Biology - How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two kinds of muscle fibers?
slow and fast muscle fibers
2
New cards
The percentage of types of fibers depends on:
the muscle and person
3
New cards
True or False: training can turn one runner into another
False
4
New cards
another name for slow muscle fibers:
slow-twitch fibers
5
New cards
most marathon runners have ___% slow fibers
80
6
New cards
what are the slow muscle fibers abundant in?
mitochondria and myoglobin molecules
7
New cards
What kind of color do myoglobin molecules give slow muscle fibers?
a reddish color
8
New cards
slow muscle fibers perform best in what kind of exercises?
endurance exercises
9
New cards
fast muscle fibers perform best in what kind of exercises?
short, intense exercises
10
New cards
most sprinters have ___% fast fibers
60
11
New cards
slow muscle fibers use ___ respiration, while fast muscle fibers use ____ respiration
aerobic, anaerobic
12
New cards
fast fibers have less ____ and ____, but produce this:
mitochondria, myoglobin, lactate
13
New cards
catabolic pathways:
break down energy
14
New cards
respiration is the transferring of ___ from ____ to ____.
hydrogen, glucose, oxygen
15
New cards
net reaction of cellular respiration:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + Heat)
16
New cards
reactions involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another:
redox reactions
17
New cards
the loss of electrons:
oxidation
18
New cards
the addition of electrons:
reduction
19
New cards
what does OIL RIG stand for?
oxidation it loses
reduction it gains
reduction it gains
20
New cards
ionic bonds involve the ____ transfer of electrons
complete
21
New cards
the electron donor is also known as the:
reducing agent
22
New cards
the electron acceptor is also known as the:
oxidizing agent
23
New cards
why are carbs and fats important fuels?
have lots of electrons and hudrogens
24
New cards
the three stages of cellular respiration are?
glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain
25
New cards
this pathway is found in ALL organisms:
glycolysis
26
New cards
glycolysis is the breaking down of what molecule?
glucose
27
New cards
what gives glycolysis energy?
ATP
28
New cards
there are __ steps in glycolysis
10
29
New cards
what are the two phases of glycolysis?
the energy investment phase and the energy payoff phase
30
New cards
how many ATP molecules are invested in glycolysis?
2
31
New cards
in the energy investment phase, glucose is broken down into:
2 three carbon G3P molecules
32
New cards
what does G3P stand for?
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
33
New cards
in the energy payoff phase, how many ATP molecules are produced?
4
34
New cards
in the energy payoff phase, the 2 G3P molecules are converted to what?
2 three carbon pyruvate molecules
35
New cards
energy investment phase equation:
glucose + 2ATP → 2G3P
36
New cards
energy payoff phase equation:
2G3P → 2 pyruvate, 2H2O, 2NADH, 4ATP
37
New cards
net reaction of glycolysis:
glucose → 2 pyruvate, 2H2O, 2NADH, 2ATP
38
New cards
how much of glucose’s energy does glycolysis release?
less than a quarter
39
New cards
glycolysis does not require this molecule, making it:
oxygen, anaerobic
40
New cards
mitochondria are organelles that:
carry out cellular respiration
41
New cards
mitochondrian are _-_ __ long
1, 10, um
42
New cards
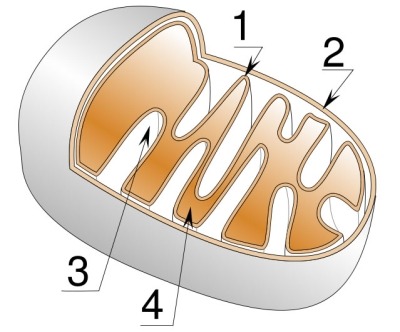
number one:
cristae (inner membrane)
43
New cards
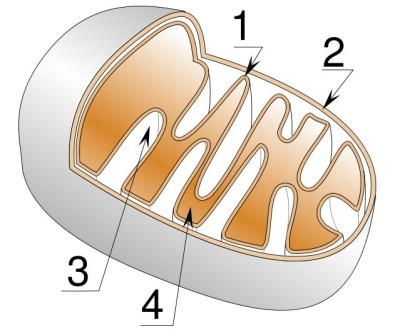
number two:
outer membrane
44
New cards
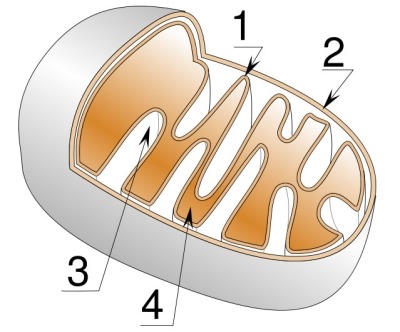
number three:
intermembrane space
45
New cards
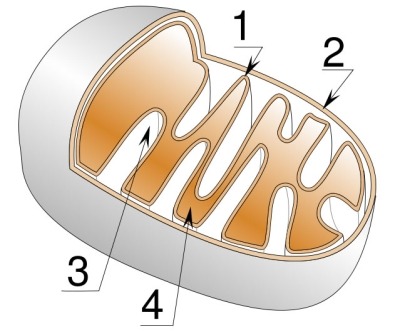
number four:
matrix (liquid part)
46
New cards
why does the inner membrane have so many folds?
increases surface area and ability to produce ATP
47
New cards
the mitochondrial matrix contains:
enzymes, DNA, ribsomes
48
New cards
the step between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle is:
conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
49
New cards
when pyruvate loses a carbon, what is it release as?
