Anatomy & Physiology (LAB 1) - Body Planes, Cavities, & Different Terms
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Describe the standard anatomical position
Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward with thumbs pointing away from body
Directional terms
allow body parts to be located precisely. Direction is always based on standard anatomical position
Superior (cranial)
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
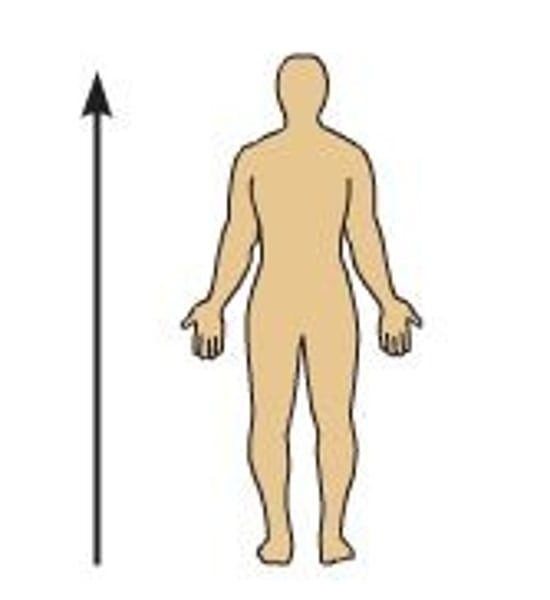
Inferior (caudal)
Away from head end or toward the lower part of the body
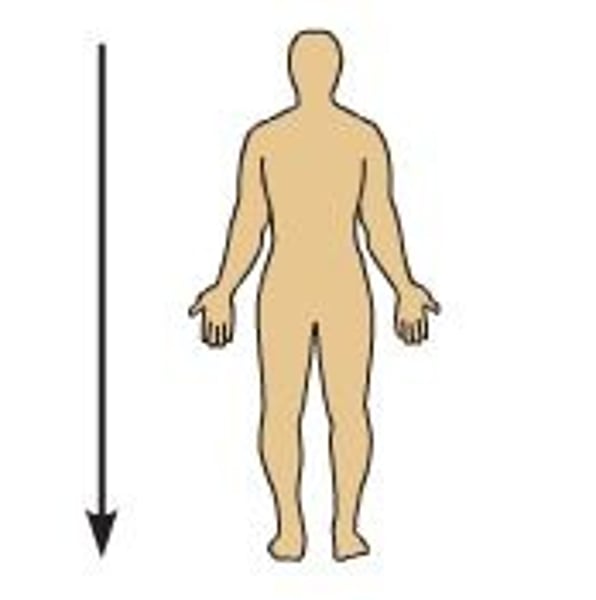
Anterior (ventral)
front of the body; toward the front
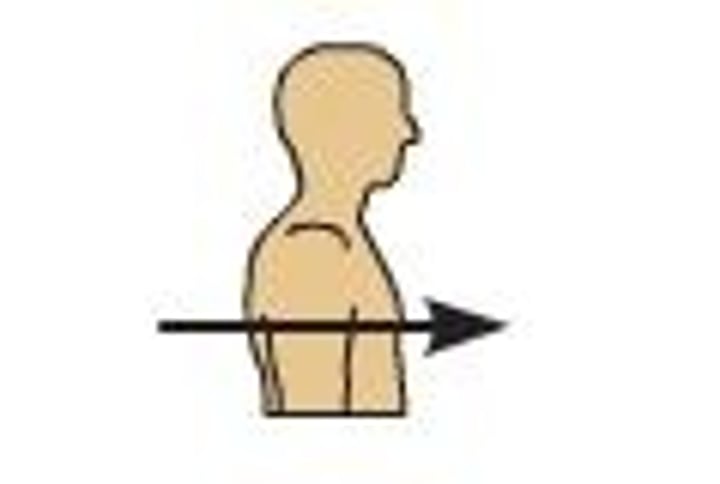
Posterior (dorsal)
back of the body; toward the back
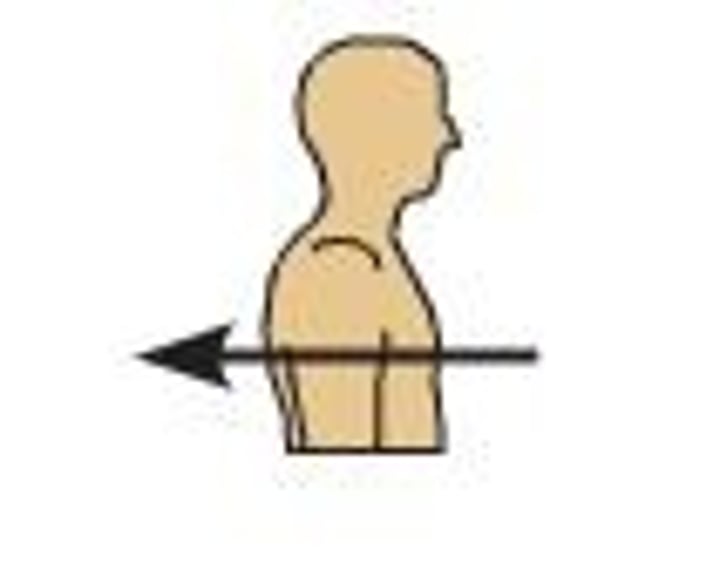
Medial
toward the midline of the body
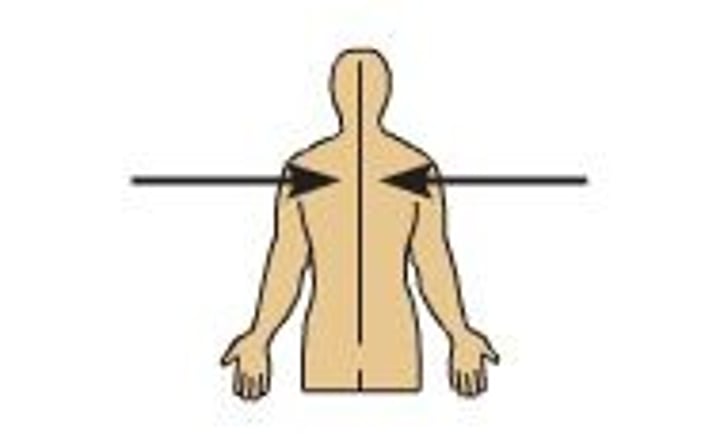
Lateral
away from the midline of the body
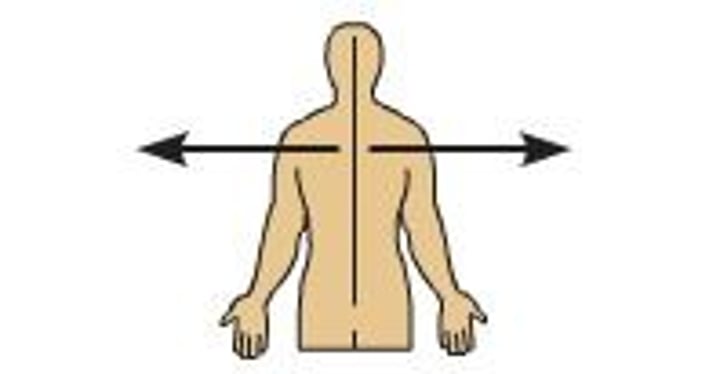
Intermediate
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
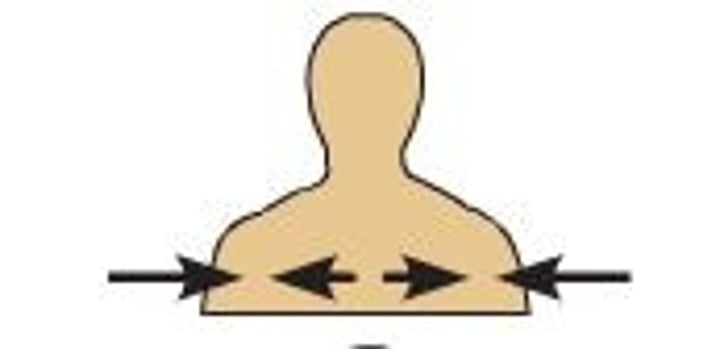
Proximal
closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
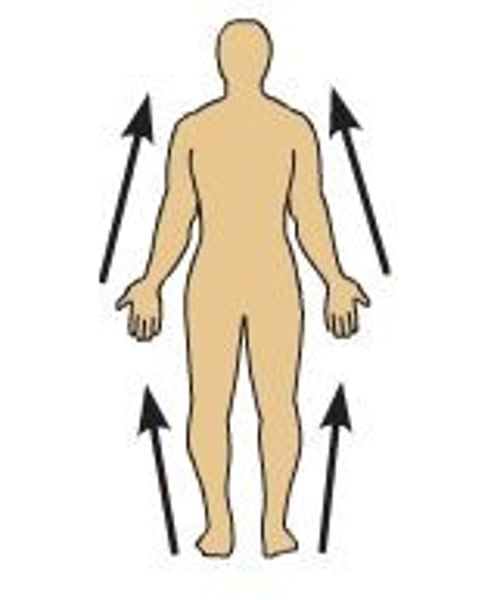
Distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
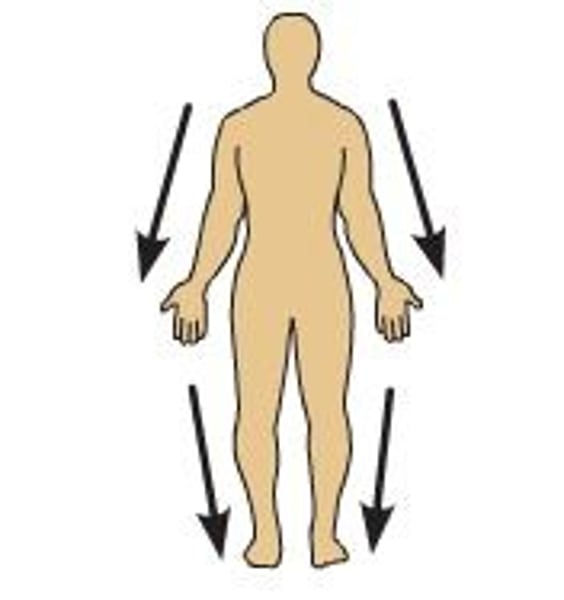
Superficial (external)
toward or at the body surface
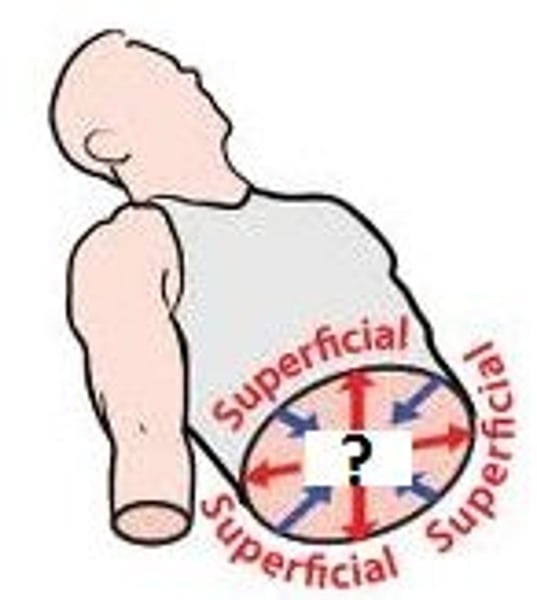
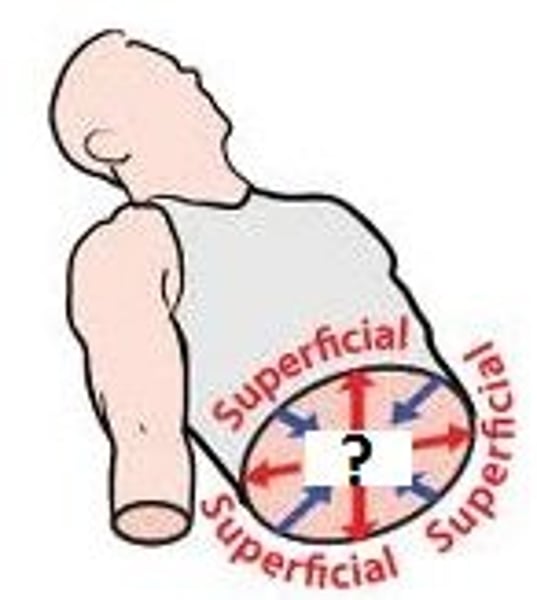
Deep (internal)
away from the body surface; more internal
Afferent
going towards
Efferent
going away from
The nose is ________ to the lips
superior
The knee is ______ to the ankle
proximal
The eyes are _______ to the ears
medial
Axial part
makes up the main axis of our body, includes the head, neck, and trunk.
Appendicular part
consists of the appendages, or limbs, which are attached to the body's axis
Body planes
surfaces along which body or structures may be cut for anatomical study. Main are...
- Sagittal
- Transverse
- Coronal
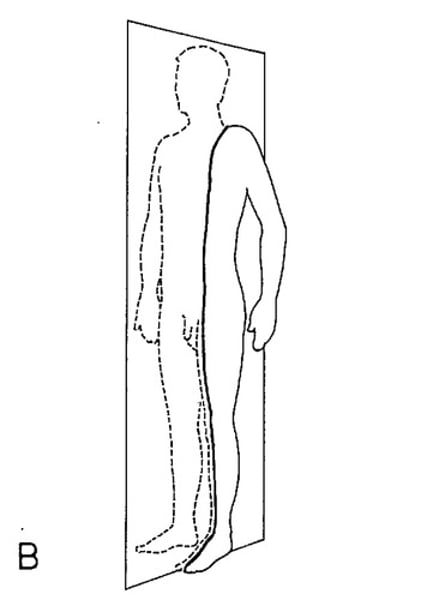
Sagittal plane (median plane)
divides body/body part into left & right sections
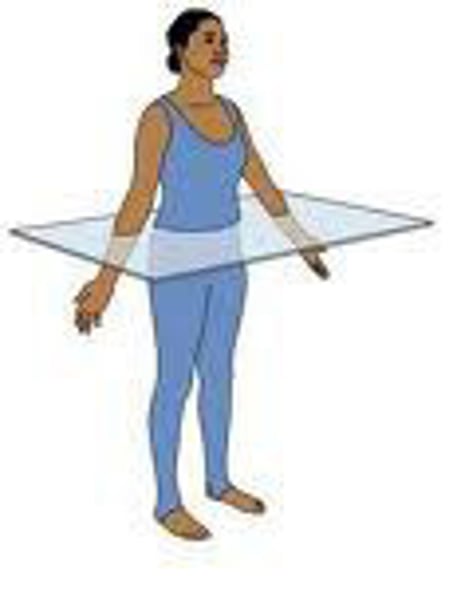
Transverse plane (horizontal plane)
divides the body into upper and lower portions
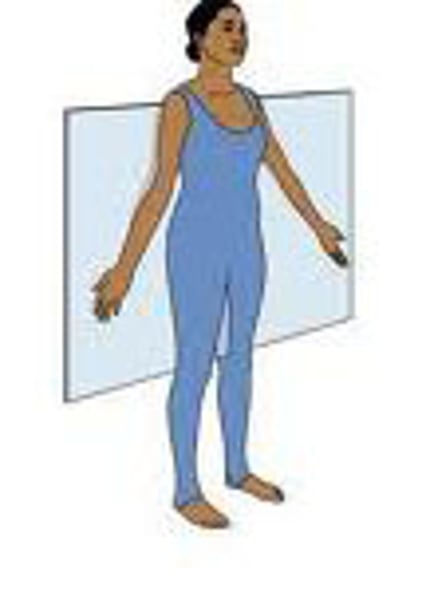
Coronal plane (frontal plane)
vertical division of the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions
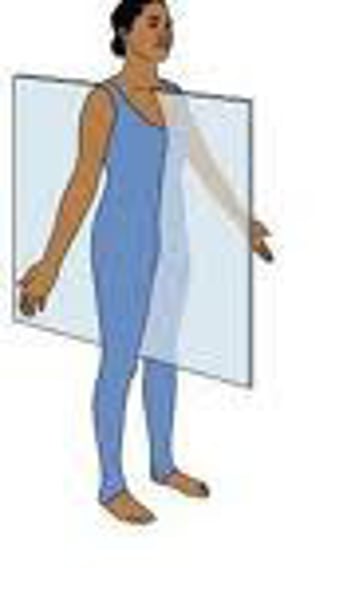
Parasagittal plane
divides body into unequal right and left sides
Oblique plane (angular)
cut made diagonally between horizontal & vertical planes
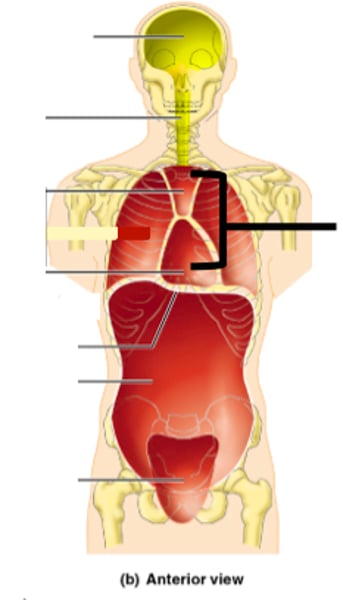
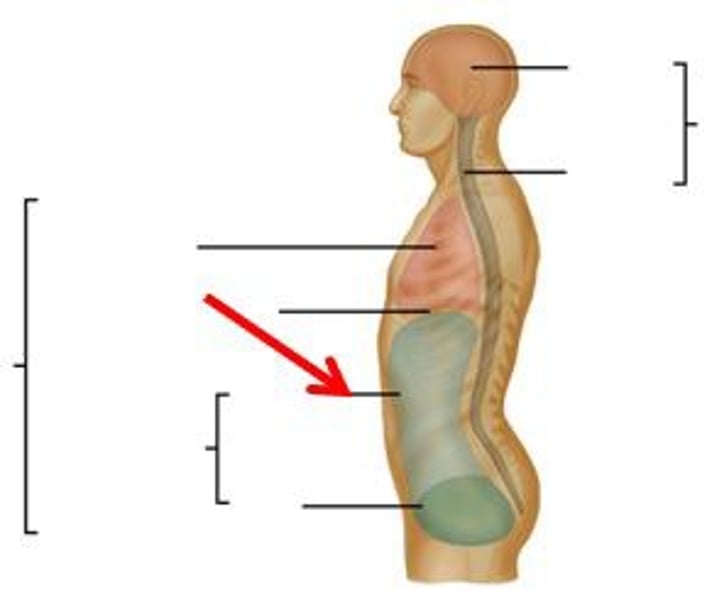
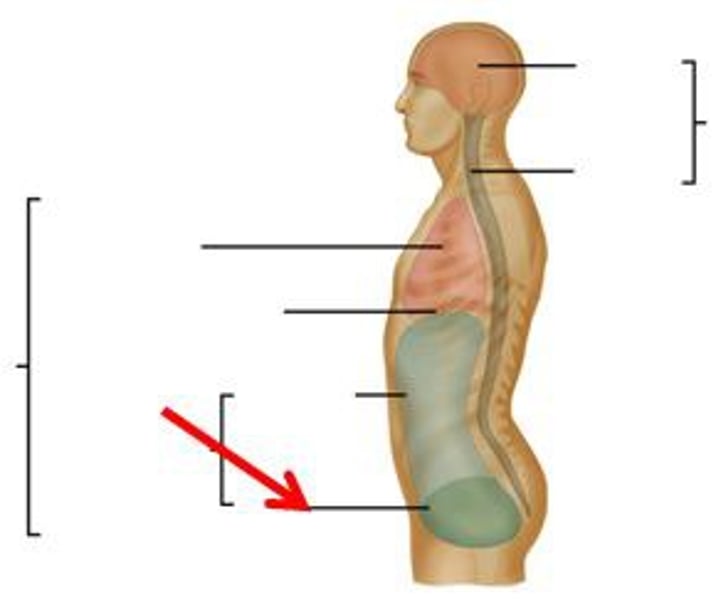
Body cavities
spaces within the body that contain vital organs
Dorsal cavity
protects fragile nervous system
- includes the cranial and spinal cavities
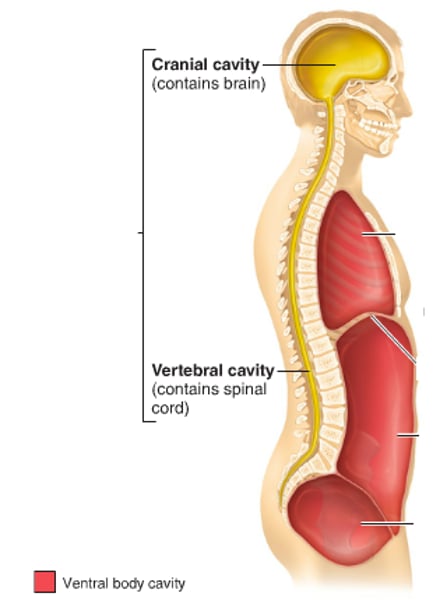
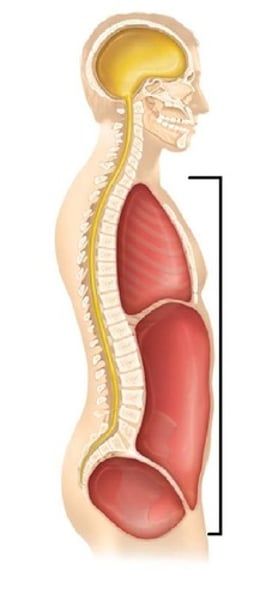
Ventral cavity
houses the internal organs (collectively called viscera)
- thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
Pleural cavities
each cavity surrounds one lung
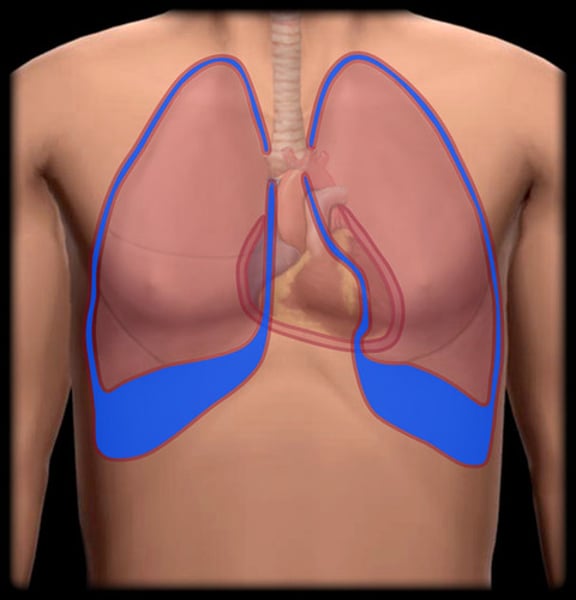
Mediastinum
contains pericardial cavity
- surrounds other thoracic organs, such as esophagus, trachea, etc
Pericardial cavity
contains the heart
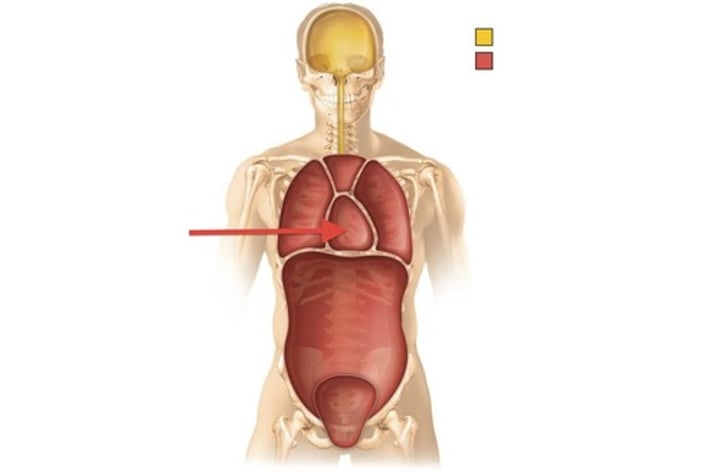
Abdominal cavity
contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Serosae
Thin double layered membranes that cover surfaces within ventral body cavity (aka serous membrane)
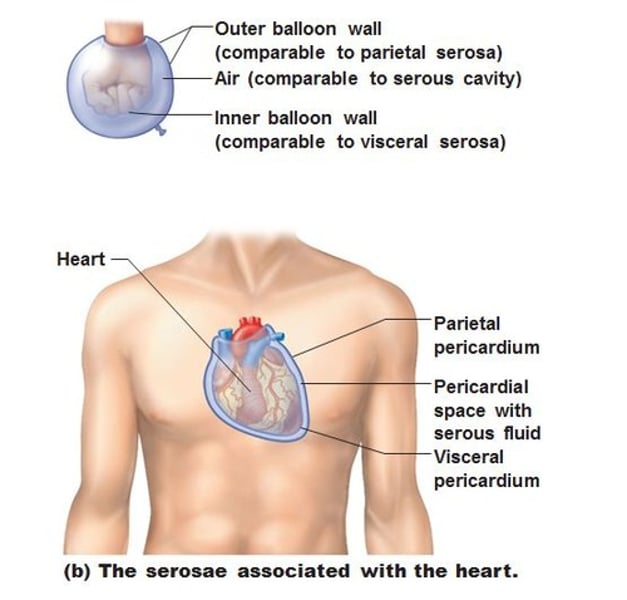
Parietal serosa
