BMS 508 P1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/223
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:53 PM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
224 Terms
1
New cards
systolic blood pressure
The pressure created in the arteries when the left ventricle contracts and forces blood out into circulation
2
New cards
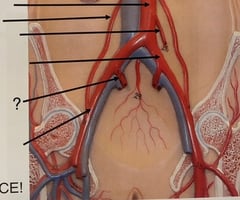
vasa vasorum
what is this
3
New cards
valve of vein
what is 6
4
New cards
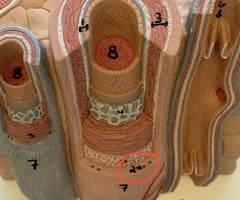
Adrenal gland
name this slide
5
New cards
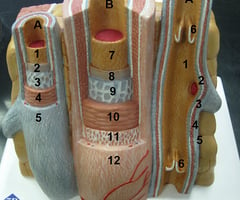
Anterior pituitary gland
name this slide
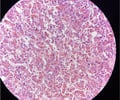
6
New cards
Arteries
name this slide
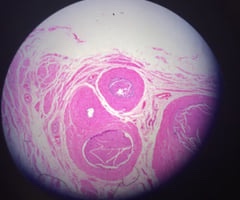
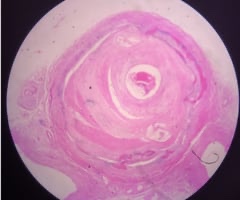
7
New cards
Atherosclerosis
name this slide
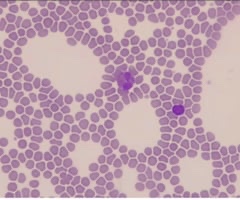
8
New cards
Blood smear with eosinophil and basophil
name this slide
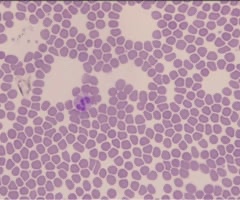
9
New cards
Blood smear with lymphocyte and monocyte
name this slide
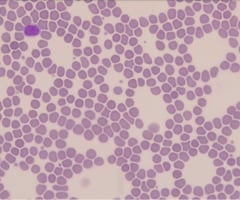
10
New cards
Blood smear with neutrophil
name this slide
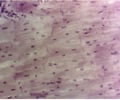
11
New cards
Cardiac muscle
name this slide
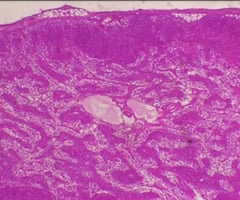
12
New cards
Lymph node
name this slide
13
New cards
Myocardial infarction
name this slide
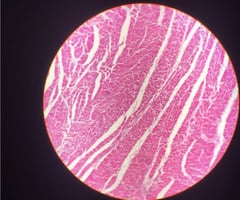
14
New cards
Ovary gland
name this slide
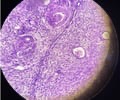
15
New cards
Pancreas gland
name this slide
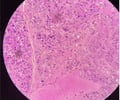
16
