[LEC] CHAPTER 2 PART 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 2 Phase I Drug Metabolism
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
PHASE I REACTIONS
redox reactions (C, O, N, S), oxidative removal, hydrolytic reactions
2
New cards
REDOX REACTIONS
C-redox, N-redox, S-redox
3
New cards
C-REDOX
aromatic hydroxylation, alpha carbon, vinylic/olefinic carbon, benzylic carbon, allylic carbon
4
New cards
C-REDOX: **AROMATIC HYDROXYLATION**
occurs readily in the presence of ring-activators at the *para-* position; attaches OH
5
New cards
C-REDOX: **ALPHA CARBON**
hydroxylated by mixed function oxidases and may undergo __immediate oxidation__; tend to form **lactam** **metabolites**
6
New cards
C-REDOX: **VINYLIC/OLEFINIC CARBON**
initially forms an epoxide intermediate which is susceptible to __enzymatic hydration__ forming a __**diol product**__
7
New cards
C-REDOX: **BENZYLIC CARBON**
undergoes oxidation as long as it holds a benzylic hydrogen (**primary benzylic C** - __RCOOH__; **secondary benzylic C** - __RCOR__)
8
New cards
C-REDOX: **ALLYLIC CARBON**
can also become substrates for hydroxylation
9
New cards
