Marine AICE final test
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/232
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:40 AM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
1
New cards
Theory
Well tested and widely accepted hypothesis
2
New cards
**Big bang theory**
14 billions year ago all matter was all in one place and then it exploded forming the universe.
3
New cards
Giant impact theory.
The theory that the molten earth was hit by an object which caused pieces of stars dust and gas to orbit and around earth. Over time gravity brought it together to form the moon, this is the reason that the earth is tilted.
4
New cards
Rotation
spin or internal axis
5
New cards
revolution
to move around an external point
6
New cards
centrifugal force
outerward force on a object moving in a circular direction.
7
New cards
barycenter
the point which 2 bodies of mass revolve around
8
New cards
Earths 3 layers
Crust, Mantle, and core
9
New cards
Mantles 3 layers
L.A.M.
Lithospere-rigid
Athenosphere- plastic like
Mesophere-moveable flexible
Lithospere-rigid
Athenosphere- plastic like
Mesophere-moveable flexible
10
New cards
Earth´s core
Is the densest layer compose of the innner core and outer core. It is made of nickle and iron and it spins internally creating a magnetic field.
11
New cards
Alfred Wegner´s theory of continental drift
Stated that all continents were together and formed a supercontinent known as pangea. Over time they slowly move apart from each other.
12
New cards
Evidence to support Alfred Wegner´s theory of continental drift.
\-shape of coastlines looked they would fit together like puzzle pieces
\-Fossil of plant and animals species where found near the coast of different countries if they matched up.
\-Rock/Mountain formation look like continued on the coast of different continents and would line up together.
\-Fossil of plant and animals species where found near the coast of different countries if they matched up.
\-Rock/Mountain formation look like continued on the coast of different continents and would line up together.
13
New cards
Mid ocean ridge
Is where sea floor spreading takes place. This can be proven because you can find the youngest rock closest to the ridge and it got older as you went farther out.Also found there were alternating magnectic polarity bands.
14
New cards
Plate tectonics theory.
Theory says that that Earth´s crust is broken into pieces of lithospheric plates that float on underlying magma that moves due to convection currents. This is proved by the tectonic forces and the boundarys created,
15
New cards
Three tectonic forces
ridge push-Upward outward for of tectonic plates
slab pull- horizontal force in the middle of the plate
slab suction-downward force on a subducted plate
slab pull- horizontal force in the middle of the plate
slab suction-downward force on a subducted plate
16
New cards
Three different boundaries
Convergent-tectonic plates moving toward each other
Transform- tectonic plates moving past each other
Divergent- tectonic plates moving away from each other
Transform- tectonic plates moving past each other
Divergent- tectonic plates moving away from each other
17
New cards
Two different types of crusts
continental crust-Thicker less dense
oceanic crust- Thinner more dense.
oceanic crust- Thinner more dense.
18
New cards
Two different types of margins
Active-when continental margin meets the ocean floor at the tectonic boundary.
Passive- when continental margin meets ocean floor on the same tectonic plate.
Passive- when continental margin meets ocean floor on the same tectonic plate.
19
New cards
Different parts of the continental margin
cont shelf, cont edge, cont slope, cont rise
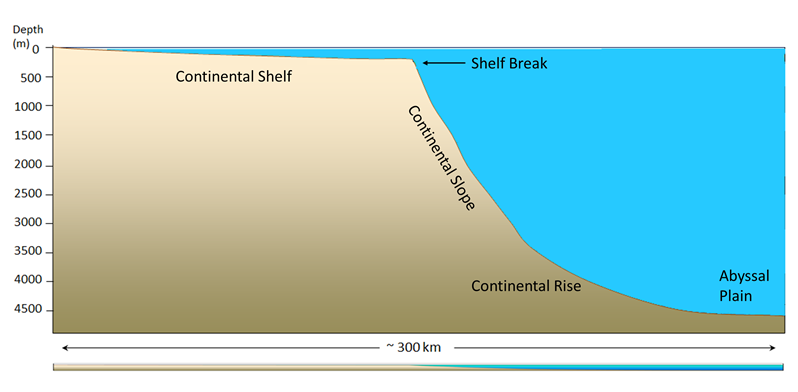
20
New cards
Mid ocean ridge
Two oceanic plates diverge because of the underlying magma push outward and up. As the plates are pushed apart magma rises and then cools forming new sea floor.