New cards
Peyer's patches of appendix
name this slide
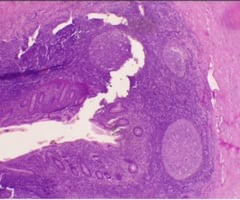
17
New cards
Posterior pituitary gland
name this slide
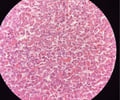
18
New cards
Skeletal muscle
name this slide

19
New cards
Smooth muscle
name this slide
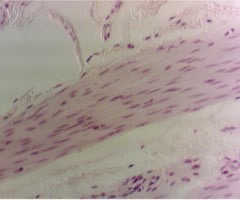
20
New cards
Spleen
name this slide
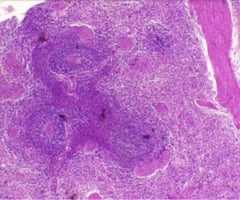
21
New cards
Testes gland
name this slide
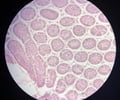
22
New cards
Thymus
name this slide
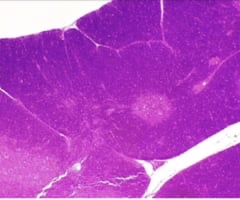
23
New cards
Thymus gland
name this slide
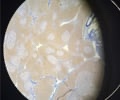
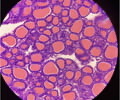
24
New cards
Thyroid gland
name this slide
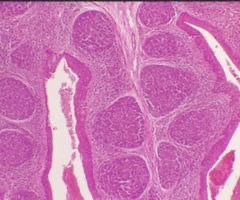
25
New cards
Tonsil
name this slide
26
New cards
Veins
name this slide
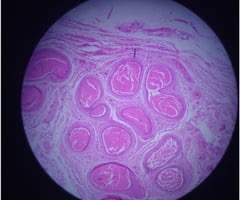
27
New cards
**Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)**
\
\
name ECG pattern
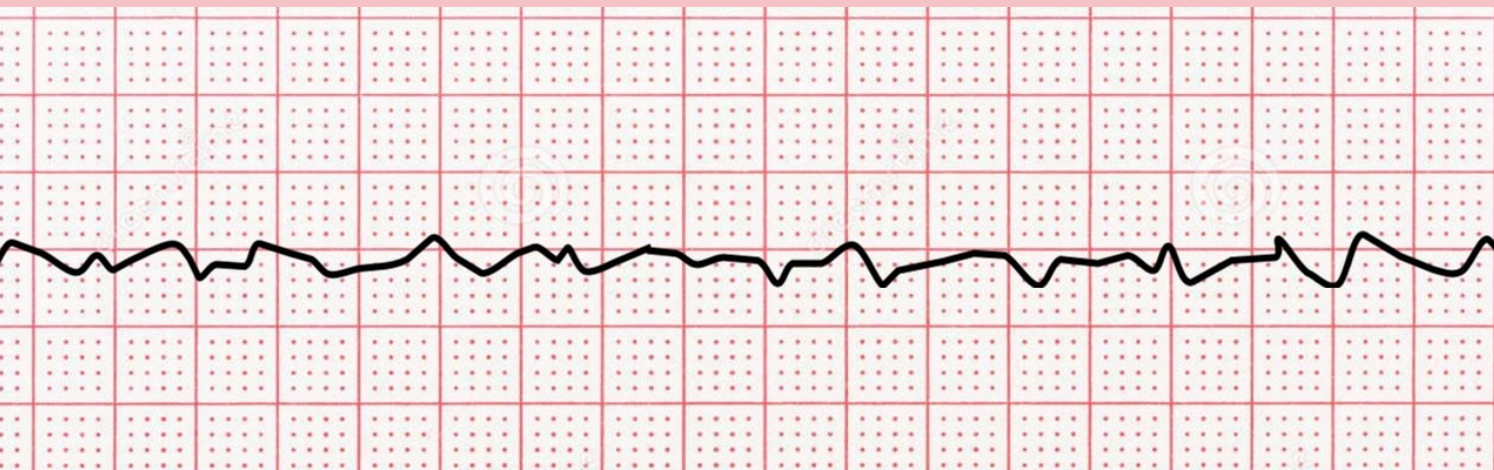
28
New cards
**Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)**
\-Non visible P wave
\-Wide QRS
\
\-Non visible P wave
\-Wide QRS
\
name ECG pattern
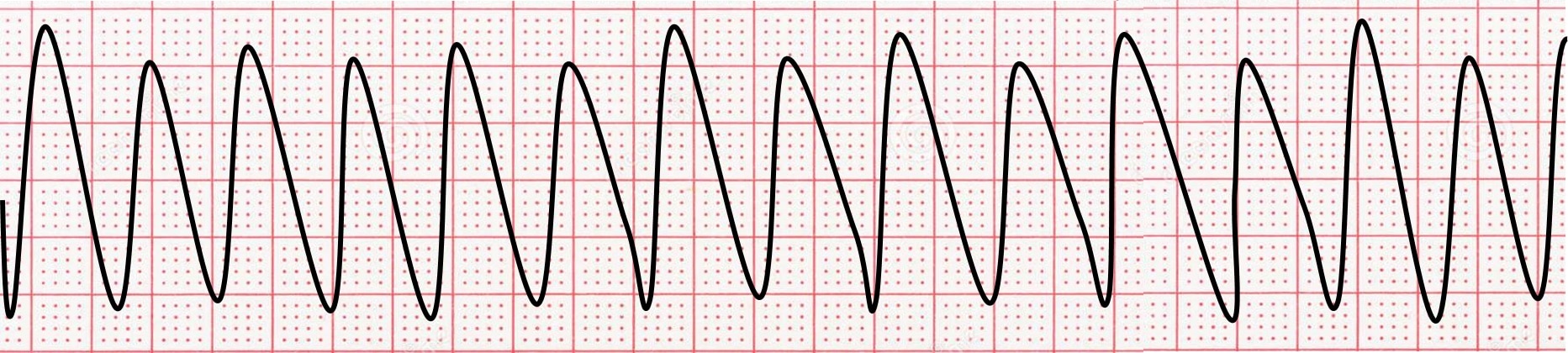
29
New cards
**Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)**
\-No p-wave seen
\-Narrow QRS
\-Normal St/T wave
\-Normal QT
\-No p-wave seen
\-Narrow QRS
\-Normal St/T wave
\-Normal QT
name ECG pattern
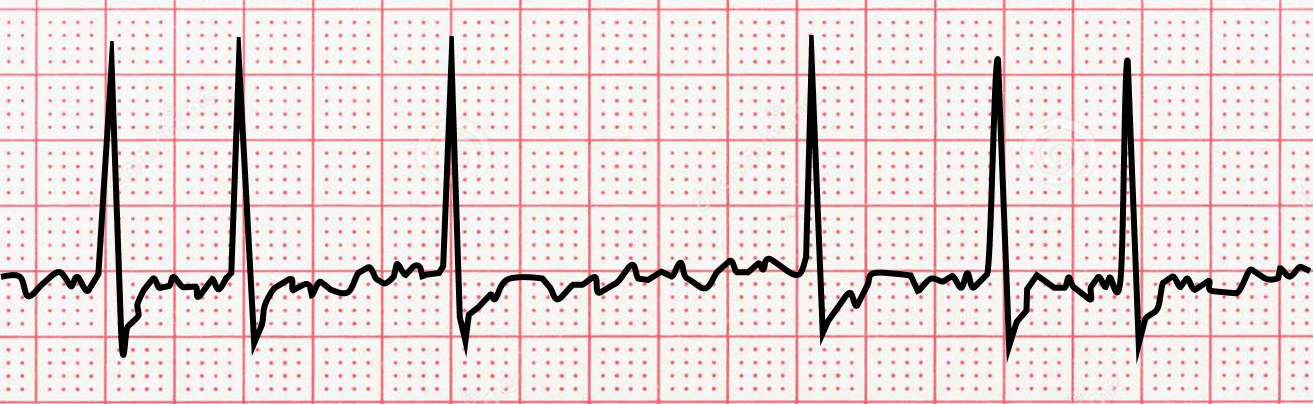
30
New cards
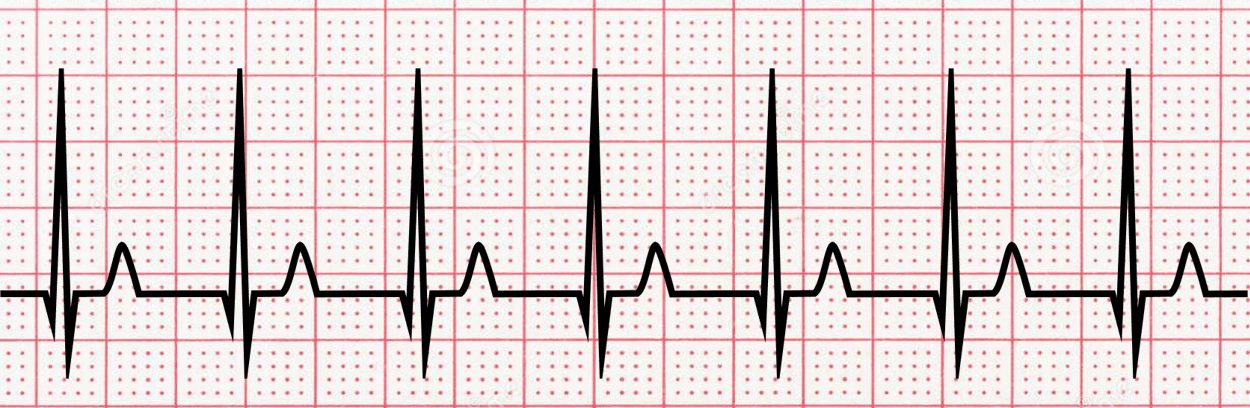
**Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)**
name ECG pattern
