AD 226 Exam 1
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Lascaux Cave Paintings, Hall of Bulls 20,000 BCE
-Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) painting
-images of animals, objects of hunt and survival, ritualistic purposes
-superstitious or magical purpose, depicting them was a way of trapping their spirit for successful hunting
-symbols of reality and human experience, way of communication
-recorded images from memory

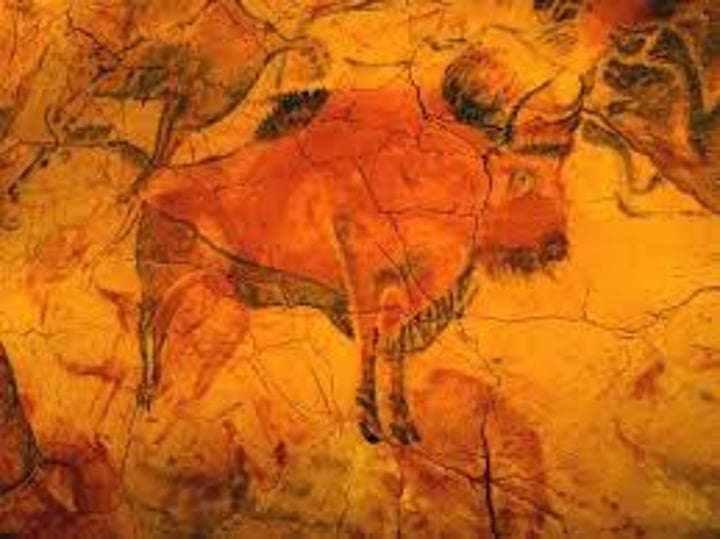
Altamira Cave Paintings, 15,000 BCE
-Paleolithic painting
-represent bison and buffalo
-depicted in disorderly fashion

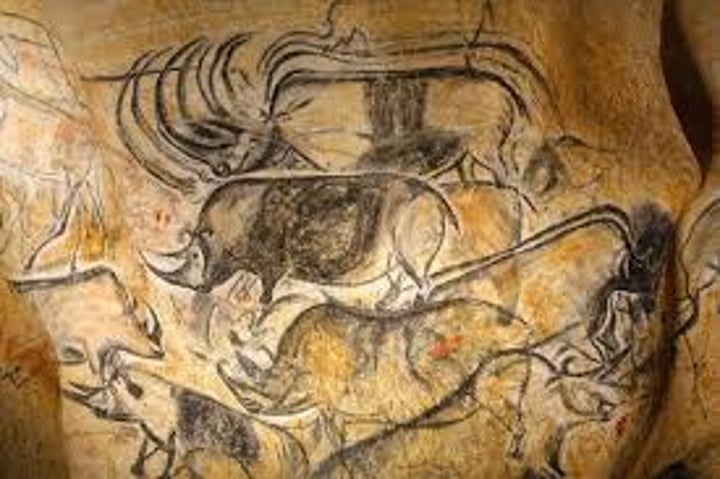
Chauvet Cave Paintings
-Paleolithic
-uses white
-shading, sense of 3d form

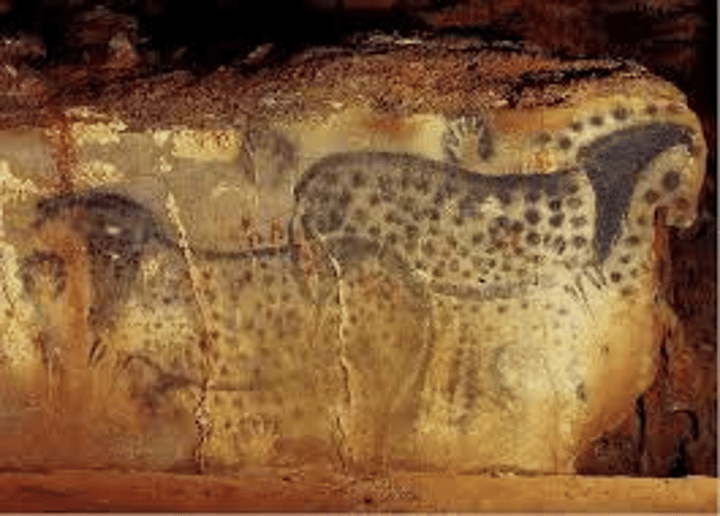
Pech-Merle Cave Paintings
-Paleolithic
-sympathetic magick, way of casting a spell
-handprints

Venus of Willendorf, 20,000 BCE
-Paleolithic
-made of limestone, carved using primitive stone tools,
-represents human sexual prowess, enlarged features
-fertility figure

-shift in human development
-new stone age (neolithic period)
-people are emerging from caves
-beginning of pottery, making of finer tools, clay, textiles
8500 BCE
Fresco Ruins from Catal Huyuk
-neolithic
-human figure in more life-like fashion

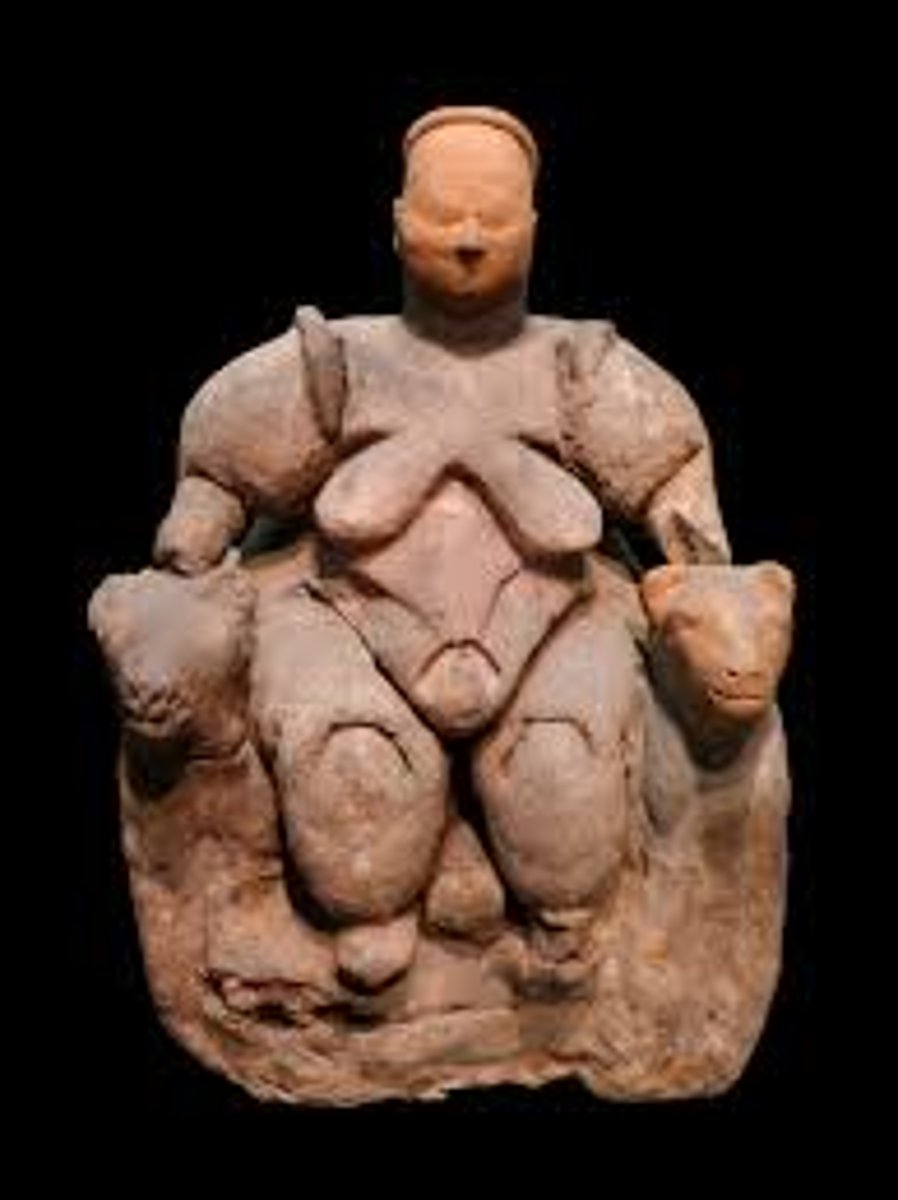
Figure from Catal Hoyuk, 6000 BCE
-neolithic
-nude, fertility associations, appears to be giving birth
-narrative of giving birth and the relationship between mother and child
-authority, sitting on throne

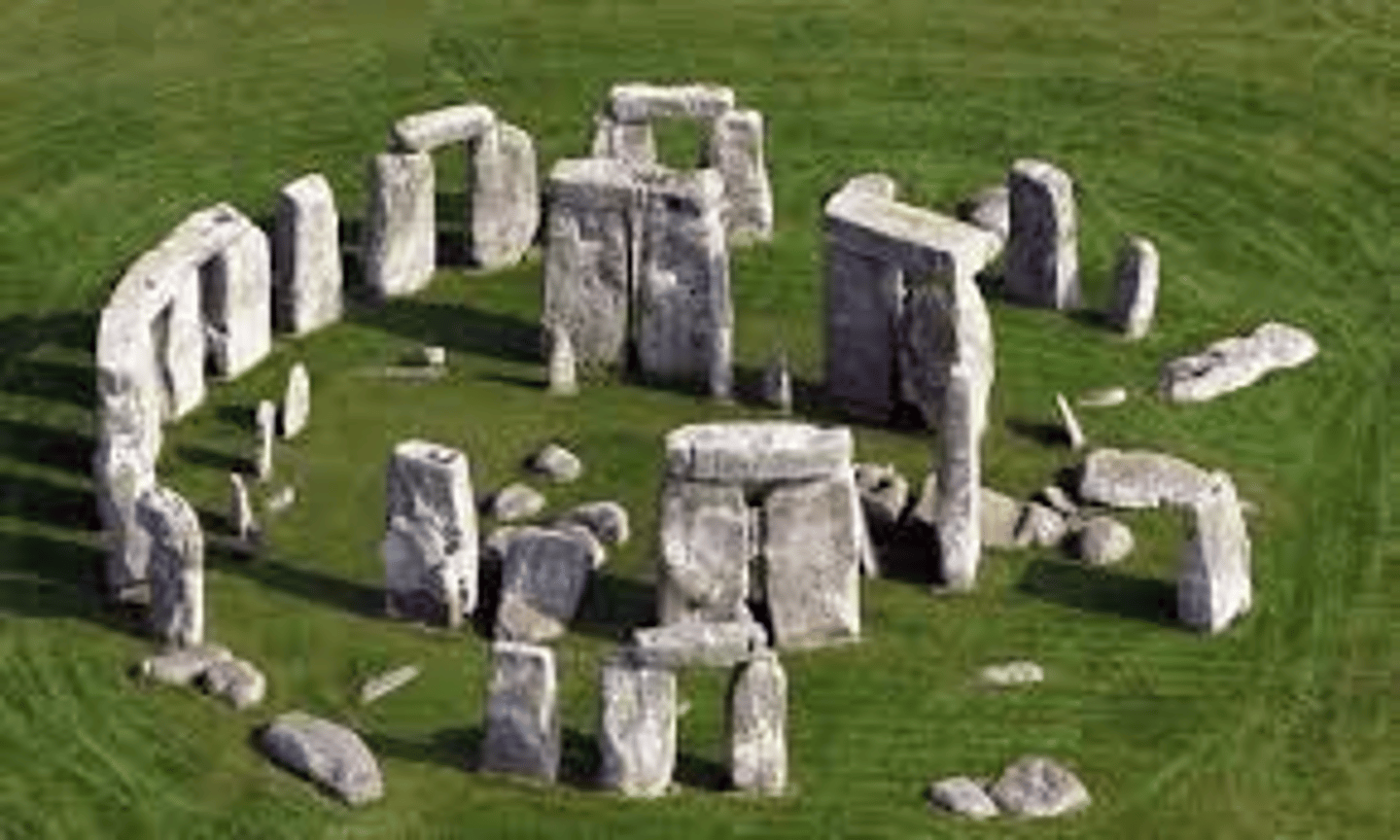
Stonehenge, 2000 BCE
-neolithic
-Megaliths; 24 ft above ground
-Transported Megaliths
-trilithon: 3 stones
-deposits of human bones found around structure, served as temple
-astronomical purpose, points in direction of solstices and equinoxes at certain points of year
-Made a giant calendar

-Mesopotamian Art
-migration to river valley in 3500 BCE, new site of human settlement
-beginning of bronze age
-invention of writing
-creation of monarchy
-polytheistic religion, Gilgamesh
-technology, bronze, weapons, art
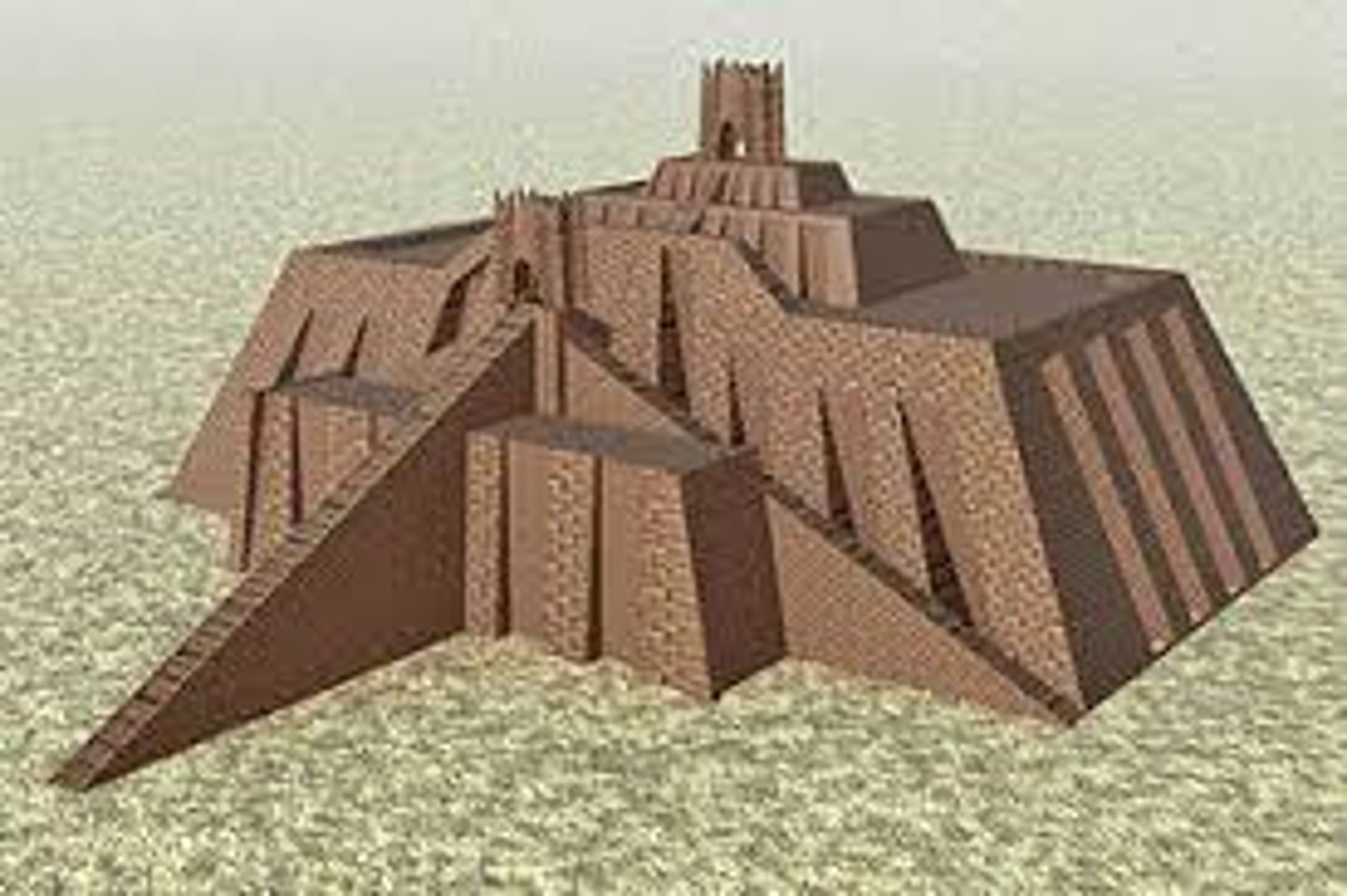
Ziggurat at Ur, 2600-2400 BCE
-mesopotamian (ancient near eastern)
-Worship deities, religious shrine
-Dedicated to a particular deity
-humans can have direct contact with deity for prayer and sacrifice
-built with mud brick

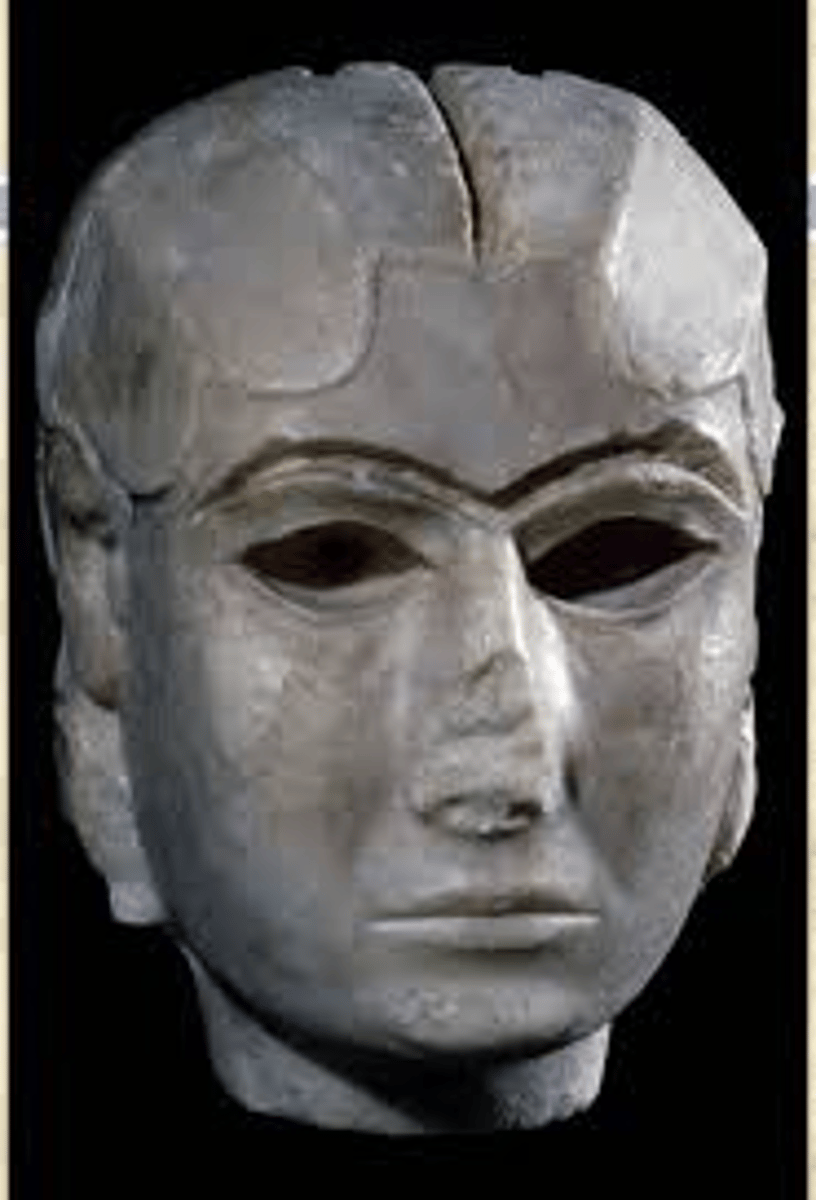
Female Head from Inanna Temple Complex at Uruk, 3000-2400 BCE
-mesopotamian
-Sumerian sculpture
-carved out of marble stone on wooden base
-eyes filled with shell or limestone, emphasis on brow, eyes reflect human/divine soul
-Godess has a noble distain
-Figure like that would've been placed in a ziggurat

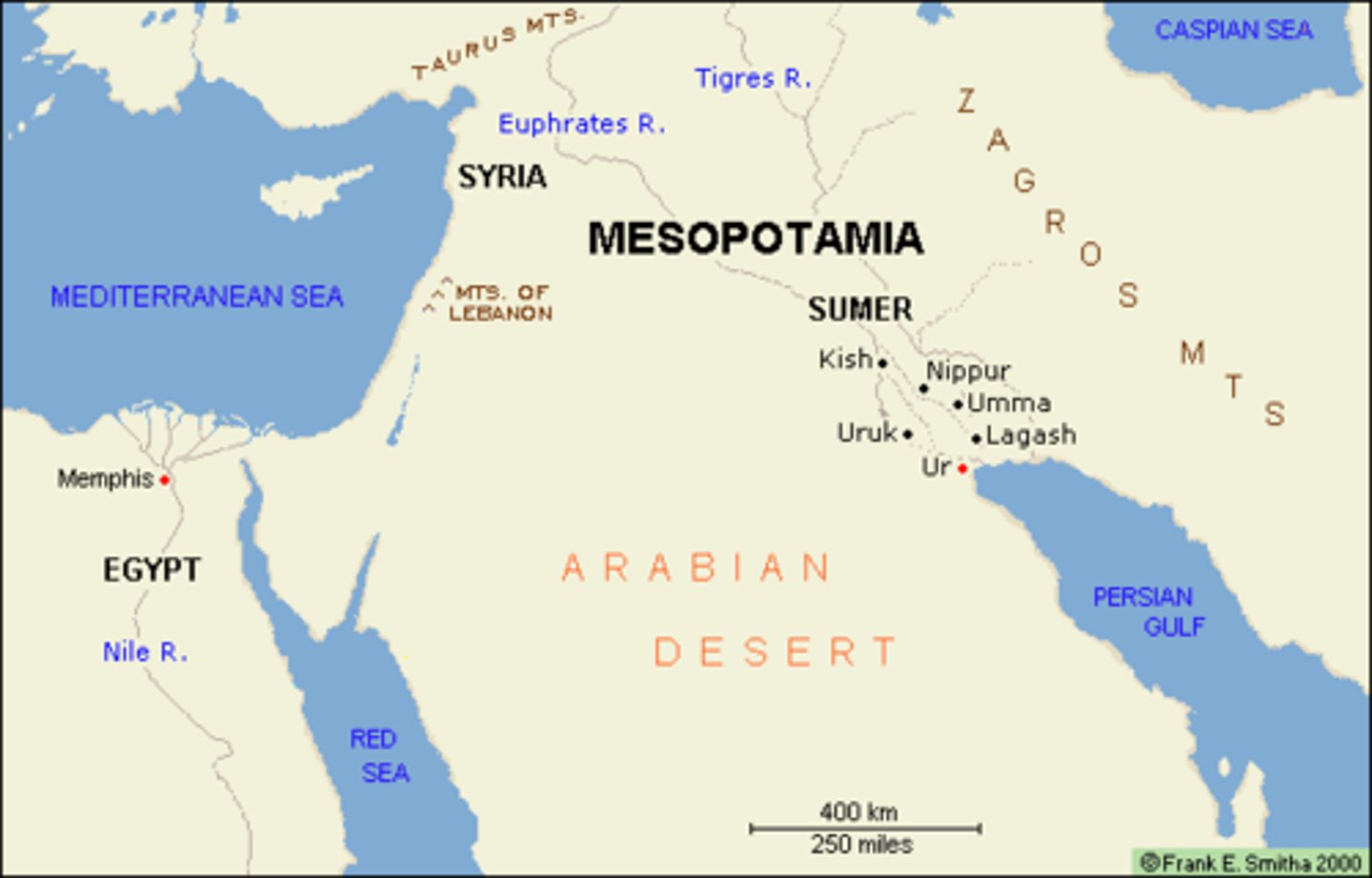
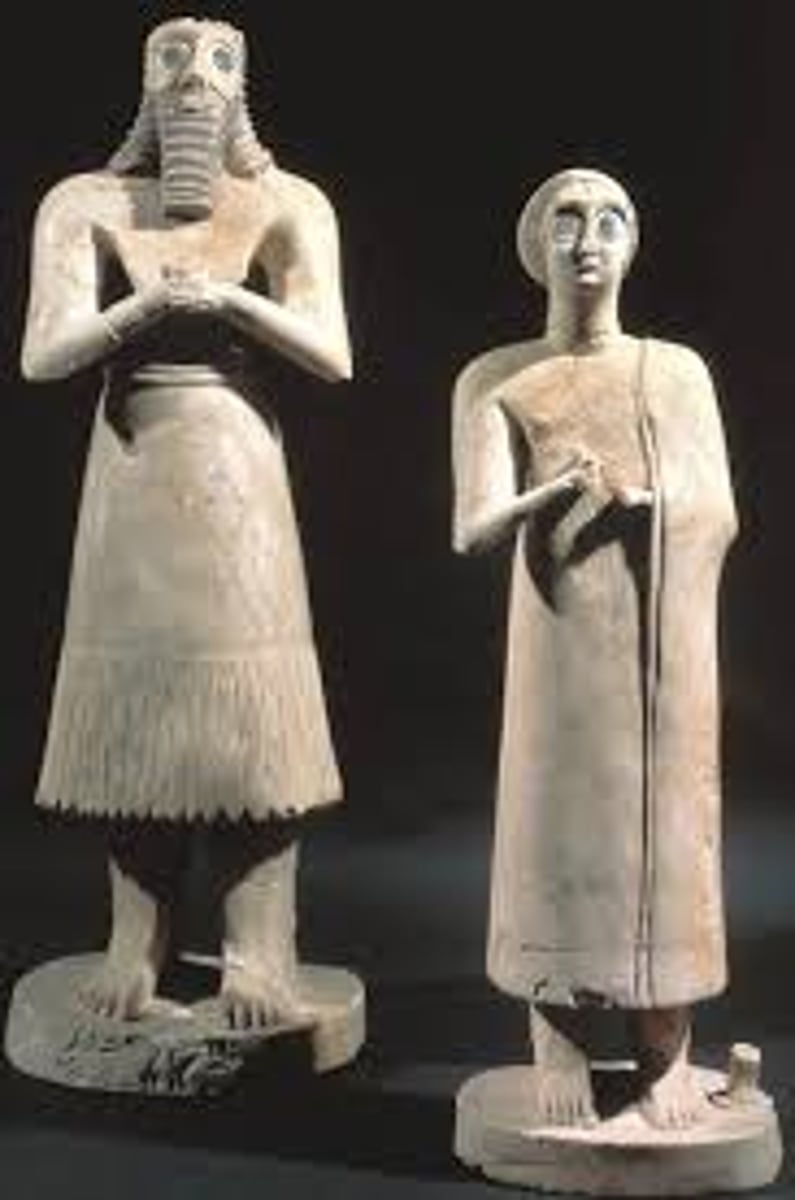
Statuettes of two worshipers from the Square Temple at Eshnunna, 2700 BCE
-Mesopotamian
-Sumerian
-marble, carved
-arms in prayer
-eyes strongly emphasized

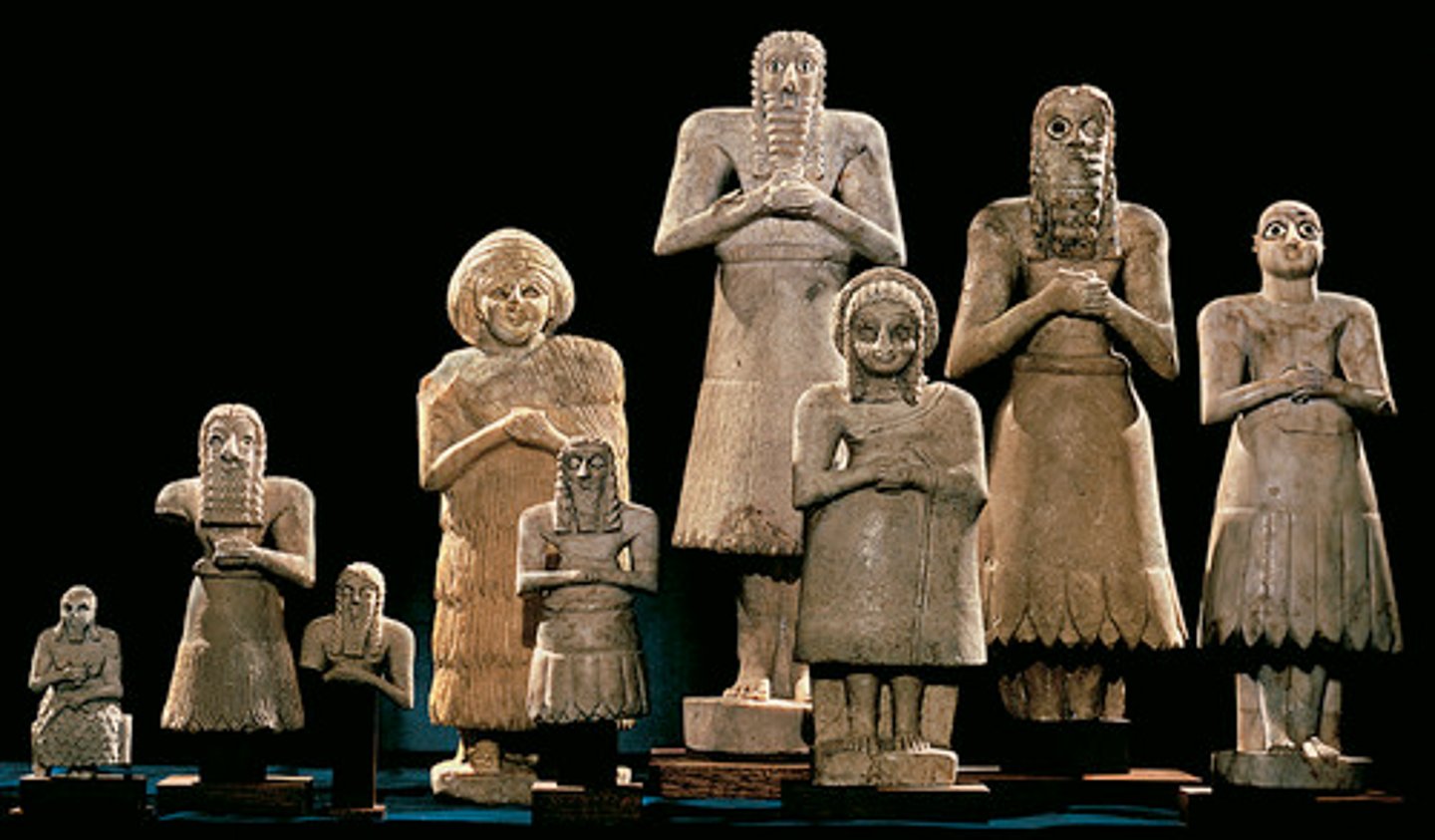
-Tell Asmar 2900-2350 B.C.E
-Range in different sizes
-Perhaps dedicated to the god Abu

-Inscription saying that name is Abu
-2900-2550 BC
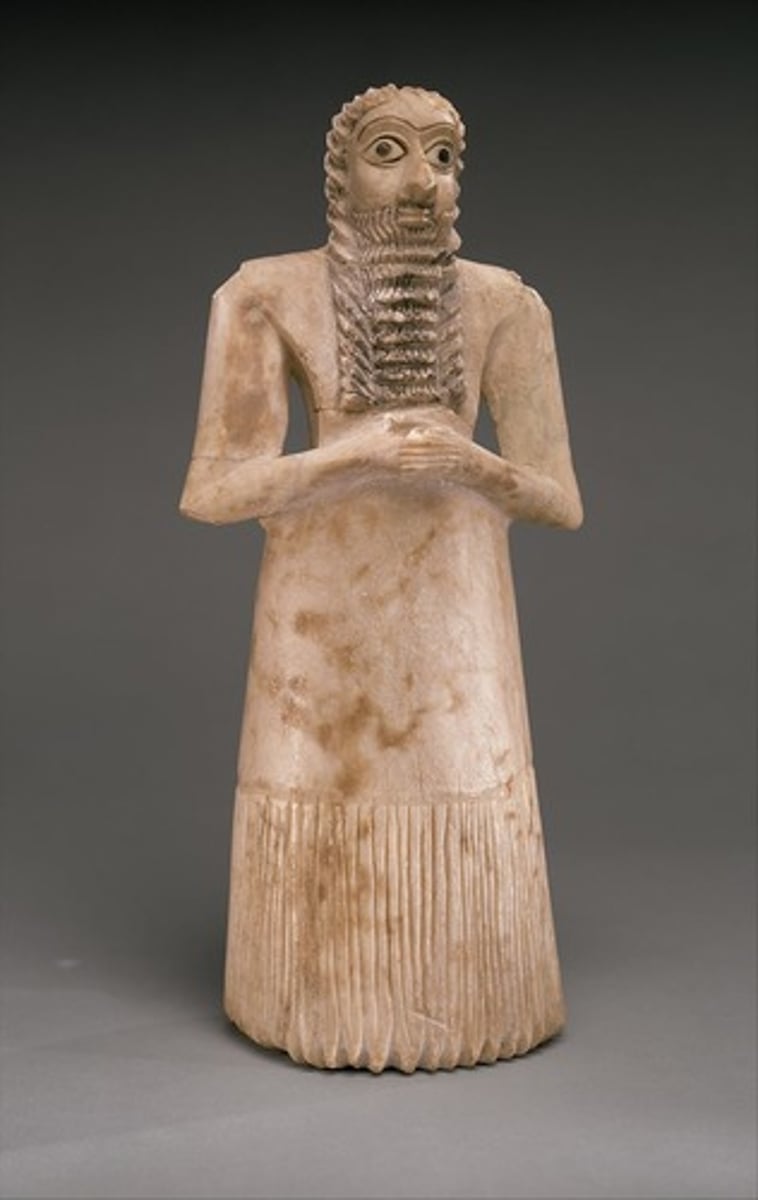

Abikhil from Mari, 2600-2500 BCE
-Mesopotamian
-ziggurat superintendent
-slightly smiling, seated
-Abikhil
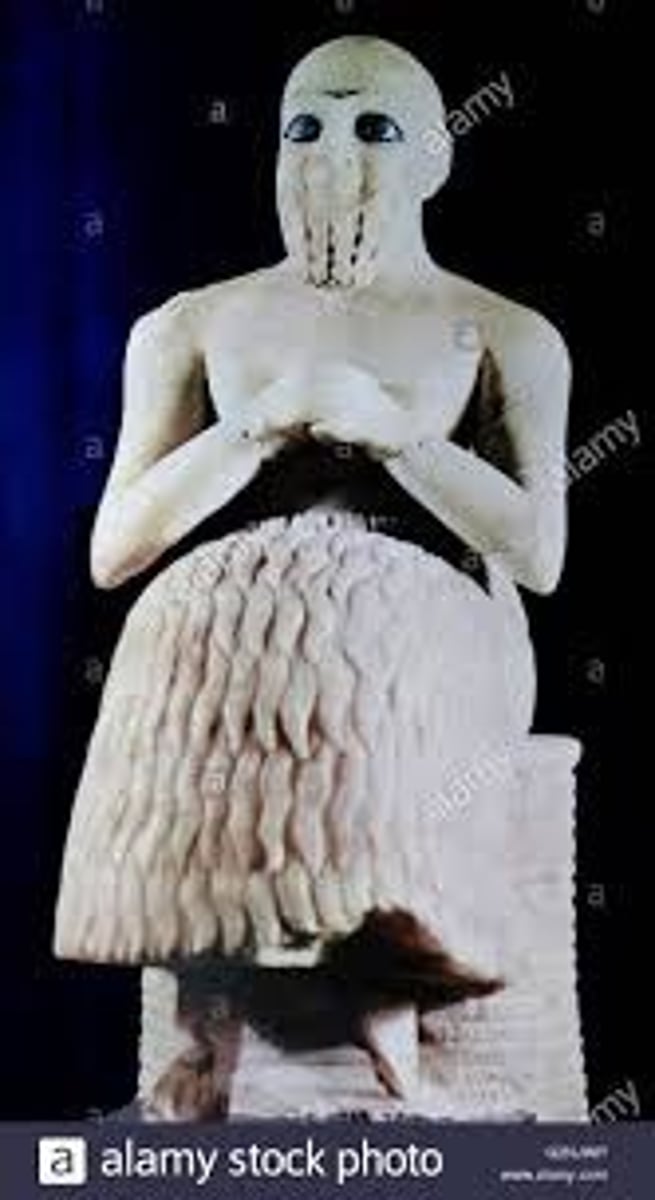
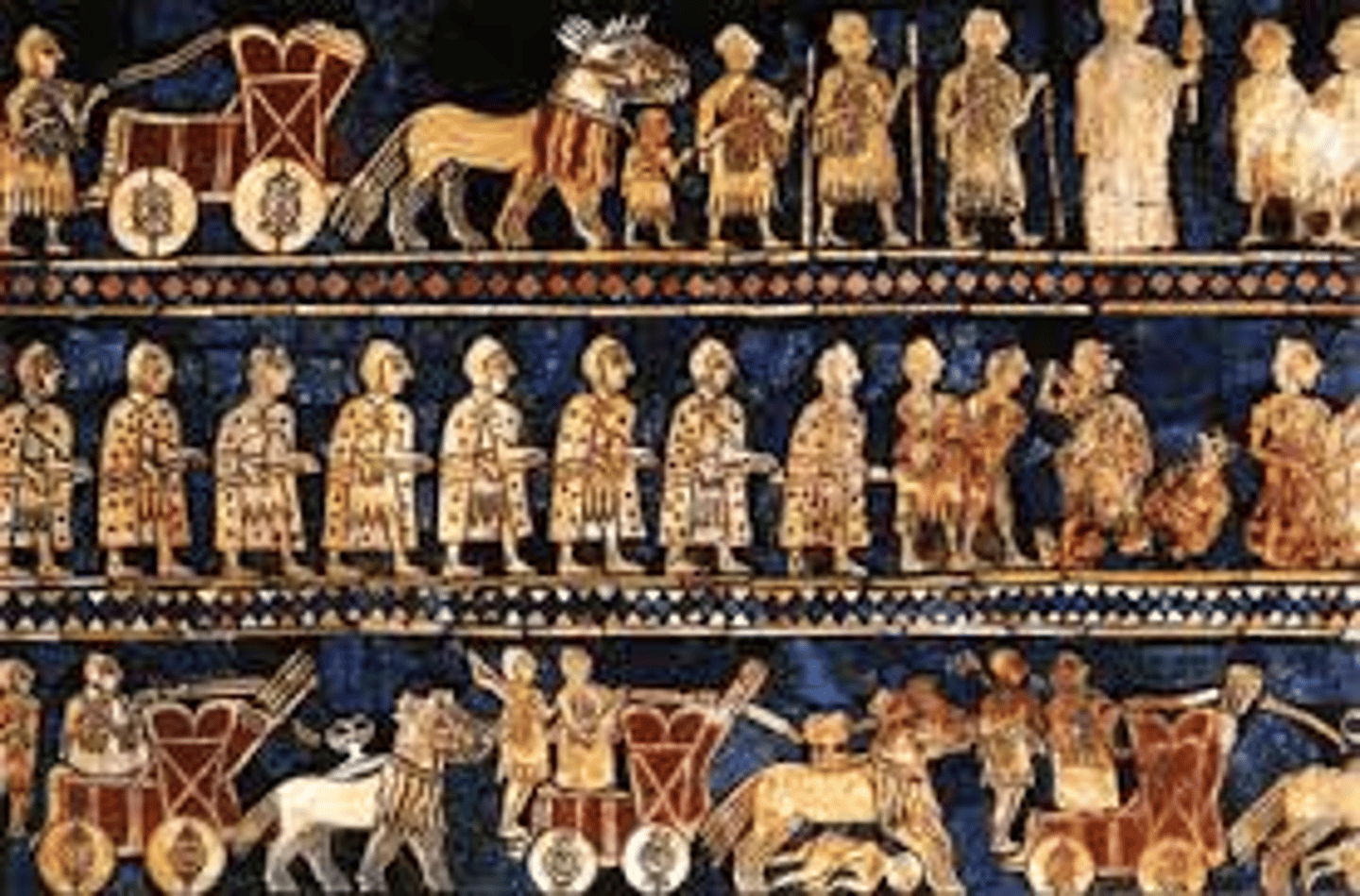
Royal Cemetery at Ur, 2600-2400 BCE
-Mesopotamian
-lined with precious stones, shells, red carnelian
-first example of narrative art in ancient sumer
-Battle depicted in 3 rows
-Reveals culture as people play harp and dance