21
New cards
Oceanic trench
Occurs at a subduction zone between continental and oceanic crust. The tectonic plate that subducts then gets melted by the magma creating more hot less dense magma to rise to form volcanoes.
22
New cards
hydrothermal vents
Cracks in the boundaries of the crust have water seep through which is then heated by the underlying magma which also dissolves minerals. This is known as hydrohtermal vent fluid which is mineral rich. Pressure builds up in these vents causing them to release into the cold water.
23
New cards
Weathering
Physical or chemical breakdown of rocks. Sediments are formed because of this.
24
New cards
Erosion
Movement of sediment out of an area.
25
New cards
Sedimentation/deposition
Sediment is deposited in areas.
26
New cards
How are sediments categorized
size,source, location, and shape.
27
New cards
Biogenous sedimentation
Sediment from living organisms such as coral fragments, skeletal remains, skeletal remain.
28
New cards
Lithogenous sediments
Sediments that come from pre existing rock.
29
New cards
Hydrogenous sediments
Sediments that precipitate out of water as it evaporates.
30
New cards
Litterol zone
Region between low tide and hide tide.
31
New cards
Nerritic zone
Shallow part of the part of the water.
32
New cards
Pelagic zone
the free open waters
33
New cards
Rocky shore
Shore line that has large waves and tends to erode small sediments and large pebbles and stones leaving only the largest rocks on the shore.
34
New cards
Sandy shore
Has a moderate slope and smaller waves. The wash away small sediments leaving behind sinde particles.
35
New cards
Flattest shore
Has smallest ripples its the muddy shore made up of silt clay.
36
New cards
Tides
rise and fall of sea level caused by gravitational forces between the earth and the sun and moon. Is affected because of one side of the earth the tide is pulled toward the moon and on opposite side there is an equal tide caused by inertia.
37
New cards
Diurnal tide
One high tide and one low tide a day.
38
New cards
Semidiurnal tide
two high tides and two low tides a day each reaching the same height.
39
New cards
Mixed semidiurnal tide
Two high tides and two low tides that reach different heights.
40
New cards
Neap tide
Its the largest tidal range. When the sun,earth, and moon from a 90 degree angel.
41
New cards
Spring tide
Its the smallest tidal range. When the sun,earth, and moon form an 180(straight line) degree angle.
42
New cards
Current
Directed movement of water.
43
New cards
Surface current
extends downward 200m and they tend to form large,rotating gyres.
44
New cards
Global conveyor belt/Deep water currents.
water that circulates through all ocean basins and move water across the bottom of the ocean, rising in certain areas to the surface to mix bottom water and surface water. *Is caused by thermohaline circulation.*
45
New cards
convection current
The movement of material due to density differences.
46
New cards
Doldrums
The area with little to no wind. Around 60 degrees.
47
New cards
Horse latitude
The area with little to no wind around 30 degrees.
48
New cards
Different types of winds in the earth
Polar Easterlies- GW between 60°-90° (N & S)
Westerlies- GW between 30°-60° (N & S)
Trade Winds- GW between 0°-30° (N & S)
Westerlies- GW between 30°-60° (N & S)
Trade Winds- GW between 0°-30° (N & S)
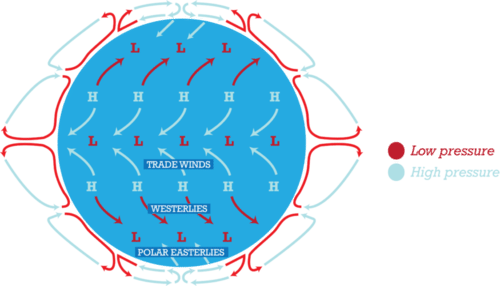
49
New cards
Coriolis affect
An effect on an object moving through earth which tends deflect it from its inteded path.