31
New cards
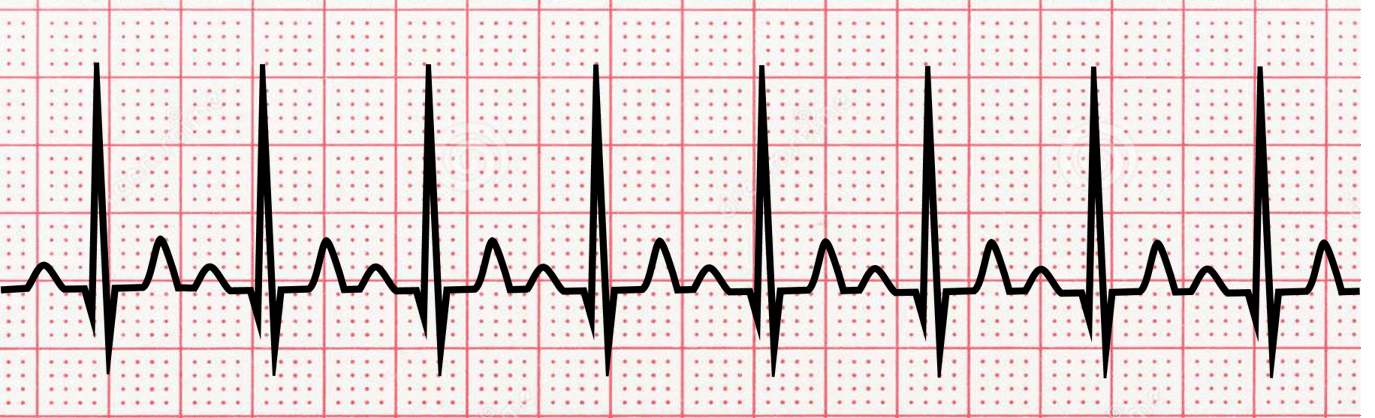
**Sinus Tachycardia**
\-Not visible P wave
\-Narrow QRS
\-Sligth lateral ST depression
\-over 100 bpm
\
\-Not visible P wave
\-Narrow QRS
\-Sligth lateral ST depression
\-over 100 bpm
\
name ECG pattern
32
New cards
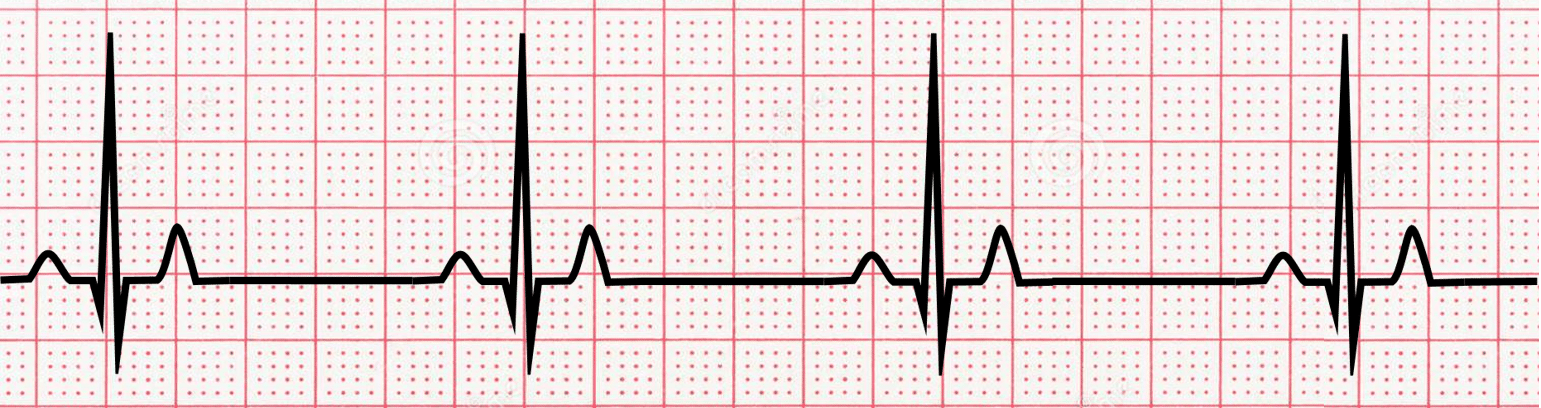
**Sinus Bradycardia**
\-Narrow QRS
\-less than 60 bpm
\-Narrow QRS
\-less than 60 bpm
name ECG pattern
33
New cards
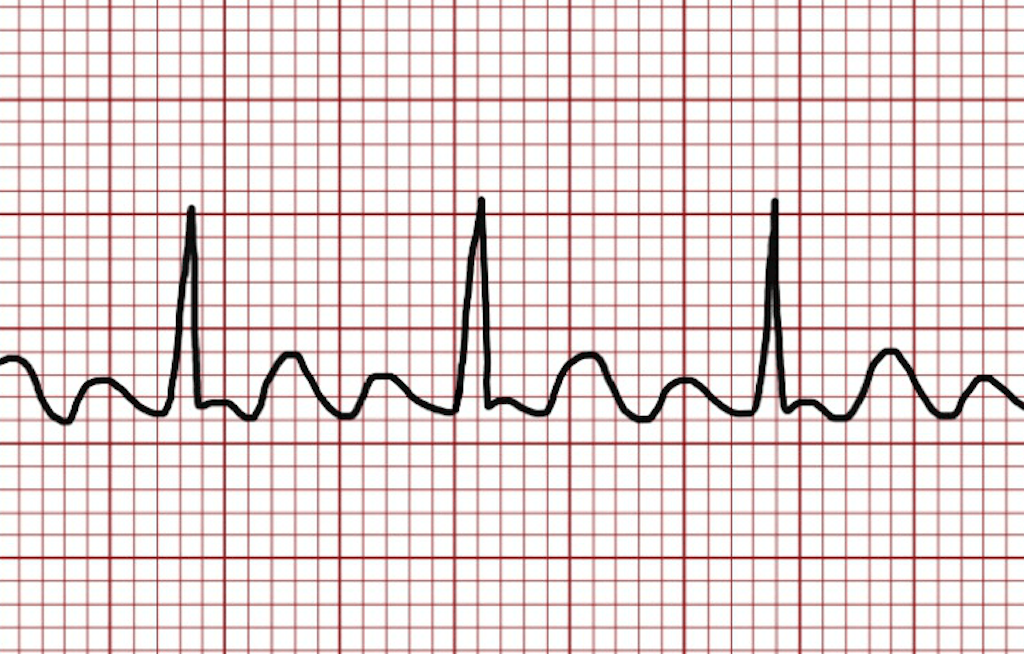
**Atrial Flutter (AFL)**
\-**irregular R-R intervals**
\-**irregular R-R intervals**
name ECG pattern
34
New cards
**Torsades de Pointes**
\-QRS complexes all look very different.QT interval
* Long QT interval
\-QRS complexes all look very different.QT interval
* Long QT interval
name ECG pattern
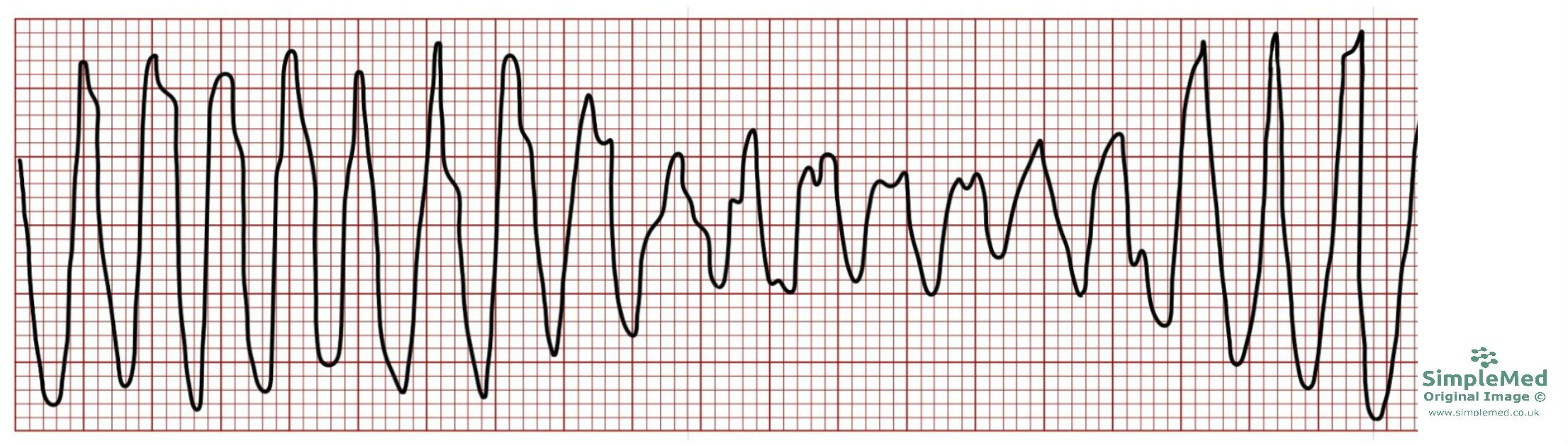
35
New cards
**Heart Block FIRST DEGREE**
\-prolonged PR interval
\-lengthened but constant distance between the P wave and QRS complex
\-prolonged PR interval
\-lengthened but constant distance between the P wave and QRS complex
name ECG pattern
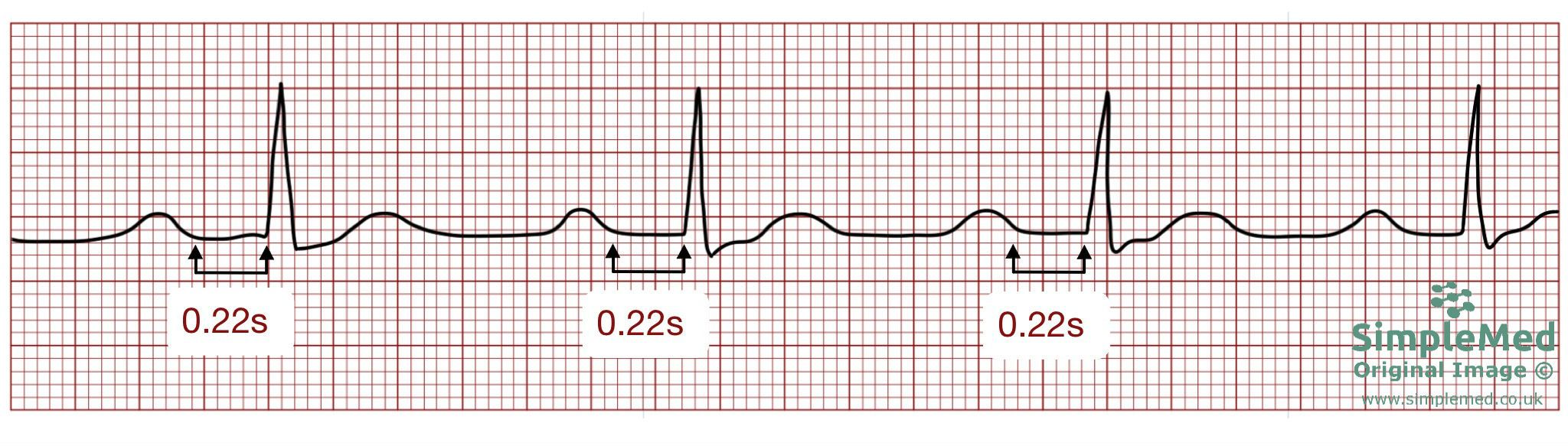
36
New cards
P wave
\-atrial depolarization
\-atrial depolarization
What does the orange represent

37
New cards
ST segment
\-ventricular depolarization
\-ventricular depolarization
what does the purple represent

38
New cards
PR interval
\-delay of Av node to allow filling of ventricles
\-delay of Av node to allow filling of ventricles
What does the green represent

39
New cards
QRS complex
\-ventricular depolarization
\-ventricular depolarization
What does pink represent

