Chapter 5 - Demand
- Law of demand: people do less of what they want to do as the cost of doing it rises.
Translating wants into demand
Marginal utility: additional utility gained from consuming an additional unit of a good.
Law of diminishing marginal utility: tendency for the additional utility gained from consuming an additional unit of a good to diminish as consumption increases beyond some point.

Rational spending rule
- Rational spending rule: spending should be allocated across goods so that the marginal utility per dollar is the same for each good.
→ The rule highlights the fact that real, as opposed to nominal, prices and income are what matter. The demand for a good falls when the real price of a substitute falls or the real price of a complement rises.
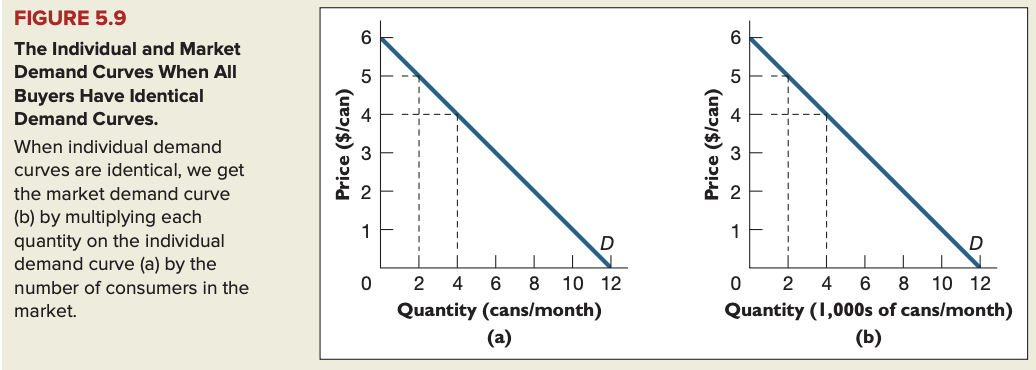
Individual and market demand curves
Horizontal addition: process of adding individual demand curves to get the market demand curve.

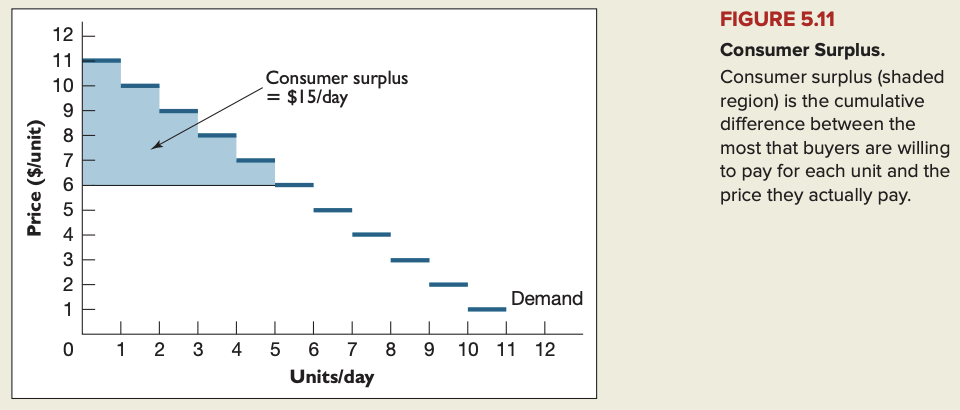
Demand and consumer surplus
Consumer surplus: difference between a buyer’s reservation price for a product and the price actually paid.