NSG 3111: Fetal Health Surveillance & Gestational/Pre-existing HTN
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
26 weeks
From what point in pregnancy should all mothers be advised to regularly monitor fetal movements?
Intermittent auscultation & continuous external EFM
What are the 2 methods to monitor a fetus?
Contractions
What does the toco monitor pick up?
Uterine fundus
Over which body part is the tocotransducer placed?
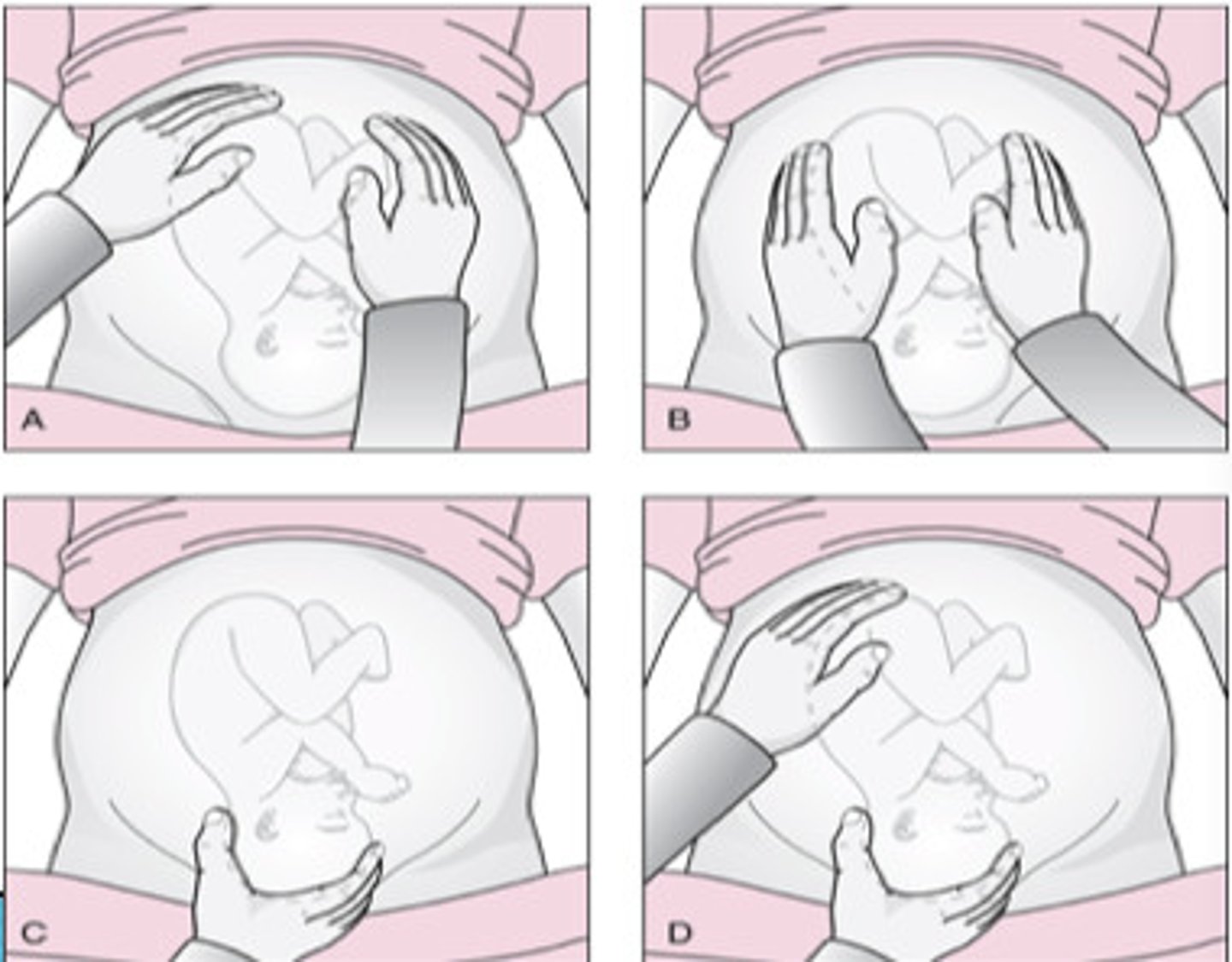
Leopold maneuvers
Series of 4 types of abdominal palpitation for determining fetal position
Right lower
In which quadrant of the mother's abdomen (anatomical position) would you place your stethoscope to listen to the FHR if the fetus presents in right occipitoanterior?
