ICCM - T4 and T5
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
what are the components to a preceptor presentation?
one-liner
past medical history
review of systems
physical exam
differential diagnosis
plan (meds, labs, imaging)
unstable angina diagnosis
history - pain at rest or a change in character of pain
additional - normal troponin, normal or minimal changes on EKG (potential ST depression or T wave inversion on EKG)
NSTEMI diangosis
positive troponin
additional - symptoms, no ST elevation on EKG, potential ST depression or T wave inversion on EKG
STEMI diangosis
ST elevation on EKG (2 continuous leads)
additional - positive troponin, symptoms, compensatory EKG changes
ACS medications
nitroglycerin
aspirin
heparin
ticagrelor - brand name is brilinta (alternative is clopidegrel)
ACS treatment
STEMI - cath lab within 90 min
unstable angina and NSTEMI - cath lab, but not immediately
nitroglycerin dosage for ACS
0.4 mg sublingual
repeat every 5 minutes for up to three doses
aspirin dosage for ACS
325 mg uncoated chewable
heparin IV bolus dosage for ACS
60 units/kg
max 4000 units
heparin IV drip dosage for ACS
12 units/kg
max 1000 units/hour
ticagrelor (brilinta) dosage for ACS
180 mg PO
clopidogrel dosage for ACS
300-600 mg loading dose
75mg PO QD after
what are the symptoms for atrial fibrillation?
palpitations, chest pain, dizziness, SOB
what are the two most common causes of atrial fibrillation?
CHF and sepsis
what are other causes of atrial fibrillation?
alcohol (holiday heart)
PE
pericarditis
myocarditis
valvular abnormalities
endocarditis
what trial supports that there is equal mortality to rhythm control vs rate control?
AFFIRM trial
what does the AFFIRM trial support?
equal mortality to rhythm control vs rate control in treatment for atrial fibrillation
the RACE II trial supports that when you rate control you should aim for a heart rate of what?
less than 110 bpm
what trial supports that you should aim for a heart rate of less than 110 bpm when rate controlling?
RACE II
what medications are used to rate control?
diltiazem or metoprolol
diltiazem dosage for rate control atrial fibrillation
bolus - 5, 10, 15, or 20 mg
drip - 5 mg/hour
what is happening during atrial fibrillation and what do you see on EKG?
multiple foci in the atria are firing, leading to the an irregularly irregular rhythm seen on EKG
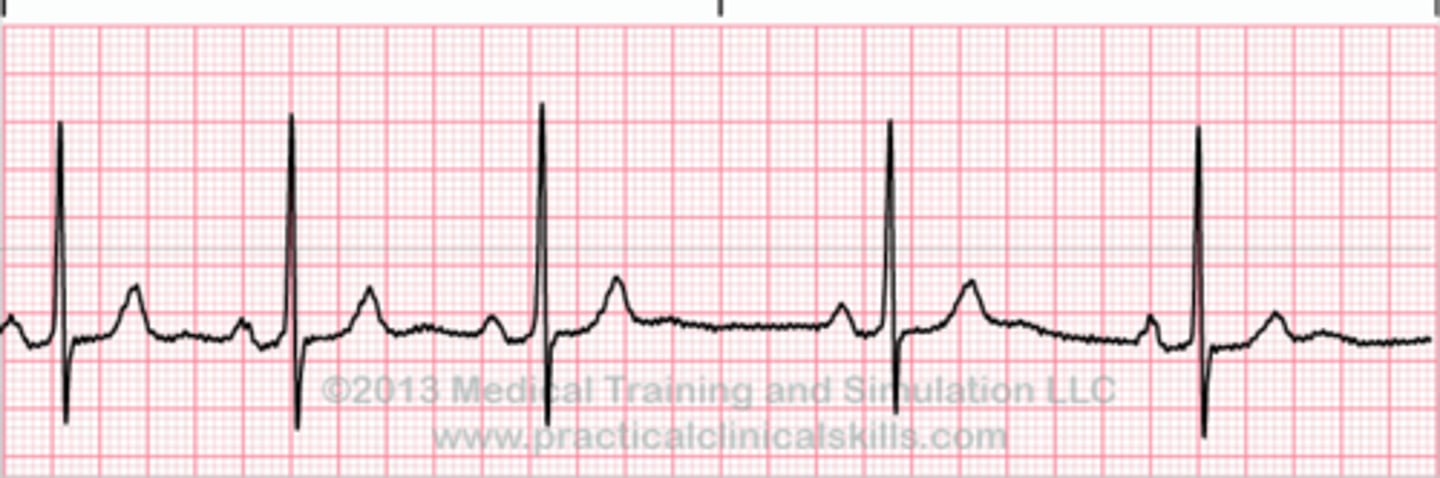
what are you at risk for with atrial fibrillation?