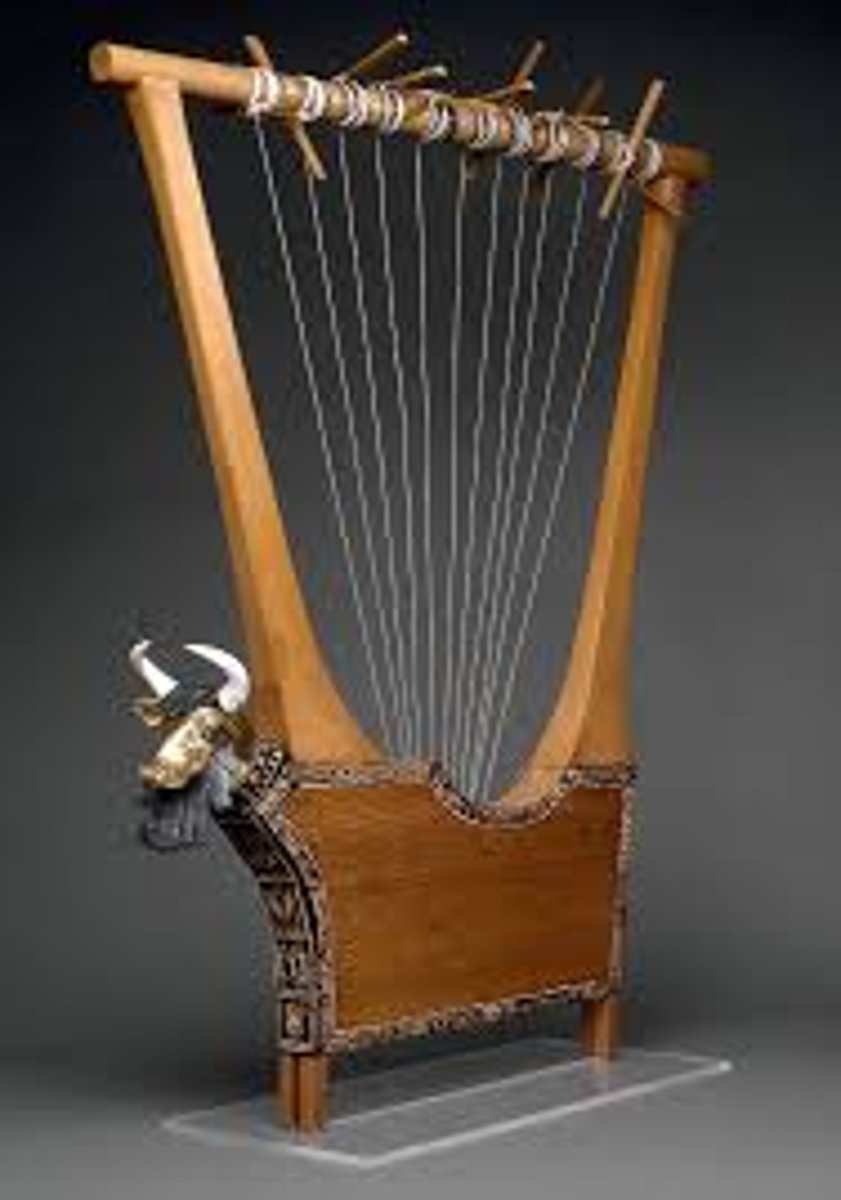
Harp from Tomb of Pu-Abi at Royal Cemetery of Ur, 2500 BCE
-mesopotamian
-made of wood
-cow with horns
-animals participating in banquet
-A fable; animals serve the guests and play harps

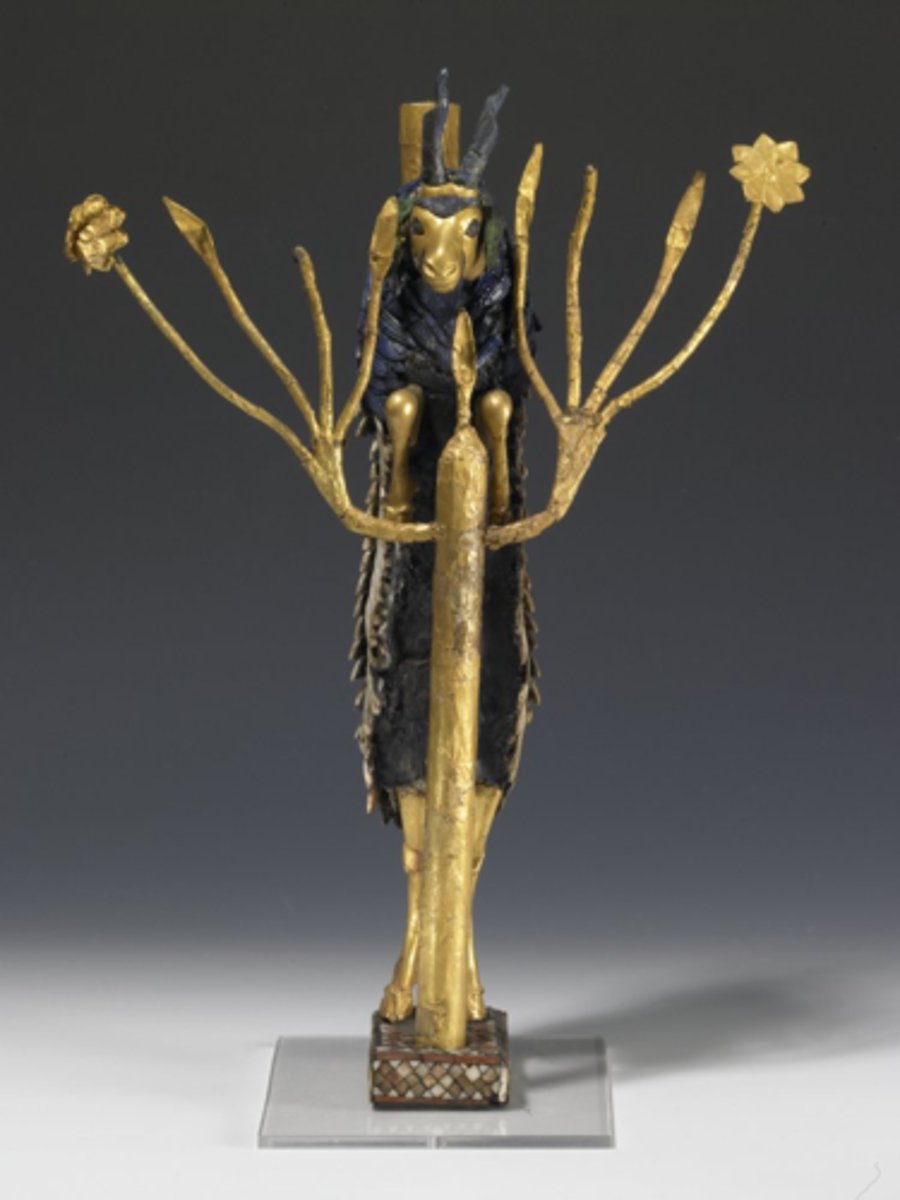
The Ram in the Thicket from Royal Cemetery of Ur, 2600 BCE
-Mesopotamian
-tree of life
-symbolizes nature
-goat in lifelike fashion
-gold

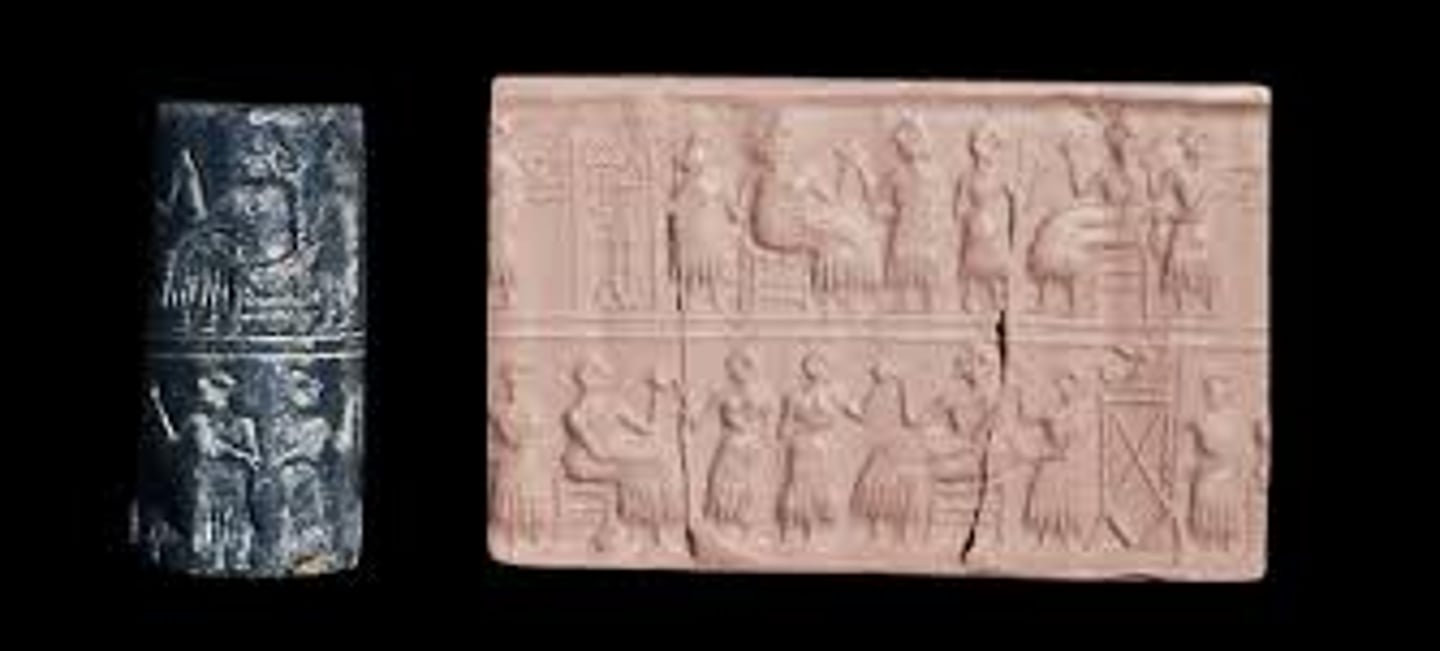
Banquet Scene and Cyclinder Seal from Tomb of Pu-abi at Royal Cemetery of Ur, 2600-2400 BCE
-mesopotamian
-seal impression made from rolling cylinder onto clay tablet
-reflects events in owners life
-personalized objects, no 2 are identical
-Cylinder seals
-Can be rolled over damp clay and once clay drys and impression is created

-Akkadians
-Royal themes glorified, actions of monarchs, narrative art
2300 BCE
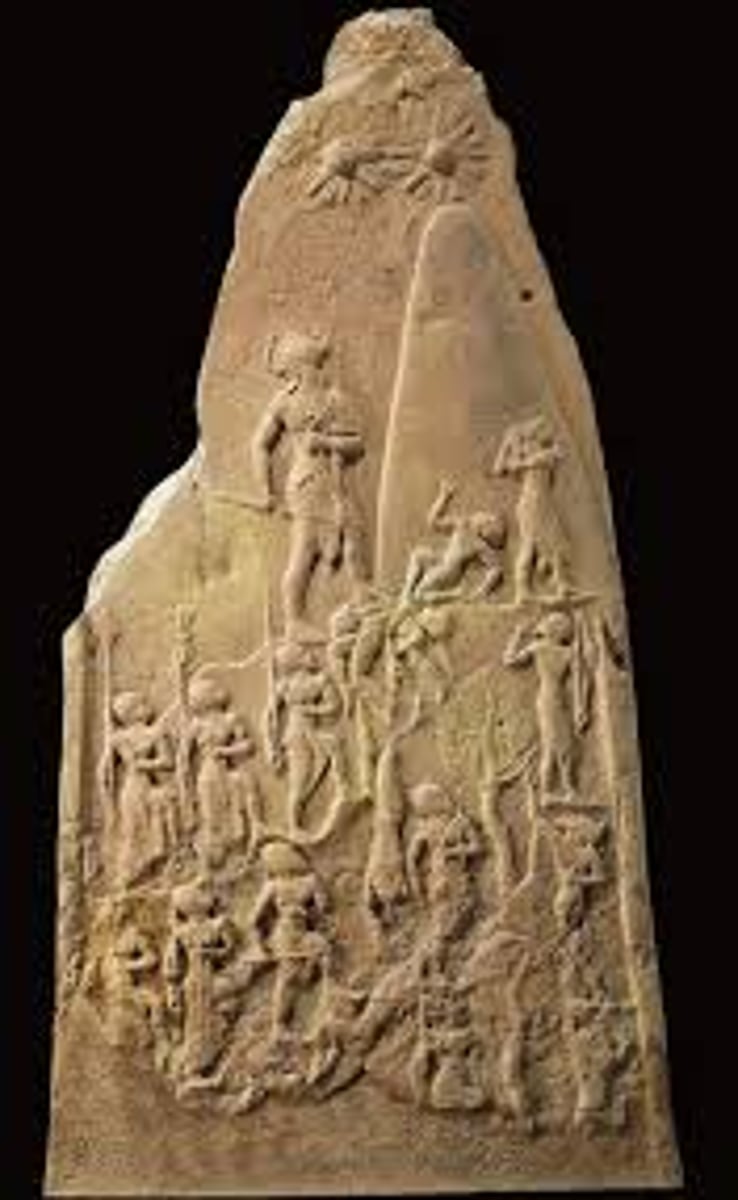
Victory Stele of Naram Sin, 2254-2218 BCE
-Akkadian
-memorative plaque
-low relief
-unified design
-divine symbols sun and moon
-sense of volume in individual forms
-shows king leading army up mountain as they defeat enemy

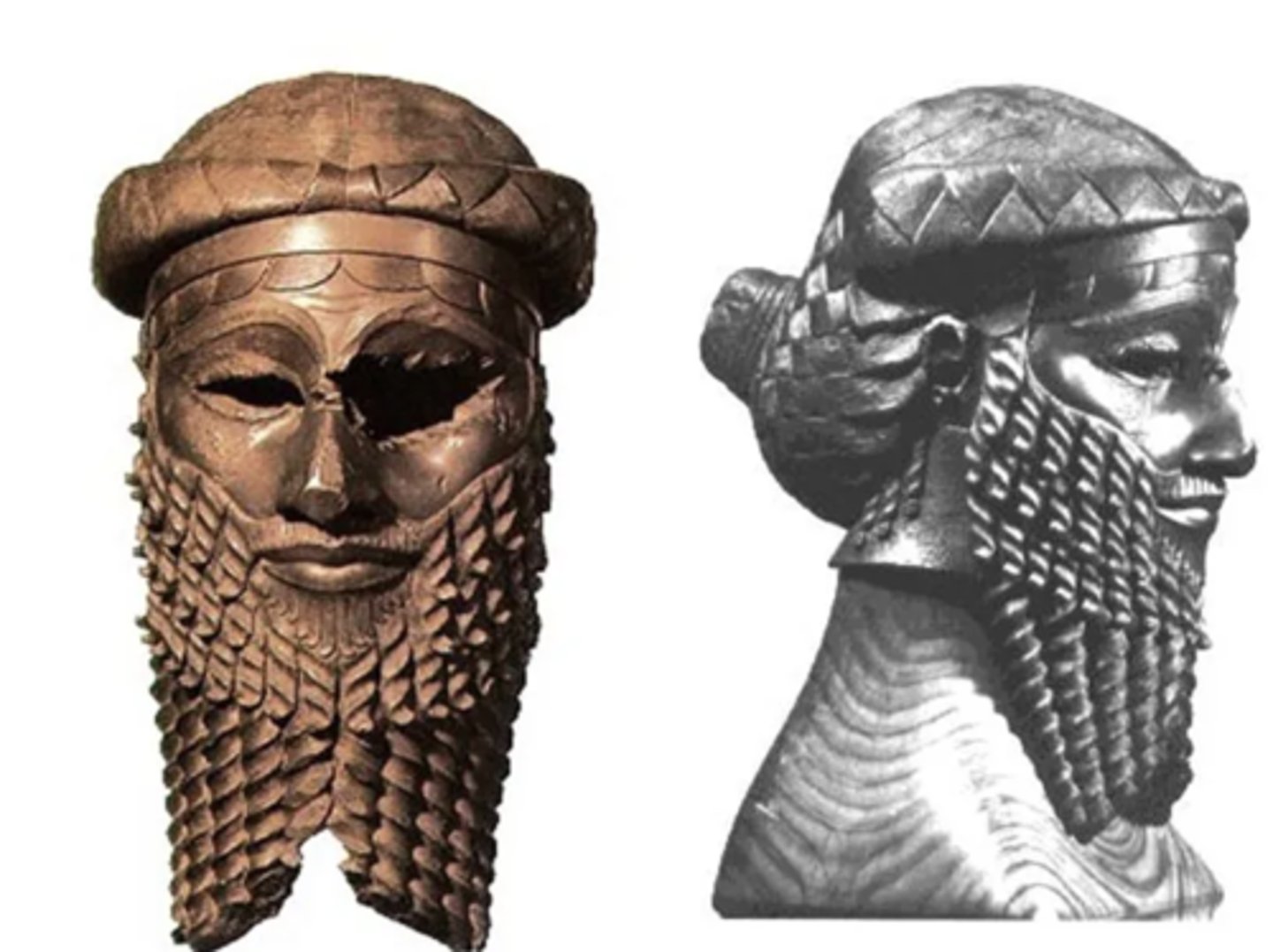
Head of Akkadian Ruler from Nineveh, 2250-2200 BCE
-mesopotamian, akkadian
-made of cast bronze
-figure of royal status
-Presumably Naram Sin

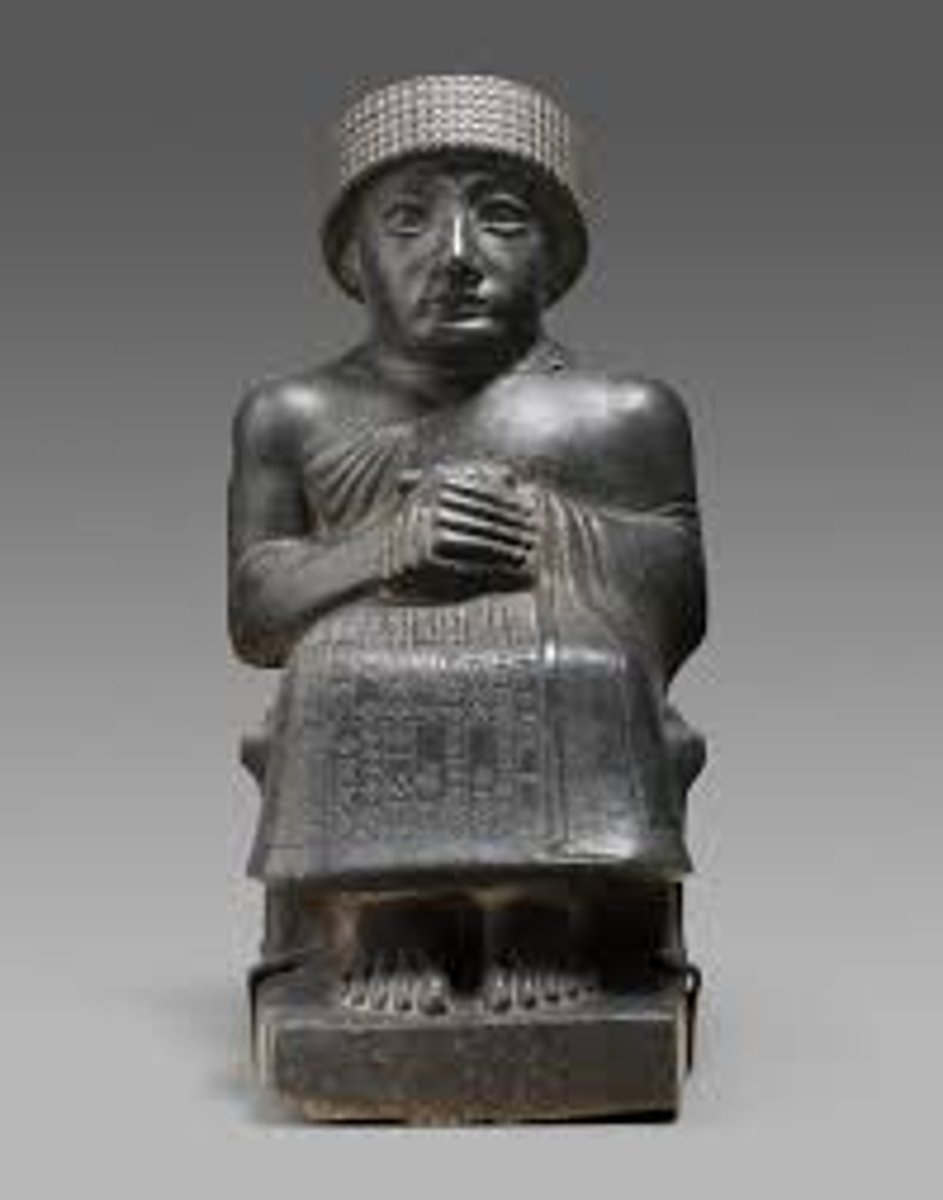
Gudea of Lagash, 2100 BCE
-mesopotamian
-Neo-Sumerian
-restored ziggurats
-smooth polished surface
-scripture on figure

-Babylonian
-hanging gardens
-fall to invaders, plunging mesopotamia into disorder
-located upstream of Euphrates
2150 BCE
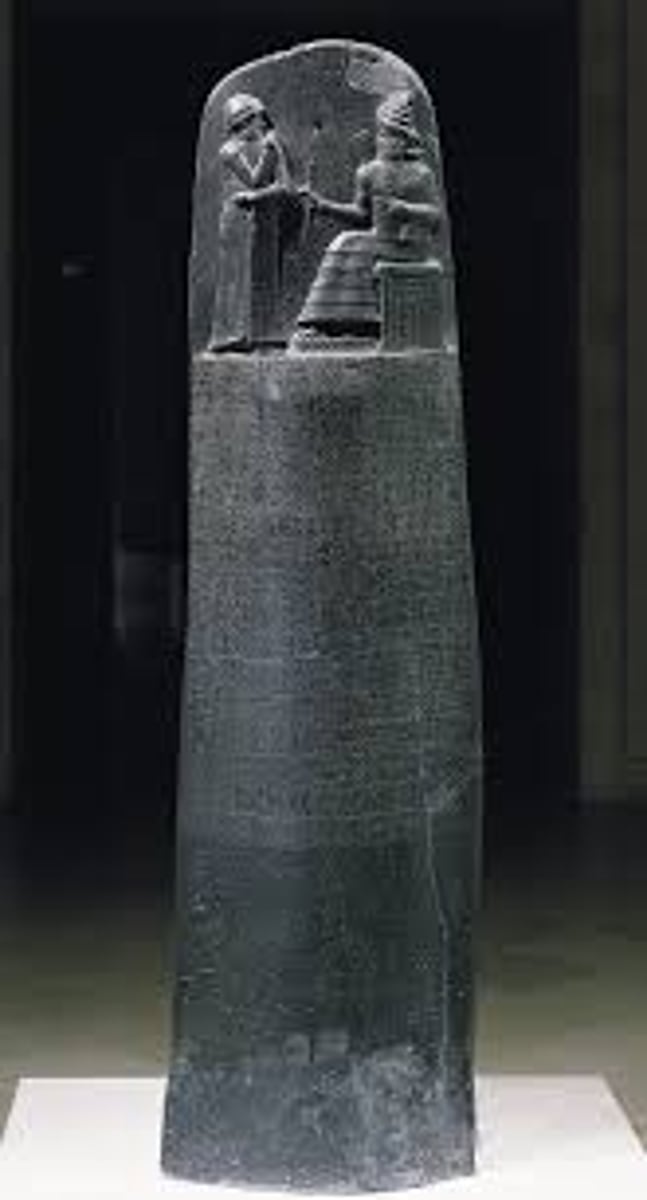
Code of Hammurabi from Babylon, 1780 BCE
-mesopotamian, babylonian
-commissioned by King Hammurabi
-carved from basalt
-relief
-narrative scene showing king in dialogue with enthroned god
-implies there is a divine source for human law
-scepter indicates divine authority
-code in cuneiform

Citadel of Sargon II, Dur-Sharrukin at Chorsaba, 721-705 BCE
-mesopotamian, assyrian
-Palace for the king of kings
-Constructed out of mudbrick
-Most prestigious part is an audience hall
-25 acres of land
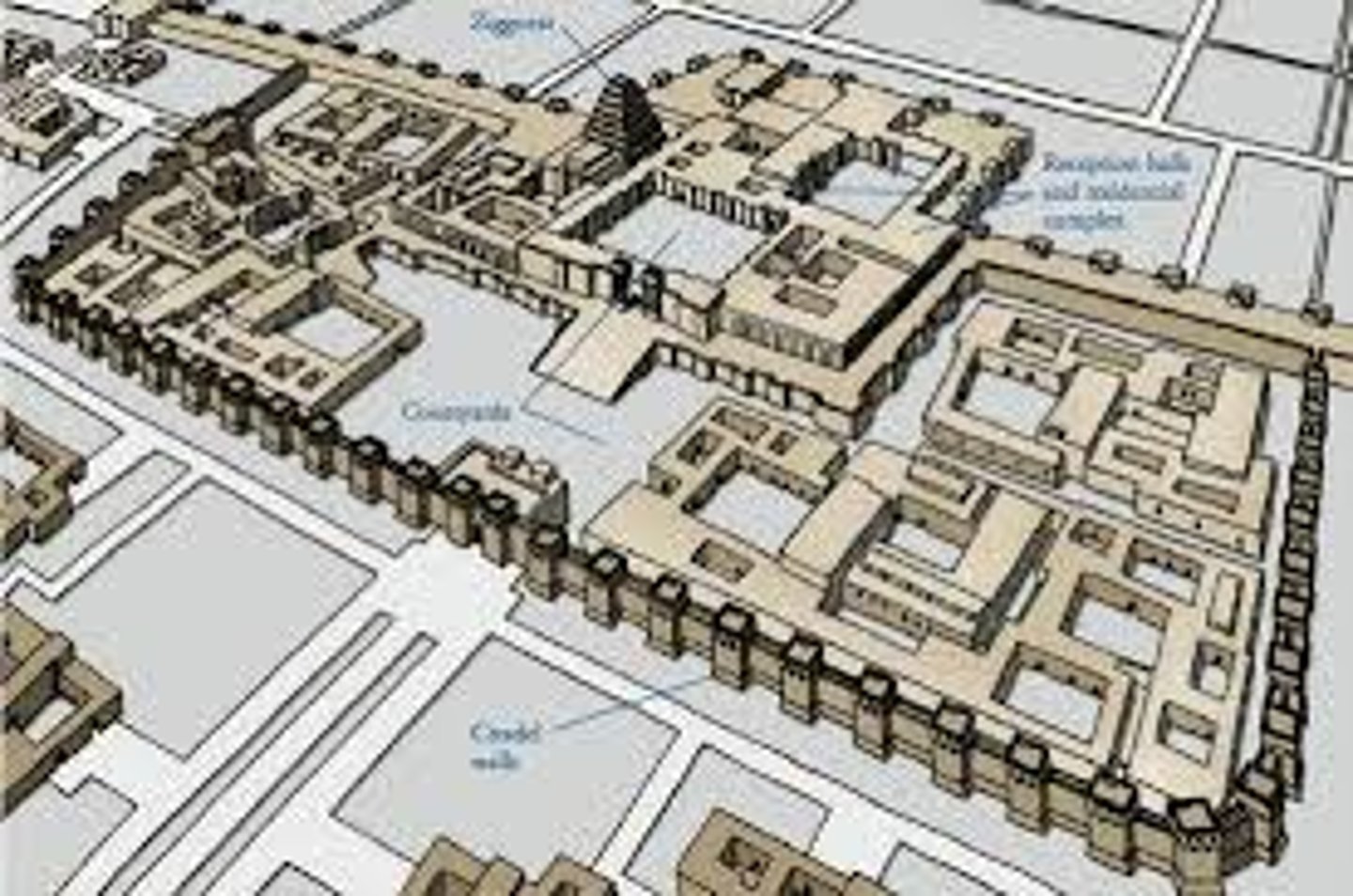
Lammassu from the citadel of Sargon II, Dur Sharrukin, 721-705 BCE
-mesopotamian
-carved from hard stone
-frames entrance to royal audience hall
-body of bull with wings and human head wearing a crown
-
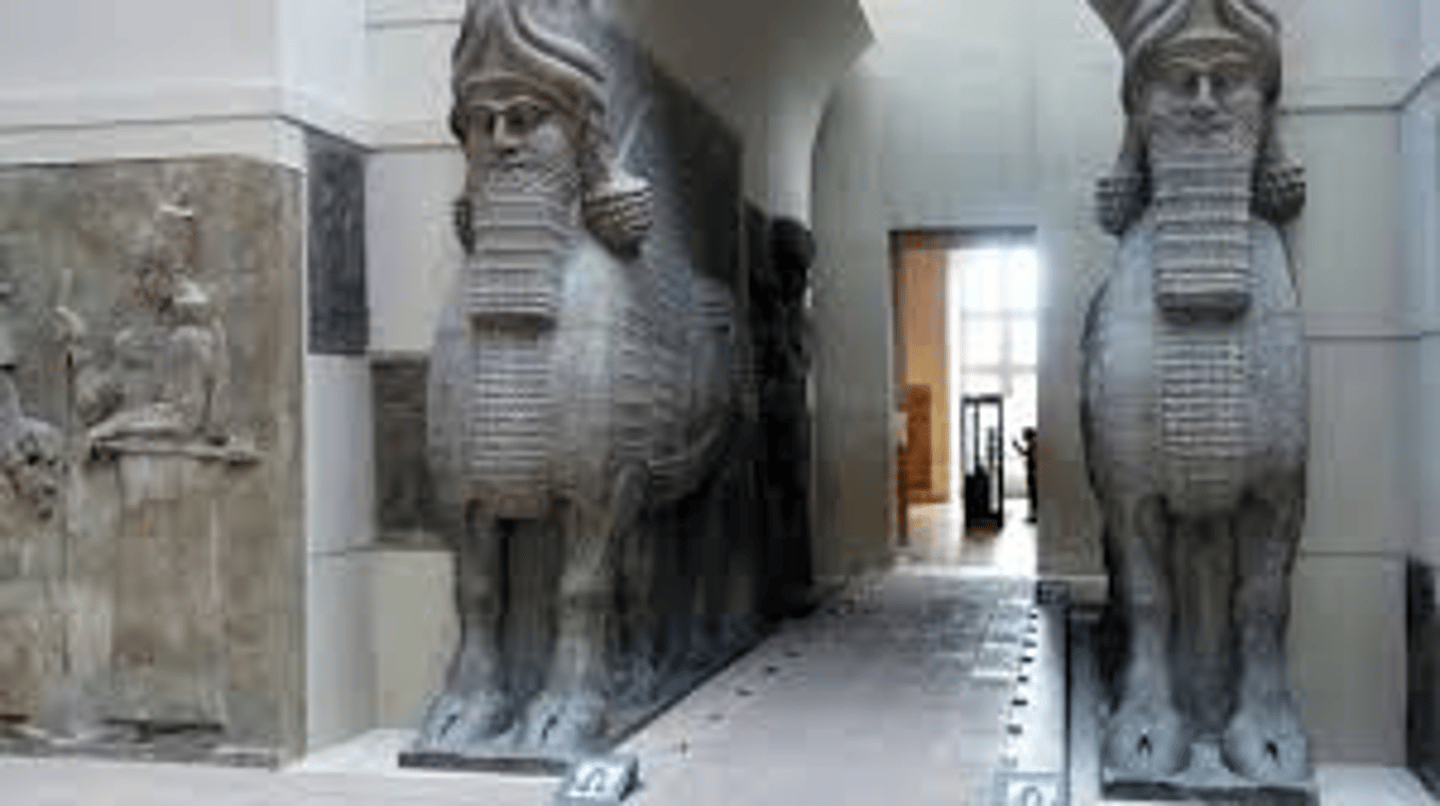

Ashurnasirpal II, 865-860 BCE
-mesopotamian, neo-assyrian
-large scale medium high relief panel
-glorifying assyrian king, Ashurnasirpal II
-Gypsin
-Leads new years festival, renewal of nature in spring
-priest wearing a mask
-Has pinecone which symbols fertility

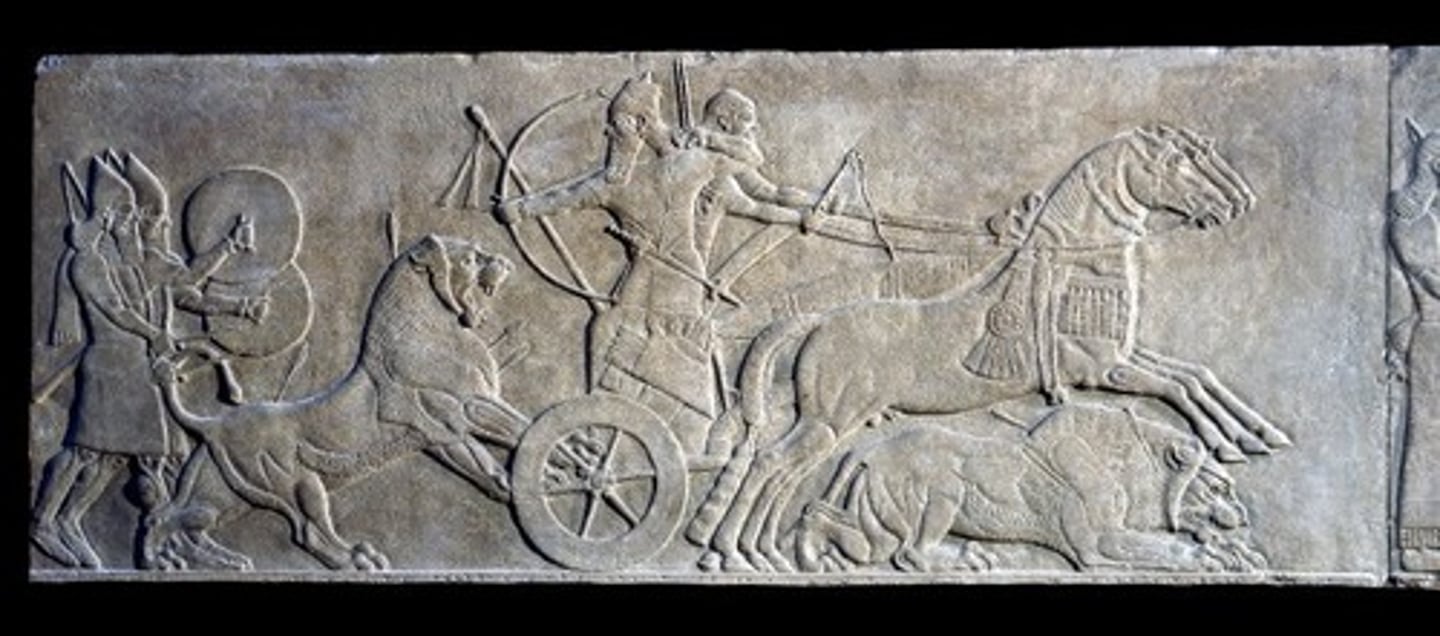
Scenes of Royal Hunt, Ashurbanipal hunting lions, 645-640 BCE
-mesopotamian
-king in the role of hunter
-from north palace of Ashurbanipal
-king slays lion with arrow
-narrative art

