9 SCI Light and Energy Waves
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What do waves do?
Transfer energy.
What are transverse waves?
When each point on the wave vibrates perpendicularly to the direction of the travel wave.
What is the crest?
The highest point in the wave?
What is the trough?
The lowest point in the wave.
What is the resting position?
How it was before the wave.
What is a medium?
It is the material through
which a wave travels.
What is a wave pulse?
A single disturbance passed through a medium. Each particle carrying energy is only dispatched for a short time before returning to resting position.
Continuous waves are created when...
There is a repetitive motion or oscillation at a wave source. Energy is carried away from the source in continuous waves.
The vibration in longitudinal waves is...
Parallel to the direction of travel.
This is a diagram of a...
Longitudinal wave.
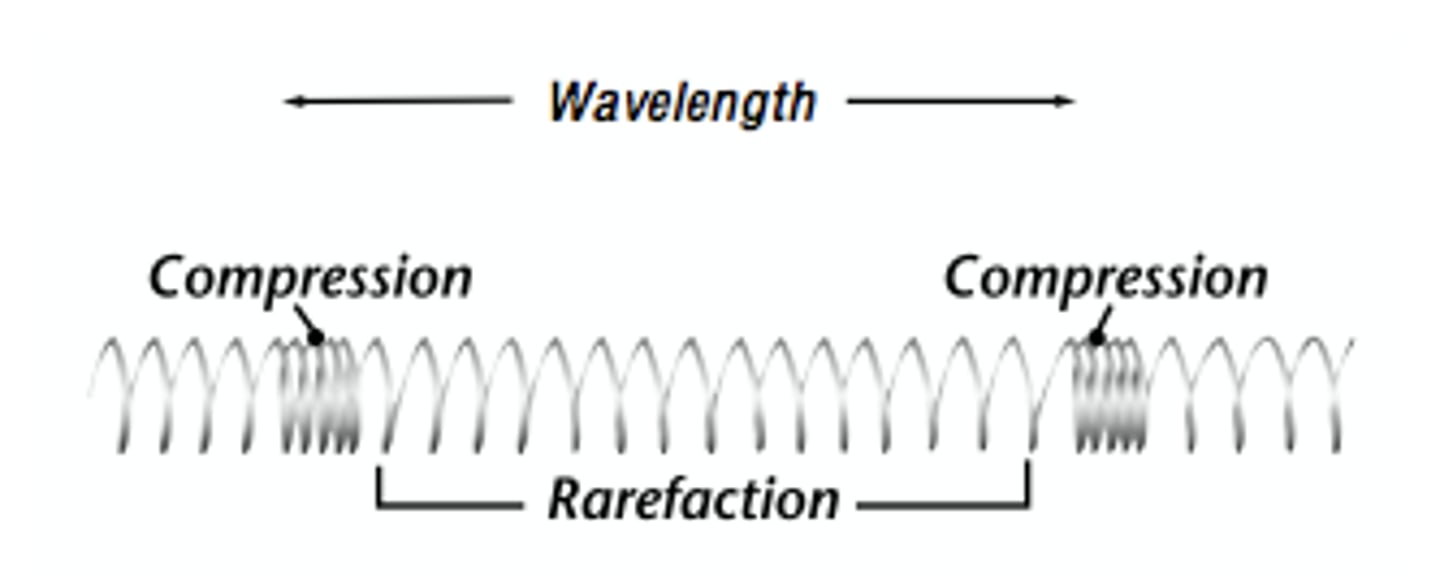
What is a wavelength?
The distance between two crests or two troughs. Measured in metres.
What is frequency (F)?
The number of waves generated by source per second or the amount passing a certain point per second.
What is frequency (F) measured in?
Cycles per second or in hertz. One hertz equals one cycle per second.
What is one hertz?
The measure of frequency. One hertz equals one cycle per second.
What is period (T)?
The time it takes for 1 complete cycle to pass a certain point. Measured in seconds.
Period (T) and Frequency (F) formula?
T=1/F. F=1/T.
What is amplitude (A)?
The maximum displacement of a point from it's resting position. Measured in metres.
When is the wave at its loudest or brightest?
At its largest amplitude. Large a means the sound is loud or bright. A small a means the sound is small and the light is dull.
How does sound travel?