stroke
what are the risk factors for atrial fibrillation?
hypertension
coronary artery disease
congestive heart failure
alcohol abuse
cocaine use
what arrhythmias are included in supra-ventricular tachycardia?
sinus tachycardia
atrial flutter
AVNRT - atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
AVRT - atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (ex. WPW)
what does an EKG look like for supra-ventricular tachycardia?
regular narrow complex tachycardia
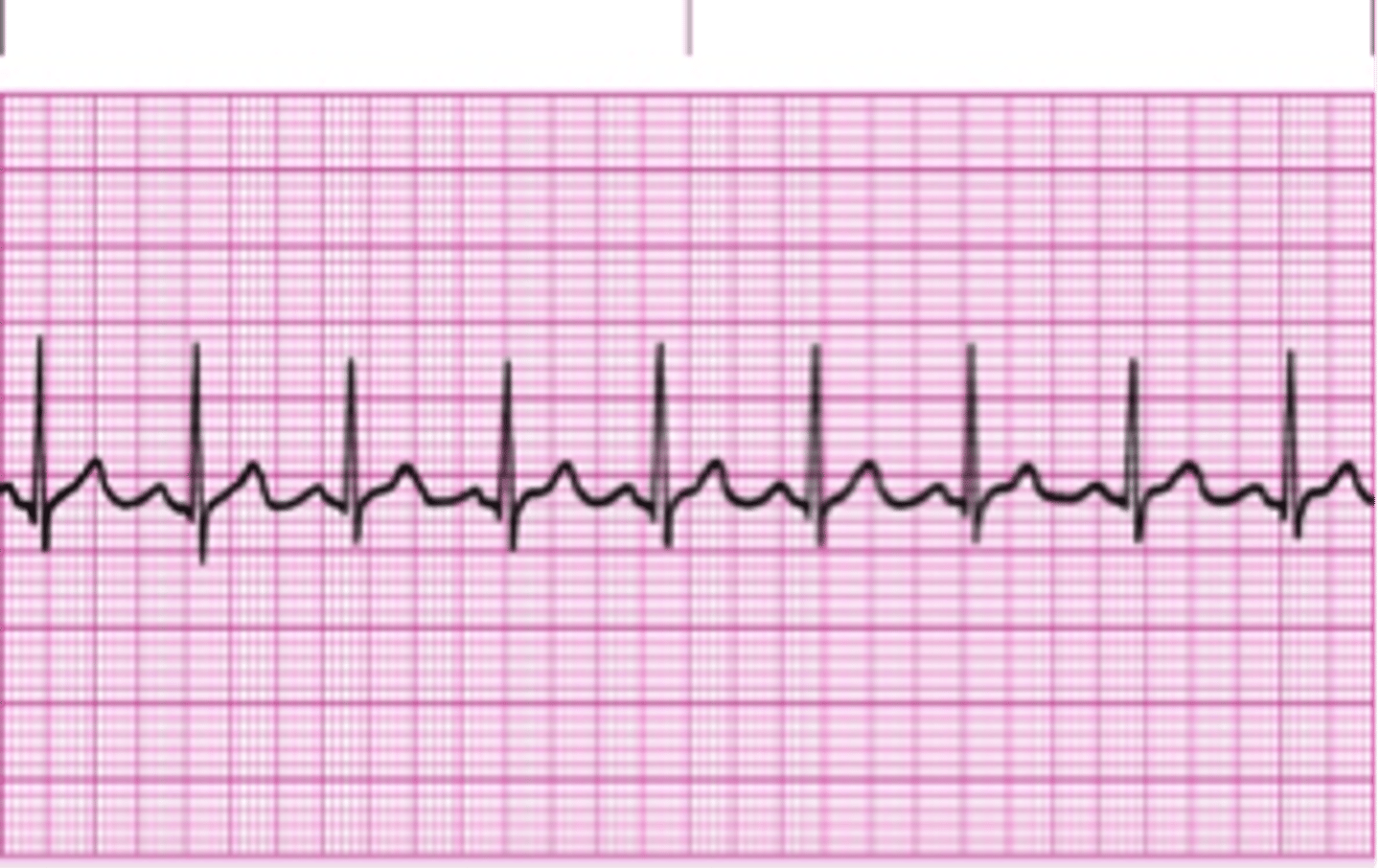
what is happening with the electrical conduction of the heart in sinus tachycardia?
