14-alpha substitution reactions of carbonyls
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
alpha substitution reactions
enolate (carbon - charge) binds to stuff
enol (C=C) binds to stuff
enolate
are better nucleophiles since they have negative charges
enol
keto-enol tautomerization
-reaction at equilibrium
-NOT a resonance
tautomers are defined
as constitutional isomers that interconvert at rapid equilibrium
although this inter convention occurs constantly
the keto form is favored
how to deprotonate alpha hydrogens
typical base (OH-) or LDA
Typical base (OH-) deprotonates
alpha hydrogens that are more substituted
multiple products form
LDA deprotonates
alpha hydrogen that are less substituted
forms one product
Base promoted alpha halogenations
all alpha hydrogens get replaced by halogen
1. OH-
2. Br2 (Xs)
Acid Catalyzed alpha Halogenation
only one alpha hydrogen is replaced with halogen
1. Acid (TFA)
2. X2
Alpha Deuteration
Replacement of all alpha hydrogen with deuterium (d).
1. acid or base.
2. D2O
Haloform reaction ( need CH3)
Complete halogenation of a methyl ketone in basic conditions.
1) OH-, (Xs) X2
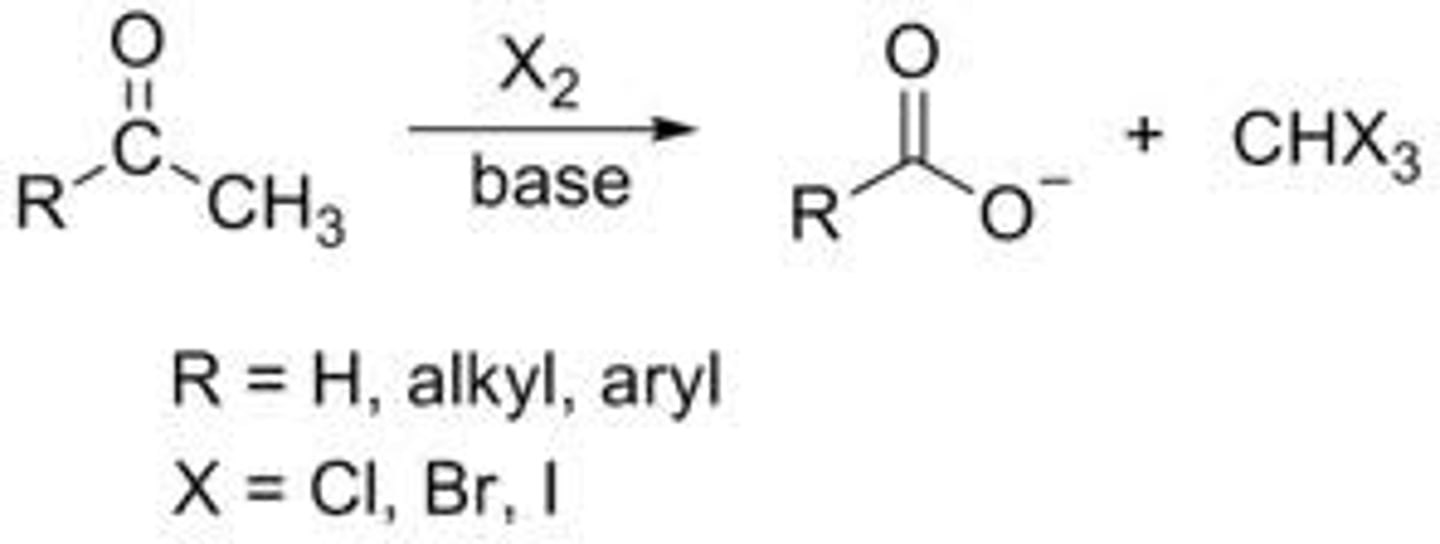
haloform reaction produces
