Chapter 2 Part 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions: Molecules, Ions, and Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Ions
Elements or molecular groups (groups of chemically bonded element) that have charge
What are the two types of Ions?
Monatomic Ions and Polyatomic Ions
Monatomic Ions
Ions formed from single atoms
Polyatomic Ions
Ions formed from two or more atoms
How are ions formed?
Through the loss or gain of electrons
Cations
Ions that carry positive charge
Anions
Ions that carry negative charge
Chemical Bonds
Forces that hold atoms together in compounds
Octet Rules
The noble gases have a particular stable octet of 8 electrons in their valence energy shell.
-Compounds are the result of formation of chemical bonds between two or more elements
-These elements have the tendency to lose, gain, or share electrons to achieve octet structure to become more stable
What are the three Intermolecular Chemical Bonding?
-Ionic Bonding
-Covalent Bonding
-Metallic Bonding
Ionic Bonding
Complete transfer of 1 or more electrons from one atom to another atom (usually between a metal and a nonmetal)
*The result in electrostatic attraction between the cations and anions
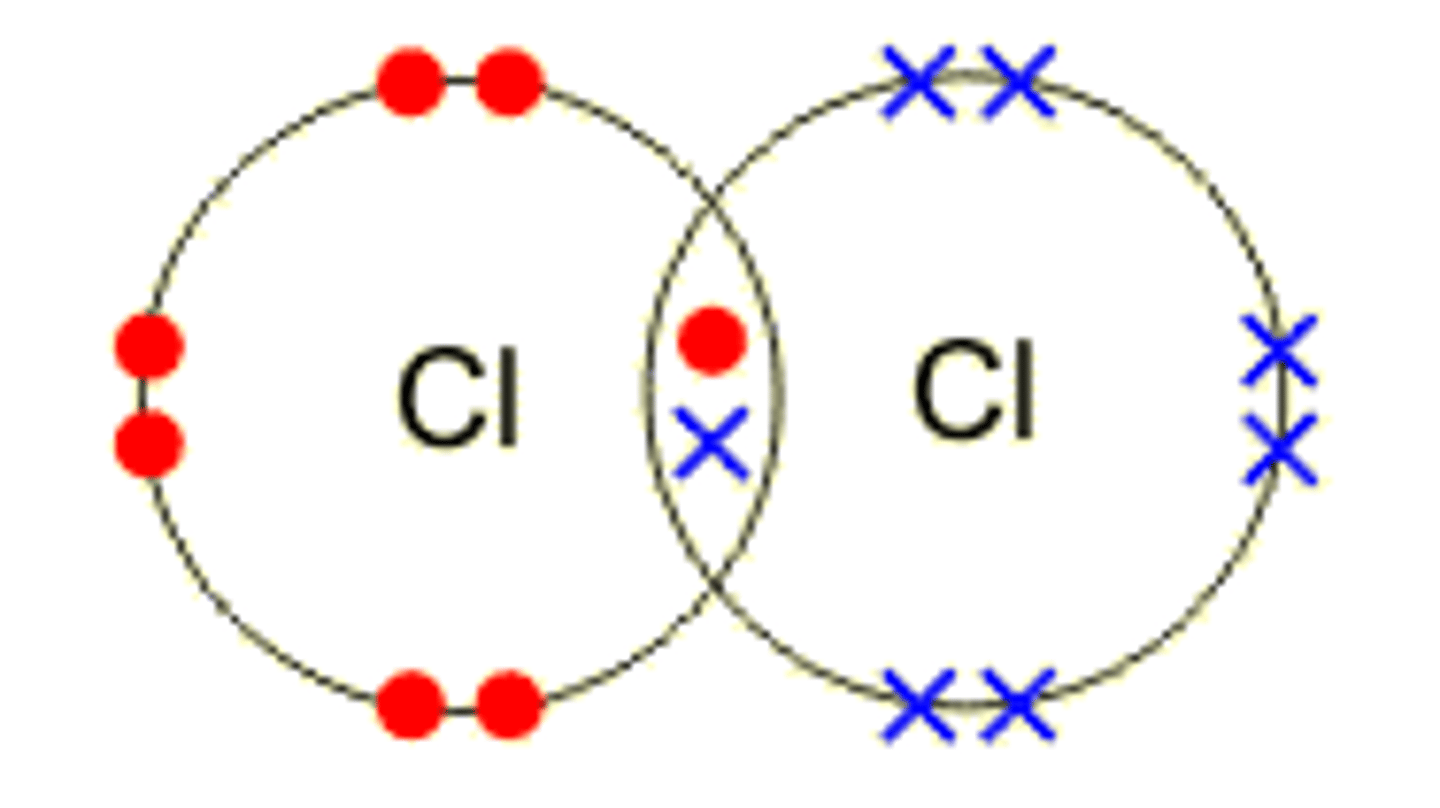
Covalent Bonding
The sharing of valence electrons (the electrons on the last shell)
-Usually between nonmetals & nonmetals OR between nonmetals & metalloids
*The result of the mutual attraction between the cations and anions
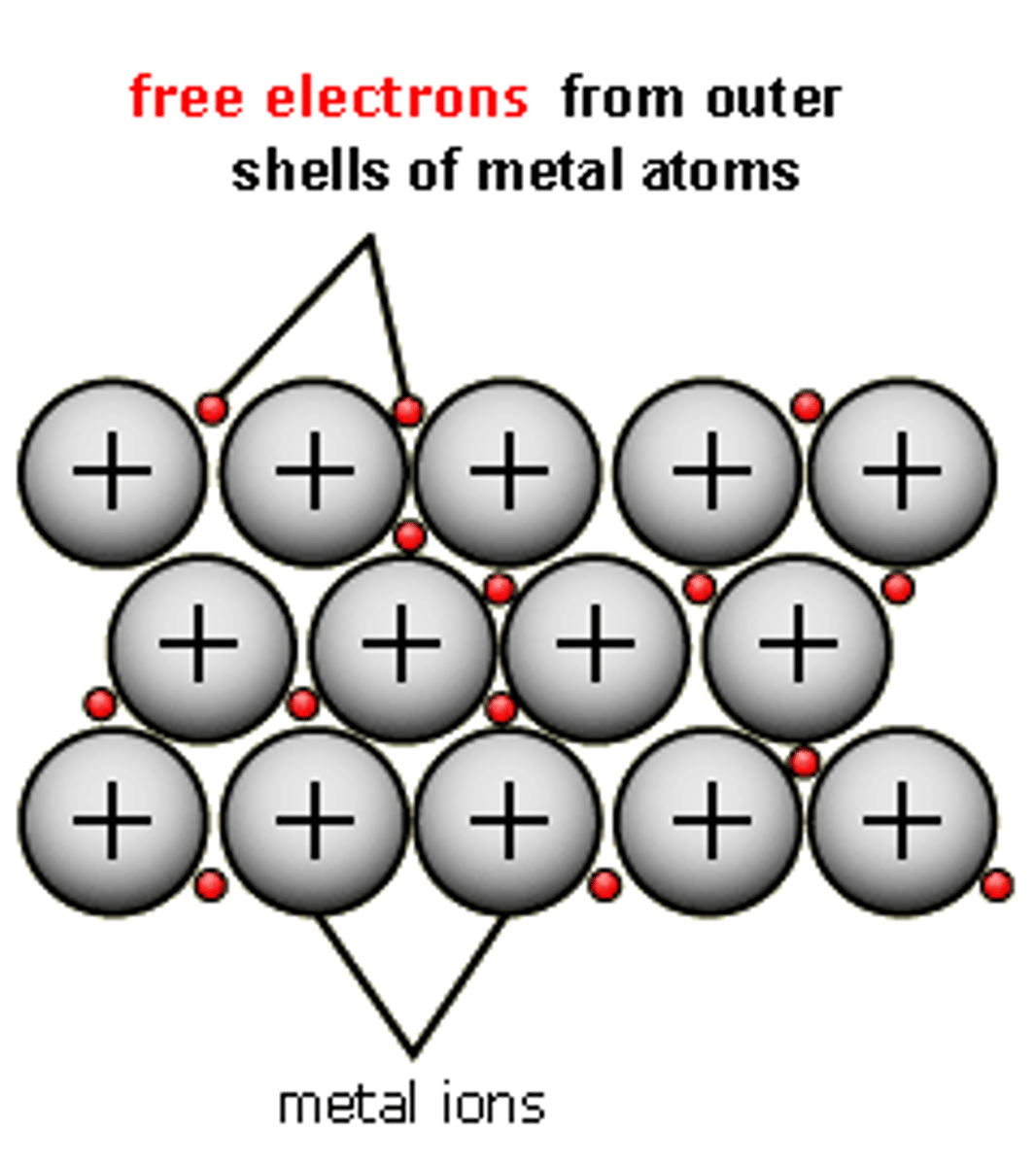
Metallic Bonding
The communal sharing of electrons between metals
*Sea of electrons
What are the two types of covalent bonds?
