Materials, Hardware, and Processes 1
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Hardness
The ability of a material to resist cutting, penetration, abrasion or permanent distortion
Hardness is measured with…
either a Rockwell or Brinell hardness tester
Stress
The internal force within a body that opposes an external force
Tension
Two forces in-line away from each other.
Tends to pull an object apart
Compression
Two forces in-line towards each other
Tends to crush a material
Shear
Two forces opposite but not in line with each other
Tends to tear objects
Torsion
A combination of compression and tension acting perpendicular
Tends to twist objects
Bending
Two forces in-line towards each other
Tends to crush (compression) or pull apart (tension) a material
Strength
a materials ability to withstand stresses without deforming or failing
Types of Strength
Tensile Strength- An object’s ability to withstand tension
Yield Strength- A metal’s ability to resist deformation
Shear Strength- A metal’s ability to resist opposing forces
Bearing Strength- The ability of a joint to withstand excessive compressive distortion
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
The relationship of the strength of a material to its weight per cubic inch
Density
The mass per unit volume of a material (can be used to identify material)
Malleability
The ability of a metal to be hammered, rolled, or pressed into shape without cracking, breaking, or leaving some other detrimental effect
Ductility
The ability of a metal that allows it to be drawn into wire, extrusions, or rods
Elasticity
The ability of a material to return to its original shape once the deforming force has been removed
Toughness
A materials ability to resist tearing or breaking when it is bent or stretched
Brittleness
materials tendency to break or shatter when exposed to stress
Fusibility
The ability of a metal to be joined by heating and melting
Conductivity
The ability of a material to transfer heat or electricity
Thermal Expansion
The change in a metal’s size due to it’s change in temperature
Coefficient of Expansion
the amount of expansion or contraction at specific temperatures
Understand the difference between hardness, strength, and toughness
Ferrous Aircraft Metals
Any material where iron is the chief constituent
Carbon
Most common alloying agent found in steel
Allows the steel to be heat treated for hardness and strength
SAE Classifications
Based on a four-digit number
First digit- generally indicates major alloying agent
Second digit- generally indicates percentage of agent
Last two digits- percentage of carbon (in hundredths of a percent)
Stainless Steel
Group of steels that exhibit excellent corrosion resistance properties
Answer and Match the quote with its source: Is it racist if you dislike all races equally?
No. -Daniel
300 Series Stainless Steel
High percentage of chromium and nickel
Most common corrosion-resistant steel used in Aviation
Also known as 18-8 steel (18% Chromium and 8% Nickel)
Identification of Ferrous Metals
Spark Testing
Color
Electrochemical Test
Aluminum
Non-ferrous Aircraft Metals
Wrought Aluminum Classification
Based on four-digit number
