Lecture 4 - OMFS (Exam2): Principles of Differential Diagnosis and Biopsy of Pathologic Lesions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
- site
- morphology
- color
When clinically identifying an oral pathology, you want to describe 3 things:
Leukoerythroplakia
What lesion color should raise suspicion of malignancy:
- ulceration persisting more than 2 week
- rapid growth
- bleeding
- indurated/firm
- fixation/immoblie
What lesion characteristics should raise suspicion of malignancy:
2 weeks
a lesion that has persisted over _______ should raise concern for malignancy
panoramic
what type of imaging is the gold standard for aiding in diagnosis after clinical exam and med history?
Nasopalatine duct cyst
All of the following are odontogenic developmental cysts or tumors EXCEPT:
- Odontogenic keratocyst (KOT)
- Dentigerous cyst
- Eruption cysts
- Nasopalatine duct cyst
- Lateral periodontal cyst
- Gingival cyst
- Glandular odontogenic cyst
- KOT
- Ameloblastoma
Dentigerous cyst
All of the following are non-odontogenic developmental cysts or tumors EXCEPT:
- Nasopalatine duct cyst
- Dentigerous cyst
- Nasolabial cyst
- Median cyst
false
t/f: if you see any lesion, it always requires a biopsy
smoking
What social habits of patients should raise suspicion for developing oral malignancy:
- floor of mouth
- ventral lateral tongue
An ulcer in what location of the mouth should raise suspicion for oral malignancy:
biopsy
Removal of tissue from a living individual for diagnostic examination:
- Aspiration
- Cytology
- Incisional
- Excisional
What are the 4 types of biopsies we can preform?
Incisional
a patient presents with a non-healing leukoerythroplakic ulcerated lesion on the ventral latereral border of the tongue. The lesion has been there for 3 weeks. What type of biopsy should you take?
- Aspiration
- Cytology
- Incisional
- Excisional

•Any lesion that persists for more than 2 weeks with no apparent etiology
•Any inflammatory lesion that does not respond to local treatment after 10 to 14 days (after removing local irritant)
•Persistent changes in surface tissue (lips or oral mucosa)
•Any persistent tumescence, either visible or palpable beneath relatively normal tissue
•Lesion that interfere with local function (fibroma)
•Bone lesions where inflammatory conditions can be ruled out
What are the indications for a biopsy:
aspiration biopsy
the use of a needle and syringe to penetrate a lesion for aspiration of cells or content:
Aspiration
Your patient presents with a fluctuant mass in the area of the neck. You are pretty sure it contains fluid. What type of biopsy should you take?
- Aspiration
- Cytology
- Incisional
- Excisional
cytology smear
When a brush is placed in contact with oral epithelium and rotated with firm pressure 5 to 10 times
•The brush collects cells from all three layers of epithelium: superficial, intermediate and basal
•Brush is smeared onto glass slide and placed in container with fixative solution
computer
Cytology smears are evaluated by both pathologist and a computer. Which one determines if adequate specimen was obtained?
- pathologist
- computer
computer
Cytology smears are evaluated by both pathologist and a computer. Which one determines if the cells are dysplastic or malignant?
- pathologist
- computer
pathologist
Cytology smears are evaluated by both pathologist and a computer. Which one classifies the findings into three categories: negative, positive, or atypia?
- pathologist
- computer
false
t/f: oral brush biopsies require either topical or local anesthesia to obtain from patients
- true
- false
false/s
t/f: you can do a brush biopsy as a substitute for a scalpel biopsy
- true
- false
Incisional
If the lesion is large or has different characteristics at different locations, What type of biopsy should you take?
- Aspiration
- Cytology
- Incisional
- Excisional
true
t/f: if the lesion is large or has different characteristics at different locations, more than one area of the lesion may require biopsy
- true
- false
false.
t/f: if a lesion is suspicious for malignancy, you should do an excisional biopsy to remove it from the patient immediately
- true
- false
true
t/f: Small lesions with high degree of suspicion should undergo incisional biopsy
- true
- false
Should not include normal tissue
all of the following are true about incisional biopsy principles EXCEPT:
- Wedge shape
- Selected area that shows complete tissue changes
- Should not include normal tissue
- Necrotic tissue should be avoided
- Narrow better than broad
Should include normal tissue
all of the following are true about incisional biopsy principles EXCEPT:
- Wedge shape
- Selected area that shows complete tissue changes
- Should include normal tissue
- Necrotic tissue should be included
- Narrow better than broad
tissue punch
What tool can be used to take a incisional biopsy?