A vibrating object compresses air, and sound waves move from the source, much like water when you drop a stone into it.
What can sound pass through?
Not only air, but also water and solids, such as brick, wood and glass.
What does sound need in order to travel?
A medium. It can't travel in space because density of particles is too low.
What is wave speed?
The distance travelled per second. It's measured in metres.
What is the speed formula?
Distance travelled divided by time taken.
The speed of sound is greater in...
Solids, then liquids, then gas. Particles are closer together and vibrate against each other faster.
Speed of light is greater in...
Vacuum, then gasses, then liquids, then solids. Doesn't vibrate against particles, it's slowed by them.
How fast does light travel?
3x10^8 metres per second.
How fast does sound travel?
340 metres per second.
What is the Doppler effect?
The change in frequency or wavelength of a wave when a wave is moving away from/towards an observer. Eg: Police car/fire truck.
What happens in the doppler effect?
The recieved frequency is different to the actual frequency. Higher F during approach, same F at instant of passing and lower F as it moves further away.
Higher F means...
Higher pitch.
Lower F means...
Lower pitch.
What is light energy?
A form of energy the eye can detect.
How does light travel?
An electromagnetic wave.
What does the wavelength of light determine?
It's colour.
Does light have to travel through a medium?
No.
What is one of the sources of light?
Vibrating atoms in hot objects.
What happens when a substance is heated?
Vibrating particles give off energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
How fast does electromagnetic radiation travel?
The speed of light, which is 300000 km/s.
What is the light you can see called?
Visible light.
What is infared?
The light below red, just outside visible light.
What is ultraviolet?
The light beyond violet, just outside the visible light.
What do infared rays do?
Cause body to feel warm.
What does ultraviolet radiation do?
Has a shorter wavelength, so it can damage skin.
What do shorter wavelength do?
The shorter the wavelength the easier it passes through.
What side of the EMR spectrum are microwaves on?
The longer wavelength.
What do microwaves do?
Use microwaves to vibrate and therefore heat water molecules in food.
What side of the EMR spectrum are radio-waves on?
Longer wavelength, to carry radio signals great distances.
What side of the EMR spectrum are X-rays on?
Shorter wavelength. They can penetrate flesh, but not bones or teeth.
What has the shortest wavelength out of all EMR?
Gamma rays. The shortest and most energetic.
What type of wave is an Electromagnetic wave?
Transverse wave.
What type of wave is a sound wave?
Longitudinal wave
What is propogation?
When lights are continuous waves that travel in straight lines.
What is reflection?
The light that has come from a source and been reflected off an object and into your eye.
How to we the the colour of coloured objects?
They reflect their colour.
What is diffuse?
When light reflecting from a screen is not smooth. You can see a piece of paper, but not other things reflected in the piece of paper.
What do smooth reflectors do?
Reflect light in an ordered manner so we can see images. This is called specular reflection. Eg: mirrors.
What is specular reflection?
When light is reflected off an object in an ordered manner so we see images.
Rough surfaces make ... reflection.
Diffuse. Eg: water images are blurry.
Smooth surfaces make ... reflection.
Specular. Eg: Mirror images are clear.
