ch 18 heart
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
systemic circulation
left side of heart → body → right side of heart (oxygenated blood to tissues)
pulmonary circulation
right side of heart → lungs → left side of heart (deoxygenated blood to lungs)
Heart Chambers, Valves, and Blood Flow Order -
Blood Flow Through the Heart:
Superior/Inferior vena cava →
Right atrium →
Tricuspid valve →
Right ventricle →
Pulmonary semilunar valve →
Pulmonary trunk/arteries →
Lungs (gas exchange) →
Pulmonary veins →
Left atrium →
Bicuspid (mitral) valve →
Left ventricle →
Aortic semilunar valve →
Aorta → body
3 layers of the heart wall
epicardium
myocardium
endocardium
epicardium
visceral layer of serous pericardium
epi- upon
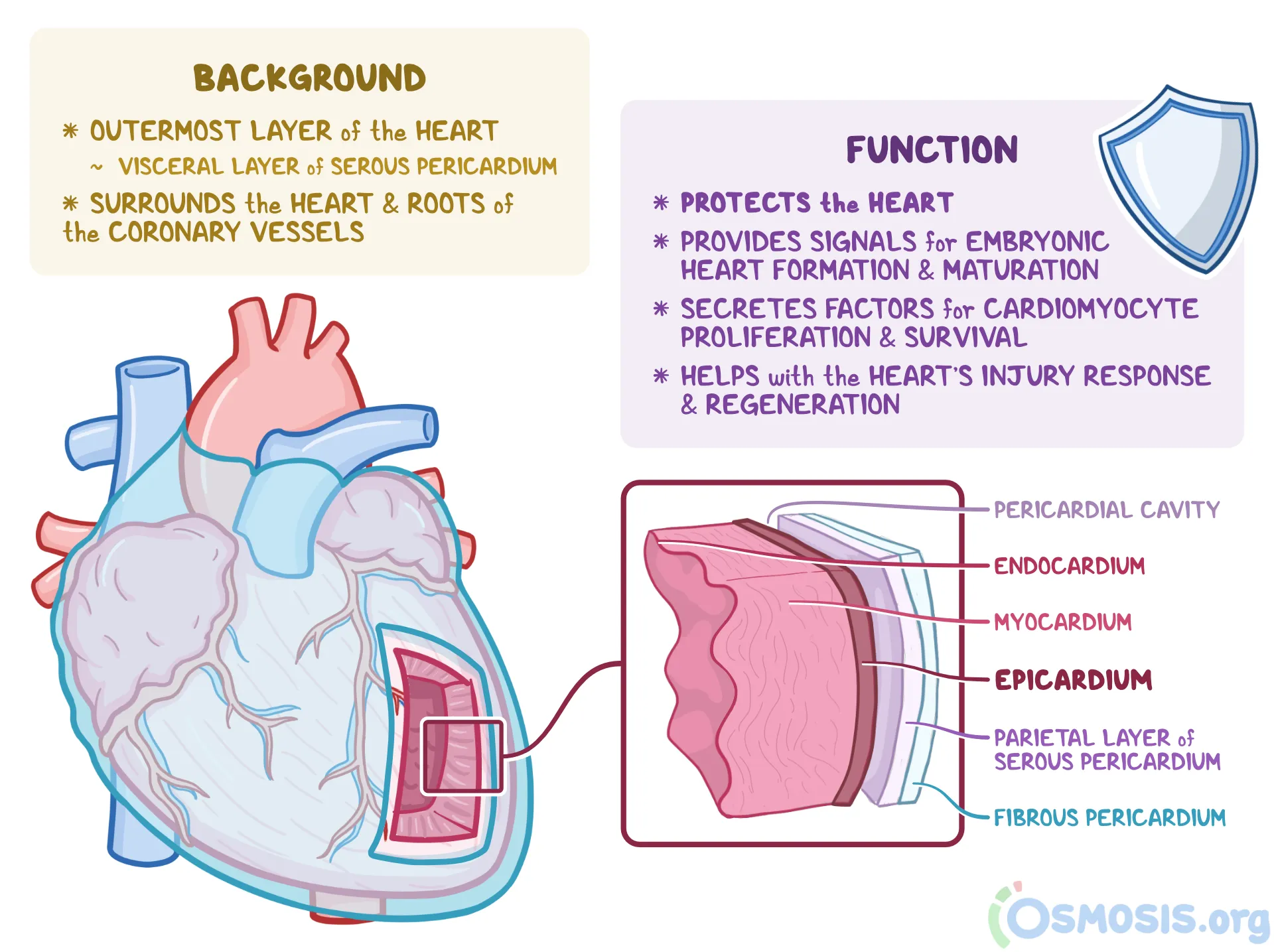
myocardium
muscular, middle layer (contracts)
myo- muscle
endocardium
inner layer (lines chambers)
endo-inner
angina pectoris
a type of chest pain (thoracic pain) caused by a temporary (fleeting) lack of blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium).
causes cells to be weakened
myocardial infarction
aka heart attack
caused by prolonged blockage of blood flow in a coronary artery.