follows normal pathway
heart rate >100 bpm
what is happening with the electrical conduction of the heart in atrial flutter?
dominant ectopic foci with an atrial rate of 250-350 bpm
what is happening with the electrical conduction of the heart in AVRT?
re-entry circuit through an accessory pathway (bundle of Kent)
what is happening with the electrical conduction of the heart in AVNRT?
re-entry circuit within or near the heart's AV node
what is the step-wise treatment for supra-ventricular tachycardia?
IV fluids
vagal maneuvers (valsalva, cough)
adenosine
which SVT would IV fluids treat?
sinus tachycardia
which SVT would vagal maneuvers treat and why?
AVRT or AVNRT
works by stimulating the vagus nerve -> blocking the AV node -> slowing down heart rate
which SVT would adenosine treat and why?
AVRT or AVNRT
works by producing a transient AV node block -> slowing down heart rate
which SVT would adenosine diagnose and why?
atrial flutter
works by slowing the conduction and can reveal the characteristic flutter waves on EKG, but won't break the rhythm/treat
why is adenosine considered diagnostic and therapeutic?
diagnostic - atrial flutter
therapeutic - AVRT and AVNRT
adenosine dosage for SVT
6, 12, 12 mg rapid IV push
what are the two types of ventricular tachycardia?
monomorphic
polymorphic
what does an EKG look like for ventricular tachycardia?
wide complex tachycardia
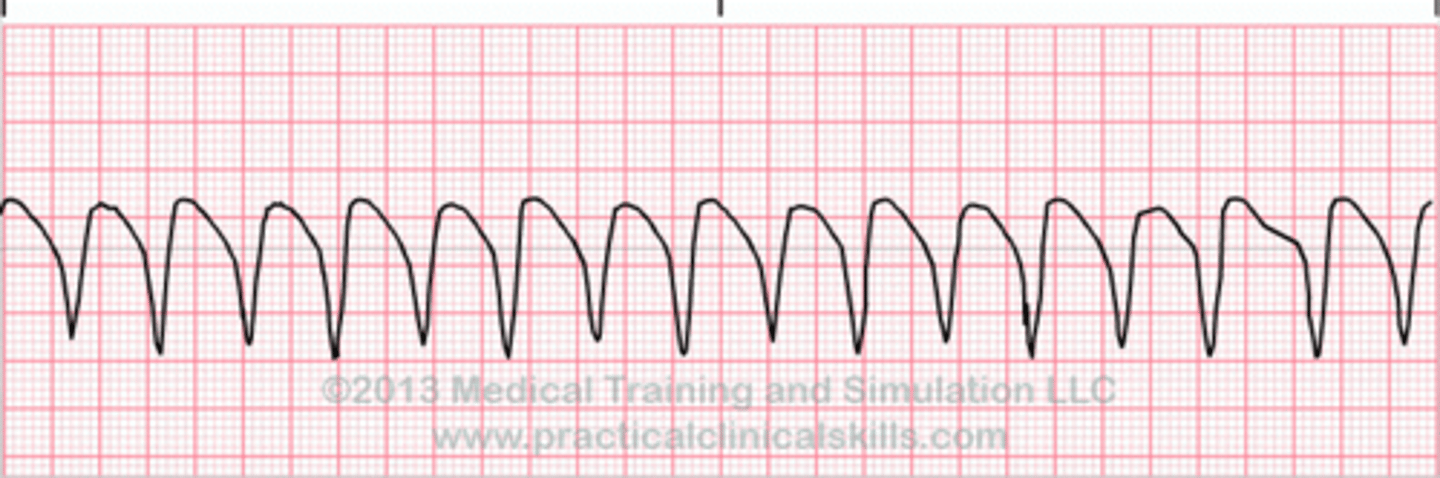
what are the treatment options for ventricular tachycardia for a patient with a pulse?
cardioversion
IV amiodarone
IV lidocaine
what is the treatment for ventricular tachycardia for a patient without a pulse?
defibrillation
what voltage is used to defibrillate a patient in ventricular tachycardia without a pulse?
