astronomy midterm #1
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what is an astronomical unit? (AU)
earth’s average distance from the sun (93 million miles)
what is a light year? (ly)
the distance that light can travel in 2 years (6 trillion miles)
how did the universe come to be?
the big bang
what happened at the birth of the universe?
big bang, the universe expands, smaller scale gravity makes galaxies
how were other elements created at the beginning of the universe?
all other elements besides hydrogen & helium were made by stars & recycled from one stellar generation to the next
how was earth made?
earth is made from elements manufactured in stars that lived & died long ago
what are the basic motions of the earth?
daily rotation (spin)
yearly orbit (revolution)
what direction does earth rotate?
east to west
in how many years does our solar system orbit the galaxy?
230 million years
what is the speed of earth’s rotation?
1,000 kilomters/hr, or 600 mph
what is earth’s orbital distance?
1 AU / 150 kilometers
at what speed does earth go around the sun?
60,000 mph
where is the north celestial pole?
directly above earth’s north pole
what is the ecliptic?
the sun’s apparent annual path around the celestial sphere
what is the celestial equator?
a projection of earth’s equator into space
where is the south celestial pole?
directly above earth’s south pole
what is the horizon?
the boundary between earth & sky
what is the zenith?
the point directly overhead
what is the meridian?
an imaginary half-circle stretching from the horizon due south, through the zenith, to the horizon due north
what is the angular size?
the angular size of an object is the angle it appears to span in your field of view
which direction does the sun appear to move along the ecliptic?
the sun appears to move steadily eastward along the ecliptic, w/the stars of different constellations along the ecliptic that we call the zodiac
what does the sun appear to be in in august?
the sun appears to be in leo in late august
why can we not see when the sun is in leo?
it is our daytime sky, but we can see aquarius at night because its location is opposite from leo on the celestial sphere
what is the axis tilt?
earth’s axis points in the same direction throughout the year, which causes changes in earth’s orientation relative to the sun
what is northern summer/southern winter?
in june, sunlight falls directly on the northern hemisphere. the solar energy is more concentrated, making it summer.
the southern hemisphere receives less direct sunlight, making it winter
what is spring/fall?
spring & fall begin when sunlight falls equally on both hemispheres, which happens twice a year
what happens in each hemisphere in march?
spring begins in the north hemisphere
fall begins in the southern hemisphere
what happens in each hemisphere in september?
fall begins in the north hemisphere
spring begins in the south
what is northern winter/southern summer?
in december, sunlight falls less directly on the northern hemisphere, and the solar energy is less concentrated, making it winter.
the southern hemisphere receives more direct sunlight & the solar energy is more concentrated, making it summer.
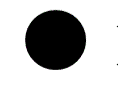
which lunar phase is this?
new moon

which lunar phase is this?
waxing crescent

which lunar phase is this?
first quarter

which lunar phase is this?
waxing gibbous
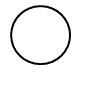
which lunar phase is this?
full moon

which lunar phase is this?
waning gibbous

which lunar phase is this?
last quarter

which lunar phase is this?
waning crescent
what happens in a lunar eclipse?
occurs when earth lies directly between the sun & moon, so earth’s shadow falls on the moon
what happens in a solar eclipse?
occurs when the moon lies directly between the sun & earth, so the moon’s shadow falls on earth
what is the saros cycle?
the combination of the changing dates of eclipse seasons & the 29 ½ day cycle of lunar phases makes eclipses recur in a cycle of about 18 years & 11 1/3 days
what did thales of miletus do? (d. 545 BCE)
predicted a solar eclipse
what did eudoxus come up with? (d. 350 BCE)
spherical astronomy, cycles of venus
what did aristarchus come up with? (d. 230 BCE)
heliocentric solar systems
what did eratosthenes do? (d. 194 BCE)
calculated the size of earth
what did hipparchus come up with? (d. 120 BCE)
stars are born & die, cataloged their positions
what did ptolemy come up with? (d. 120 CE)
almagest, tables of planetary positions, nested spheres cosmology
what did hypatia come up with? (d. 415 CE)
commentaries, edited volume on mathematics & astronomy
how did copernicus change our view of the universe?
accepted the notion of a heliocentric universe, but still required plants to follow circular orbits
how did brahe change our view of the universe?
conducted precision astronomical observations w/angular resolution of 1’
observed a nova (1572)
observed a comet (1577)
how did kepler change our view of the universe?
strong desire to “know the mind of god”
obsessed with perfect shapes
published 3 laws of planetary motion (1618-1621)
how did galileo change our view of the universe?
operations & experiments supported the copernican revolution
what is kepler’s first law?
planets orbit the sun in ellipses, with the sun at one focus
what is kepler’s second law?
planets sweep out equal areas in equal times (planets move faster closer to the sun & slows further away)
what is kepler’s third law?
closer plants orbit the sun more rapidly than more distant planets
implies that planetary motion is caused by a force from the sun
what is newton’s first law?
an object moves at constant velocity unless a net external force acts upon it
what is newton’s second law?
mass x acceleration
what is newton’s third law?
for any force, there is an equal & opposite force
what are the conservation laws?
conservation of momentum
conservation of angular momentum
conservation of energy
what are interactions between light & matter?
emission
absorption
transmission: light passes through
reflection/scattering: light bounces off (directionally organized/disorganized)
light…
acts as both a particle & a wave
light consists of…
photons, each with precise bits of energy (wavelength frequency)
what are atoms made up of?
photons, neutrons, and electrons
what is the atomic number?
the number of protons in the nucleus
what is the atomic mass number?
total number of protons & neutrons in a nucleus
what is an isotope?
versions of the same element, but with different number of neutrons in the nucleus
what are molecules?
two or more atoms that are bonded together
what is spectra?
continuous spectrum
emission line spectrum
absorption line spectrum
what can spectra tell us about an object?
composition, temperature & motion
what does spectra tell us about the composition?
emission & absorption lines are unique to the element and “state” it is in
electrons inhabit energy levels
absorption/emissions of photons causes electrons to change energy levels
what does spectra tell us about the temperature?
blackbody radiation (thermal radiation)
what is the doppler effect?
motion of an object along our line of sight causes changes in the frequency/wavelength of the light it emits
what is blueshift?
light is shifted to shorter wavelengths as an object approaches
what is rearshift?
light is shifted to longer wavelengths as an object moves away
what is the stefan-boltzmann law?
each sq meter of a hotter objects surface emits more light at all wavelengths
what is wein’s law?
hotter objects emit photons with a higher average energy
what is your “cosmic address” in the correct order?
you, earth, solar system, milky way galaxy, local group, local supercluster, universe
in what sense are we “star stuff”?
nearly every atom from which we are made was once inside a star
how are galaxies important to our existence?
galaxies recycle material from one generation of stars to the next, and without this recycling we could not exist
when we look at an object that is 1,000 light-years away, we see it ……
as it was 1,000 years ago