causes of myocardial infarction
Most commonly due to:
Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries)
Blood clot (thrombus) that forms at the site of the plaque rupture
early signs of heart attack
pressure in center of chest
pain in shoulders, neck or arms
chest discomfort with fainting, sweating or nausea
intercalated discs
junctions between cells
anchor cardiac cells
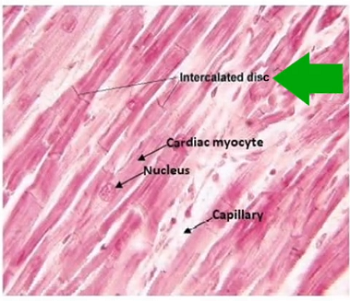
desmosomes
prevents cells from separating during contraction
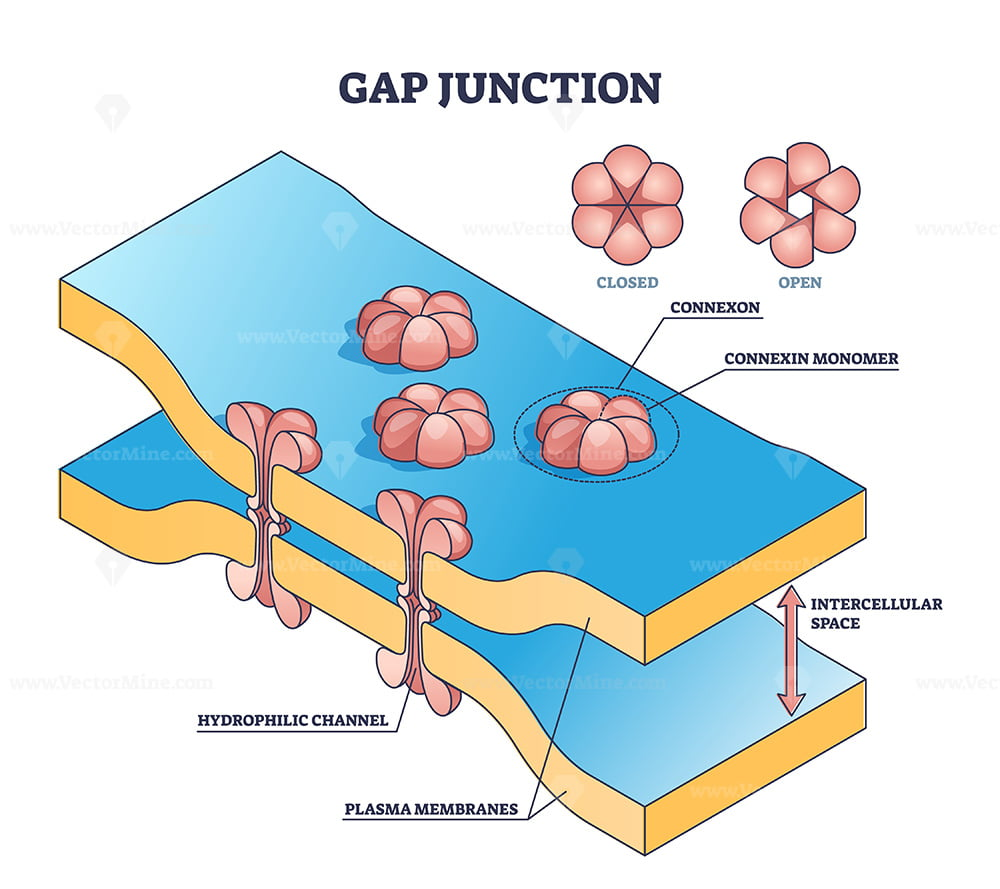
gap junction
allows ions to pass from cell to cell; electrically couple adjacent cells
-allows heart to be functional syncticum (behaved as single coordinated unit)
contractile cardiac cells
working muscle cells that are responsible for pumping blood
ex) ventricular muscle cells
rapid depolarization
Na+ in
Na+ influx thru fast voltage gated Na+ channels
rapid upstroke (membrane potential becomes positive)
positive feedback opens more Na+ channels
ends w/ na+ channels are inactive
plateau phase
Ca²⁺ in
Ca²⁺ influx thru slow voltage gated Ca²⁺ channels
only a few K+ channels open so flow is limited
maintains depolarization allows for sustained contraction
repolarization
K+ out
Ca²⁺ channels close & K+ channels open fully
K⁺ flows out and restores membrane potential to resting state
cell becomes negative inside again
pacemaker cells
cells set the rhythm of the heartbeat
-are self excitable (generate own electrical signals
found in SA node
pacemaker potential (slow depolarization)
caused by Na+ influx thru slow “funny” channels
followed by some Ca²+ entry
slowly drifts towards threshold w/o resting potential
pace maker:depolarization
at threshold fast CA²+ influx thru voltage gated Ca²+ channels
not Na+ like contractile cells
pace maker: repolarization
Ca²+ channels close
K+ channels open
K+ efflux restores negative resting potential
ap nerve cell depolarization
Na⁺ influx via fast voltage-gated Na⁺ channels
ap nerve cell repolarization
K⁺ efflux via voltage-gated K⁺ channels
ap nerve cells: no plateau phase
Much faster than cardiac action potentials
Resting potential restored quickly
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight