Chemistry Unit 4: Electronic Structure of an Atom
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
Frequency
The number of cycles that pass through a point per second
2
New cards
Amplitude
the height of a wave from the origin to a crest or a trough
3
New cards
Electromagnetic Spectrum
All frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
4
New cards
Quantum
The minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
5
New cards
Planks Constant
6\.626x10^-34 J/s
6
New cards
Photoelectric Effect
Phenomenon where electrons are emitted from a metal’s surface when light of a certain frequency shines on the surface
7
New cards
Photon
A particle of electromagnetic radiation that has no mass, and carries a quantum of energy
8
New cards
Atomic emission spectrum
Set of frequencies of electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of an element
9
New cards
As wavelength increases the frequency….
decreases
10
New cards
As wavelength decreases the frequency…
increases
11
New cards
Speed and amplitude of light are not affected by…. and frequency
wavelength
12
New cards
What relationship is there between wavelength and frequency?
Inverse relationship
13
New cards
What relationship is there between photons and wavelength/frequency?
Direct relationship
14
New cards
What has more energy, red or blue light?
Blue light. The photon that corresponds to red light carries less energy than the photon that corresponds to blue light. The longer the wavelength of light the lower the energy of its photons
15
New cards
Orbitals
probability envelopes are regions of space where there is a high (90%) probability of finding an electron.
16
New cards
