Atoms, Ions & Molecules
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Atom Diagram Structure
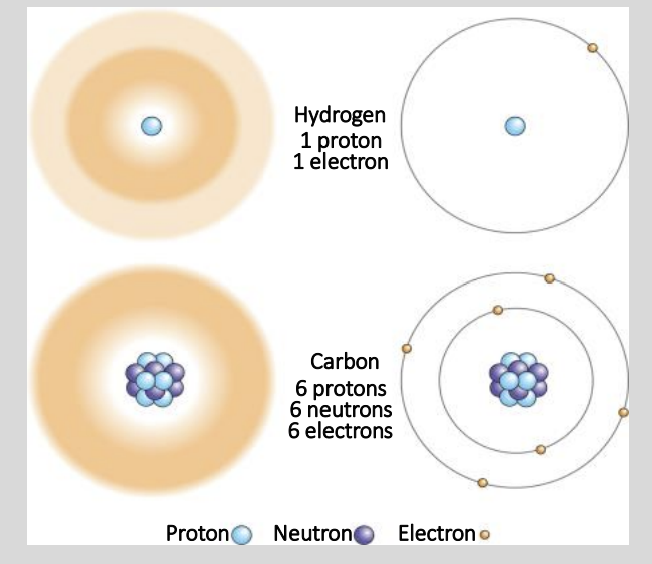
What are the 3 Subatomic Structures seen in an Atom?
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Describe Protons, Neutrons and Electrons?
Proton
Positively Charged (+)
Neutron
No Charge
Electron
Negatively Charged (-)
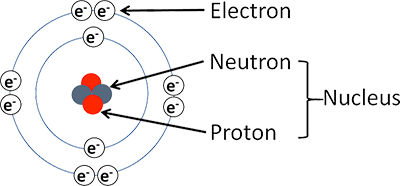
Protons & Neutrons are found where in the Atom?
The Centre (Nucleus) of the Atom
Where are the Electrons found?
Orbiting the Positively charged nucleus.
The 1st Shell can accomodate how many electrons?
2
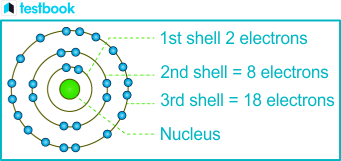
The 2nd Shell can accomodate how many electrons?
8 Electrons
All subsequent shells after the 2nd Shell can accomodate how many electrons?
8
If an Atom has more Electrons than Protons that makes the Atom?
Negatively Charged
If an Atom has more Protons than Electrons the Atom is ?
Positively Charged
An atom or a molecule that carries a net positive or a net negative charge is known as ?
Ion
A Positively (+) Charged Atom is called a?
Cation
A Negatively (-) Charged Atom is called a?
Anion
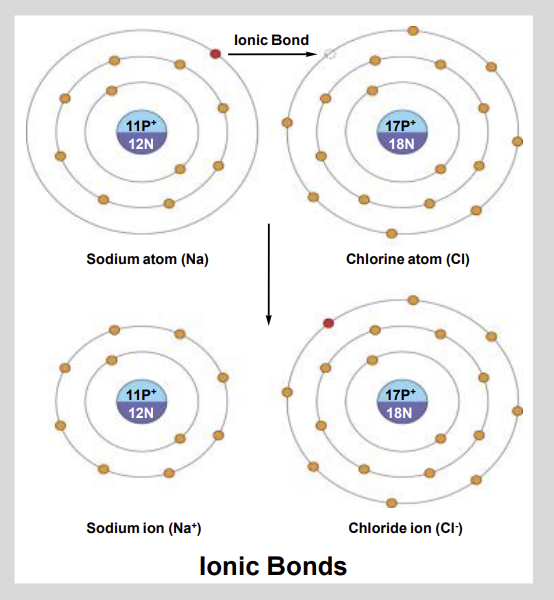
Is Sodium positive or Negative?
Positive
Is Chloride negative or Positive?
Negative
What is an Ionic Bond?
Bond formed when one atom transfers electrons to another atom.
Creating oppositely charged ions that are held together by electrostatic attraction.