40
New cards
T wave
\-ventricular depolarization
\-ventricular depolarization
what does blue represent

41
New cards
Bottom dip at end of QRS
Where is S wave

42
New cards
Neutrophil
\-50-70%
\-ingest pathogens using \n phagocytosis
\-Lobed nuclei (aka polymorphonuclear \n leukocytes) \n -Anti-bacterial activity
\-granulocyte \n
\-50-70%
\-ingest pathogens using \n phagocytosis
\-Lobed nuclei (aka polymorphonuclear \n leukocytes) \n -Anti-bacterial activity
\-granulocyte \n
Identify leukocyte:
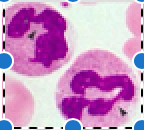
43
New cards
Eosinophil
\-2-4%
\-use enzymes against parasitic \n worm
\-2 nuclear lobes connected by stalk
\-Secrete enzymes onto surfaces of parasite
\-granulocyte
\-2-4%
\-use enzymes against parasitic \n worm
\-2 nuclear lobes connected by stalk
\-Secrete enzymes onto surfaces of parasite
\-granulocyte
Identify leukocyte:
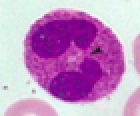
44
New cards
Basophil
\-0.5-1%
\-release pro-inflammatory \\n histamine
\-large coarse cytoplasmic granules, purple/blue black
\-Produce the pro-inflammatory \n molecule called histamine
\-U or S shaped nucleus – often \n difficult to see because of granules
\-granulocyte
\-0.5-1%
\-release pro-inflammatory \\n histamine
\-large coarse cytoplasmic granules, purple/blue black
\-Produce the pro-inflammatory \n molecule called histamine
\-U or S shaped nucleus – often \n difficult to see because of granules
\-granulocyte
Identify leukocyte:
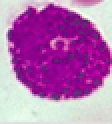
45
New cards
Lymphocyte
\-25-45%
\-have large nuclei & will \n inhabit lymph nodes