Each principal energy level is assigned a principal quantum number…
n
17
New cards
The lowest principal quantum number….is assigned to the smallest and lowest energy level immediately next to the nucleus
n=1
18
New cards
with…value of n, the principal energy levels get larger and are higher in energy and further away from the nucleus
increasing
19
New cards
Each principal energy level is made up of energy sublevels……
ns,np,nd,nf,etc
20
New cards
Energy sublevels consist of….
orbitals
21
New cards
An energy sublevel is a group of orbitals with …energy but …… orientation
similar, different
22
New cards
s-sublevel
Each energy level has an s-sublevel from n=1-∞
23
New cards
p-sublevel
All energy levels n=2 and higher have p-sublevels. There are 3 orientations in space corresponding to 3 orbitals per p-sublevel
\
\
24
New cards
d-sublevel
All energy levels n=3 and higher have d-sublevels. There are orientations, corresponding to 5 orbitals per d-sublevel. 4 orientations look like a clover, one is nicknamed the donut whole.
25
New cards
f-sublevel
All energy levels n=4 and higher have f-sublevels. There are 7 orientations, corresponding to 7 orbitals per f-sublevel. Complex shape.
26
New cards
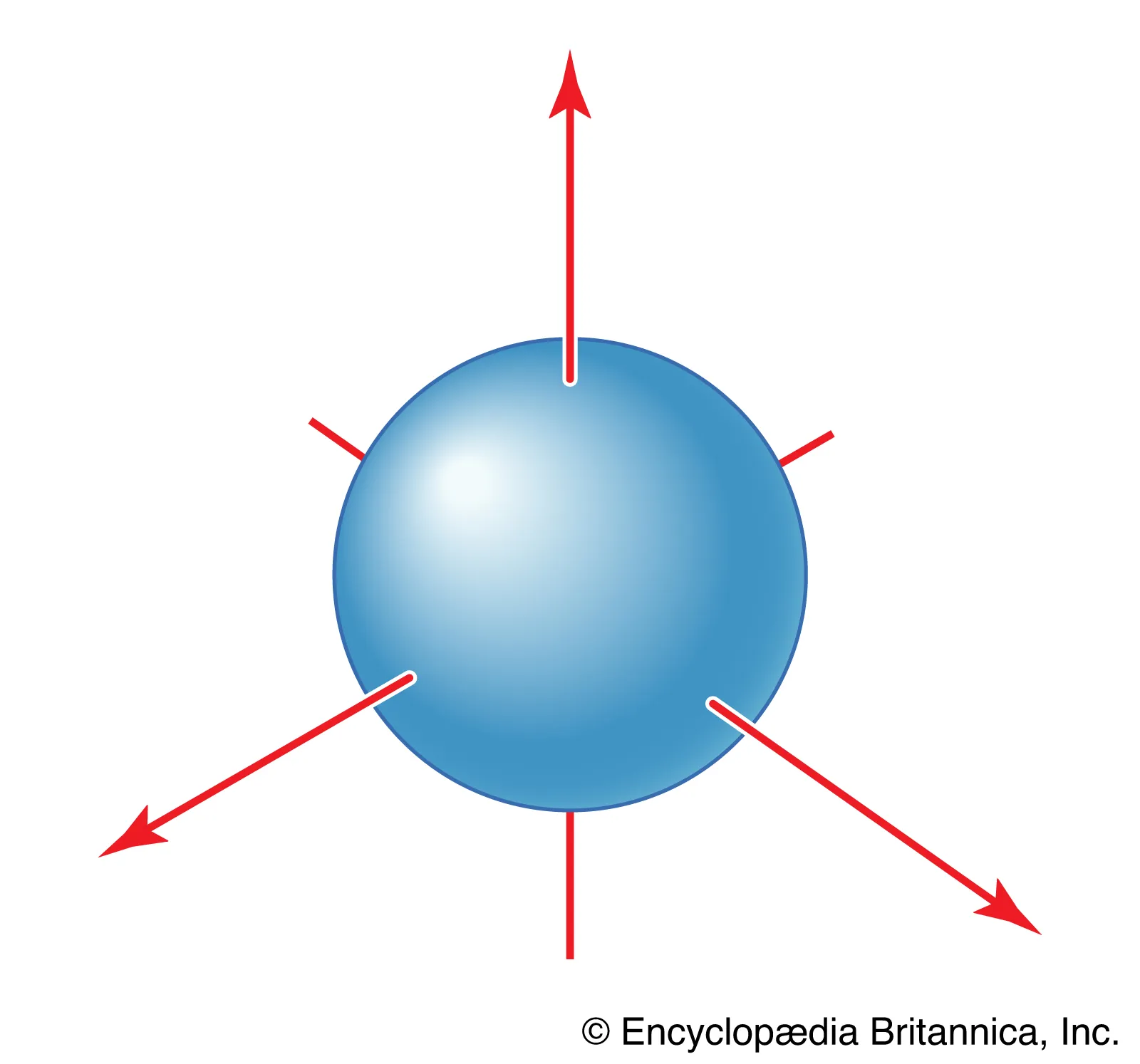
What energy level is this?
An ns sub-level where n=1-∞
27
New cards
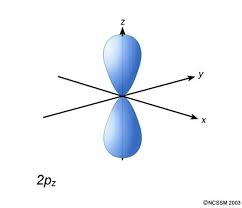
What energy level is this?
An np sub-level where n=2-∞
28
New cards
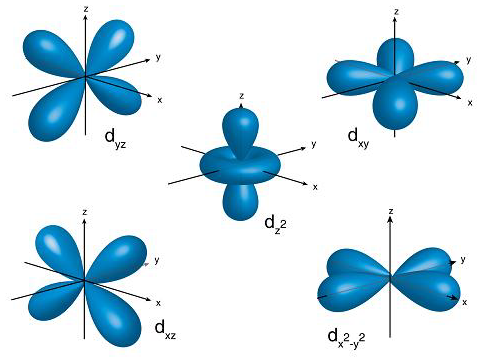
What energy level is this?
An nd sub-level where n=3-∞
29
New cards
What does an nf energy sublevel look like?
A complex shape
30
New cards
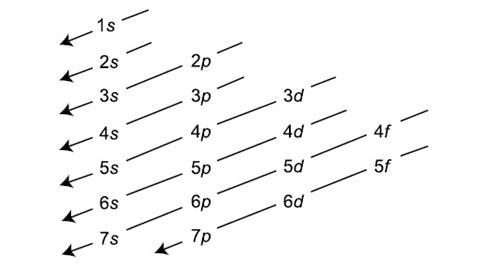
Aufbau principle
Electrons are placed in the lowest energy sublevels.