First Digit- Major alloying agent
Second Digit- Variations of initial alloy “modification”
Last Two Digits- Other alloying agents (except 1xxx series)
1xxx – Pure Aluminum
2xxx – Copper
3xxx – Manganese
4xxx – Silicon
5xxx – Magnesium
6xxx – Magnesium and silicon
7xxx - Zinc
8xxx – Other Elements
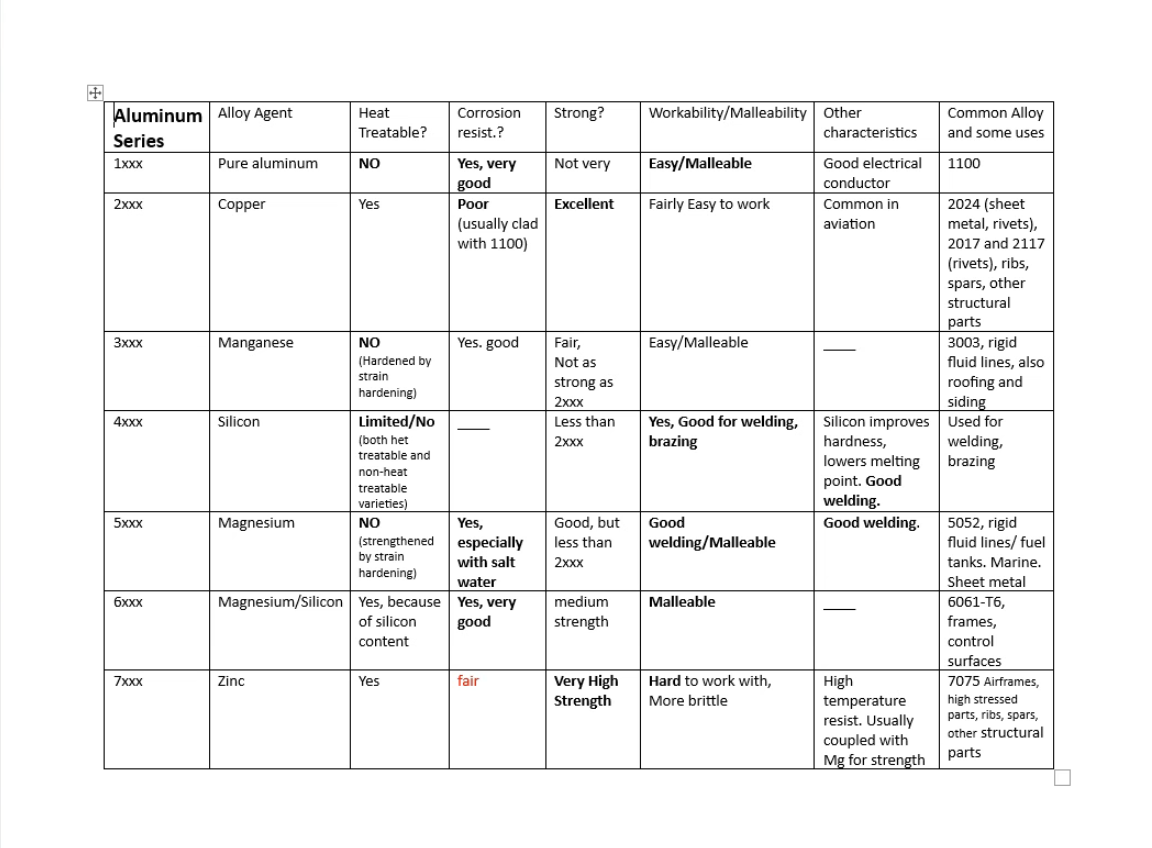
Alloy Structure Adjustments
F – As fabricated
W – Solution heat treating no aging
O – Annealed
T3 – Solution heat treated then cold worked
T4 –Solution heat treated
T6 – Solution heat treated then artificially aged
T8 – Solution heat treated, cold worked then artificially aged
H – Strain hardened
H1 – Strain hardened only
H2 – Strain hardened and partially annealed
H3 – Strain hardened then stabilized
There will typically be another digit following the H1, H2, H3. This indicates to what degree the material was hardened. 2 = ¼ hard, 4 = ½ hard, 6 = ¾ hard, 8= full hard
Monel
68% nickel, 29% copper
Inconel
80% nickel, 14% chromium
Four requirements when selecting replacement parts
Maintain original strength (and flexibility) of the structure (most important)
Maintain contour or aerodynamic smoothness
Maintain original weight if possible, or at least minimum weight
Maintain original corrosion resistant properties
Hot-Working
Process of forming a metal at an elevated temperature
Pressing
Used to form large and heavy parts
Drop Forging
Hammering process where hot metal is placed between formed dies and a weight of several tons is dropped on the upper die, forcing the metal to take the shape of the die
Hammering (Smith Forging)
Metal worker physically hammers a piece of metal into its finished shape
Cold working
working with a metal below it's critical temperature
Cold rolling
A form of cold working where a metal is rolled at a room temperature until it is the appropriate size
Cold drawing
Used to make seamless tubing, wire, and other stock
Extruding
The process of forcing a metal through a die which imparts the required cross-section to the metal
Hardening
process of heating metal above it's critical temperature and then quench with water, oil or brine
Tempering
The process of heating metal below It’s critical temperature,
soaking, and then allowing to cool at room temperature
Annealing
the process of heating metal above it's critical temperature, soaking, and then allowing to cool very slowly in the furnace
Normalizing
the process of heating metal above it's critical temperature, soaking, and then allowing it to cool in still air
Case Harding
A process which gives the surface of a metal a hard, durable bearing surface, but allows the core material to remain strong but not brittle
Carbonizing
Nitriding
Alclad aluminum
consists with an aluminum-alloy core coated with a layer of pure aluminum
Solution heat treatment
heated above critical temperature, allowed to soak, then quenched.
designated with a "t"
Precipitation heat treating
designed to increase the strength of the alloy beyond the level provided by solution heat treatmen
Strain Harding
a process by which non-heat treatable alloying can have their strength increased
Brazing
a non-ferrous metal usually brass Or bronze, is used as the adhesive material.