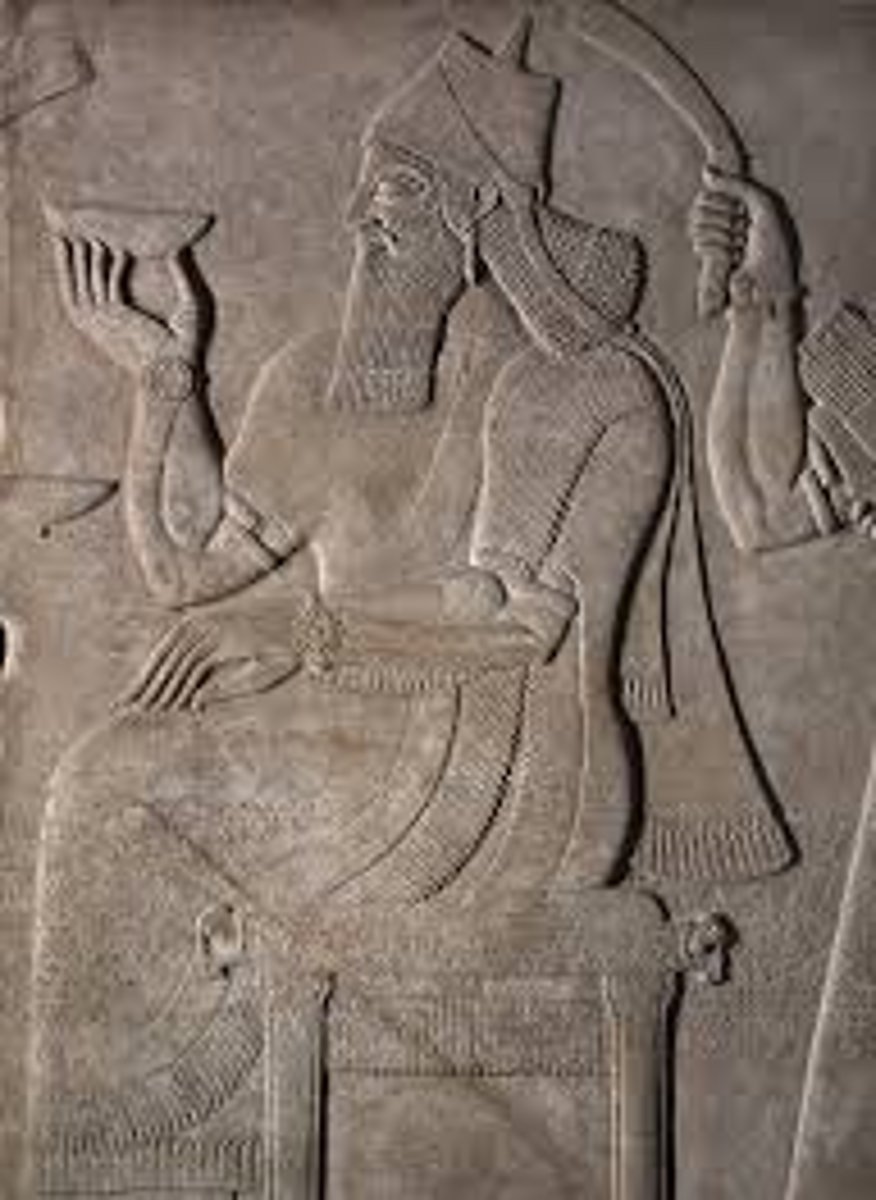
Nimrod Honorating King Ashurnasirpal II, 9th century BCE
-mesopotamian, ancient assyrian
-low relief
-priest of new years festival on left, to enhance powers of king
-king seated on throne
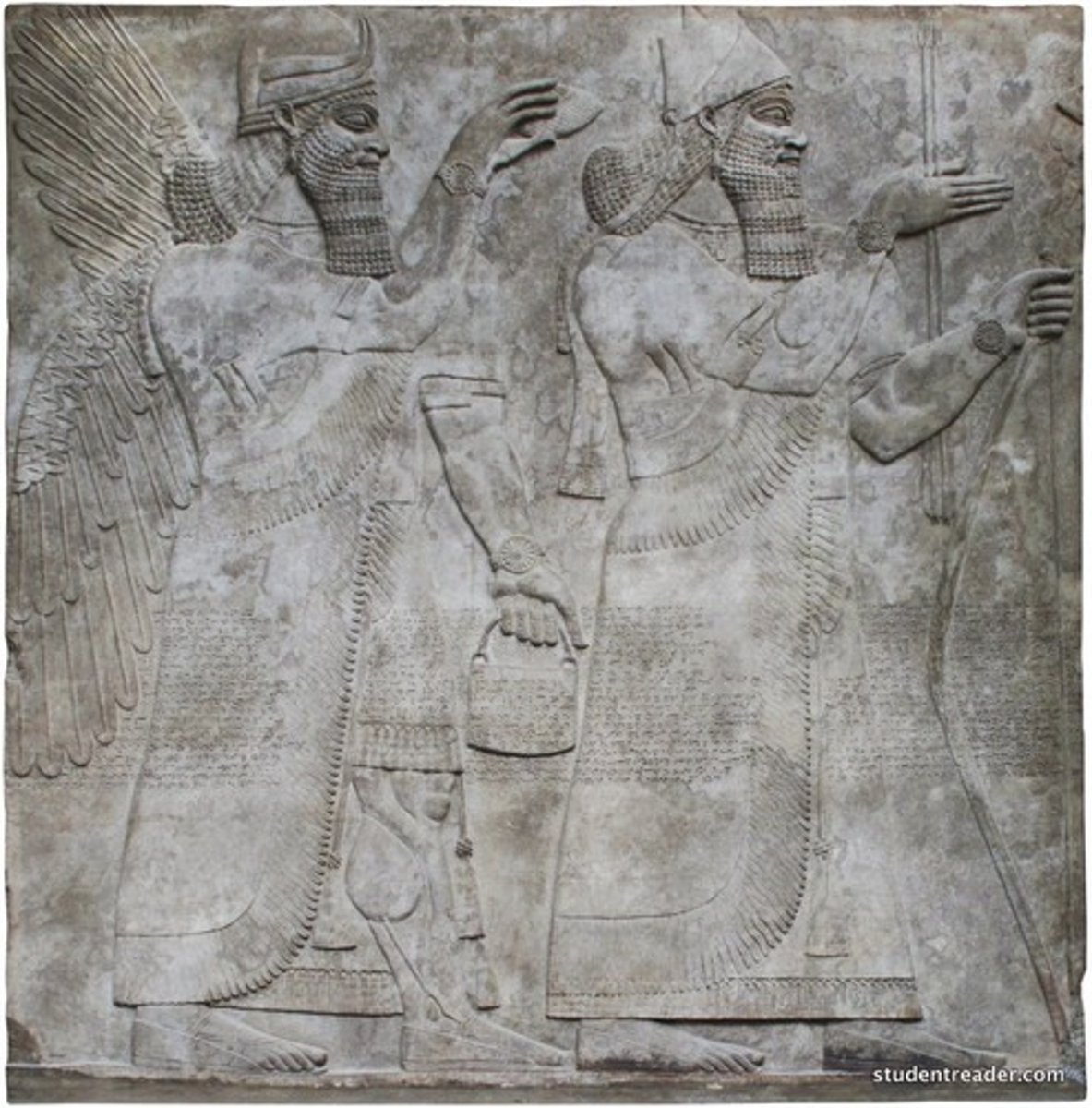

Ishtar Gate at Babylon, 575 BCE
-mesopotamian
-constructed out of glazed brick fired in a kiln
-Created using relief
-Neobabylonian period
-animals indicate abundance of nature and mans control over it
-texture of animals surface captured
-Famous gateway to the city of Babylon
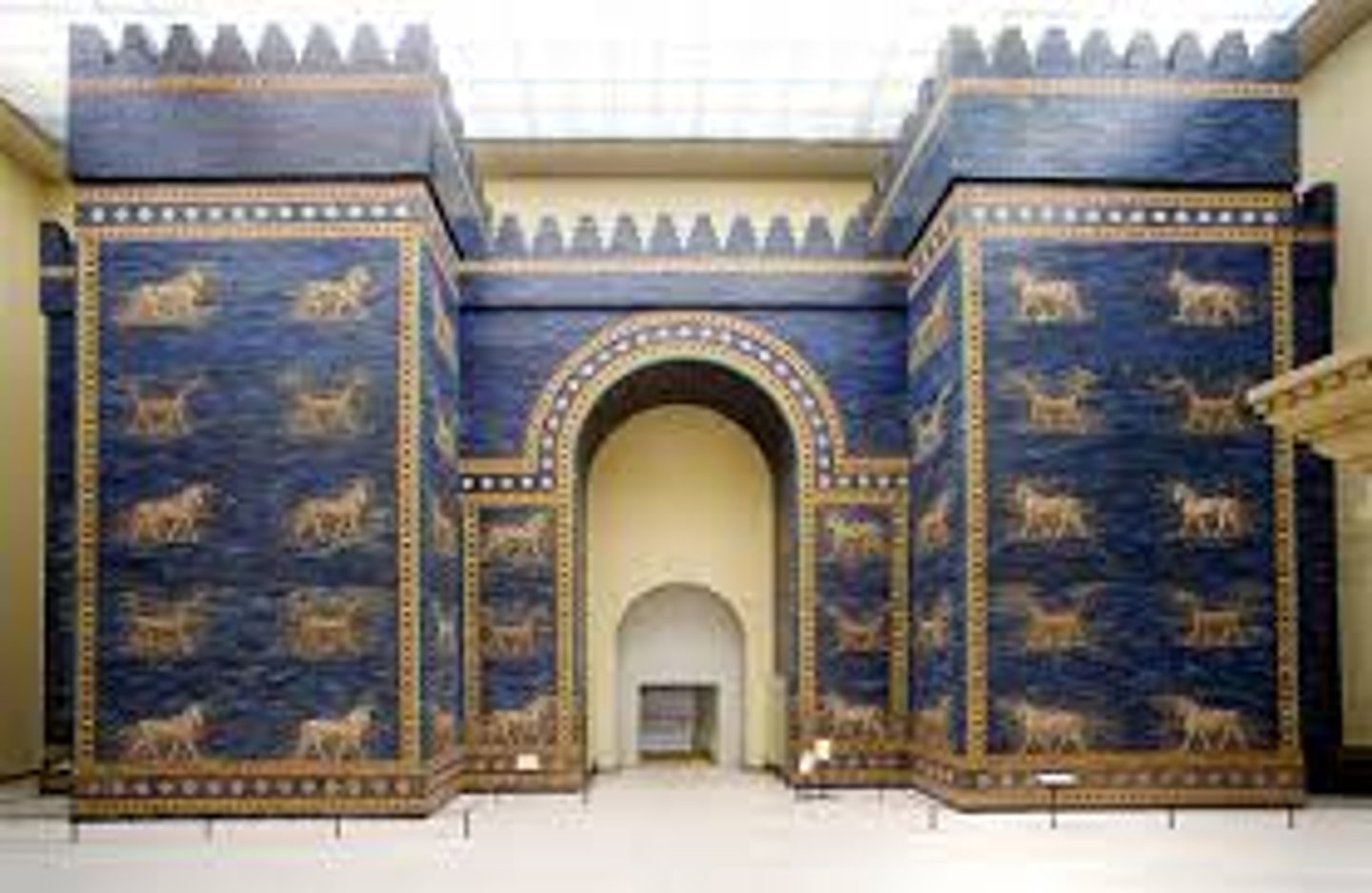

Site of Persepolis, 521-465 BCE
-Persian
-Greek characteristics, columns, first example of columns as an architectural motif in eastern architecture
-main administrative center
-Apadana, people came to pay tribute to persian king
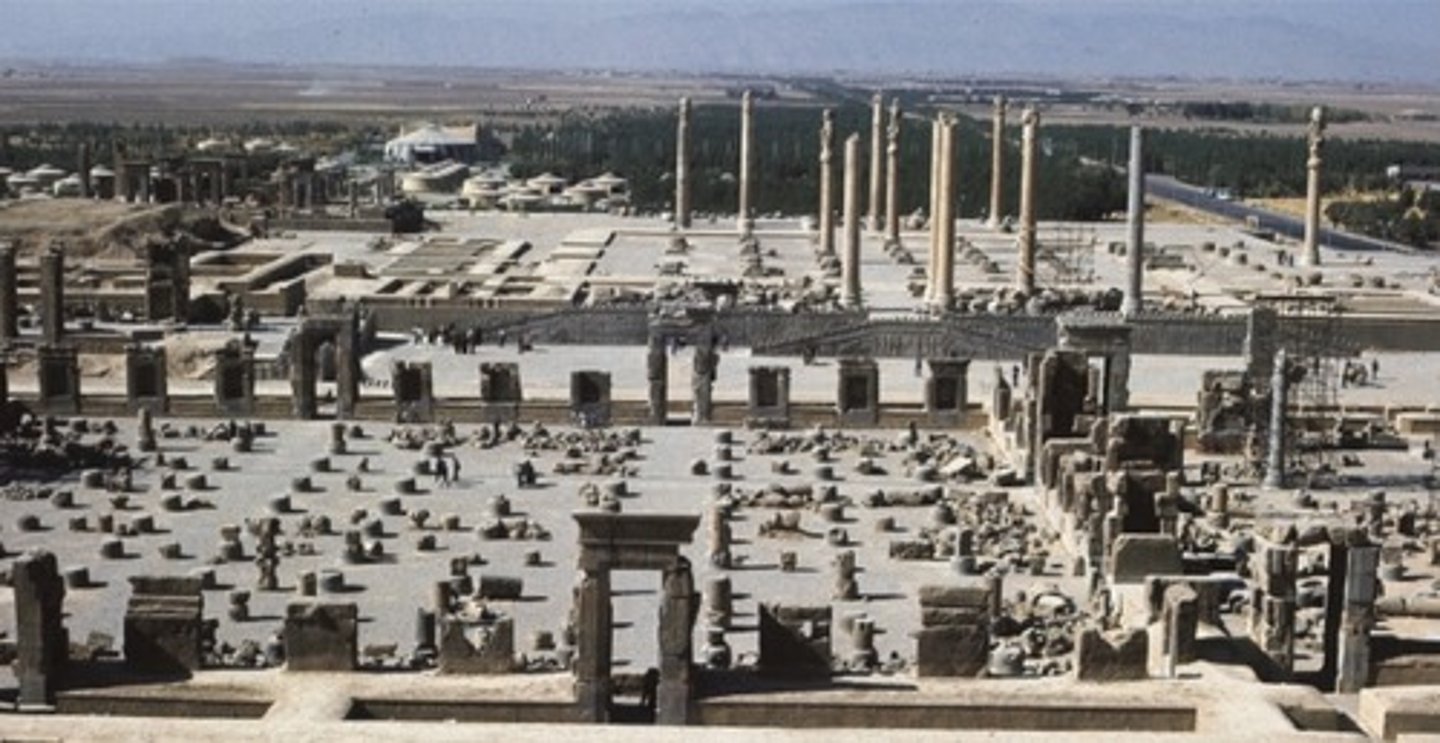

Entrance to Apadana at Persepolis, 521-465 BCE
-Persian
-animal combat, lion devouring a bull
-carved in medium high relief
-two parallel staircases to terrace
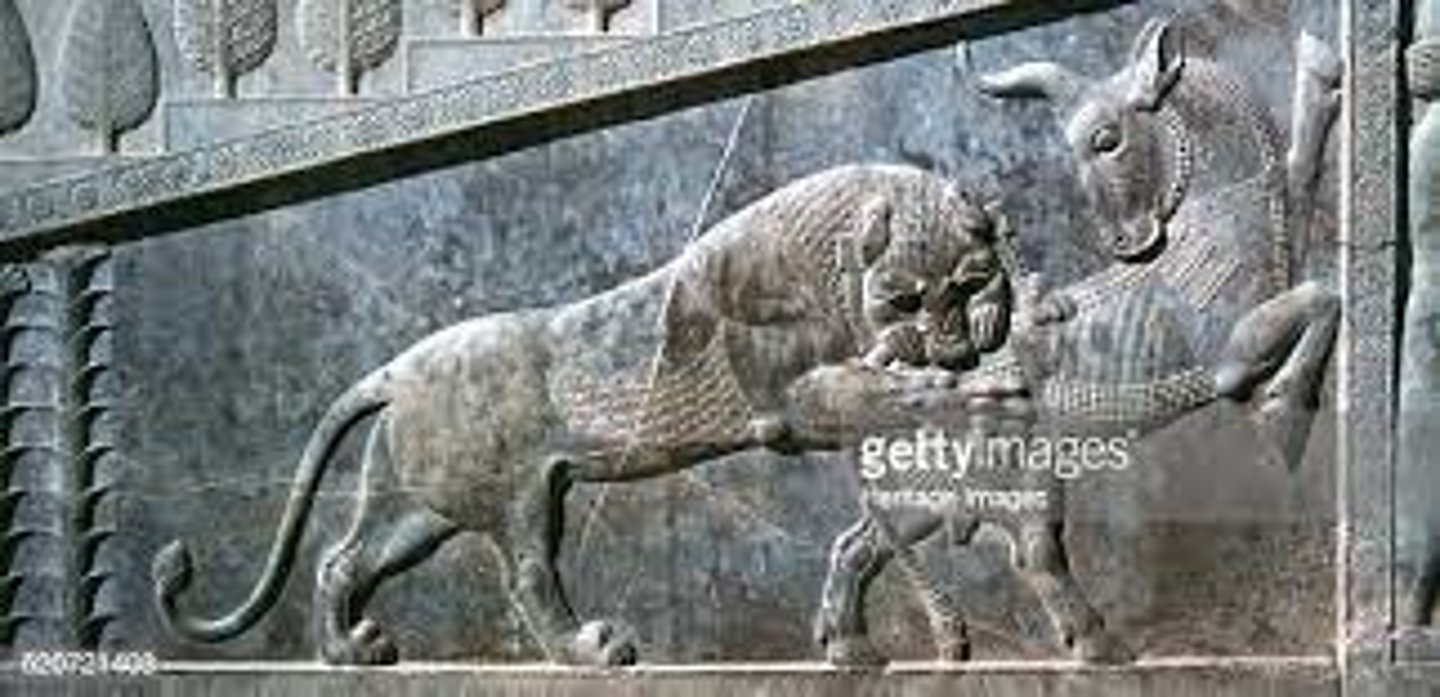

Entrance to Apadana at Persepolis, 521-465 BCE
-Persian
-first time shown in true profile, showing influence of greek art
-narrative procession
-persian soldier holding spear
-reliefs also on staircase rising towards apadana
-shown in true profile for the entire figure, as a result of greek influence

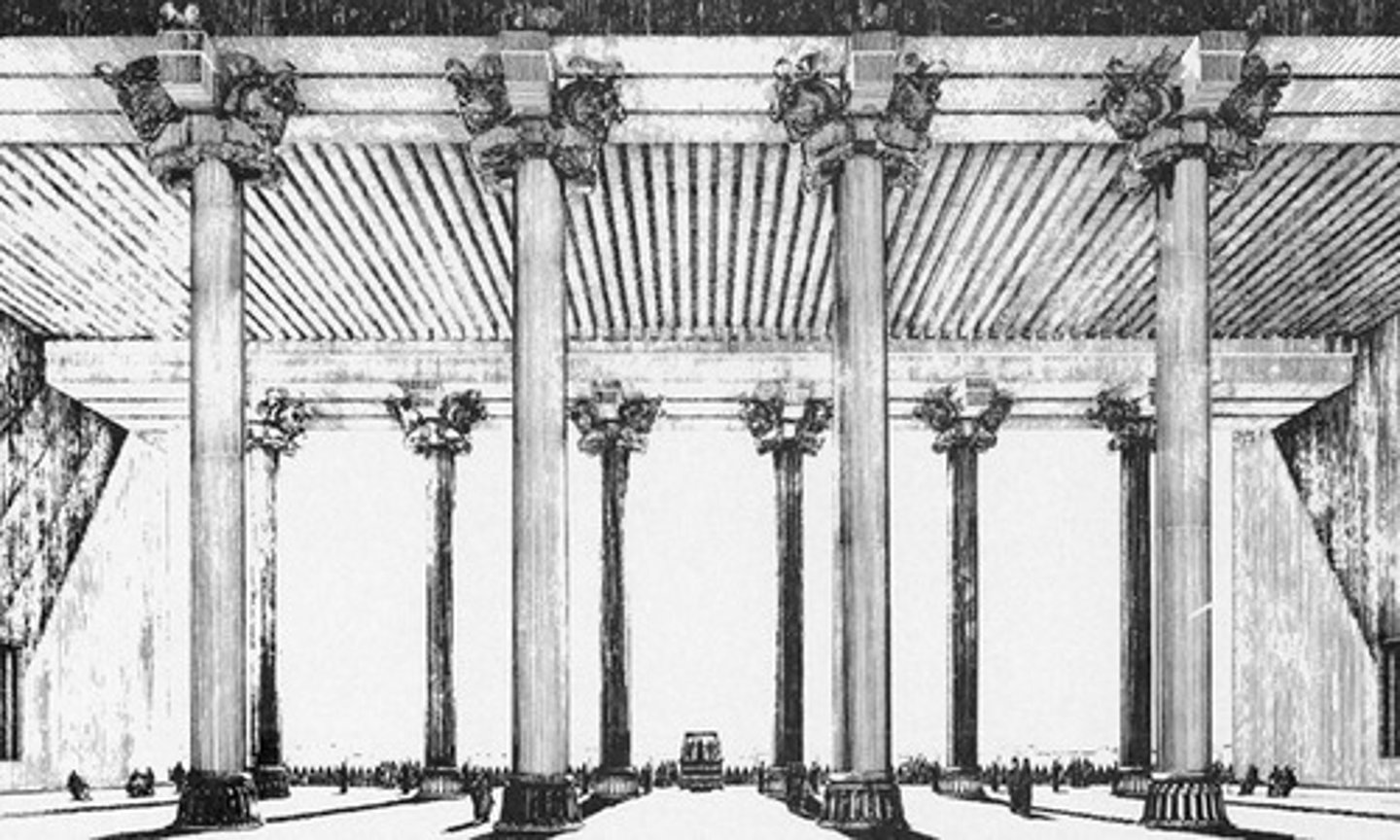
Apadana columns, 521-465 BCE
-Persian
-made of stone supporting wooden roof
-64ft tall
-top contains 4 parts of animals, Griffin
Treasury of Palace at Apadana, 519-465 BCE
-persian
-where precious materials of Persepolis were stored
-scene of royal court ceremony, king portrayed in larger scale, raising hand to symbolize speech
-uses greek symbols to sign artwork
-Hurodotus
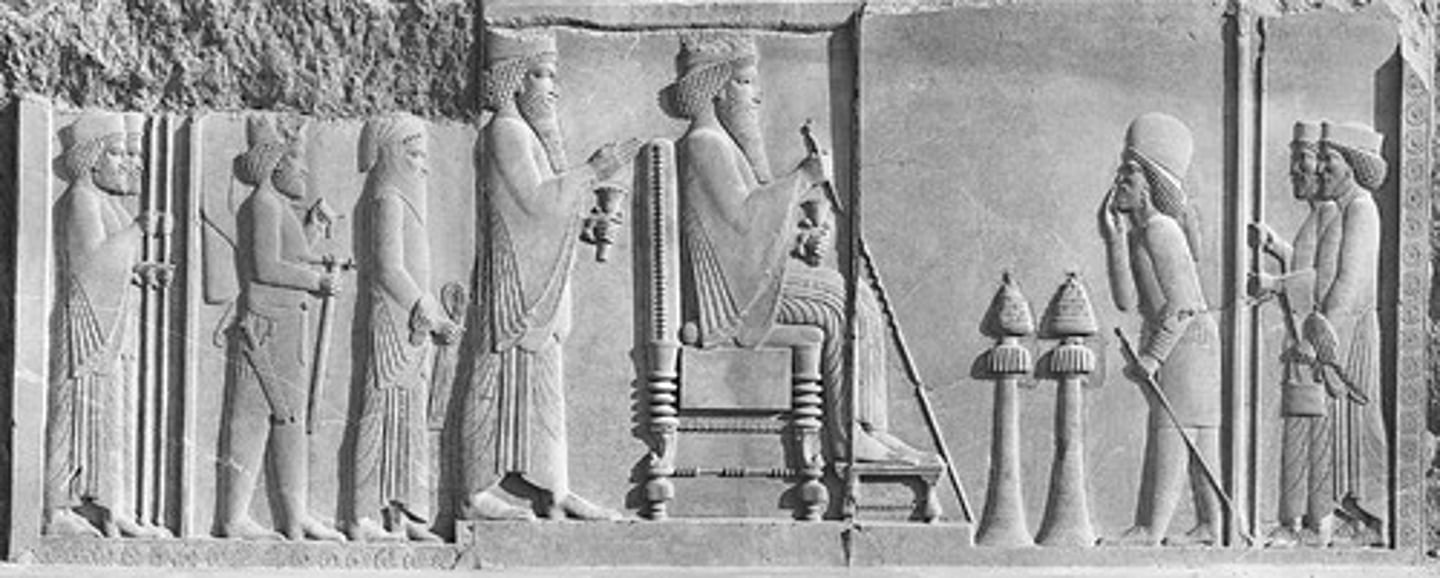

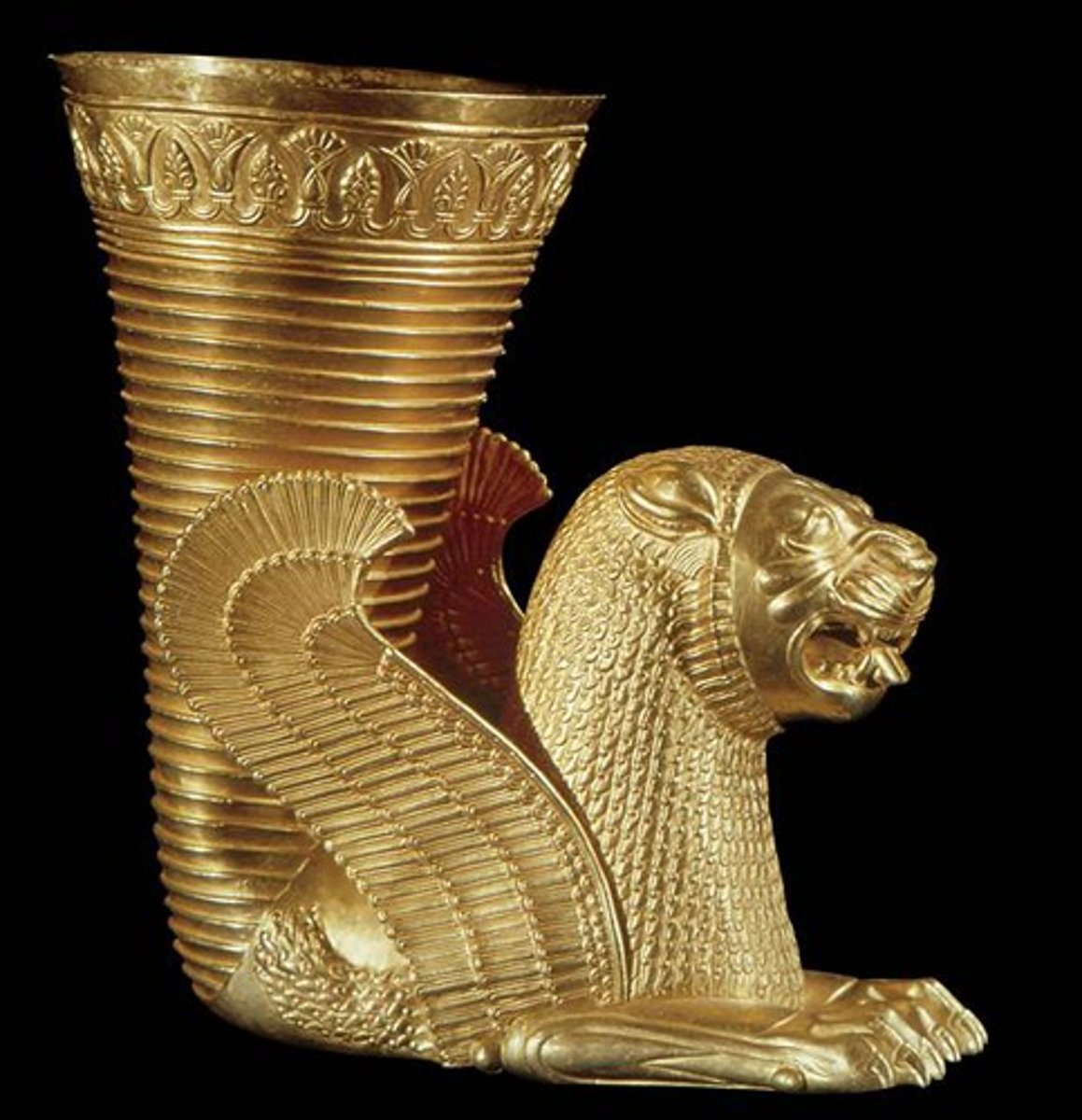
Rhyton in the form of winged lion, 400-200BCE
-Persian
-Lion with wings, goat with horns
-made of gold
-cone shape for wine, open mouth is a spout to drink out of

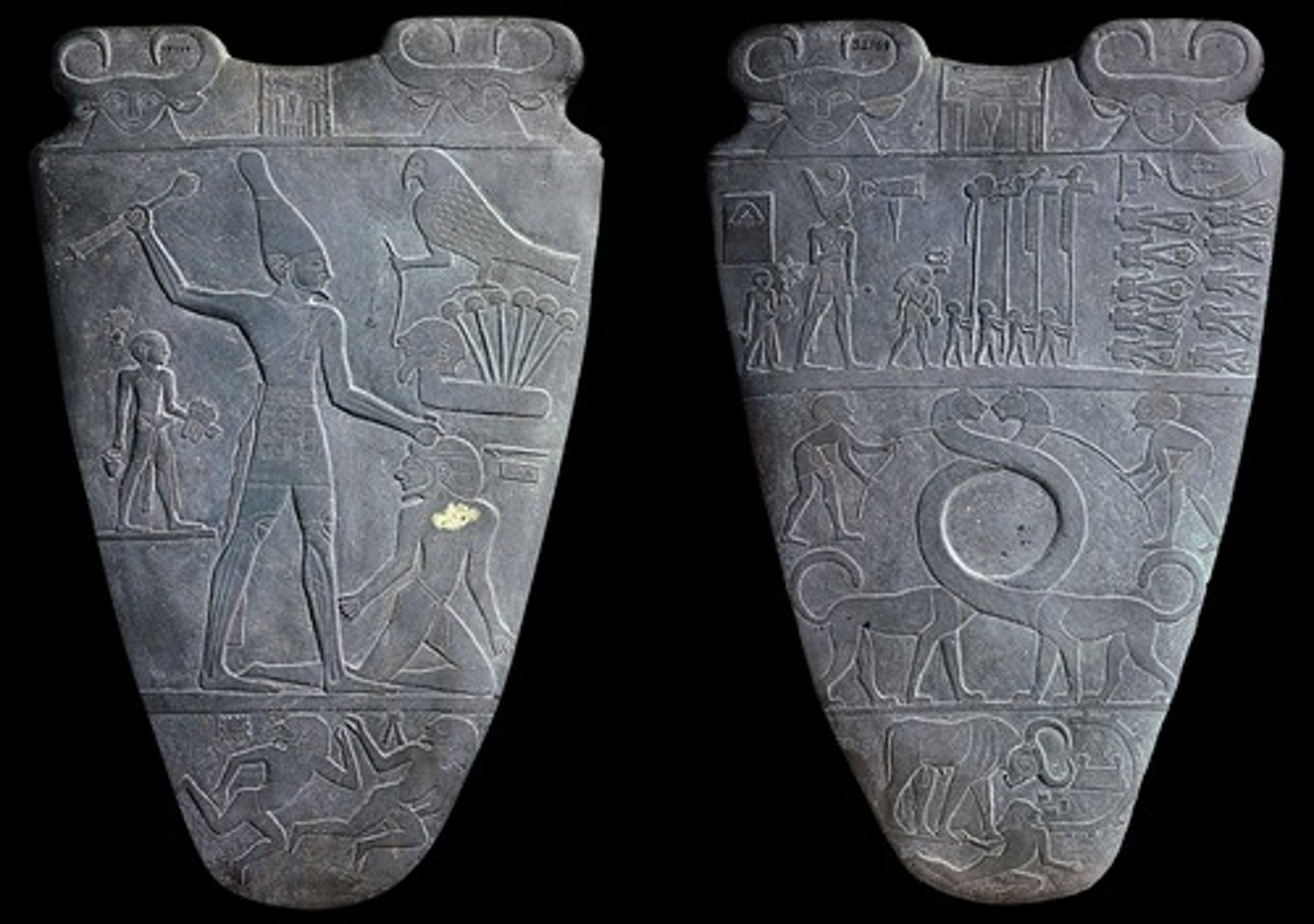
Palette of Narmer from Hierakinpolis, Egypt, 3000-2920BCE
-egyptian
-made of hard stone
-decorated in low relief
-king in center conquering his enemies, wears a crown of upper egypt
-Horus represented by falcon
-symbolism: falcon, cattle
-use of hieroglyphics

Rosetta Stone, 196BCE
-egyptian
-stele, basalt slab
-unlocked key of ancient egyptian writing and history
-same text written in 3 different languages: Greek, hieroglyphics, Demotic
-Kept today in London, England

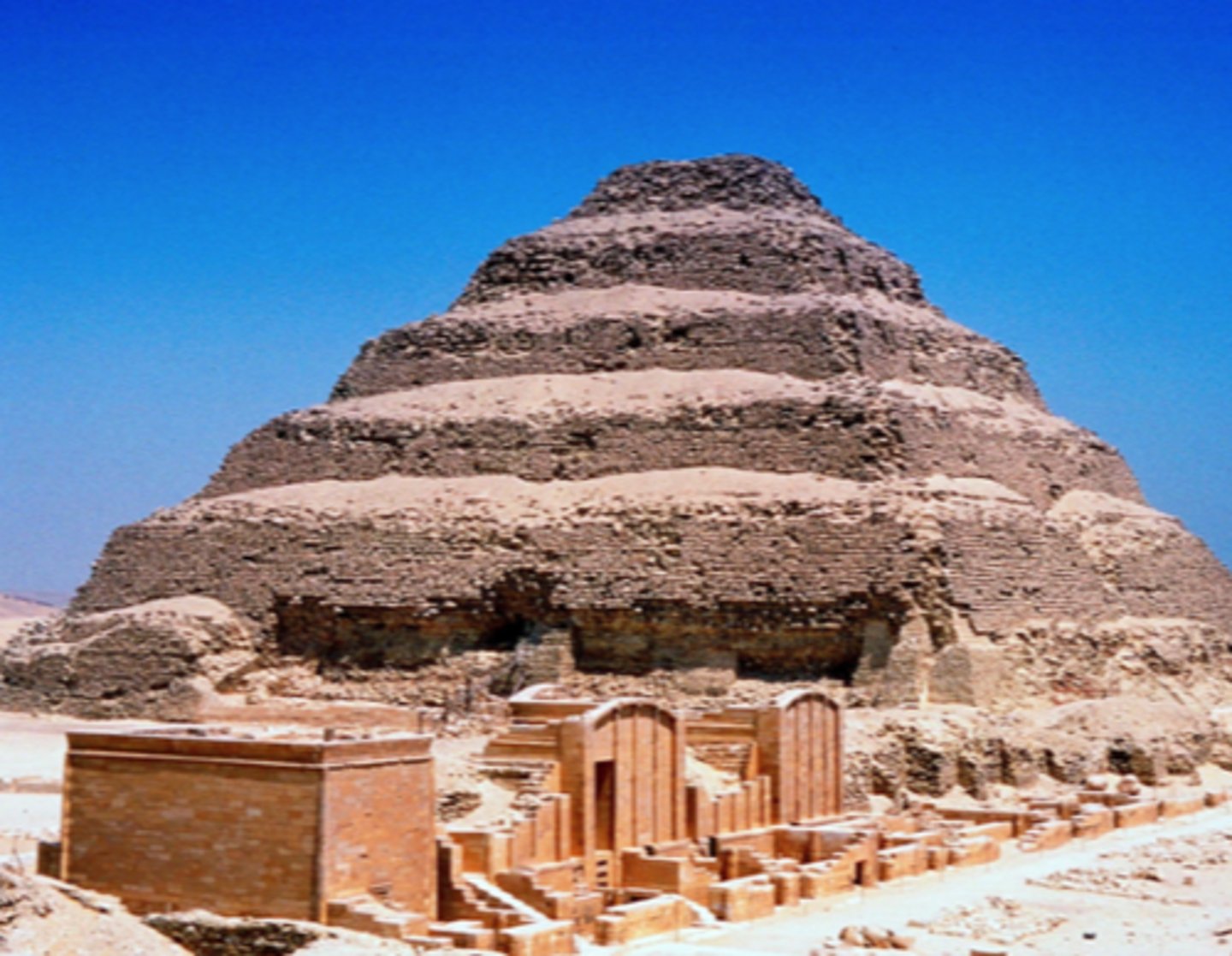
Stepped Pyramid of Zoser (Djoser) at Sakkara, 2750BCE
-egyptian, third dynasty
-first monument constructed
-tomb for Pharoah Zoser who ruled 3rd dynasty of old kingdom
-hard stone, built to preserve body and house the spirit, which survives after death
-Dedicated to king who commissioned it (Djoser)
-King is considered a god in Egypt
-symbolizes egyptian preoccupation with death

