Atomic Structure and Periodicity - Unit Test Review
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes: Theories of Atomic Structure, Isotopes: Average atomic mass and determine % of abundance, Modern Atomic Theory: quantum Mechanic Modal of Atom( wave modal), Emission Spectra, Electron Configuration: ground state , noble gas and Orbital Notation, Periodic Table – classification and blocks, Periodic Trends
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Dalton’s atomic theory
Explained conservation of mass as the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms
John Dalton
Matter is composed of small particles called atoms
Atoms are indivisible and indestructible (proven false)
Atoms of a given element are identical in every way (proven false: isotopes)
Atoms of different elements are different
Different atoms combine in a whole number ratios to make compounds
Atoms
The smallest particle of an element that retains its properties of the element
Cathode Ray
When electric charge is applied, a ray of radiation travels from cathode to anode
Electrons
Particles carrying a negative charge
JJ Thomson
man who created the cathode ray tube and discovered electrons
Also came up with the plum pudding model
Robert Milikan
man who used the oil drop apparatus to determine the charge of an electron (coulombs)
Ernest Rutherford
studied how positively charged alpha particles interacted with solid matter using the gold foil experiment
atoms are mostly empty space
if they pass through, they go between the nucleus and the electronic field
opposite charges attract
Democritus
All things are composed of the atomos or the fundamental particles, atoms
Atoms cannot be destroyed
Atoms are separated by the void or empty space
Atoms are in constant motion and undergo constant change through the void.
HIs theories weren’t widely accepted at the time because of Aristotle’s more popular ideas
Aristotle
argued that the four elements were not composed of atoms but were continuous forms of matter. He also denied that a 'void' between atoms could exist.
Coloumbs
measuring unit of electron charge
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom. All atoms of the same elment have the same number of protons
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons
Mass Number
The weight of the atom and the total number of protons and neutrons combined.
Isotopic Notation
A z X
A = Mass number
z = Atomic number
x = Chemical Symbol
Hyphen Notation
C-12, C-14
Atomic Mass unit (amu)
1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. (the approximate weight of a proton or a neutron)
Nuclear Fission
The splitting of a heavy nucleus into 2 small nuclei
Isotope Abundance Formula
(isotope atomic mass)(% abundance in decimal form) + (isotope atomic mass)(% abundance in decimal form)
Nuclear Fusion
Combining 2 light nuclei to forma heavier and more stable nucleus
Ion
any atom that bears one or more positive or negative electrical charge
Cation
Positive ions
Anions
Negatively charged ions
Electron cloud structure
Electrons within clouds have different amounts of energy
Electromagnetic radiation
a kind of radiation including visible light, radio waves, gamma rays, and X-rays, in which electric and magnetic fields vary simultaneously.
Wavelength
λ symbol
Shortest distance on points on a continuous wave (meters)
Frequency
v symbol
Number of waves/second (hertz)
Amplitude
Height from the origin to the crest
Speed of light
c symbol
3.00 ×108 m/s
understando
c = λ/v
understando?
Quantum
minimum amount of energy gained or lost by an atom
Plancks Constant
h symbol
6.636e-34 J * S
Alles klar
E quantum = hv
alles klar?
Photoelectric effect
when electrons are emitted from a metal surface when light of a certain frequency shines on it
Photon
light particle with no mass, only energy
Todo Claro
E photon = hv
todo claro?
Atomic Emission Spectrum
Set of frequencies of the Em waves emitted by atoms of the element
Ground State
the lowest allowable energy state of an atom
Excited state
a state of a physical system, such as an atom, molecule, or nucleus, that has more energy than its ground state
Quantum Numebr
The number given to an orbit
Electron Configuration
The arrangement of electrons
Heisenburg uncertainty principle
Its impossible to know the velocity and position of a particle aat the same time (only probability)
Quantum Mechanical model
Model in which schrödinger treats electrons as waves
Principal Quantum Number (n)
relative size and energy of atomic orbitals
Principal Energy levels
Atoms major energy levels
energy sublevels
Contained within the principel energy levels
Aufbau principle
states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available
Pauli exclusion principle
2 electrons can occupy one orbital if they have opposite spins
Hund’s Rule
Single electrons with the same spin must occupy equal energy orbitals before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same energy level orbitals
TO DUMB IT DOWN: You have to put one electron in each “room” before adding another in the first sub-level
Valence electrons
Electrons in the outermost orbital (highest energy level)
Electron-dot Structure
The element’s sumbol (representing the nucleus) surrounded by the dots representing the valence electrons
Also called the lewis structure
Orbital Notation
offers a visual account with boxes and arrows to depict electrons and their spins in respective orbitals
Cu, Ag, Cr, Mo, Au
The exceptions to regular electron configuration rules
Noble Gas Notation
an abbreviated notation of an atom's electron configuration.