lines internal body cavity walls
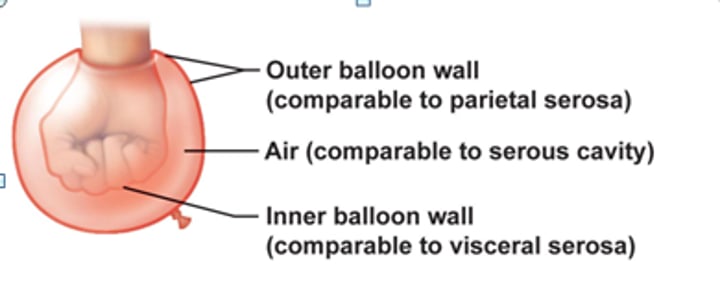
Visceral serosa
covers internal organs (viscera)
Serous Membrane Relationships
serous membranes are named for specific cavities & organs
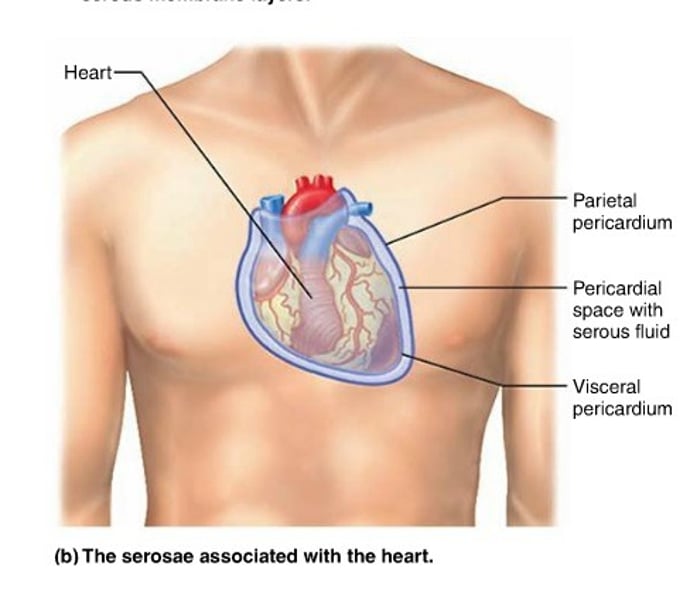
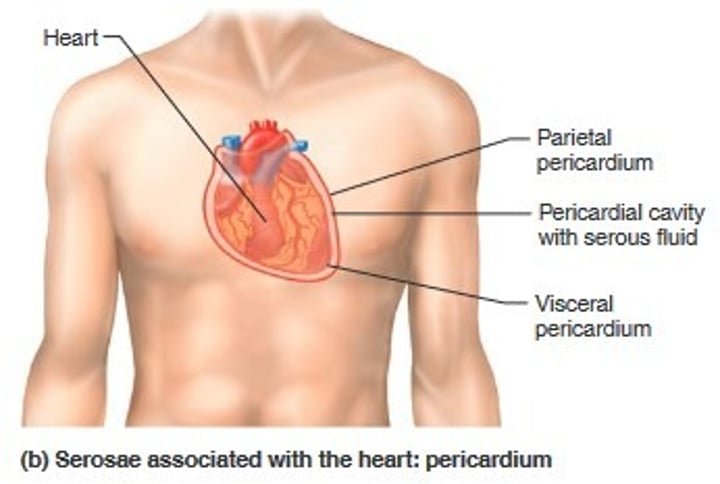
Pericardium serosae
parietal pericardium line the pericardial cavity and fold back as the visceral pericardium
- covers the Heart
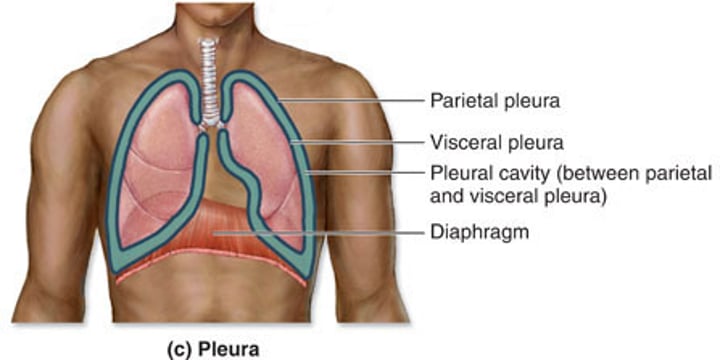
Pleurae serosae
parietal pleurae line the walls of the thoracic cavity
- visceral pleurae cover the lungs
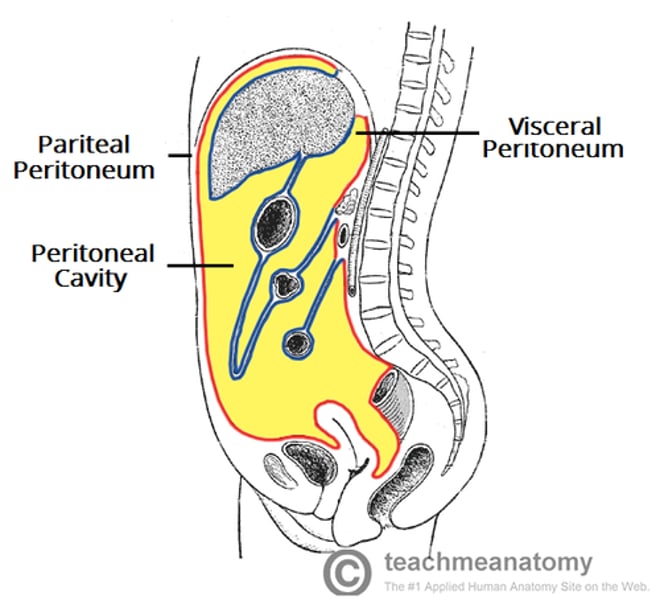
Peritoneum
parietal peritoneum associated with walls of abdominopelvic cavity
- visceral peritoneum covers most of the organs within that cavity
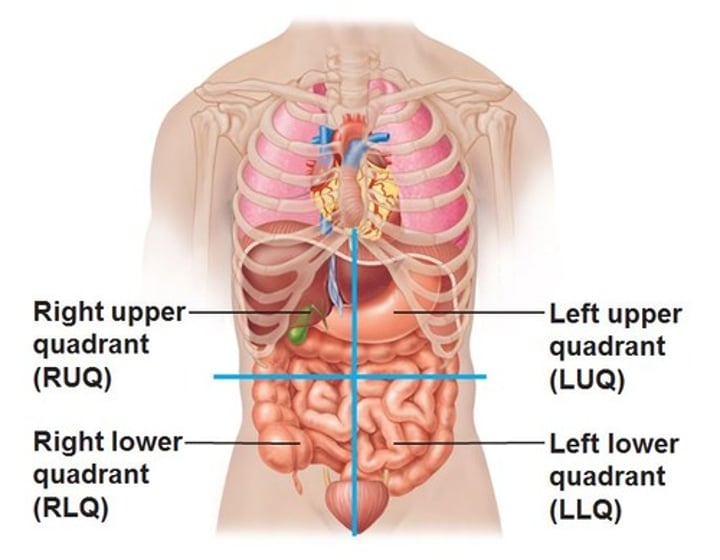
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
divisions used primarily by medical personnel
- Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
- Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
- Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
- Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
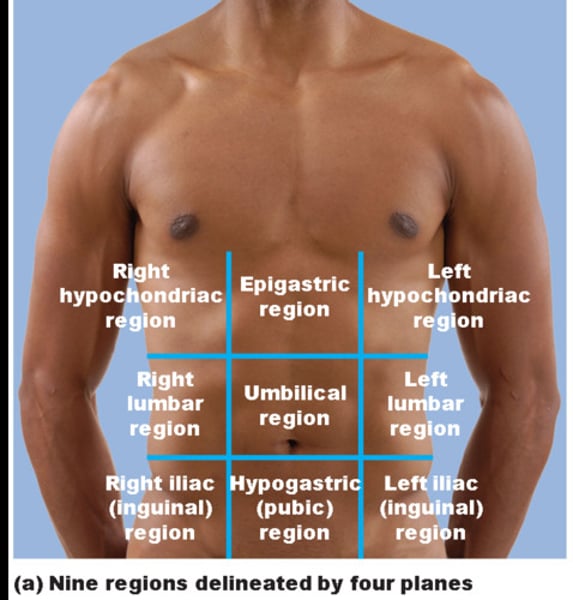
Nine Abdominopelvic Regions