N-REDOX: **AROMATIC NITRO AND AZO COMPOUNDS**
ar-nitro (NO2) and azo (N=N) compound reduces into 2 Ar-NH2 (aromatic amine)
10
New cards
S-REDOX: **S-OXIDATION**
oxidized by adding an oxygen then forming the corresponding oxidation product (**sulfoxide/sulfone**); can also oxidize __without__ oxygen forming **disulfide bonds** (RSSR’)
11
New cards
OXIDATIVE REMOVAL
dealkylation, deamination, desulfuration, dehalogenation reactions
12
New cards
OXIDATIVE REMOVAL: **DEALKYLATION**
alkyl group bonded directly to a heteroatom (N, O, S) __can be removed__ by adding a **hydroxyl moiety** (OH) to the R group (usually an alpha carbon); methyl group removal that results in NH, OH, or SH
13
New cards
OXIDATIVE REMOVAL: **DEAMINATION**
amine alpha carbon is hydroxylated by **monoamine oxidase (MAO)** which results to amine cleavage; produced RCOH/RCOR is acted upon by __aldo-keto reductase__ which reduces the substrate to its alcohol counterparts
14
New cards
OXIDATIVE REMOVAL: **DESULFURATION**
converts C=S bonds to C=O
15
New cards
OXIDATIVE REMOVAL: **DEHALOGENATION**
