nutriotnotgknrkv
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:39 AM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Thiamin sources
whole grain and enriched grain
2
New cards
Thiamin functions
coenzyme in energy metabolism
nerve system transmission
nerve system transmission
3
New cards
Thiamin deficiency symptoms
beri beri
edema
muscle wasting
fatigue
confusion
apathy
high risk for alcoholism
edema
muscle wasting
fatigue
confusion
apathy
high risk for alcoholism
4
New cards
riboflavin sources
milk
dairy
dairy
5
New cards
riboflavin fucntion
coenzyme
helps make niacin from tryptophan
helps make niacin from tryptophan
6
New cards
riboflavin deficiency symtpoms
glossitis and cheilosis
alcoholism
dermatitis
alcoholism
dermatitis
7
New cards
niacin sources
protein rich foods- animal protein
whole grains and enriched
tryptophan
whole grains and enriched
tryptophan
8
New cards
niacin functions
coenzyme
nerve system function
medicinally- lower cholesterol
nerve system function
medicinally- lower cholesterol
9
New cards
niacin deficiency
pellagra- 4Ds (dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia, death,
high risk for alcoholism
high risk for alcoholism
10
New cards
niacin toxicity
when megadosed s a drug for lowering cholesterol
niacin flush
can cause liver dmg
niacin flush
can cause liver dmg
11
New cards
vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) fucntions
helps make niacin from tryptophan
drug/nutrient interaction
therapeutic use
drug/nutrient interaction
therapeutic use
12
New cards
vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) sources
legumes
M/F/P
nuts and seeds
whole grains and enriched
\
M/F/P
nuts and seeds
whole grains and enriched
\
13
New cards
biotin sources
produced by bacteria in colon but essential
widespread in foods
widespread in foods
14
New cards
when does a biotin supplement help w hair and nail growth
when biotin levels are low in blood
15
New cards
folate sources→ folic acid (synthetic name)
green leafy veggies
legumes
avocado
nuts and seeds
oranges
fortified grains
\
legumes
avocado
nuts and seeds
oranges
fortified grains
\
16
New cards
which folate is better absorbed?
synthetic
17
New cards
folate fucntions
coenzyme in DNA synthesis
vital for new cell synthesis
integral for GI function
reduced risk of neural tube defects
activates b12
vital for new cell synthesis
integral for GI function
reduced risk of neural tube defects
activates b12
18
New cards
folate deficiency symptoms
macrocytic anemia
mental status change
depression
high risk for alcoholism
mental status change
depression
high risk for alcoholism
19
New cards
B12 sources
found in all animal products
no plant sources unless fortified
no plant sources unless fortified
20
New cards
which is better absorbed synthetic/fortified or natural b12
synthetic
21
New cards
B12 functions
DNA synthesis
RBC maturation
myelin sheath integrity
activates folate
RBC maturation
myelin sheath integrity
activates folate
22
New cards
B12 deficiency
macrocytic anemia
mental status change
depression
high risk for alcoholism
mental status change
depression
high risk for alcoholism
23
New cards
what happens as you age w absorption of b12?
atrophic gastritis
decreased (HCL) and intrinsic factor
\
decreased (HCL) and intrinsic factor
\
24
New cards
no toxicity for b12 why?