Left upper
In which quadrant of the mother's abdomen (anatomical position) would you place your stethoscope to listen to the FHR if the fetus presents in complete breech
False
True or false? Repetitive decelerations are normal when listening to the FHR using intermittent auscultation
Ultrasound transducer
Placed below the umbilicus where the FHR is best heard
≥2 within a 40-min window over max 80 min
Normal amount of accelerations during a non-stress test
6-25 bpm
Moderate amount of variability (normal)
5 bpm
Minimal amount of variability; normal if under 40 min period
Causes of fetal bradycardia
Maternal hypotension, maternal position, cord prolapse w/ ROM, fetal cardiac problems
Causes of fetal tachycardia
Maternal fever or infection
10 seconds
What does each box on the x axis represent on a FHR tracing?
Absent
How would you classify this variability?
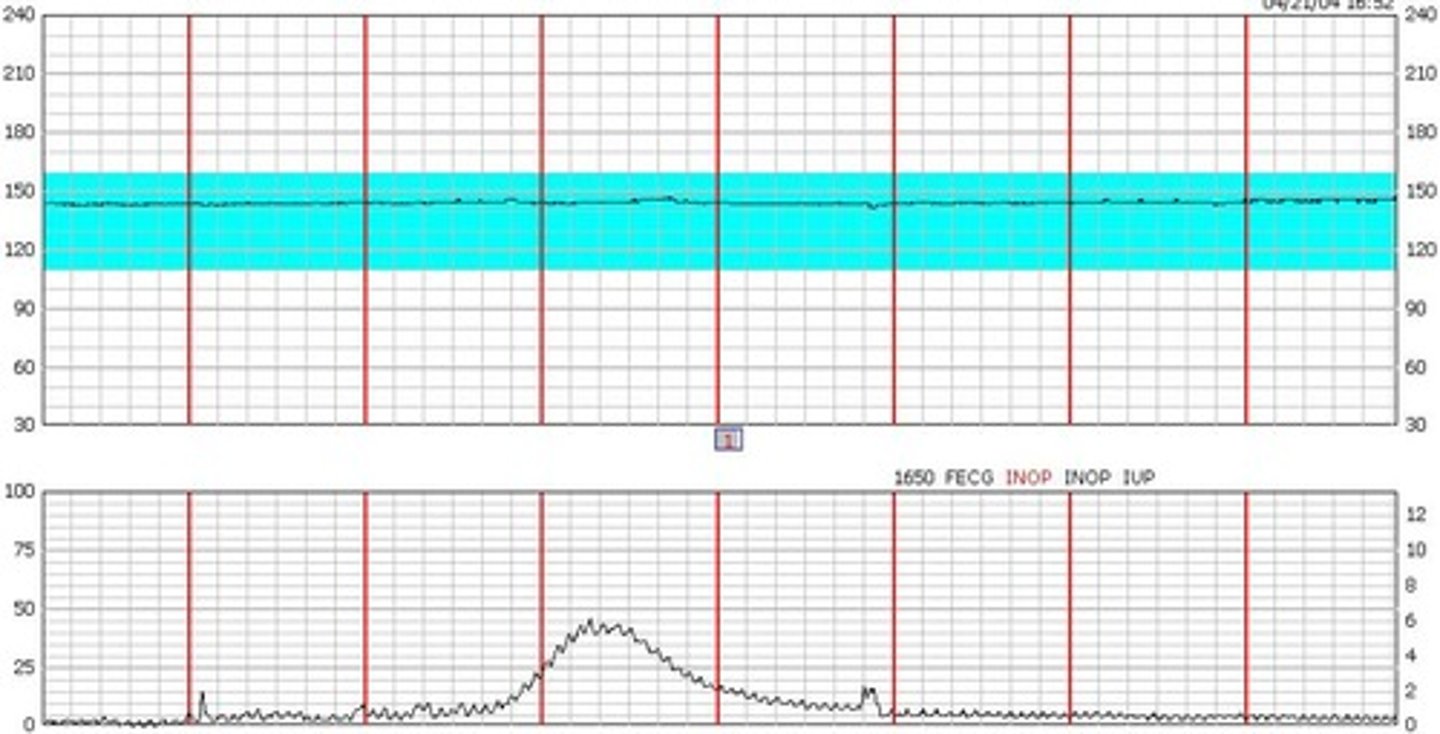
Minimal
How would you classify this variability?