Excisional Biopsy
The removal of the entire lesion, along with 2 to 3 mm of normal-appearing surrounding tissue, is excised
2 to 3
In an Excisional Biopsy, the entire lesion, along with _____ mm of normal-appearing surrounding tissue, is excised
- Oncologic margin
- Closure
What are 2 reasons you would include a perimeter of normal tissue surrounding the lesion in an excisional biopsy?
Excisional
Your patient presents will a yellow 1cm x 1cm nodule on the lateral border of the tongue. It looks mostly like a lipoma.
What type of biopsy should you take?
- Aspiration
- Cytology
- Incisional
- Excisional
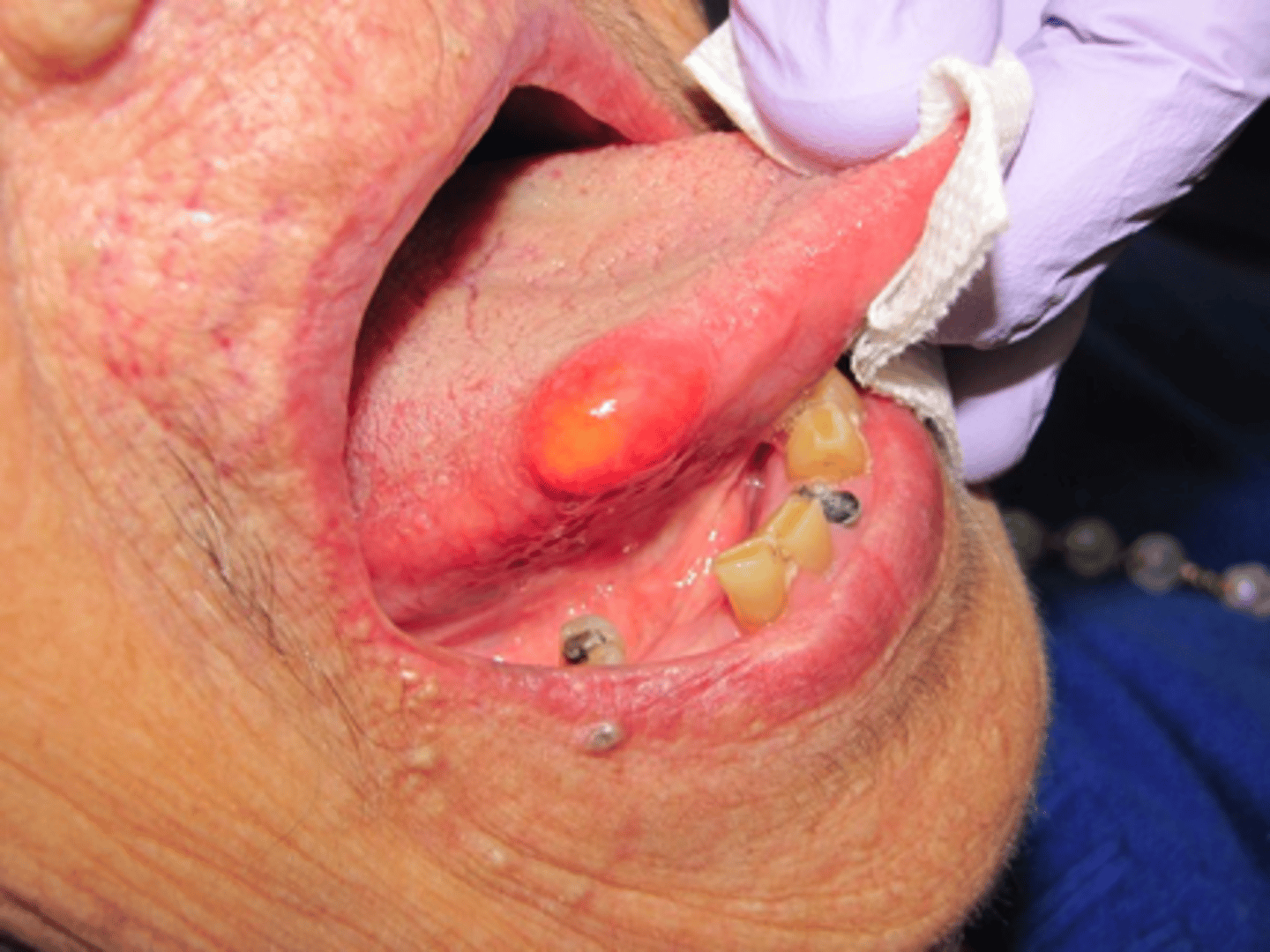
true
t/f: LA should not be injected within the tissues to be removed
- true
- false
use of suction device
Which of the following is not suggested when considering the principle of hemostasis during a biopsy:
- use of suction device
- Gauze only
- Gauze over suction device
traction suture
The use of a ________ through the specimen is an excellent method for avoiding specimen trauma
take two biopsies, put one in 10% formalin solution, and one in Michel's solution for immunofluorescence studies
If your suspect an autoimmune disease is the cause of your patients oral pathologies, how should you take a biopsy?