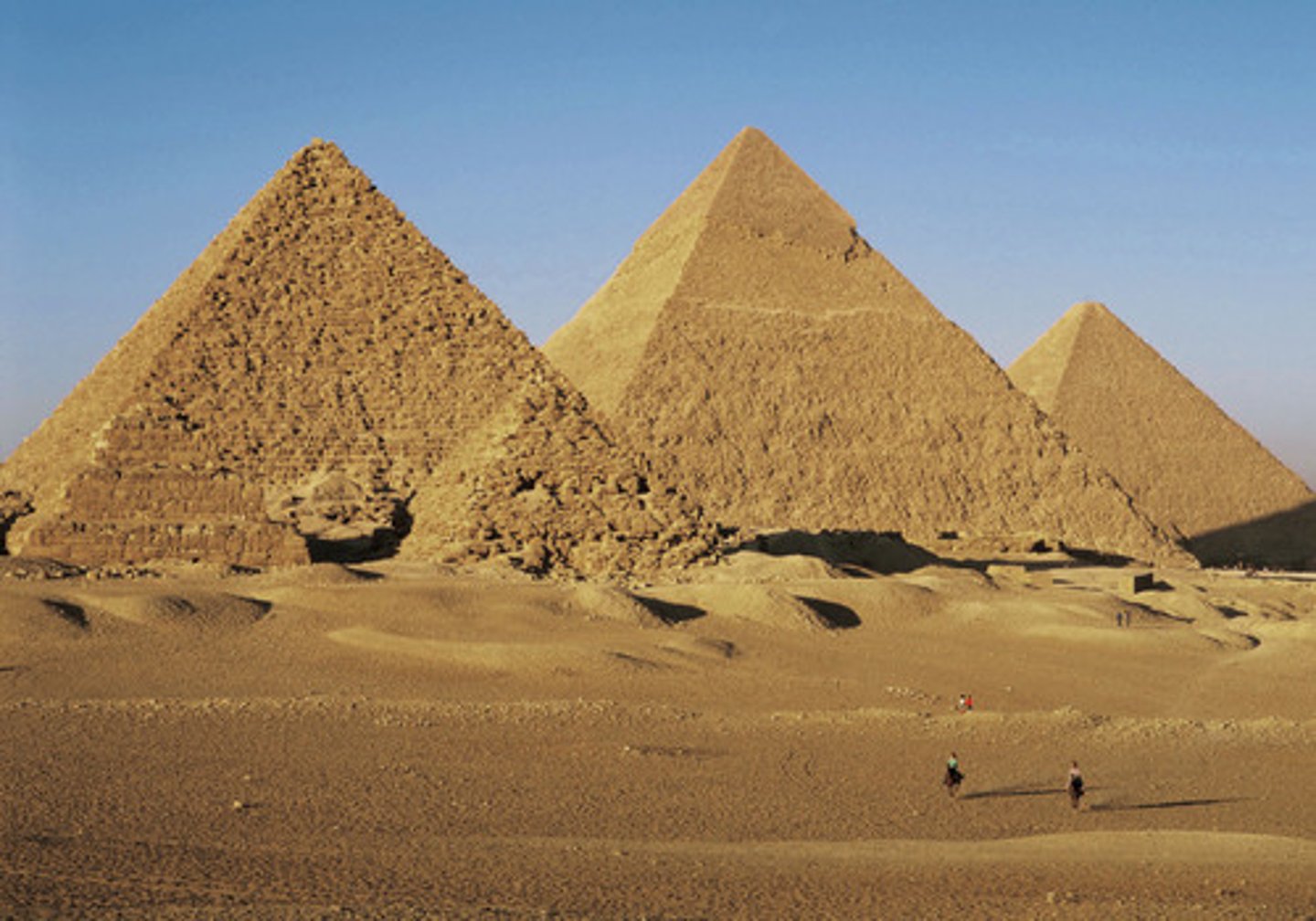
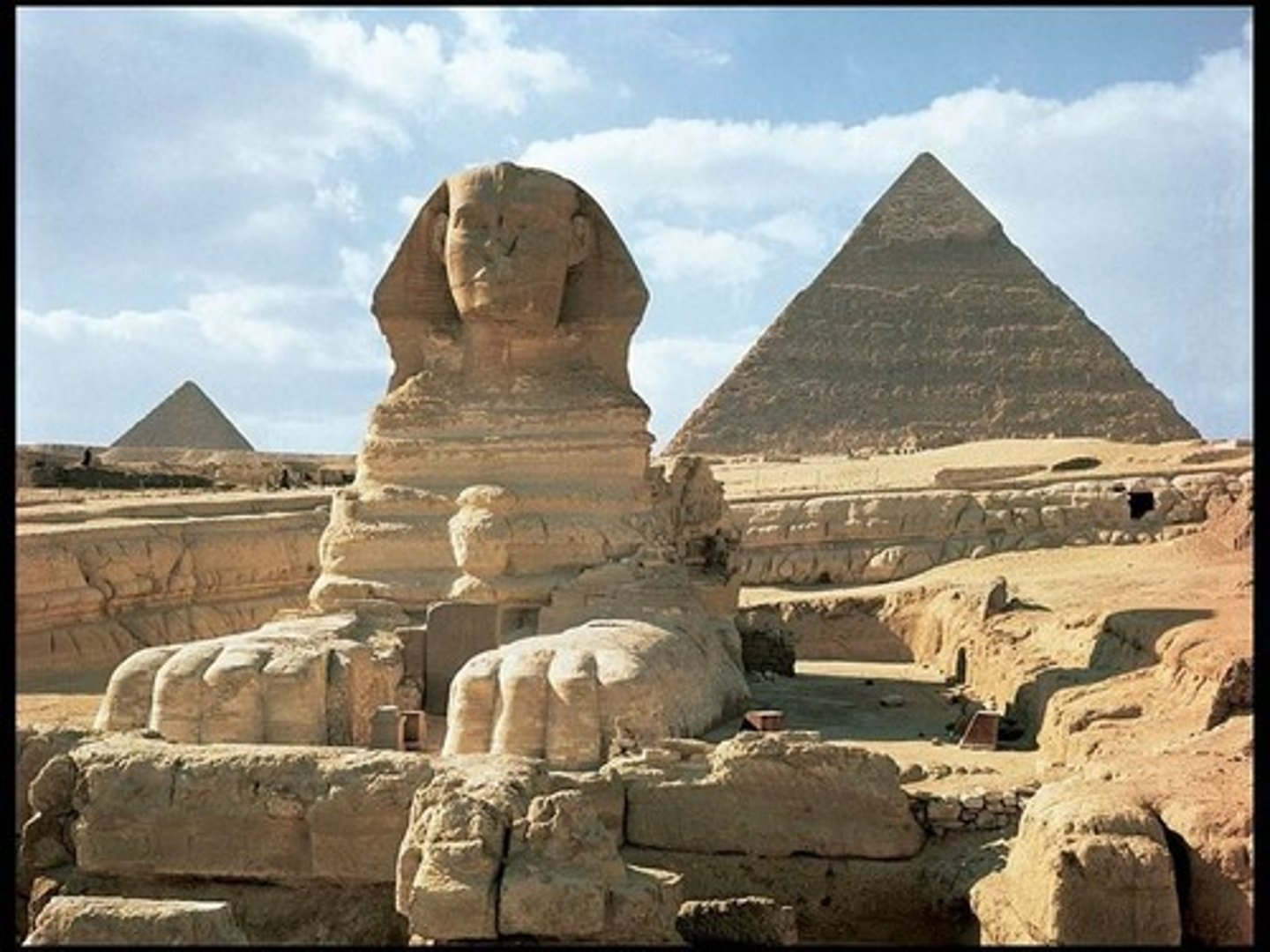
The Great Pyramids of Giza, 2550-2472 BCE
-egyptian, 4th dynasty of old kingdom
-Middle pyramid: Pyramid of Khufu, 480 ft tall (know as the great pyramid)
-Left: Khafre
-Right: Menkare
-They were not all built at the same time
-mummy and treasure placed inside
-linked to Nile river
-It was free labor and spent decades building a single pyramid

Great Sphynx at Great Pyramids, 2520-2494BCE
-Egyptian, 4th dynasty,
-carved from sandstone
-crouching lion with human head of Pharaoh--Khufu
-Wearing nemes crown
-symbol of royal power
-Made out of native rock
-240 ft long and 65ft in height

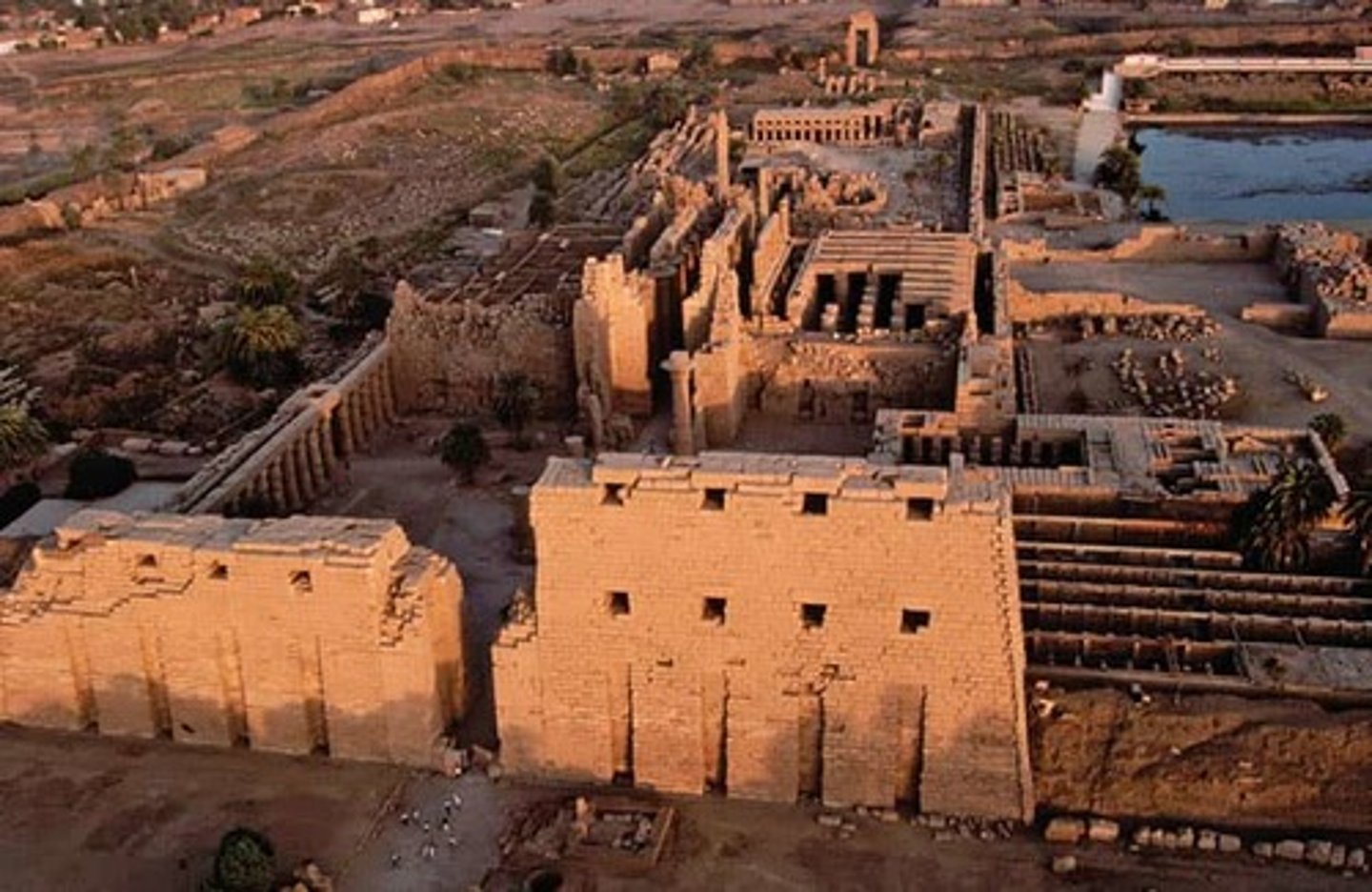
Temple of Amun-re at Karnak, 1479-1425BCE
-egyptian, new kingdom, upper egypt
-in the city thees
-Amun-re is the god of creation
-located in Thebes
-temple to celebrate deities, dedicated to Amun the Sun God
-built along central exis
-refers to passage of the soul into the afterlife
-sphynx

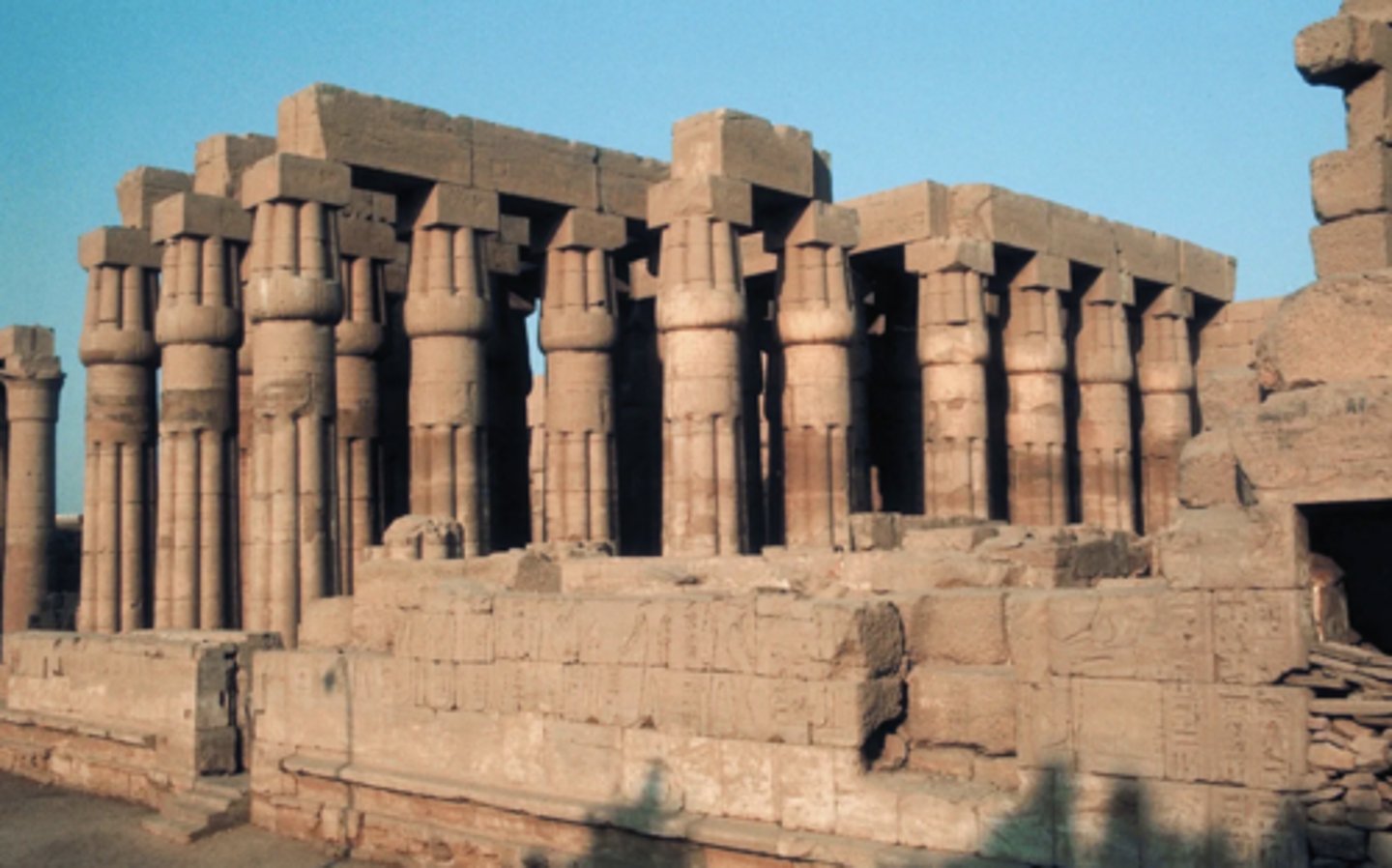
Great Courtyard inside at Temple of Amun,
-egyptian
-perimeter of columns around all sides that support horizontal beam
-example of post and lentil structure initiated by ancient egyptian architects
-roofless
-looks like papyrus flower which grows around nile

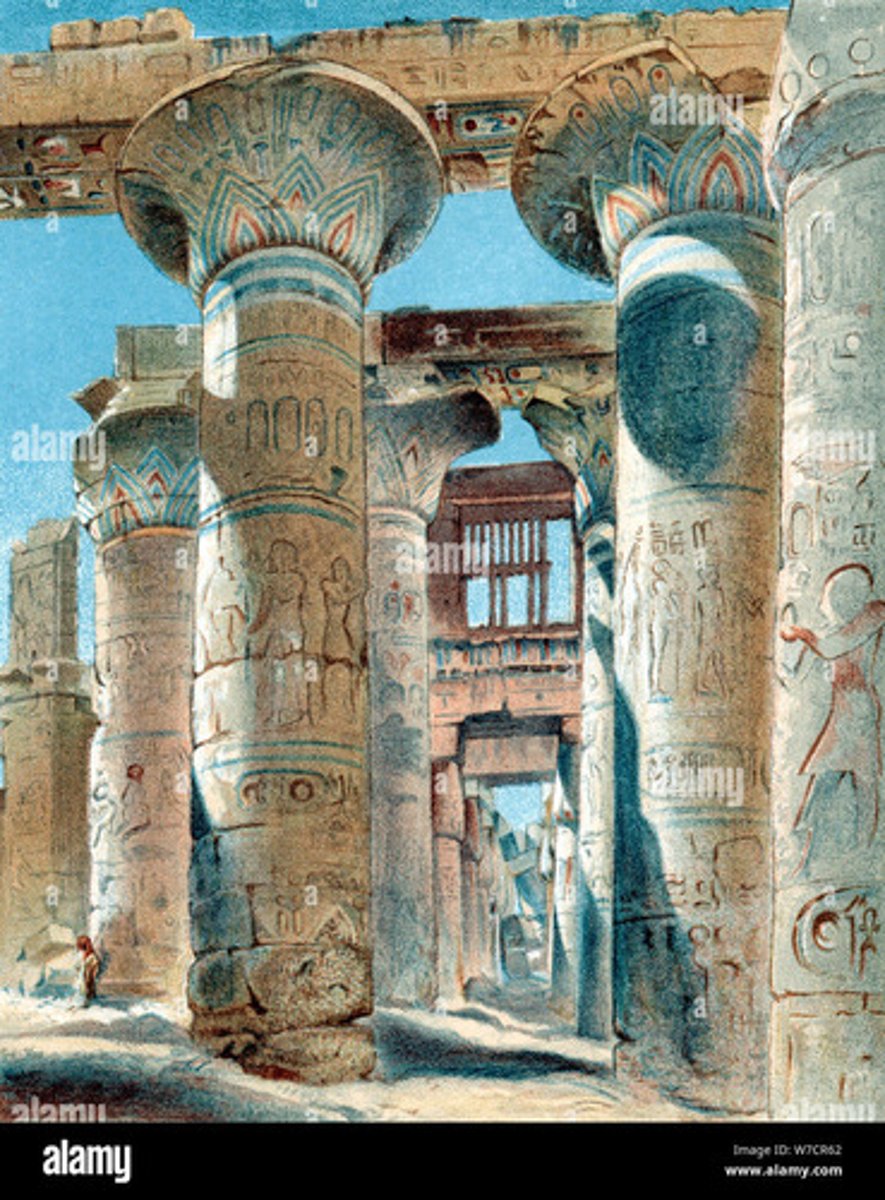
Hypostyle Hall of Temple of
Amun-re, 1290-1224BCE
-Egyptian
-where god would reveal himself to worshippers
-opened up papyrus flower
-carved from stone, painted on surface, mythological figures
-4 sided monument

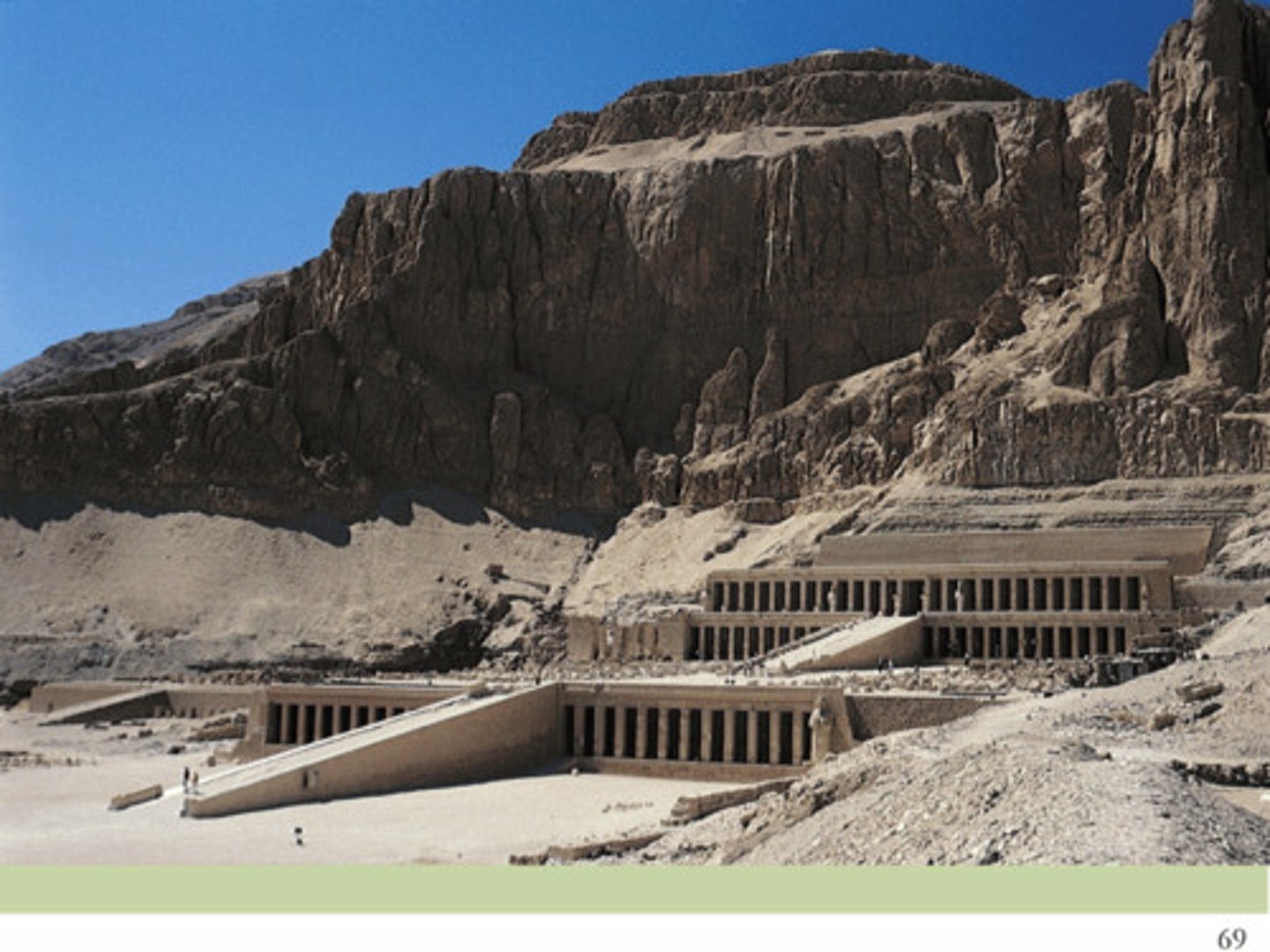
Queen Hatshepsut Temple, 1460BCE
-egyptian, 18th dynasty of new kingdom
-located at deir-el-bahari
-funerary/mortuary temple, commemorates egyptian queen
consists of several levels arranged along central axis in form of terraces
-innermost chamber is inside rock
-Again the post and lentil system

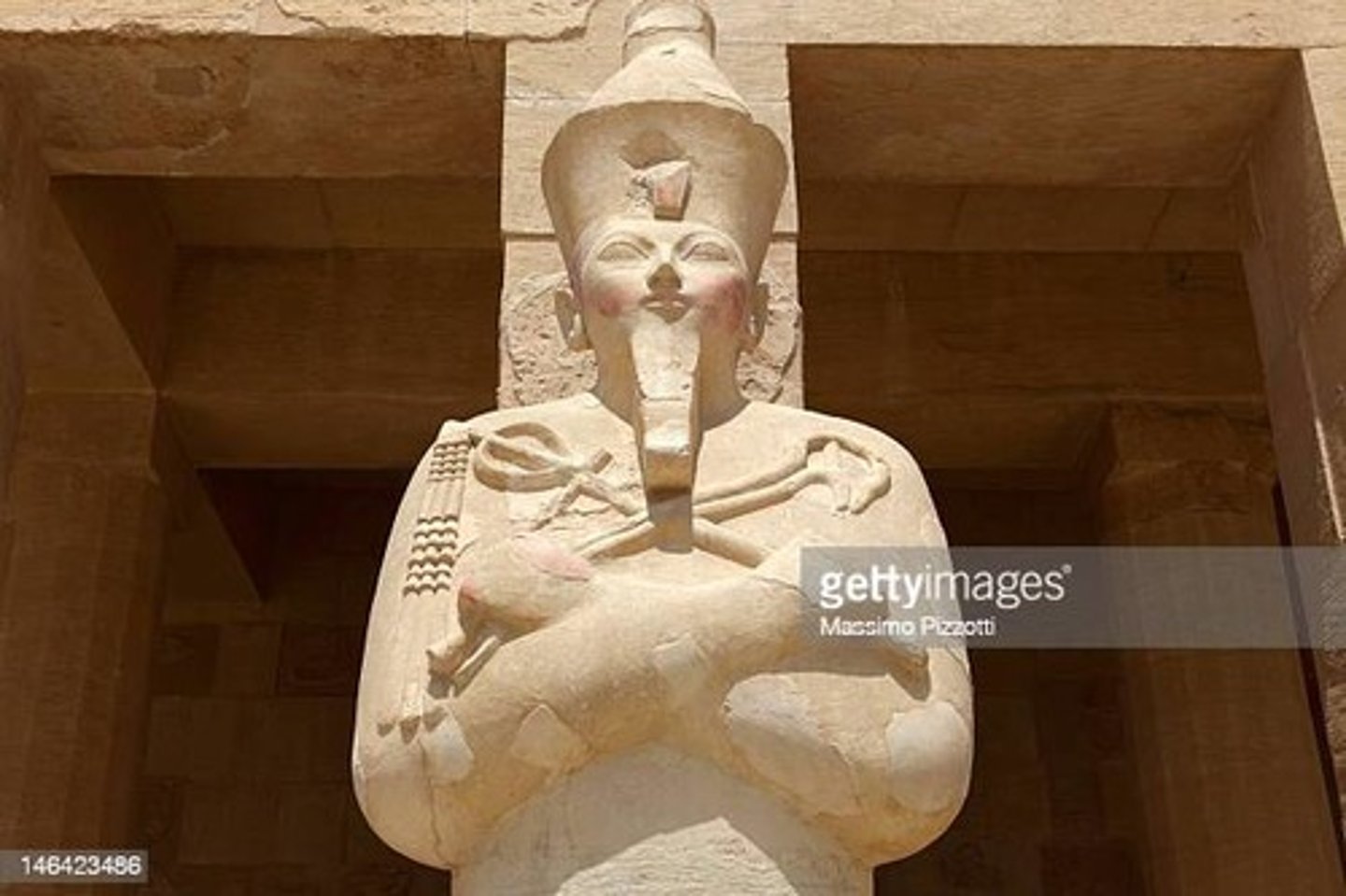
Statue of Osiris at Deir el-Bahri, 1473-1458BCE
-egyptian, 18th dynasty
-god of underworld
-was once a Pharaoh

Anubis from Temple of Hatshepsut, 1473-1458BCE
-egyptian
-fresco painting
-prepares mummy of pharoah for passage into afterlife
-royal association
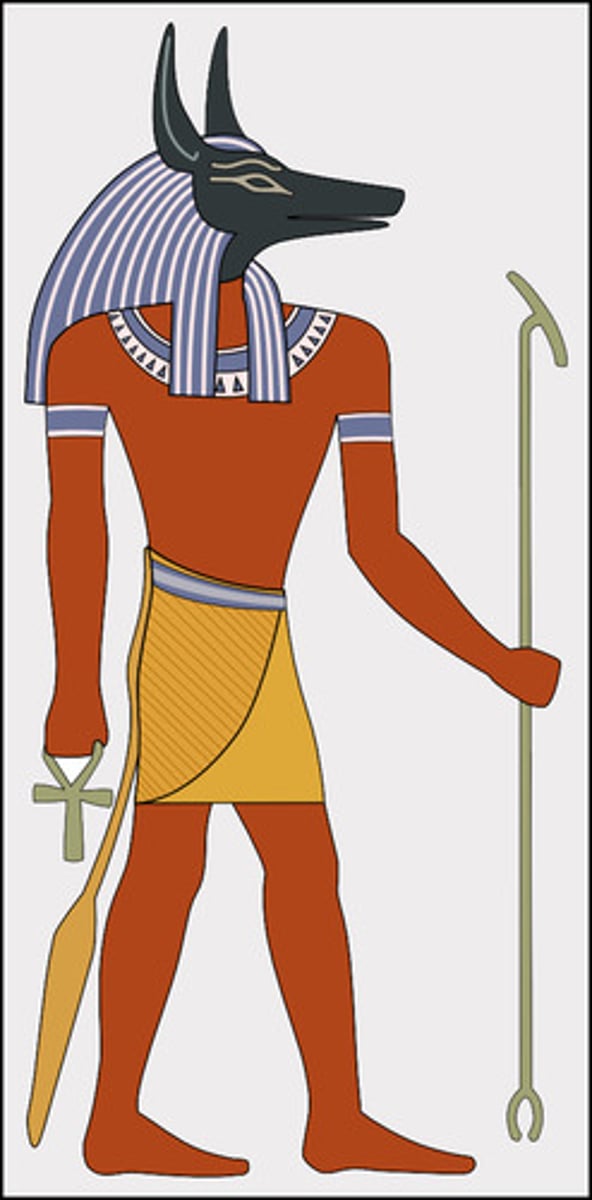
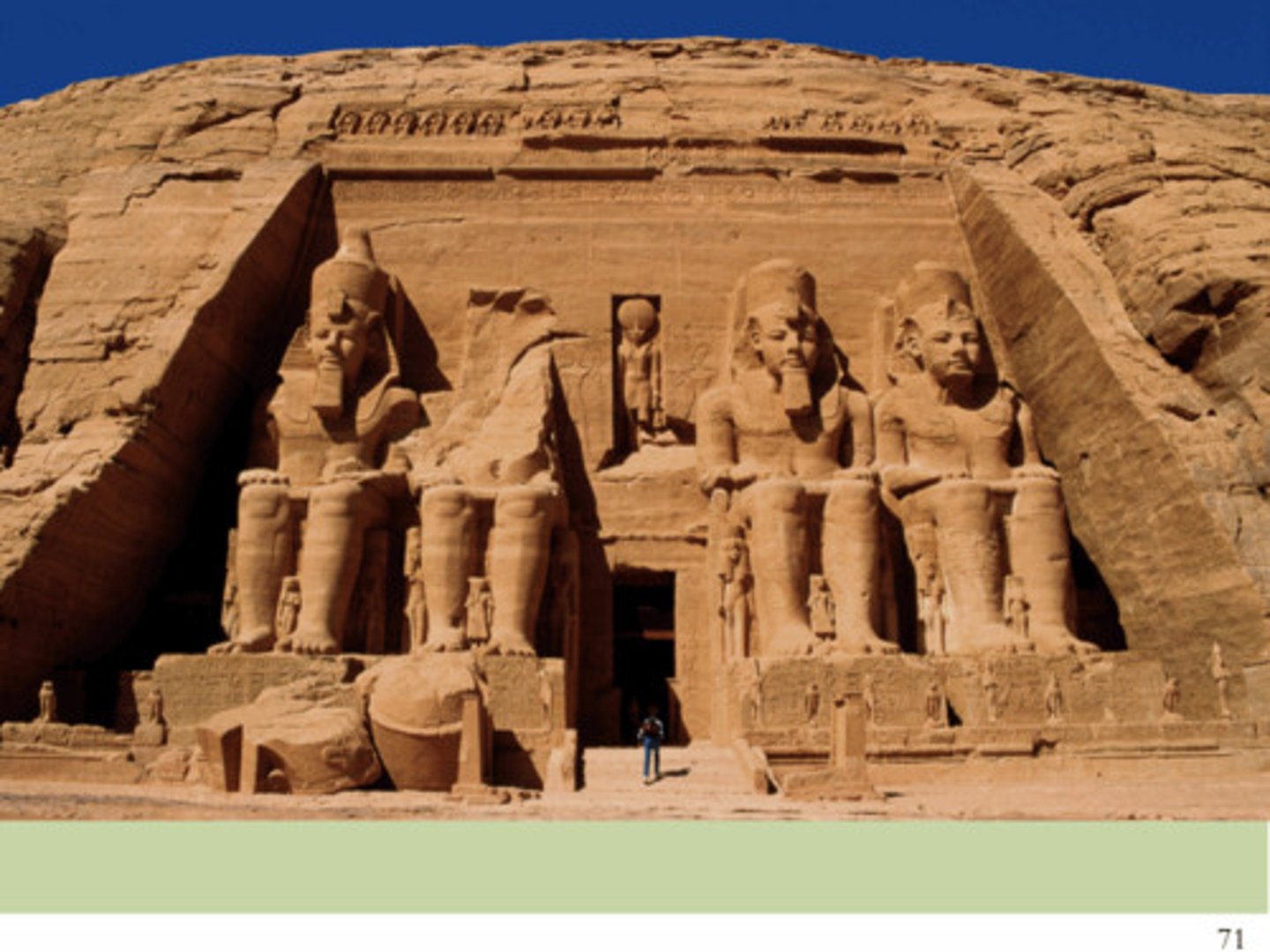
Abu Simbel Temple honoring Ramses II, 1290-1224BCE
-egyptian, 19th dynasty
-traditional temple of new kingdom
-along nile river
-Rock-cut temple; carved out of cliff space, interior passes into rock hollowing out spaces
-colossal statues of Ramses II in seated pose
-contain inscriptions
-uraes on statue which is a royal symbol

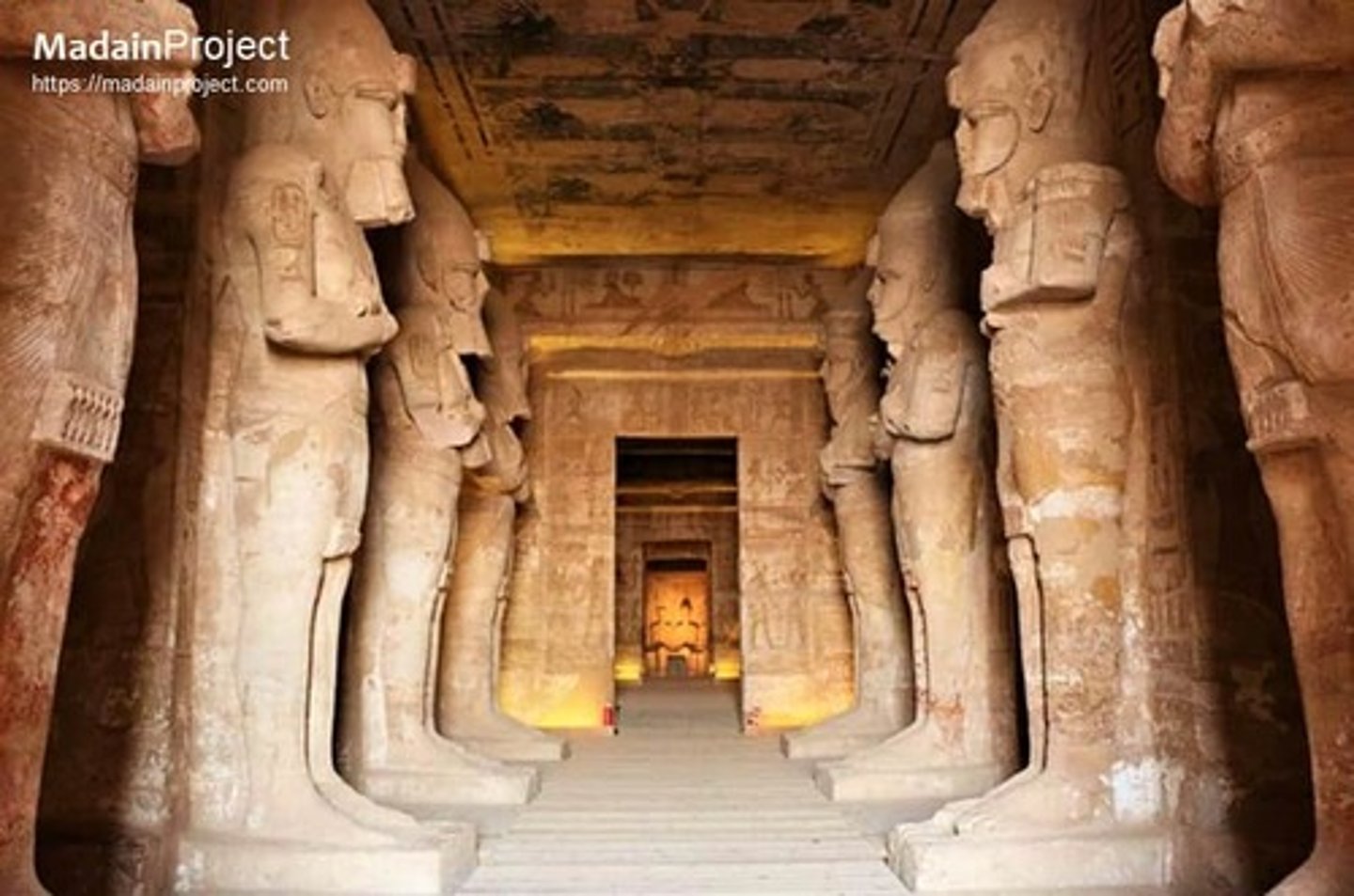
Hall of Pillars at Abu Simbel Temple, 1290-1224 BCE
-egyptian
-ramses adopting pose of osiris
-built in a way that during one time of the year (spring equinox) the sun rays follow a path right through the center of the temple
-renews the power of the earth and authority of king
-Relief images carved on the stone surface
-attempted to save the temple by cutting it up and transferring it (1960s)
-rescue archaeology, saving it from being destroyed by transferring it
-equinox was preserved after transportation