-Nonpolar Covalent Bond
-Polar Covalent Bond
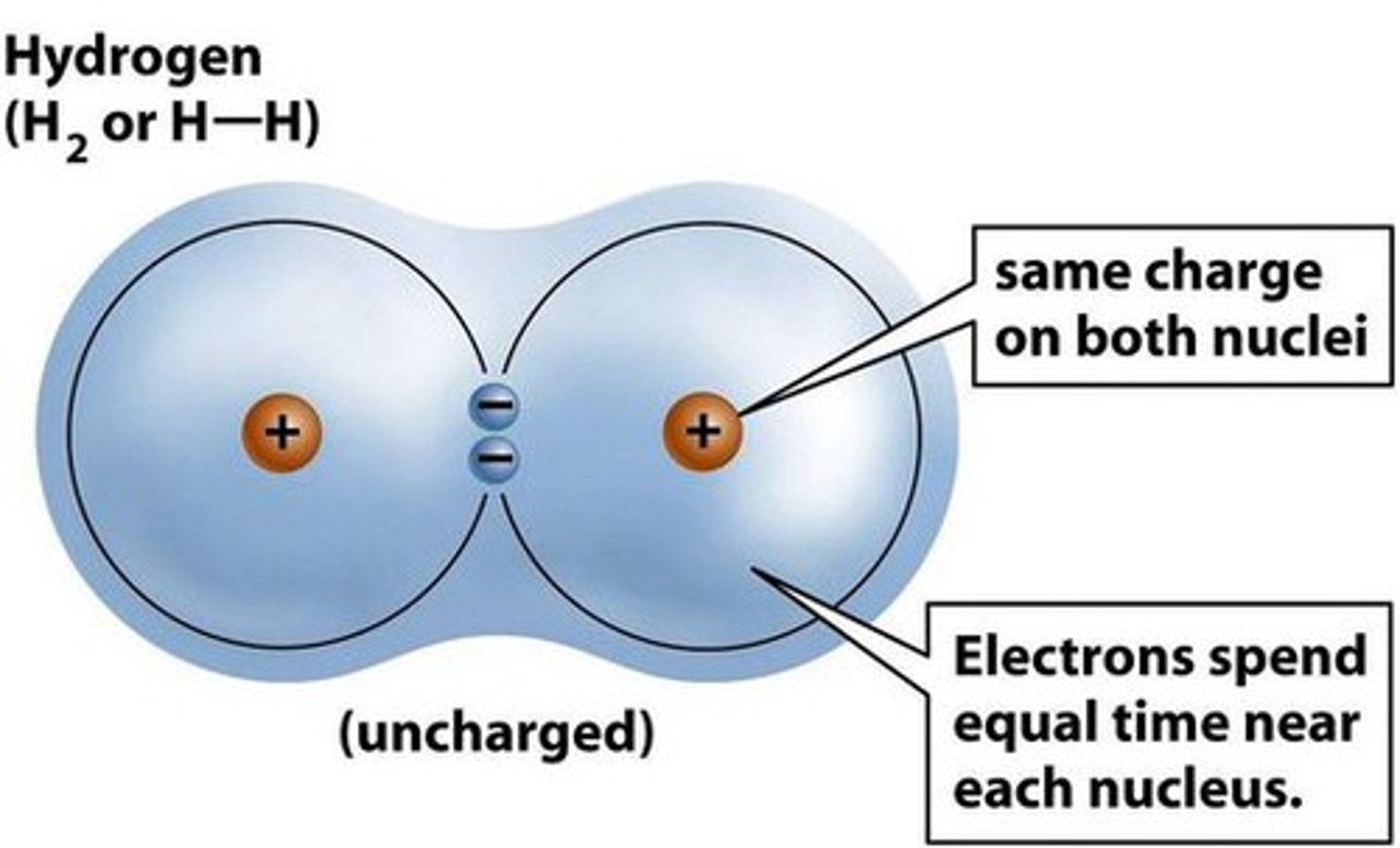
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
Bonding electrons shared equally between two atoms
-No charges on atoms
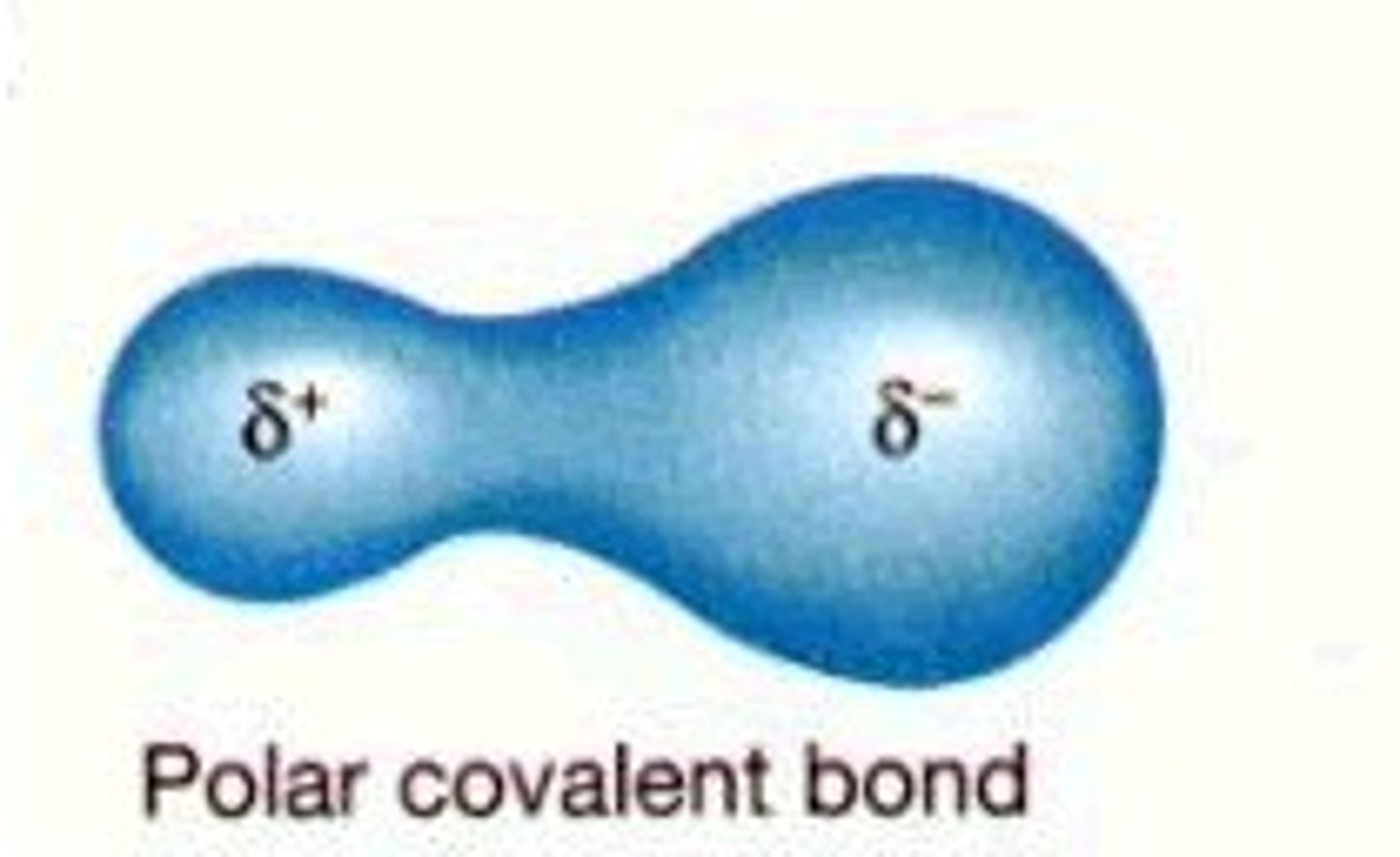
Polar Covalent Bond
Bonding electrons shared unequally between two atoms
-Partial charges on atoms
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract bonding electrons to itself
-The value of the electronegativity increases going from left to right in a period and from bottom to top in a group
What side to what side does the value of the electronegativity increase on a periodic table?
The value of the electronegativity increases going from left to right in a period and from bottom to top in a group
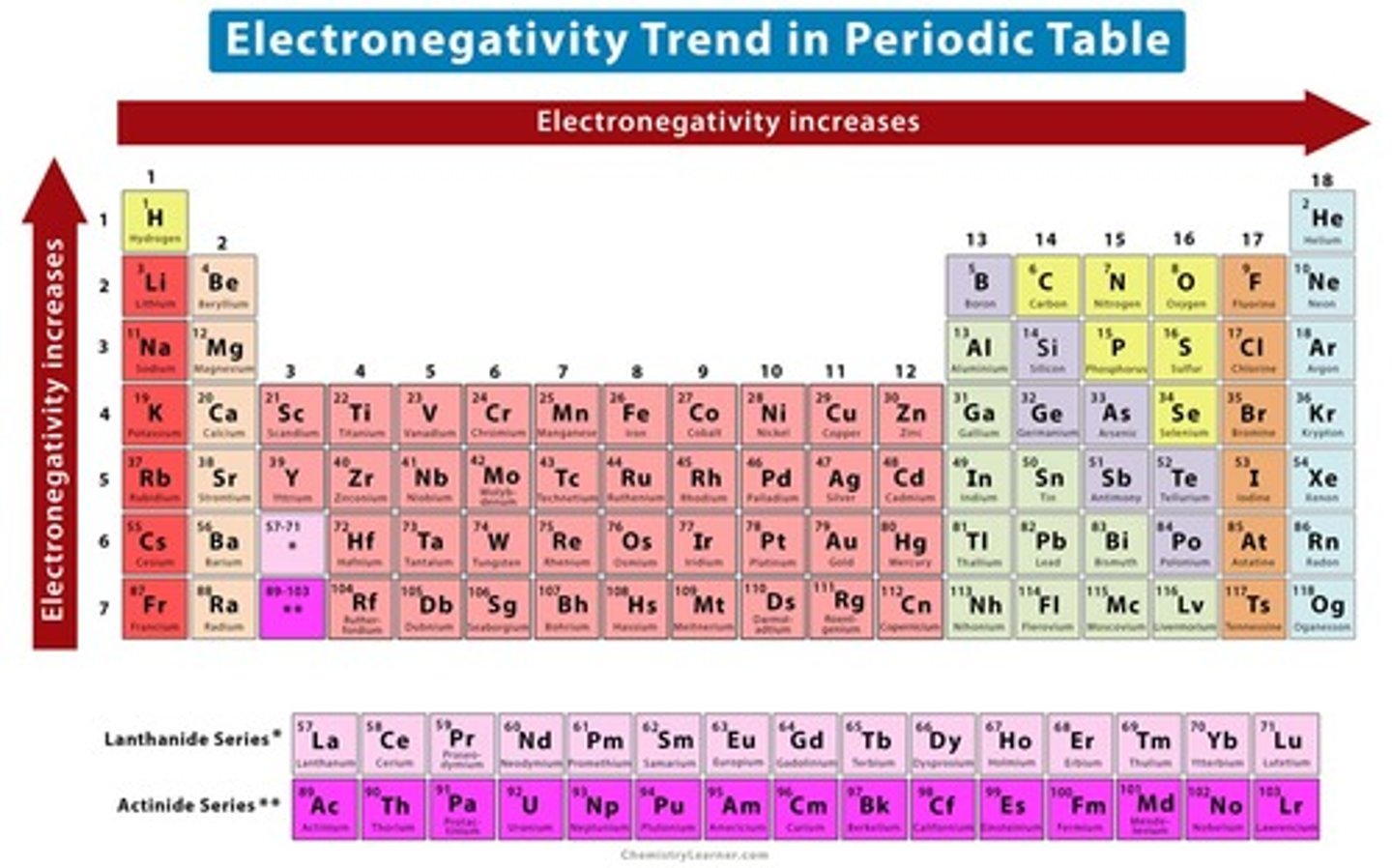
Which element has the highest electronegative value?