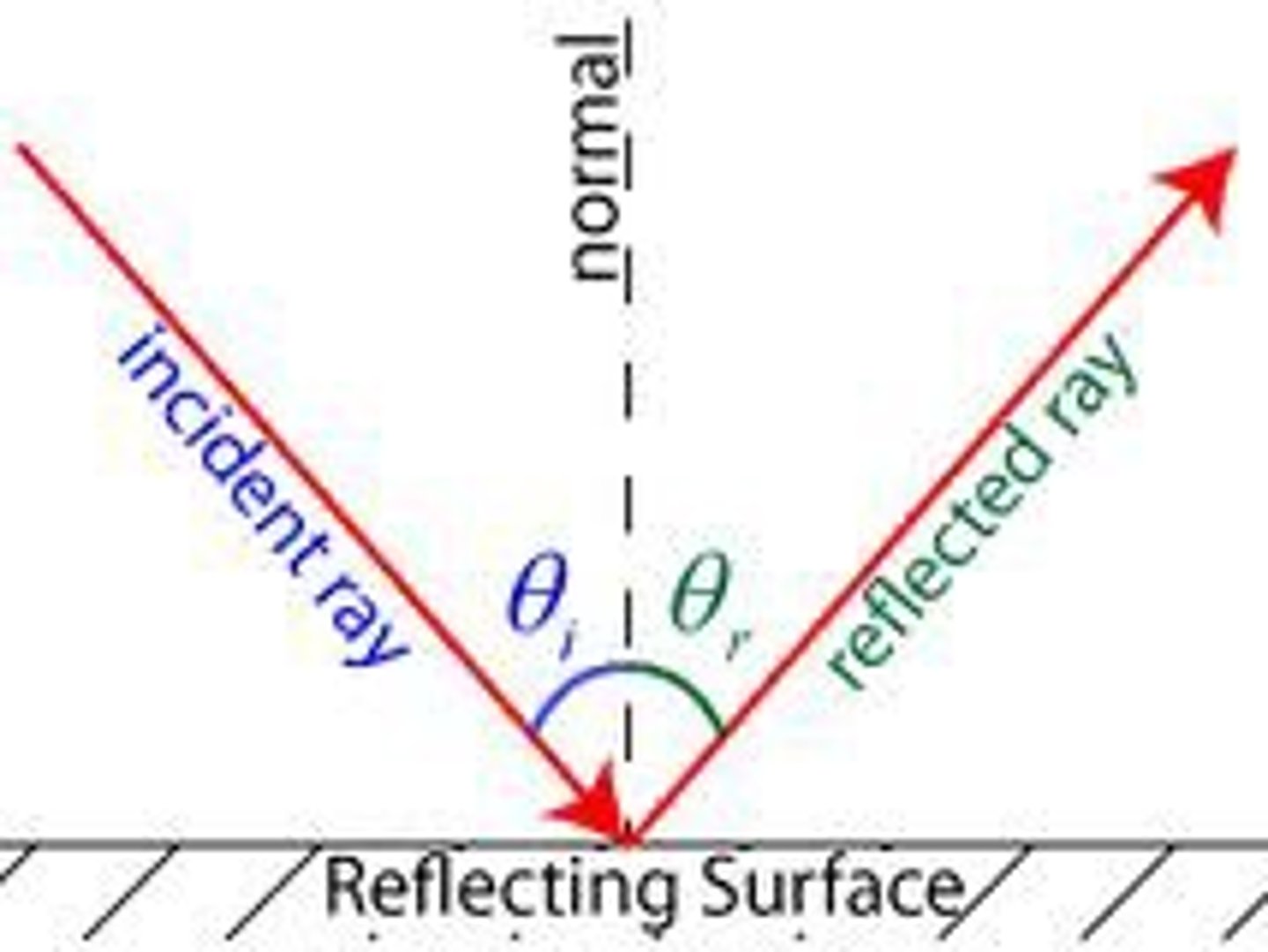
How to rays reflect off an equal angle?
When a straight ray of light is incident on a plain mirror, it is reflected off an equal angle. Angle of incidence (i) is equal to angle of reflection (r).
What is the law of reflection?
i (incident ray)=r (reflected ray)
At any boundary between 2 media, some incident waves are...
reflected and some are transmitted.
What does the proportion of light that is transmitted, reflected or absorbed depend on?
The relative characteristics of the medium.
What do transparent materials do?
Allow light to pass through.
What do opaque materials do?
They transmit no light. They are coloured because they reflect light.
What do translucent materials do?
Allow light to pass through, but it diffuses the beams.
What is refraction?
The bending of lights path as it passes from one transparent material to another.
Why does refraction occur?
Because light travels at different speeds in different speeds in different media.
What is the normal?
A straight path through the medium.