\-Large dark staining nucleus that occupies \n most of the cell volum, thin pale blue rim of cytoplasm
\-Agranulocytes
\-25-45%
\-have large nuclei & will \n inhabit lymph nodes
\-Large dark staining nucleus that occupies \n most of the cell volum, thin pale blue rim of cytoplasm
\-Agranulocytes
Identify leukocyte
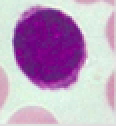
46
New cards
Monocyte
\-3-8%
\-large, monstrous, & will \n become macrophages
\-Dark staining kidney/U-shaped nucleus
\-Abundant pale-blue cytoplasm
\-Agranulocytes
\-3-8%
\-large, monstrous, & will \n become macrophages
\-Dark staining kidney/U-shaped nucleus
\-Abundant pale-blue cytoplasm
\-Agranulocytes
Identify leukocyte
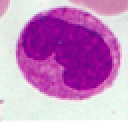
47
New cards
O-
Universal donor
48
New cards
AB+
Universal receiver
49
New cards
O-, A-, B-, AB-
If you have type AB- you can receive:
50
New cards
ALL
If you have type AB+ you can receive:
51
New cards
O-, B-
If you have type B- you can receive:
52
New cards
O+, O-, B+, B-
If you have type B+ you can receive:
53
New cards
O-, A-
If you have type A- you can receive:
54
New cards
O+, O-, A+, A-
If you have type A+ you can receive:
55
New cards
O-
If you have type O- you can receive:
56
New cards
O+, O-
If you have type O+ you can receive:
57
New cards
connects the heart to all cells & body tissues
• Arteries move away from the heart, deliver blood • Veins move towards the heart, collect blood
• Arteries branch and get smaller
• Veins merge and get larger
• Almost all arteries are paired with a same-name vein
• EXCEPT: carotid arteries & jugular veins
