BISC220 Lecture 3
5.0(1)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:08 PM on 1/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
what are cells?
the smallest unit of life
2
New cards
what do cells form when connected?
tissues
3
New cards
what do tissues form?
organs
4
New cards
what do organs form?
organ systems
5
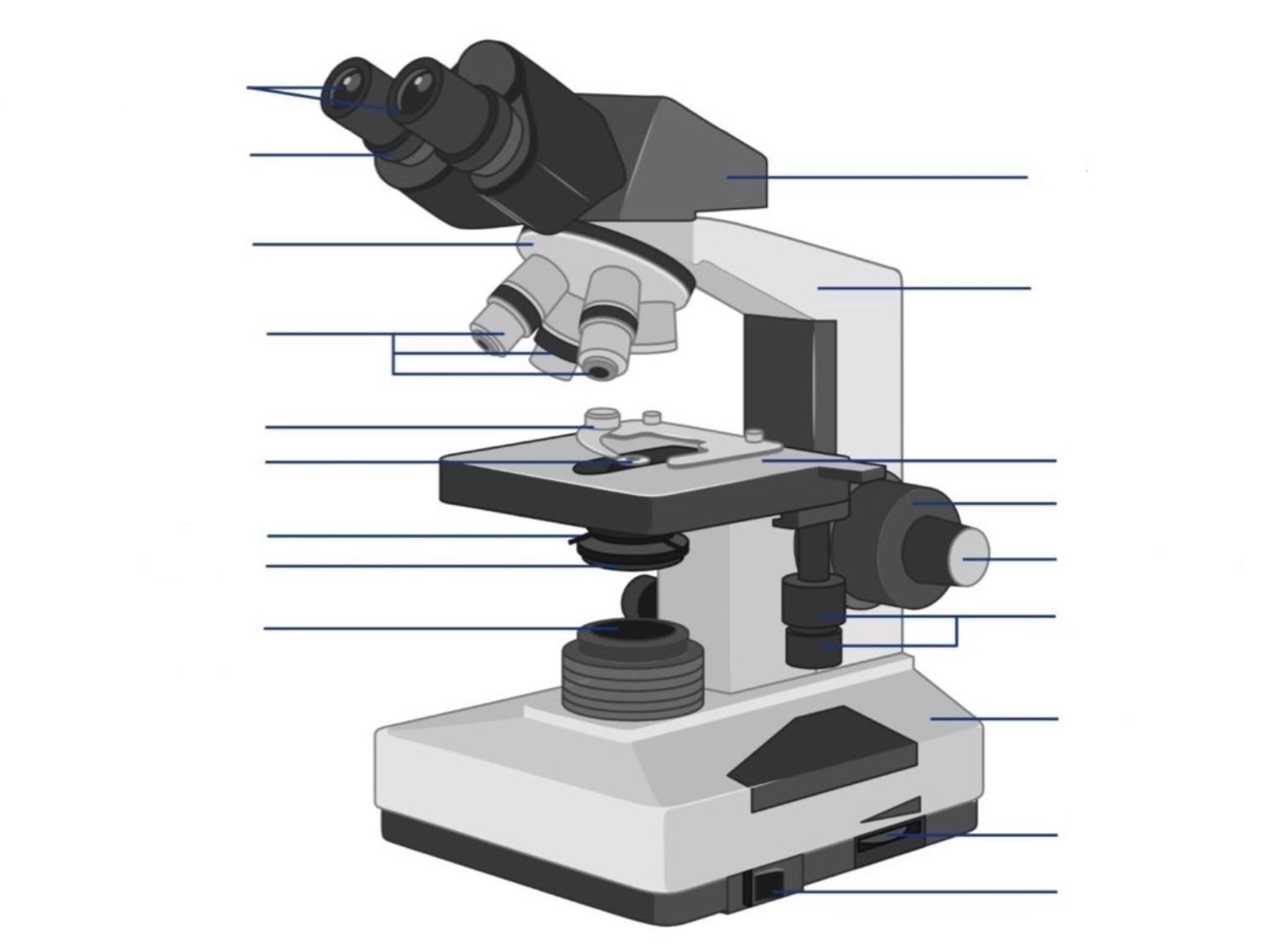