a carboxylate and HCX3
HCX3 is a yellow precipitate, useful lab test
Aldol condensation
aldehyde + aldehyde
-ketone + ketone
-or aldehyde reacts with a ketone
reagent (OH-, H2O)
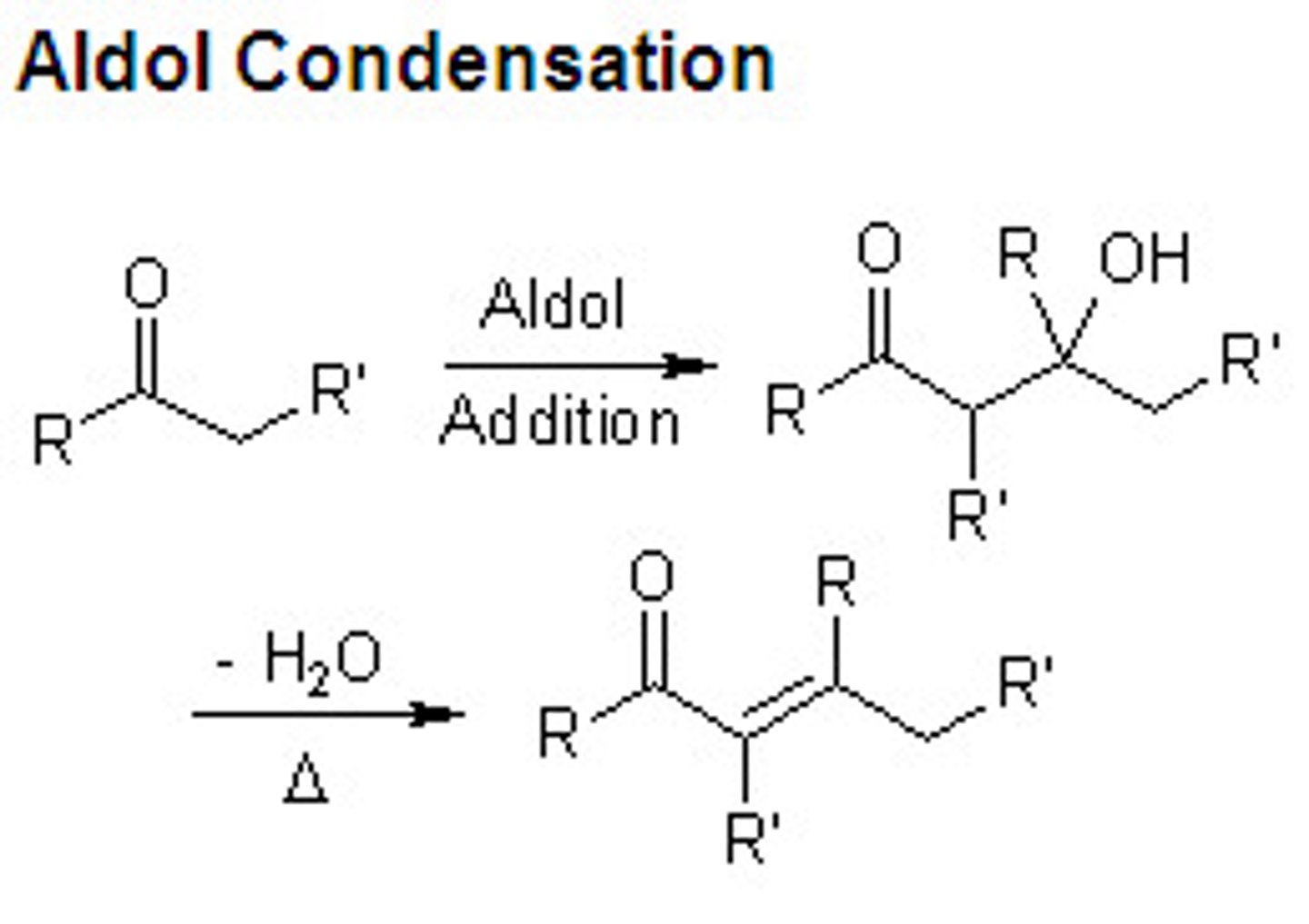
aldol condensation reaction mechanism
OH - takes a H from the alpha carbon
the carbanion adds to the carbonly carbon of an aldehyde or ketone
initial product is a
beta hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
plus acid and heat
a, b, unsaturated aldehyde/ ketone
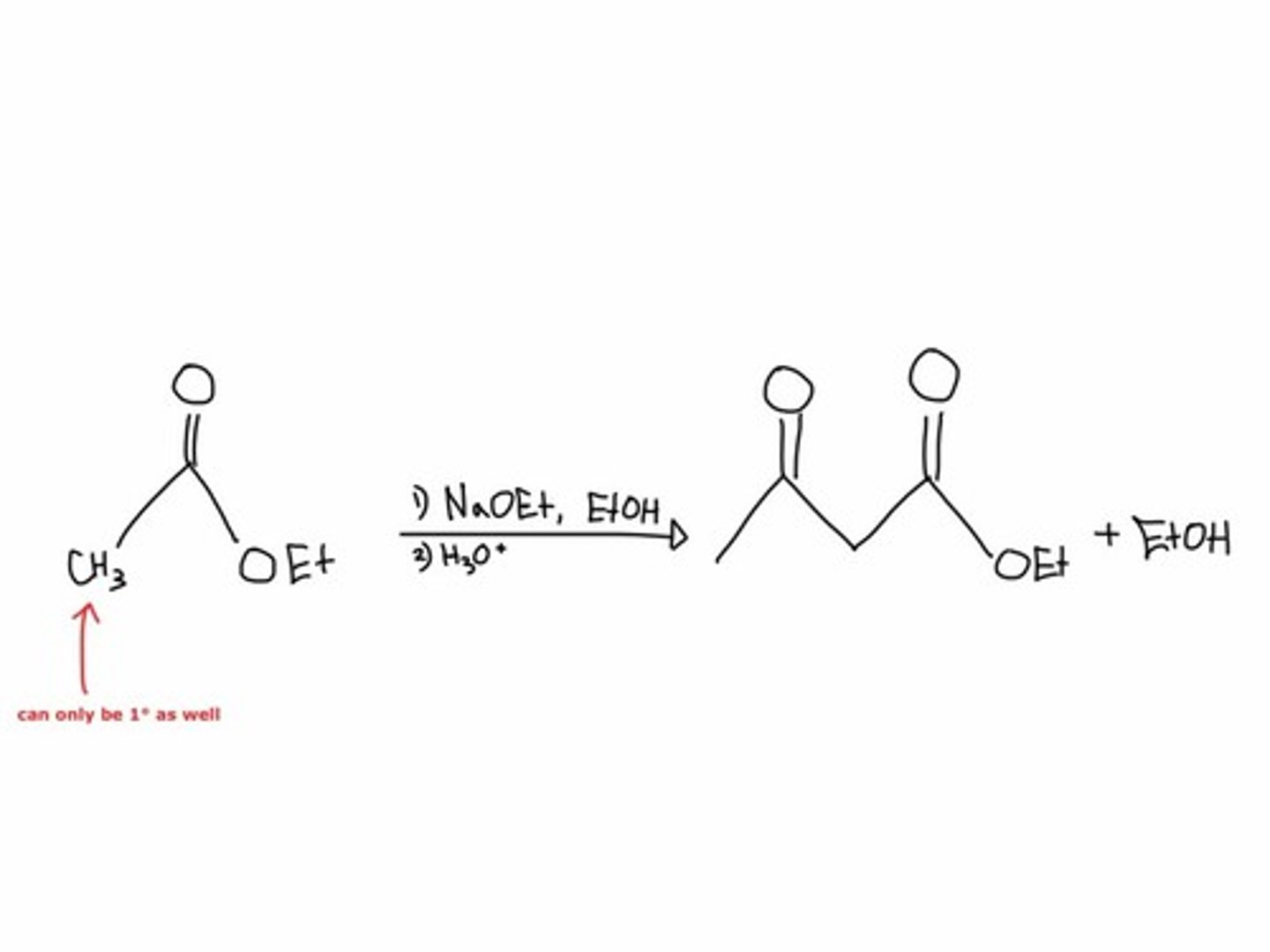
Claisen Condensation Reaction
- the aldol reaction with an ester.
