Cellular Biology - CH6 - Enzymes: the Catalysts of Life
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is considered an unstable molecule, whereas ATP is considered a metastable molecule. Which of the following is likely true about the nonenzymatic hydrolysis of PEP and the hydrolysis of ATP?
The hydrolysis of ATP and PEP will be spontaneous, but the hydrolysis of ATP will be much slower than the hydrolysis of PEP.
In general, enzymes are what kinds of molecules?
Proteins
Enzymes work by _____.
reducing EA
An enzyme _____.
is an organic catalyst
What name is given to the reactants in an enzymatically catalyzed reaction?
substrate
As a result of its involvement in a reaction, an enzyme _____.
is unchanged
Energy of Activation Ea is what part of the graph
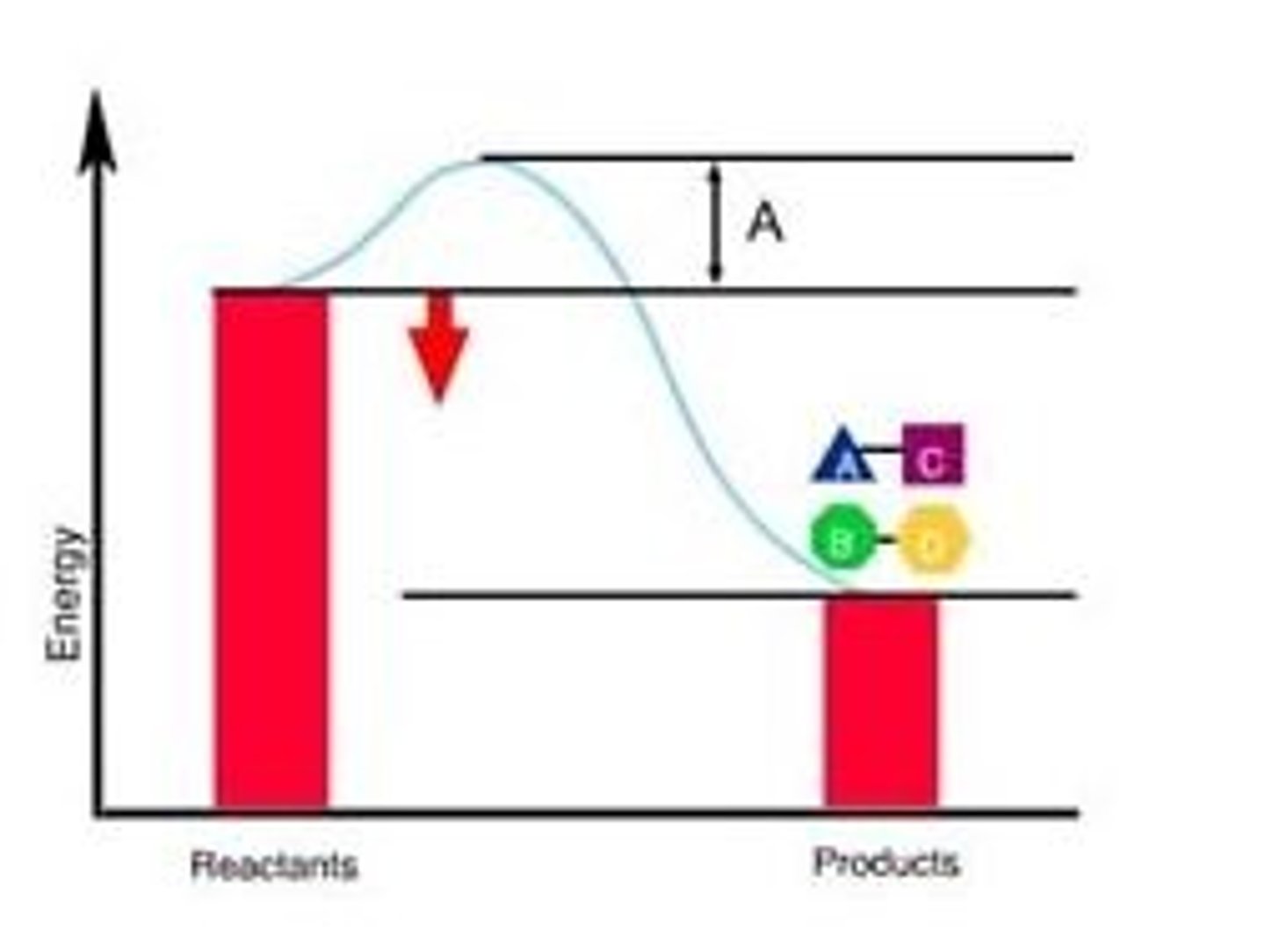
A plot of enzyme velocity against temperature for an enzyme indicates little activity at 0 degrees Celsius and 40 degrees Celsius, with peak activity at 35 degrees Celsius. The most reasonable explanation for the low velocity at 0 degrees Celsius is that __________.