liver can store b12
25
New cards
Vitamin C- water soluble, aka ascorbic acid sources
fruits
veggies
citrus
cantaloupe
kiwi
berries
red/green peppers
veggies
citrus
cantaloupe
kiwi
berries
red/green peppers
26
New cards
Vitamin C functions
collagen synthesis
antioxidant
promotes non heme iron absorption
immune system function
thyroxine synthesis
\
antioxidant
promotes non heme iron absorption
immune system function
thyroxine synthesis
\
27
New cards
vitamin c deficiency
scurvy
pin point hemorrhaging
bone softenin
bleeding gums
anemia
prone to infection
skin changes
pin point hemorrhaging
bone softenin
bleeding gums
anemia
prone to infection
skin changes
28
New cards
vitamin A sources
preformed (animal- whole milk, fish, liver, fortified in low fat)
provitamin (plant-beta carotene-- yellow and orange color produced,
fortified cereals
provitamin (plant-beta carotene-- yellow and orange color produced,
fortified cereals
29
New cards
vit. a functions
vision
skin maintenance
reproduction
growth of bone and teeth
immune funtion
antioxidant in form of beta carotene (from food is better vs. supplement)
skin maintenance
reproduction
growth of bone and teeth
immune funtion
antioxidant in form of beta carotene (from food is better vs. supplement)
30
New cards
vit. a deficiency
storage in liver can be up to a year
deficiency rare in US but world wide problem
can lead to blindness
for rhodopsin production
xerophthalmia-- dryness of eyes that can lead to night blindness
deficiency rare in US but world wide problem
can lead to blindness
for rhodopsin production
xerophthalmia-- dryness of eyes that can lead to night blindness
31
New cards
vit. a toxicity
non toxic is beta carotene
toxic is preformed animal sources
can cause liver dmg and hair loss
CNS dmg and bone + skin changes
toxic is preformed animal sources
can cause liver dmg and hair loss
CNS dmg and bone + skin changes
32
New cards
vit. D source
sunlight
liver
fatty fish, eggs, cod liver oil, fortified yogurt and fortified milk, fortified foods
liver
fatty fish, eggs, cod liver oil, fortified yogurt and fortified milk, fortified foods
33
New cards
vit. D Functions
increases absorption of calcium in GI tract and reabsorption from kidneys
maintains serum calcium levels
maintains serum calcium levels
34
New cards
vit. D toxicity
not from sun, from oversupplementation
increases rusk for kidney stones, headache
increases rusk for kidney stones, headache
35
New cards
vit k sources
leafy green veggies
36
New cards
vit. e sources
oil, wheat germ, nuts seeds, veggie oils
37
New cards
vit e function
antioxidant
protects vit A and PUFA in body
protects LDL from oxidation
immune support
protects vit A and PUFA in body
protects LDL from oxidation
immune support
38
New cards
vit e deficiency
preterm babies high risk for RBC hemolysis
39
New cards
vit k function
prothrombin and osteocalcin (blood clotting, bone formation)
40
New cards
sodium functions
preservative for frozen foods
41
New cards
sodium sources
frozen meals
canned foods
prepackaged snacks
canned foods
prepackaged snacks
42
New cards
sodium needs and AI daily recommendation and UL
180 mg needed
AI-- 1,500mg
UL-- 2,300mg
AI-- 1,500mg
UL-- 2,300mg
43
New cards
potassium sources
potatoes, spinach, avocado, medium banana, baked potato, white beans, yogurt, fatty fish, orange
44
New cards
potassium AI
4700 mg/day
45
New cards
relationship w potassium and sodium
More processed the food the more sodium (bp increase)and less potassium
Less processed more potassium and less sodium
Less processed more potassium and less sodium
46
New cards
calcium sources
yogurt, milk, cheese, cereals, spinach, cauliflower
47
New cards
\
\
48
New cards
why is calcium and iron in spinach not well absorbed?
oxalate
(bad for absorption) raw in leafy greens, cooked greens is better and higher amt of minerals (iron calcium) cause no oxalate
(bad for absorption) raw in leafy greens, cooked greens is better and higher amt of minerals (iron calcium) cause no oxalate
49
New cards
how can calcium and iron in spinach be better absorbed?
cooked greens cause no oxalate
50
New cards
how is the serum calcium regulated w the help of vit. D and PTH?
release of PTH causes calcium to be pulled out from bone
both PTH and vitamin D increase absorption of Ca from SI
increase reabsorption/decrease excretion from kidneys
both PTH and vitamin D increase absorption of Ca from SI
increase reabsorption/decrease excretion from kidneys
51
New cards
what 3 minerals play a role in bone structure?
Ca, Mg, Phosphorus
52
New cards
what does some evidence suggest abt the correlation b/w phosphoric acid in soda and calcium absorption
phosphoric acid found in soda, interferes w calcium
→ excessive soda consumption can hurt bone density
→ excessive soda consumption can hurt bone density
53
New cards
calcium deficiency
rickets in children, osteomalacia in adults-- decayed teeth malformed
54
New cards
calcium servings for RDA
3-4 servings of fortified dairy
55
New cards
what is the function of magnesium w respect to muscles?
helps relax muscles
56
New cards
what two interventions can magnesium sulfate be used for?
helps constipation and cuts bruises and relax muscles
57
New cards
what are the sources of heme and non heme iron?