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac (inguinal), hypogastric, left iliac (inguinal)
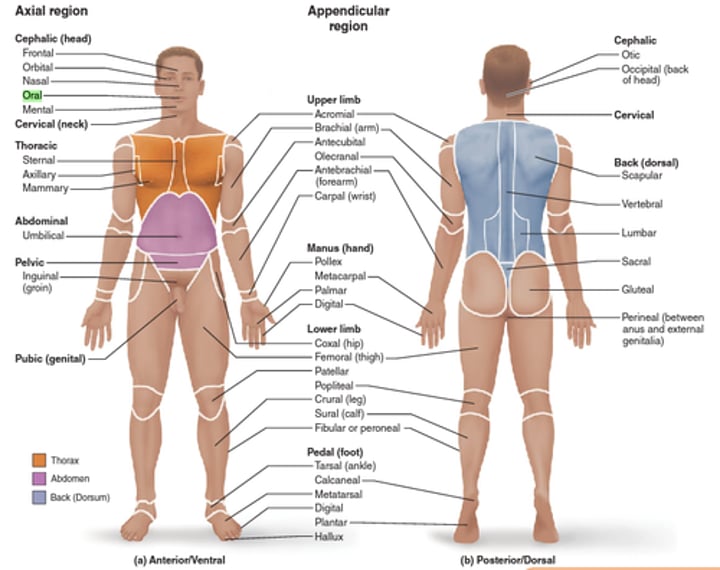
Regional terms
Anatomical terms that refer to specific visible landmarks on the surface of the body
Frontal
pertaining to the forehead
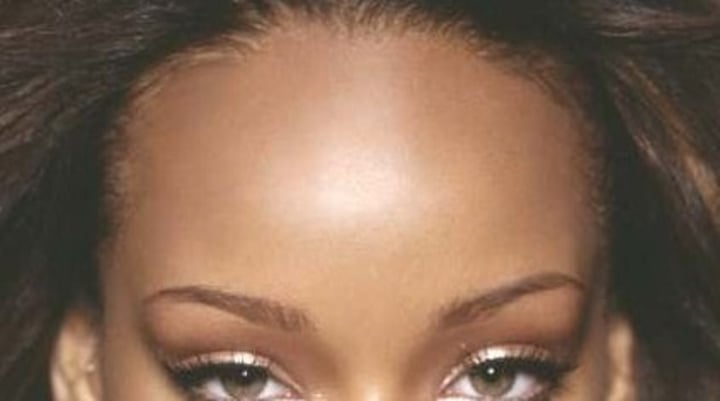

Orbital
pertaining to the eyes

Buccal
pertaining to the cheek
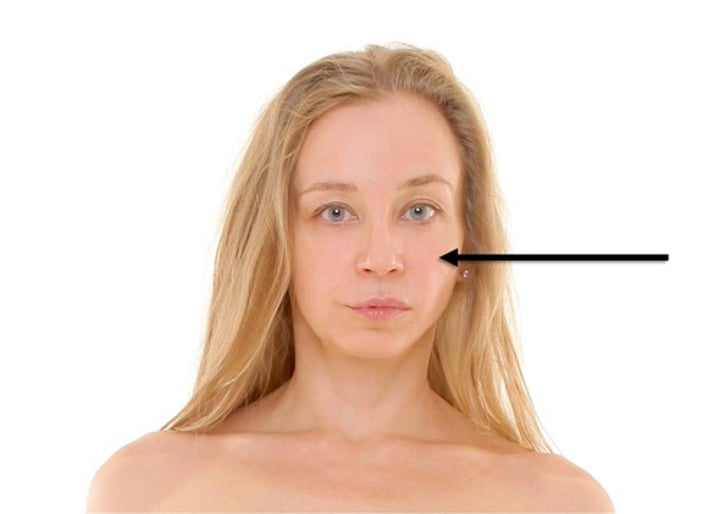
Mental
pertaining to the chin

Acromial
pertaining to the shoulder

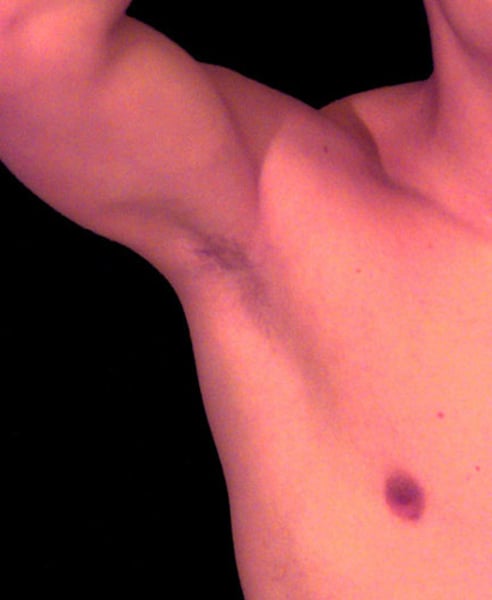
Axillary
pertaining to the armpit
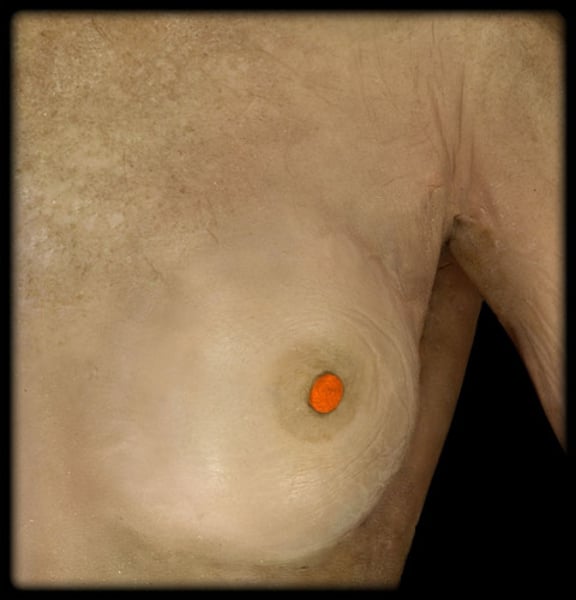
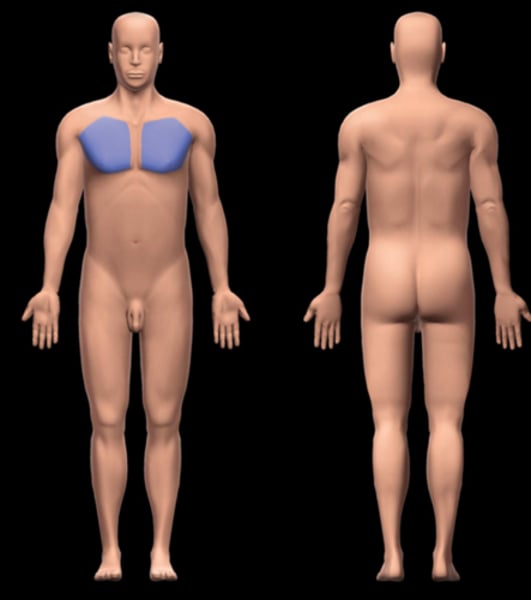
Mammary
pertaining to the nipples
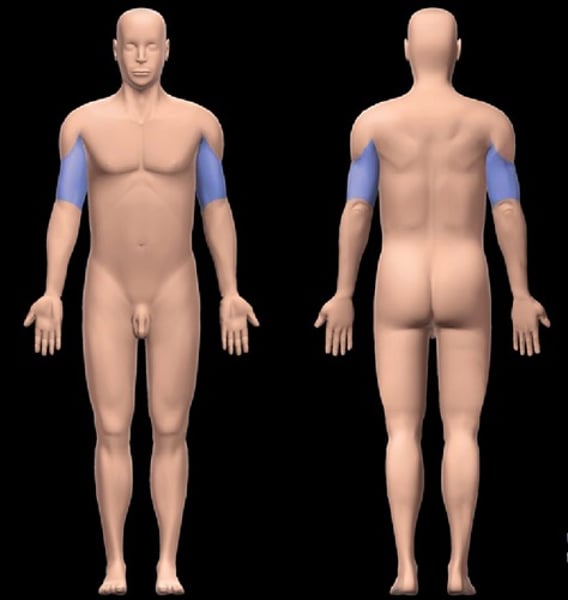
Brachial
pertaining to the upper arm
Olecranal
pertaining to the elbow
Antecubital
pertaining to the front of elbow
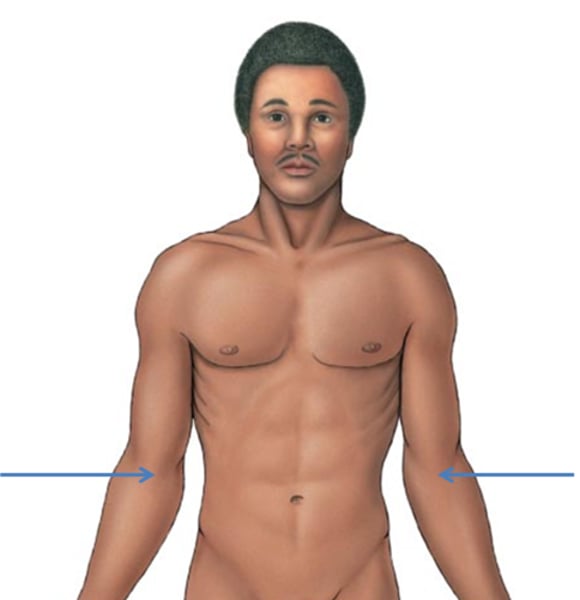
Antebrachial
pertaining to the forearm
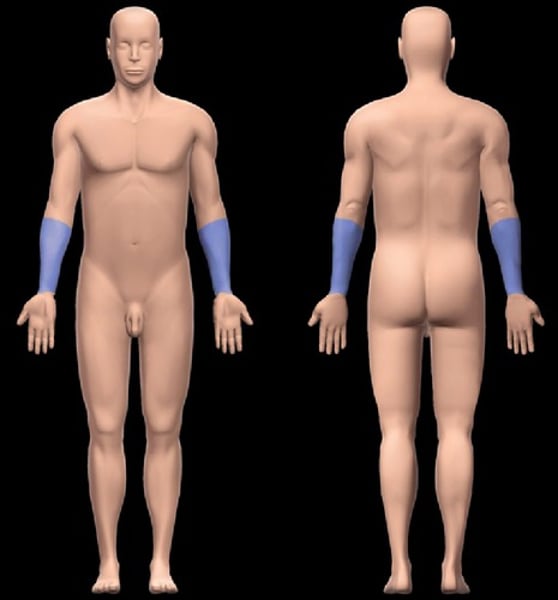
Carpal
pertaining to the wrist
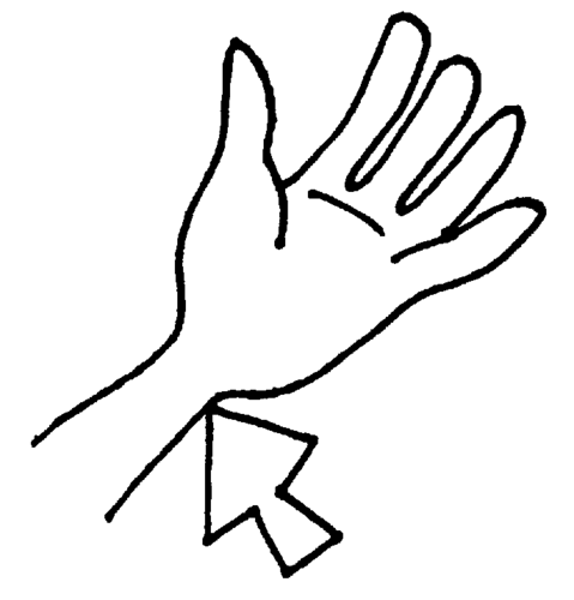
Cervical
pertaining to the neck
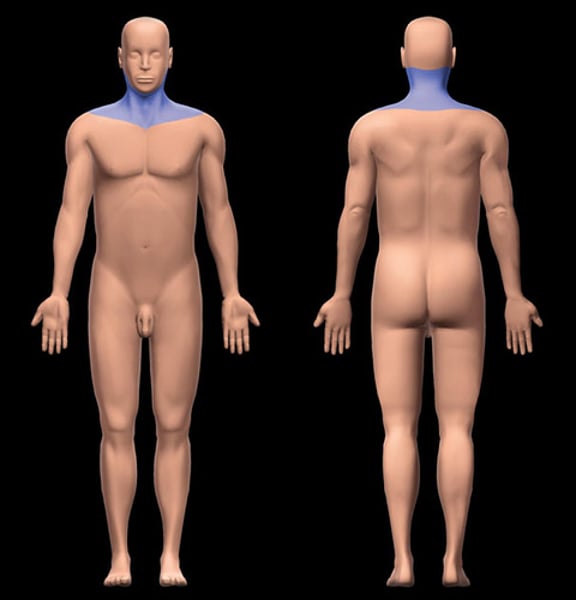
Abdominal
pertaining to the abdomen
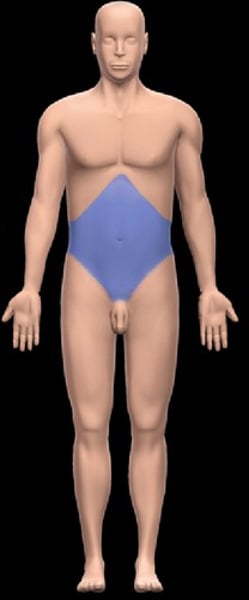
Umbilical