Soldering
follows the same concept as brazing
Hard/Silver soldering
variant term for brazing
Proper preparation is key to a quality soldered joint. T or F
True
Flux
cleans material & improves adhesion
Welding
a method of joining pieces of metal by fusion
Types of welding
gas, electric arc welding ( shielded metal arc welding, gas metal arc welding, tungsten arc welding)
Types of weld repairs
simple welded patch, welded split reinforcing sleeve, figerpatch, tube splice, cluster replacement, engine mount
Good welds should
weld should be of consistent width throughout, the two edges should form a parallel line, face of the weld should be slightly convex not more than 1/16", free of excessive spatter, scale, and pitting, etc…
Wood
(standard) - Sitka spruce; high strength to weight ratio, relatively free from defects, available in large sizes
Wood quality
must have straight grain, no spike knots, hard knots up to 3/8" D.I.A.,
Pitch pockets
Compression wood not acceptable
Checks, Shakes, splits not acceptable
Thermoplastics & thermo setting
Materials that are hard in their normal state, but become soft and pliable when heated
Harden upon heating and reheating has no softening effect. Typically used in composite layups
Composite
material made up a mixture of different materials
Cloth
Linen cloth impregnated with a thermosetting resin called phenol-formaldehyde (Phenolic Material), used to make control cable pulleys
Metal-Faced Honeycomb
Honeycomb core material is bonded to thin sheets of Aluminum Alloy
Types:
Paper and glass, metal, wood, and foam
Rubber
Natural
Synthetic
Synthetic types:
Butyl
Bunas
Neoprene
Magnesium is one of the world's lightest structural metals and has excellent fire protection capabilities. T or F
False
The main alloying ingredient for 6001 aluminum is [x]
Magnesium and Silicon

On an aircraft, (a), (b), and (c), structural and (d), (e), (f), (g), and (h) are manufactured from stainless steel.
a. Exhaust Collectors
b. Stacks
c. Manifolds
d. Machined Parts
e. Springs
f. Castings
g. Tie Rods
h. Control Cables
[x] is the primary alloying agent in bronze.
Tin
18-8 stainless steel is made up of x Chromium and y Nickel.
x = 18 %
y = 8 %
Composite structures can be made with or without an inner core of material. T or F
True
Aluminum that is in its annealed condition is designated with a [x].
O
Titanium is not subject to [a] corrosion, [b] corrosion, [c] corrosion, or [d] corrosion.
Galvanic
Intergranular
Fatigue
Stress
When adding nickel to steel, hardness, tensile strength, and elastic limit increase while appreciably decreasing the ductility. T or F
False
An alloy is created when other metals are added to a base metal. T or F
True
Molybdenum is added to a steel alloy because it (a) the strength of steel without affecting Ductility or (b)
a. Raises
b. Workability
What two reasons allow aluminum to be the most widely used metal in aviation construction?
Ease of fabrication
High strength-to-weight ratio
The main alloying ingredient for 5052 aluminum is [x].
Magnesium

A metal that has been hardened using solution heat treating and then artificially aged has the designation of [x].
T6
Monel is not good to use for gears and chains. T or F
False
The main alloying ingredient for 2024 aluminum is [x].
Copper

What is Hardness (Match Terms Selection 1)
What is Malleability (Match Terms Selection 2)
(1) The ability of a material to resist cutting, penetration, or abrasion.
(2) The ability of a metal to be bent, formed, or shaped without cracking.
Copper is normally used in an aircraft's electrical system for:
Bus Bars
Bonding
Lock Wire
The two classes of plastics used in aircraft construction are:
Thermosetting
Thermoplastic
When classifying aluminum, which digit indicates the major alloying agent?
First
The process of softening a material is known as [x].
Annealing
What two reasons allow aluminum to be the most widely used metal in aviation construction?
Ease of fabrication
High strength-to weight ratio
Magnesium is very corrosive and brittle. T or F
True
Drop forging is the process where a worker physically hammers a piece of metal into its finished state. T or F
False
What is the agent that is added to a resin to increase its viscosity to prevent it from running off a surface?