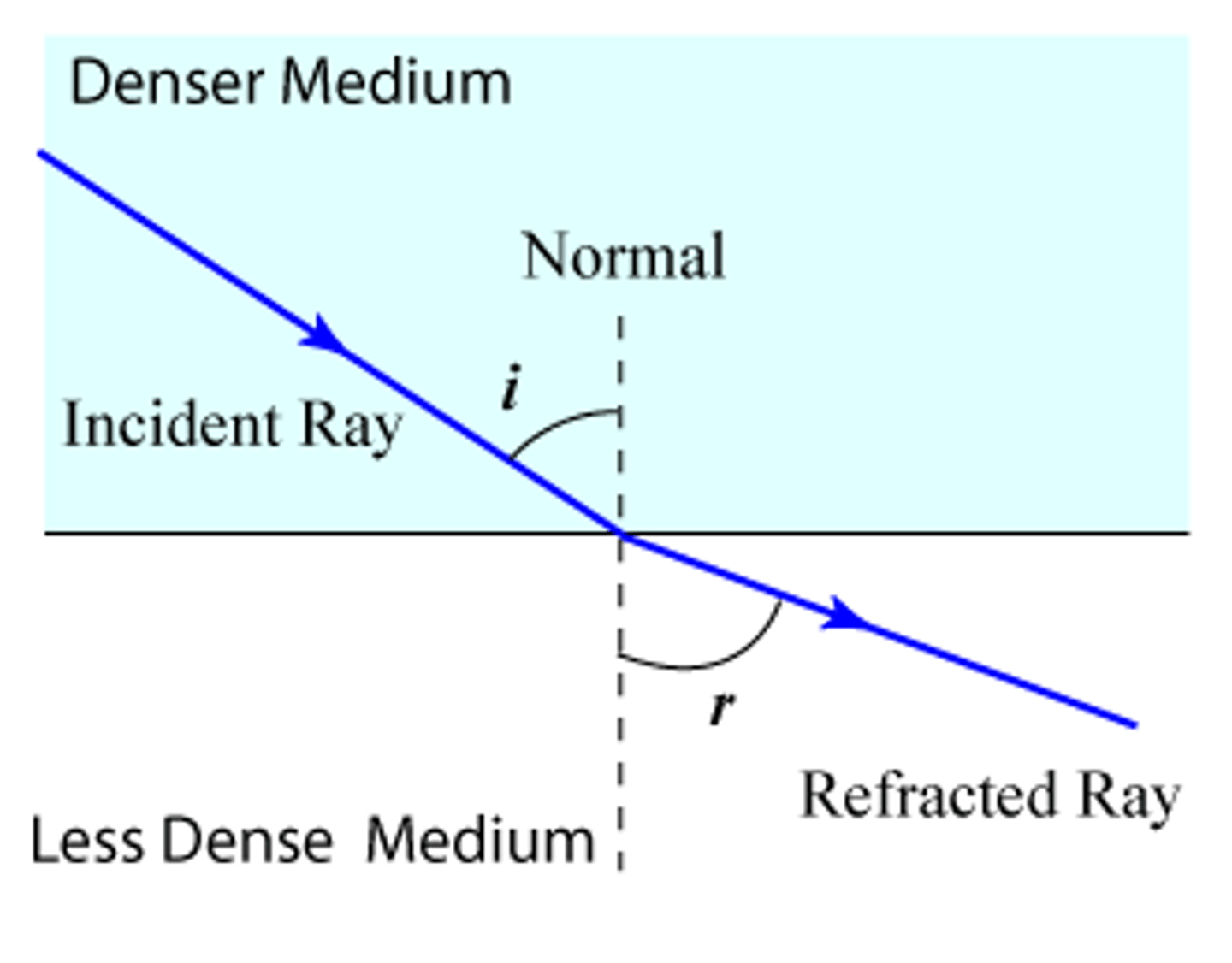
What does refraction do?
Changes the angle of which light travels. When light rays pass into a thicker medium (in which it travels slower) it is refracted towards the normal.
What happens when light rays pass into a thicker medium?
It travels slower and is refracted towards the normal.
What happens when light rays pass into a thinner medium?
It travels faster and is refracted away from the normal.
What is dispersion?
When white light is split up into the visible spectrum after passing through a prism.
Why does dispersion occur?
Because the different colours of light are refracted (due to change in speed) in different amounts by the prism.
What colour is refracted the most?
Violet.
What colour is refracted the least?
Red.