The _____ ___s's electron configuration is substituted and replaced with the elemental symbol in brackets.
Periodic Law
Periodic repittion of chemical and physical properties of the elmeents when increasing atomic number
Group
Columns of elements
Periods
Rows of elements
Representative elements
Elements in groups 1, 2, 13 - 18 that have a wide variety of chemical/physical properties
Transition elements
Elements in groups 3-12. Can be metals, non-metals, and metalloids
Metals
Generally shiny, when clean and smooth, solid at room temperature. Good conductors
Alkali metlas
reactive elements in group 1 (except for hydrogen)
Alkaline Earth Metals
Reactive metals of group 2
Inner transition metals
The lanthanide and actinide series
Non-metals
Gases or dull-looking, brittle solids. Good insulators
Halogens
Highly reactive elements in group 17
Noble Gases
Unreactive gases in group 18
Metalloids
Elements woth both physical and chemical properties of metals and nonmetals
S-block
What block is this
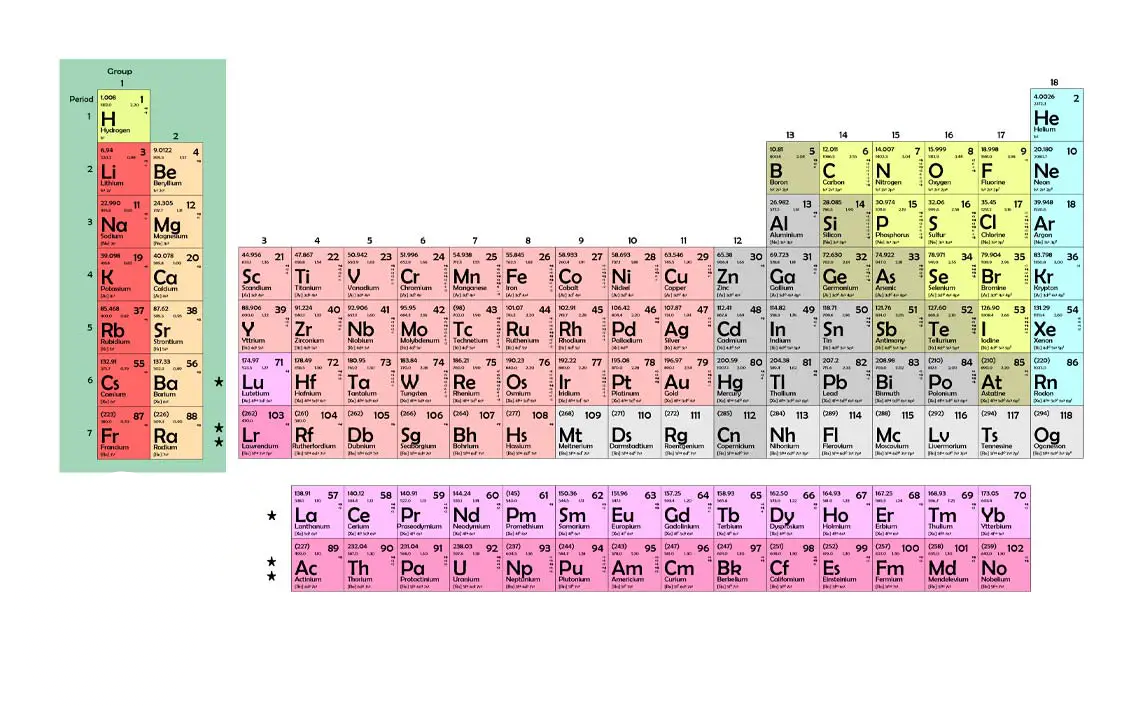
P-block
what block includes groups 13-18 (except for helium)
d-block
what block includes groups 3-12
f-block
What block includes the lanthanide and actinide series
Atomic Radius
Periodic trend - half the distance between nuclei or identical atoms
Decreases across the period and increases down the group
Ion size
Decreases as you move across the period and increases down the group
Ionization energy
The energy needed to remove an electron (measured in joules)
increases across the period and decreases down the group
Octet rule
Atoms gain or lose or share electrons to get a set of 8 valence electrons
(metals = 4+, non metals = 4-)
Electronegativity
The ability to attract electrons
Increases across a period and decreases down the group