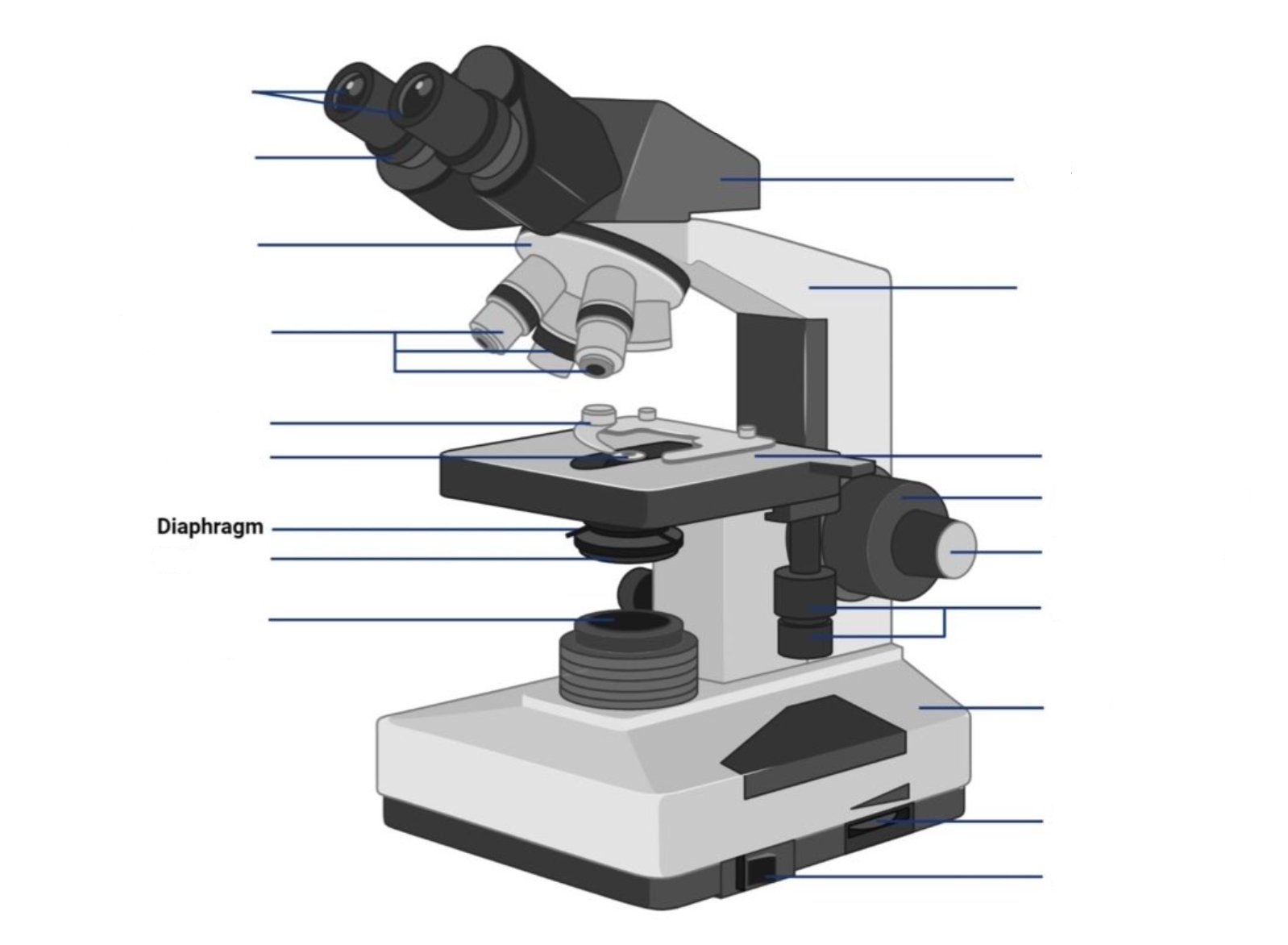
New cards
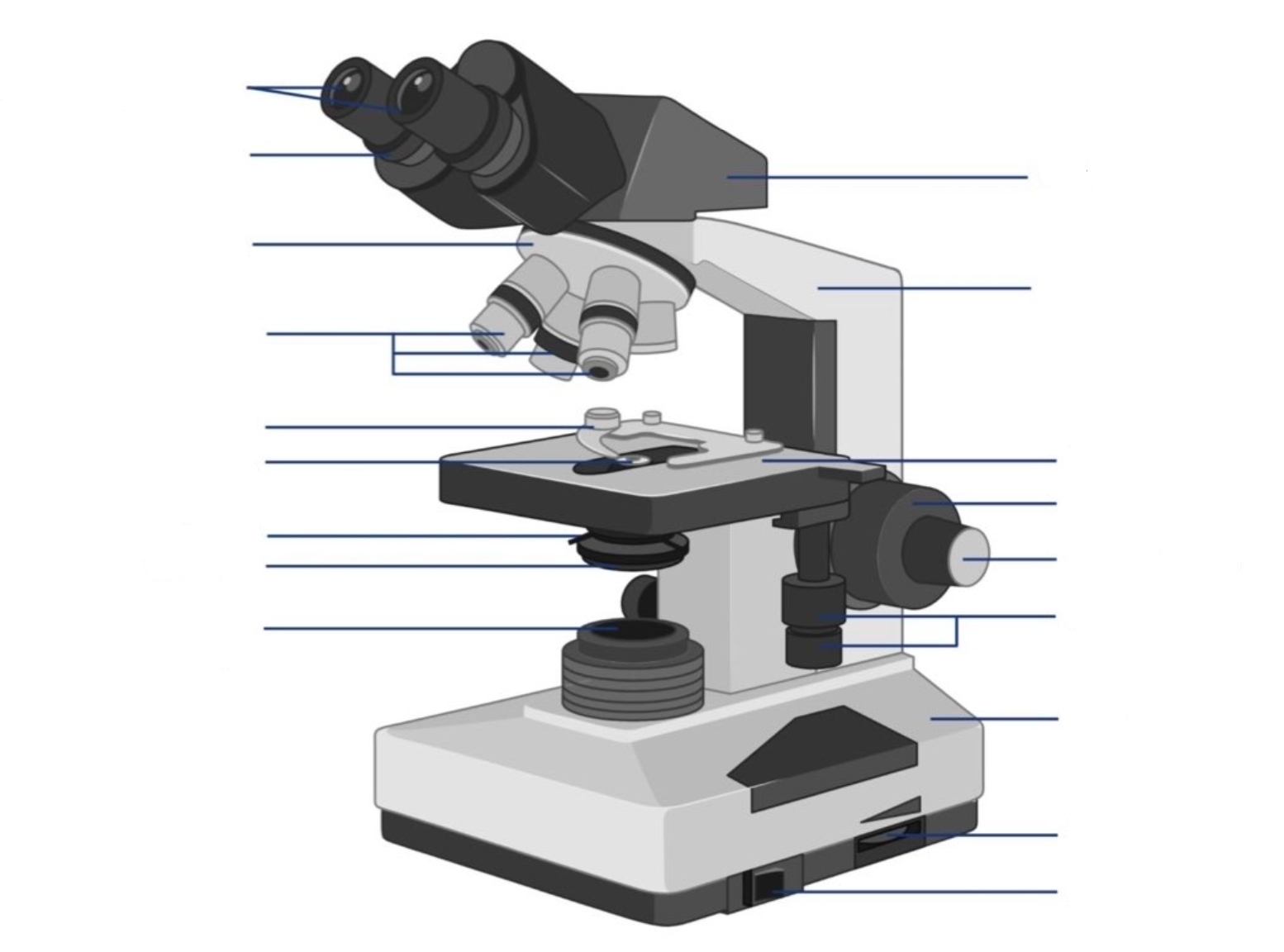
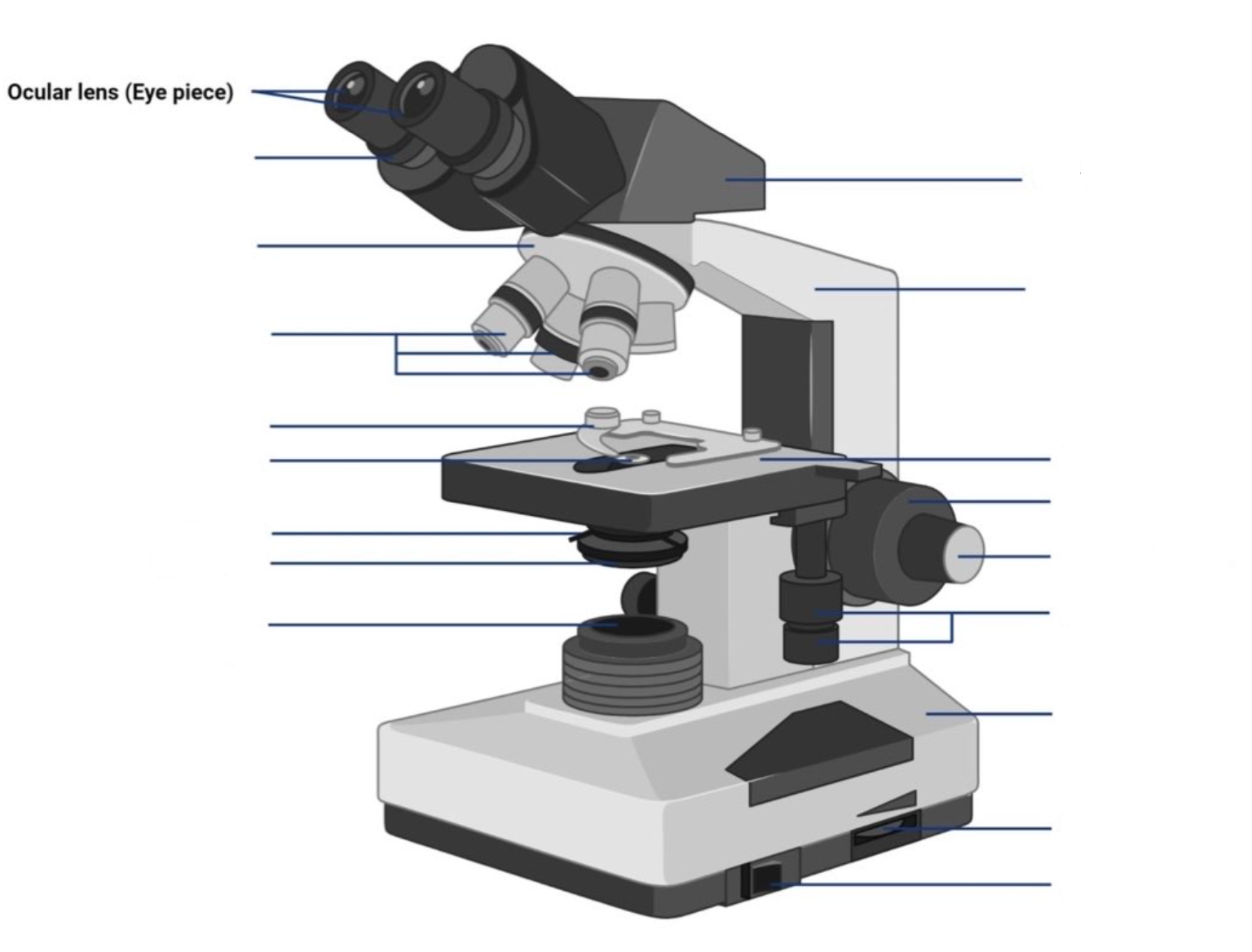
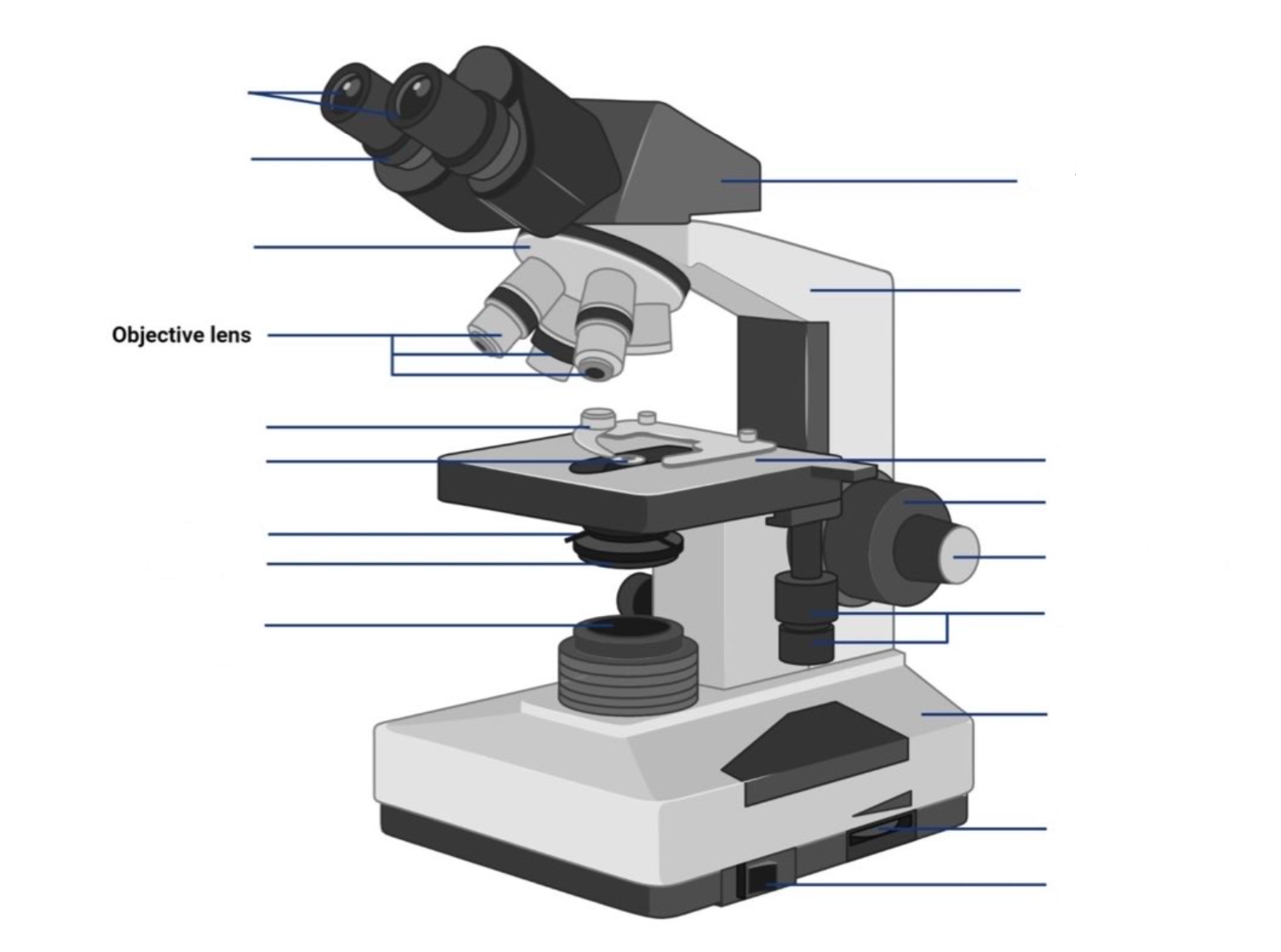
where is the ocular lens located?
