[A&P 1] Unit 3 Review Questions
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
B
Narrow, plate-shaped regions of dense protein material called _________________ separate one sarcomere from the next.
A. A band
B. Z discs
C. I band
D. H zone
D
Which muscle protein is the main component of the thin filament?
A. Myosin
B. Tropomyosin
C. Dystrophin
D. Actin
A
What protein is indicated by the arrow in this image?
A. Troponin
B. Actin
C. Tropomyosin
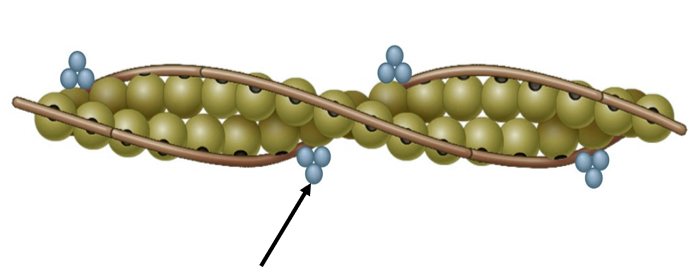
B
The layer of connective tissue that surrounds a fascicle is called ______________.
A. Epimysium
B. Perimysium
C. Endomysium
D. Sarcolemma
C
What happens when calcium binds to troponin?
A. Myosin detaches from actin
B. ATP binds to myosin
C. Troponin moves tropomyosin, exposing myosin binding sites on actin
D. Myosin heads return to the "cocked" position
D
Which neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular to stimulate skeletal muscle?
A. Dopamine
B. Serotonin
C. Norepinephrine
D. Acetylcholine
B
What area is indicated by the arrow in this image?
A. I band
B. H zone
C. Z disc
D. A band
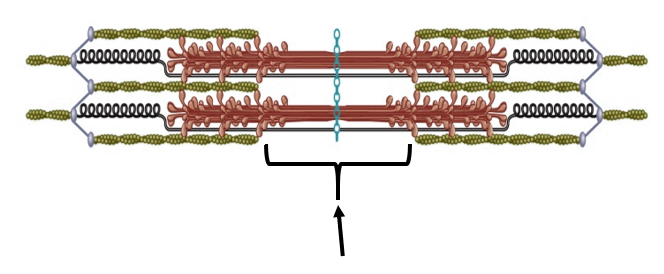
D
A single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates is called what?
A. Sarcomere
B. Cross bridge
C. Neuromuscular junction
D. Motor unit
A
During muscle fiber contraction, which areas of the sarcomere are shortened?
A. H zone and I band
B. M line and Z disc
C. A band and M line
D
All the following are true regarding smooth muscle fibers, except which one?
A. The autonomic nervous system innervates smooth muscle fibers.
B. Smooth muscle fibers lack course connective tissue sheaths.
C. Smooth muscle fibers lack T tubules.
D. Troponin binds with calcium on the thin filaments of smooth muscle fibers,
C
In which type of contraction do muscles lengthen while contracting?
A. Concentric
B. Isometric
C. Eccentric
D. Twitch
D
The strength of a muscle contraction may be increased by all the following, except which one?
A. Increased frequency of stimulation of the muscle fibers.
B. Recruiting additional motor units to contract.
C. Recruiting of larger and larger muscle fibers.
D. None of the above
D
I am a marathon runner. I may run for an hour or two hours at a time, without stopping. Which of the following is not a characteristic of my predominant skeletal muscle fiber type?
A. Lots of mitochondria
B. Slower contractions
C. Lots of myoglobin
D. Short intense contractions
A
Cardiac muscle fibers have a longer refractory period than skeletal muscle fibers.
A. True
B. False
A
A somatic motor neuron releases acetylcholine at the motor end plate, stimulating an action potential along the sarcolemma, which triggers the released of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
A. True
B. False
B
Progressive resistance exercise results in the formation of additional muscle fibers.
A. True
B. False
A
The contraction of skeletal muscle fibers is impaired when it is significantly stretched.
A. True
B. False
A
Muscle fatigue can occur if the muscle's stores of glycogen, myoglobin or creatine phosphate are depleted.