• EXCEPT: “bonus” veins: cephalic, basilic, great saphenous
• EXCEPT: hepatic portal system
\
(oxygenated blood)
lungs –> pulmonary veins –> left atrium –> bicuspid valve –> left ventricle –> aortic SL valve -> aorta -> body
\
• Arteries move away from the heart, deliver blood • Veins move towards the heart, collect blood
• Arteries branch and get smaller
• Veins merge and get larger
• Almost all arteries are paired with a same-name vein
• EXCEPT: carotid arteries & jugular veins
• EXCEPT: “bonus” veins: cephalic, basilic, great saphenous
• EXCEPT: hepatic portal system
\
(oxygenated blood)
lungs –> pulmonary veins –> left atrium –> bicuspid valve –> left ventricle –> aortic SL valve -> aorta -> body
\
The systemic circuit
58
New cards
Pulmonary trunk, arteries deliver blood to the lungs; pulmonary veins deliver blood back to the heart
\
(deoxygenated blood)
body –> inferior/superior vena cava –> right atrium –> tricuspid valve –> right ventricle –> pulmonary SL valve -> pulmonary arteries –> lungs
\
\
\
(deoxygenated blood)
body –> inferior/superior vena cava –> right atrium –> tricuspid valve –> right ventricle –> pulmonary SL valve -> pulmonary arteries –> lungs
\
\
Pulmonary circuit
59
New cards
\-Closing of AV valves creates ... sound
• The start of ventricular systole
• Ventricular contraction
• End of QRS complex
• The start of ventricular systole
• Ventricular contraction
• End of QRS complex
Lub:
60
New cards
• Closing of SL valves creates … sound
• The start of ventricular diastole
• Ventricular relaxation
• End of T wave