both the frequency and energy of enzyme-substrate collisions are low
substrate binding at the active site is thermodynamically unfavorable at low temperature
the hydrogen bonds that define the enzyme's active site are broken as temperature increases
the enzyme was denatured at this temperature
both the frequency and energy of enzyme-substrate collisions are low
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate binds to acetylcholinesterase and permanently inactivates the enzyme. Paralysis results.
competitive
irreversible
noncompetitive
irreversible
Vitamin K is a coenzyme involved in blood clotting. An anticoagulant drug binds at the site of vitamin K bonding, blocking vitamin K binding and preventing clotting. Clotting resumes after the patient stops taking the drug.
competitive
irreversible
noncompetitive
competitive
A toxin binds to the surface of an enzyme. The enzyme then binds the substrate, but no product is produced. The toxin may disassociate and the enzyme will become active again.
competitive
irreversible
noncompetitive
noncompetitive
Aspirin binds to prostaglandin synthetase and permanently stops its ability to produce prostaglandin.
competitive
irreversible
noncompetitive
irreversible
A drug binds to the active site of an enzyme but disassociates and leaves the enzyme active.
competitive
irreversible
noncompetitive
competitive
`Explain what it means for the activation energy to be lowered from 18 to 13 kcal/mol by ferric ions but from 18 to 7 kcal/mol by catalase.
Choose two properties of catalase that make it a more suitable intracellular catalyst than ferric ions.
Suggest yet another way that the rate of hydrogen peroxide decomposition can be accelerated.
increase in temperature
increase in products concentration
decrease in temperature
increase in pressure
increase in temp
Is the increase in temperature a suitable means of increasing reaction rates within cells? Why or why not?
Not suitable; Most cells can function only within a rather limited temperature range.
Suitable; That works well in living cells.
Not suitable
Ammonia, NH3, is used in numerous industrial processes, including the production of pharmaceuticals such as sulfonamide and antimalarials and vitamins such as the B vitamins. The equilibrium equation for the synthesis of ammonia (sometimes known as the Haber process) is
N2(g)+3H2(g)⇌2NH3(g)
Four parts
A. The Haber process is typically carried out at a temperature of approximately 500∘C. What would happen to the rate of the forward reaction if the temperature were lowered to 100∘C?
Decrease
What would happen to the rate of the forward reaction if the concentration of nitrogen were decreased?
The reaction rate would decrease .
Which of the following would increase the rate of the reverse reaction?
increasing the concentration of ammonia
decreasing the temperature
increasing the concentration of nitrogen
increasing the concentration of ammonia
What will happen to the rates of the forward and reverse reactions when a catalyst is added?
Forward rate increases; reverse rate decreases.
Both forward and reverse rates increase.
Both forward and reverse rates decrease.
Forward rate decreases; reverse rate increases
Both forward and reverse rate increase
An enzyme is __ when it loses its native conformation and its biological activity.
denatured
An enzyme is considered a __ because it speeds up chemical reactions without being used up.
catalyst
An enzyme is considered __ because of its ability to recognize the shape of a particular molecule.
specific
A ___, such as a vitamin, binds to an enzyme and plays a role in catalysis.
Cofactor
When properly aligned, the enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate (ES)___
complex
A substrate binds to an enzyme at the ___, where the reaction occurs.