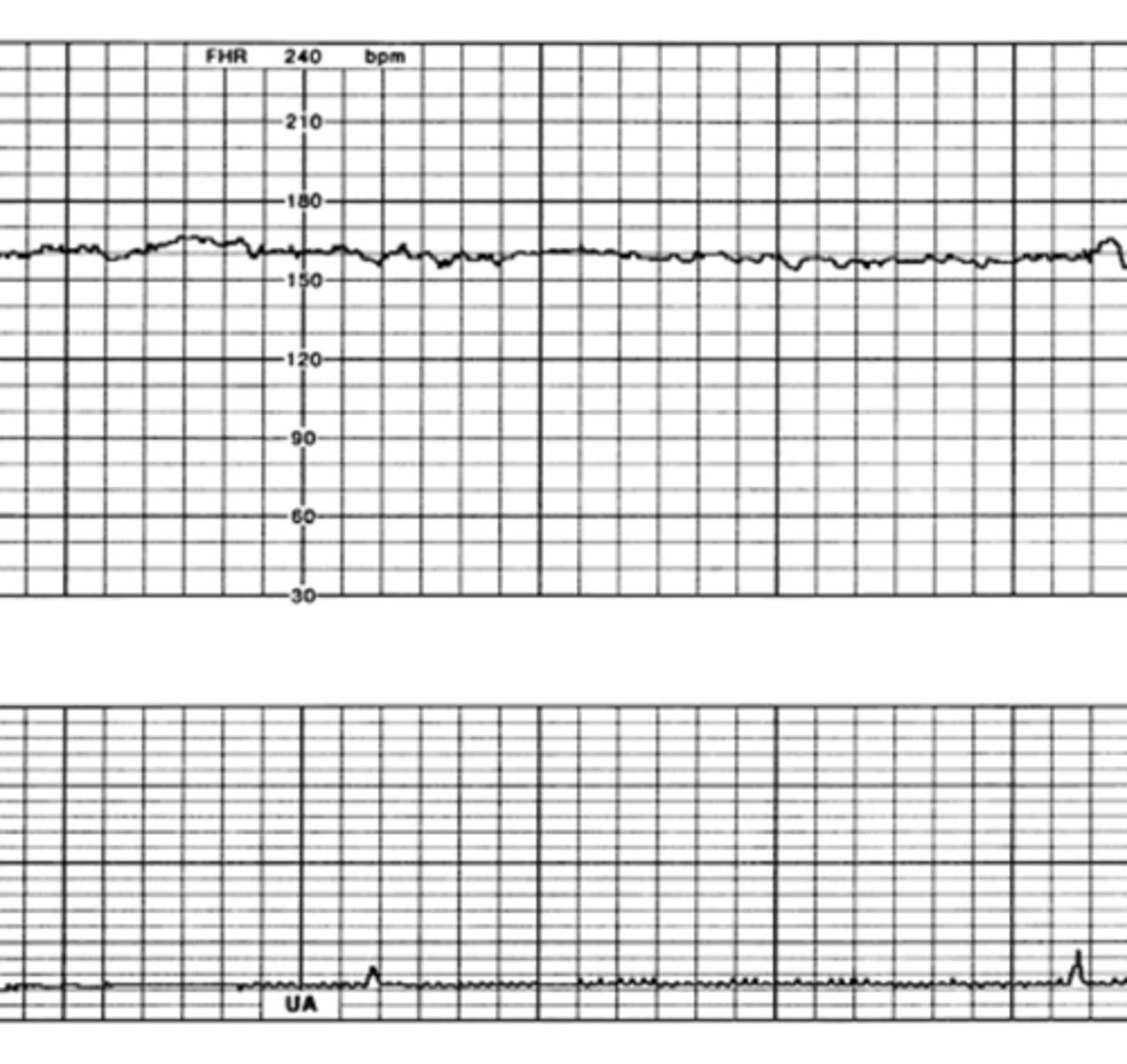
Acceleration
Abrupt (onset to peak in <30 seconds) increase in FHR above baseline; ≥15 bpm above baseline lasting ≥15 seconds
Fetal wellbeing/optimal oxygenation & fetal movement
Presence of accelerations indicate...
Decelerations
Decrease from baseline by ≥15 bpm lasting ≥15 seconds