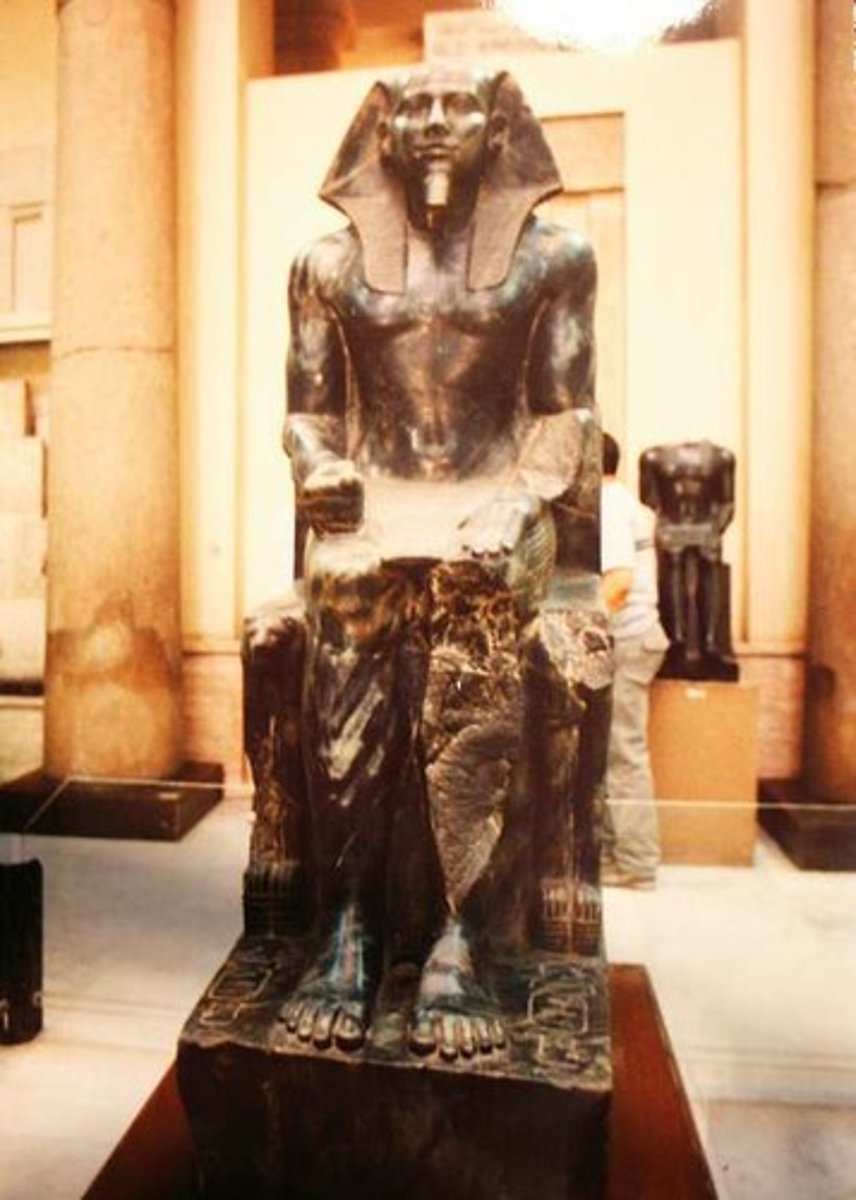
King Khafre, 2500 BC
-life-size in scale
-seated pose
-made out of diarite
-4th dynasty

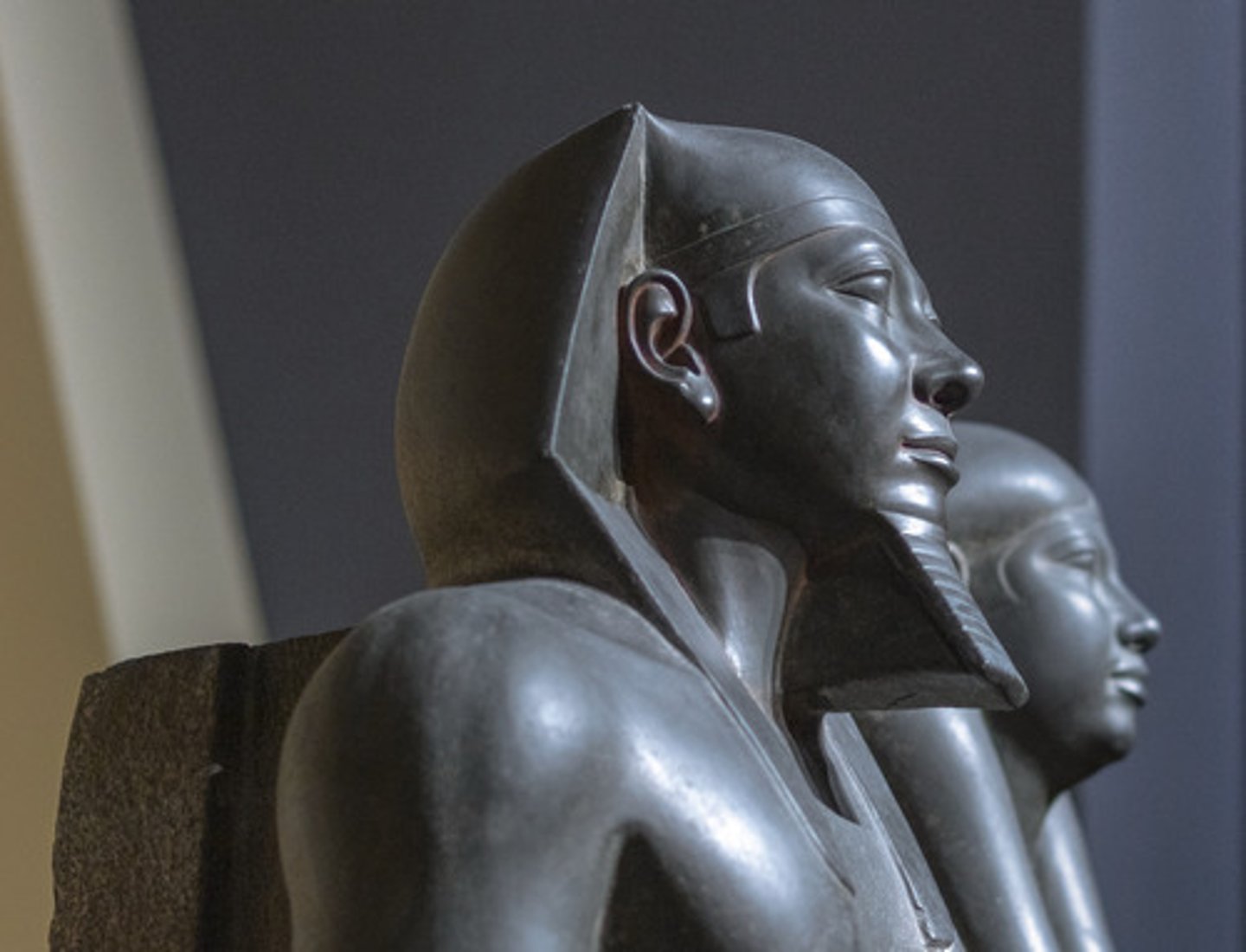
Menkaure, 2530 BCE
-egyptian sculpture
-placed in valley temple connected to his pyramid
-diorite
-portrait, formal pose, wearing false beard
-figure of falcon god Horace, associated with kingship in Italy
-carved using bronze tools
-calm, composed expression on face, has complete authority

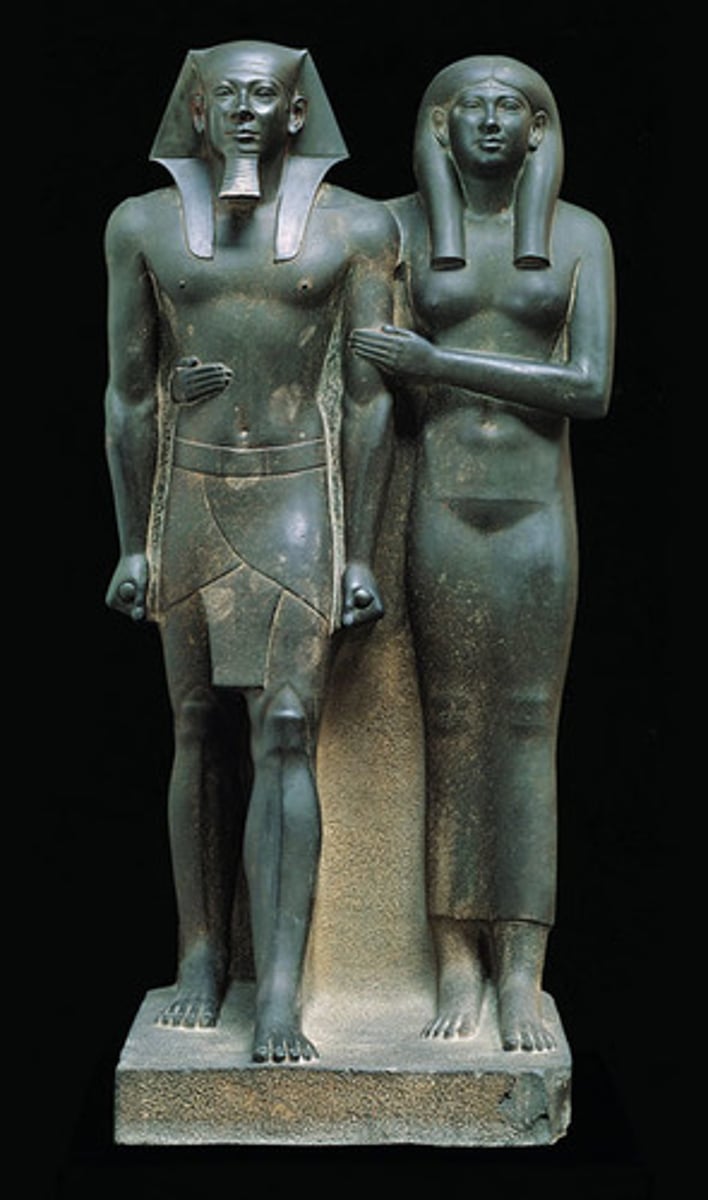
Menkaure and His Wife, 2490-2472 BCE
-egyptian sculpture
-in standing pose, a traditional pharoah pose
-moving forward with left leg first
-clenching fists, pursuing path into afterlife
-represents notion that king is following prescribed path into the afterlife

Canon of proportions
formula for shaping figures
-18 units to the top of the head
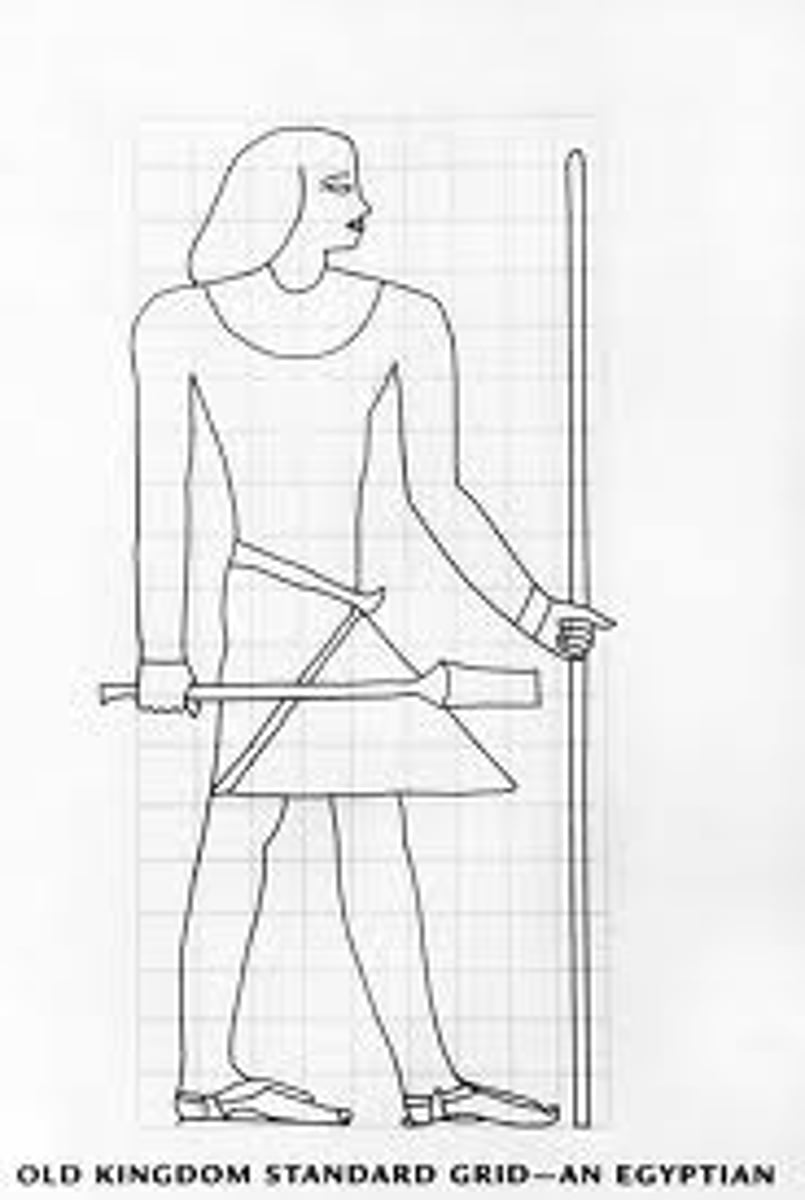
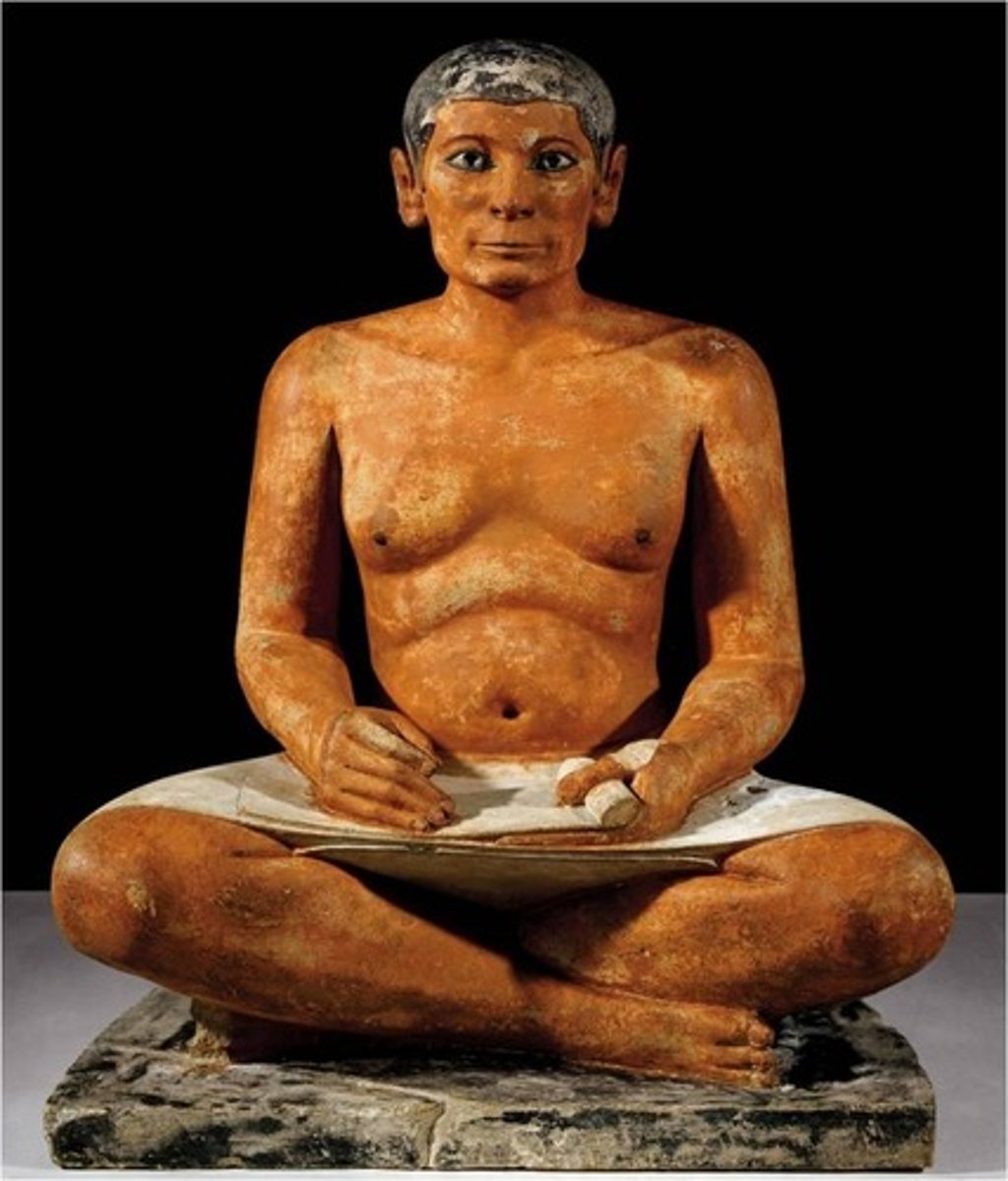
Seated Scribe, 2500 BCE
-egyptian sculpture, 4th dynasty, old kingdom
-scribe, high status, recorded laws pharoah commissioned
-painted limestone
-canon of proportions did not apply, show signs of ages, eyes are made of crystal

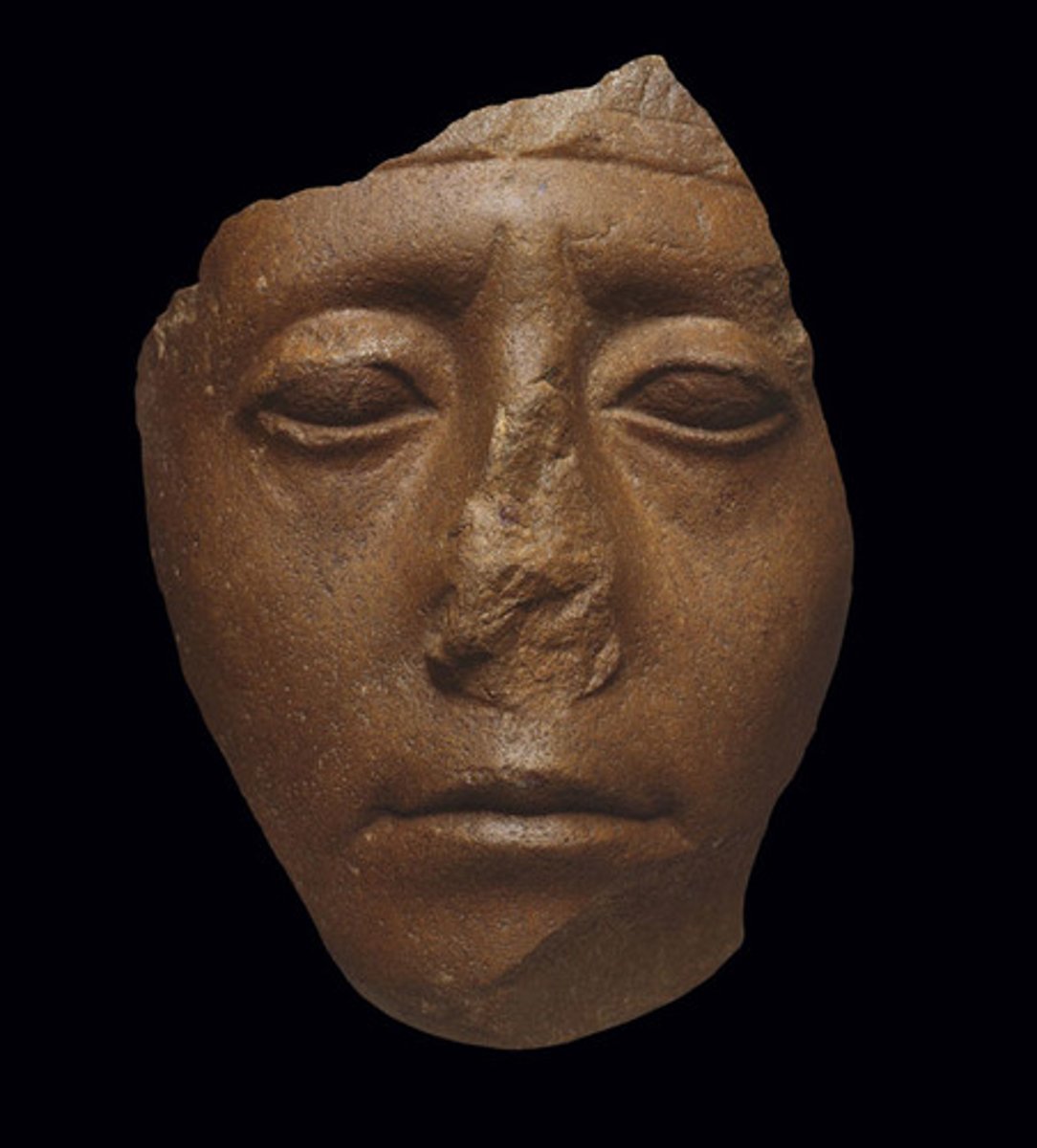
Pharoah Senusret III, 1850 BCE
-egyptian sculpture, 12th dynasty of middle kingdom
-hyskos, caused destruction in egypt, changed egyptian sculpture
-change is reflected in royal portraiture; heavy lids, creases by nose, contributes to mood, captures prevailing attitude of the time

Amenemhat III, 1850 BCE
-egyptian sculpture, 12th dynasty of middle kingdom
-heavy lids and creases
-wearing crown of upper egypt
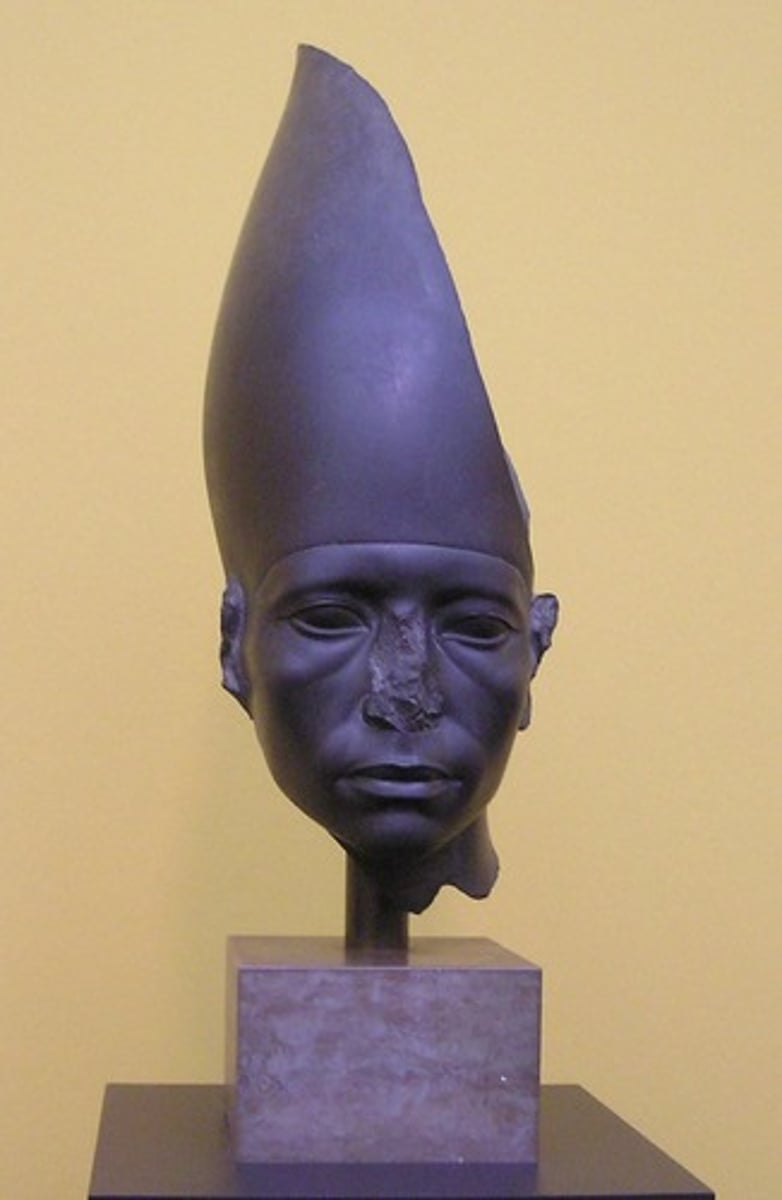

Akhenaten, 1360 BCE
-egyptian sculpture, ruled 18th dynasty of new kingdom
-maverick, unorthodox pharoah, shifted capital to amarna in upper egypt, religion transformed, tried to establish monotheistic religion (Aten)
-declared himself sole priest of aten and son of aten
-pillar statue
-defies canon of proportions

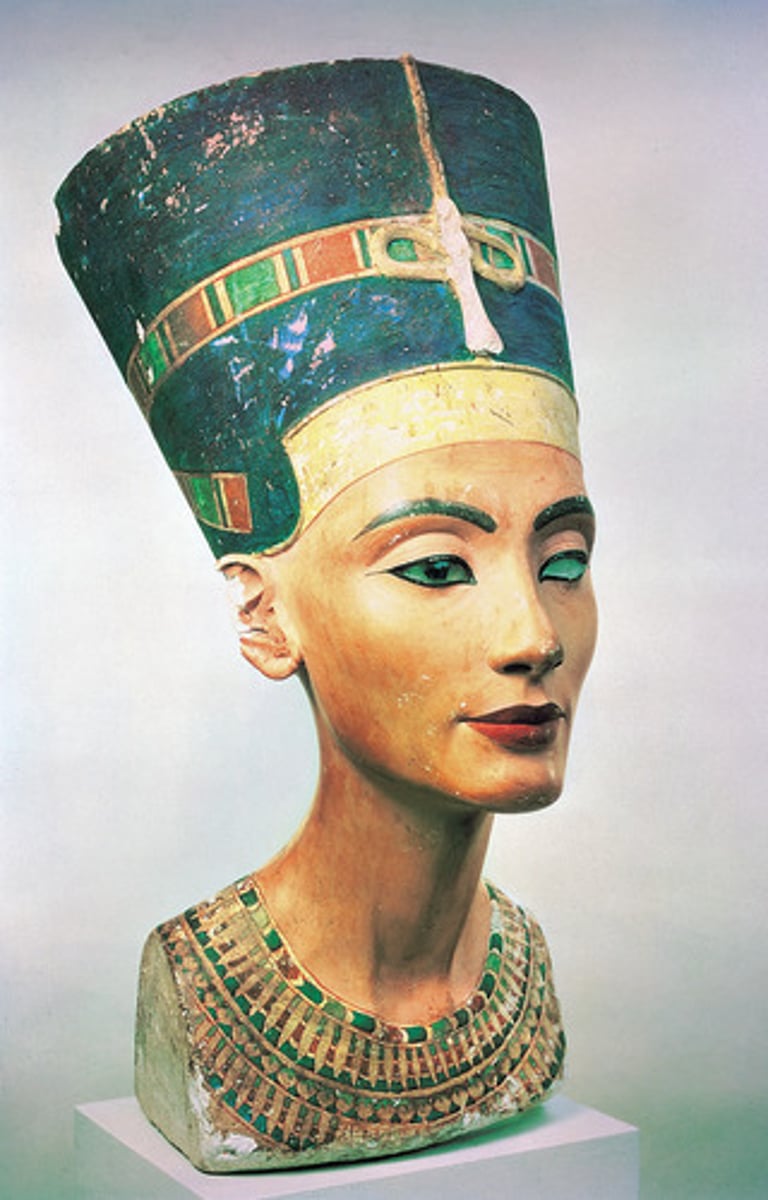
Queen of Akhenaten, Queen Nefertiti, 1353-1335 BCE
-egyptian sculpture
-elongated eyes, long slender neck
-wearing crown of new kingdom
-wearing famous necklace made of gold, and encrested stone; cloisonné
-captures her warmth
-painted limestone

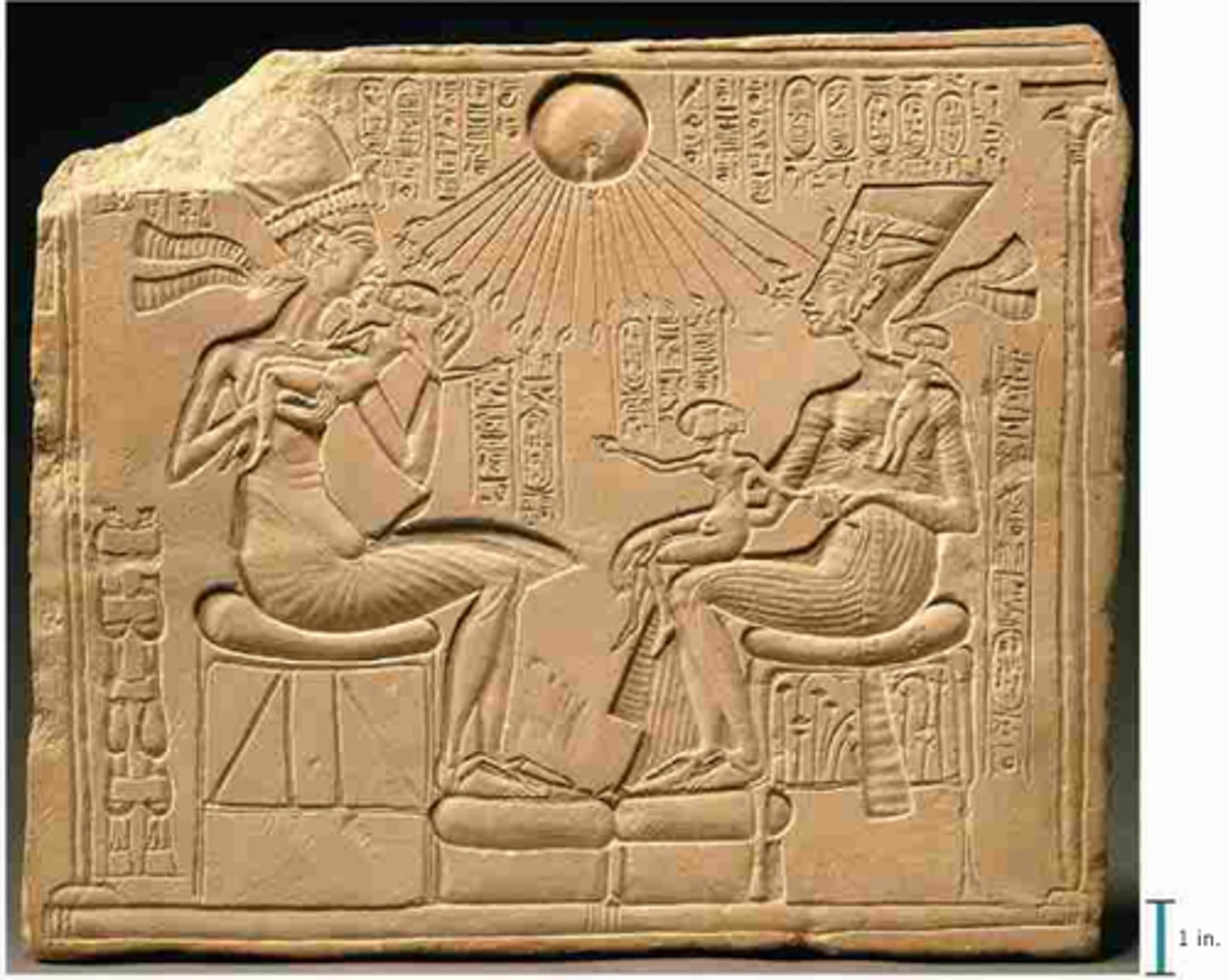
Akhenaten and Nerfertiti relief, 1353-1335BCE
-egyptian, 18th dynasty
-holding daughters, showing royal family, new sort of intimacy in court scenes
-sunken relief panel
-Aten sending sun rays out to bring fertility to the world

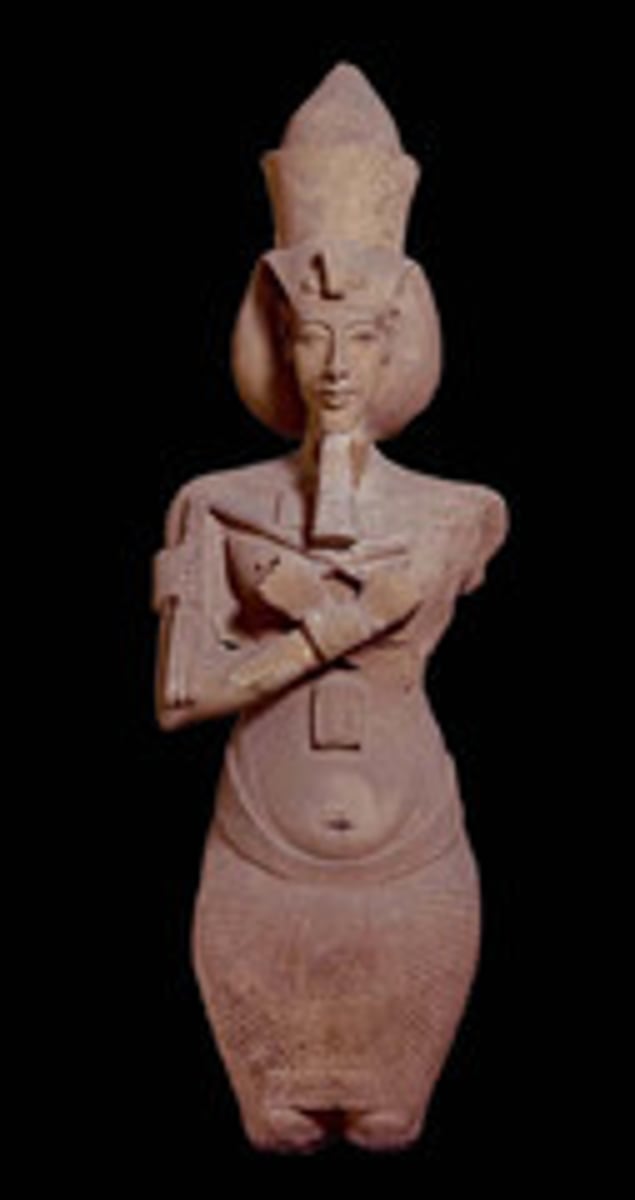
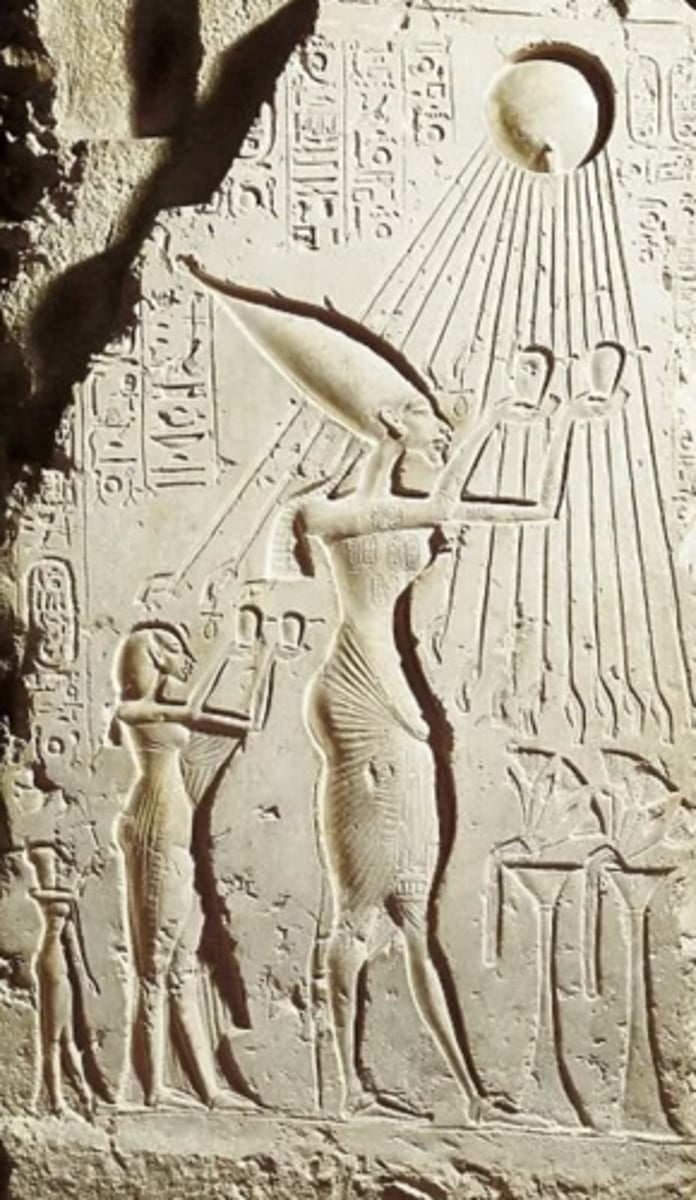
Akhenaten Making Offering to God, 1352-1336BCE
-egyptian,
-wearing pointed crown of upper egypt
-formal representation of worship of aten
-offerings placed on alter down below