halogens are reactive with H2O, which allows addition of OH to the alpha carbon and subsequent cleavage of the halogen atom; results to inactivation of the molecule
16
New cards
HYDROLYSIS
addition of H2O (carried out by hydrolases) to esters and amides results into cleavage and subsequent formation of metabolite (may be active)
17
New cards
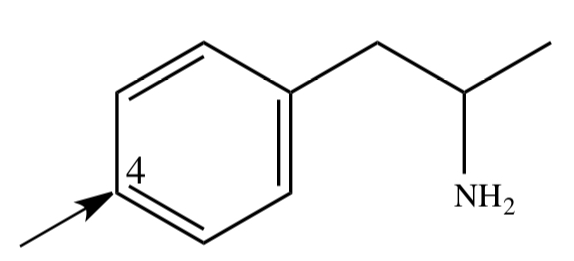
AMPHETAMINE
1) c-redox: aromatic hydroxylation
18
New cards
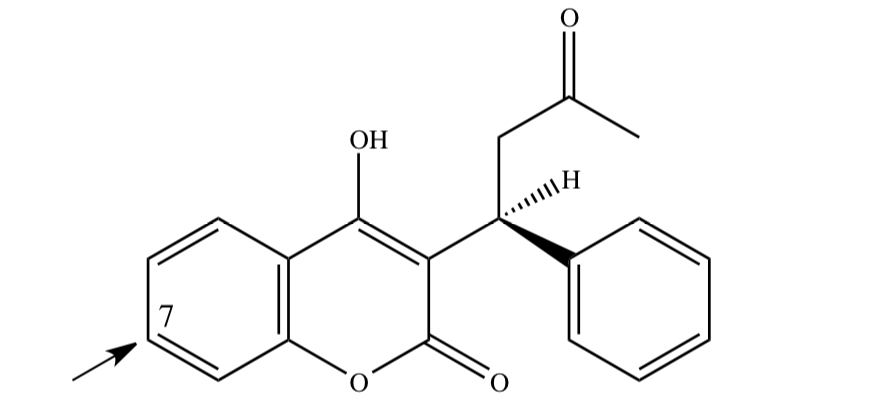
WARFARIN
2) c-redox: aromatic hydroxylation
19
New cards
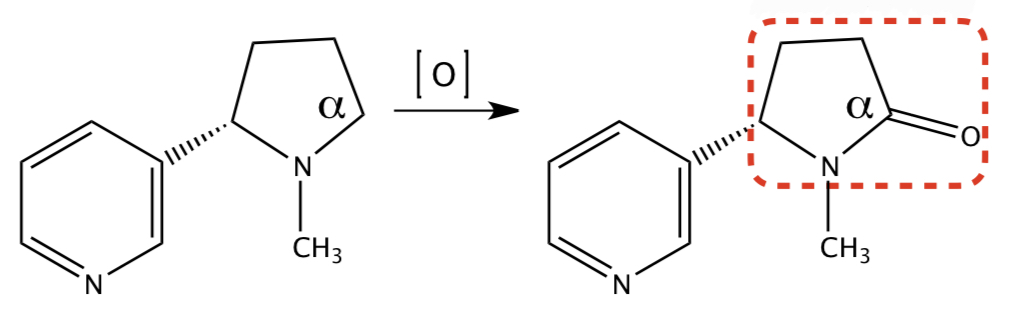
**NICOTINE** TO **COTININE**
1) c-redox: alpha carbon
