Neurons and Neural Firing
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1.3.A: Differentiate among the subsystems of the human nervous system and their functions. Unit 1.3.B: Explain how the basic process of neural transmission is related to behavior and mental processes. Unit 1.3.C: Explain how psychoactive drugs affect behavior and mental processes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Soma
The cell body, which contains all the DNA,
and other essential parts for keeping the neuron alive
Axons
A neuron's long projection that transmits electrical impulses from the cell body to other cells, covered by the fatty myelin sheaths
Myelin sheaths
A fatty insulating layer that surrounds the axon of a neuron, significantly increasing the speed at which electrical impulses (action potentials) are transmitted along the axon.
Synapses
Junctions between neurons where information is transmitted (axon terminal
Schwann cells
Produce myelin for the myelin sheath, with the Nodes of Ranvier being the spaces between them
Nodes of Ranvier
The spaces between Schwann cells.
Glial cells
Support cells in the nervous system that assist with various functions such as support, providing homeostasis, removing waste during sleep, and maintenance of neurons.
Major parts of a neuron
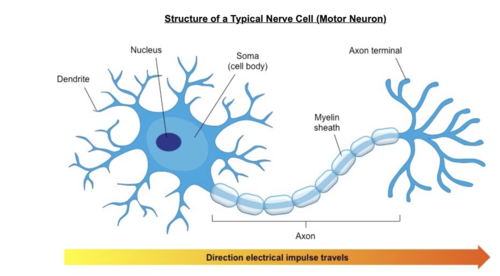
Reflex arc of the Spinal Cord
A neural pathway that mediates automatic responses to stimuli. Sensory neurons transmit information; some reactions occur when these neurons reach only the spinal cord
Sensory/Afferent neurons
Interneurons
Motor/Efferent neurons
resting potential
threshold
depolarization
All-or-Nothing Law/Response
refractory period
reuptake
excitatory
inhibitory
Dopamine
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Glutamate
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
Endorphins
Substance P
Acetylcholine