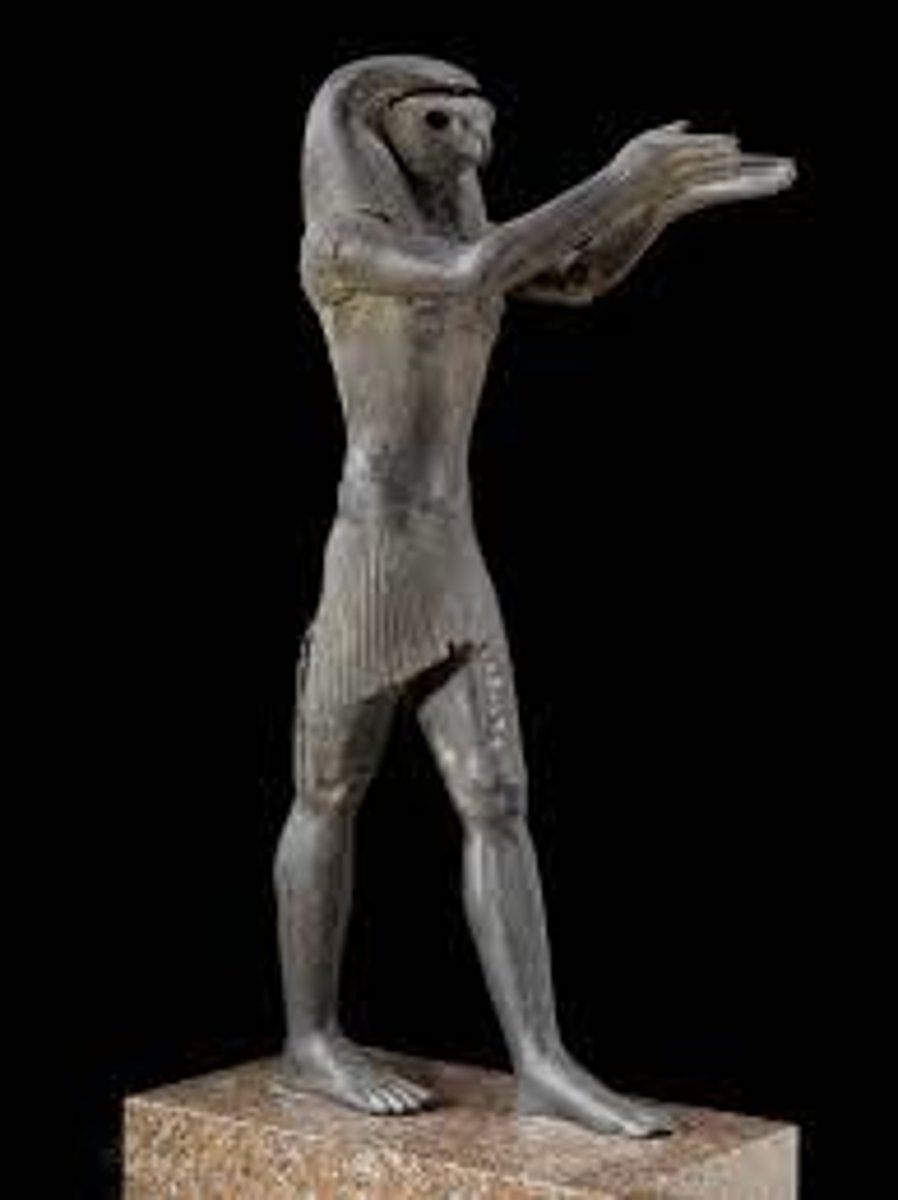
Horus
-egyptian
-falcon head attached to male body
-past reasserted importance

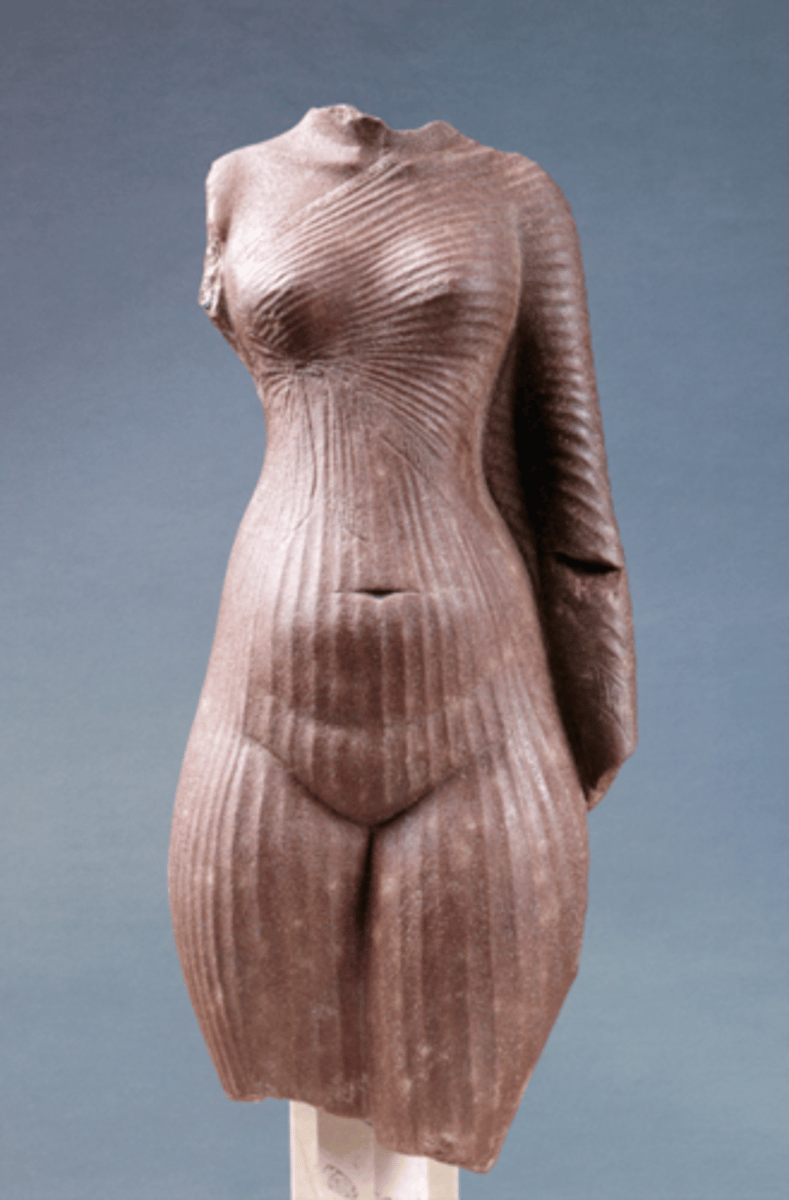
Nefertiti Torso
-egyptian

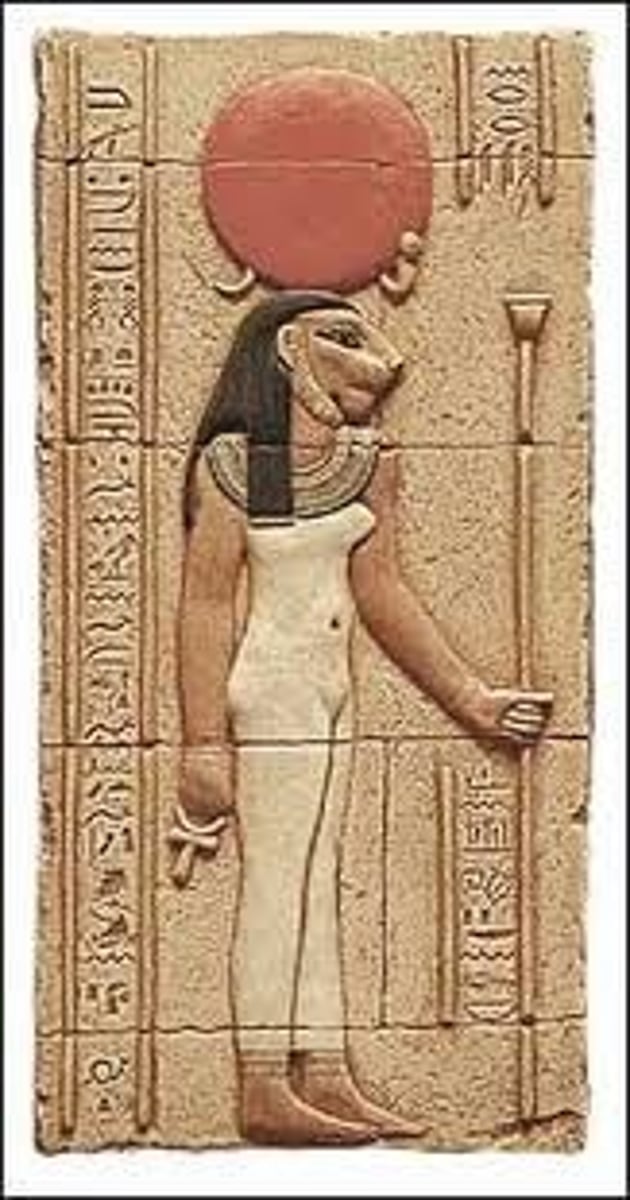
Sekhmet,
-egyptian, post armana period
-head of lion on female body
-goddess of war, plague and healing

Tomb dedicated to high official Ti, 2400 BCE
-egyptian, 5th dynasty of old kingdom
-at site of saqqara
-visions of afterlife and activities deceased will enjoy, a continuation of life
-royal hunt along nile river, hunting hippos
-low relief, painted
-papyrus plants
-narrative art in egyptian context
-canon of proportions
-sensitivity to natural world

Geese of Medum,
-egyptian
-fresco painting
-panel of geese, females coupled with males

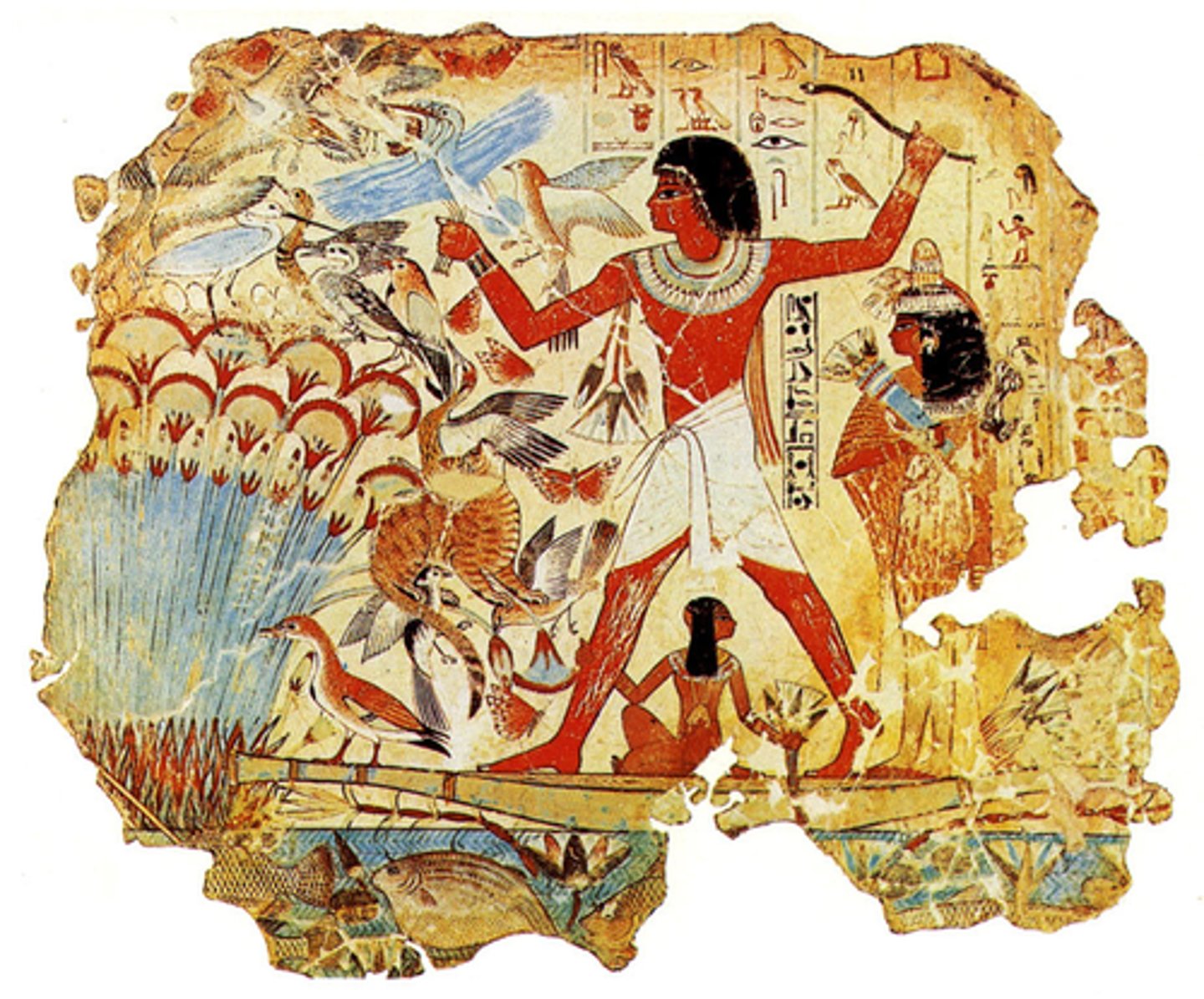
Fowling Scene from Tomb of Nebamun, 1400 BCE
-egyptian, 18th dynasty of new kingdom
-successful hunt
-prince shown with dark red fleck while females are shown in different color
-colorful scene

Book of the Dead, 1300 BCE
-egyptian
-new theme in funerary episodes, events occurred proceeding dead of high official
-document written in ink on papyrus
-frieze, continuous horizontal band for ornament
-servants carrying mummy on boat
Tomb of Rahmose,
-egyptian, 18th and 19th dynasty
-mourning the deceased as a group, official mourners
-carrying a coffin and throne
-canopic jars, contains soft organs of deceased
-color difference between males and females

Tomb of Amanakht
-egyptian
-funeral banquet in honor of deceased, vizer (overseer)
-men and women placed separately in space
-wearing wax cone on head filled with perfume
-blind harpist
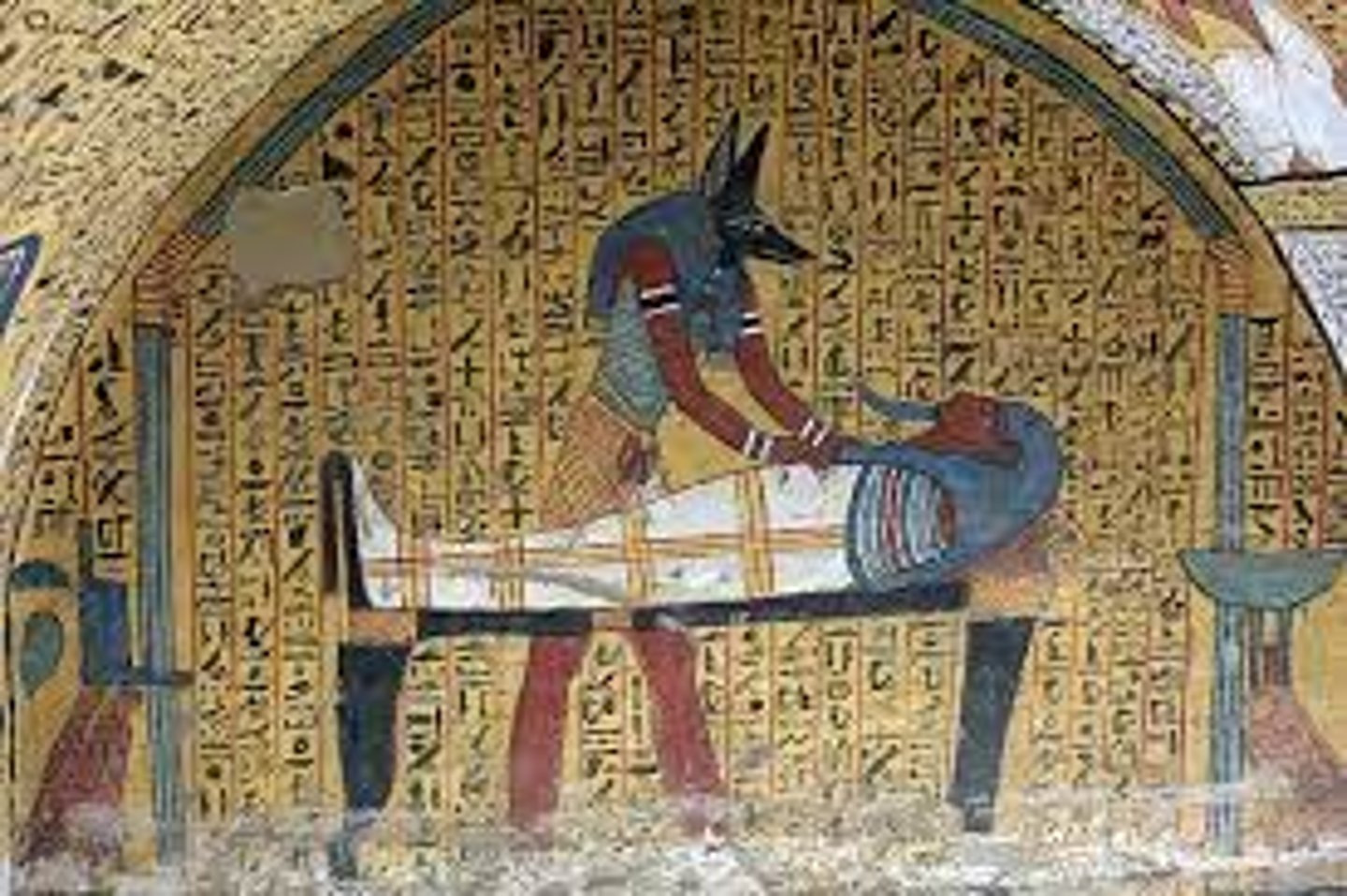
Annubis in Queen Hatshepsut Temple,
-egyptian
-completing preparation of mummy of dead pharoah
-bier

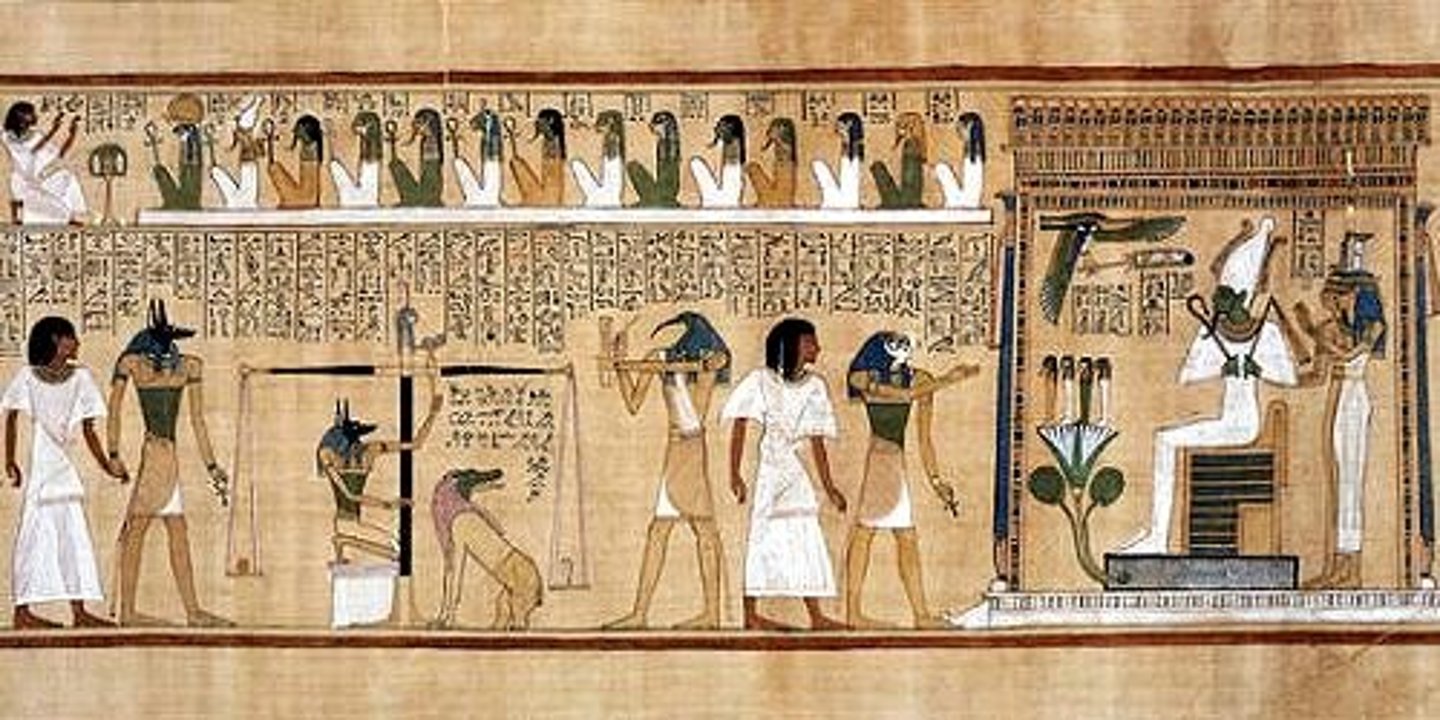
Tomb of Amanat,
-egyptian,
-weighing heart of pharoah on scale, feather on opposite side
-if balanced, pharoah earned passage to afterlife
-eschatlogy
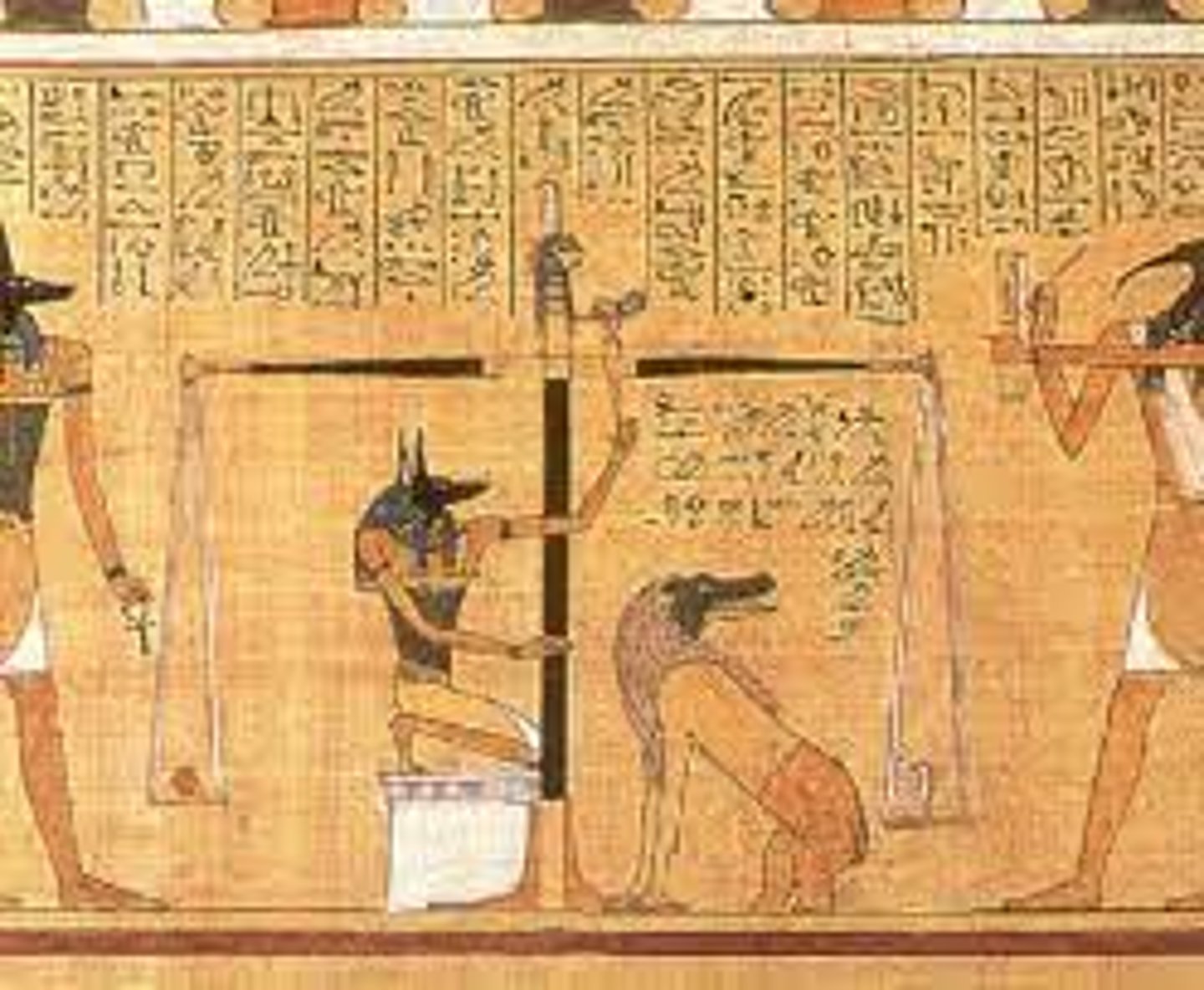
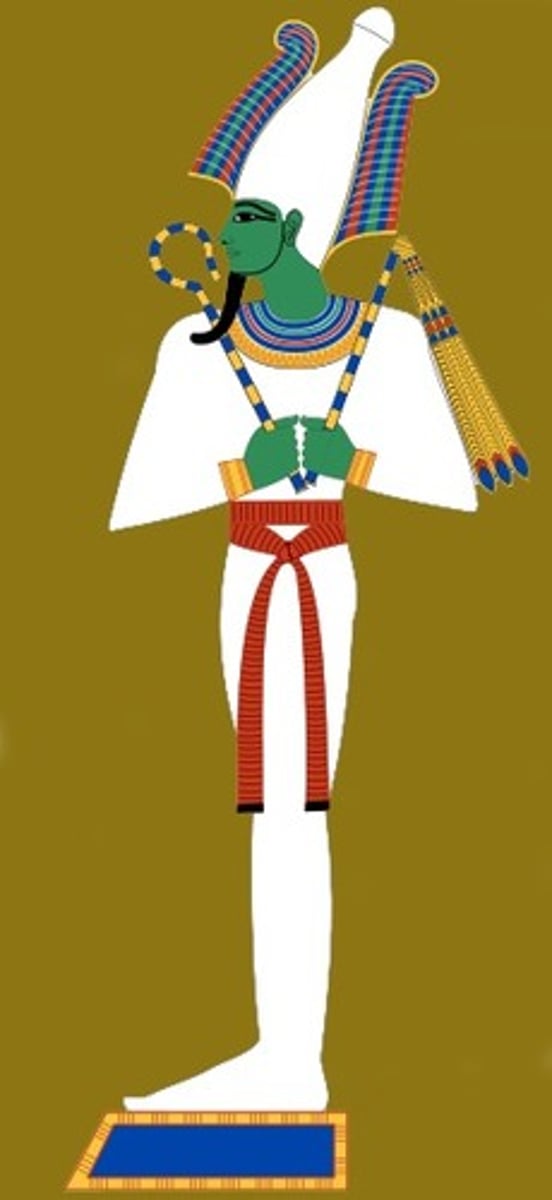
Osiris
-Important funerary deity
-God of underworld, Verifies condition of after life making sure king has happy existence after death,
-Characteristic pose
-Switch in one hand, crook in other, Symbol of authority
-Tall crown of upper egypt
-White garment down to feet
-Holds ankh Symbol of eternity

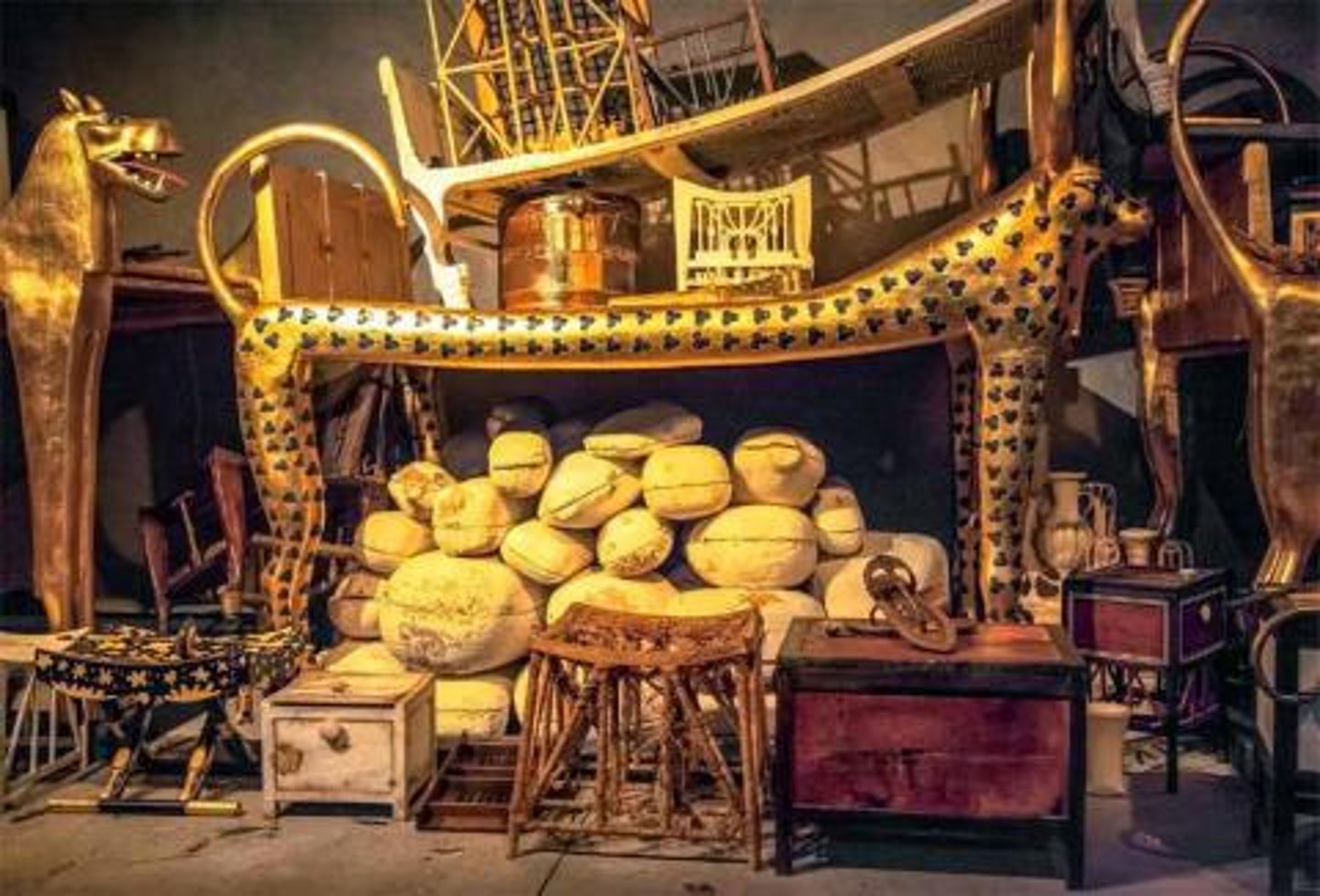
Treasure of King Tutankhamun
-egyptian,
-valley of kings
-Howard Cater found in 1920s
-nothing but gold inside, royal coffin made of gold placed inside large stone chest, done with technique called Cloisonne, inlayed gold
-mummified body of king found inside, wearing funerary mask

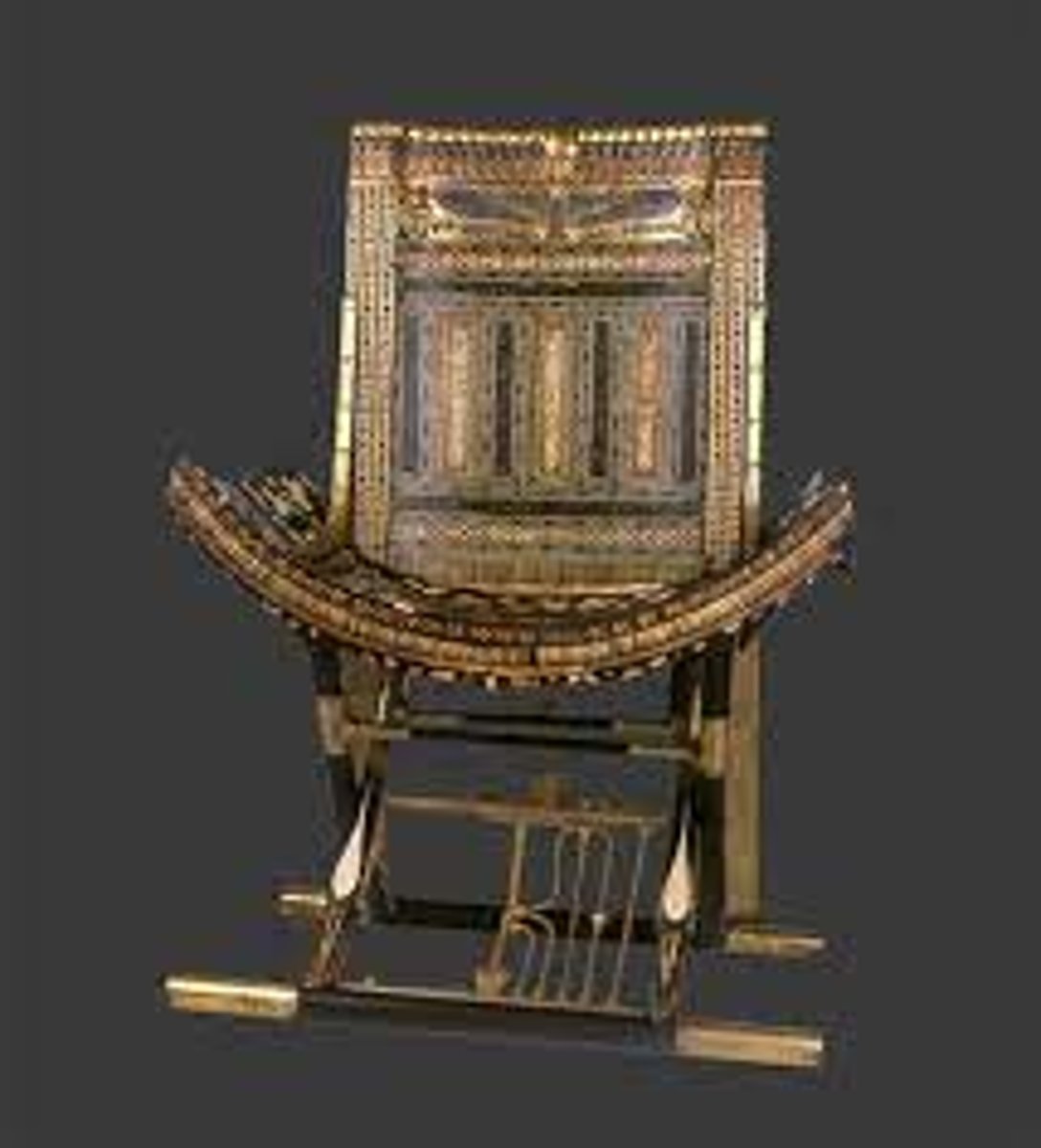
Ceremonial Throne from Tomb of Tutankhamen, 1300 BCE
-egyptian
-animal heads, lions, paws as legs of throne
-decorated in relief technique on back

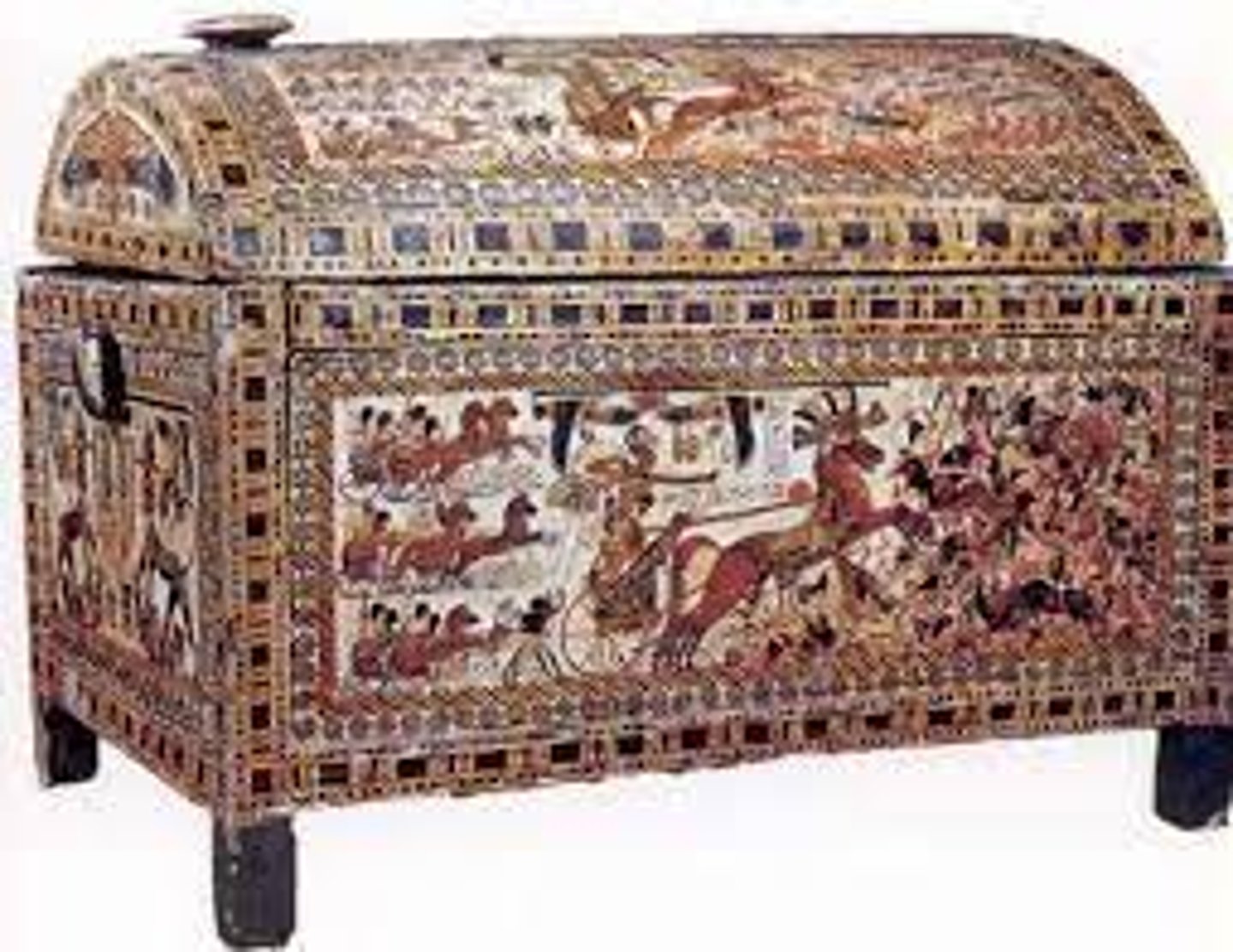
Funerary Chest from Tomb of Tutankhamen, 1333-1323 BCE
-egyptian
-decorated with gold
-relief
-falcon of horus, deity symbols