Variable deceleration
Abrupt deceleration; onset to nadir <30 seconds; complicated and uncomplicated
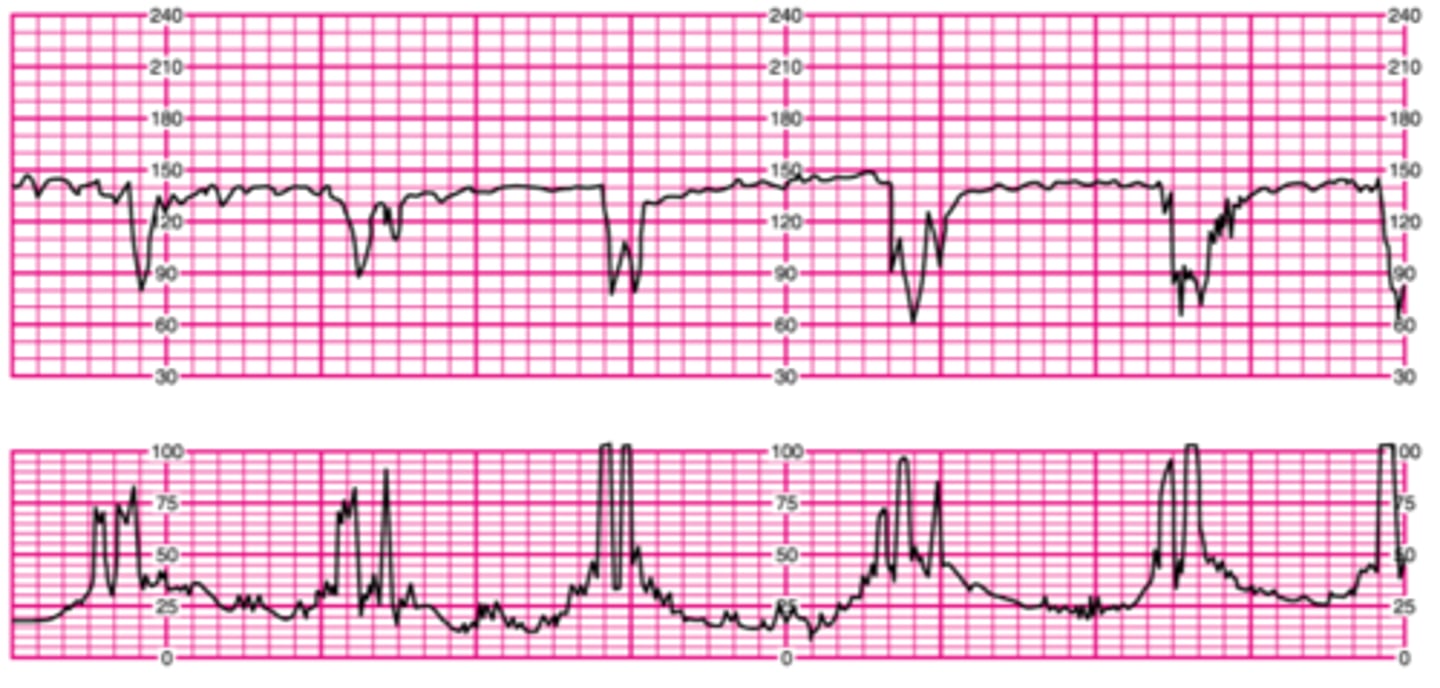
Uncomplicated decelerations
Type of variable deceleration; ≥15 bpm below baseline for ≥15 sec BUT <60 seconds
Cord compression
What is the main cause of uncomplicated variable decelerations?
True
True or false? Uncomplicated variable decelerations are normal as long as they are not repetitive
Complicated decelerations
A type of variable deceleration that lasts >60 secs AND decreases to 60bpm or less OR the heart rate deceleration is equal or greater than 60bpm below the baseline
Cause of complicated deceleration
Fetal depletion of reserves/hypoxemia related to significant cord compression
Early decelerations
Type of deceleration with a smooth and gradual decrease and return to baseline; onset, nadir, and recovery occur at the same time as the mother's contraction
Head compression
What are early decelerations caused by?
False (early decels are normal)
True or false? Early decelerations are a sign of fetal hypoxia and require immediate intervention
Late decelerations
Type of deceleration which begins after the contraction starts, the nadir occurs after the contraction's peak, and the recovery occurs after the contraction ends; always concerning
Uteroplacental insufficiency (decreased fetal oxygenation)
Cause of late decelerations
Repositioning, maternal VS, IV, O2, oxytocin
What are some interventions the nurse could execute after observing late decelerations?
Increment
Phase of the contraction in which the uterus slowly increases in tension, pressure rises from resting tone towards the peak
Acme (peak)
The strongest point of the contraction, uterine pressure is at its maximum, early FHR decelerations often hit their nadir at this time
Decrement
Uterine tension decreases from the peak back to its resting tone and blood flow to the placenta increases again
Frequency
Start of one contraction to the start of the next, taken over a 10 minute period
Duration
The length of the contraction (in seconds) from the increment to the decrement
Intensity
The palpable strength of the contraction at its peak; subjective to the mother, but also can be palpated by HCP
Mild
When palpating the mother's uterus, this uterine contraction has the same firmness as the tip of the nose
Moderate
When palpating the mother's uterus, this uterine contraction has the same firmness as the chin
Strong
When palpating the mother's uterus, this uterine contraction has the same firmness as the forehead
Placental abruption
What is a significant complication and cause of mortality from HTN in pregnancy?
≥140 mmHg
What must the systolic BP be to diagnose HTN disorder in pregnancy?
≥90 mmHg
What must the diastolic BP be to diagnose HTN disorder in pregnancy?
Systolic >160 mmHg OR Diastolic >110 mmHg
What values of BP are classified as severe hypertension?