CO2
50
New cards
after pyruvate loses a carbon, the remaining two combine with what to form acetyl CoA?
coenzyme A
51
New cards
acetyl CoA stands for:
acetyl coenzyme A
52
New cards
equation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA:
pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A → acetyl CoA, NADH, CO2
53
New cards
for each glucose molecule that entered glycolysis, these many acetyl CoA molecules enter the citric acid cycle:
2
54
New cards
these enzymes remove two hydrogens from the substrate:
dehydrogenases
55
New cards
what do dehydrogenases give NAD+?
two electrons and a proton, the other proton is released as a hydrogen ion
56
New cards
the structure of NAD+ is 2 ___ joined together by their ____
nucleotides, phosphate group
57
New cards
other names for the citric acid cycle include:
the tricarboxylic acid cycle, the krebs cycle
58
New cards
where does the citric acid cycle take place in the mitochondria?
the matrix
59
New cards
the citric acid cycle has __ steps
8
60
New cards
in the citric acid cycle, the carbons from acetyl CoA bond to __ to form __
four carbon oxaloacetate, six carbon citrate
61
New cards
what is the role of coenzyme A in the citric acid cycle?
helps the two carbons enter the cycle and is recycled
62
New cards
the citric acid cycle is called a cycle because oxaloacetate ___ to repeat the cycle.
regenerates
63
New cards
citric acid cycle equation (full equation with 2 puruvate)
2 pyruvate → 4CO2, 6NADH, 2FADH2, 2ATP
64
New cards
the citric acid cycle completes what?
the breakdown of glucose
65
New cards
the final stage of cellular respiration is:
oxidative phosphorylation
66
New cards
the two parts of oxidative phosphorylation are:
the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
67
New cards
where does oxidative phosphorylation occur in the mitochondria?
the inner mitochondrial membrane
68
New cards
each electron transport chain has:
3 main multiprotein complexes and 2 mobile carrier proteins
69
New cards
what molecules carry the electrons extracted from food?
NADH and FADH2
70
New cards
in the electron transport chain, what atom takes the electrons at the end?
a highly electronegative oxygen atom
71
New cards
the production of ATP occurs from this:
energy released from diffusion of H+ ions from the intermembrane space to the matrix
72
New cards
the two functions of the electron transport chain include easing the fall of electrons from ___ to ___, and to release ___ ions into the ______
food, oxygen, H+, intermembrane space
73
New cards
chemiosmosis is an ____ mechanism
energy-coupling
74
New cards
chemiosmosis involves using the energy released by the ___ of __ ions used to fuel the __ of __ to create __
diffusion, H+, phosphorylation, ADP, ATP
75
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation makes around __ ATP
34
76
New cards
1 glucose molecule → __ ATP molecules
38
77
New cards
most electrons’ route throughout cellular respiration:
food → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
78
New cards
efficiency of respiration is __%
40
79
New cards
the two different kinds of phosphorylation are:
substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation
80
New cards
this kind of phosphorylation involves an enzyme DIRECTLY giving a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP
substrate-level phosphorylation
81
New cards
substrate-level phosphorylation produces how many ATP molecules during cellular respiration?
6
82
New cards
this kind of phosphorylation involves an enzyme transferring an inorganic phosphate from the outside solution to ADP:
oxidative phosphorylation
83
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation creates how many ATP molecules during cellular respiration?
around 34
84
New cards
in aerobic conditions, the citric acid cycle occurs after glycolysis. in anaerobic conditions, what happens after glycolysis?
fermentation
85
New cards
Fermentation regulates the supply of this molecule in order to keep glycolysis going:
NAD+
86
New cards
the two kinds of fermentation are:
alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
87
New cards
in this kind of fermentation, pyruvate is converted into ethanol in two steps:
alcohol fermentation
88
New cards
the first step in alcohol fermentation involves the release of __, leading to the two carbon compound ____
CO2, acetaldehyde
89
New cards
in the second step of alcohol fermentation, acetaldehyde is reduced to what molecule?
ethanol
90
New cards
alcohol fermentation equation:
pyruvate + NADH → ethanol + CO2 + NAD+
91
New cards
examples of alcohol fermentation include:
bacteria, yeast, beer
92
New cards
in this kind of fermentation, pyruvate is converted to lactate:
lactic acid fermentation
93
New cards
there is ___ step in lactic acid fermentation:
1
94
New cards
during lactic acid fermentation, what happens to pyruvate?
it is reduced by NADH to become lactate
95
New cards
examples of lactic acid fermentation:
cheese, yogurt, strenuous exercise
96
New cards
these organisms require oxygen for respiration:
obligate aerobes
97
New cards
these organisms require oxygen-free conditions:
obligate anaerobes
98
New cards
these organisms can make energy with or without oxygen:
facultative anaerobes
99
New cards
carbohydrates are ___ into ___, which enters __
hydrolyzed, glucose, glycolysis
100
New cards
Proteins are ___ into amino acids to make their own proteins, but excess ____ are converted into _____ of __ or _____
hydrolyzed, amino acids, intermediates, glycolysis, citric acid cycle