- deprotonation of the α-C of an ester and the addition of the anion to the carbonyl carbon of a second ester.
- forms a β-ketoester
- has a biological application in fatty acid synthesis
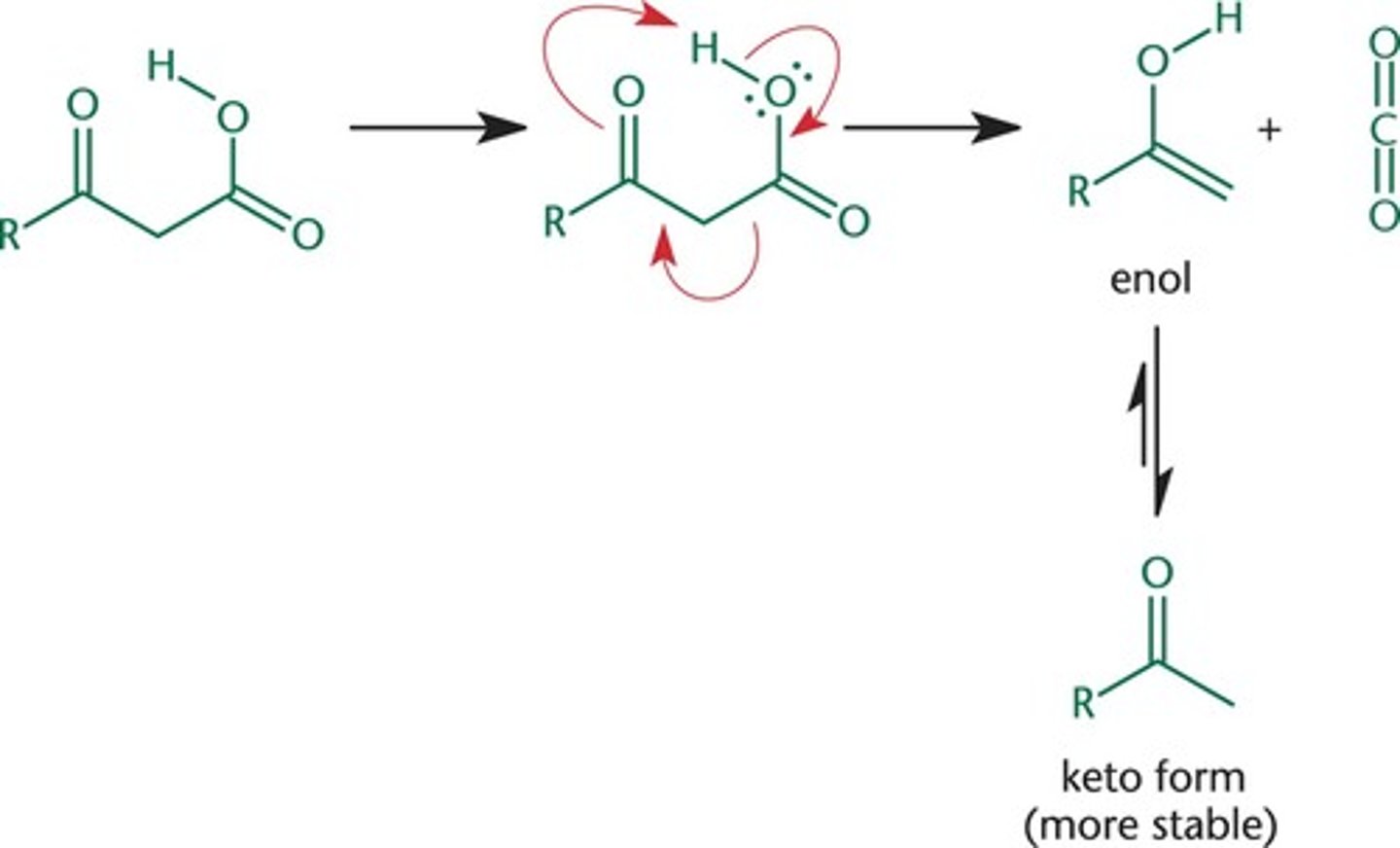
Beta -decarboxylation
B-keto esters are converted to the original ester reactants