Chronic HTN (pre-existing)
HTN predates pregnancy or appears before 20 weeks without evidence of pre-eclampsia
Gestational HTN
HTN occurs after 20 weeks without evidence of pre-eclampsia
Transient HTN
HTN related to environmental stimuli
White coat HTN
HTN present only in clinician's office, normal otherwise
Masked HTN
BP normal in clinician's office, abnormal otherwise
Pre-eclampsia
Multisystemic vasospastic disease process of reduced organ perfusion; HTN + new proteinuria OR evidence of organ dysfunction
Symptoms of CNS dysfunction (related to pre-eclampsia)
Severe headache/visual symptoms; eclampsia, cortical blindness/retinal detachment, GCS <13, stroke, TIA
Symptoms of cardiorespiratory dysfunction (related to pre-eclampsia)
Chest pain/dyspnea, SpO2 <97, myocardial ischemia or infarction
Symptoms of hematological dysfunction (related to pre-eclampsia)
Low platelet count
Symptoms of renal dysfunction (related to pre-eclampsia)
Elevated serum creatinine, AKI, new indication for dialysis
Symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (related to pre-eclampsia)
RUQ or epigastric pain, elevated AST, ALT, hepatic hematoma or rupture
Symptoms of uteroplacental dysfunction (related to pre-eclampsia)
Atypical/abnormal NST/CTG, fetal growth restriction, oligohydramnios, absent/reversed end-diastolic flow by umbilical artery, angiogenic imbalance
Effects of maternal arteriolar vasospasm
Diminished diameter of BV, impeded BF to all organs (eyes, kidneys, placenta, brain, liver), hypertension
Proteinuria
Protein concentration ≥0.3g/day OR ≥30mg/mmol of urinary creatinine in a spot (random) urine sample
Pre-eclampsia high risk factors
Prior pre-eclampsia, pre-pregnancy BMI >30, chronic HTN, pre-gestational DM, CKD, systemic lupus erythematous/antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, assisted reproductive therapy
Eclampsia
Seizure activity or coma from profound cerebral effects of pre-eclampsia
HELLP syndrome
Laboratory diagnostic variant of severe pre-eclampsia that involves hepatic dysfunction characterized by decreased RBCs due to damage from vasospasms, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets
Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets
What does HELLP syndrome stand for?
Magnesium toxicity
What does an absent or sluggish reflex response indicate?
Cerebral S&S of severe pre-eclampsia
What do more brisk, hyperactive, or a clonus reflex response indicate?
Betamethasone
Glucocorticosteroid given to enhance fetal lung maturity; given at <36+4
Magnesium sulphate
Anticonvulsant given to prevent seizures; antidote is calcium gluconate
Labetalol
First choice of antihypertensive drug to control pre-eclampsia
Nifedipine, methyldopa
Other drugs used to control blood pressure during pregnancy
2+
Normal grade for reflex response
Hyperemesis gravidarum
When nausea and vomiting in pregnancy is excessive; weight loss, electrolyte imbalance, nutritional deficiencies, ketonuria
Cholestasis
Stoppage of bile flow due to disruption of hepatic blood flow; generalized pruritis
Chorioamnionitis
Bacterial infection of amniotic cavity; S&S include maternal fever, maternal/fetal tachycardia, uterine tenderness, foul odor of amniotic fluid
True
True or false? Insulin cannot cross the placental barrier
1st trimester
In which trimester(s) is there increased insulin production, increased peripheral use of glucose (therefore decreased blood glucose), and lower fasting blood glucose?
Hypoglycemia
What is the mother at risk for during the 1st trimester due to increased insulin production?
2nd & 3rd trimesters
In which trimester(s) does pregnancy have a diabetogenic effect, increasing insulin resistance and glucose sparing to meet the needs of the growing fetus?
Hypoglycemia
What are these S&S of? Irritability, hunger, sweating, weakness, pallor, rapid pulse, shallow respirations, dizziness
Hyperglycemia
What are these S&S of? Nausea/vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, drowsiness, increased urination, weak & rapid pulse, rapid breathing
3.4-6.7 mmol/L
Normal blood glucose levels (euglycemia)
In assessing the knowledge of a pre-gestational patient with T1DM concerning changing insulin needs during pregnancy, a nurse recognizes that further teaching is warranted when the patient states
"I will need to increase my insulin dosage during the 1st 3 months of pregnancy"
3 multiple choice options
Antiretroviral therapy
What should HIV be treated with before and during pregnancy?
Decrease risk of transmission to fetus
What is the goal of HIV management during pregnancy?