6
New cards
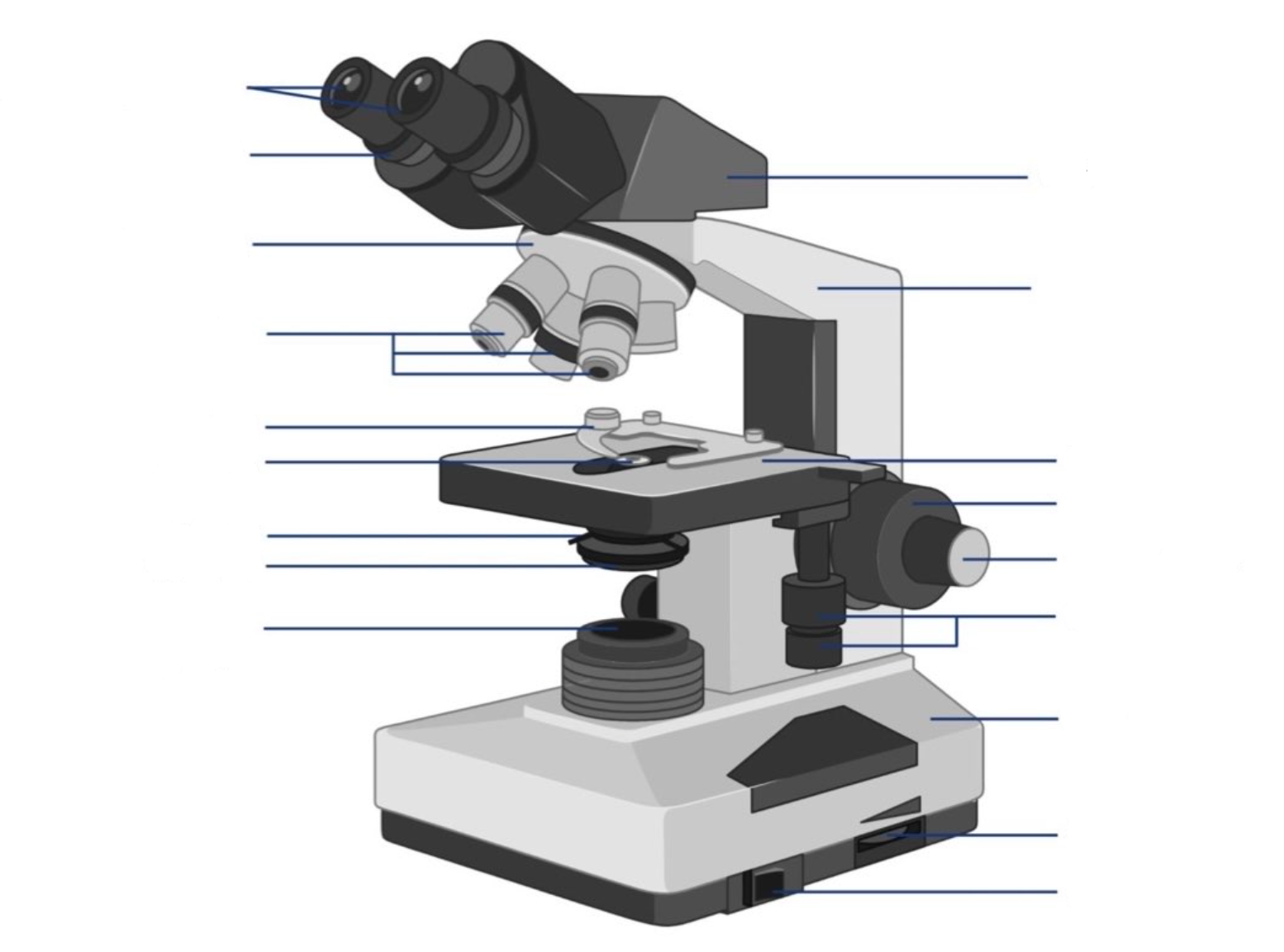
where is the objective lens located?