add OH- ( deprotonates OR group)
Add heat and forces CO2 group to leave
quench (H2O)
get your original reactant
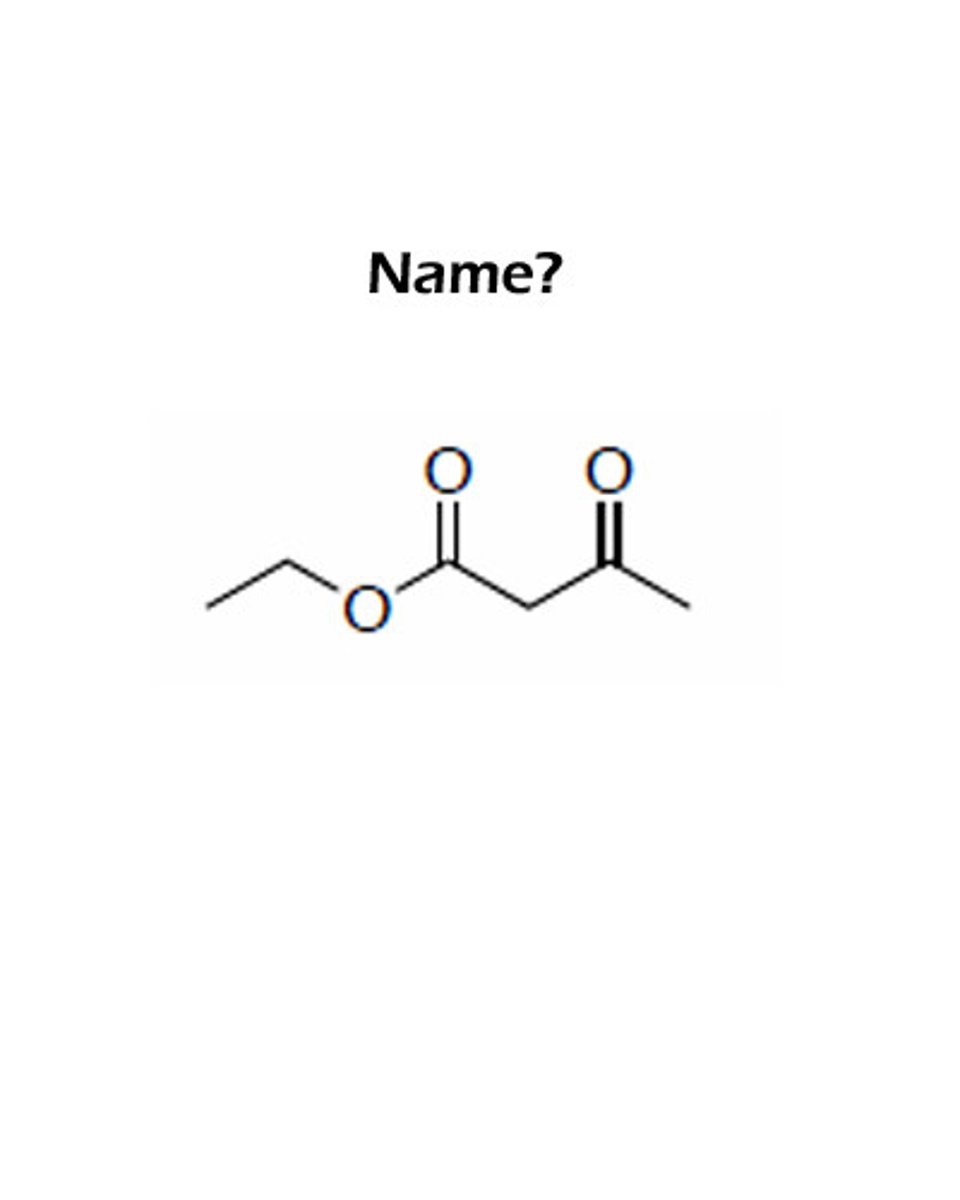
Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis reagents
1. NaOEt
2. R-X
3. NaOEt
4. R-X
5. H3O+, ∆
OEt-, or OR- must be matching (reagents and on the ester)
