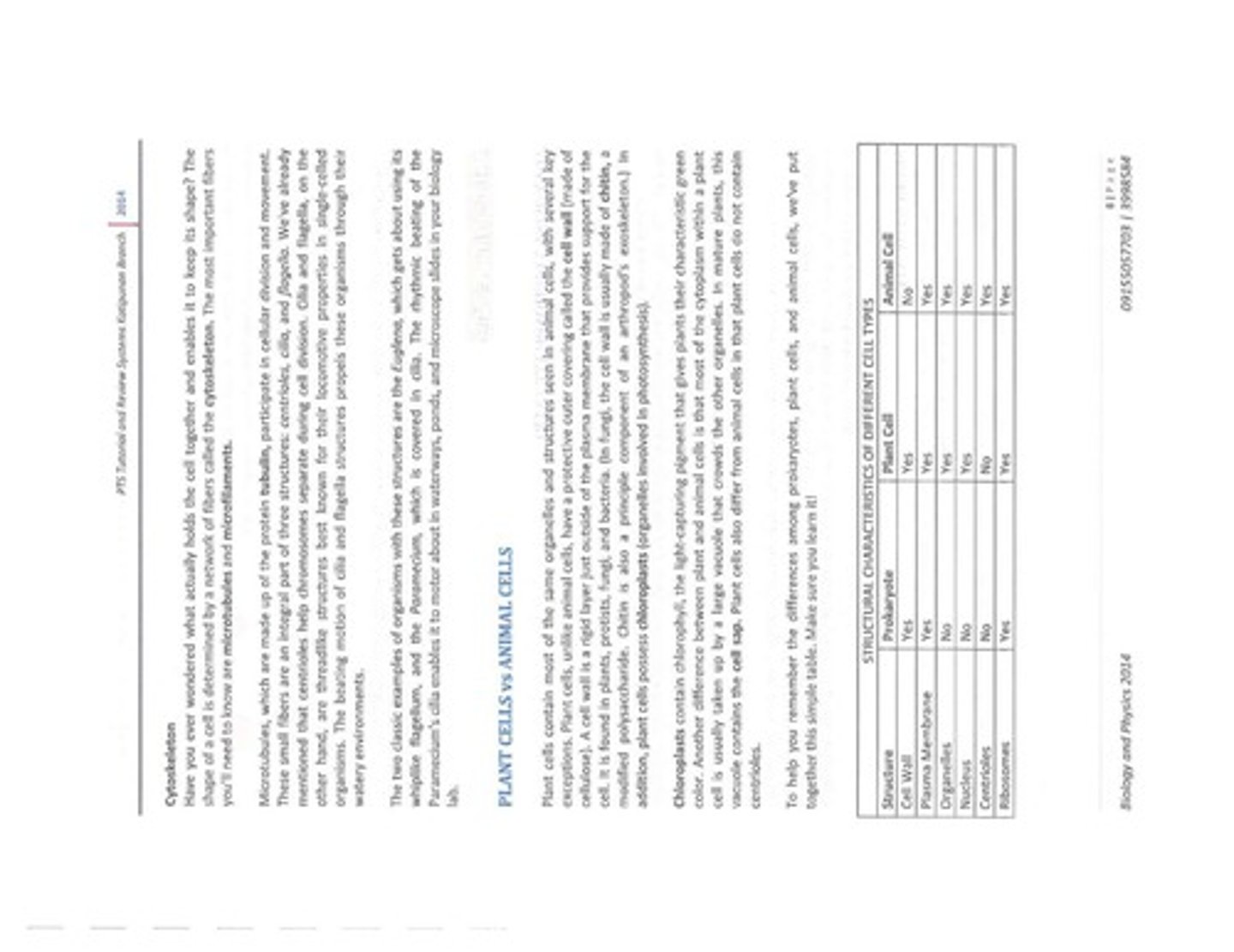
What are the structural characteristics of prokaryotes compared to plant and animal cells?
Prokaryotes have a cell wall, lack a nucleus and organelles, while plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts, and animal cells have centrioles.
What is catabolism in the context of cell metabolism?
Catabolism is the process by which a cell breaks down complex molecules to produce energy and reducing power.
What is the role of ribosomes in cells?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in both plant and animal cells.
Do plant cells contain centrioles?
No, plant cells do not contain centrioles.
What is the primary pigment found in chloroplasts?
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment found in chloroplasts.
What is the difference in organelle presence between prokaryotes and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes do not have organelles, while eukaryotic cells (plant and animal) do.
What is the significance of the plasma membrane in all cell types?
The plasma membrane is present in all cell types (prokaryotic, plant, and animal) and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
What is the role of the cell wall in plant cells?
The cell wall provides support and protection for the plant cell.
What is the function of cilia in organisms like Paramecium?
Cilia enable Paramecium to move through water by their rhythmic beating.
What is anabolism?
The process by which cells construct complex molecules and perform other biological functions.
What does the first law of thermodynamics state?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; the sum of energy in the universe is constant.
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Energy transfer leads to less organization, meaning the universe tends toward disorder (entropy).
What is ATP and what is its significance?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that stores a large amount of energy in its phosphate bonds, particularly the third bond.
How is ATP produced?
ATP is produced through photosynthesis or cellular respiration.
What is the role of photosynthesis in ATP production?
Photosynthesis transforms solar energy into chemical energy, allowing plants to capture sunlight and make glucose.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
The light reaction (light-dependent reaction) and the dark reaction (light-independent reaction).
What happens during the light reaction of photosynthesis?
Photons of sunlight activate chlorophyll, exciting electrons that are passed down an electron transport system to produce ATP and NADPH.
What are the end products of the light-dependent reactions?
Energy in the form of ATP and electron carriers, specifically NADPH.
What is the purpose of the dark reaction in photosynthesis?
To use ATP and NADPH, along with carbon dioxide, to make carbohydrates.
What is the basic equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP.
What is aerobic respiration?
ATP production that occurs in the presence of oxygen.
What is anaerobic respiration?
ATP production that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
What happens during fermentation in muscle cells?
Muscle cells convert glucose to ATP without oxygen, which can lead to cramps.
What is the significance of glucose in cellular respiration?
Glucose is a key organic molecule that provides energy-rich nutrients for ATP production.
What are the two types of respiration based on oxygen presence?
Aerobic respiration (with oxygen) and anaerobic respiration (without oxygen).
What is the main function of NADPH in photosynthesis?
To act as an electron carrier that helps in the synthesis of carbohydrates during the dark reactions.
Where do light-dependent reactions occur?
In the thylakoids of chloroplasts.
Where do light-independent reactions (C3 cycle) occur?
In the stroma of chloroplasts.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll captures sunlight and excites electrons to initiate the light-dependent reactions.
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy, while cellular respiration breaks down nutrients to release energy.
What is the result of anaerobic respiration in human muscle cells?
The production of ATP without oxygen, which can lead to muscle cramps.
What is the significance of the third phosphate bond in ATP?
It contains a large amount of energy that can be released for cellular processes.
What happens when your muscles don't get enough oxygen during exercise?
They switch to anaerobic respiration, converting pyruvic acid to lactic acid, which causes muscle ache.
What is DNA often referred to as?
The hereditary blueprint of the cell.

What structures contain DNA in a cell?
Chromosomes.
What are chromosomes made of?
DNA wrapped around proteins called histones.
What is euchromatin?
Loose form of genetic material in the nucleus where genes are active.
What is heterochromatin?
Condensed form of genetic material in the nucleus where genes are generally inactive.
Who deduced the structure of DNA and in what year?
James Watson and Francis Crick in 1956.