7
New cards
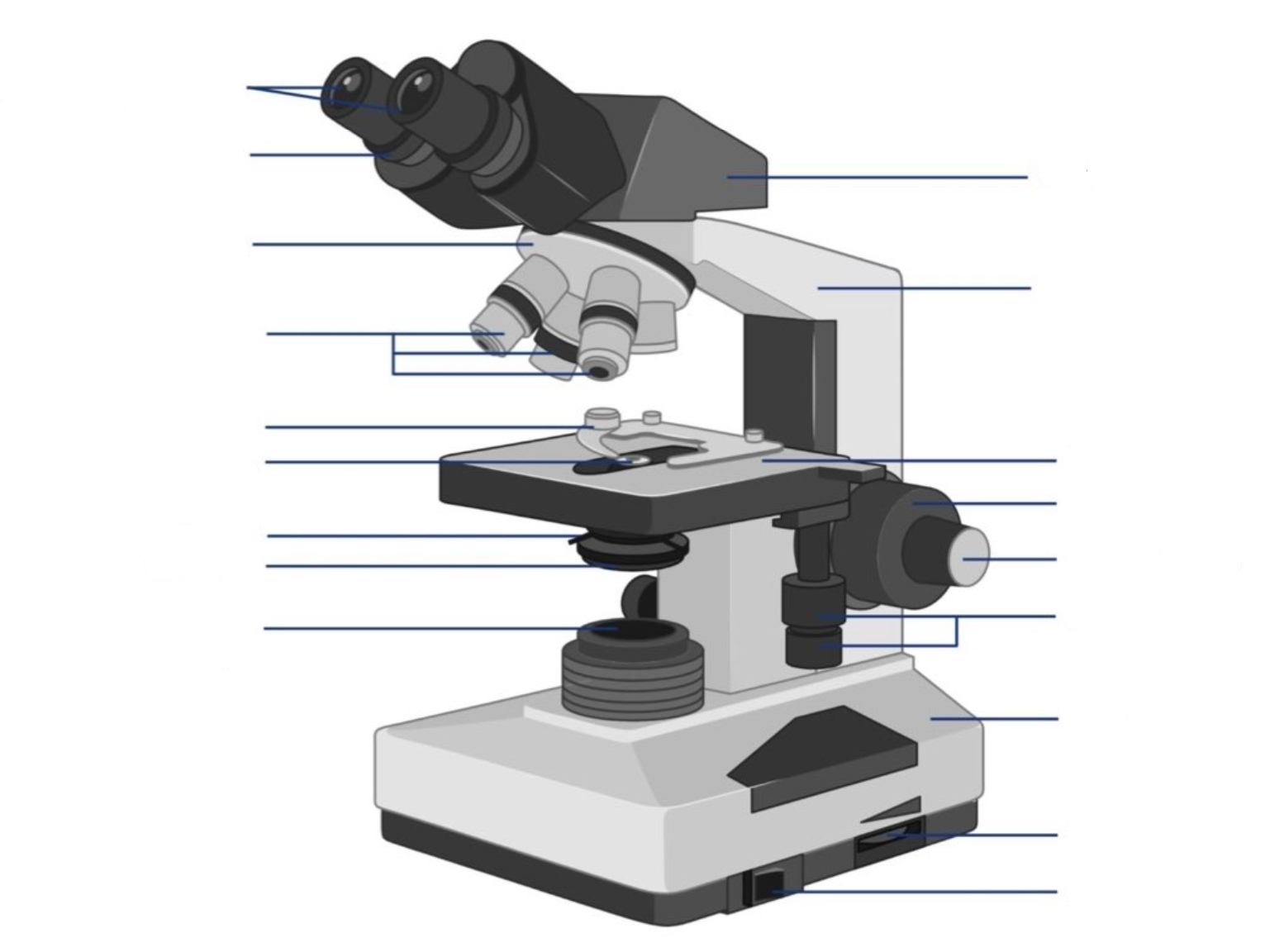
where is the stage located?
8
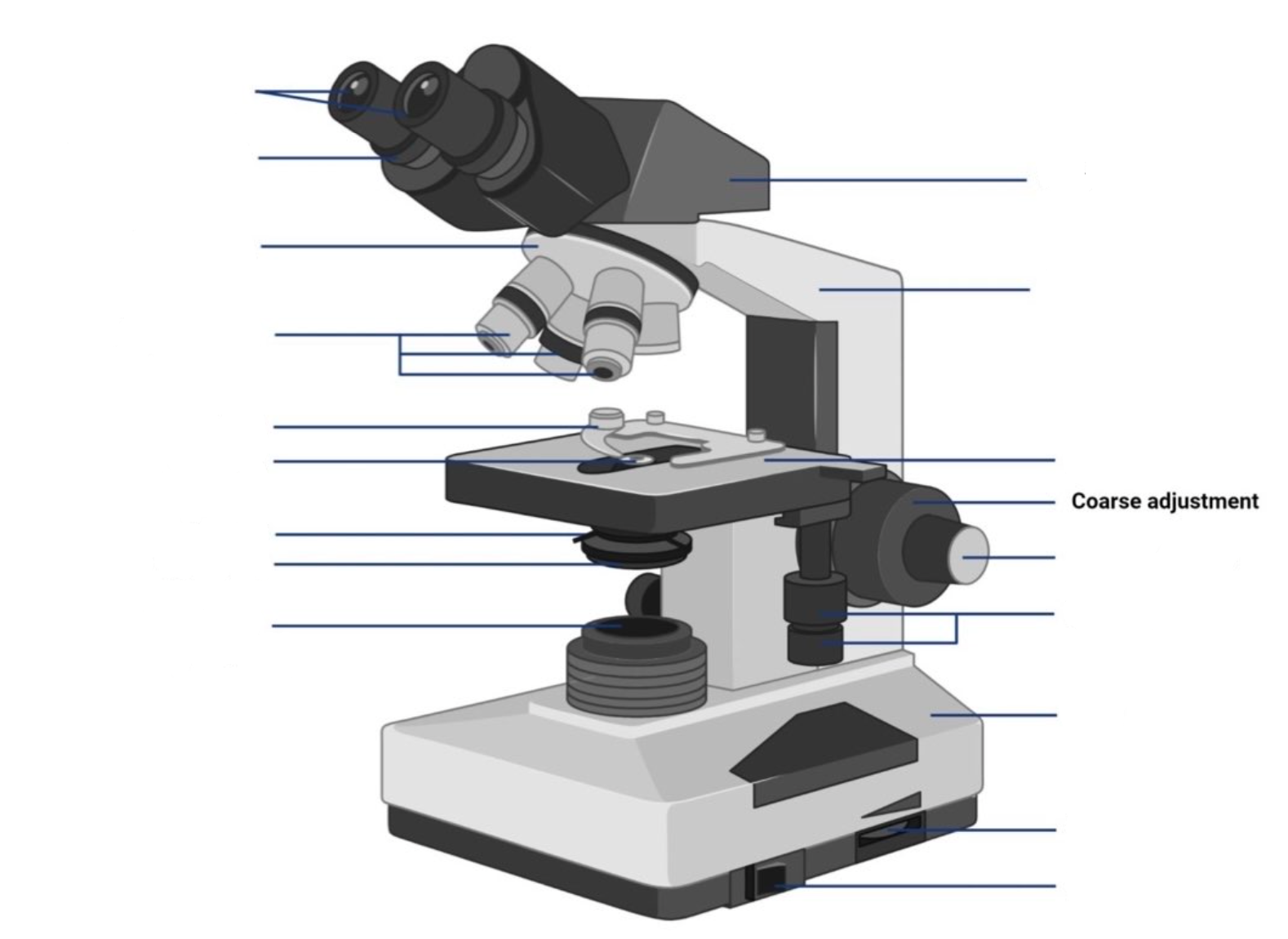
New cards
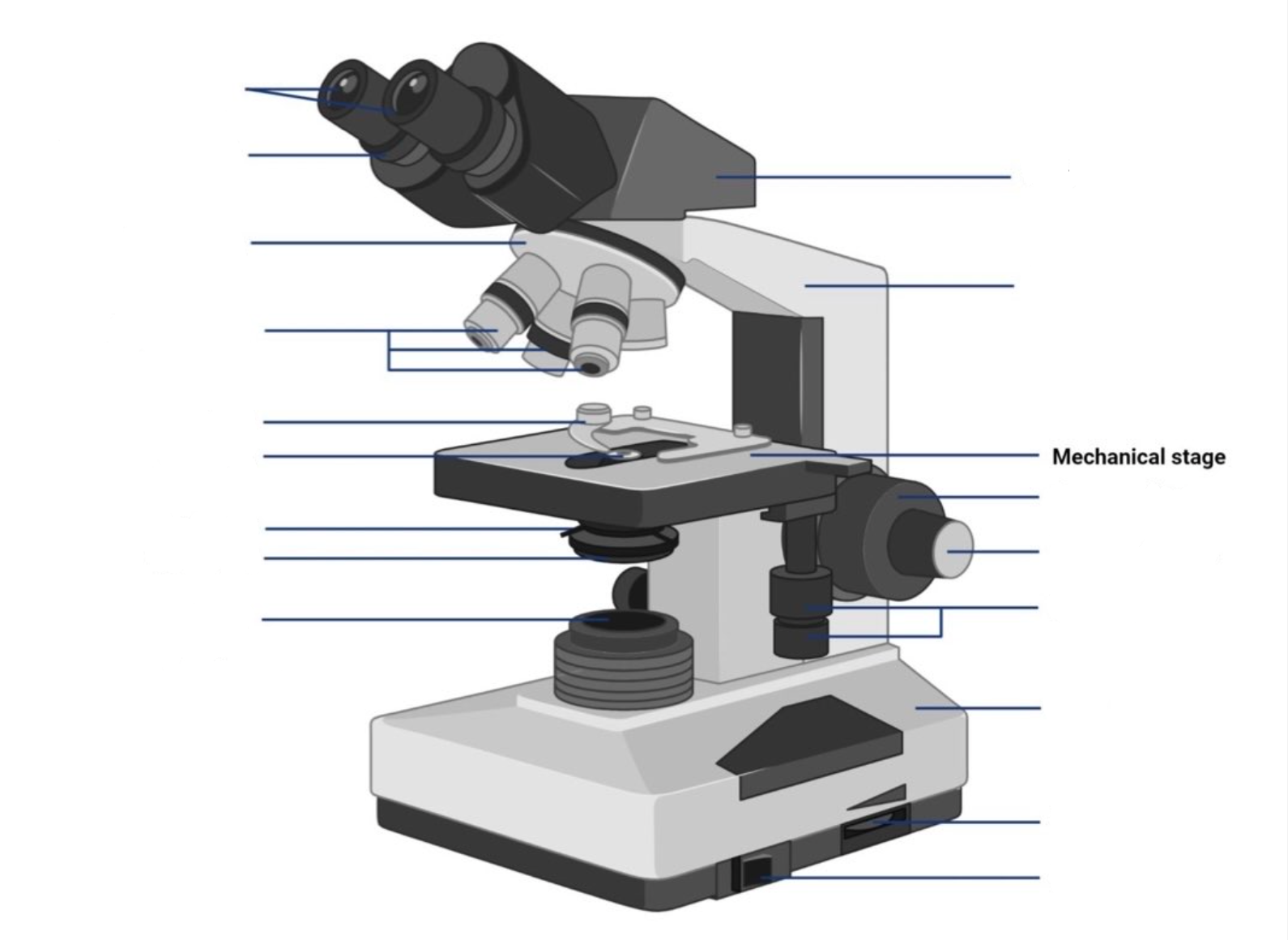