(non heme are plant sources (legumes ex.) (Egg not good for heme) other animal products sources for heme
58
New cards
which source of iron is better absorbed?
Heme better absorbed
59
New cards
What vitamin helps with absorption of non-heme iron?
vit. c
60
New cards
What is the main function of iron?
Helps make hemo and myoglobin
61
New cards
What is the term for iron-deficiency anemia and what are its characteristics and symptoms?
microcytic hypochromic anemia
→ involves palor, fatigue, weakness, hyperactivity
→ involves palor, fatigue, weakness, hyperactivity
62
New cards
How is iron easily stored in the body? Is it easily excreted?
Stored in liver and other organs not readily excreted
63
New cards
what is the role of iodine w respect to thyroid gland?
Helps make thyroid hormones (t3 t4)
help make thyroid gland to function properly
help make thyroid gland to function properly
64
New cards
what can a deficiency iodine increase the risk for?
Can cause goiter → enlarged thyroid gland
65
New cards
what are good sources of iodine?
Iodized salt
66
New cards
what are the imp. functions of zinc in terms of sexual maturation?
Helps produce sex gonads
67
New cards
what is the relationship of zinc w respect to colds, pressure wounds, and smell and perception?
Optimize smell and taste, not prevent cold but decrease cold length can also help heal pressure wounds
68
New cards
what can a deficiency of zinc increase the risk for?
Can increase risk for dwarfism
69
New cards
what condition is caused by excessive fluoride intake and what pop. is at high risk?
fluorosis → cosmetic issue of teeth not detrimental
children under 8 are most at risk
children under 8 are most at risk
70
New cards
what is the main function of chromium
Coenzyme in optivating insulin
increases insulin sensitivity
decreasing insulin resistance
maintains blood sugars
increases insulin sensitivity
decreasing insulin resistance
maintains blood sugars
71
New cards
when are chromium supplements helpful for type 2 dm?
Only when found low serum lvl in bloo
72
New cards
define energy balance and how does it related to body weight in terms of negative, neutral and positive
the relationship b/w the amt of energy input and the amt of energy output
* negative→ calorie output is exceeds calorie intake=weight loss
* neutral→ calorie intake is = to calorie output, no weight change
* positive→ calorie intake exceeds calorie output= weight gain
* negative→ calorie output is exceeds calorie intake=weight loss
* neutral→ calorie intake is = to calorie output, no weight change
* positive→ calorie intake exceeds calorie output= weight gain
73
New cards
what are the four sources of energy intake
carbs (4cal/g), protein (4cal/g) , fats (9cal/g), alcohol (7cal/g)
74
New cards
what are the three sources of energy expended
* BMR (basal metabolic rate)
* thermic effect of food TEF
* PA physical activity
* thermic effect of food TEF
* PA physical activity
75
New cards
what is the relationship of aging w respect to BMR, LBM, fat tissue, weight gain after 30
bmr decrease
lean body mass decrease
fat tissue increase
1 lb per yr after 30
lean body mass decrease
fat tissue increase
1 lb per yr after 30
76
New cards
define the dif. levels of PA
sedentary, light, moderate, high activity
sedentary, light, moderate, high activity
sedentary→ typical desk worker, sleeping, sitting all day
light→ less than 2 hrs
moderate→gym 3x/week, not rlly sitting
high activity→ sports, manual labor, runner
light→ less than 2 hrs
moderate→gym 3x/week, not rlly sitting
high activity→ sports, manual labor, runner
77
New cards
how do each factor affect BMR
decreases
growth increases
physiological stress ?
abnormal thyroid regulation hypo→slow, hyper→fast
fever increase
height increase
extrem temps increases
starving, fasting, malnutrition decreases
weight loss from calorie deficit decreases
smoking nic increases
caffeine increases
medication depends on med
growth increases
physiological stress ?
