In depth study guide
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Signalment
name, age, breed, sex, production status, presenting for…
CBC
complete blood count
WBC
LYN
MON
NU
EOS
BAS
RBC
HCT
PLT
wbc
white blood cells
lym
lymphocytes
mon
monocytes
NU
neutrophils
eos
eosinophils
bas
basophils
hct
hematocrit/pcv
plt
platelits
glu
glucose
high = hyperglycemia
may be high due to stress
alb
albumin
produced by liver
protein in blood stream
alp
alkaline phosphate
alt
if elevated can signal liver damage
Amy
amylase
if elevated can show signs of pancreatitis
bun
blood urea nitrogen
cre
creatinine
blood urea nitrogen and creatinine
look at both for kidney function
if both are high means bad kidneys
azotemia
TP
total protein
if high animal may be dehydrated
globulin and albumin
glob
globulins
proteins/immunoglobulins
high if infection is present
specific gravity
“10-62” = 1.062
high = more concentrated
low = dilute
dysfunction kidneys = lose inability to concentrate urine
more dilute
protein
should be negative because don’t want to lose protein in urine
clip around horn buds
done to avoid risk of fire and allows us to visualize horn buds
corneal nerve
nerve that supplies sensation to horn bud
the nerve that will be blocked for dehorning procedure
find divot adjacent to lateral cantos
administer 5mL of 2% lidocaine to each side
aspirate to ensure you are not in blood vessel
inject PERPENDICULAR angle
meloxicam
used as an anti-inflammatory drug
NSAID
analgesic
3 tablets/100 lbs
3 seconds
the amount of time the hot iron was held to horn bud
this time allows us to avoid thermal injury to skull or brain while also allowing us 360 degree separation
aluminum spray
protective barrier to prevent infection
cartron IV fly spray
must be sprayed over poll NOT directly on dehorned site
AAEP grade 1
inconsistently lame under special circumstances
AAEP grade 2
consistent lame under special circumstances
AAEP grade 3
lameness at trot
AAEP grade 4
lameness at walk
AAEP grade 5
non-weight bearing
palmar digital nerve block
desensitizing caudal/palmar 1/3 to 2/3 of foot
2ml lidocaine both medial and lateral
tells us % improvement of lameness
abaxial nerve block
done after the palmar digital nerve block
desensitize entire foot/part of pastern
sound limb
head will go down
affected limb
head will go up
streptococcus equi subspecies equi
bacteria that causes strangles
gram positive
streptococcus bacteria strain
strangles clinical signs
fever
enlarged lymph nodes
mainly in head/throat latch region
may rupture
dyspnea (difficulty breathing)
lethargy
potassium penicillin
infused into guttural pouch of horse that has strangles
targets the gram positive bacteria
strangles vaccine
NON-CORE / risk based
modified live vaccine
intranasal = administer last
air particles settle onto skin causing IM abscess
can cause inappropriate immune response if horse has a high antibody titer level then receives vaccine
purpura hemorrhagica
inflammation of blood vessels
inappropriate immune response
horse heart rate
28-44 bpm
horse temp
99.0 - 101.0
horse respiratory rate
10 - 24 bpm
pneumorectum
rectal gas bubble making it appear horse has hypothermic temp
horse PCV
30-35%
low pcv
anemia
high pcv
dehydration
splenic contraction due to stress
horse total protein
6.0 g/dl - 8.0 g/dl
albumin and globulins
low TP
loss/use of antibodies
starvation
failure to transfer passive immunity
liver failure
kidney disease
GI bleed
inflammatory bowel disease
high TP
infection or illness
dehydration
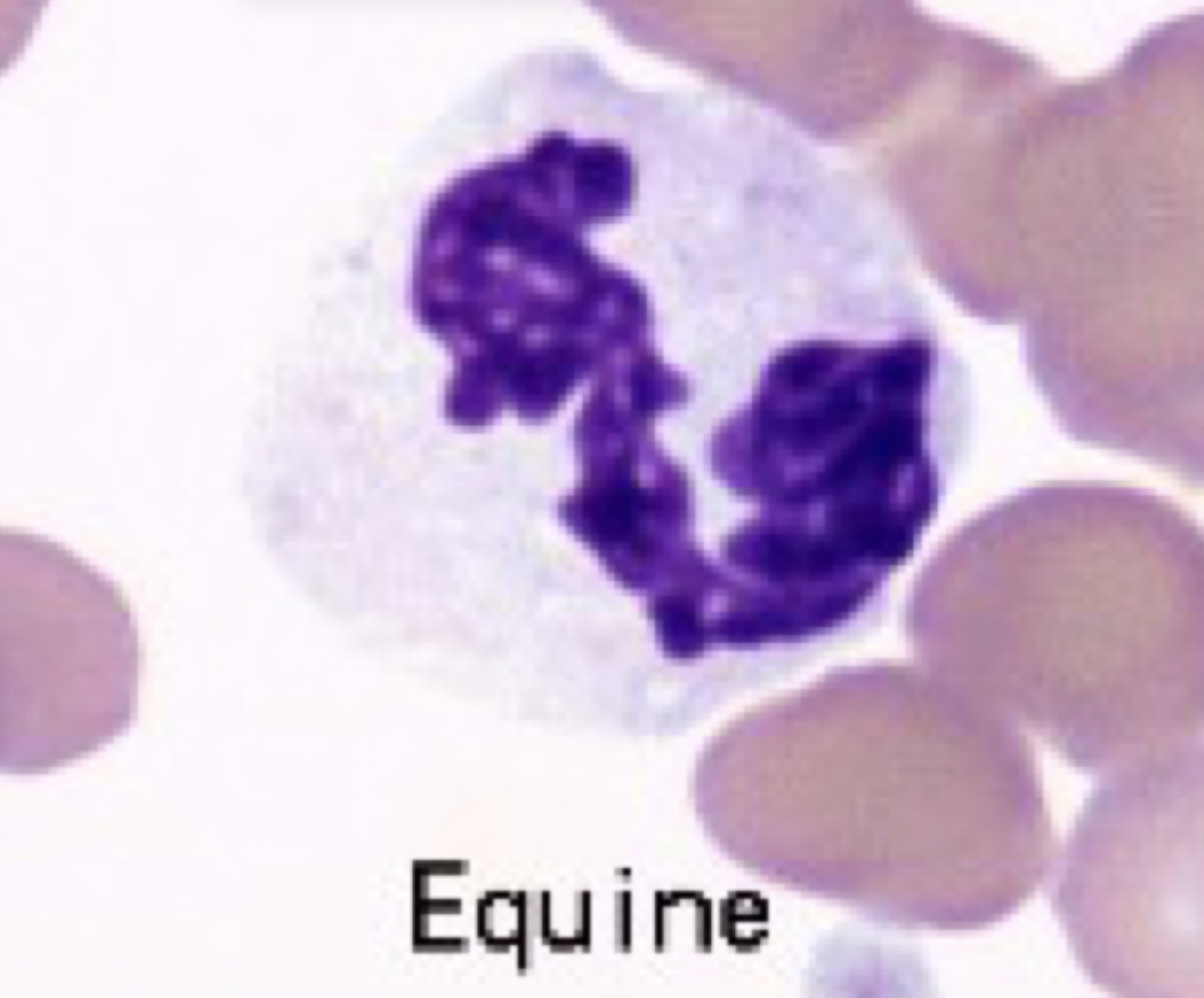
neutrophil
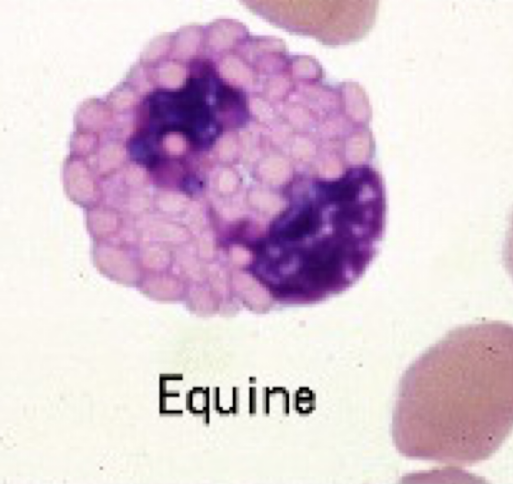
eosinophil
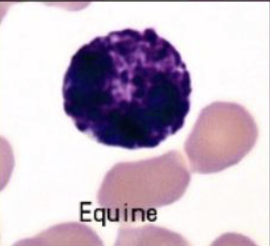
basophil
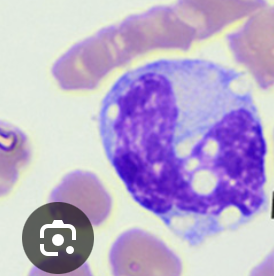
monocyte
lymphocyte
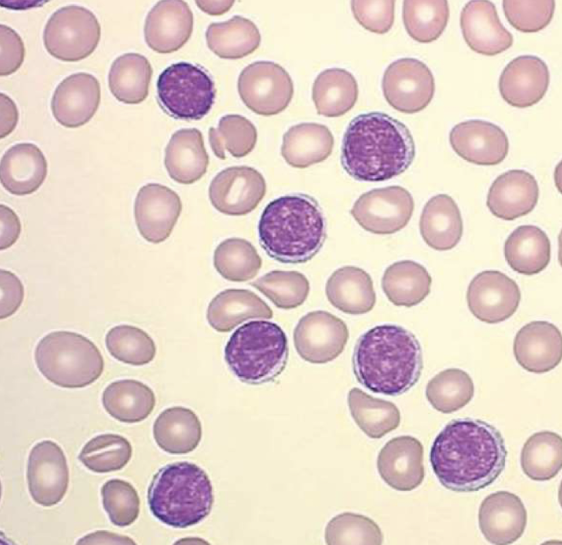
bovine lymphoma
masses found on:
right atrium
in uterus
in abomasum
in lymph nodes
on spinal cords/behind eye
bovine leukemia virus
often the cause of bovine lymphoma
often caused by unsanitary needle handling
reusing needles between cows and spreading the disease
necropsy presentation
presented on health index for low rumination and activity
sheet white mucus membranes
FAMACHA score 5
tachycardia (HR 108 bpm)
melina → black tarry stool
did not scootch on dorsal whither pinch
PCV of 13%
30%
normal bovine PCV
bovine heart rate
50-80 bpm
left lateral recumbency
the position we place deceased cow when performing necropsy
the rumen is not obstructing other internal organs