where are the coarse adjustment knobs located?
9
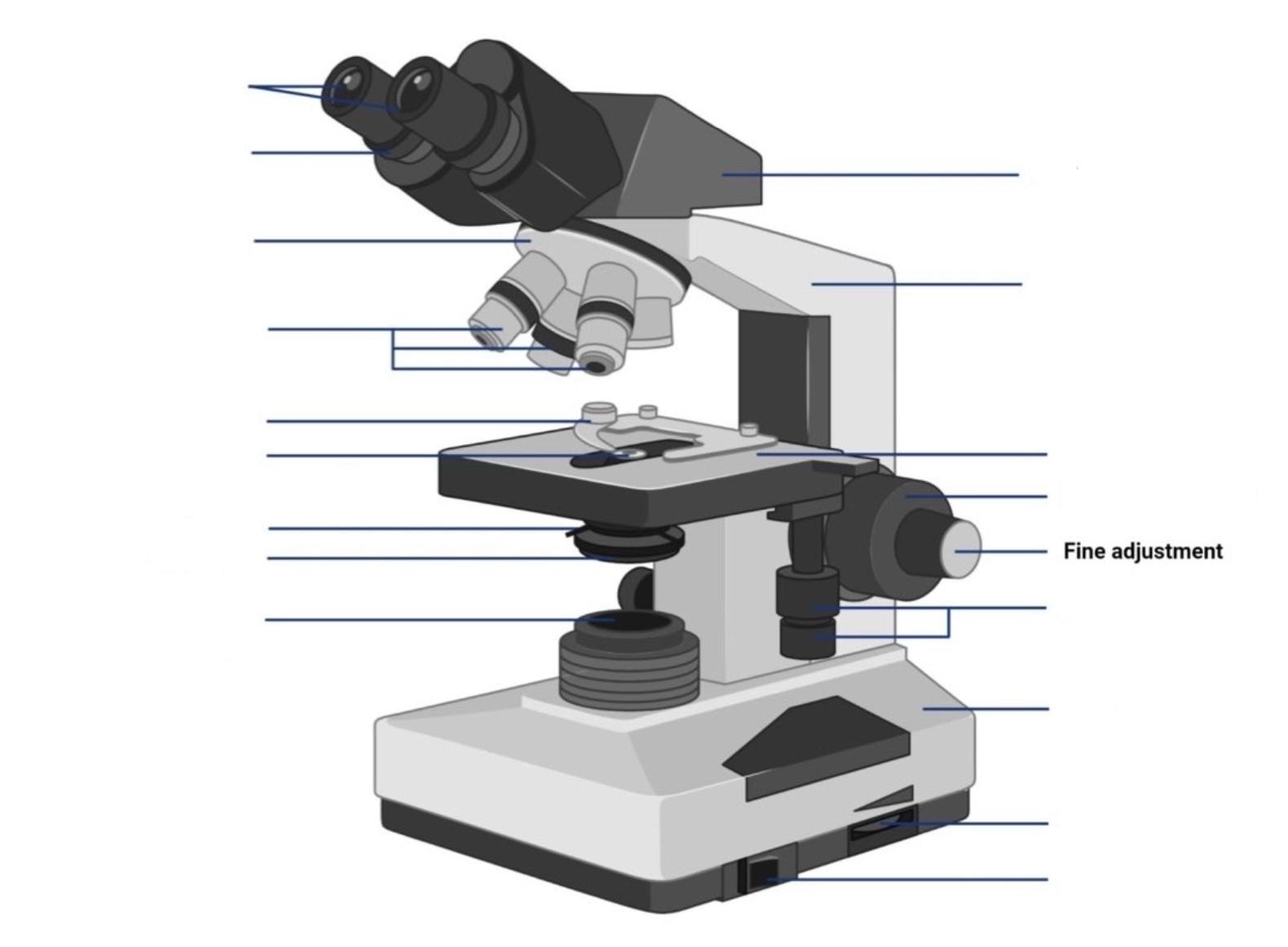
New cards
where are the fine adjustment knobs located?
10
New cards
where is the light arperture/diaphragm located?
11
New cards
what is the ocular lens?
This is the part used to look through the microscope. Its found at the top of the microscope. Its standard magnification is 10x with an optional eyepiece having magnifications from 5X to 30X.
12
New cards
what is the objective lens?
These are the major lenses used for specimen visualization. They have a magnification power of 40x-100X. There are about 1- 4 objective lenses placed on one microscope, in that some are rare facing and others face forward. Each lens has its own magnification power.
13
New cards
what is the stage?
This is the section in which the specimen is placed for viewing. They have stage clips that hold the specimen slides in place. The most common stage is the mechanical stage, which allows the control of the slides by moving the slides using the mechanical knobs on the stage instead of moving them manually.
14
New cards
what are the coarse adjustment knobs?
A rapid control which allows for quick focusing by moving the objective lens or stage up and down. It is used for initial focusing.
15
New cards
what are the fine adjustment knobs?
A slow but precise control used to fine focus the image when viewing at the higher magnifications.
16
New cards
what is the light aperture/diaphragm?
the lens system beneath the microscope stage, positioned to concentrate light correctly on the specimen and direct the light rays into the objective
17
New cards
SEM
scanning electron microscopy. produces high resolution images of the outside of a specimen.
18
New cards
TEM
transmission electron microscopy. produces high resolution image of the inside of a specimen.
19
New cards
what is florescent microscopy?
a tool that allows scientists to examine specimens which have been pre-labeled with fluorescent markers under a microscope capable of filtering the different fluorescent light wavelengths from these markers.
20
New cards
what is taxonomy?
the study of classification of organisms and often overlaps with comparative anatomy, integrative/evolutionary biology, etc.
21
New cards
what are the 3 domains of life on Earth?
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
22
New cards
what are the 6 kingdoms?
eubacteria, archaea, protista, fungi, plantae, animalia
\
Please Ask For Peanutbutter Two
\
Please Ask For Peanutbutter Two
23
New cards
eukaryotic cells have ___ organelles
membrane-bound
24
New cards
prokaryotic cells do not have ___ organelles
membrane-bound
25
New cards
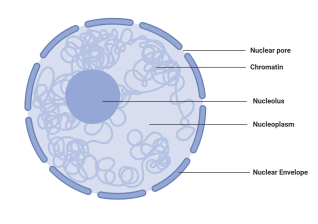
what is the function of the nucleus?
membrane bound. the center of the cell and location of the cell’s/organisms’s genetic material (DNA)
26
New cards
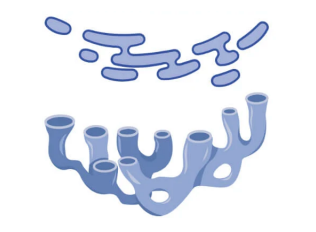
what is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)?
membrane bound. packaging of lipids and other macromolecules for intra and inter-cellular transport
27
New cards
what is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER)?
membrane bound. connected to the nucleus to package and transport proteins

28
New cards
how does the rough ER differ from the smooth ER?
rough ER is speckled with ribosomes, smooth ER lacks ribosomes
29
New cards
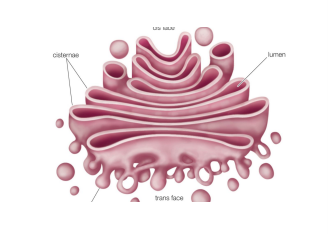
what is the function of the golgi apparatus?
membrane bound. packaging of macromolecules received from ER into vesicles for intra and inter cellular transport.
30
New cards
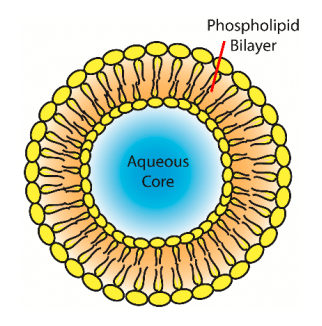
what is the function of the vesicles?
membrane bound. transports small molecules in and out of cell by endo and exocytosis, merging with other membrane-bound organelles.
31
New cards
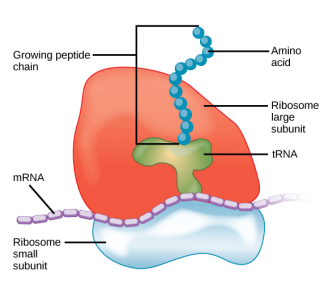
what is the function of the ribosomes?
site of protein synthesis (translation), creating proteins from an mRNA template.
32
New cards
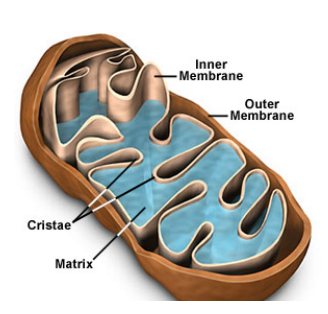
what is the function of the mitochondria?
membrane bound. site of ATP synthesis from the metabolism of glucose (cellular respiration)
33
New cards
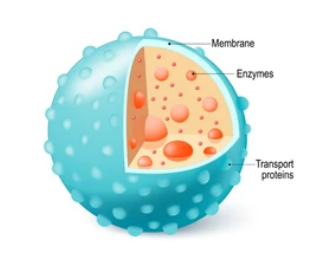
what is the function of the lysosomes?
membrane bound. contains an acidic (pH
34
New cards
what is the function of the peroxisomes?
membrane bound. break down toxins (such as H2O2) into less harmful chemicals, “toxin filter”.

35
New cards
what is the function of the vacuoles?
membrane bound. Large, pouch-like structure capable of storing water and other aqueous solutions.
36
New cards
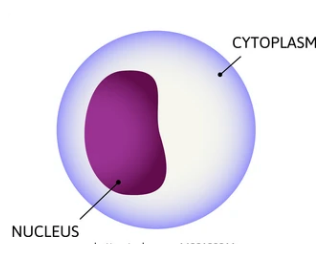
what is the function of the cytoplasm?
aqueous solution that suspends cell organelles and macromolecules while maintaining an optimized internal cell environment (pH, ionic concentration, etc.)
37
New cards
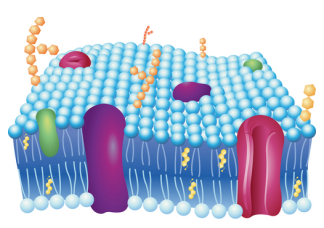
what is the function of the plasma (cell) membrane?
semi-permeable membrane that protects the internal environment of the cell and allows for selective transport of molecules in and out of the cell
38
New cards
what are some parts of the cytoskeleton?
intermediate filaments, microfilaments (actin), microtubules
39
New cards
what is the cytoskeleton?
a microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm that provide shape and coherence to a cell
40
New cards
what is the function of the intermediate filaments?
type of protein part of the cellular cytoskeleton, critical for maintaining the internal boundaries of the cell
41
New cards
what is the function of the microfilaments (actin)
a protein that is part of the cellular cytoskeleton, uses ATP to promote internal movement of cell organelles and in some cases, movement of the entire cell
42
New cards
what are 3 unique plant cell organelles?
chloroplasts, large central vacuole, cell wall
43
New cards
what is the function of the chloroplasts?
membrane bound. similar to mitochondria, critical for the process of photosynthesis in plants (uses ATP to synthesize glucose, reverse of cellular respiration)
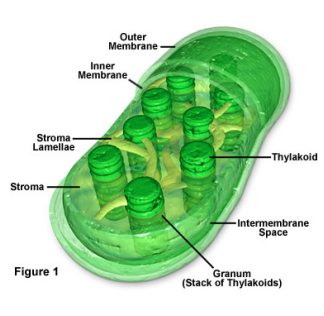
44
New cards
what is the function of the cell wall?
preserve the structural integrity of the (plant) cell, typically made of a fibrous carbohydrate such as cellulose (in plants) and/or chitin (in fungi)
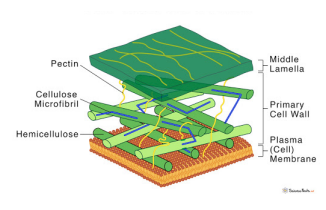
45
New cards
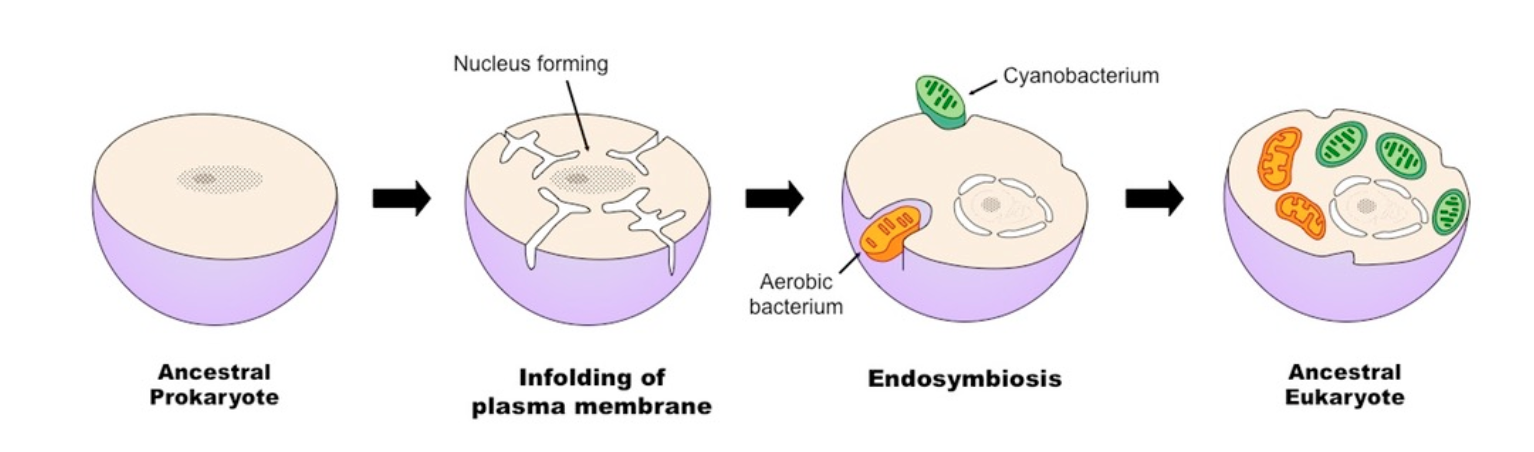
what is the endosymbiotic theory?
leading theory explaining the evolution of the modern eukaryotic cell.
\
states that the ancestral prokaryotic cells exhibited folding of the plasma membrane that gave rise to the internal membrane-bound organelles (such as the nucleus), and this combined with uptake of mitochondria and chloroplasts through the consumption of bacteria led to the development of eukaryotic cells.
\
states that the ancestral prokaryotic cells exhibited folding of the plasma membrane that gave rise to the internal membrane-bound organelles (such as the nucleus), and this combined with uptake of mitochondria and chloroplasts through the consumption of bacteria led to the development of eukaryotic cells.