unit 5 biology test
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/114
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
who was gregor mendel?
the “father of genetics”
2
New cards
define: chromatin
dna in thin strands
3
New cards
define: chromosome
chromatin coiled around protein forming an X shape
4
New cards
what does a chromosome consist of?
two sister chromatids joined by a centromere
5
New cards
define: gene
a DNA segment that codes for a trait
6
New cards
define: character
an inheritable physical feature
7
New cards
define: trait
a variation of a character
8
New cards
define: allele
a different version of a gene
9
New cards
define: dominant allele
the stronger gene that physically shows on an organism
10
New cards
define: recessive allele
the weaker gene that does not physically show on an organism
11
New cards
define: homozygous
the organism either has two dominant alleles or two recessive alleles
12
New cards
define: heterozygous
the organism has one dominant and one recessive allele
13
New cards
define: phenotype
the physical trait that can be seen
14
New cards
define: genotype
the genetic combination for a trait
15
New cards
define: punnett square
a chart showing possible genetic outcomes for a child
16
New cards
where does the mothers genotype go on a punnett square?
the left side
17
New cards
where does the fathers genotype go on a punnett square?
the top
18
New cards
define: mendels law of segregation
to separate the two alleles of one parent
19
New cards
define: law of independent assortment
chromosomes line up independently from each other so that genes from different chromosomes do not affect each other
20
New cards
when does the law of segregation occur?
during anaphase 1 and 2 of meiosis
21
New cards
when does the law of independent assortment occur?
during metaphase 1 and anaphase 1 of meiosis
22
New cards
define: complete dominance
the dominant allele is only expressed all the way
23
New cards
define: incomplete dominance
both alleles are expressed and blended together
24
New cards
define: codominance
both alleles are expressed and are equally present but separate
25
New cards
define: multiple alleles
when there are multiple versions of the same allele
26
New cards
define: pedigree
a chart showing the family history of a specific trait
27
New cards
what shape are males in pedigrees?
squares
28
New cards
what shape are females in pedigrees?
circles
29
New cards
what does it mean when a shape on a pedigree is shaded in?
that person has the trait
30
New cards
what does a horizontal line between two people mean on a pedigree?
a breeding couple
31
New cards
what does a vertical line between two people mean on a pedigree?
offspring
32
New cards
name a recessive disorder
cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell disease
33
New cards
name a dominant disorder:
dwarfism, huntingtons disease
34
New cards
define: locus
the location of a gene on a chromosome
35
New cards
define: genome
organisms complete dna sequence
36
New cards
define: asexual reproduction
one parent making a clone of itself
37
New cards
name benefits of asexual reproduction
quick reproduction, only one parent needed
38
New cards
name disadvantages of asexual reproduction
no genetic variation, massive death rate
39
New cards
define: sexual reproduction
two parents combining dna resulting in different offspring
40
New cards
name benefits of sexual reproduction
variation in offspring, evolution over time
41
New cards
name disadvantages of sexual reproduction
takes two parents, takes longer
42
New cards
define: somatic cells
regular body cells
43
New cards
how do somatic cells reproduce?
mitosis
44
New cards
define: germ cells
sex cells
45
New cards
how do germ cells reproduce?
meiosis
46
New cards
define: trisomy
too many chromosomes
47
New cards
define: monosomy
too few chromosomes
48
New cards
why are microinsertions and microdeletions hard to see on a microscope?
they’re too small
49
New cards
define: homologous
identical chromosomes
50
New cards
define: heterogous
chromosome pair that is different
51
New cards
does mitosis make haploid or diploid cells?
diploid
52
New cards
does meiosis make haploid or diploid cells?
haploid
53
New cards
define: haploid
having only one set of chromosomes
54
New cards
define: diploid
having two sets of chromosomes
55
New cards
what happens in meiosis 1?
the 46 chromosomes are separated
56
New cards
what phases are in meiosis 1?