Thixotropic Agents
The mass unit volume of a metal is known as
density
Monel and Inconel two common alloys of magnesium. T or F
False
[x] is the standard wood used in aircraft construction.
Sitka Spruce
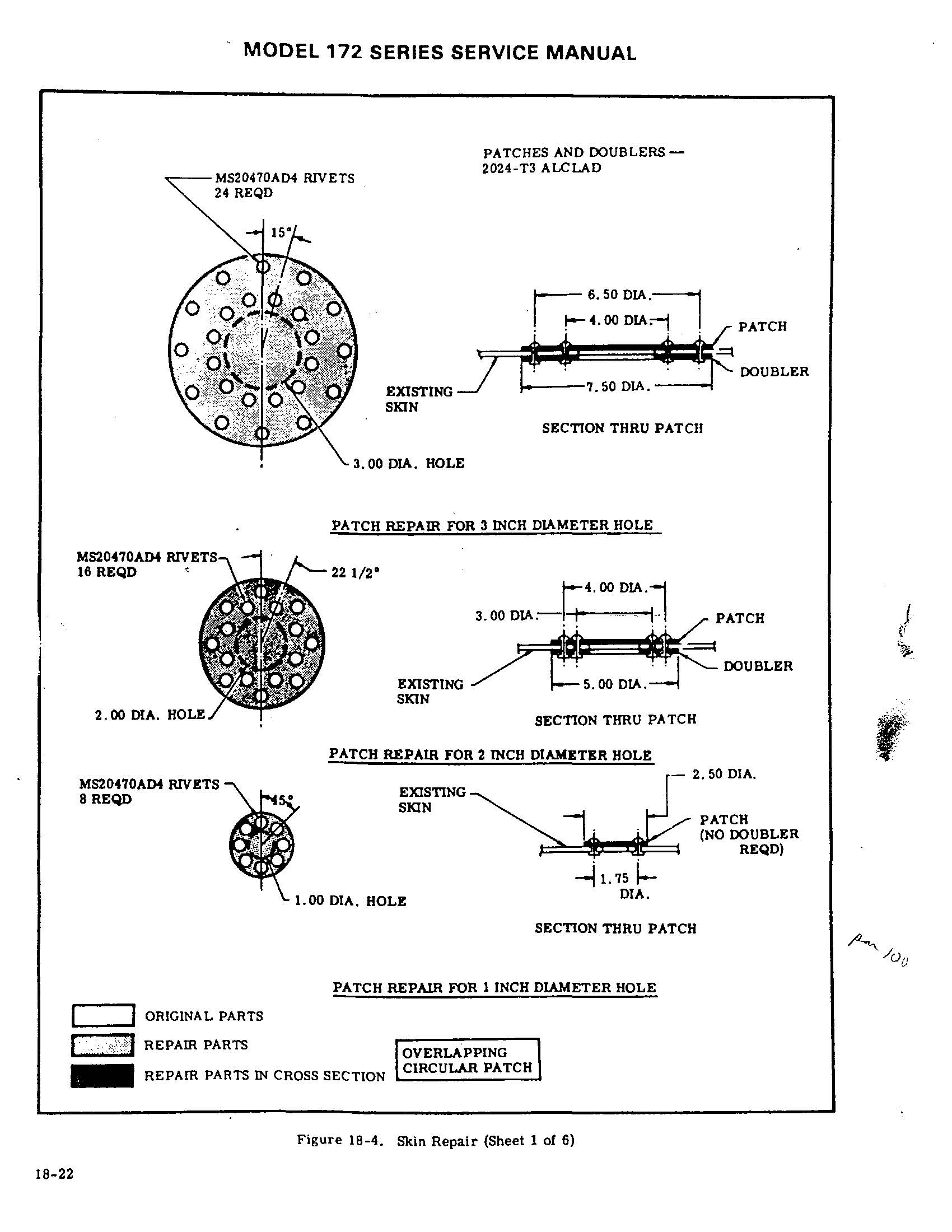
Utilizing the provided manual, 2024-T3 should be used to perform the assigned patch repair and it is Heat Treated .
2024-T3
Heat Treated

Two enthusiastic thumbs up
Why did you flip the cat over, he’s gonna fall