pertaining to the belly button
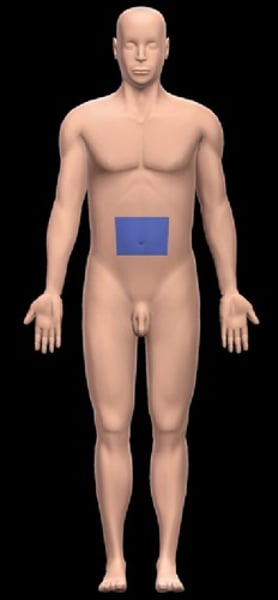
Sternal
pertaining to the breastbone
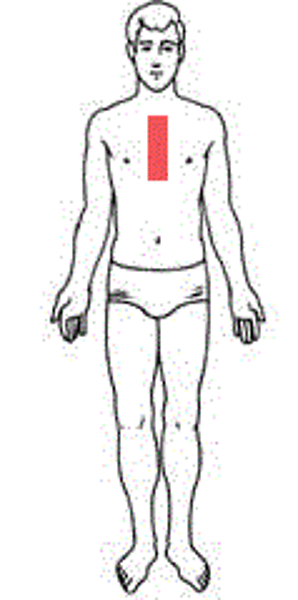
Pectoral
pertaining to the chest
Nasal
pertaining to the nose
Oral
pertaining to the mouth
Manus
pertaining to the hand

Metacarpal
pertaining to the back of the hand
Palmar
pertaining to the front of the hand
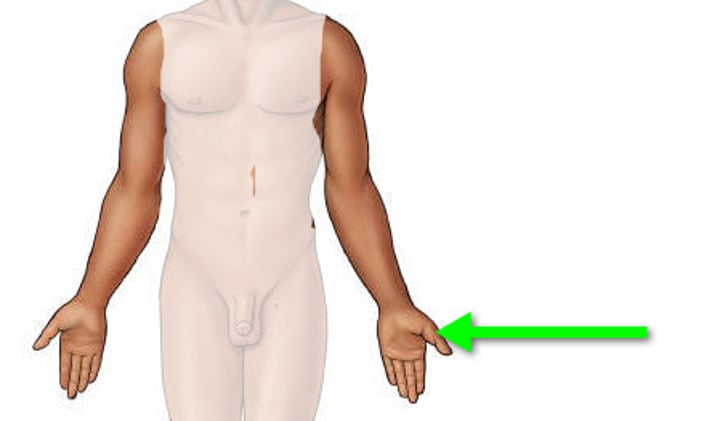
Pollex
pertaining to the thumb
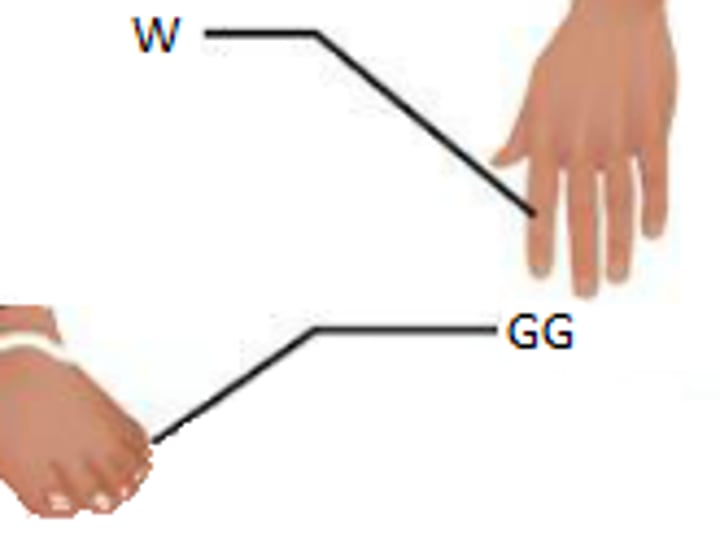
Digital
pertaining to the fingers/toes
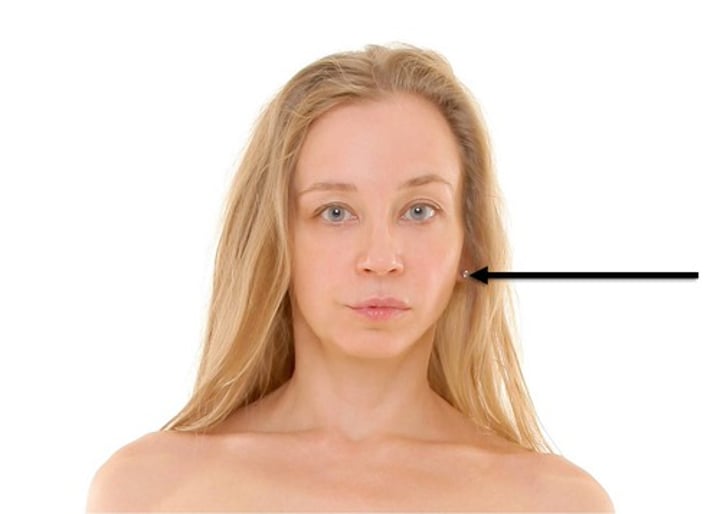
Otic
pertaining to the ear
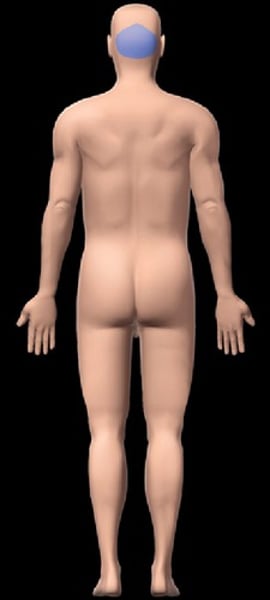
Occipital
pertaining to the back of the head
Dorsal
pertaining to the back
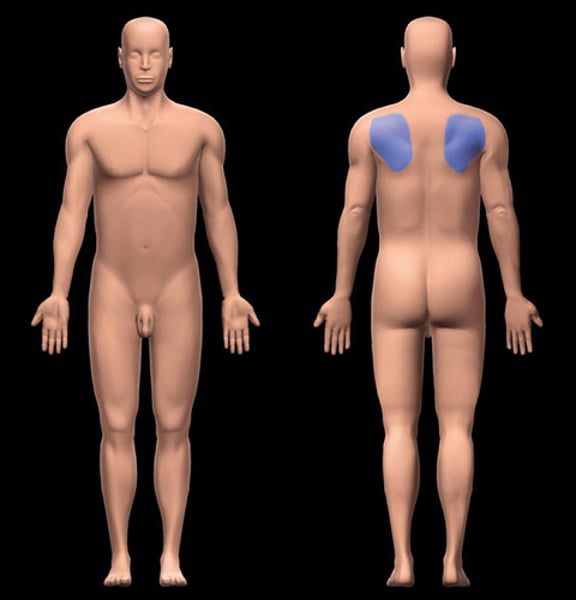
Scapular
pertaining to the shoulder blades
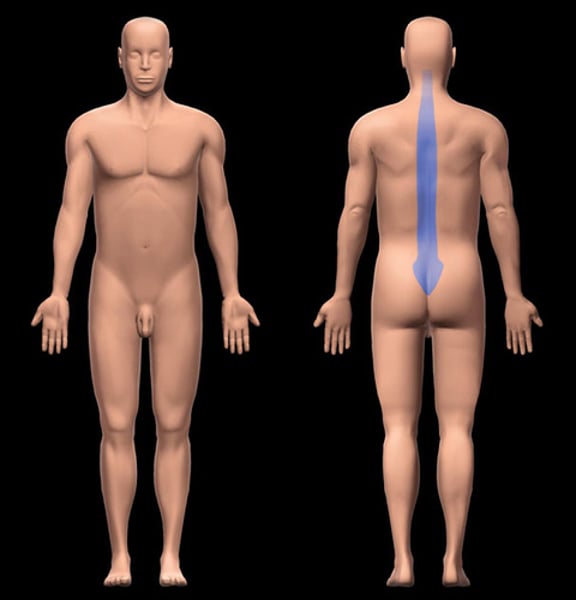
Vertebral
pertaining to the spine
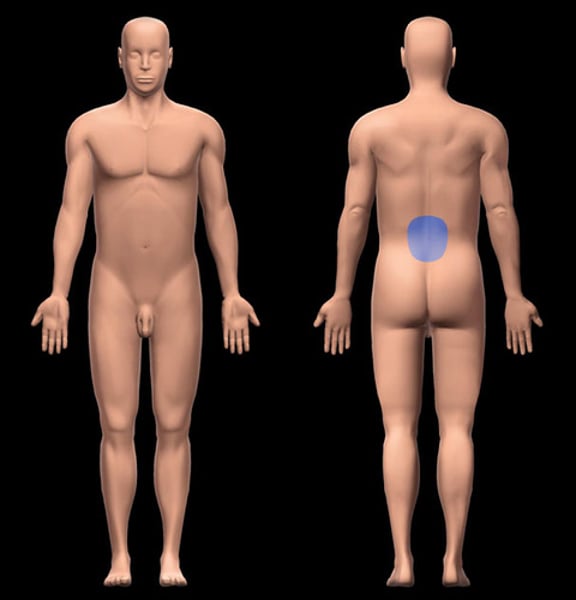
Lumbar
pertaining to the lower back
Sacral
pertaining to the posterior area between hips
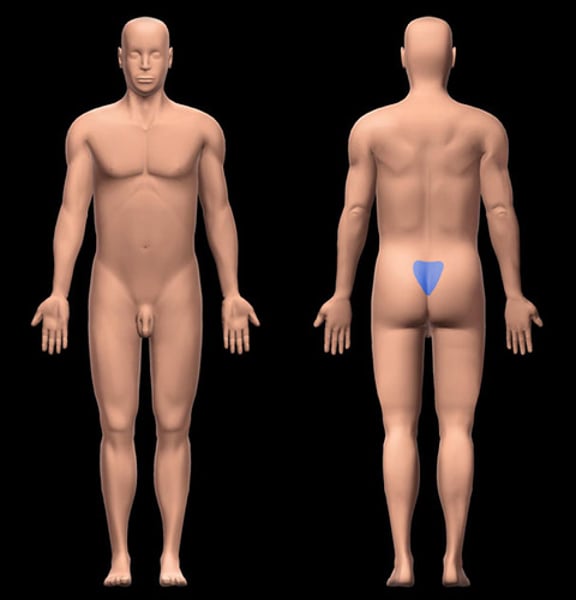
Gluteal
pertaining to the buttocks
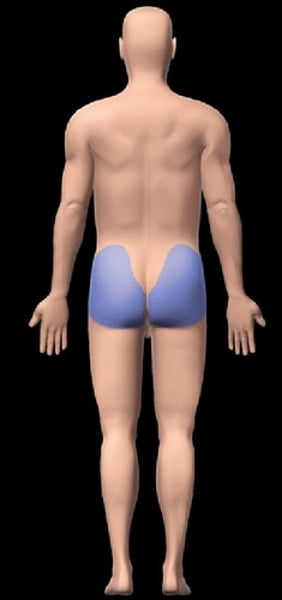
Perineal
pertaining to the area between anus and external genitalia