A. True
B. False
A
In skeletal muscle, rapid and repeated stimulation of a muscle fiber may result in a prolonged, sustained contraction, without a period of relaxation.
A. True
B. False
B
In multi-unit smooth muscles, whole sheets of smooth muscle fibers contract in unison in response to stretch.
A. True
B. False
B
Of the following muscle types, which is the only one subject to conscious control?
a) Smooth
b) Skeletal
c) Cardiac
d) All of these muscle types are subject to conscious control.
D
Which of the following muscular functions serves a metabolic function?
a) Movement
b) Posture maintenance
c) Joint stabilization
d) Heat generation
B
In order to receive a signal to contract, each skeletal muscle must be served by a(n) __________.
a) artery
b) nerve
c) vein
d) ligament
C
Which of the following components accounts for the bulk of muscle fiber volume (up to 80%)?
a) Glycosomes
b) Mitochondria
c) Myofibrils
d) Sarcoplasm
B
The thin filaments are not comprised of which of the following components?
a) Actin
b) Titin
c) Troponin
d) Tropomyosin
A
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is an elaborated __________.
a) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
b) Golgi apparatus
c) rough endoplasmic reticulum
d) vesicle
D
What is the significance of the muscle fiber triad relationship?
a) The terminal cisternae subdivide the sarcolemma.
b) The T tubules bring calcium to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
c) The sarcoplasmic reticulum transfers calcium to the T tubules.
d) The T tubules conduct electrical impulses that stimulate calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C
At the neuromuscular junction, the muscle contraction initiation event is __________.
a) a release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
b) conduction of an electrical impulse down the T tubules
c) binding of acetylcholine to membrane receptors on the sarcolemma
d) sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other
A
What would be the first response of a muscle fiber treated with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor?
a) There would be a continued muscle fiber contraction in the absence of additional nervous system stimulation.
b) The muscle fiber would be nonresponsive to acetylcholine.
c) Acetylcholine would be retained in the axon ending.
d) The muscle fiber would continuously contract for a prolonged period of time
B
In a muscle fiber, the key intracellular event that stimulates muscle contraction is known as __________.
a) polarization
b) depolarization
c) repolarization
d) potential
A
During depolarization, the sarcolemma is most permeable to __________.
a) sodium ions
b) potassium ions
c) calcium ions
d) chloride ions
A
The time period between action potential initiation and mechanical activity of a muscle fiber is called the __________.
a) latent period
b) refractory period
c) action potential
d) excitation period
A
What is calcium's function during muscle contraction?
a) Calcium binds to troponin, changing its shape and removing the blocking action of tropomyosin.
b) Calcium binds to troponin to prevent myosin from attaching to actin.
c) Calcium depolarizes the muscle fiber.
d) Calcium flows down the T tubules to stimulate the influx of sodium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
A
Small precise movements are controlled by__________ motor units.
a) small
b) large
c) many
d) few
A
A sprinter is likely to depend on __________respiration to generate ATP, and a Tour de France cyclist is likely to rely on __________ respiration.
a) anaerobic; aerobic
b) aerobic; anaerobic
c) aerobic; aerobic
d) anaerobic; anaerobic
C
Which of the following is not a fatigue-producing factor in moderate exercise?
a) Potassium imbalances
b) Inorganic phosphate accumulation
c) Damage to the SR
d) None of the above
C
Theoretically, contraction would not occur if:
a) Z discs contact the thick myofilaments
b) Actin and myosin filaments do not overlap
c) Both a and b
d) Neither a or b
C
Marathon runners typically possess more __________ muscle fibers.
a) slow glycolytic
b) fast glycolytic
c) slow oxidative
A
What type of exercise can convert fast oxidative fibers to fast glycolytic fibers?
a) Resistance exercise
b) Aerobic exercise
c) Both a and b
d) Muscle fibers cannot change type
C
A major difference between smooth muscle fibers and skeletal muscle fibers in terms of calcium influx is that __________.