50
New cards
What directions do the winds in the northern hemisphere go.
Counterclock wise
51
New cards
What directions do the winds in the southern hemisphere go.
Clock wise
52
New cards
Coriolis affect
Apparent deflection of an object when viewed in a rotating frame of reference
53
New cards
upwelling
upward movement of cold,nutrient rich bottom water.
54
New cards
El nino
Global climatic event. When water near equator and South America becomes warmer. This warm water creates a low pressure system which reverses trade winds this causes upwelling to stop in the coast of south america. It causes droughts and recieve plenty of rainf
55
New cards
Ocean basins
Are divided by the depths of the water going from epopolagic,mesopolagic, bathypolagic, then abbysialpolagic.
56
New cards
Atmospheric dissolution
when atmospheric gasses dissolve into the water. Due to the space between the atmosphere and the surface water gasses can also be realeased back into the atmosphere.
57
New cards
Coral reefs
Need a rocky surface to attach itself, warm water, clear so that since there is least turbidity more light can penetrate through, and shallow so that light can reach through for photosynthesis. Found mainly in tropical waters,
58
New cards
Reef building corals
Hard corals that have a mutualistic relationship with zooxanthalea. They create a calcium carbonate eskeleton to protect themselves. They are helpful because they provide for shelter and biodiversity. They protect shorelines from erosion because they decrease the wave energy of strong waves.
59
New cards
Fringing reef
Closest to the shore and in the shallowest water.
60
New cards
Barrier reef
Is separated from the shore of the mainland by shallow lagoon and divided into three parts.
61
New cards
Forereef
Is the part of the reef that faces the open ocean and slopes upward toward the reef crest, the highest point in the reef.
62
New cards
Reefcrest
After the reef crest is the back reef which slopes gradually downward towards the lagoon. Inside the lagoon there may be clumps of reef structure also known as patch reefs.
63
New cards
Atoll
circle or coral with a shallow lagoon in the middle and surrounded by deep ocean water. Usually volcaninc acitvies occur here.
64
New cards
Threats to coral reefs
The formation of carbonic acid lowers the ph of the ocean which is ocean acidification. This makes it hard for the corals to make their calcium carbonate skeletons. Additionally if there is a rise of 2 degrees C coral will bleach which means they lose their zooxanthellae.
65
New cards
Reef erosion
When coral reefs lose more calcium than it gains each year. It can be caused by damage to coral from large storms, dropping anchors on reef, mining, coral bleaching, and ocean acidifcation.
66
New cards
the shore
where the ocean meets the land
67
New cards
Rocky shore
Composed of rocks,sediments and large bolders. This gives the ecosystem stability which results in biodiversity. Different zones in the shore are influenced by the tides.
68
New cards
Splash zone
Highest zone on a rocky shore that is located above the average high tide and gets splashed with was as wave break on rocks. The organisms that live in the zone are used to extreme temperatures as the only recieve water occasionally.
69
New cards
Upper shore
Is the part submerged during the highest high tide but left dry the rest of the day. Not much diversity here.
70
New cards
Middle shore
Is submerged twice a day during the high tides and is splashed with water from breaking waves at other times. The diversity is higher in this area than the ones above it.
71
New cards
Lower shore zone
Almost always submerged the only time its exposed to air for a small period during the lowest tide of the day. The animals here cant resist drying out. This area has the highest biodiversity in the rocky shore ecosystem.
72
New cards
Sandy shore
Made up of small sediments, that often disrupted by waves moving making this habitat unstable, because organisms cant hang on to small sediments to hold on. Sandy shores have low biodiversity.
73
New cards
Muddy shore
Made up of small sediments such as slit and clay, it is unstable and has little biodiversity.Marine plant can stablize these shores by allowing animals to hold on and preventing erosion.