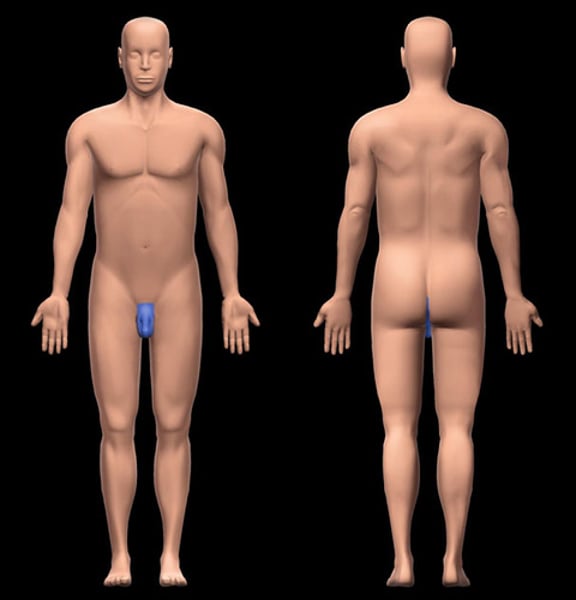
Inguinal
pertaining to the groin
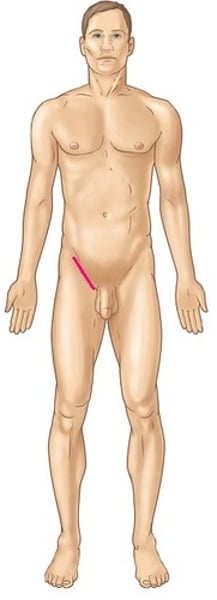
Genital
pertaining to the genitalia
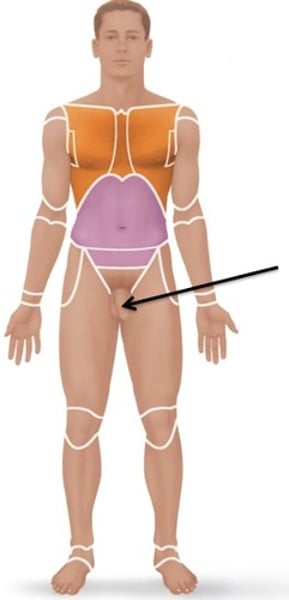
Coxal
pertaining to the hip
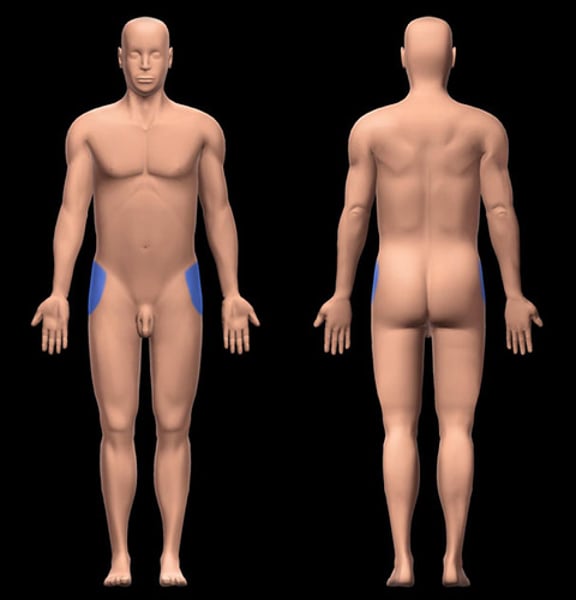
Femoral
pertaining to the thigh
Patellar
pertaining to the knee cap
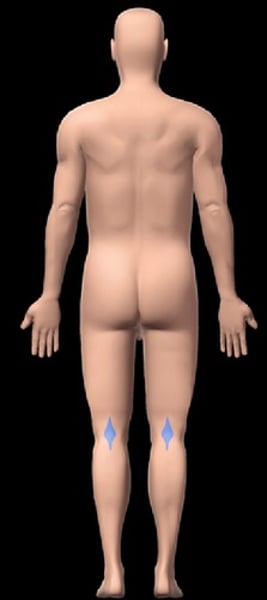
Popliteal
pertaining to the area posterior to knee cap
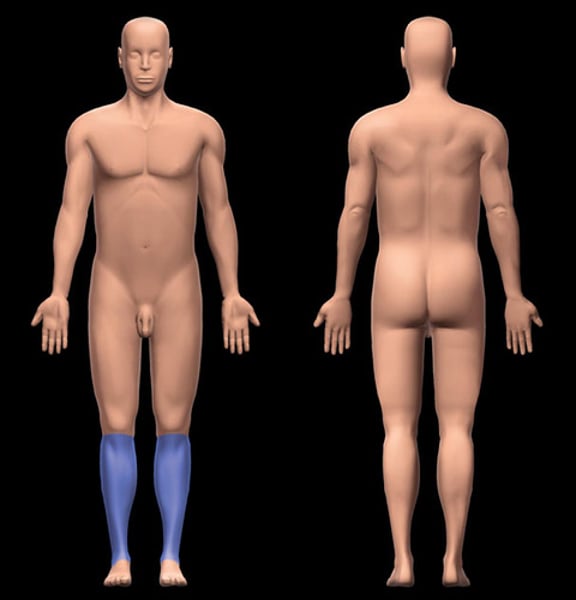
Crural
pertaining to the lower leg
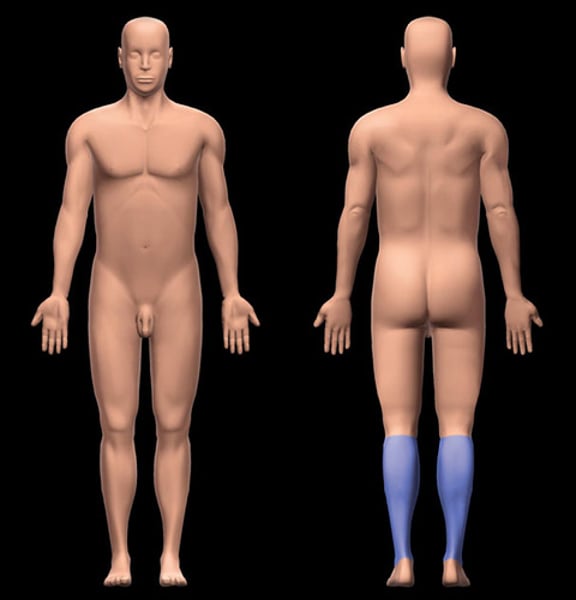
Sural
pertaining to the calf
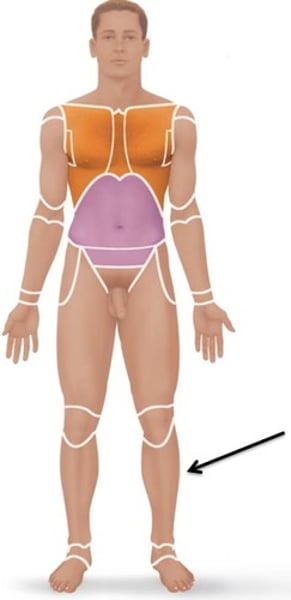
Fibular/Peroneal
pertaining to the lateral side of leg
Pedal
pertaining to the foot
Tarsal
pertaining to the ankle

Calcaneal
pertaining to the heel
Metatarsal
pertaining to the top of foot
Plantar
pertaining to the bottom of foot
Hallux
pertaining to the big toe
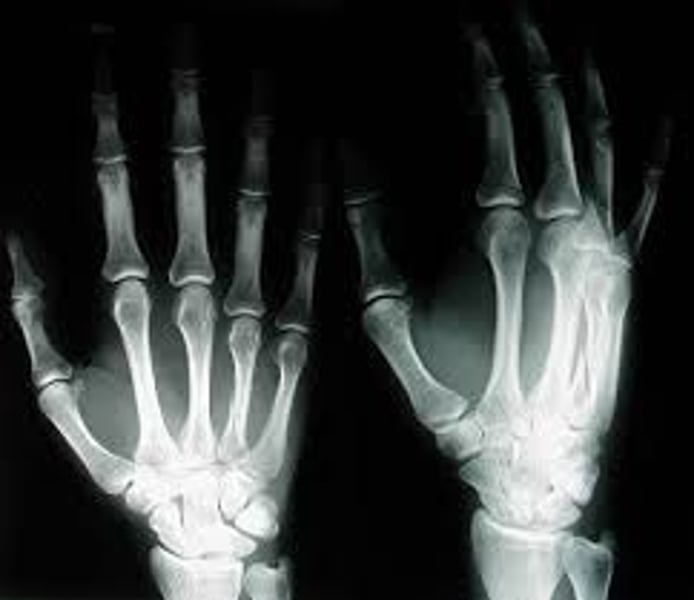
x-ray imaging
pass though soft tissue to observe hard tissue such as bone. best for showing bony structures & abnormally dense structures like tumors, areas of pneumonia, & tuberculosis nodules
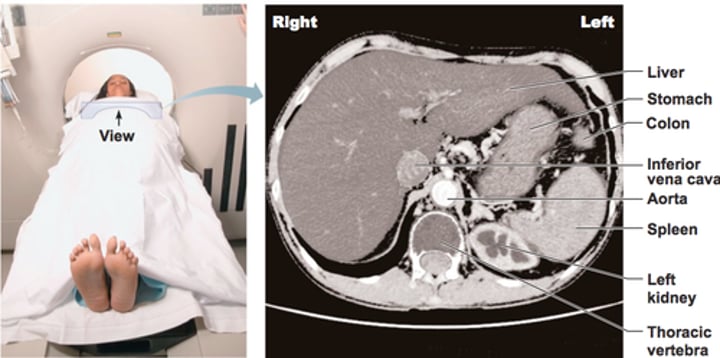
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