a) smooth muscle fibers have a sarcoplasmic reticulum
b) calcium ions are stored in the sarcoplasm of smooth muscle
c) calcium ion influx occurs mostly from the extracellular fluid in smooth muscle
d) smooth muscle contraction does not involve calcium
D
The principal neurotransmitter of skeletal muscle is acetylcholine. The major neurotransmitter(s) of smooth muscle is (are) _______.
a) acetylcholine
b) epinephrine
c) norepinephrine
d) all of the above
B
As an axon enters a muscle, it branches into a number of axon terminals, each of which makes contact with a single muscle fiber. The portion of the sarcolemma in contact with the axon terminals is called the ________.
a) synaptic cleft
b) motor end plate
c) neuromuscular junction
d) synaptic knob
e) motor unit
E
At the neuromuscular junction, calcium ions act to________.
a) increase the conduction speed of action potentialstransmitted along the sarcolemma
b) release the inhibition on Z discs
c) remove the blocking action of tropomyosin
d) cause ATP binding to actin
e) release synaptic vesicles from the axon terminal
D
The first thing that occurs when the axon terminal releases ACh is ________.
a) calcium ions return to the terminal cisternae of the SR
b) the troponin blocks the tropomyosin
c) calcium diffuses into the axon terminal of the motor neuron
d) diffusion across the synaptic cleft
e) the tropomyosin blocks the myosin
E
What type of ion channel opens in response to an action potential arriving at the axon terminal?
a) Ligand-gated anion
b) Voltage-gated sodium
c) Voltage-gated potassium
d) Ligand-gated cation
e) Voltage-gated calcium
C
What is the name of the enzyme that degrades ACh?
a) Lipase
b) ATPase
c) Acetylcholinesterase
d) Serine hydroxylase
e) N-methyl transferase
E
The elaborate network of membranes in skeletal muscle cells that functions in calcium storage is the _________.
a) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
b) Mitochondria
c) Intermediate filament network
d) Myofibrillar network
e) Sarcoplasmic reticulum
E
What is the function of T tubules?
a) They store calcium.
b) They provide elasticity to the muscle.
c) Actin and myosin are synthesized here.
d) They hold the thick filaments to the Z line.
e) They conduct action potentials from the sarcolemma to the interior of the muscle cell.
B
One transverse tubule plus two adjacent terminal cisternae form a ___________.
a) Sarcomere
b) Triad
c) Calcium release channel
d) Fiber
e) Regulatory complex
C
Which ion links excitation to contraction in a skeletal muscle fiber?
a) Sodium
b) Magnesium
c) Calcium
d) Potassium
e) Chloride
C
As action potentials travel down a T tubule, a voltage-sensitive protein changes shape. This shape change opens a ____________.
a) voltage-gated sodium channel
b) voltage-gated potassium channel
c) calcium release channel
d) ligand-gated ion channel
e) leak channel
B
What is the role of calcium ions in the contraction of skeletal muscle?
a) The release of calcium ions triggers the immediate regeneration of creatine phosphate to power the contraction.
b) Calcium ions bind to the troponin-tropomyosin complex and remove their inhibitory action on actin/myosin interaction.
c) Calcium ions directly activate ATPase in the myosin head.
d) Calcium ions bind to lactic acid to remove it from the contracting muscle.
A
The functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber is the________.
a) sarcomere
b) myofibril
c) sarcolemma
d) sarcoplasmic reticulum
e) myofilament
E
Interactions between thin and thick myofilaments of the sarcomere are responsible for ________.
a) the striped appearance of skeletal muscle
b) muscle relaxation
c) muscle fatigue
d) the conduction of action potentials in the muscle fiber
e) muscle contraction
c
During muscle contraction, all of the following occur EXCEPT ________.
a) calcium binds to troponin
b) myosin heads bind to actin
c) calcium concentrations in the sarcoplasm decrease
d) ATP is hydrolyzed
e) calcium concentration in the sarcoplasm increase
C
During a muscle contraction, muscle fibers shorten when ________.
a) actin filaments become shorter when they combine with myosin heads
b) myosin heads rotate when they attach to actin, causing the myosin filaments to fold in the middle
c) thin myofilaments are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere by the pivoting of the myosin heads
d) ACh reduces the friction between thin and thick myofilaments, so they slide over each more easily
A
The myosin head has ATP binding site and actin binding site
A. true
B. false
A
Calcium binds to troponin on actin filament
A. true
B. false
A
The structural organization of skeletal muscle(from largest to smallest) includes
A. the entire muscle → fascicles → muscle fibers → myofibrils
B. fascicles → muscle fibers →myofibrils
C. myofilaments → the entire muscle → fascicles
B
A motor unit is....