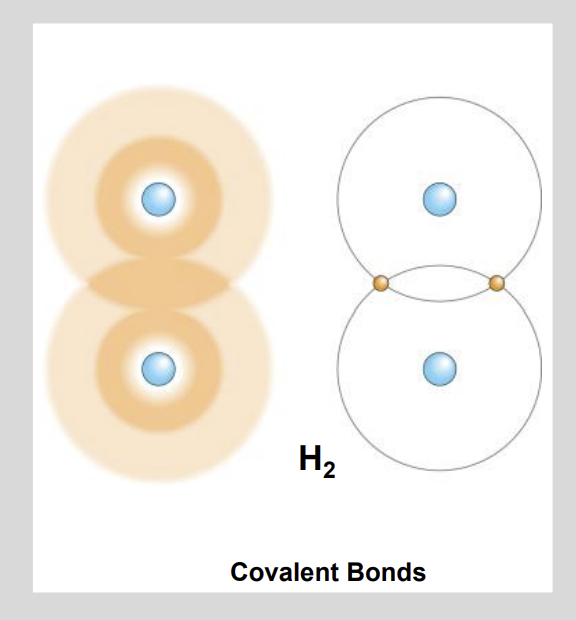
What is a Covalent Bond?
When Atoms Share Electrons.
Instead of fully donating.
Organic molecules are molecules that contain?
Carbon
What is Polarity?
When 2 Identical Atoms form Covalent Bonds.
They Share Equally.
Atoms attracted equally to both Nuclei of an Atom are called?
Non Polar
Atoms attracted not equally to both Nuclei of an Atom are called?
Polar
A Hydrogen Cation is simply a ?
Free Cation
Why do Free Cations never exist for very long?
As it is Strongly attracted to the electrons of other atoms/molecules.
The concentration of protons (H+ ) in a solution is the basis of the?
pH scale
An Acid is a solution with a pH lower than?
7
An Alkaline or Basic Solution has a pH Higher than?
7
A Substance than can reduce the availability of H+ ions is known as ?
A Buffer
pH scale diagram
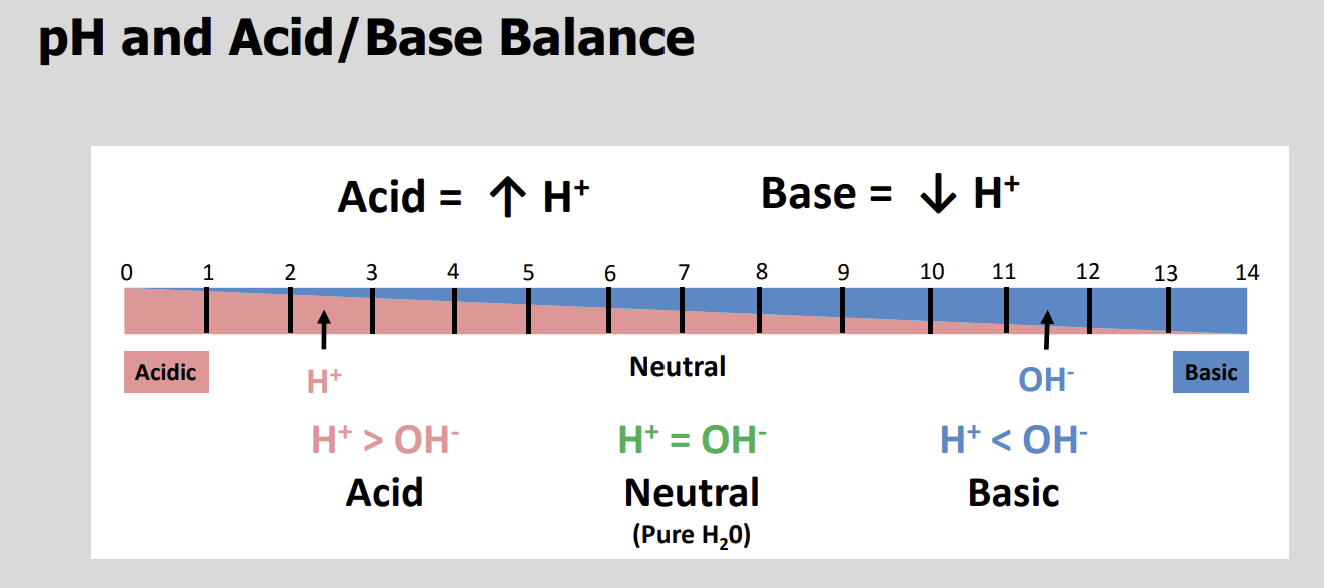
The pH of arterial blood is normally?
7.4
The acceptable physiological range for arterial pH is?
7.35 to 7.45