Aegean
-Many islands
-Where ancient greek civilization rises
-Cycladic art Crete - large island
-New people invade land around 2000 BCE
-Settling on island of Crete
-Spoke another language, few written records
-Minoans
-King midas Wife pasafi, Owned many large horses
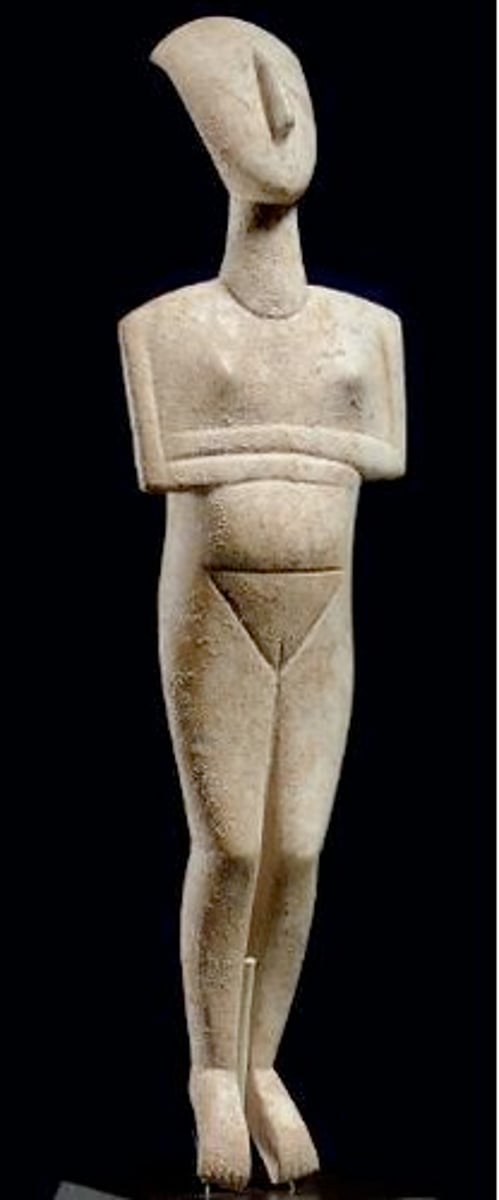
Cycladic Idol, 3300 to 1100 BCE
-Cycladic
-carved from hard marble stones, in abundance
-alert, erect statuettes
-nude female, fertility object
-votive object
-emery used to polish surface
-30 inches in heigh
-Clear sense of form
-Assumed to have religious significance

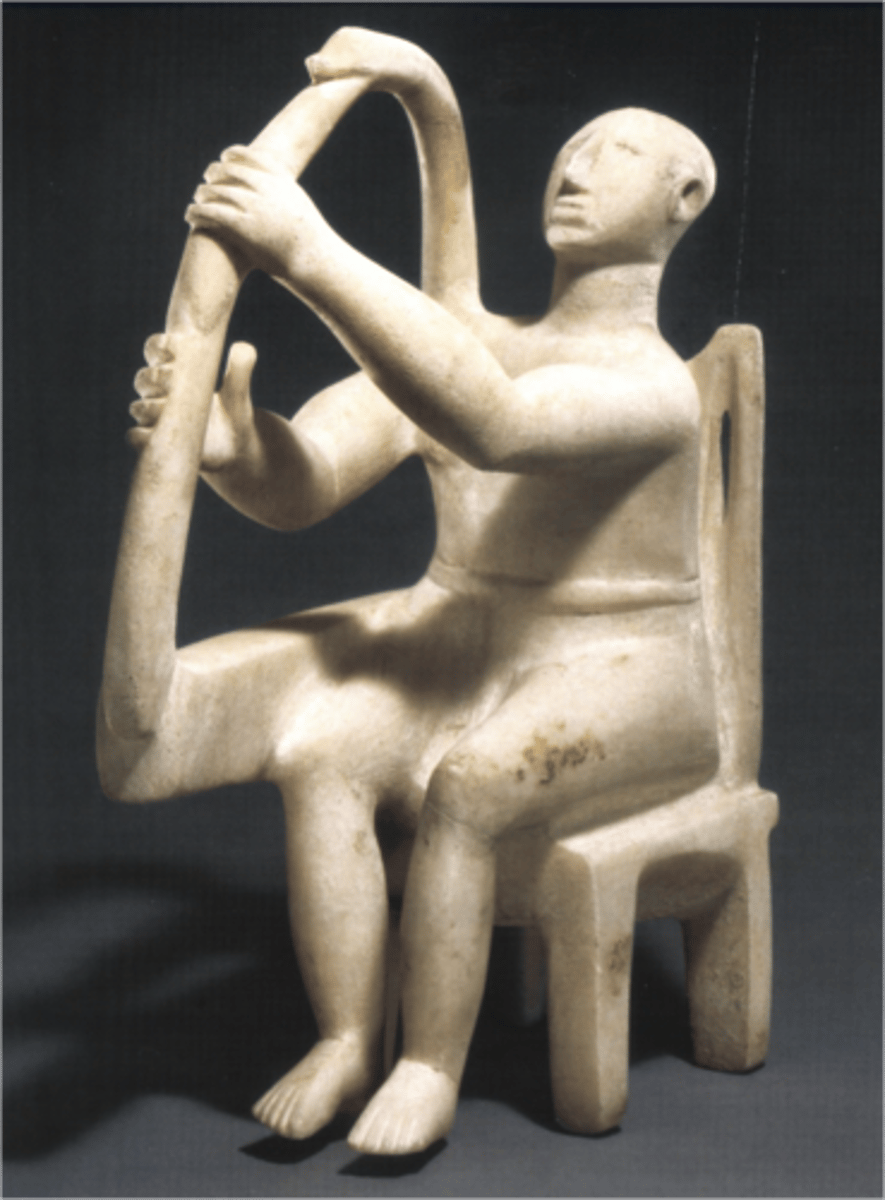
Cycladic Harpist, 2300 BCE
-cycladic
-male musician, seated, playing harp
-contemporary
-defined features on head to indicate sound, ears are profound
-early cycladic art
-There are other musician players, such as a flute
-surfaces are highly polished and finely cut using bronze tools

Palace of Midas Plan, 1700-1370 BCE
-Minoan
-Throne room
-served as administrative center for island of Crete, for gatherings
-private apartments for king
-Sir Arthur Evans looked at the site of Knossos and uncovered the Palace of Midas
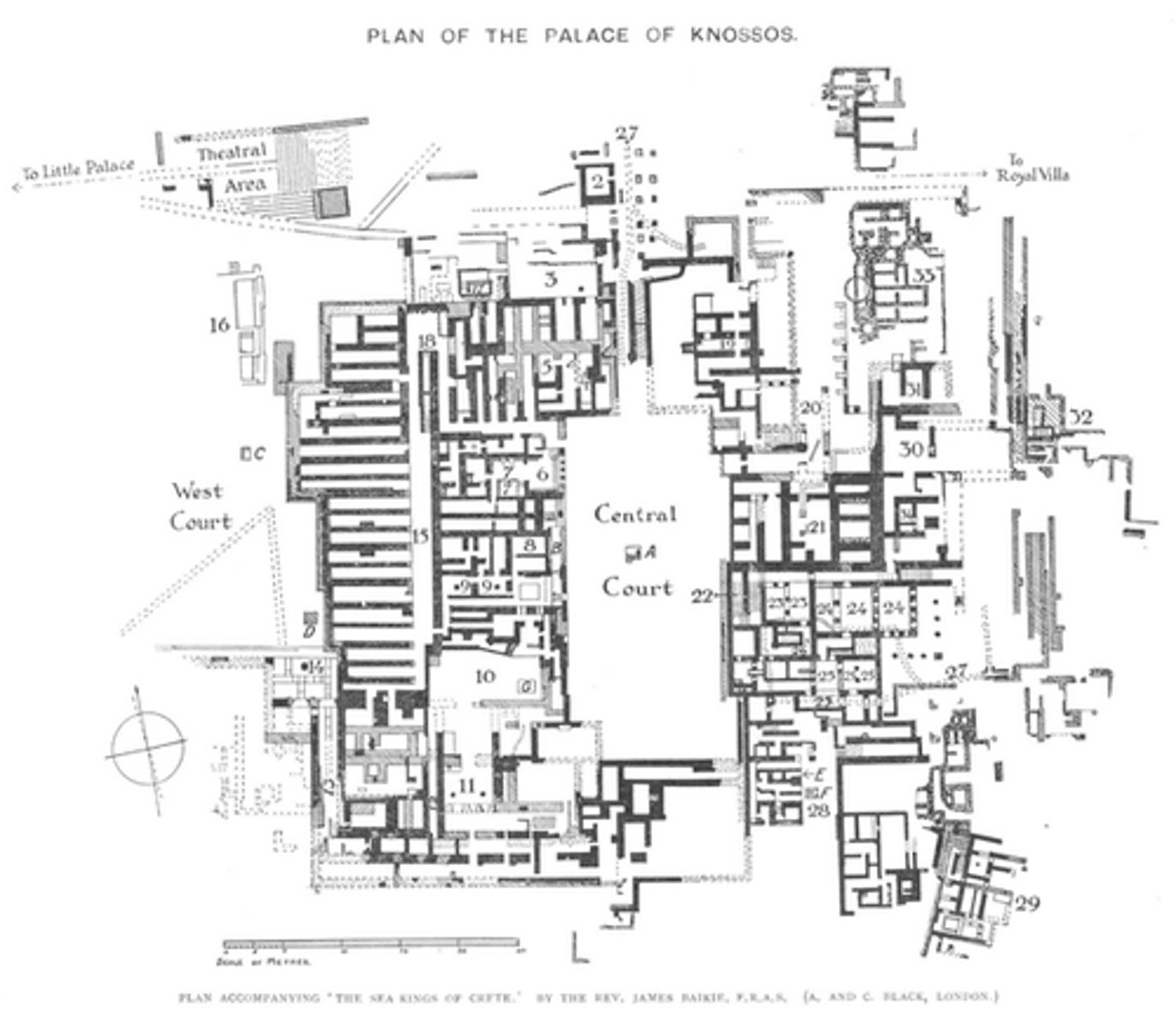
North Entrance of Palace of Midas (left side of map), 1700-1370 BCE
-minoan
-a new type of column, different from previous ones
-storage rooms where wine, grain, and oils were kept
-pithos, coil built
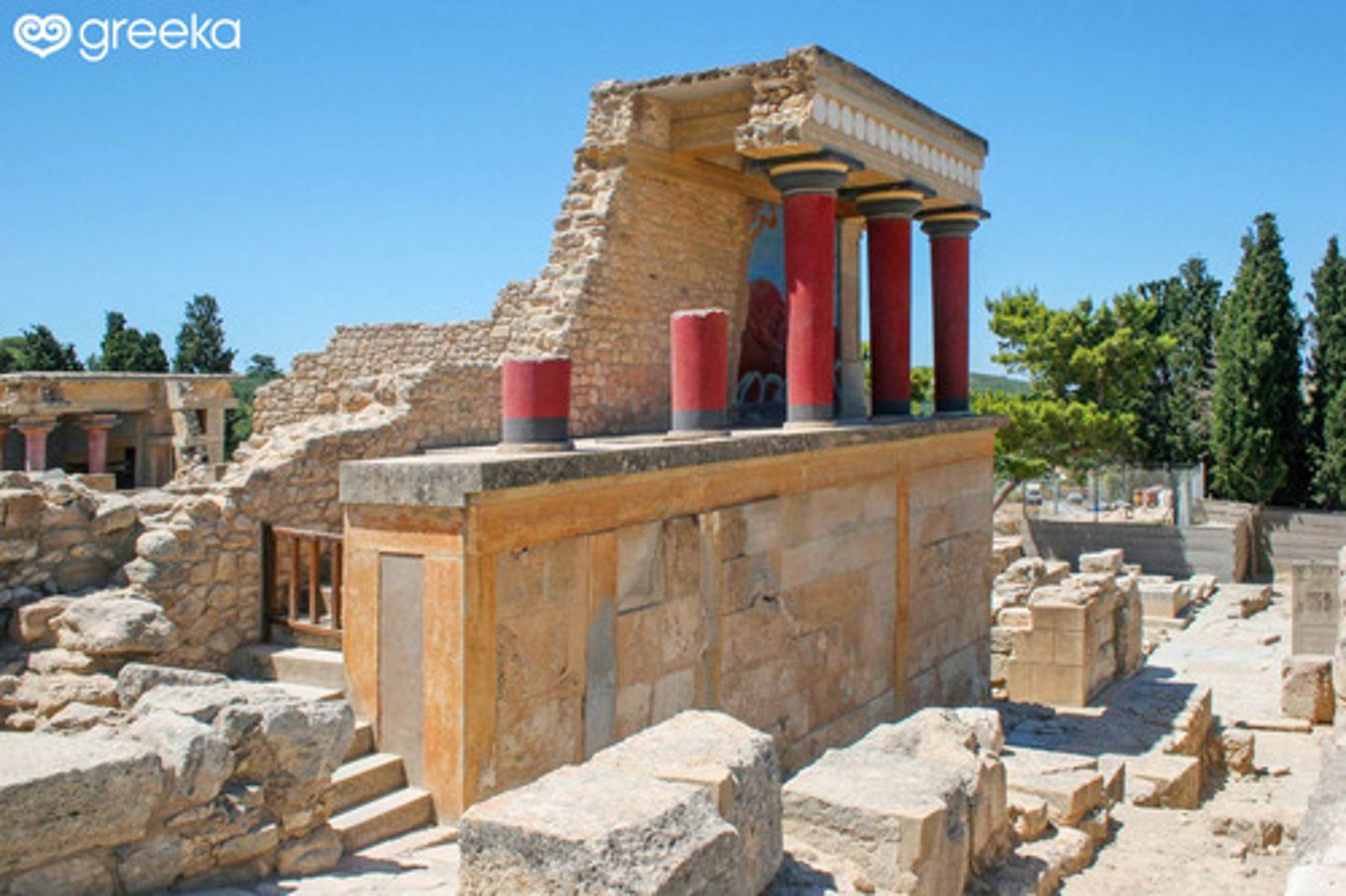

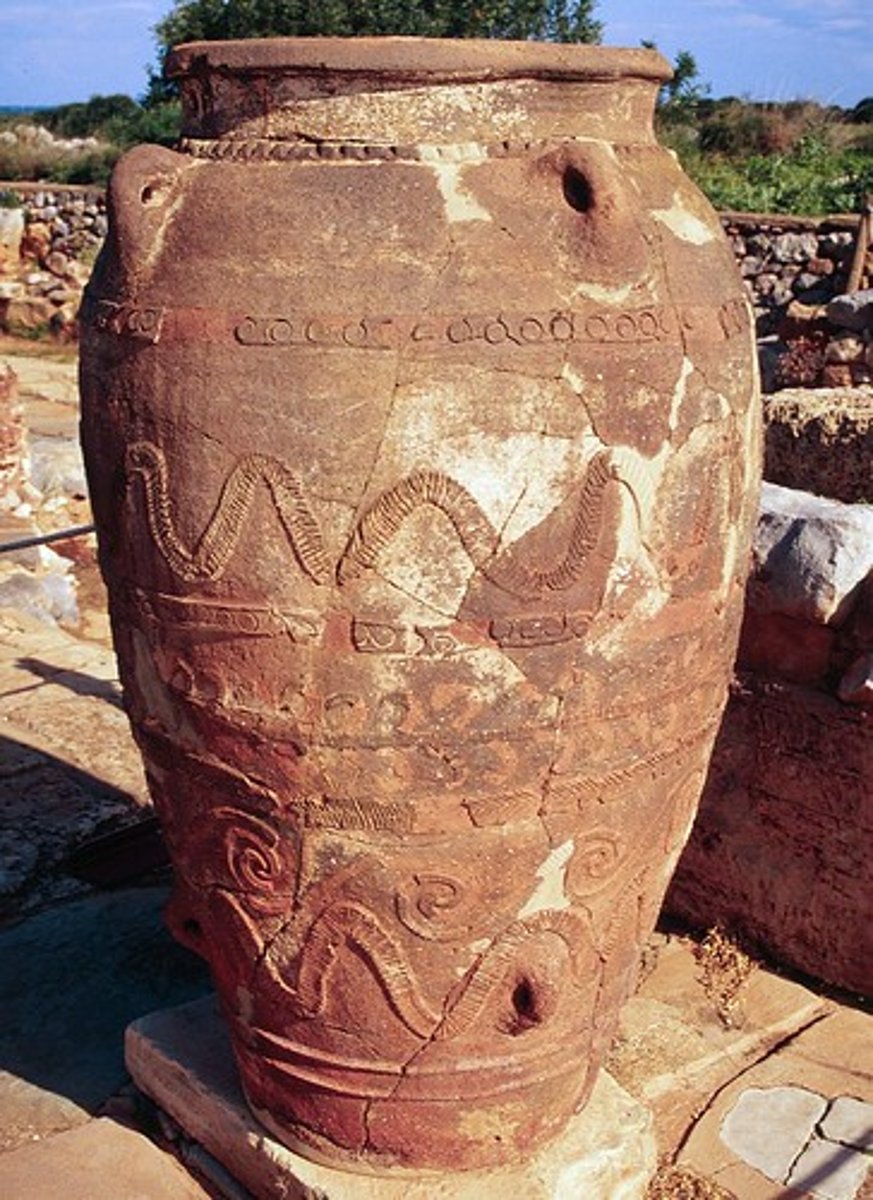
-Pithos
-Located in storage rooms at the North Entrance of Palace of Midas
-Sense of movement in design

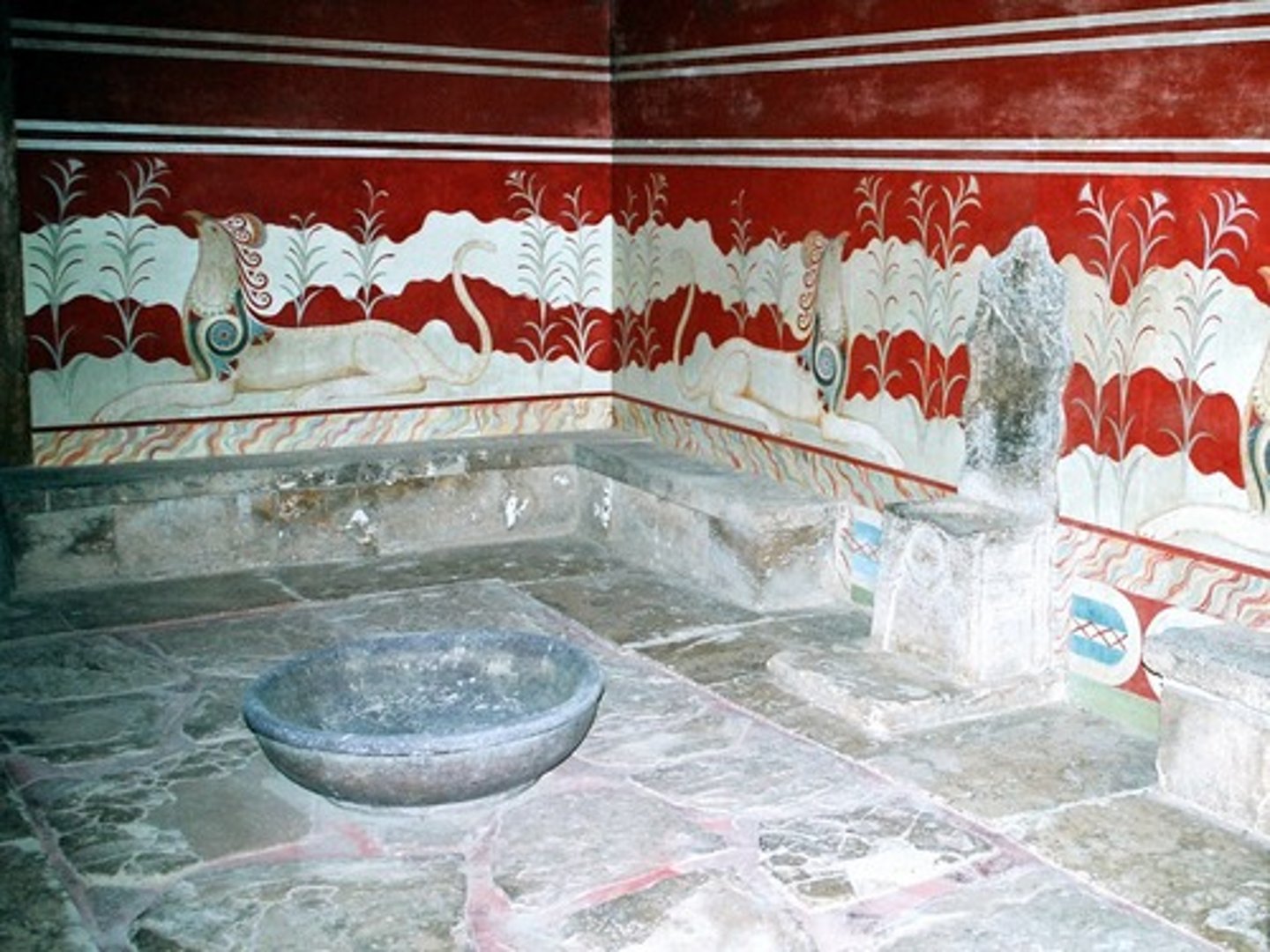
Throne Room of Palace of Midas, 1700-1370 BCE
-minoan
-ceremonial occasions where king would receive visitors
-fresco paintings on walls
-wavy design on seat, creates a sense of movement

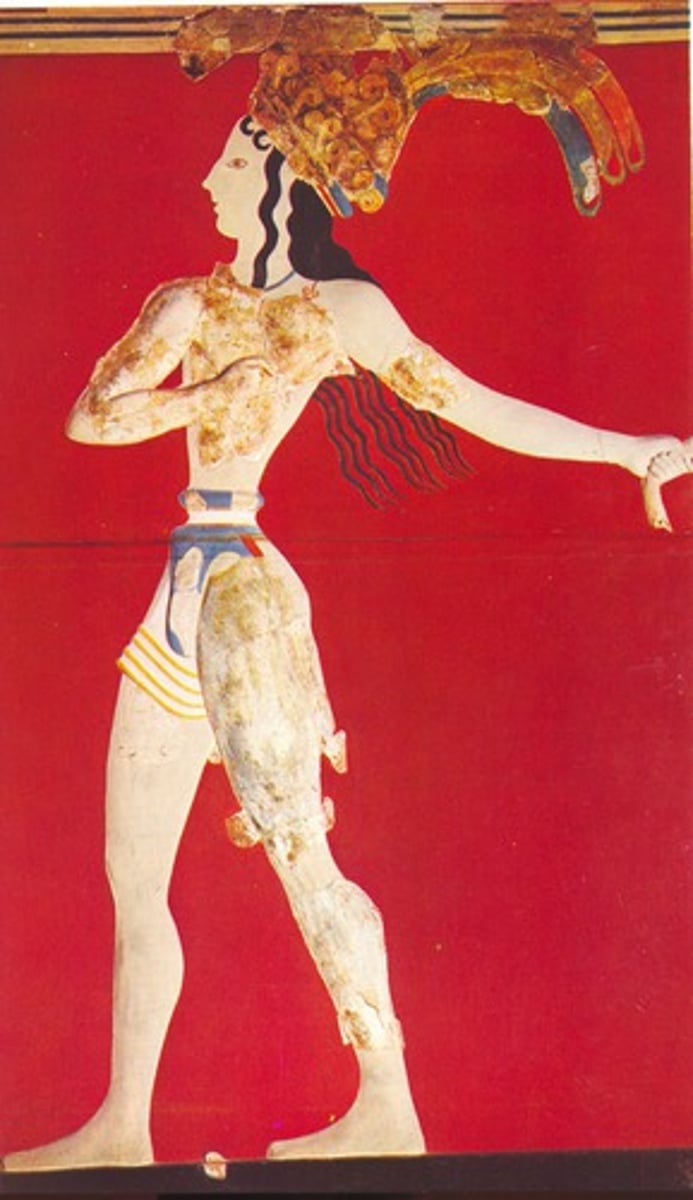
Priest King fresco at Palace of Midas, 1700-1370 BCE
-minoan
-implies motion
-refered to as priest king
-crown on head implies religious role and prestige
-naturalism as found in Minoan art

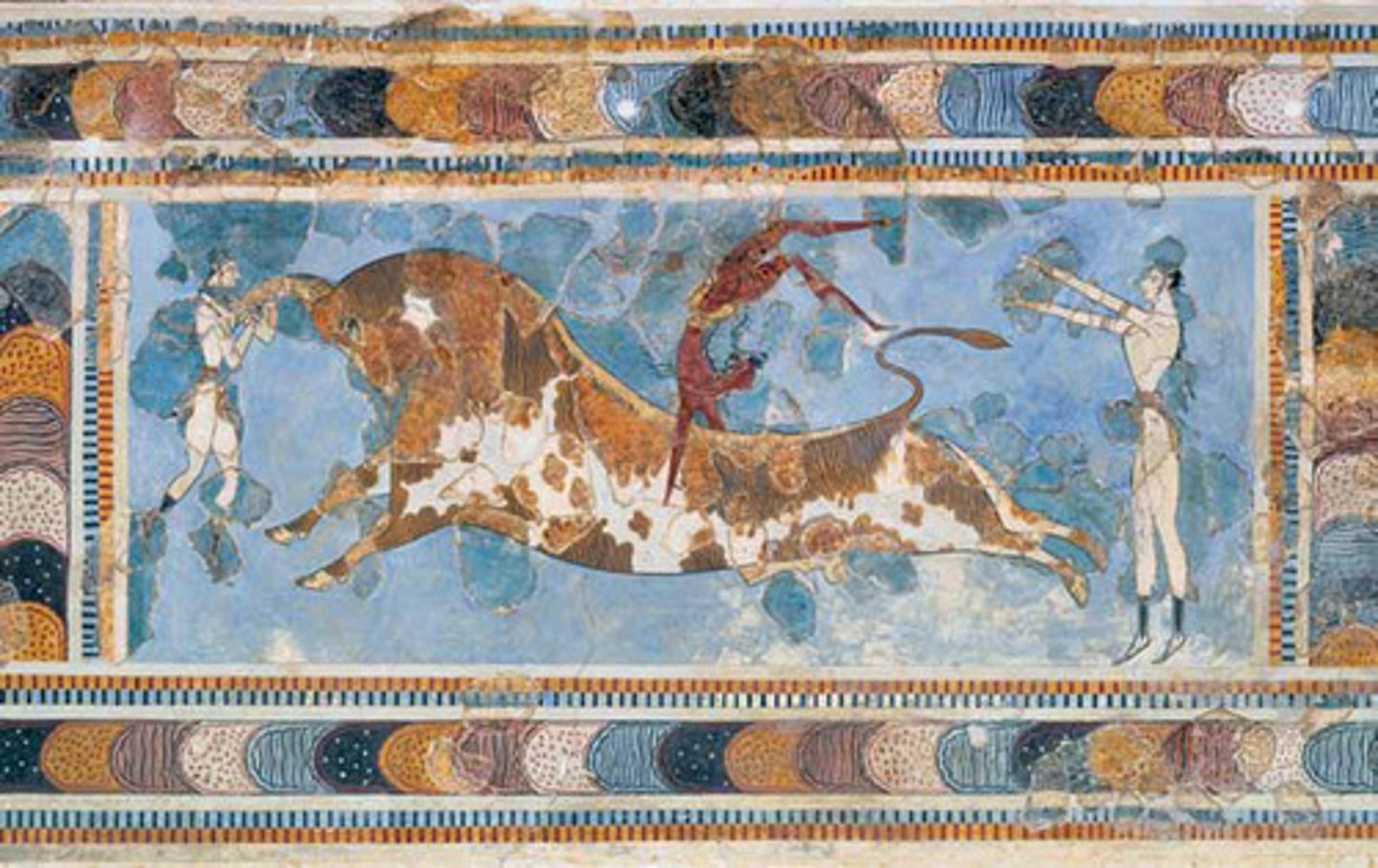
Bull in Courtyard from Palace of Knossos, 1500 BCE
-Minoan
-fresco painting
-open courtyard palace where bull is introduced and children somersault over back of bull, making reference to legend
-sense of motion, carries out of frame

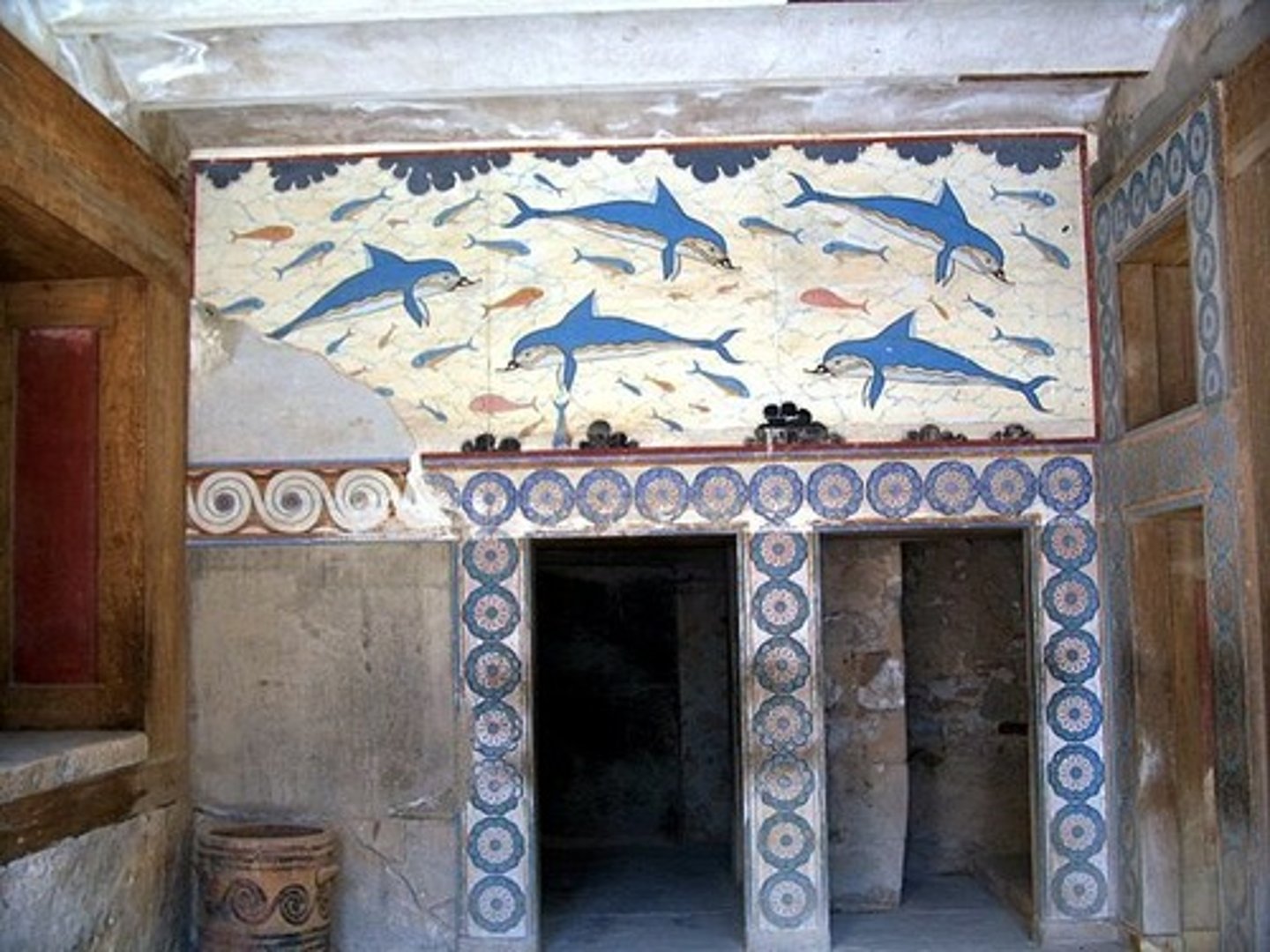
Dolphins at Palace of Midas
-Minoan
-fresco painting
-reflecting minoan interest in nature and sea
-represent love of nature in a convincing matter
-architectural design, window walls

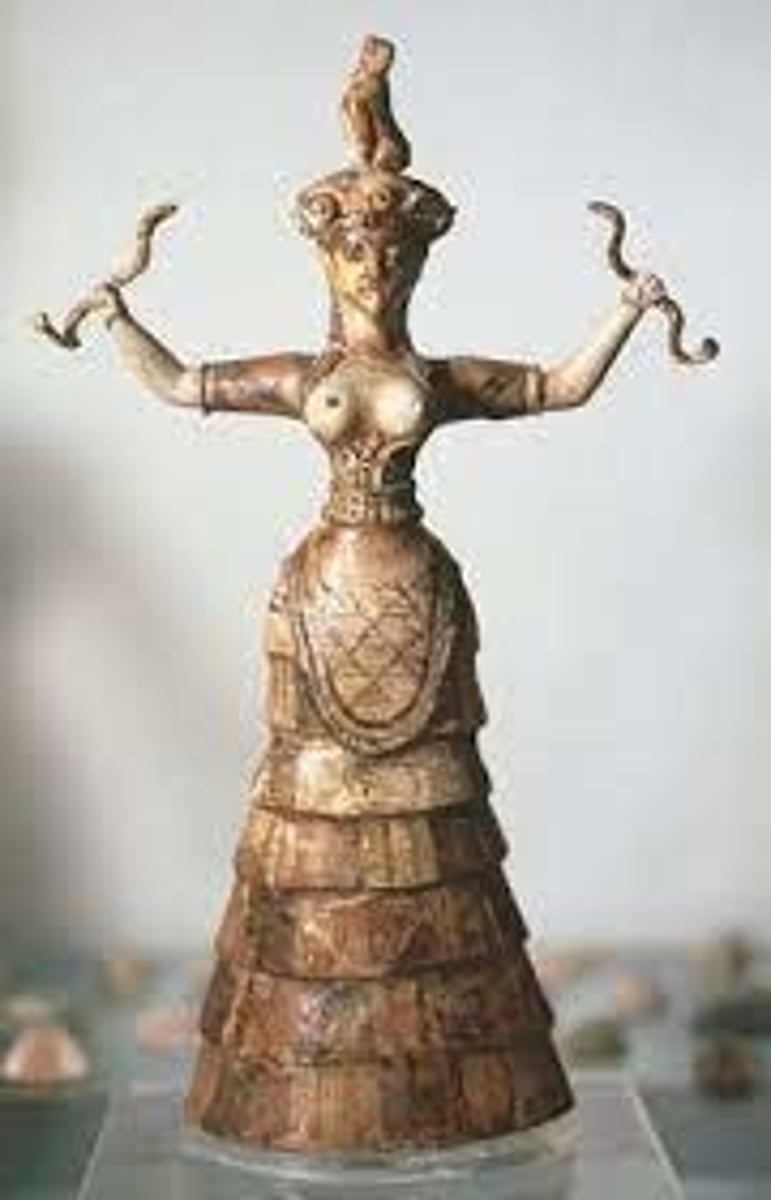
Snake Goddess from Palace of Knossos, 1600 BCE
-minoan
-made in palace workshops
-free standing sculpture
-religious significance
-sense of movement
-made from terracotta
-used with faience

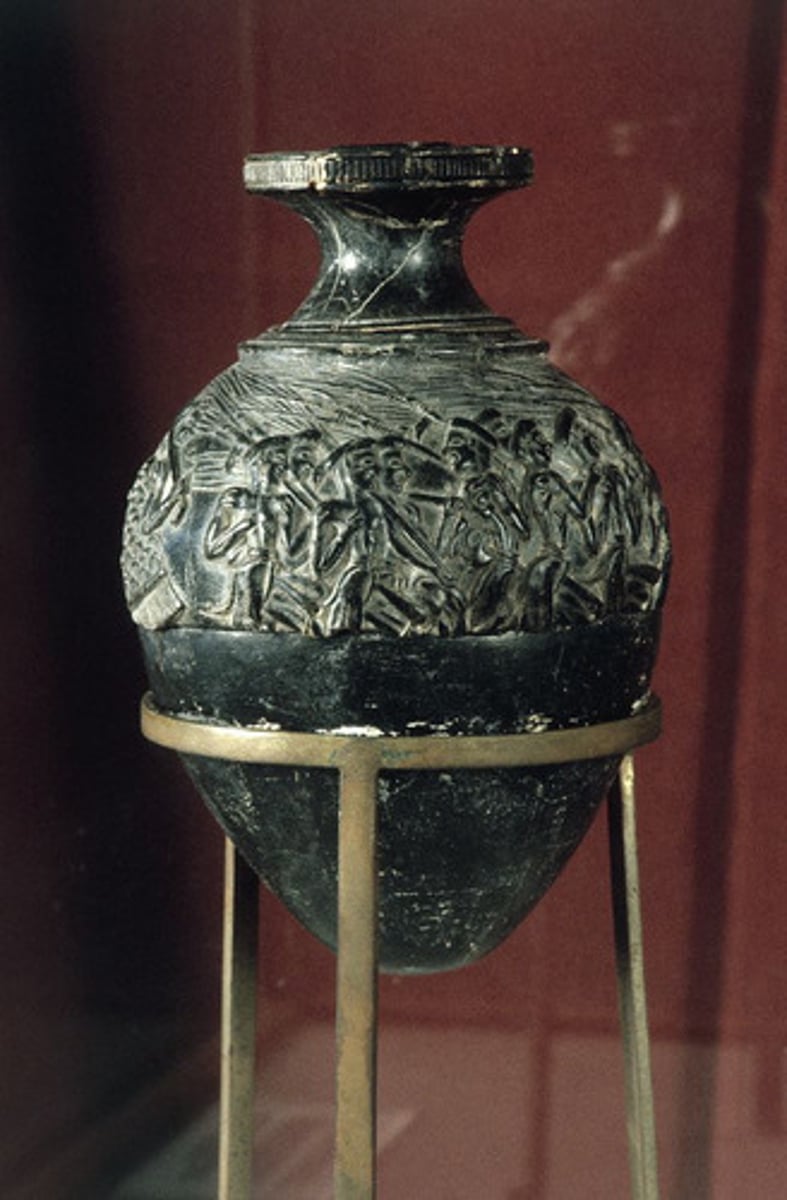
Harvesters Vase, 1500 BCE
-minoan
-made of steatite, a hard black stone
-shows scenes of daily life
-group of farmers holding pitch forks, singing
-joyous expression
-typical minoan form
-shaking rattle or sistrum