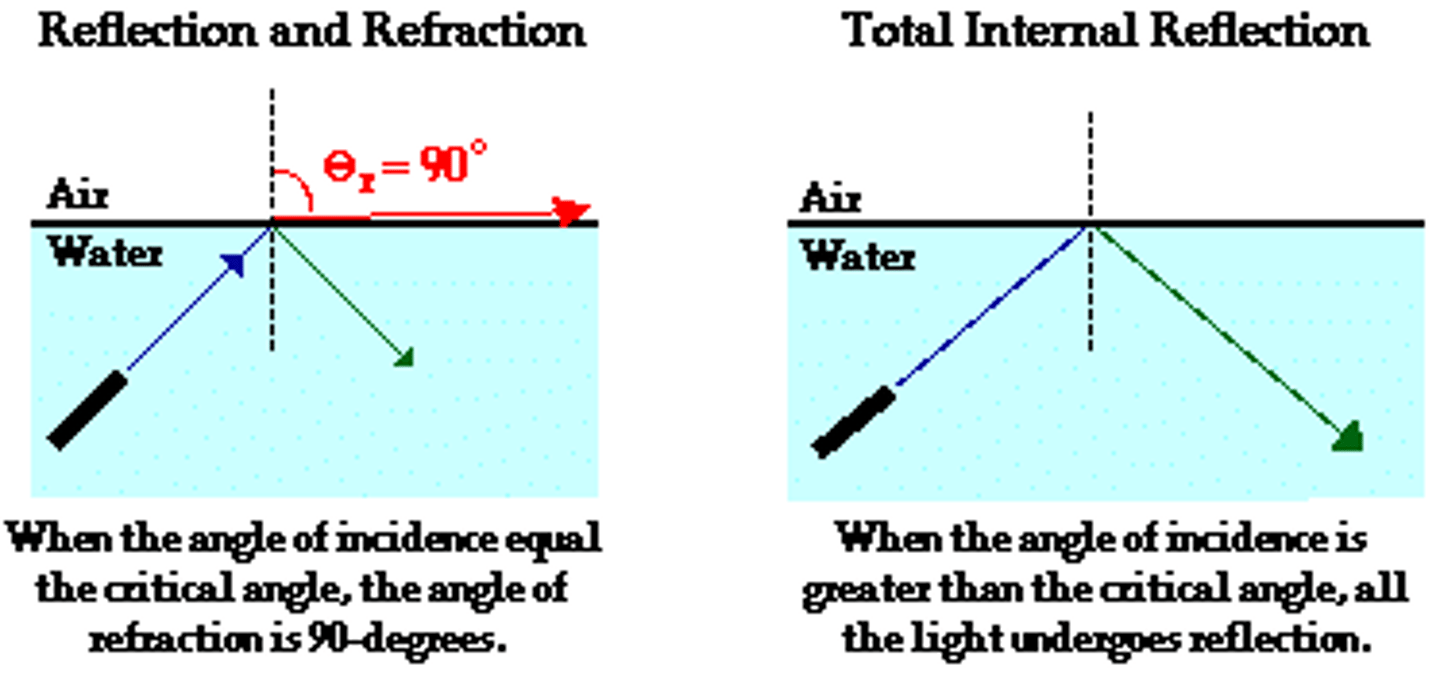
What is total internal reflection?
When refraction doesn't occur at every angle of incidence.
How does total internal reflection work?
When a ray of light travels from a medium of high refractive index (dense) to one of lower refractive index (less dense).
What does high refractive index mean?
Dense medium.
What does a low refractive index mean?
Less dense material.
What happens as the angle of incidence increases?
The angle of refraction also increases.
What is the critical angle of a medium?
The angle of incidence that won't give an angle of refraction. *varies depending on material and size.
What happens when the angle of incidence increases further than the critical angle?
There is no refraction at all, the incidence ray is totally internally reflected.
A diagram of normal refraction looks like...
Normal refraction.