Fluorine with a value of 4.0 electronegativity
What type of bond between two elements has a electronegativity between 0.0<(change in electronegativity)<0.4?
-Covalent (Nonpolar, Electron bonding equal, Electron shared)
What type of bond between two elements has a electronegativity between 1.8<(change in electronegativity)<3.3?
-Ionic (Electron Transfer)
What type of bond between two elements has a electronegativity between 0.4<(change in electronegativity)<1.8
-Covalent (polar, electron bonding non equal, electron shared)
Atomic Elements
Elements where particles are single atoms
-Ex: Na, K, He, Fe
Molecular Elements
Elements whose particles are multi-atom molecules
-Ex: H2, N2, S8, P5
Molecular Compounds
Compounds whose particles made of only nonmetals
-Ex: H2O, HCl, NH3, H2SO4
Ionic Compounds
Compounds whose particles are cations and anions
-Ex: NaCl, MgO, K2S, FeCl3
Molecule
A group of two or more atoms held together in a definite arrangement by forces called covalent bonds
Group 1A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 1A?
-Loses 1e
-Ionic Charge: 1+
Group 2A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 2A?
-Loses 2e
-Ionic Charge: 2+
Group 3A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 3A?
-Loses 3e
-Ionic Charge: 3+
Group 4A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 4A?
-Loses none
-Ionic Charge: none
Group 5A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 5A?
-Gains 3e
-Ionic Charge: 3-
Group 6A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 6A?
-Gains 2e
-Ionic Charge: 2-
Group 7A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 7A?
-Gains 1e
-Ionic Charge: 1-
Group 8A loses/gains how many electrons? What is the Ionic Charge of Group 8A?
-No change in electrons
-Ionic Charge: none
Oxidation Number
the charge an atom would have if the electrons in the bond were assigned to the more electronegative element
-also known as an apparent charge
When writing a chemical formula, what goes first, the cation or anion?
The cation THEN the anion
Hydrates
An ionic compound in which the formula unit includes a fixed number of water molecules associated with the cations and anions
-Ex: FeCl3 * 6H2O is named "iron (III) chloride hexahydrate"
Binary Acids
An aqueous solution of a compound formed by a hydrogen and a more electronegative nonmetal
-Ex: HCl (aq) is named "hydrochloric acid"
Tertiary Acids
An aqueous solution of a compound formed by hydrogen and polyatomic anion
If polyatomic anion ends in...
-ate, the acid will end in -ic acid
-ite, the acid will end in -ous acid