A. Several nerves innervate one muscle fiber
B. Motor neuron innervates group of muscle fibers
C. None of the above
D. Both of the above
A
Perimysium is a....
A. layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds each fascicle
B. layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle
C. layer of loose connective tissue that surrounds each individual muscle fiber
A
Regarding sarcomere, which one of the following is correct?
A. the functional unit of skeletal muscle
B. it is made of thin and thick filaments
C. it is the distance between 2 subsequent Z discs
D. all of the above
A
Neuromuscular junction is made of
A. synaptic knob, synaptic cleft, and motor end plate
B. synaptic knob only
C. motor end plate only
D. none of the above
C
Calcium is stored in __________
A. T tubule
B. Sarcolemma
C. Terminal cisterna
D. None of the above
E
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of skeletal muscles?
A. excitability
B. conductivity
C. elasticity
D. contractility
E. none of the above
C
The nervous system has three overlapping functions. Which of the following represents a logical sequence of these three functions?
a) Sensory input, motor output, integration
b) Motor output, integration, sensory input
c) Sensory input, integration, motor output
d) Integration, sensory input, motor output
D
While studying for an exam, you reach for a beverage. To extend your arm, your __________ nervous system is activated.
a) afferent
b) autonomic
c) sympathetic
d) somatic
B
The door slams shut loudly and you flinch. After a few seconds, you realize that your heart is beating very rapidly and forcefully. This response is the result of your __________ nervous system.
a) afferent
b) autonomic
c) central
d) somatic
A
Complete the following analogy: Electrical wire is to electrical insulating tape as peripheral neurons are to __________.
a) Schwann cells
b) oligodendrocytes
c) astrocytes
d) ependymal cells
D
Each neuron in our bodies has a life span of__________.
a) 120 days
b) 10 years
c) 10 months
d) an average human life span
A
Movement of substances towards the cell body of a neuron is termed __________ movement.
a) retrograde
b) axongrade
c) anterograde
d) dendrograde
C
The portion of an axon that communicates with its target cell is the __________.
a) dendrite
b) axon
c) axon terminal
d) cell body
B
The basis for differentiation between gray matter and white matter in the CNS is the presence of__________ in white matter.
a) unmyelinated fibers
b) myelinated fibers
c) Schwann cells
d) ependymal cells
D
__________ are the most common structural type of neuron in humans.
a) Pseudounipolar
b) Unipolar
c) Bipolar
d) Multipolar
C
When considering the relationship between a structural classification and a functional classification of neurons, it can be said that __________.
a) all multipolar neurons are interneurons
b) all motor neurons are unipolar neurons
c) essentially all bipolar neurons are sensory neurons
d) unipolar neurons only function as motor neurons
B
Which type of potential does not decay with distance?
a) Graded potential
b) Action potential
c) Generator potential
d) Both a and b
B
Neurons generally repolarize once the membrane potential reaches approximately +30 mV because:
a) voltage-gated sodium channel gates close.
b) voltage-gated potassium channel gates open.
c) chemically gated sodium channels open.
d) voltage-gated calcium channel gates open.
A
You would expect a neuron that depolarizes to -75 mV would:
a) return to resting membrane potential without generating an action potential.
b) fire a much more intense action potential with a peak of +100 mV.
c) fire a much less intense action potential with a peak of +15 mV.
d) hyperpolarize.