20
New cards
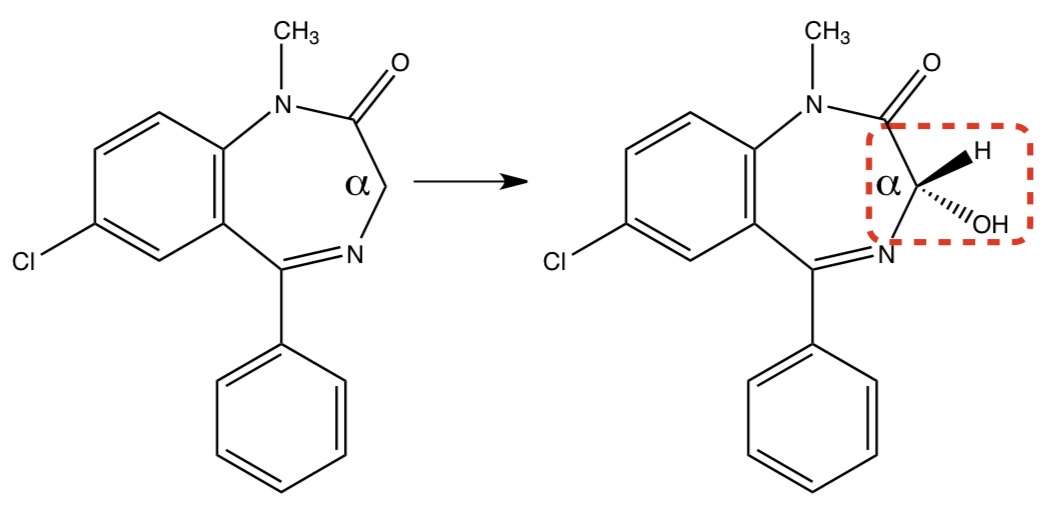
**DIAZEPAM** TO **3-HYDROXYDIAZEPAM**
2) c-redox: alpha carbon
21
New cards
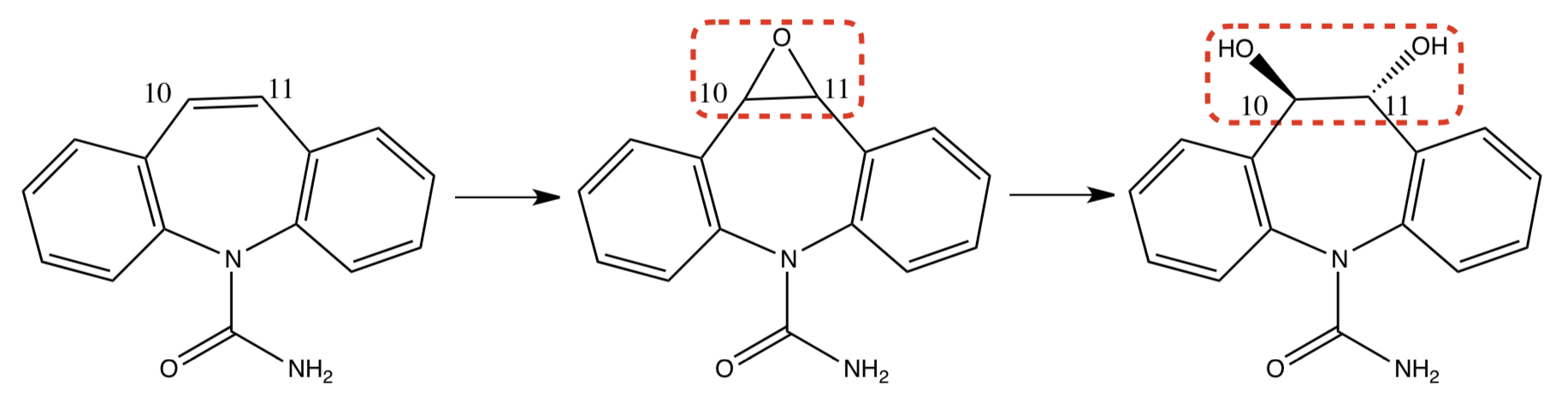
**CARBAMAZEPINE** TO **CARBAMAZEPINE-10,11-EPOXIDE** TO **TRANS-10,11-DIHYDROXYCARBAMAZEPINE**
c-redox: vinylic/olefinic carbon
22
New cards
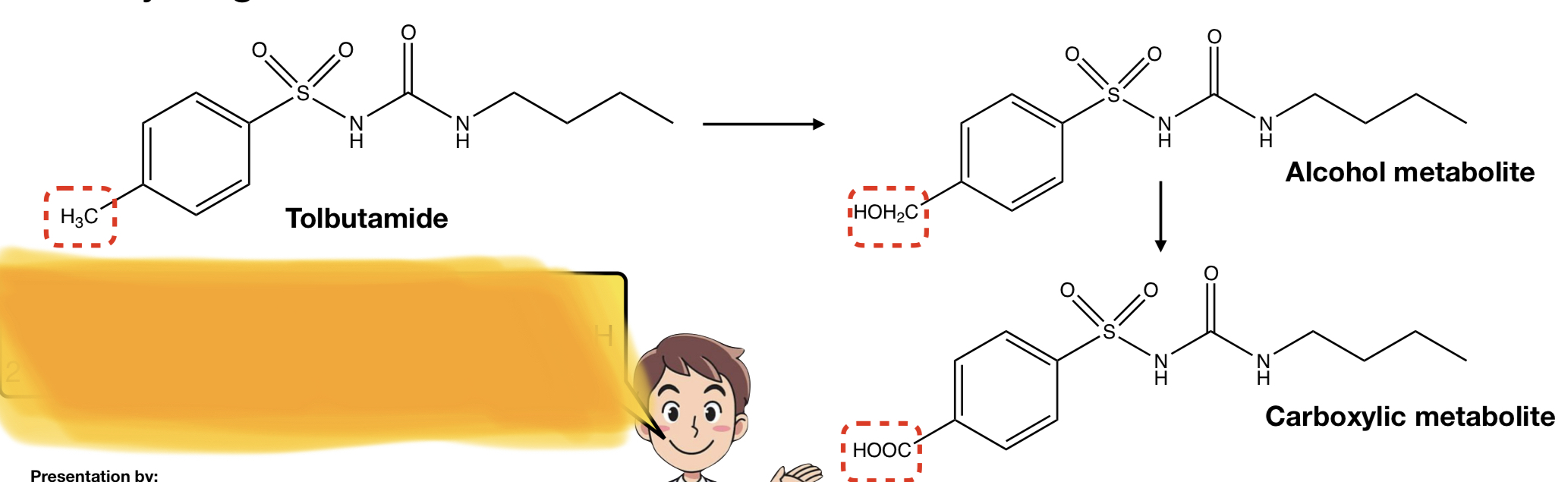
**TOLBUTAMIDE** TO **ALCOHOL METABOLITE** TO **CARBOXYLIC METABOLITE**
c-redox: benzylic carbon
23
New cards
**QUININE** TO **3-HYDROXYQUININE**
c-redox: allylic carbon
24
New cards
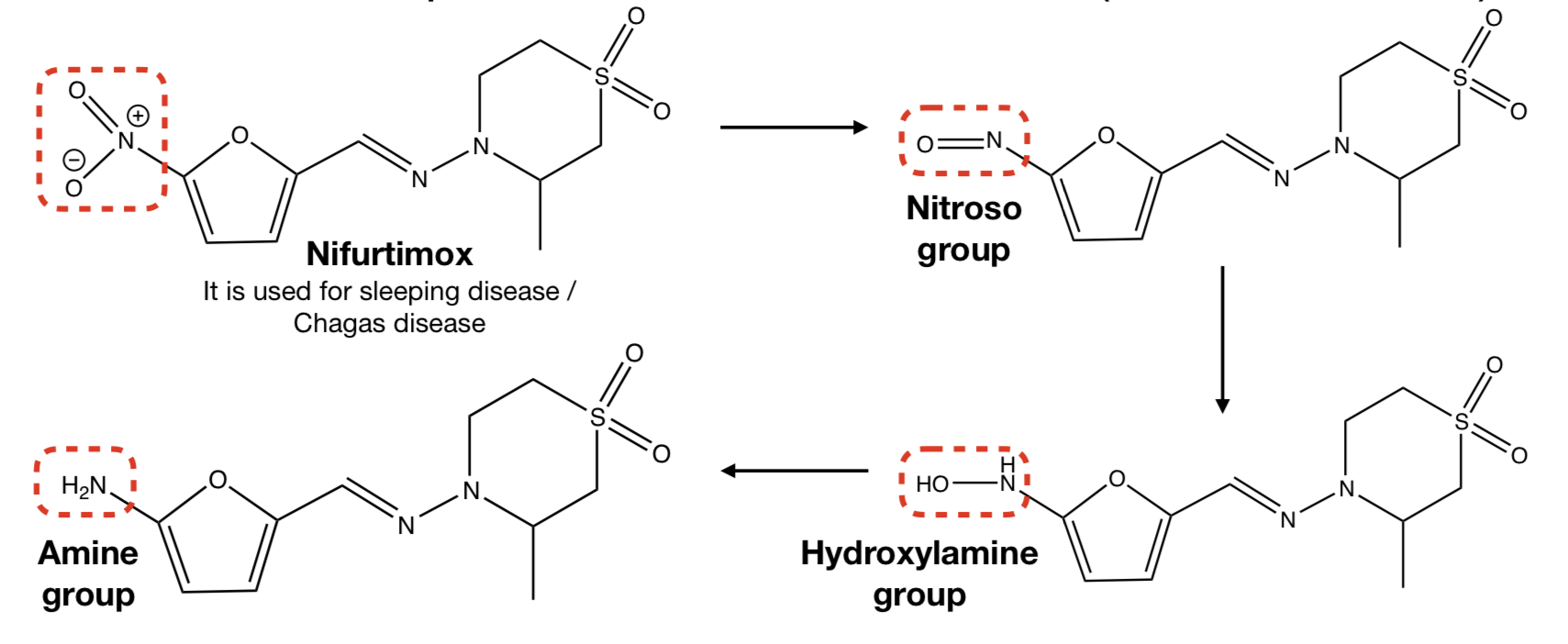