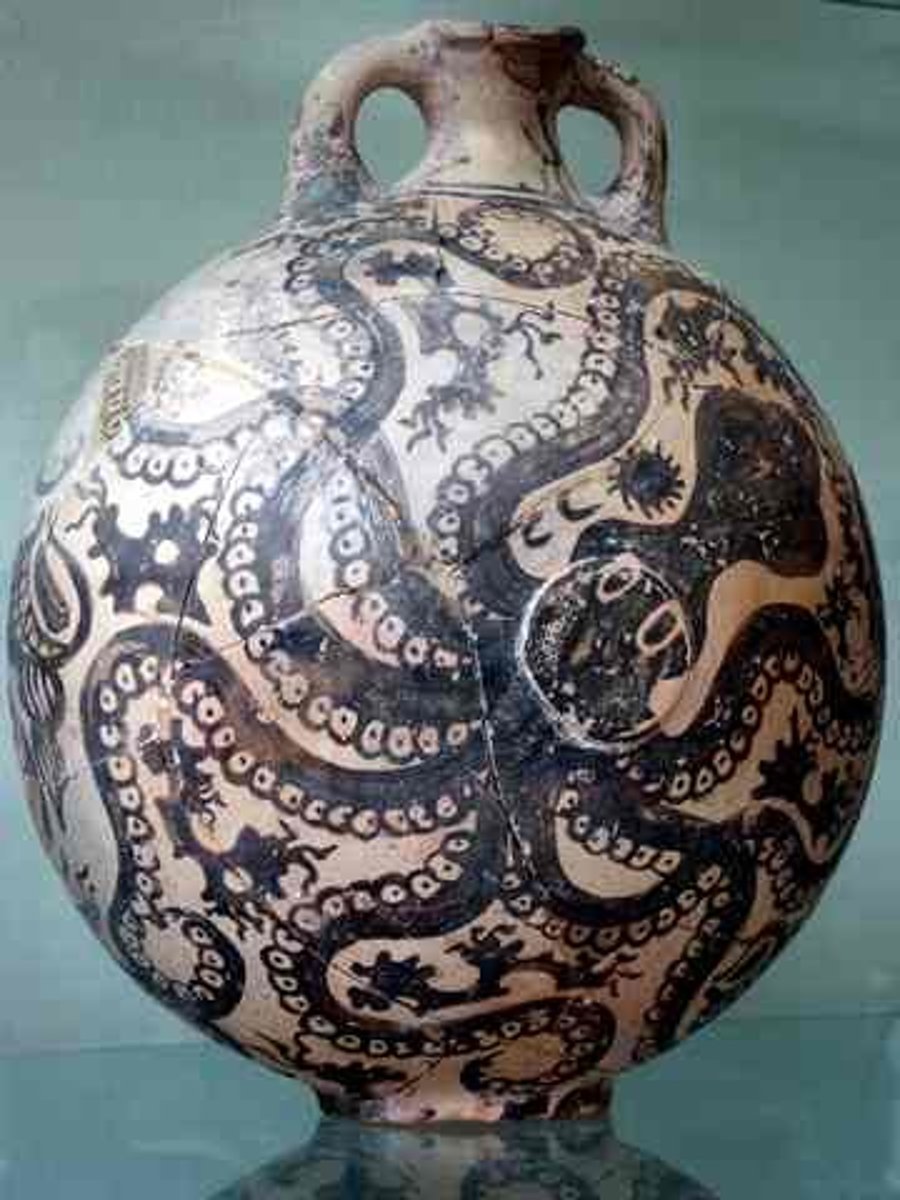
Octopus Vase, 1300 BCE
-minoan
-common date for later phase when palace was made
-bottle, short neck spherical shape, filled with win
-terracotta, high quality clay
-shows movement, energy
-design covers whole surface
-marine style

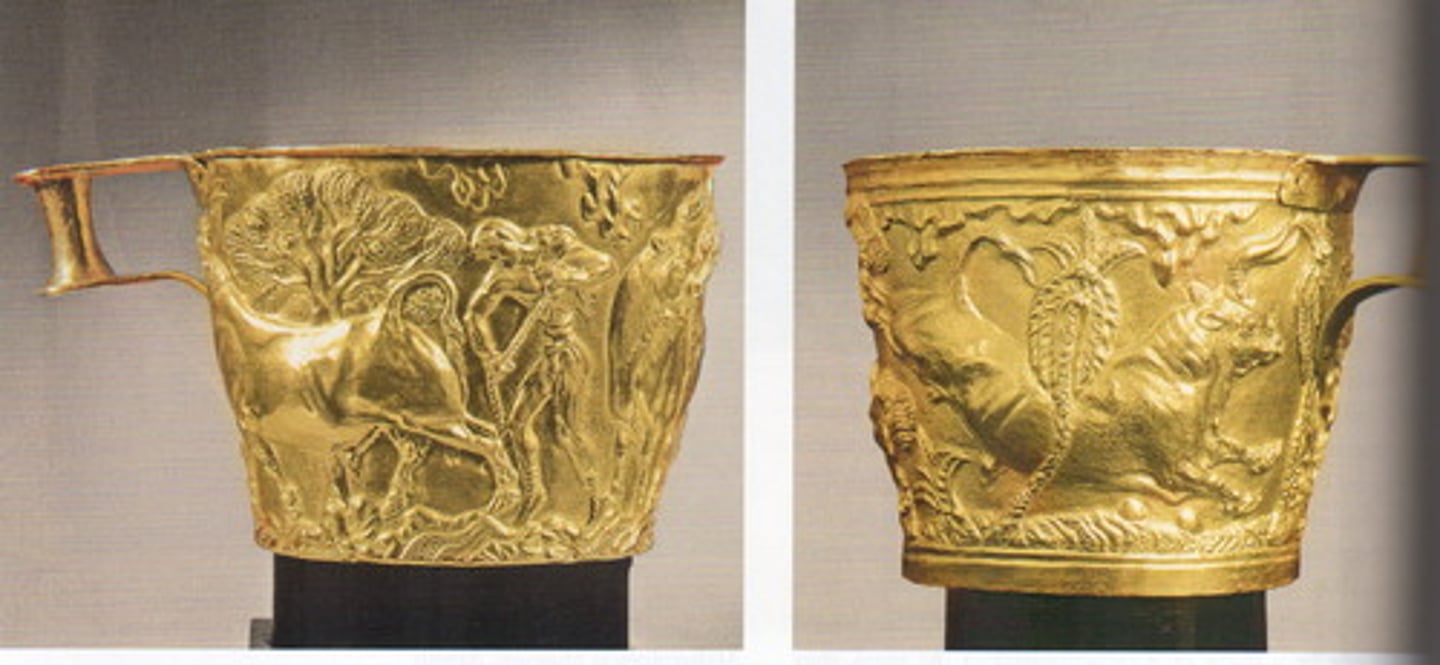
Vaphio Cups, 1500 BCE
-Minoan
-made of gold, relief image on front
-scene of hunting, bulls (popular in culture)
-single handle
-sense of movement
-Made in repoussé (beating design from behind)

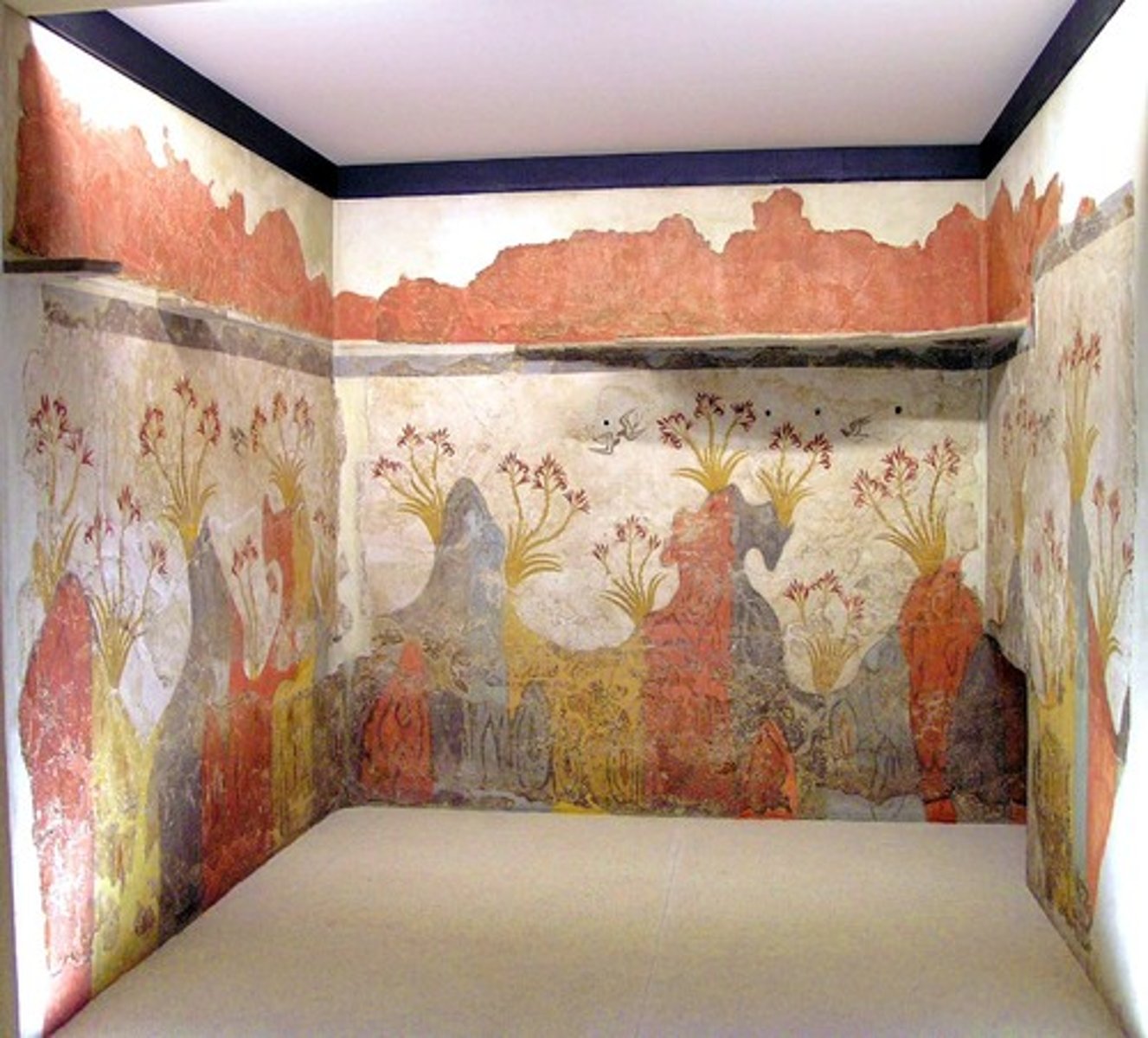
Spring Fresco, 1650 BCE
-Minoan
-fresco representing natural landscape on walls
-nature blossoming during spring, lily plants, birds
-creates airy atmosphere
-spontaneous view of natural world
-represents pure landscape of nature
-private house on island of Thera

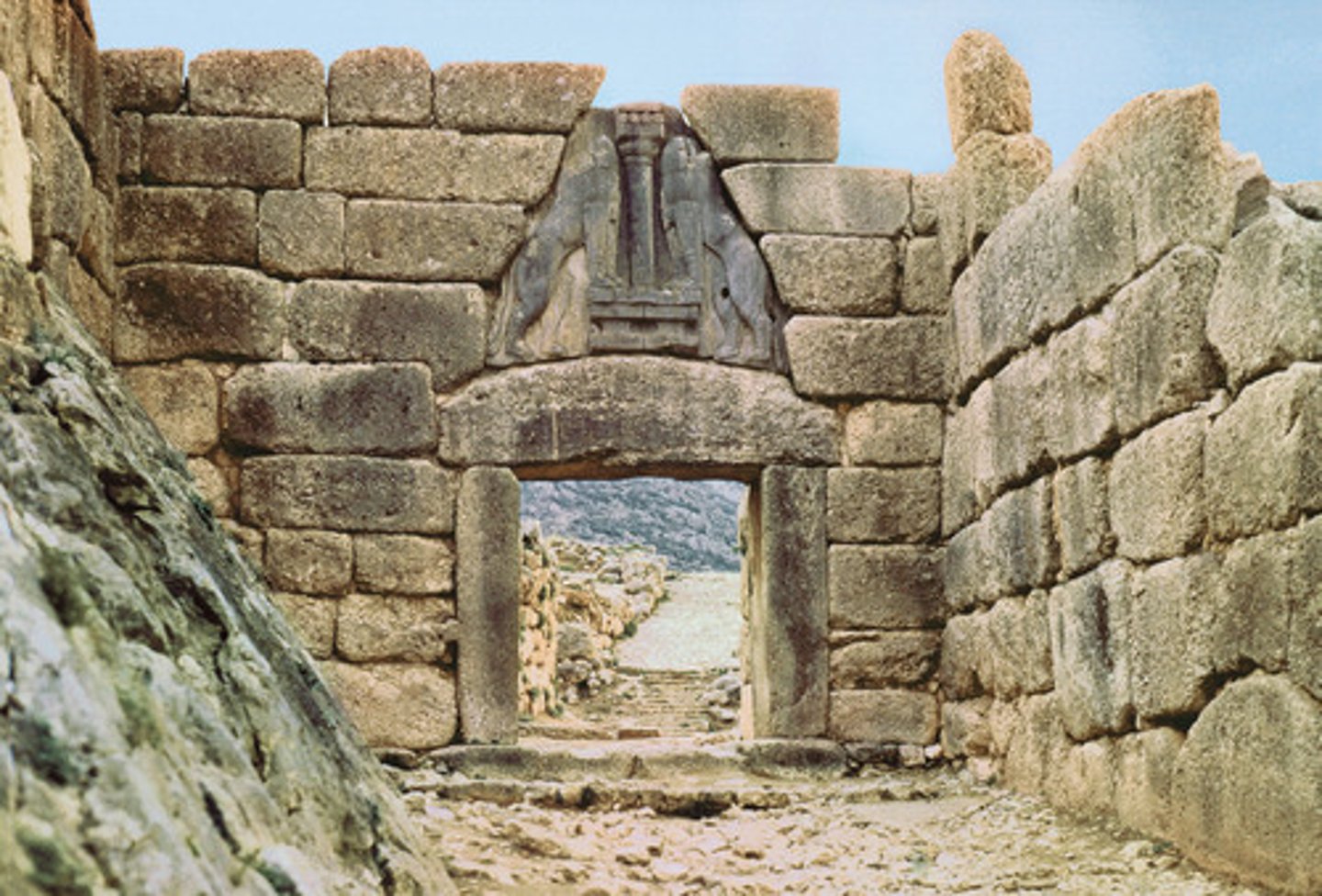
Entrance to Mycenaean Palace, 1300-1250 BCE
-Mycenaean
-excavated by Schiliemann
-gate known as lion gate
-triangular block channels weight of wall above to sides preventing caving in
-symbols of royal power, influences of minoan art

Grave Circle A, 1600-1500 BCE
-Myceanaean
-schilliemann discovery
-grave circle
-each grave contained gold treasure
-death masks place on deceased
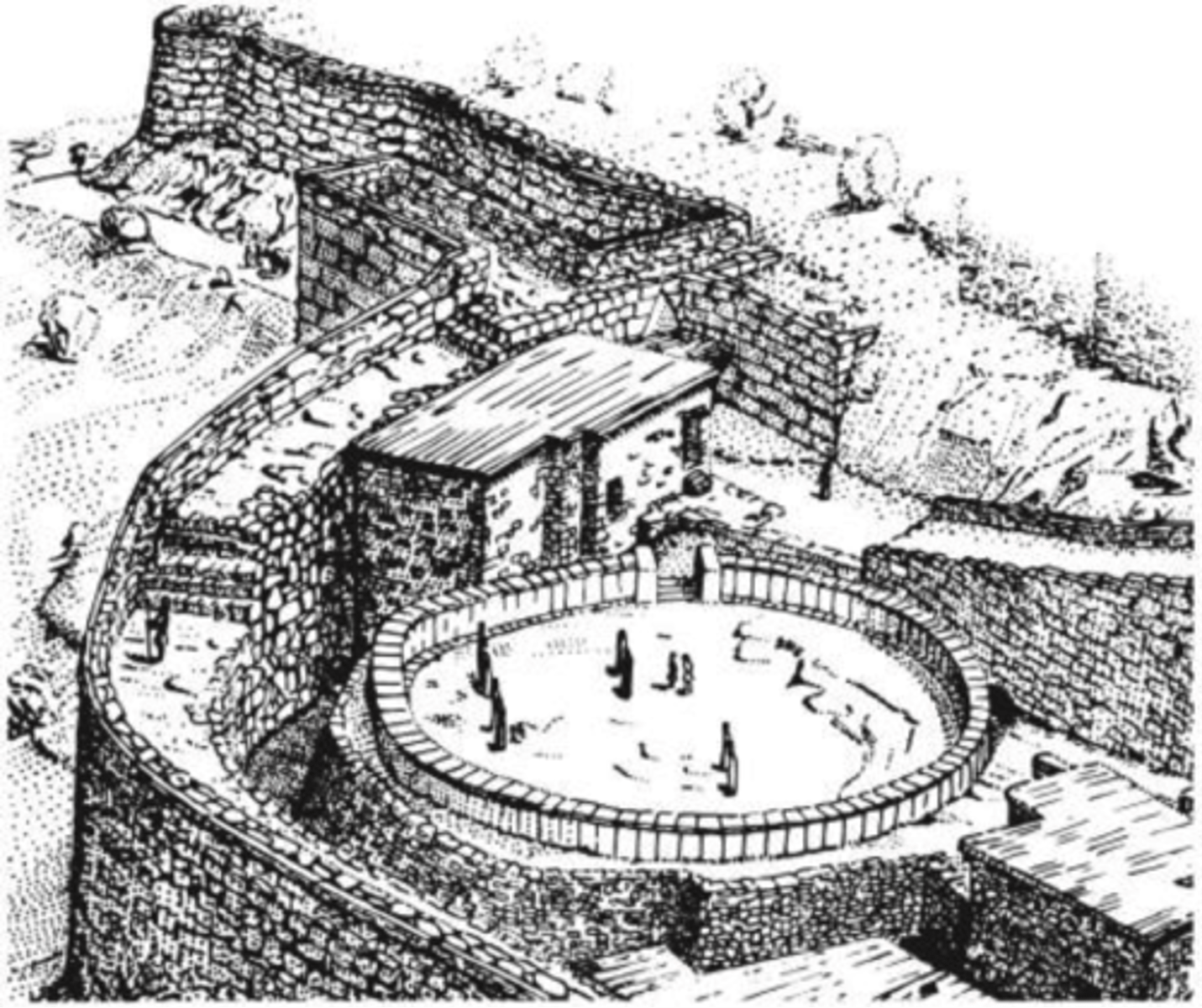
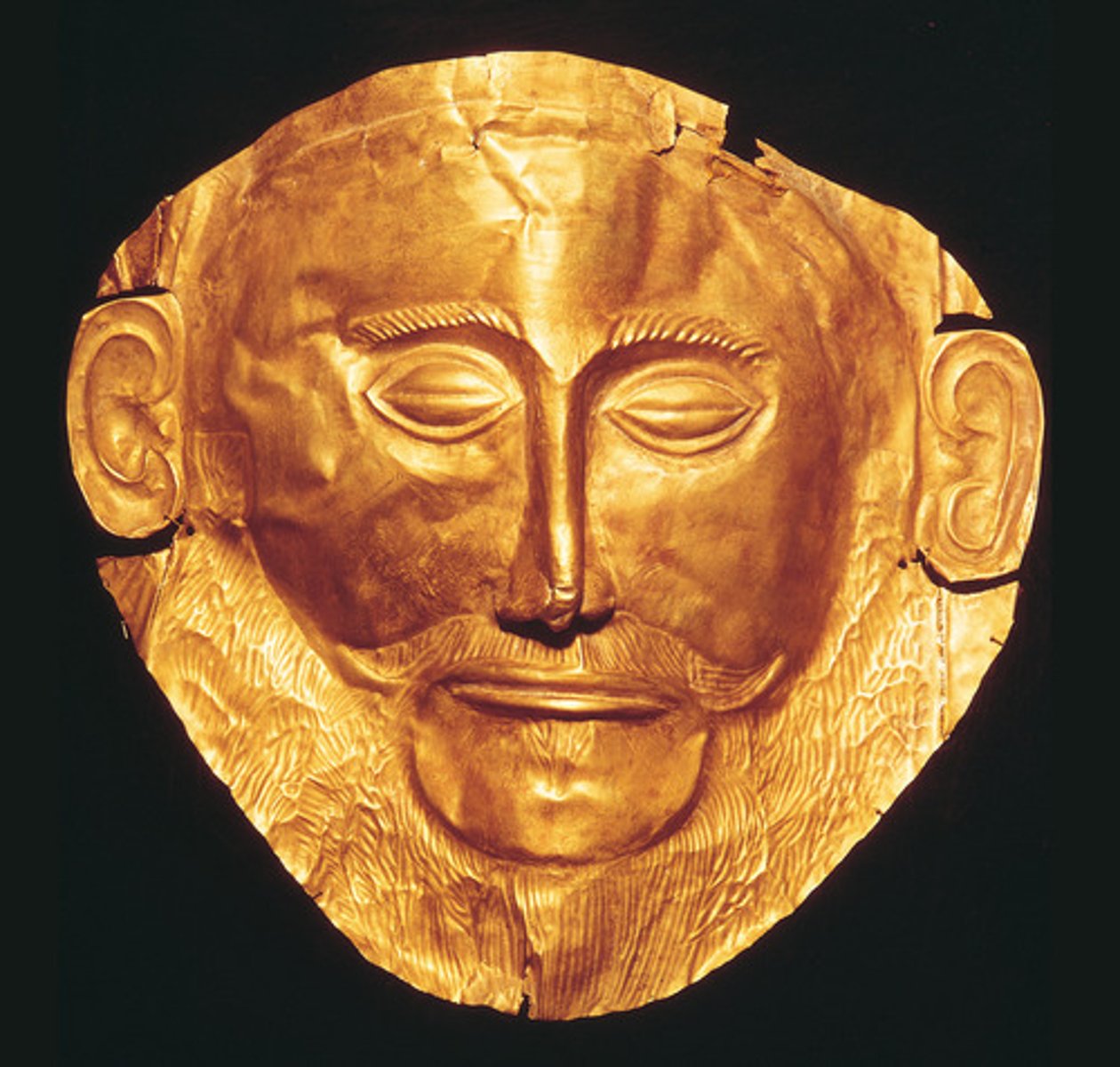
Mask of Agamenon from Grave Circle, 1600-1500BCE
-Myceanaean
-gold death mask placed over shaft graves
-repousse, sheet of gold metal beat with hammer to make figure
-eyes closed as in death

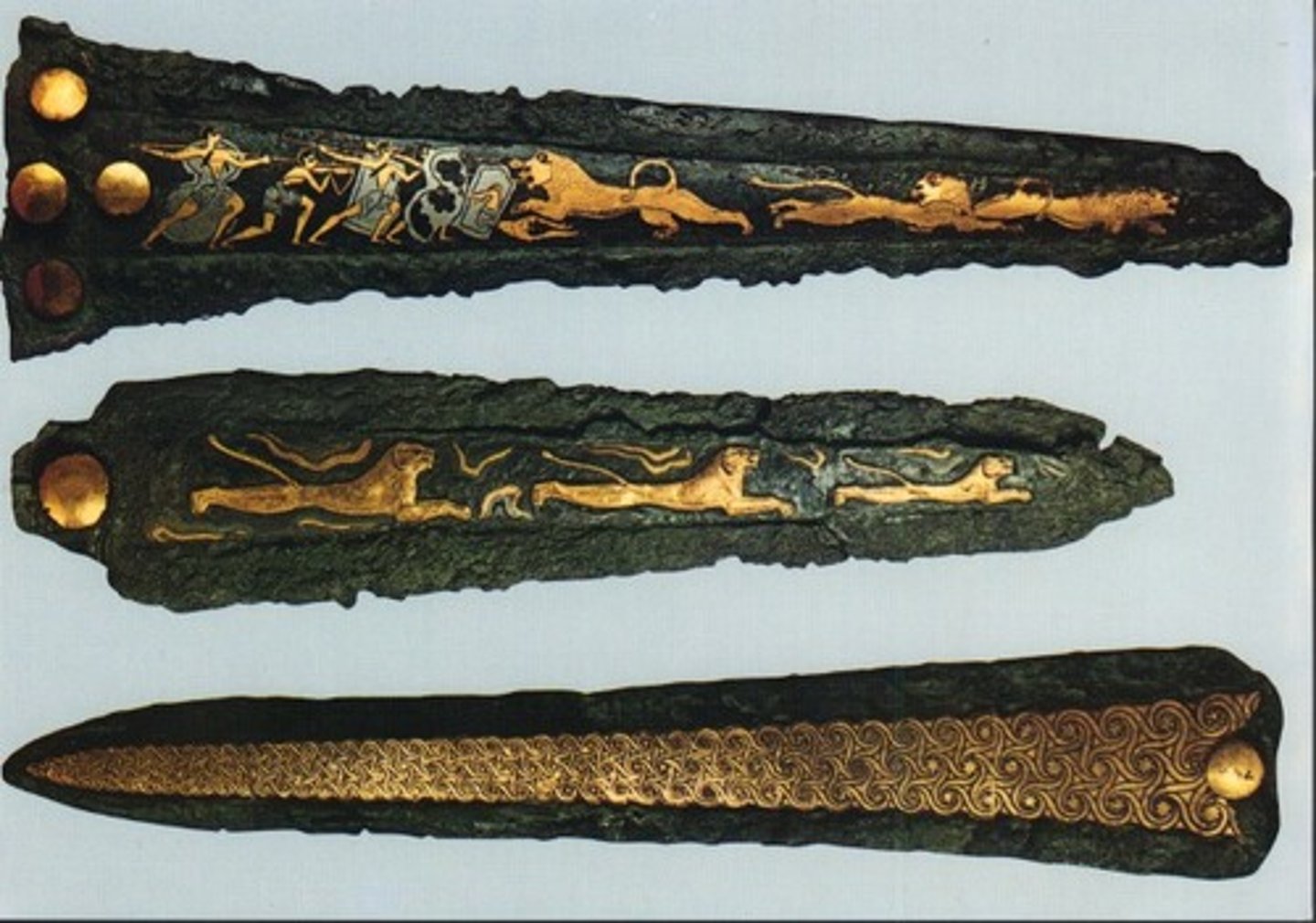
Ceremonial Dagger from Grave Circle, 1600-1500 BCE
-Myceanaean
-made of bronze, inlaid with gold and silver
-lions, leopards, lion hunt
-lion is an important royal symbol

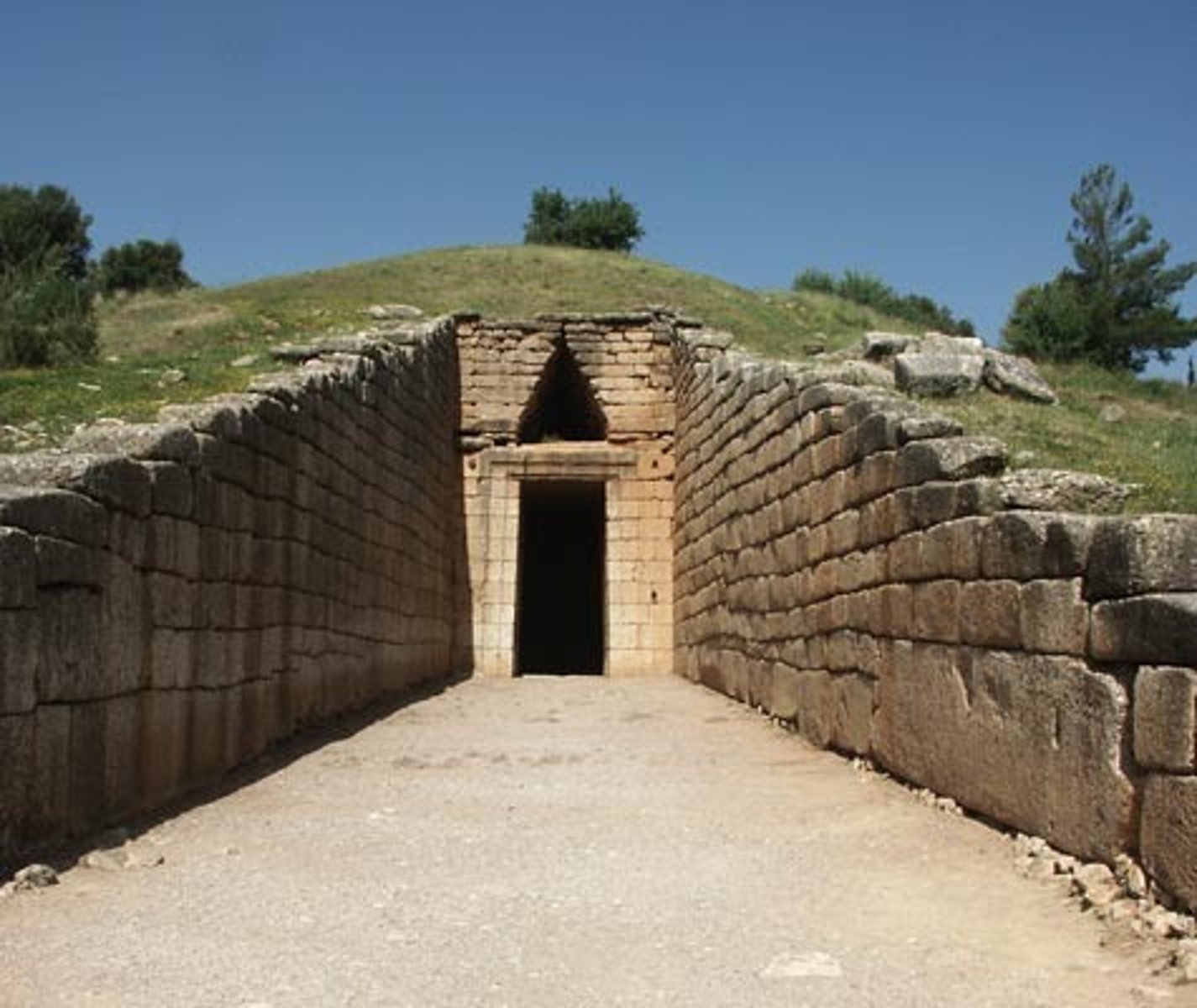
Treasury of Atreus, 1300-1250BCE
-Myceanaean
-Thlos tomb
-Atreus was father of agemenon
-corbal ball, dome shape from inside
-made from dry, laid masonry
-contains corpse and treasure

1200 BCE
-invasion occurred, the dorians
-new greek dialect spokem
-dark ages, disorder
-"true greek culture"
-left bronze age, entering iron age, iron used to make weapons
-geometric period of art
-new greek cities, police
-humanism, valued achievements of mankind
-rational thinking and logic
-democracy
-pride in human figure
-athletes, olympic games
-new art in athens, pottery
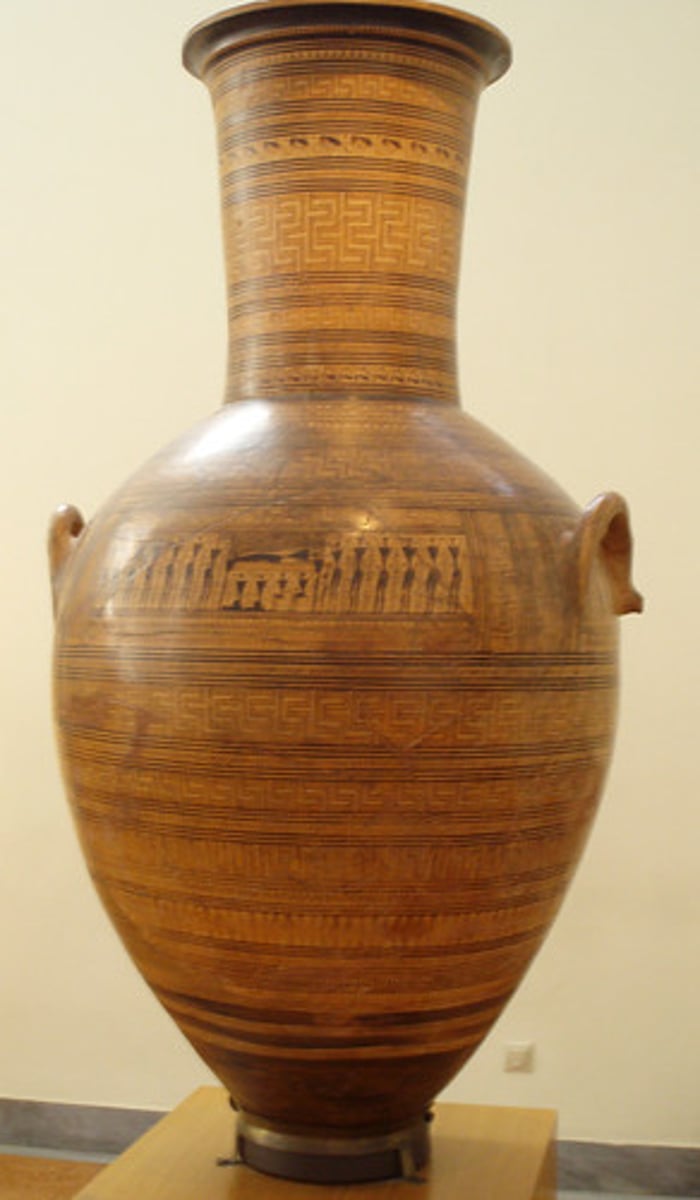
Dipylon Amphora, 750 BCE
-geometric greek pottery
-vessels made as grave markers, signified important rank in society
-described in humanistic terms, neck, shoulder, body
-painted decoration, filled spaces between lines with geometric designs, lines and bands,
-panel representing funeral, expressing grief, carrying corpose,
-new interest in narrative art
-Gods and heros of ancient Greece are like humans in the way that they act
-man-sized

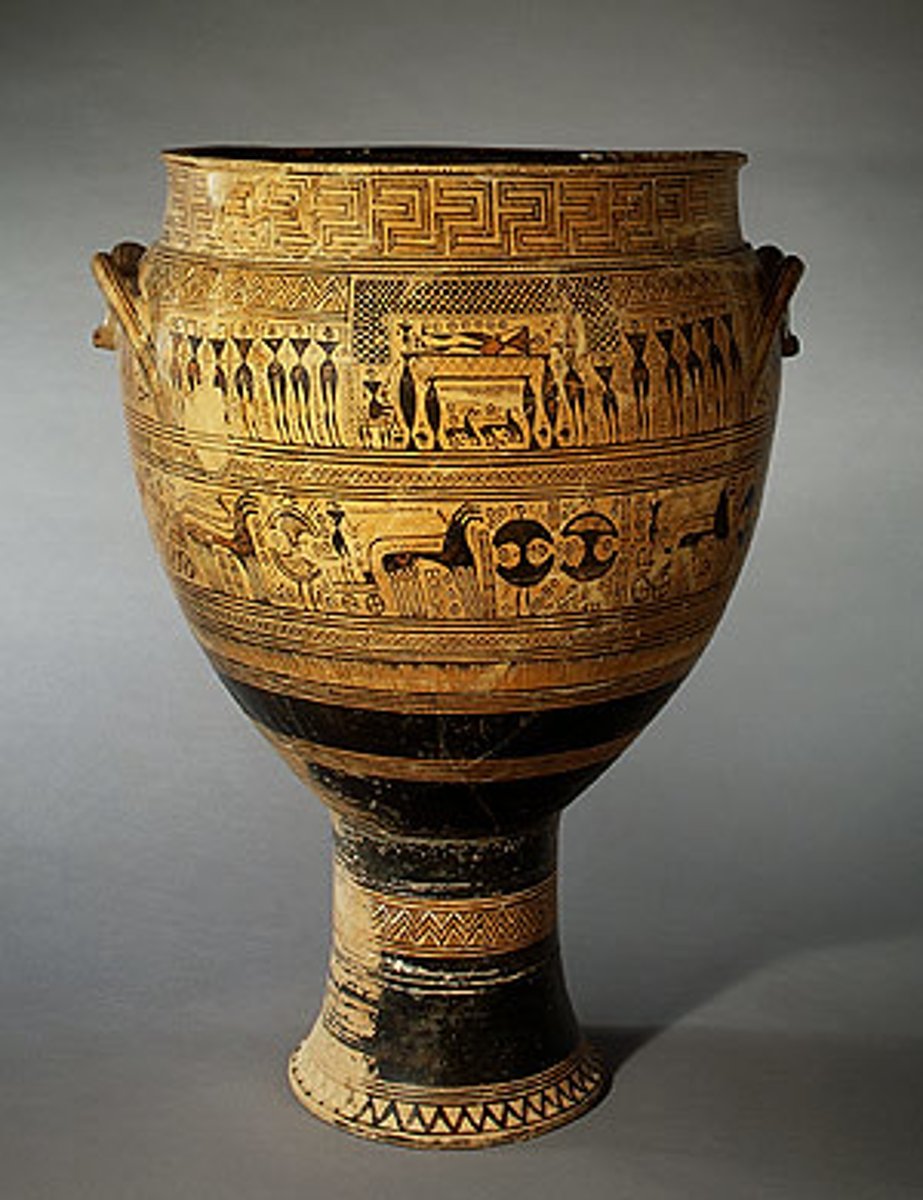
Krater
-Geometric greek pottery
-vase with wide mouth, wide belly, tall base
-double frieze, bands of ornaments and figures, funeral procession, horse drawn chariots
-done in abstract style, typical of geometric manner
-mythological, the abduction of hellen
-strong sense of structure
-abstract silhouette style
-prothesis and ekphora