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
57
New cards
what happens in meiosis 2?
the sister chromatids are separated into four daughter cells
58
New cards
what phases are in meiosis 2?
prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2, cytokenisis
59
New cards
define: crossover
the male and female chromosomes swapping genes
60
New cards
when does the crossover occur?
prophase 1
61
New cards
what is the purpose of crossover?
genetic variation
62
New cards
how has genetic variation evolved?
prophase 1-crossover, metaphase 1-independent assortment, anaphase 1-law of segragation
63
New cards
define: sex linked gene
genes only passed down through x sex chromosome
64
New cards
is colorblindness dominant or recessive?
recessive
65
New cards
what kind of disorder is colorblindness?
sex linked
66
New cards
is hemophilia recessive or dominant?
recessive
67
New cards
define: karyotype
a picture of all a persons chromosomes
68
New cards
when is karyotype taken?
metaphase
69
New cards
how many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
23
70
New cards
what is the first step to creating a karyotype?
collect cells and place in petri dish, add cyclin and make cells go into mitosis
71
New cards
what is the second step to creating a karyotype?
allow cells to continue dividing until metaphase, then add chemical to stop mitosis
72
New cards
what is the third step to creating a karyotype?
add dye to chromosomes to stain genes and create banding pattern
73
New cards
what is the fourth step to creating a karyotype?
take picture of chromosomes through microscope
74
New cards
what is the fifth step to creating a karyotype?
cut out chromosomes and arrange them largest to smallest
75
New cards
what is the first step in interpreting a karyotype?
length of chromosomes
76
New cards
what is the second step in interpreting a karyotype?
centromere position
77
New cards
what is the third step in interpreting a karyotype?
banding pattern
78
New cards
what is the fourth step in interpreting a karyotype?
locus of gene
79
New cards
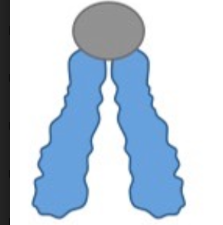
define:
telocentric
80
New cards
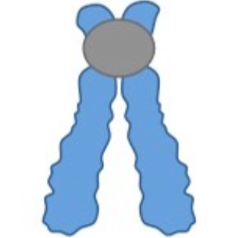
define:
acrocentric
81
New cards
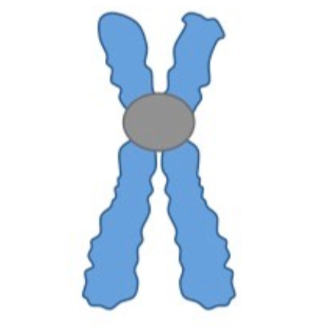
define:
submetacentric
82
New cards
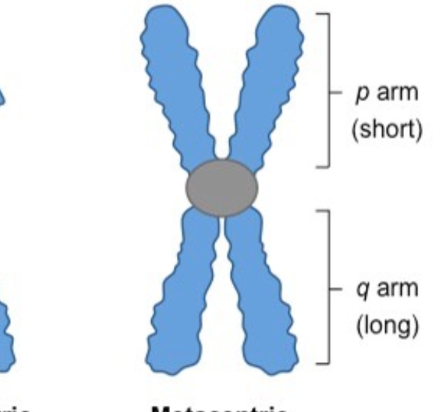
define:
metacentric
83
New cards
define: top and short arm of a chromosome
p arm
84
New cards
define: bottom and long arm of a chromosome
q arm
85
New cards
define: aneuploidy
having the wrong number of chromosomes
86
New cards
define: polyploidy
having many extra sets of chromosomes
87
New cards
define: 3N
three sets of each chromosome
88
New cards
define: 4N
four sets of each chromosome
89
New cards
define: part of a chromosome segment is missing
deletion
90
New cards
define: a chromosome segment was copied twice. two genes on the same chromosome and one missing on the other
duplication
91
New cards
define: a chromosome segment is backwards
inversion
92
New cards
define: a chromosome segment is attached to a different autosome; not where it should be
translocation
93
New cards
what is the first stage of mitosis?
interphase
94
New cards
what is the second stage of mitosis?
prophase
95
New cards
what is the third stage of mitosis?
metaphase
96
New cards
what is the fourth stage of mitosis?
anaphase
97
New cards
what is the fifth stage of mitosis?
telophase
98
New cards
what is the sixth stage of mitosis?
cytokenesis
99
New cards
what are the three sub-stages of interphase?
G1, S, G2
100
New cards
what happens in interphase?
growth, copy DNA, self check