Science biology - Term 2
4.8(9)Studied by 293 people
Card Sorting
1/58
Last updated 11:48 AM on 11/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
What is photsynthesis
Light, carbon dioxide + water ------- glucose + oxygen + water = energy
Photosynthesis occurs in a plant’s (producers). Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that occurs when carbon dioxide + water + light energy turns into glucose + oxygen , to allow producers to capture the sun’s energy and produce their own food in the form of simple sugars.
2
New cards
Cellular Respiration
Glucose + oxygen ---→ carbon dioxide + water + energy
Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in both producer’s and consumers which uses the glucose and oxygen to release contained chemical potential energy producing energy for the functioning of the organism.
Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in both producer’s and consumers which uses the glucose and oxygen to release contained chemical potential energy producing energy for the functioning of the organism.
3
New cards
5 types of sensory receptors
1. thermoreceptors (temp)
2. Mechanoreceptors (touch/movement)
3. Chemoreceptors (sensitive chemicals)
4. Photoreceptors (light)
5. Nociceptors (pain)
4
New cards
Gland
An organ that produces and releases chemicals either through ducts or into the bloodstream such as hormones, digestive juices, sweat, tears, saliva, or milk
5
New cards
Body System
a body system is a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function.
6
New cards
Homeostasis
The process of maintaining a constant internal environment is known as homeostasis.
\
Optimal blood sugar level is 140mg/dl
Optimal body temperature = 36.5 -37 degrees Celsius.
Optimal ph level in the blood is 7.35 – 7.45.
\
Optimal blood sugar level is 140mg/dl
Optimal body temperature = 36.5 -37 degrees Celsius.
Optimal ph level in the blood is 7.35 – 7.45.
7
New cards
Nervous system
The nervous system controls everything you do, including breathing, walking, thinking, and feeling. This system is made up of your brain, spinal cord, and all the nerves of your body.
8
New cards
Endocrine system
The glands and organs that make hormones and release them directly into the blood so they can travel to tissues and organs all over the body
9
New cards
Reflex arc
the pathway by which a reflex travels it is a nerve pathway that does not involve the brain but to the spine ()—from the stimulus to sensory neuron to motor neuron to reflex muscle movement.
10
New cards
Voluntary action
when an action is produced with the involvement of thoughts, they are called voluntary action. It involves actions like walking, eating, jumping and running.
11
New cards
CNS (central nervous system)
the central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord: the brain controls how we think, learn, move, and feel. The spinal cord carries messages back and forth between the brain and the nerves that run throughout the body.
12
New cards
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
feeds information into your brain from most of your senses. It carries signals that allow you to move your muscles.
13
New cards
Neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body can't function without. Their job is to carry chemical signals (“messages”) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell.
14
New cards
Hormones
one of many substances made by glands in the body. Hormones circulate in the bloodstream and control the actions of certain cells or organs
15
New cards
Motor neuron
Carry messages from CNS to effectors like muscle glands to put message into effect.
16
New cards
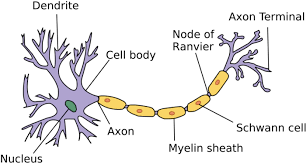
Label this neuron and which way the signal flows
click on picture to make bigger
17
New cards
Sensory neuron
carry messages to the brain and spinal cord (CNS) from your sense organs (receptors).
eyes, ears, nose, skin
eyes, ears, nose, skin
18
New cards
Hypothalamus
the area of the brain that controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep as it connects the endocrine system and nervous system to the brain
Nerve cells in the hypothalamus make chemicals that control the release of hormones secreted from the pituitary gland
Nerve cells in the hypothalamus make chemicals that control the release of hormones secreted from the pituitary gland
19
New cards
Pituitary Gland
a pea-sized organ attached to the part of the brain called the hypothalamus, which deals with hormonal body processes. This major endocrine gland is attached to the base of the brain and releases nine different hormones. Controls growth and development and the functioning of other endocrine glands.
20
New cards
Thyroid gland
a gland located beneath the larynx (voice box) that makes thyroid hormone and calcitonin. The thyroid gland helps regulate growth and metabolism.
21
New cards
ANS ( autonomic nervous system)
22
New cards
Parathyroid
one of four pea-sized glands found on the surface of the thyroid. The parathyroid hormone made by these glands increases the calcium level in the blood
23
New cards
Adrenal gland
a small gland that makes steroid hormones, adrenaline, and noradrenaline. These hormones help control heart rate, blood pressure, and other important body functions. On kidneys
24
New cards
Ovaries
one of a pair of female glands in which the eggs form and the female hormones estrogen and progesterone are made
25
New cards
Cerebellum
the portion of the brain in the back of the head between the cerebrum and the brain stem. The cerebellum controls balance for walking and standing, and other complex motor functions.
26
New cards
Cerebrum
located in the frontal lobe and consists of two hemispheres, left and right, separated by fissures. It is responsible for the integration of complex sensory and neural functions and the initiation and coordination of voluntary activity in the body.
27
New cards
Brain stem
the bottom, stalk-like portion of your brain. It connects your brain to your spinal cord. Your brainstem sends messages to the rest of your body to regulate balance, breathing, heart rate and more.
28
New cards
Spinal cord:
a column of nerve tissue that runs from the base of the skull down the center of the back. It connects nearly all parts of the body to the brain, with which it forms the central nervous system.
29
New cards
Negative feedback loop
Negative feedback - feedback that tends to stabilize a process by reducing its rate or output when its effects are too great. The body acts to counteract disturbances in the body and restore balance.
30
New cards
Insulin
a hormone made by the islet cells of the pancreas. Insulin controls the amount of sugar in the blood by moving it into the cells, where it can be used by the body for energy.
31
New cards
Glucagon
a hormone produced by the pancreas that increases the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
32
New cards
Synapse
the space between the end of a nerve cell and another cell.
33
New cards
Dendrites
the structures on neurons that allow the cell to receive signals from other neurons.
34
New cards
Myelin sheath
An insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord, it allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells.
35
New cards
Axon
the appendage (long skinny part) of the neuron that transmits impulses away from the cell body.
36
New cards
Cell-body
the spherical part (head) of a neuron that contains the nucleus.
37
New cards
Terminal branches
branches at the end of the axon that releases neurotransmitters that relay signals across the synapse.
38
New cards
Population
a group of organisms of the same species within a community.
39
New cards
Community
a group of different populations that are commonly found together
40
New cards
Ecosystem
A community with abiotic and biotic surroundings
41
New cards
Abiotic
non-living physical and chemical elements in an ecosystem
(eg. Light intensity, CO2 concentration, wind, temp., moisture, PH level of soil)
(eg. Light intensity, CO2 concentration, wind, temp., moisture, PH level of soil)
42
New cards
Biotic
living or once living organisms in an ecosystem (eg. animal, plants, bacteria fungi)
43
New cards
Food chain
a food chain describes how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem through a linear network of links/arrows.
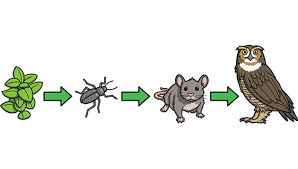
44
New cards
Food web
a food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem. (arrows up)
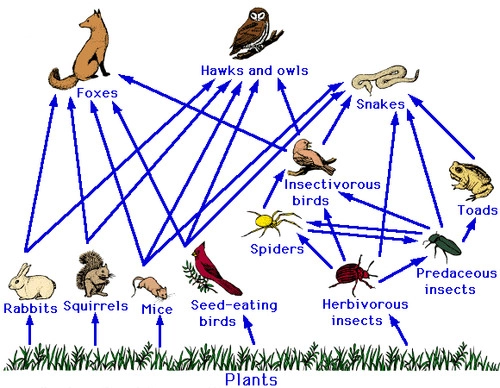
45
New cards
Trophic level/Consumer order
the position of an organism in the food chain
(1,2,3,4)
1. Producer, Primary producer
2. Primary Consumer,
3. Secondary consumer
4. tertiary consumer
5. apex predator
46
New cards
Predation (predator/prey)
Biological relationship where one species (predator) feeds on another (prey).
A predator is the organism that hunts. and the prey is what is being hunted
A predator is the organism that hunts. and the prey is what is being hunted
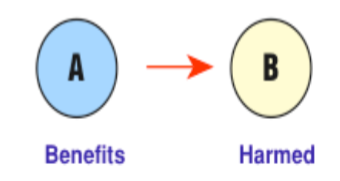
47
New cards
Transmission of message in nervous system
receptor → sensory neuron → interneuron → motor neuron → effector
48
New cards
Competition
the interaction (fight) between organisms for limited resources
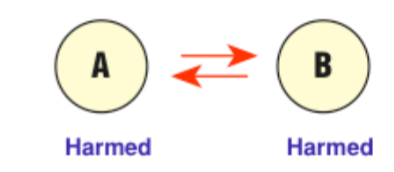
49
New cards
what are heterotrophs and autotrophs
Are organisms which create their own food through photosynthesis - autotrophs
living things that hunt and gather to eat their food; cannot use solar energy to produce their own food – heterotrophs.
living things that hunt and gather to eat their food; cannot use solar energy to produce their own food – heterotrophs.
50
New cards
what is a Carnivore, Herbivore, Omnivore
Carnivore: an organism that mostly eats the meat of other organisms.
Herbivore: an organism that mostly eats plants.
Omnivore: an organism that eats both meat and plants.
51
New cards
Decomposer
an organism that breaks down organic matter.
52
New cards
Mutualism (symbiosis)
A close interaction between two species where both species benefit in some ways.
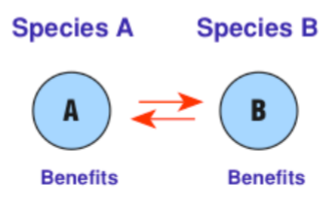
53
New cards
Commensalism (symbiosis)
An interaction between two species where one benefits from the relationship while the other neither benefits nor is harmed.
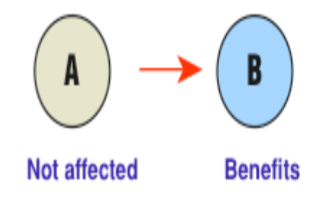
54
New cards
Parasitism (symbiosis)
A close relationship between two species where one exploits the resources of a host. The host is negatively affected yet usually does not die.
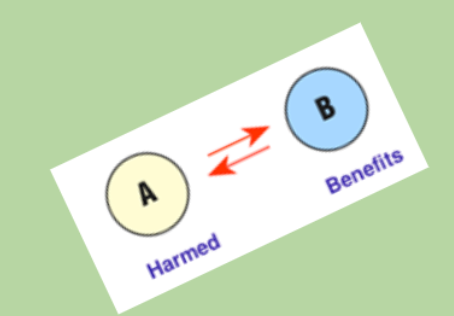
55
New cards
Symbiosis
Two species living in close proximity
56
New cards
Types of ecological pyramids
Energy pyramid: a graphical representation of the energy found and lost within the trophic levels of an ecosystem.
Numbers pyramid: shows the number of organisms at each trophic level.
Biomass pyramid: represents the total living biomass or organic matter in each trophic level of an ecosystem.
57
New cards
Energy transfer
the changes in energy that occur between organisms within an food web
58
New cards
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a genetic, autoimmune condition where the pancreas progressively reduces the production of insulin – a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels – in the body until it stops the production all together. If the amount of glucose in the blood exceeds stable levels, it can be severely damaging to our organs.
59
New cards
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin to function properly, or when the body cells do not react to insulin. Thus, sugar stays in the blood and isn't used as fuel for energy. It is often associated with obesity and is more commonly diagnosed in older people.