Strong Nuclear Force Notes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Discovery of Fundamental Forces
Built on work of Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford, and Bohr
20th-century scientists discovered that protons & neutrons (nucleons) are held together in the nucleus by the Strong Nuclear Force
Strong Nuclear Force
One of the Four Fundamental Forces
Others: Gravity, Electromagnetic Force, Weak Nuclear Force
Strongest of the four forces
Shortest range – only acts when particles are extremely close
How Does the Strong Nuclear Force Work?
Like charges repel (+ vs. + or - vs. -)
Unlike charges attract (+ vs. -)
Protons in the nucleus are all positively charged, so they should repel each other (repulsive force)
How Do Protons in an atomic nucleus Stay Together?
strong nuclear force is created by nucleons exchanging particles called mesons.
Conditions for strong nuclear force to work
As long as mesons are exchanged, the Strong Nuclear Force holds nucleons together
nucleons must be extremely close together, in order for exchange to happen.
If a proton or neutron gets close enough to another nucleon → Meson exchange happens → Particles stick together
If Nucleons Are Too Far ApartStrong Nuclear Force weakens
Electromagnetic force (repulsion between protons) takes over → Particles move apart
Electrostatic Repulsion (Barrier to Strong Force)
Dotted line around a nucleon (proton or neutron) represents the electrostatic repulsion (proton repelling proton)
To activate the Strong Nuclear Force, a nucleon must cross this barrier
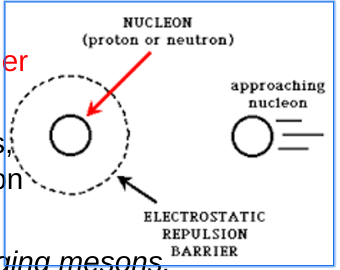
Proton-Proton Repulsion
As a proton approaches another proton, it feels increasing repulsion due to the electromagnetic force
To overcome this repulsion and allow meson exchange, nucleons must get extremely close
Overcoming barriers to create strong nuclear force and to get Nucleons to get 2 nucleons close together to begin exchange mesons.
✔ Extremely high speed (high temperature) 🔥
✔ Immense pressure (forced closer together) 💥
Role of Neutrons in strong nuclear force
Neutrons have no charge → They do not contribute to electrostatic repulsion
Neutrons separate protons → This weakens the repulsive force between protons forcing nucleons to stay bound together
neutrons can participate in meson exchange
Role of neutrons in experiment
Better than protons for this task because:
✔ No charge → Not repelled by the positively charged nucleus
✔ Can easily pass through the electrostatic repulsion barrier
Changing the Number of Neutrons Affects the Nucleus
Mass changes → Creates radioactive isotopes
Energy changes → Can trigger chain reactions (used in nuclear reactors & atomic bombs 💥)