n-redox: ar-nitro compound
25
New cards
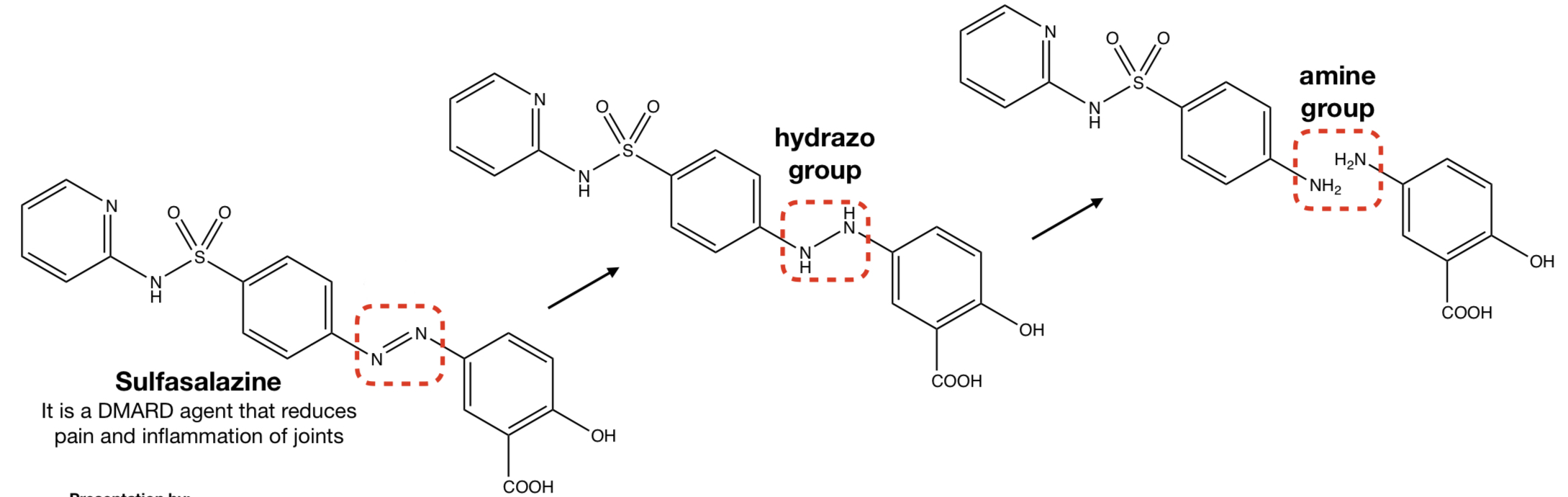
n-redox: ar-azo compound
26
New cards
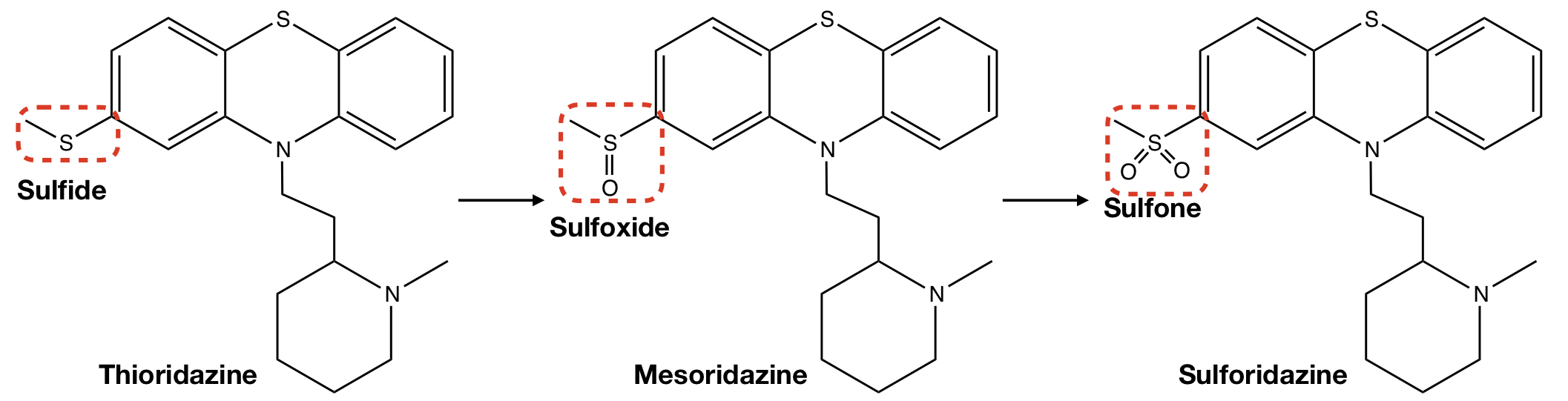
**THIORIDAZINE** TO **MESORIDAZINE** TO **SULFORIDAZINE**
s-redox: s-oxidation
27
New cards
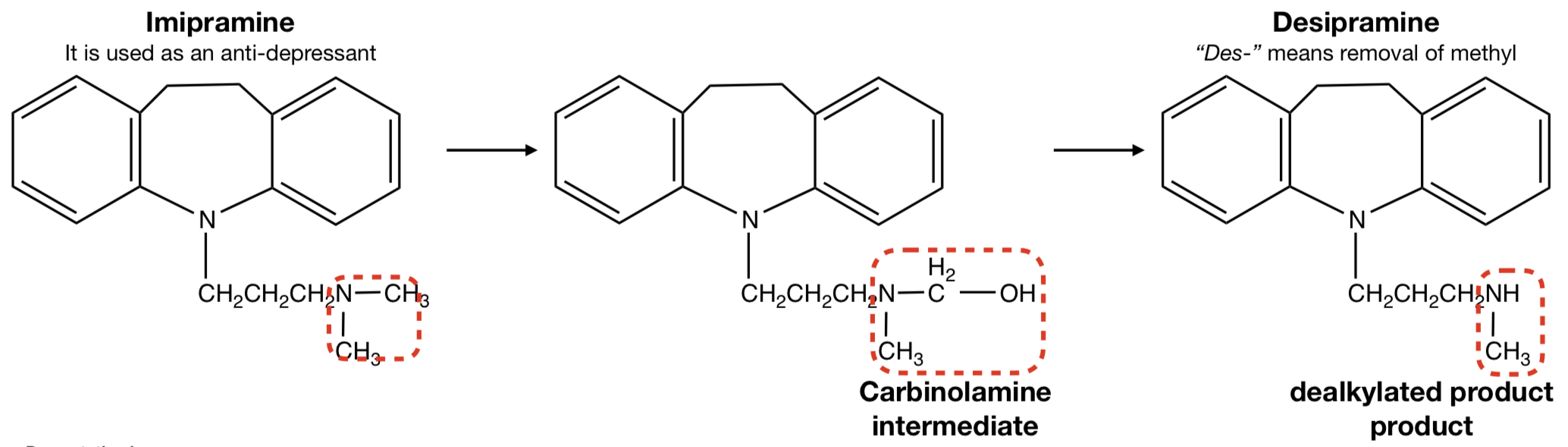
**IMIPRAMINE** TO **DESIPRAMINE**
oxidative removal: N-dealkylation
28
New cards
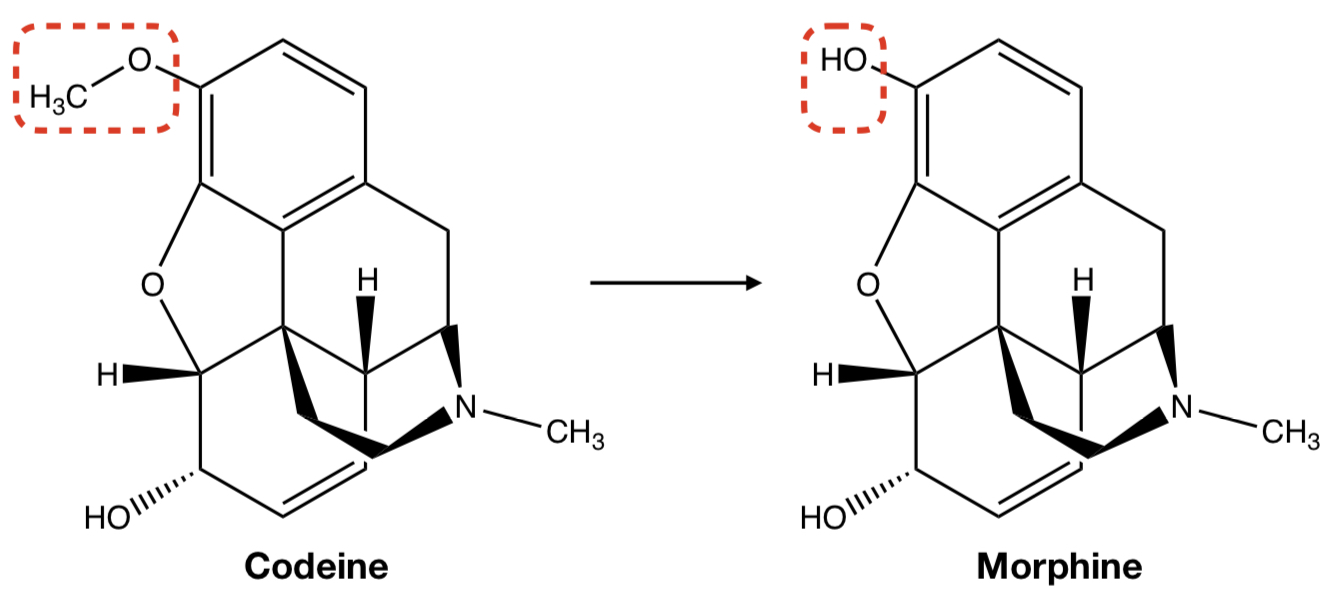
**CODEINE** TO **MORPHINE**
oxidative removal: O-dealkylation
29
New cards
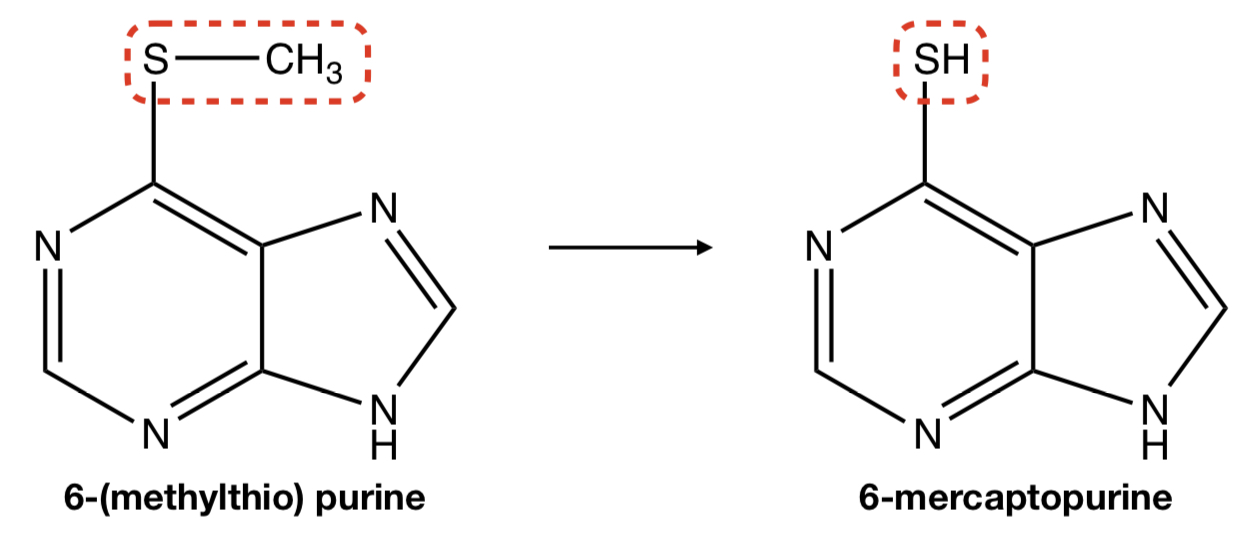
