Unit 5: Analytical Applications of Differentiation
The Mean Value Theorem (MVT)
The MVT links the average rate of change and the instantaneous rate of change
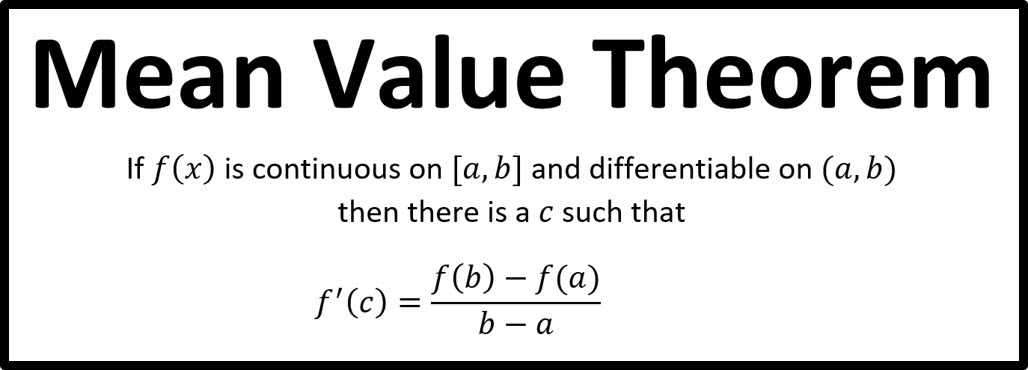
There must be some point in the interval where the slope of the tangent line equals the slope of the secant line (that connects the endpoints)
Rolle’s Theorem is a special case of the MVT
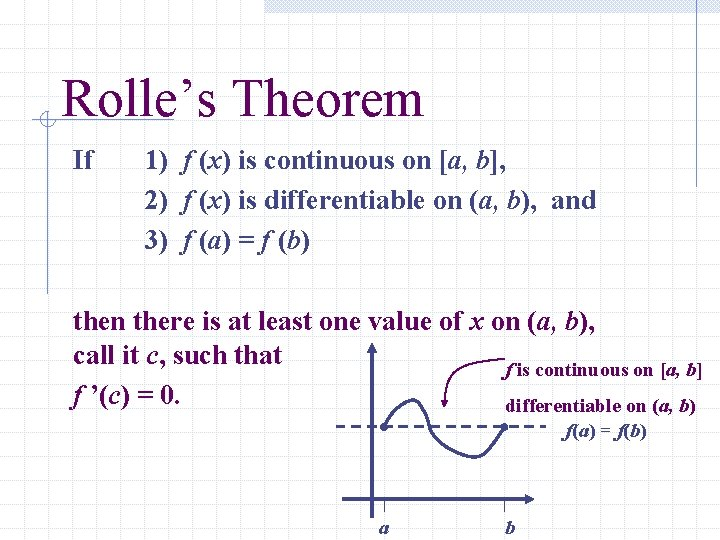
It means that a continuous, differentiable curve has a horizontal tangent between any two points
Extreme Value Theorem
- The Extreme Value Theorem states that if a function is continuous on a closed interval, then it must have both a maximum and a minimum value on that interval.
- The maximum and minimum are called extrema and there are two types of each:
- Absolute (global) → No other value is higher/lower than an absolute
- Local (relative) → The highest/lowest in the nearby area
- Any place an extrema could exist are called critical points
Intervals of Increase and Decrease
- Using the first derivative we can identify when the original function is increasing or decreasing
- For all the values that f’(x) > 0, the function is increasing
- For all the values that f’(x) < 0, the function is decreasing
Take the derivative of the function
Set it equal to zero to find your critical numbers
Plug in a number above the critical point and below the critical point to find the sign of f’(x)

- In this example we can see that if we plug in a number higher than 1 (such as 2) we get a negative number → f(x) is decreasing
- If we plug in a number less than than 1 (such as zero) we get a positive number → f(x) is increasing
- Let’s say that we are given the function f(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 + 9x + 2, and we need to find where the function is increasing or decreasing.
- To solve this problem, we need to take the derivative of the function f(x) and set it equal to zero to find the critical points.
- f'(x) = 3x^2 - 12x + 9
- Setting f'(x) equal to zero, we get:
- 3x^2 - 12x + 9 = 0
- Solving for x, we get:
- x = 1 or x = 3
- Now, we need to determine whether the function is increasing or decreasing on each interval between the critical points. We can do this by plugging in test values into f'(x) and seeing if the result is positive or negative.
- When x < 1, f'(x) is negative, so the function is decreasing.
- When 1 < x < 3, f'(x) is positive, so the function is increasing.
- When x > 3, f'(x) is negative, so the function is decreasing.
- Therefore, the function f(x) is increasing on the interval (1, 3) and decreasing on the intervals (-∞, 1) and (3, ∞).
Relative Extrema
- The first derivative also tells us relative maxima and minima of a function
- When the first derivative shifts from positive to negative there will be a relative maximum
- When the first derivative shifts from negative to positive there will be a relative maximum
- For example, our function above has a relative maximum at x=1 because our derivative changes from positive to negative
Candidate’s Test & Absolute Extrema
To find the absolute (global) extrema you have to consider the endpoints and critical numbers
Make a table of these values
Then plug back into your ORIGINAL FUNCTION

Function Concavity
The first derivative tells us if the function is increasing or decreasing
The second derivative tells us if this is happening at an increasing or decreasing rate
This is given to us by something called concavity
- For all the values that f”(x) > 0, the function is concave up
- For all the values that f”(x) < 0, the function is concave down

Take the second derivative of the function
Set it equal to zero to find your points of inflection
- Points of inflection are where the second derivative changes sign
Plug in a number above the critical point and below the critical point to find the sign of f”(x)
- Suppose we have a function f(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 + 9x + 2. Find the intervals where the function is concave up or concave down using the second derivative test.
- To find the intervals where the function is concave up or down, we need to take the second derivative of f(x).
- f(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 + 9x + 2
- f'(x) = 3x^2 - 12x + 9
- f''(x) = 6x - 12
- To find the critical points, we set f''(x) = 0:
- 6x - 12 = 0
- x = 2
- Now we can use the second derivative test to determine the intervals of concavity:
- When x < 2, f''(x) < 0, so the function is concave down.
- When x > 2, f''(x) > 0, so the function is concave up.
- Therefore, the function is concave down on the interval (-∞, 2) and concave up on the interval (2, ∞).