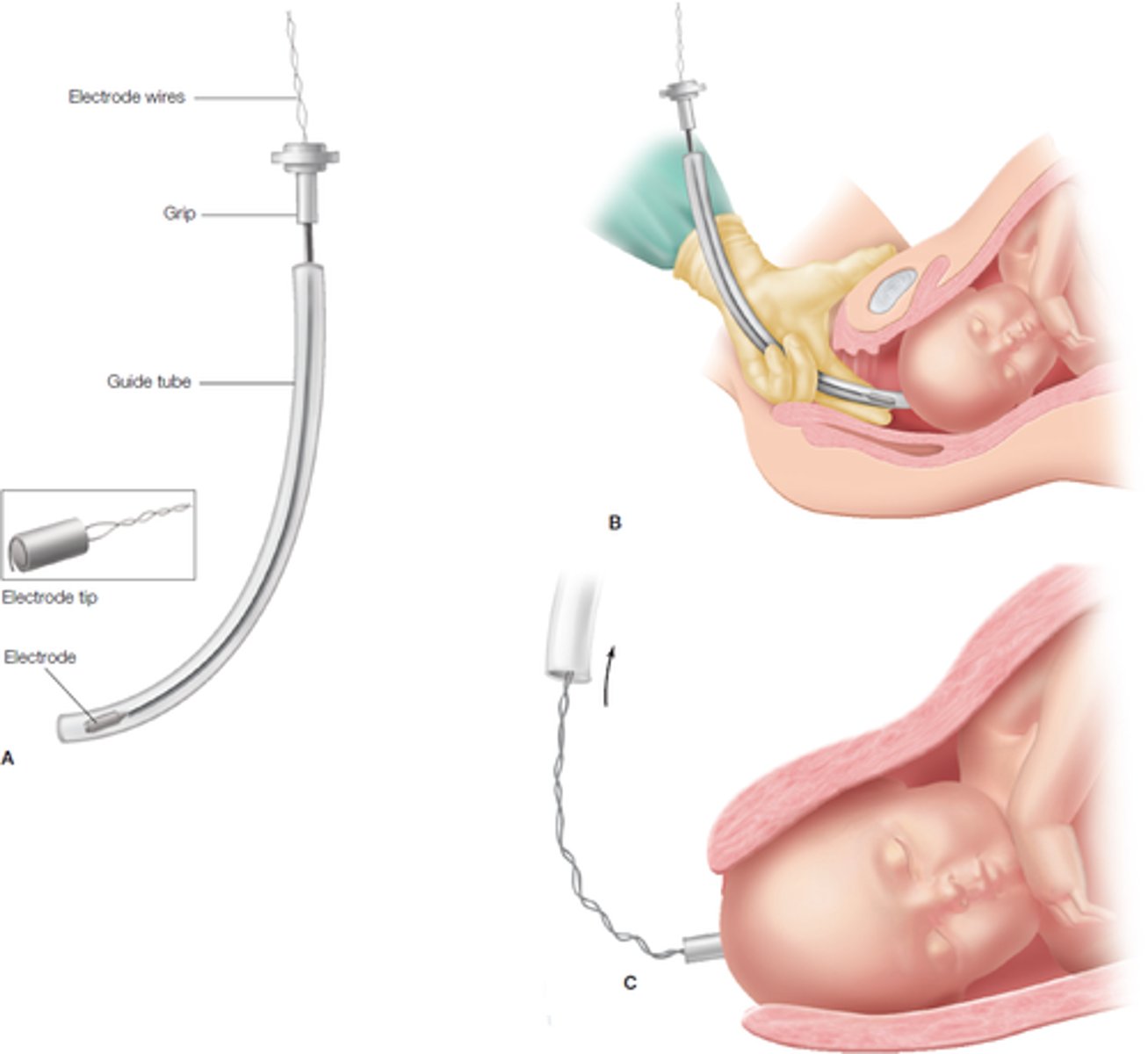
Fetal scalp electrode
Small electrode attached to the fetal scalp that senses the potential differences created by the depolarization of the fetal heart