abnormal thyroid regulation hypo→slow, hyper→fast
fever increase
height increase
extrem temps increases
starving, fasting, malnutrition decreases
weight loss from calorie deficit decreases
smoking nic increases
caffeine increases
medication depends on med
78
New cards
how does weight statistically correlate to health
idk
79
New cards
define and calculate BMI and categories of BMI
bmi is body mass index
categories:
categories:
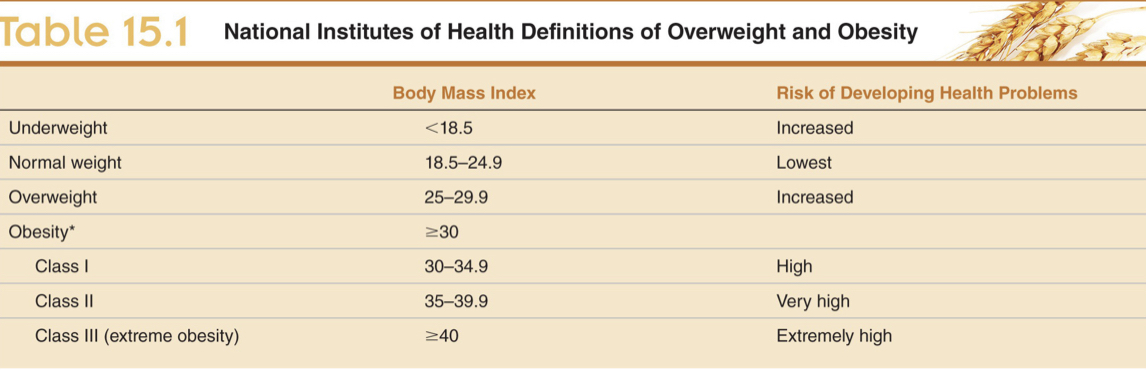
80
New cards
what are the pitfalls of BMI
does not take into account gender, LBM-muscle, bone and water and fat composition
81
New cards
what does research recommend w respect to BMI for the asain pop.
lower cutoff point
82
New cards
body distribution in terms of male and female numerical references
females >35 in.
males >40 in.
= higher chances of mortality and comorbidities
males >40 in.
= higher chances of mortality and comorbidities
83
New cards
what is the difference b/w visceral and subcutaneous fat
Visceral more toxic and detrimental fat is at wasit visceral @ waist and butt
\
\
84
New cards
what is the difference b/w pear and apple shaped in terms of health risks
pear shaped less detrimental
85
New cards
what are the 6 potential causes of obesity
calories
set point theory: whatever body weight is currently at is where the bod wants to stay
hormones
behavior
genetics
obesogenic envorni
set point theory: whatever body weight is currently at is where the bod wants to stay
hormones
behavior
genetics
obesogenic envorni
86
New cards
what are the 6 factors of an obesogenic environment
accessibility to food
increased snack consumption
food budget allotment
portion sizes
labor saving devices
increased sedentary behaviors
increased snack consumption
food budget allotment
portion sizes
labor saving devices
increased sedentary behaviors
87
New cards
what are the potential complications of obesity
comorbidites like cancers, osteoarthiritis, hypertension
88
New cards
what are the 5 stages of change under the transtheoretical model
1. pre contemplation
2. contemplation
3. planning
4. action
5. maintanence
89
New cards
what stages should the client not be in to receive effective counseling
pre contemplatin and conteplation
90
New cards
what is the dif. b/w ideal and reality of treatment
ideal-m healthy bmi (18.5-24.9)
reality- sustain a weight loss that is 3-5%of initial body weight
reality- sustain a weight loss that is 3-5%of initial body weight
91
New cards
A sustained weight loss of 3-5% will decrease the risk of what parameters?
death idk
92
New cards
16\. How is prevention of additional weight gain an active intervention?
93
New cards
17\. Know the 3 parts of the lifestyle approach for weight management.
change diet, PA, behaviour change
94
New cards
18\. What does the NIH recommend for weight loss with respect to a low calorie diet (LCD)?
men- 1500-1800 cal/day
women- 1200-1500 cal/day
women- 1200-1500 cal/day
95
New cards
19\. What is a VLCD?
800 cal/day
supervised liquid diet
supervised liquid diet
96
New cards
20\. In regards to the types of macronutrient diets, what does the research suggest about the best outcome for weight loss?
97
New cards
21\. What does the research suggest about the effectiveness of portion control, eating frequency, breakfast, eliminating SSB and meal replacements in terms of weight loss?
98
New cards
22\. Know the benefits of exercise.
99
New cards
23\. Know the optimal recommendation for maintaining weight loss.
100
New cards
. Know and understand the following behavior modification strategies: self-monitoring, goal setting, stimulus control and problem solving