300 joules (max)
amiodarone dosage for ventricular tachycardia
bolus - 150 mg IV over 10 minutes
drip - 1 mg/min for 6 hours
lidocaine dosage for ventricular tachycardia
bolus - 1 mg/kg IV
drip - 1-1.5 mg/kg at rate of 1-3 mg/min
T/F - amiodarone and IV lidocaine are equal mortality for treatment of ventricular tachycardia
true
what are the inferior EKG leads and artery associated?
II, III, aVF
RCA
what are the anterior EKG leads and artery associated?
V1-V4
LAD
what are the lateral EKG leads and artery associated?
I, aVL, V5, V6
LCfx
after an anterior STEMI what rhythm will a patient go into?
ventricular fibrillation
pulseless ventricular tachycardia
after an inferior STEMI what rhythm will a patient go into?
3rd degree heart block
normal PR interval for EKG
120s - 200 ms
normal QRS interval for EKG
< 120 ms
normal male QTc interval for EKG
< 440 ms
normal female QTc interval for EKG
< 460 ms
what does a prolonged QTc put a patient at risk for?
torsades de pointes
what labs and imaging should be obtained for all chest pain patients?
labs - CBC, CMP, magnesium, and troponin
imaging - EKG and chest x-ray
what is the dose for morphine and ondansetron (zofran) in the ED?
4 mg
gram positive bacteria list
staphylococcus
streptococcus
enterococcus
clostridium
listeria
bacillus
corynebacterium
gram negative bacteria list
escherichia
vibrio
salmonella
haemophilus
moraxella
pseudomonas
bartonella
pasturella
proteus
neisseria
klebsiella
enterobacter
helicobacter
yersinia
campylobacter
shigella
brucella
francisella
treponema
anaerobe bacteria list
bacteroides
eikenella
fusobacterium
eubacterium
atypical bacteria list
chlamydia
legionella
mycoplasma
what is unique about legionella
confirmatory diagnostic test - urine antigens
hyponatremia and elevated LFTs
what is the #1 cause of UTIs?
E. coli
what is the #2 cause of UTIs?
staphylococcus saprophyticus
what are 95% of blood culture contaminants?
staph epidermidis
staph hominis
staph haemolyticus
what are the different types of staphylococcus?
staph aureus
staph saprophyticus
staph epidermidis
staph hominis
staph hemolyticus
what are the different types of streptococcus?
alpha hemolytic - strep pneumoiae, strep viridans
beta hemolytic - group A (strep pyogenes), group B (strep agalactiae)
what are the different types of clostridium?
clostridium difficile
clostridium botulinum
clostridium perfringens
what are the different types of bacillus?
bacillus anthraces
bacillus cereus (reheated rice)
what are the non-STI chlamydias?
chlamydia pneumoniae
chlamydia psittaci
what is the history of penicillins?
discovered in 1928 by Dr. Fleming
a mold, Penicillium notatum, inhibited the growth of bacteria
what is the mechanism of action of penicillins?
inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
penicillin G (IM)
covers gram pos, gram neg, anaerobes
100% covers syphilis (treponema pallidum) and strep pyogenes
amoxicillin and ampicillin
covers gram pos, gram neg, anaerobes
100% covers strep pyogenes (not 100% for syphilis)
nafcillin, oxacillin, methacillin
covers gram pos ONLY
made to cover staph - good for MSSA
beta-lactamase inhibitors
covers gram pos, gram neg, anaerobes
amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (augmentin)
ampicillin/sulbactam (unasyn)
piperacillin/tazobactam (zosyn)
what is the MRSA and pseudomonas coverage for beta-lactamase inhibitors?
MRSA - no coverage from augmentin, unasyn, or zosyn
pseudomonas - no coverage from augmentin or unasyn; 95% coverage from zosyn