• The start of ventricular diastole
• Ventricular relaxation
• End of T wave
Dub:
61
New cards
valves do not fully open
• Sounds like higher-pitched screeching
• Sounds like higher-pitched screeching
Stenosis
62
New cards
valves do not fully close,
causing leaking across the valve
• Sounds “swishy” or “gurgley
causing leaking across the valve
• Sounds “swishy” or “gurgley
Regurgitant
63
New cards
temporal artery
1
\
\
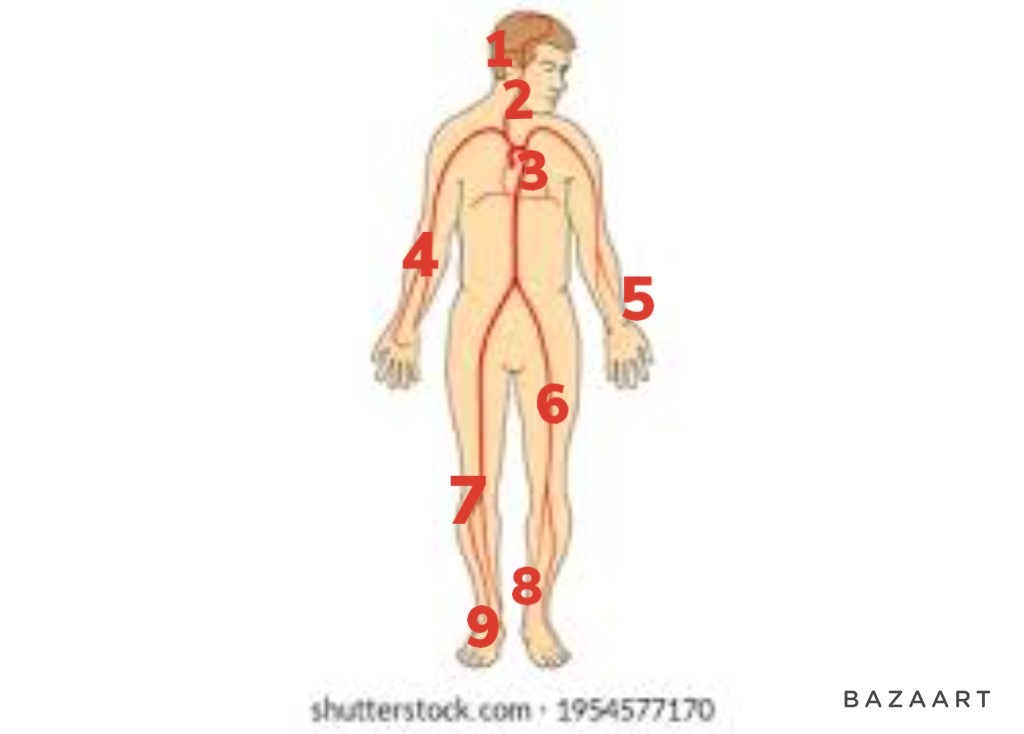
64
New cards
carotid
2
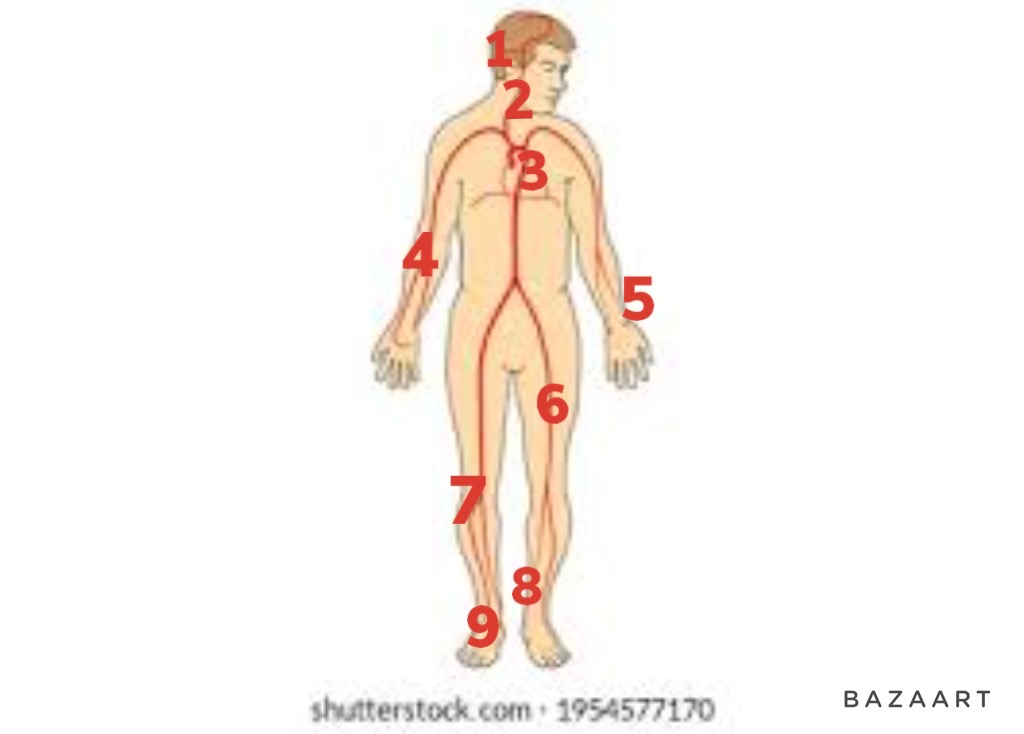
65
New cards
apical pulse
3
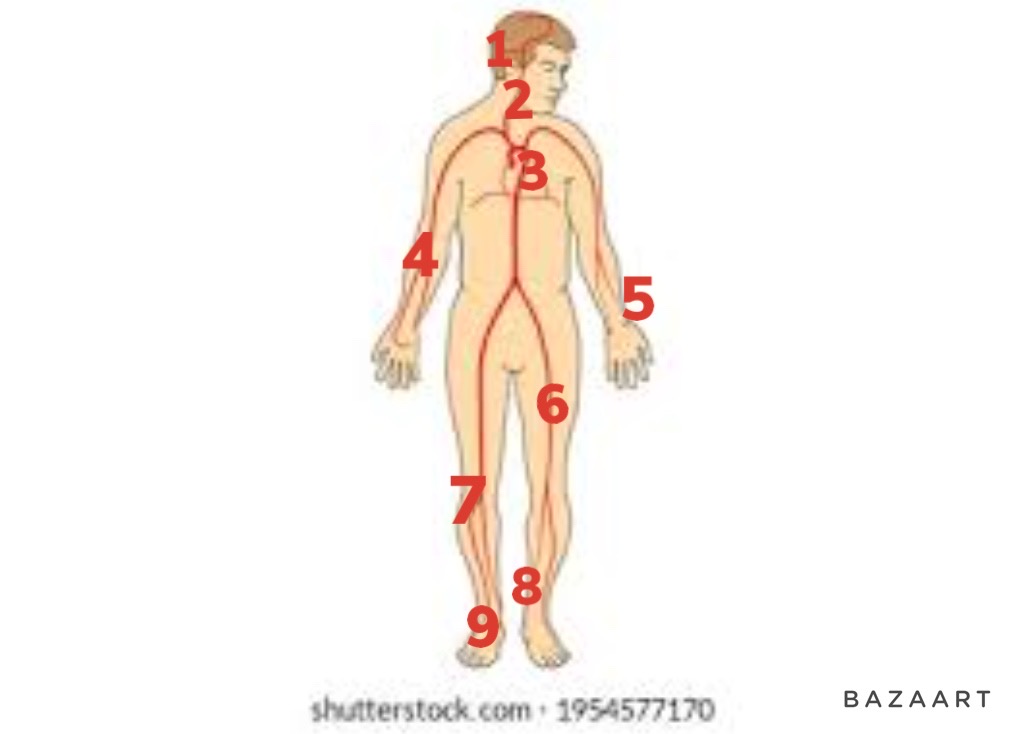
66
New cards
brachial
4
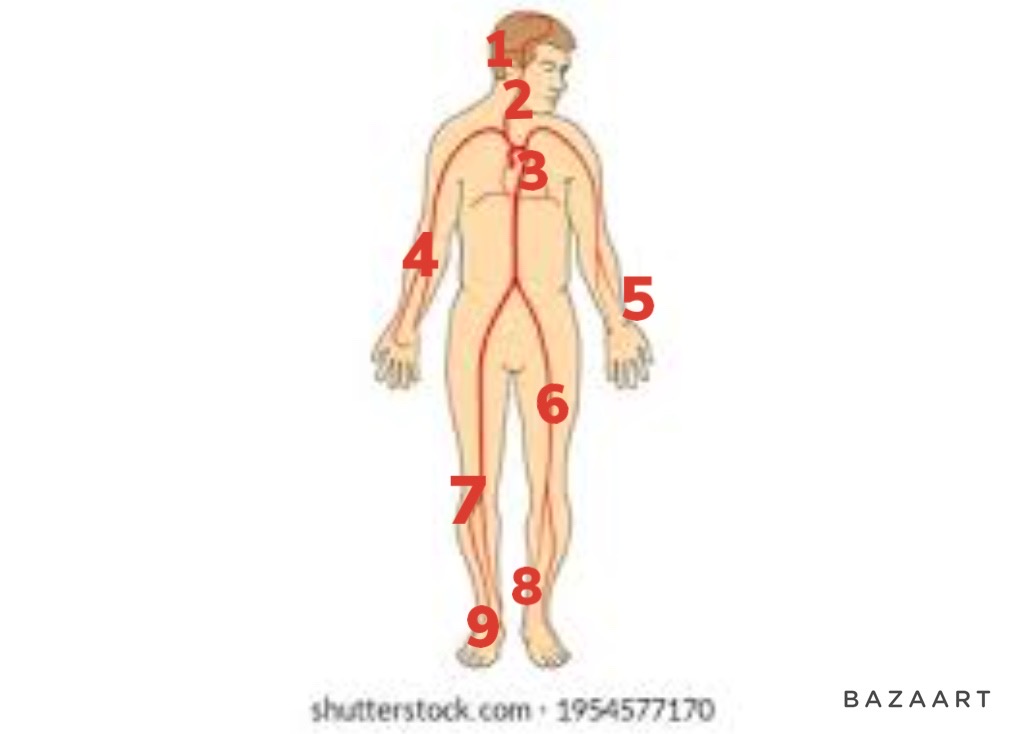
67
New cards
radial
5
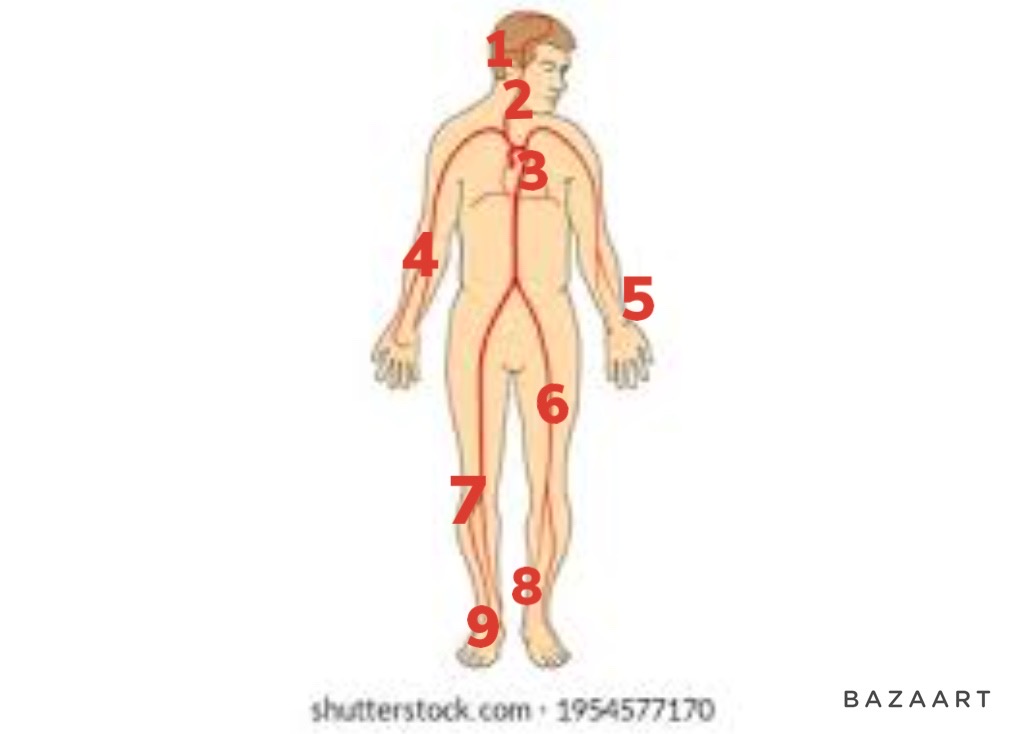
68
New cards
femoral
6
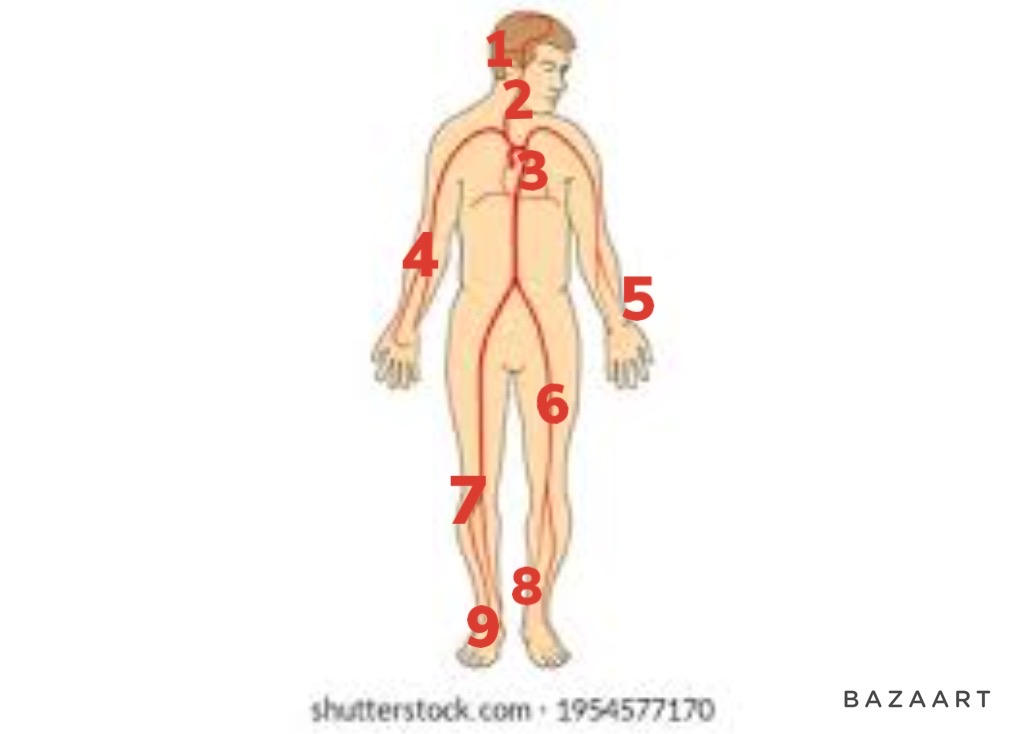
69
New cards
popliteal artery
7
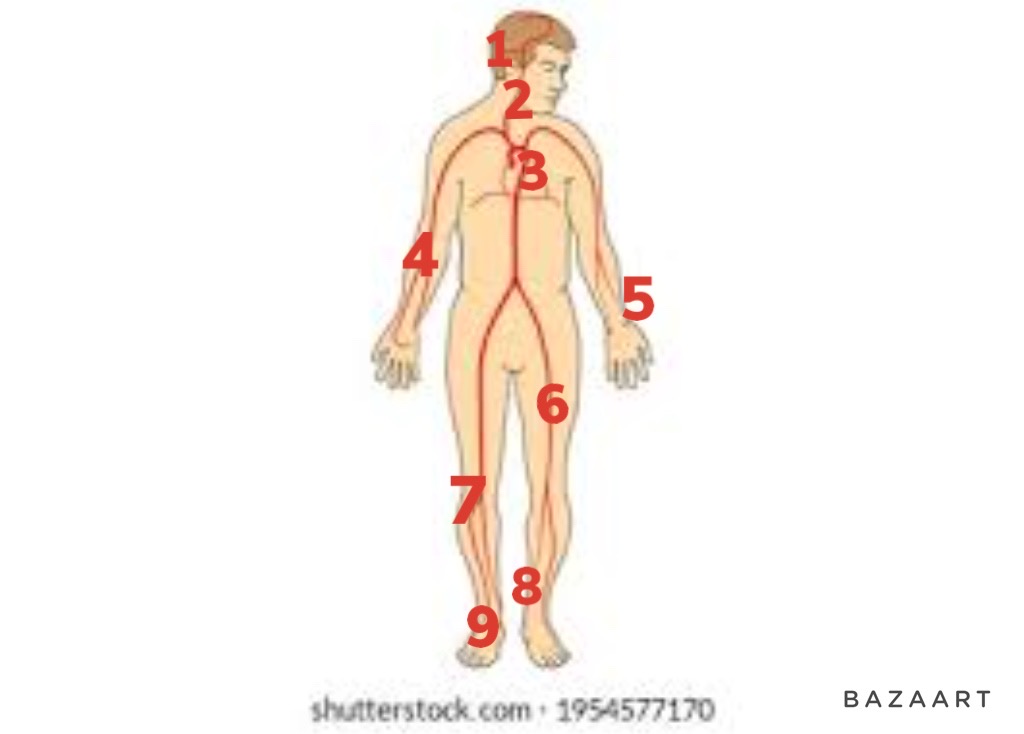
70
New cards
posterior tibial artery
8
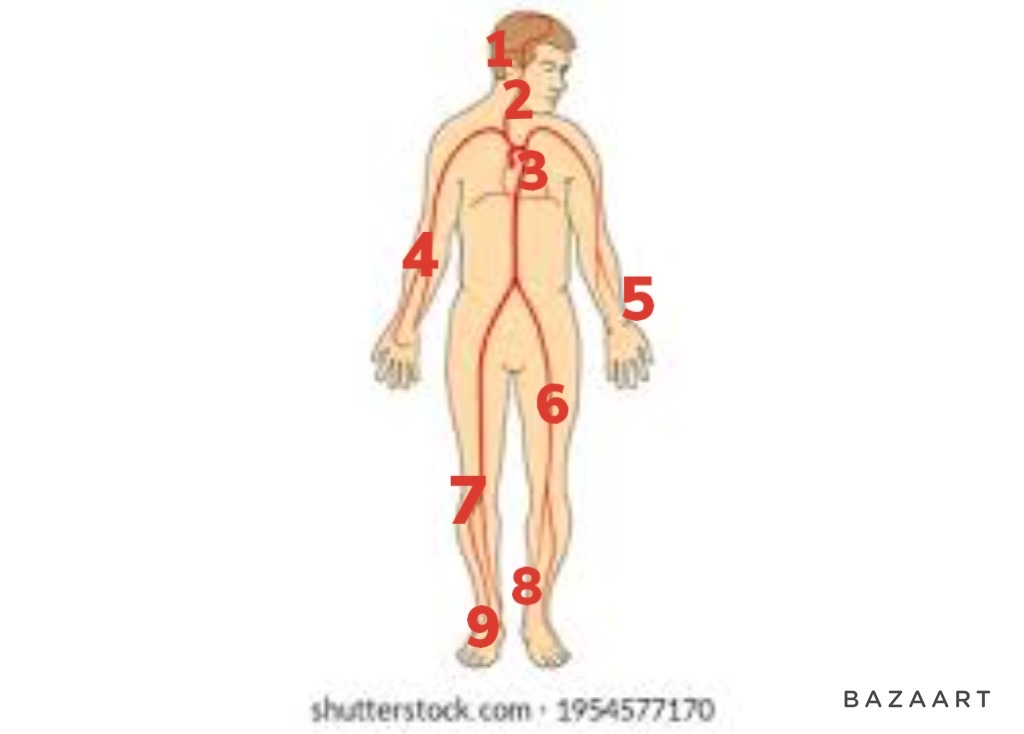
71
New cards
pedal
9
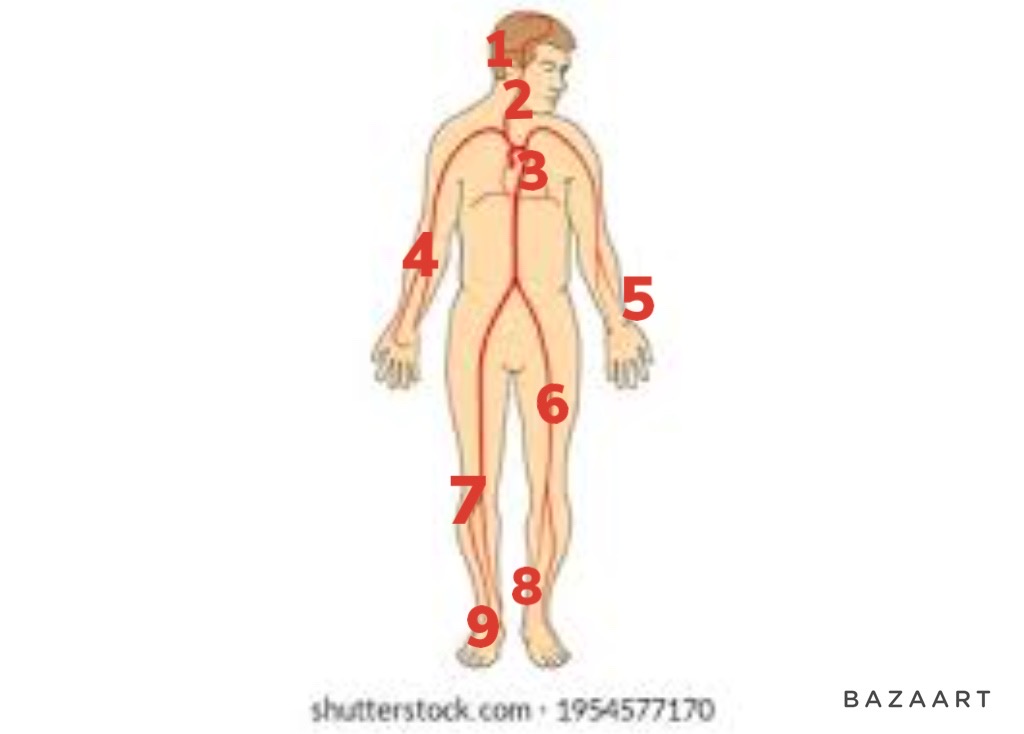
72
New cards
Right Common Carotid Artery
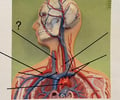
73
New cards
Left Common Carotid Artery
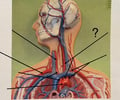
74
New cards
Right Subclavian Artery
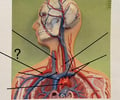
75
New cards
Left Subclavian Artery
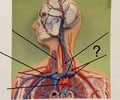
76
New cards
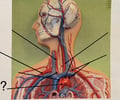
Brachiocephalic Trunk
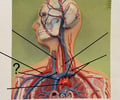
77
New cards
Aortic Arch
78
New cards
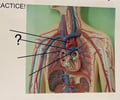
Aortic Arch
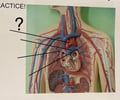
79
New cards