product from acetoacetic ester synthesis
methyl ketone with 2 & 4 attached at alpha carbon
+CO2
undergoes beta decarboxylation
Malonic Ester synthesis (reagents)
1. NaOEt
2. R-X
3. NaOEt
4. R-X
5. H3O+, ∆
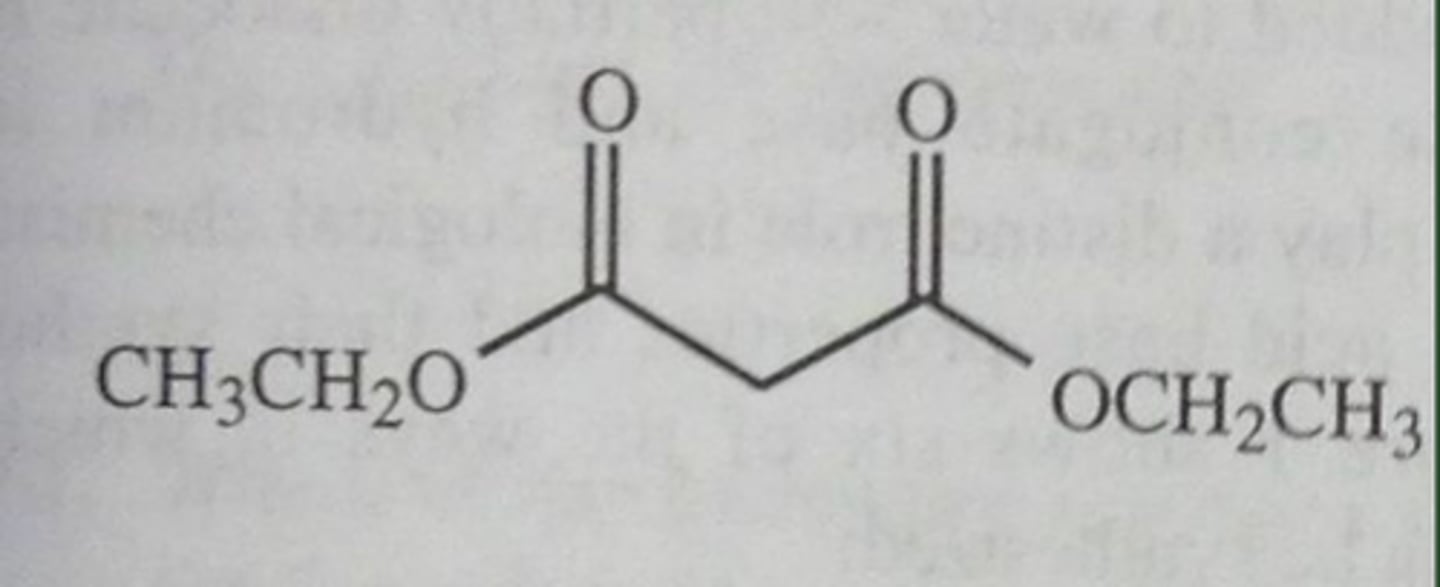
Malonic Ester Synthesis products
carboxylic acid