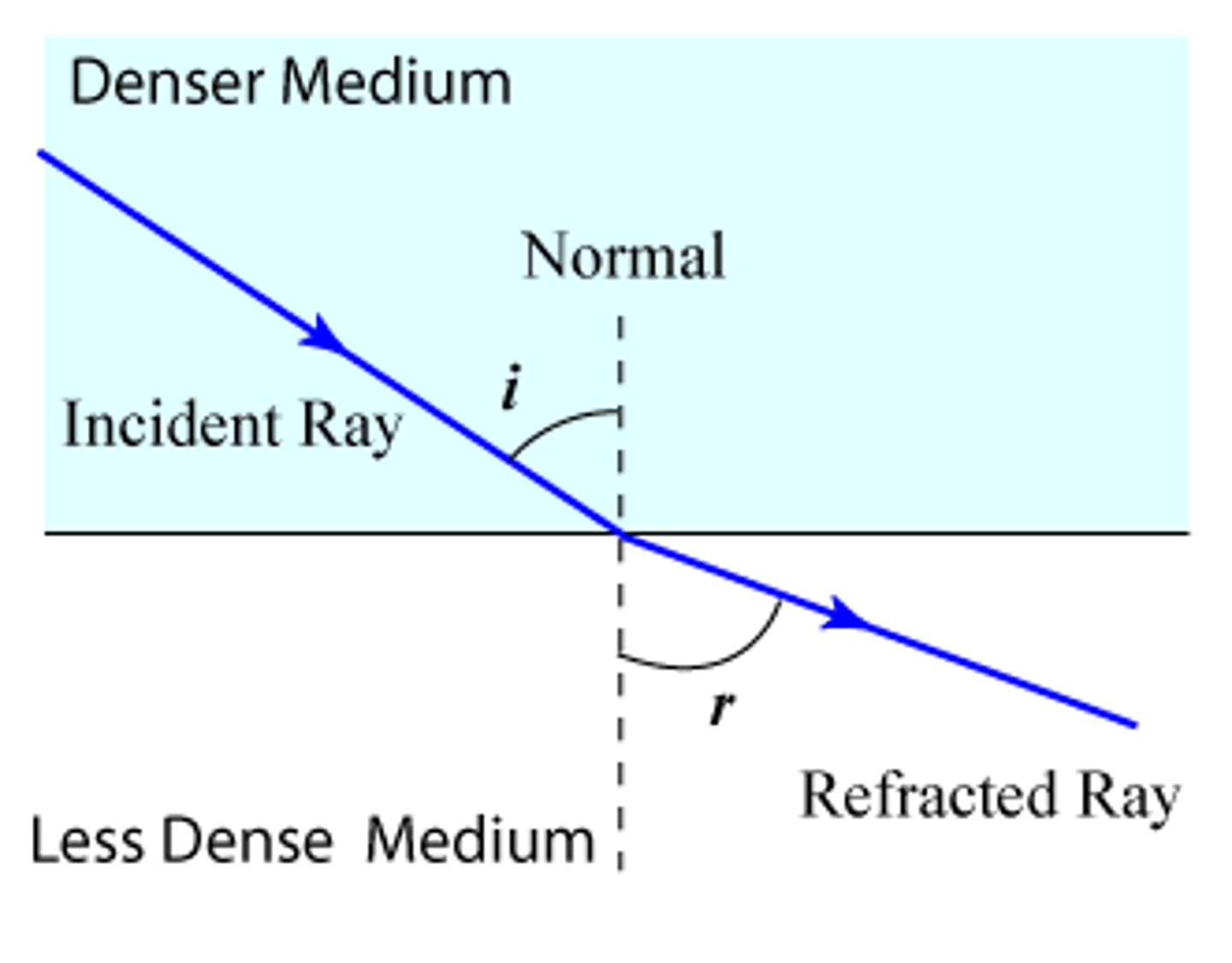
A diagram of critical angle refraction looks like...
Critical angle refraction.