31
New cards
Sublevels are added in order of increasing…….Larger energy levels, with more sublevels, are higher in energy and further away from the nucleus
energy
32
New cards
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
States that each atomic orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. Electrons act like a tiny magnet, so if two have the same poles line up, they repel each other and move in directions to realign. Therefore opposite spins overcome repulsive forces
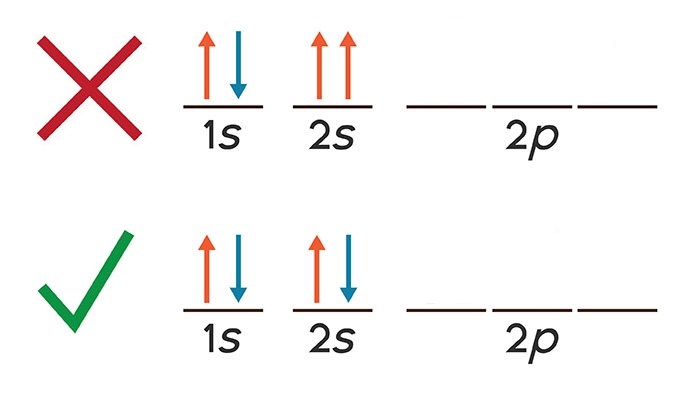
33
New cards
Hund’s Rule
Which states that for a set of orbitals of similar energy, each orbital must be filled singly with parallel spins before electron paring can occur
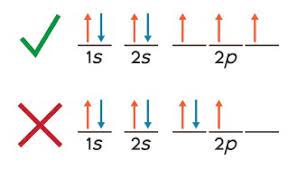
34
New cards
S-block elements are those with their…..in the ns subshell
valence electrons
35
New cards
d-block elements are the….. block of the periodic table in which the valence electrons enter the inner d sub-shell
middle
36
New cards
p-block elements are those with their valence electrons in the np sub-shell. These are all the elements in groups…
13-18
37
New cards
Closed configuration
A configuration in which ns and np sub-shells are filled is called a closed configuration
38
New cards
Ground state electron configurations are the… possible energy states, written by following the increasing energy order of energy levels according to the Aufbau principle
lowest
39
New cards
The excited state is a state of a ….. energy that an atom attains by absorbing energy from its surroundings
higher
40
New cards
atoms can have…. excited states
multiple
41
New cards
The excited state for an atom would correspond to the placement of electrons in…. energy levels than that allowed for the ground state
higher
42
New cards
Octet Rule
Atoms become energetically stable by attaining a full valence shell. They do this either by forming a full octet or a full duet
43
New cards
If an atom gains electrons it acquires a ….. charge
negative charge.
44
New cards
Negatively charged ions are called anions and are…
non-metals
45
New cards
.If it loses electrons, it becomes… charged
positively
46
New cards
Positively charged ions are…
cations and are metals
47
New cards
Elements in Groups 1a,2a,3a…..1,2, and 3 electrons to become isoelectronic with the noble gas preceding them. These elements form…charged ions with charges of +1,+2, and +3.
lose
48
New cards
Elements in 5a,6a,7a,… 3,2, and 1 electrons to become isoelectronic with the noble gas proceeding them. These elements for negatively charged ions with charges of -3,-2, and -1 respectively
gain
49
New cards
period
horizontal across the periodic table (row of elements)
50
New cards
group/family
vertical up/down the periodic table (column of elements)
51
New cards
What does a column/family/group of elements have in common?
Same number of valence electrons
52
New cards
What does a period/row of elements have in common?
Same number of energy sublevels
53
New cards
What type of metal is column 1a?
Alkali Metals
54
New cards
What type of metal is column 2a?
Alkaline Earth Metals
55
New cards
What type of non-metal is column 3a?
Boron Family
56
New cards
What type of non-metal is column 4a?
Carbon Family
57
New cards
What type of non-metal is column 5a?
Nitrogen Family
58
New cards
What type of non-metal is column 6a?
Chakogens or Oxygens Family
59
New cards
What type of non-metal is column 7a?
Halogens
60
New cards
What type of non-metal is column 8a?
Noble Gasses
61
New cards
What are d block elements called?
transition metals
62
New cards
What are f block metals called?
intertransition metals