the right cranioventral lung field can be easily visualized
abomasum
true acid stomach
melina
black and tarry stool
often attributed to proximal GI bleed
dorsal aspect
where the marker is placed for a lateral medial view
lateral aspect
where the marker is placed for a dorsal palmar view
dorsal palmar view

dorsal palmar
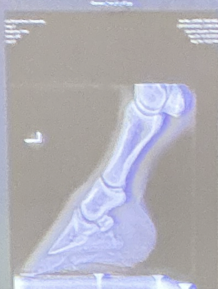
lateral medial view

lateral medial
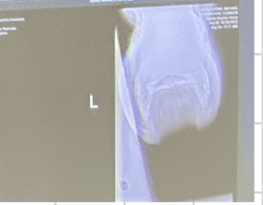
navicular skyline view

navicular skyline
flexion test
test helps to distinguish between upper from lower limb pain
non-specific
should not be used as a primary tool to localize lameness
diagnostic nerve block
main too used to localize the lameness to a specific anatomical region
perineurial local anesthetic blocks performed initially to determine general anatomical region of the discomfort
itrasynovial nerve blocks performed after to pinpoint area of pain
begin distally on limb then progress proximally with additional blocks in systematic manner
x-ray generator
the machine used to omit x-rays
kVPs
determines the energy with which the x-rays are produced and encounter the tissue
determines CONTRAST on radiograph
mAs
determines the number of electrons generated from the cathode
determines the DENSITY
x-ray plate
digital detector that records the x-ray images. placed behind the area being imaged to capture the radiation passing through horses body
exposure switch
the button you push to take an x-ray
collimator
direct and narrow or enlarge the beam
penicillin MOA
interfere with bacterial cell wall synthesis
part of a group called beta lactase
physical exam case
“momo is a 5-yr-old MN DSH cat presenting for routine BW, UA, and NT” premedicated with gabapentin
medial saphenous vein
cat blood draw
butorphanol
tranquilizer + analgesic
controlled substance (opioid)
controlled substance
requires strict logs:
patient name
client information
schedule
drug name
drug strength
bottle number
amount
explanation
detomidine
alpha 2 agonist
sedative, analgesic
type of tranquilizer
alpha 2 agonist
type of tranquilizer
stimulate ____ receptors in CNS leading to reduced sympathetic nervous system activity causing drop in heart rate and blood pressure