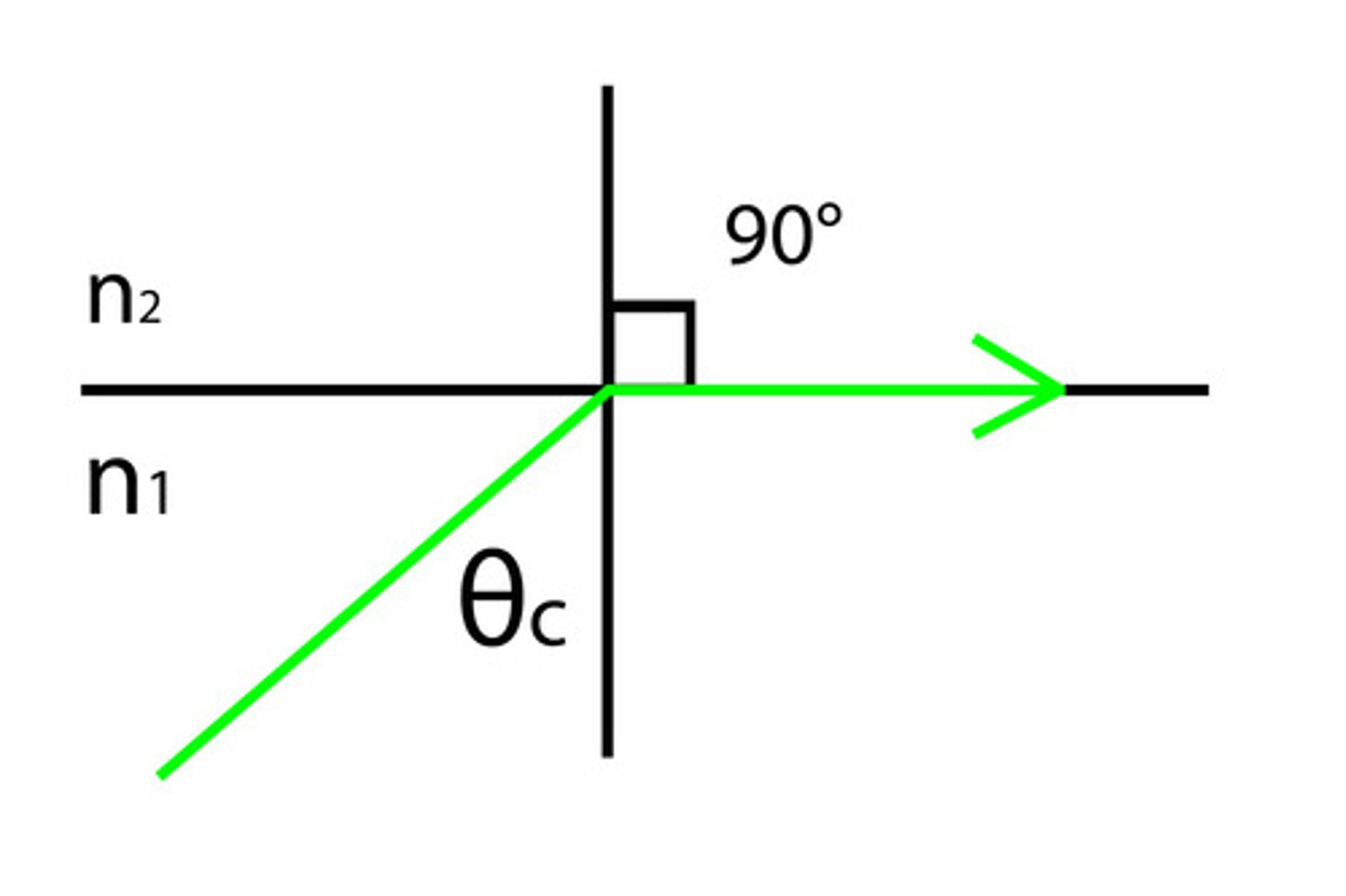
A diagram of total internal reflection looks like...
Total internal reflection.
What does the kinetic theory of matter state?
That matter is made up of very tiny particles or molecules which constantly move at different speeds because of the kinetic energy they possess.
What is temperature?
The measure of the average kinetic energy, measured with a thermometer.
What does more heat equal?
More kinetic energy.
Heat travels from...
hot object to cold object.
What does heat energy do when an object is hotter than its surroundings?
Flows from the object to its colder surroundings.
What does heat energy do when an object is colder than its surroundings?
It flows form the warmer surroundings to the colder object.
What is conduction?
The movement of heat through a material without carrying any of the material with it.
Give an example of conduction.
Heat from a gas stove travels to frying pan via conduction.
What happens as an object heats up?
Particles vibrate more.
How does conduction work?
Heat from source makes particles vibrate. Vibrating particles cause other particles to vibrate.
Why are metals good conductors of heat?
They contain free electrons that can move independently among the metal atoms and rapidly transfer the energy by collisions with metal atoms and other electrons.
Some poor conductors of heat are...
Wood, glass, cork, plastics and fabrics. Often, liquids and gasses are too.
What is convection?
Heat transfer in a fluid in which hot fluid rises and cold fluid sinks, setting up a
cycle
How does heat generally travel through liquids and gases?
By convection.