**6-(METHYLTHIO) PURINE** TO **6-MERCAPTOPURINE**
oxidative removal: S-dealkylation
30
New cards
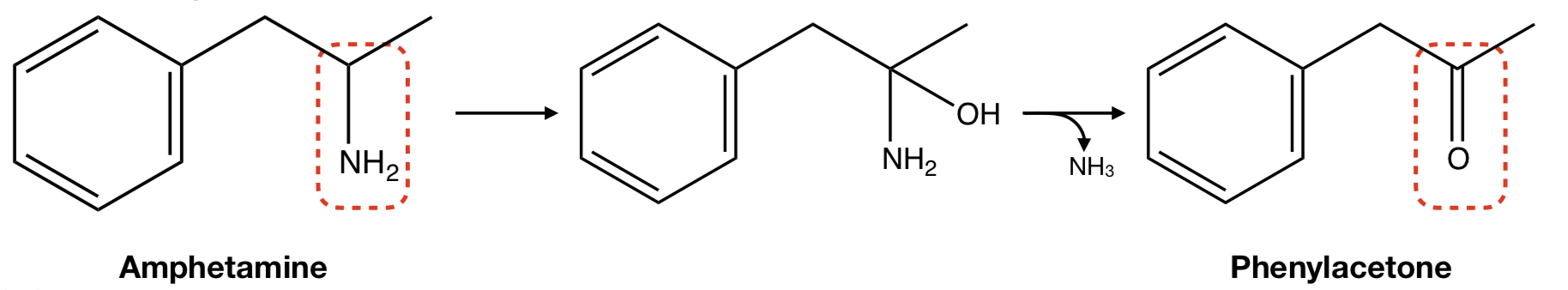
**AMPHETAMINE** TO **PHENYLACETONE**
oxidative removal: deamination
31
New cards
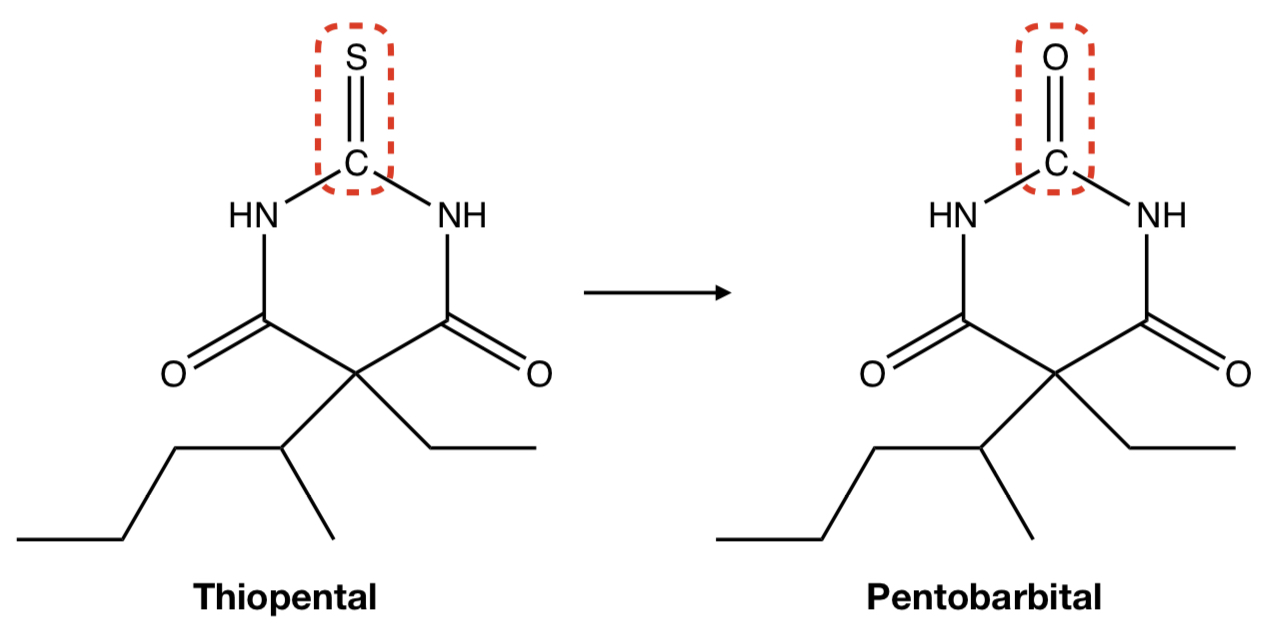
**THIOPENTAL** TO **PENTOBARBITAL**
oxidative removal: desulfuration
32
New cards
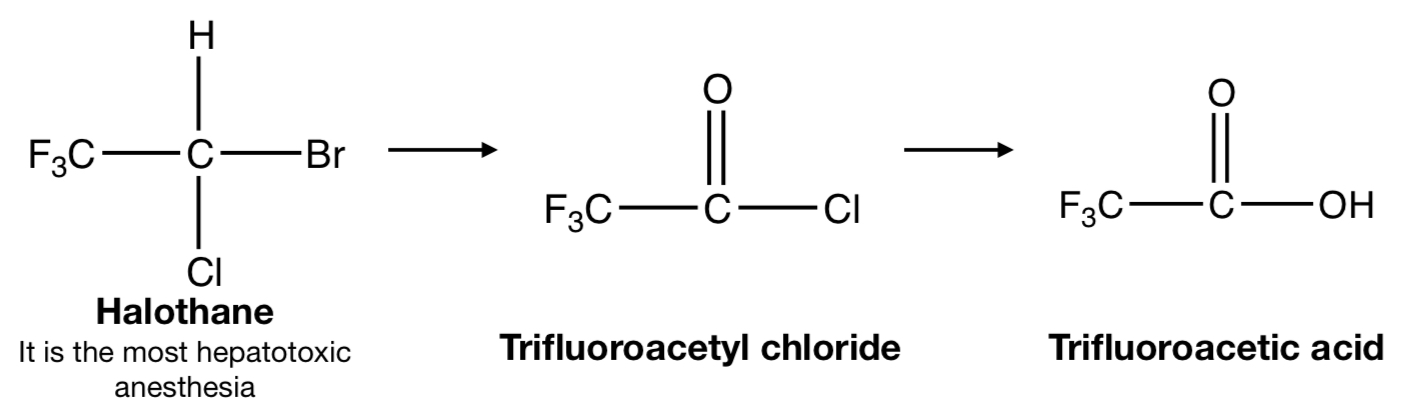
**HALOTHANE** TO **TRIFLUOROACETYL CHLORIDE** TO **TRIFLUOROACETIC ACID**
oxidative removal: dehalogenation
33
New cards
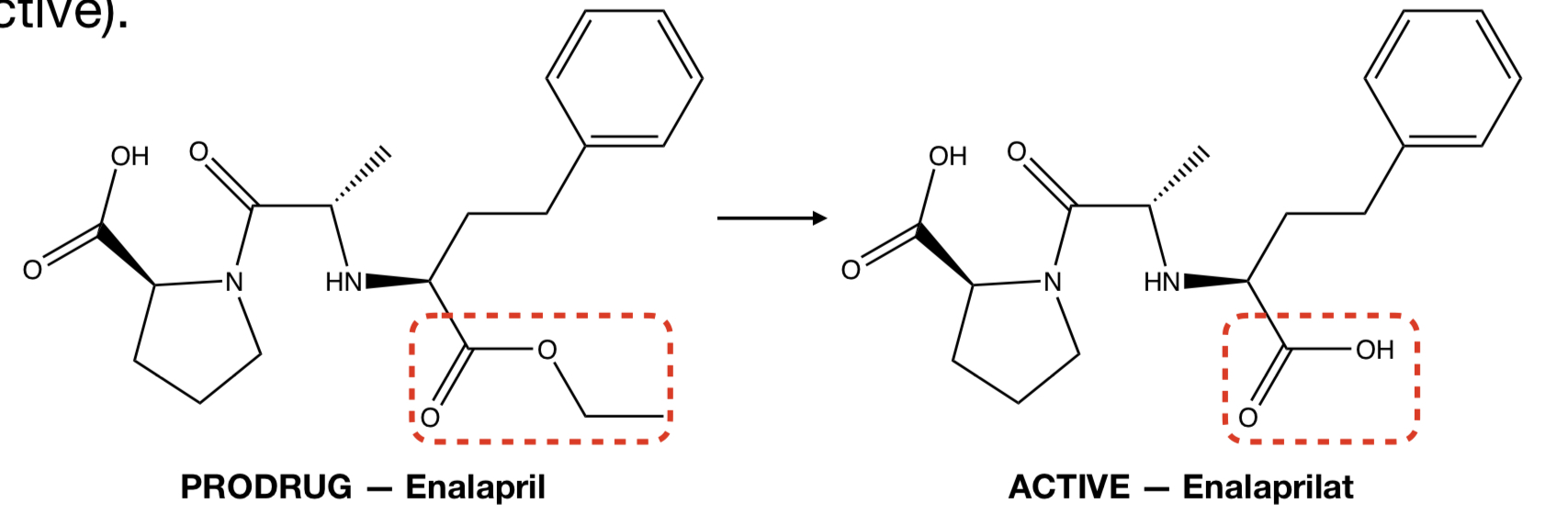
**PRODRUG (ENALAPRIL)** TO **ACTIVE (ENALAPRILAT)**
hydrolysis