74
New cards
Mangrove forest
Is a tidal ecosystem, meaning the tidal flow is not too strong to wash away the saplings away. They grow in tropical areas where there is moderate temperature. Are threatened by coastal development
75
New cards
Red mangrove
Have a special adpatation known as prop roots, which stabilize the tree against the tidal flow. Lenticles(pores) on the roots also allow for gas exchange.
76
New cards
Importance of Mangroves
Allow for stability in the ecosystem because they reduce wave energy and protect coastlines from erosion. The also provide habitats for the organisms that live on the mangroves. They increase biodiversity.
77
New cards
Cnidarians
Are a group of organisms that have cnidocil(stinging cells). This group includes jellyfish and corals. They are usually corals.
78
New cards
Taxonomic Hierarchy
The organization known as taxanomic hierarchy
79
New cards
Levels of classification
Kingdom Domain Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
80
New cards
Binomial Nomenclature
Is a two naming system made up of genus and species.
81
New cards
Dichotomous key
Series of yes or no questions to indentify an organism.
82
New cards
Zooplankton
Larger are heterotrophic known as drifters and the organism connecting the consumers to producers in a food chain.
83
New cards
Phytoplankton
Very small photosynthetic producers and base of many marine food chains, they produce most of the O2 in the ocean.
84
New cards
Echinoderms
Are important to the benthic system, they are bottom dwellers meaning they stay in the bottom of the ocean or stuck on a sturcture. They are mainly herbivores and filter out sediment. Some examples include sea stars, brittle stars, sea cucumbers, and urchins.
85
New cards
Corals relation w Zooxanthallea
Have mutualistic relationship with zooxanthellae that produces 90% of the corals food. The zooxanthellae are important for the coral because they produce a calcium carbonate skeleton to build a coral reef.
86
New cards
Crustaceans
A group of organisms that have a hard exoskeleton. This includes shrimps,crabs, lobsters. They filter sediment for organic material and clean parasites off of fish. And control the growth of algae since they feed on it.
87
New cards
Marine fish
Fish with bones(Osteichthyes) those with cartilage system (chondrichthyes). Talk about the marine parts of the fish
88
New cards
K strategists
Have few offspring but invest a substantial amount of energy to make sure they survive.
89
New cards
R-Strategists
Have many offspring but invest little energy in parenting.
90
New cards
Biodiversity
The amount of species that live in a particular ecosystem. The higher the biodiversity there will be more specific the ecological niche will be.
91
New cards
Ecological diversity
Is influence by the productivity, stability, and how extreme the environment is. This important for the ecosystem because the more diverse species means that there is higher chance of survival in the ecosystem.
92
New cards
Genetic diversity
All the different variations of a gene that exists in a reproductive population. Usually, there are two type of genes for each trait but some traits have multiple alleles.
93
New cards
Transect
Is a line that is stretched through an ecosystem and any individual, of the species is counted that touches the line. This line can be placed within the ecosystem in a random way such as computer generating mesurements.
94
New cards
Quadrat
A plastic or metal square divided into smaller squares is put down and any individual falling within the boundaries is counted.
95
New cards
Mark-release-recapture
Individuals are captured,counted, tagged, and then released. After a time period the species are once again captured and counted but the total number of inviduals and tagged inviduals are also counted, Then using the lincoln index the population is estimated.
96
New cards
The Lincoln index
N\= n1+n2/ m2 N\=estimated population n1\=all of the individuals captured, tagged, and released n2\=All of the individuals capture and the second time m2\=All of the marked indivduals recaptured during the second capture
97
New cards
D\=1-( ∑(n/N)²
D\=is the diversity index n\=is the number of individuals of each species N\= is the total number of individuals of all species ∑\=Is a mathmatical symbol that requires that the exprssion be added up.
98
New cards
kinetic particle theory
All matter is composed of atoms that are in motion and that the speed with which the particles in the matter move is directly related to the temperature of the matter and the physical state of the matter. The particles move slowest in solids and fastest in liquids.
99
New cards
Element
A substance that is made up of only one kind of atom
100
New cards
Molecule
When two or more atoms are bonded together