active site
In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called a ____
substrate
Chapter 6, Question 7
Just going to have to log on the mastery and learn that one real good
Next couple questions
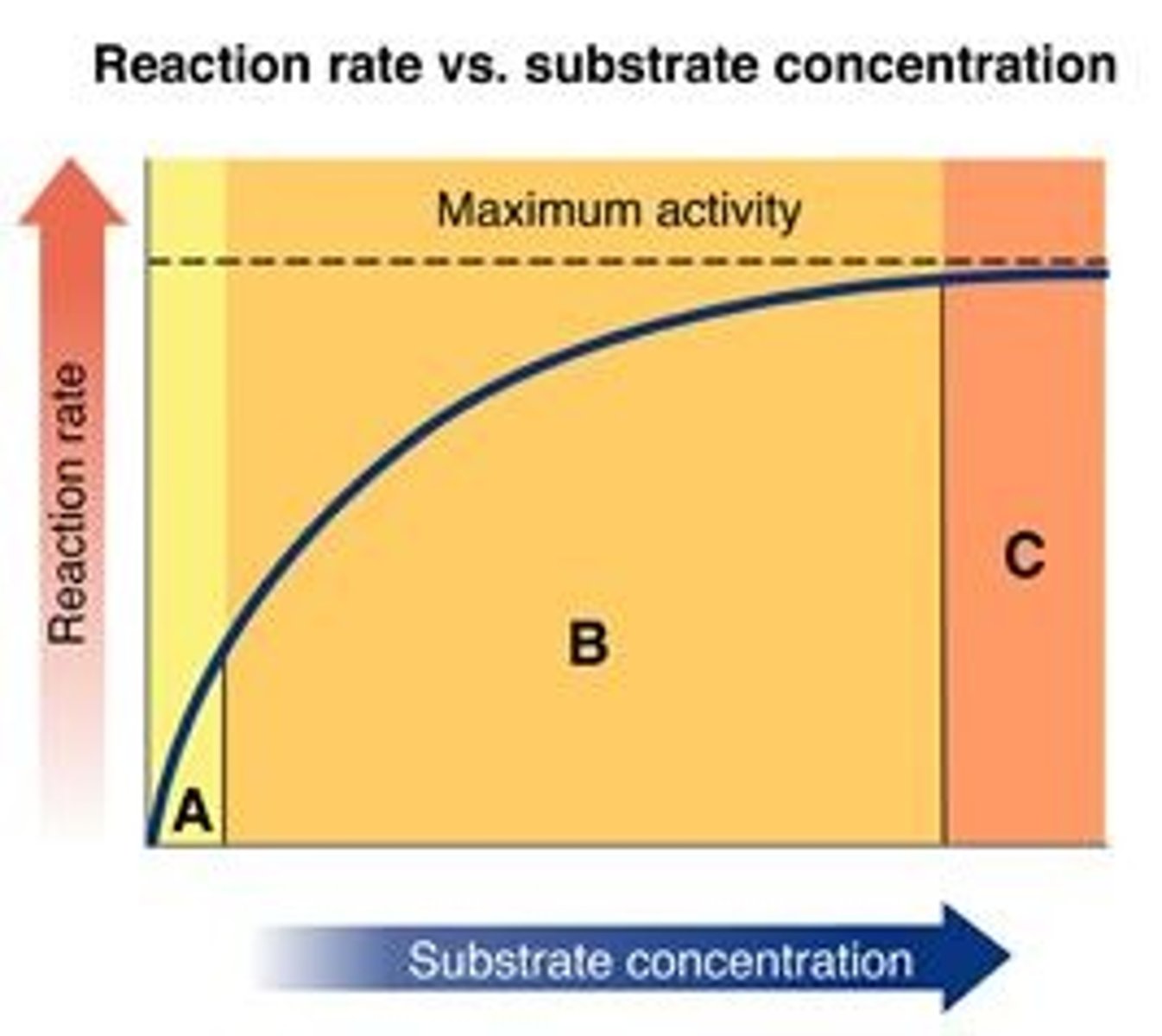
Look at the graph of reaction rate versus substrate concentration for an enzyme. (Figure 1)
In which region does the reaction rate remain constant?
C
In which region is the enzyme saturated with substrate?
C
Consider a situation in which the enzyme is operating at optimum temperature and pH, and has been saturated with substrate. What is your best option for increasing the rate of the reaction?
Increase the pH.
Increase the temperature.
Increase the enzyme concentration.
Increase the substrate concentration.
increase enzyme concentration
1. A (n)___ inhibitor has a structure that is so similar to the substrate that it can bond to the enzyme just like the substrate.
competititive
2. A (n)____inhibitor binds to a site on the enzyme that is not the active site.
noncompetititive
3. Usually, a(n) ______ inhibitor forms a covalent bond with an amino acid side group within the active site, which prevents the substrate from entering the active site or prevents catalytic activity.
irreversible
4. The competitive inhibitor competes with the substrate for the _____ on the enzyme.
active site
5. When the noncompetitive inhibitor is bonded to the enzyme, the shape of the _______is distorted.
enzyme
Enzyme inhibitors disrupt normal interactions between an enzyme and its _______.
substrate
You have added an irreversible inhibitor to a sample of enzyme and substrate. At this point, the reaction has stopped completely.
What can you do to regain the activity of the enzyme?
Removing the irreversible inhibitor should get the reaction working again.
The enzyme is inactive at this point. New enzyme must be added to regain enzyme activity.
Adding more substrate will increase the rate of reaction.
Adding more inhibitor should get the reaction up to speed again.
The enzyme is inactive at this point. New enzyme must be added to regain enzyme activity.
You have an enzymatic reaction proceeding at the optimum pH and optimum temperature. You add a competitive inhibitor to the reaction and notice that the reaction slows down.
What can you do to speed the reaction up again?
Add more inhibitor to speed up the reaction.
Add more substrate; it will outcompete the inhibitor and increase the reaction rate.
Increase the temperature.
Increase the pH.
Add more substrate; it will outcompete the inhibitor and increase the reaction rate.
Four ways enzymes lower Ea
Stress molecular bonds
create charge distribution
reduce delta S by molecular orientation
change pathway