C
The point at which the all-or-none principle of action potential generation is reached is termed the __________.
a) peak
b) depolarization point
c) threshold
d) point of no return
D
During the relative refractory period:
a) no action potentials can be generated.
b) the threshold is substantially elevated.
c) exceptionally strong stimuli could trigger action potentials.
d) both b and c apply.
A
The location at which a neuron interacts with its target cell (either another neuron or a muscle cell, etc.) is called the __________.
a) synapse
b) junction
c) connection
d) axoaxonic target
B
Which of the following synapse types is the most rapid?
a) Chemical synapse
b) Electrical synapse
c) Presynaptic synapse
d) None of these is more rapid than the others.
A
During the events involved in information transfer across a chemical synapse, which of the following steps would be directly interrupted by exposing a neuron to a calcium channel blocker?
a) Neurotransmitter exocytosis from the presynaptic neuron
b) Depolarization of the presynaptic neuron
c) Binding of neurotransmitters to the postsynaptic membrane
d) Depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
C
Generally speaking, opening chloride channels in the postsynaptic membrane will result in an __________.
a) excitatory postsynaptic potential
b) excitatory presynaptic potential
c) inhibitory postsynaptic potential
d) inhibitory presynaptic potential
D
Identify the false statement.
a) Temporal summation occurs with graded potentials
b) EPSPs and IPSPs can summate spatially
c) EPSPs and IPSPs can summate temporally
d) Spatial summation occurs with action potentials
C
Certain psychosomatic drugs exert their effects by keeping the concentration of neurotransmitters elevated within the synapse. These drugs could exert their effects by:
a) inhibiting enzymes associated with the postsynaptic membrane that degrade the neurotransmitter.
b) inhibiting reuptake of the neurotransmitter by astrocytes or the presynaptic terminal.
c) doing both a and b.
d) doing neither a nor b.
A
Neurotransmitters are important in functioning of __________ synapses.
a) chemical
b) electrical
c) gap
d) converging
C
Spinal reflexes are an example of:
a) Parallel processing
b) Temporal summation
c) Serial processing
d) Spatial summation
D
Which process of a neuron releases neurotransmitters in a synapse with another neuron?
A. Axons
B. Dendrites
C. Soma
D. Axon terminals
B
What type of neurons form the nerves of special senses?
A. Multipolar
B. Bipolar
C. Unipolar
D. Pseudounipolar
D
Which of the following are false regarding somatic motor neurons?
A. They innervate muscles.
B. They are multipolar.
C. They conduct impulses from the CNS to the PNS.
D. They are afferent.
D
Which of the following is true regarding action potentials?
A. Action potentials travel in both directions along an axon.
B. Action potentials sometimes dissipate, or stop, midway along an axon.
C. Some action potentials, within a given neuron, are larger than others, depending on the strength of the stimulus.
D. The peak of the action potential is followed by a refractory period.
C
Identify the type of neurons whose cell bodies are found in the dorsal root ganglia.
A. Bipolar
B. Multipolar
C. Unipolar
A
Which of the following neurotransmitters stimulate skeletal muscle contraction?
A. Acetylcholine
B. Norepinephrine
C. Dopamine
D. Serotonin
B
Which processes are the primary receptive or input regions of neurons?
A. Axons
B. Dendrites
C. Soma
D. Axon Terminals
A
Which glial cells create a myelin sheath covering peripheral nerve fibers?
A. Schwann Cells
B. Oligodendrocytes
C. Ependymal cells
D. Astrocytes
B
True or false, afferent signals originate in the central nervous system and extend to the peripheral nervous system.
A. True
B. False
D
Which glial cells phagocytize microorganisms and clean up cellular debris in the central nervous system?
A. Schwann Cells
B. Oligodendrocytes
C. Astrocytes
D. Microglia
A
Which classification of neurons have one process coming off the cell body and form our somatic sensory neurons?
A. Unipolar Neurons
B. Multipolar Neurons
C. Bipolar Neurons
D. Artic Polar Neurons
A
Which of the following best describes the point at which voltage-gated sodium channels open, in the generation of an action potential?
A. Threshold
B. Absolute Refractory Period
C. Relative Refractory Period
D. Hyper polarization