the defect
Undermine the wound margins by at least the width of _____ in each direction which allows approximation of the tissue with little to no tension
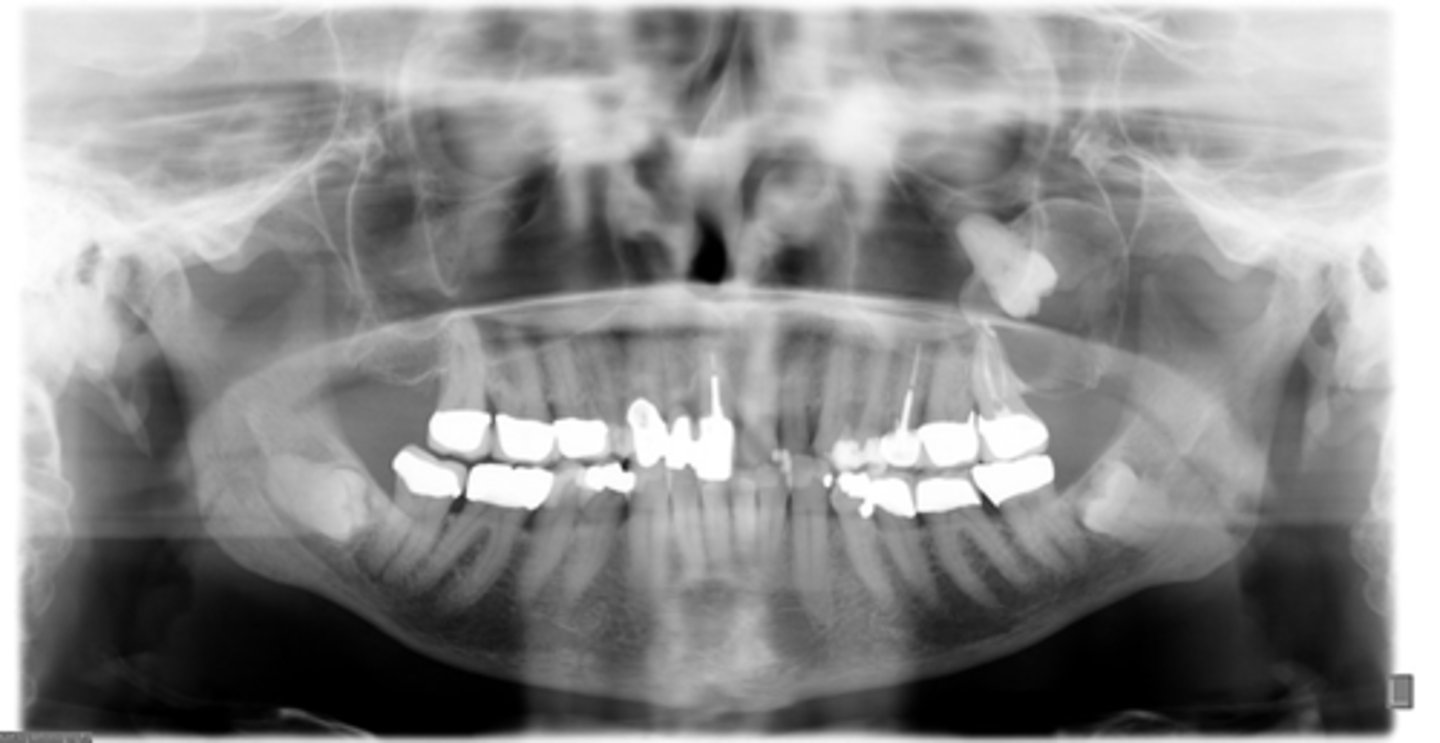
Aspiration
You patient presents with a pano exhibiting a well defined, corticated, unilocular radiolucency associated with the crown of an unerupted #16. What type of biopsy should you take first?
- Aspiration
- Cytology
- Incisional
- Excisional
cental curette
A _____ is used keeping the concave surface in contact with the osseous surfaces of the bony cavity
•All specimens need to be labeled
•History and clinical description
•Radiographs / pictures
What all should you include on your biopsy sheet?
7 to 10 days
After a biopsy, you can follow up with a patient within _____