Animal Behaviour
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Umwelt
this means point of view of a particular animal
-each animal senses the environment in its own way
-Self centered subjective world
comparative psychology
the study of general rules of behaviour that apply both to humans and other animals
Ethology
the study of animal behaviour in natural environments
Behavioural ecology
the study of evolutionary and environmental context of animal behaviour and how behaviour maximizes reproductive or evolutionary success
Sociobiology
term for using ethology to study social behaviour
Chemical cues
this lets animals convey messages to one another
by pheromones sensed by antennae or jacobson's organ

Mechanoreception
this lets animals convey/receive messages by detection of sound, touch, electroreception
Visual displays
these are visual messages animals send and receive
-body language
-Aposematic coloration
aposematic coloration
term for Bright warning colors in animals with a chemical defense.

Stereotyped behaviour
term for the continuous repetition of simple acts such as gnawing, rearing, or head bobbing
-egg retrieval pattern in greylag geese
-sign stimulus (particular aspect of the releaser; sound, shape, color)
-territorial behaviour
Innate behaviour
behaviour based on genetic or epigenetic constitution
-spider webs
-herding dogs

Instincts
term for nervous system reinforcing a subset of behaviour and these modes are eventually genetically stabilized

learned behaviour
behaviour of an individual organism not common to all members of its species and which is acquired by experience
-Habituation
-sensitization
Habituation
an organism's decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
Sensitization
an increase in behavioral response after exposure to a stimulus
Imprinting
this is a learned behaviour.
-process by which certain animals form strong attachments during an early-life critical period

Monogamy
this means only one mate
Polygamy
this means many mates
-many females (polygyny)
-many males (polyandry)
Socially coordinated behaviour
when an individual adjusts its actions to the presence of others in order to increase its own reproductive success
Cooperative behaviour
when an individual performs activities that benefit others
-behavior ultimately benefits the individual's genetic contribution to future generations
Aggression
when offensive physical actions or threats are used to intimidate competitors
Agonistic behaviours
term for any activities involving Fighting and aggressive displays between members of the same species
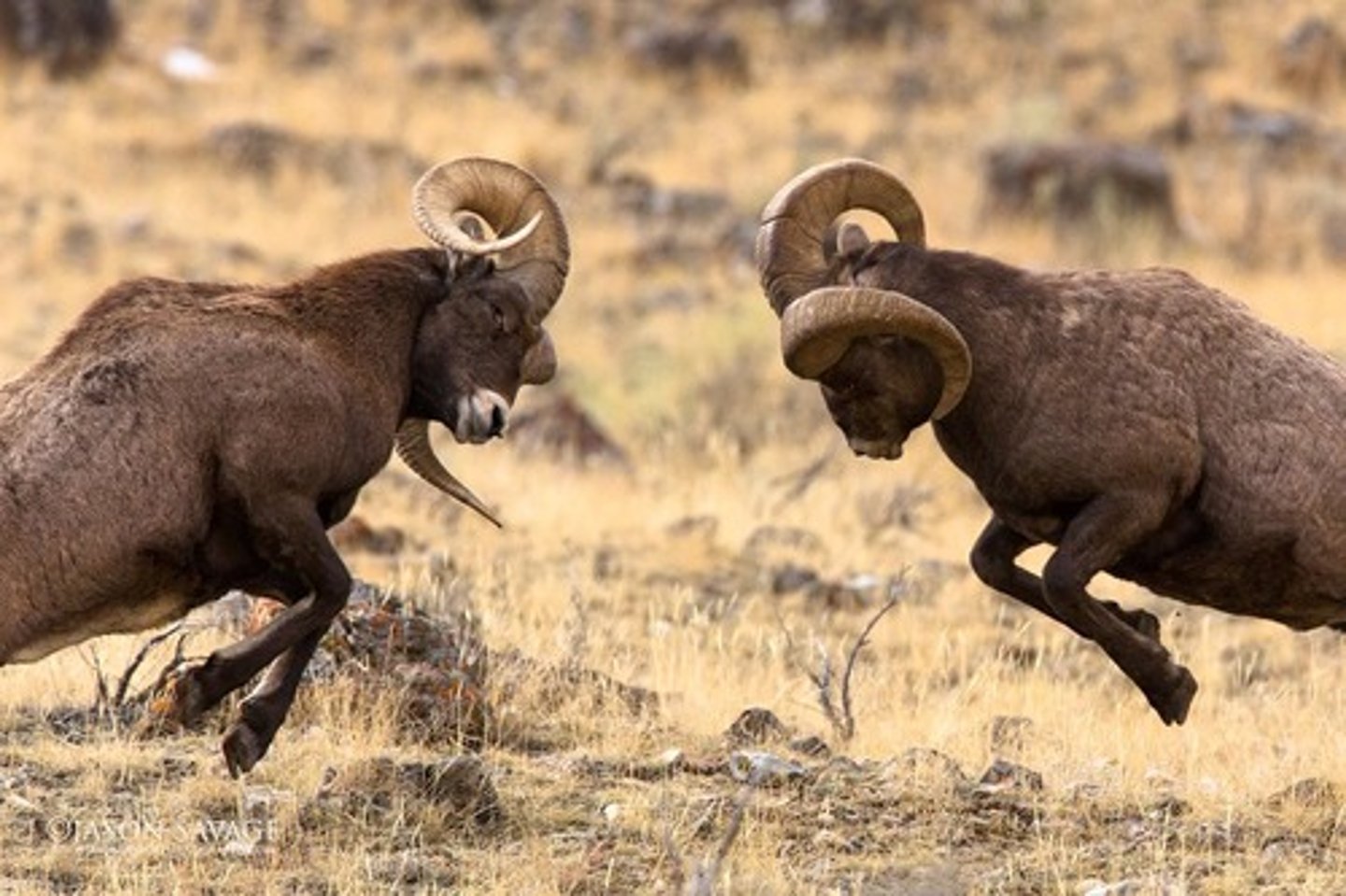

Territoriality
term for individual defending a fixed area from intruders
-Agonistic behaviour
Ritualized threat displays
displays that prevent actual injury or death due to a mutual understanding of aggression
-Agonistic behaviour
dominance hierarchy
ordering of individuals within a group in which group members with lower status defer to those with greater status
-Agonistic behaviour
Altruism
term for unselfish regard for the welfare of others

social aggregation
term for the tendency of individuals to come together and form groups for various reasons, ranging from small pairs to large herds

Eusociality
An extreme form of sociality in which there is cooperative brood care, division of labor, and overlapping generations.

Animal congnition
term for mental function including perception thinking and memory