computerized reconstruction of x-ray images to provide detailed cross-sectional pics of scanned body regions. best for showing bone, soft tissues, & blood vessels
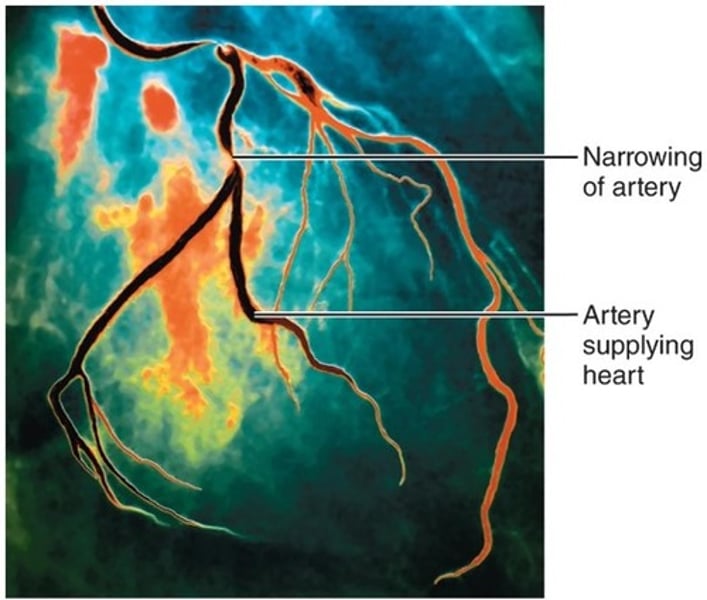
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
visualizing blood vessels/arteries by x-ray/CT. requires injection of dye to be able to view and identify blockages in arteries.
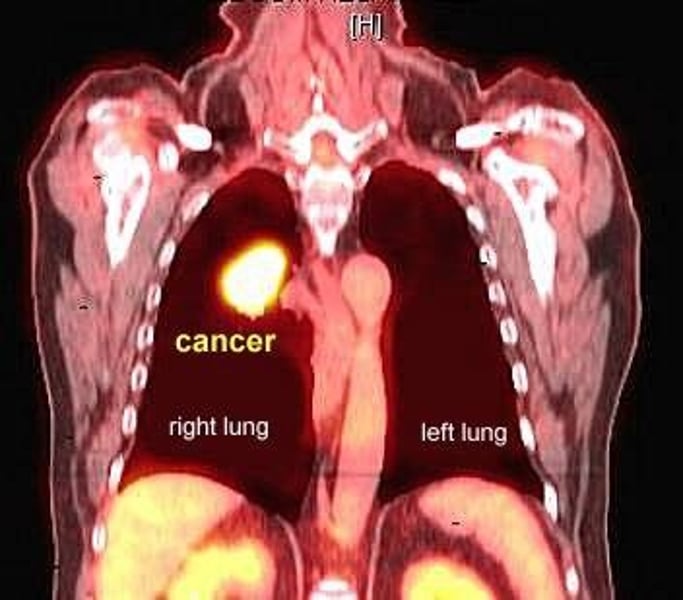
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
uses gamma rays. detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task. used for detecting cancer spread/response to cancer treatment & may diagnose Alzheimer's disease
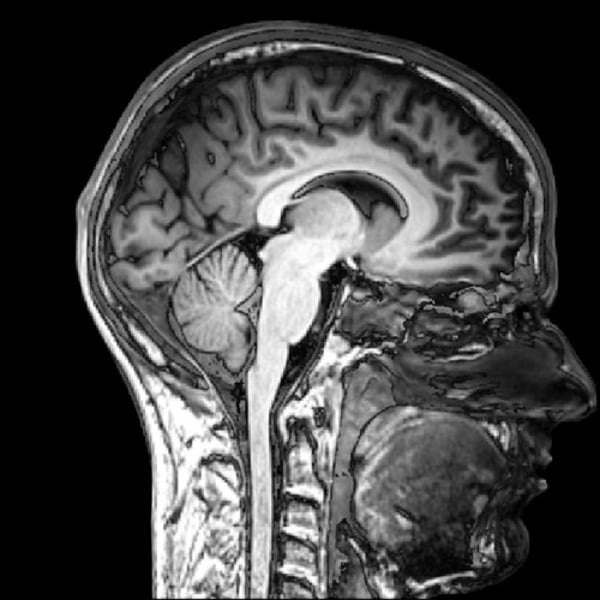
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
powerful magnets image location of H atoms. distinguishes high water content tissues, such as the brain, and dense structures don't show up. used to look at brain & spinal cord
Ultrasonography
high-frequency sound waves are directed at soft tissue and reflected as "echoes" to produce an image on a monitor of an internal body structure. used to monitor fetus during pregancy & view abdominopelvic & heart disorders