Pulmonary Trunk
80
New cards
Right Pulmonary Artery
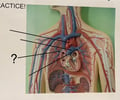
81
New cards
Left Pulmonary Artery
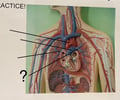
82
New cards
Right Subclavian Artery
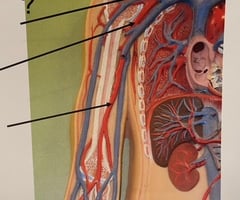
83
New cards
Axillary Artery
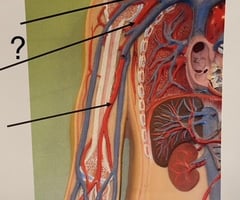
84
New cards
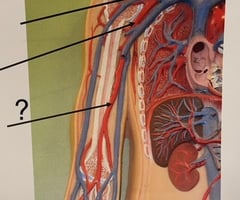
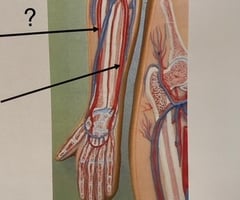
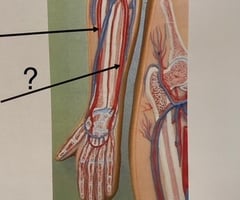
Brachial Artery
85
New cards
Radial Artery
86
New cards
Ulnar Artery
87
New cards
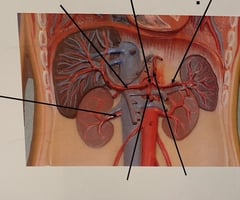
Splenic Artery
88
New cards
Celiac Trunk
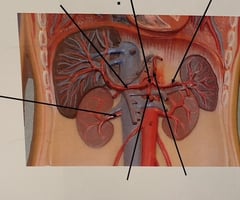
89
New cards
Common Hepatic Artery
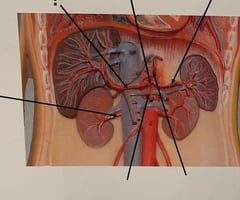
90
New cards
Renal artery
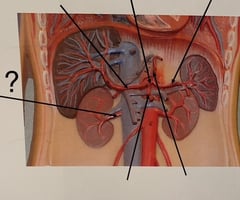
91
New cards
Right Gastric Artery
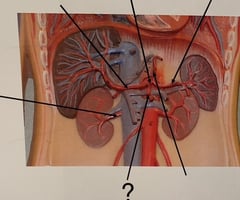
92
New cards
Left Gastric Artery
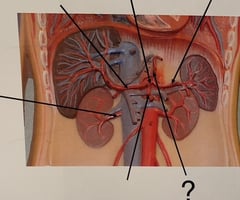
93
New cards
Superior Mesenteric Artery
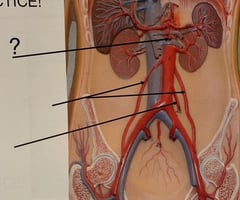
94
New cards
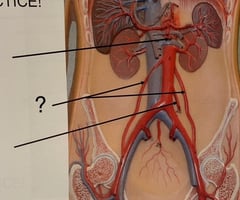
Right & Left Gonadal Arteries
95
New cards
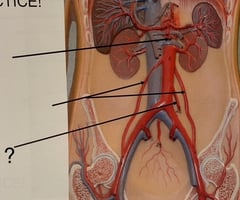
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
96
New cards
Abdominal Aorta
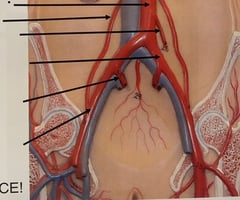
97
New cards
Gonadal Artery
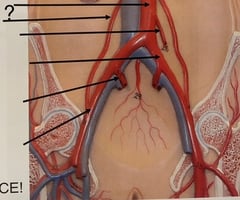
98
New cards
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
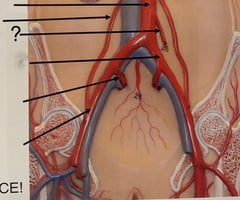
99
New cards
Common Iliac Artery
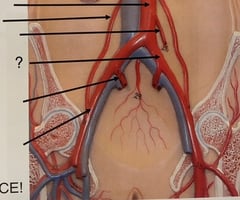
100
New cards
Internal Iliac Artery