CNS acting drugs
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
antipsychotics MOA
generally involes modulation/blockade/decrease of limbic (emotional nervous system) dopamine (DA) neurotransmission
mostly Ix w/ dopamine D2 receptors but also display affinity for other neuroreceptors
triggering bioactivity at other receptors can lead to SE’s, but also can be responsible for the drug’s efficacy
structure of antipsychotics
are lipophilic dopamine mimetics (look alikes)
high drug logP/lipophilicity accounts for significant CNS/brain penetration and accumulation
what are the 3 key chemical features of antipsychotics, and what are their roles?
aromatic unit (lipophilic)
increases drug lipophilicity + permeability thru membrances, esp the BBB to act and accumulate in the CNS
single/multi ring system, often w halogen groups to boost lipophilicity
amino unit (basic)
ionisable alkyl or heterocyclic 3* amine group
can be reacted w strong acids to form water sol. salts → to deliver drug in aq dosage form
aliphatic linker unit
small fatty unit, often alkyl (carbon) based
first gen antipsychotics
function as potent dopamine D2 antags
but display lack of receptor specificity → can lead to undesireable SE’s
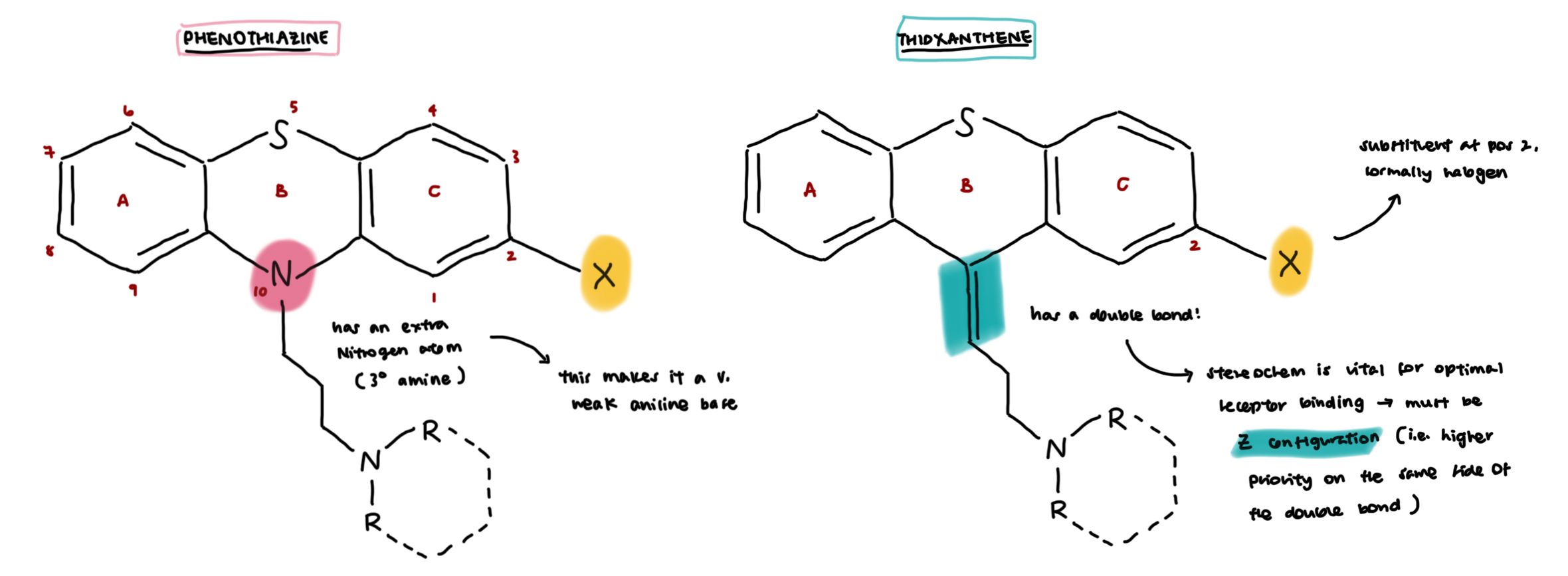
phenothaizines v.s. thioxanthenes
phenothiazines → extra N in aromatic ring structure
thioxanthenes → double bond in linker chain unit
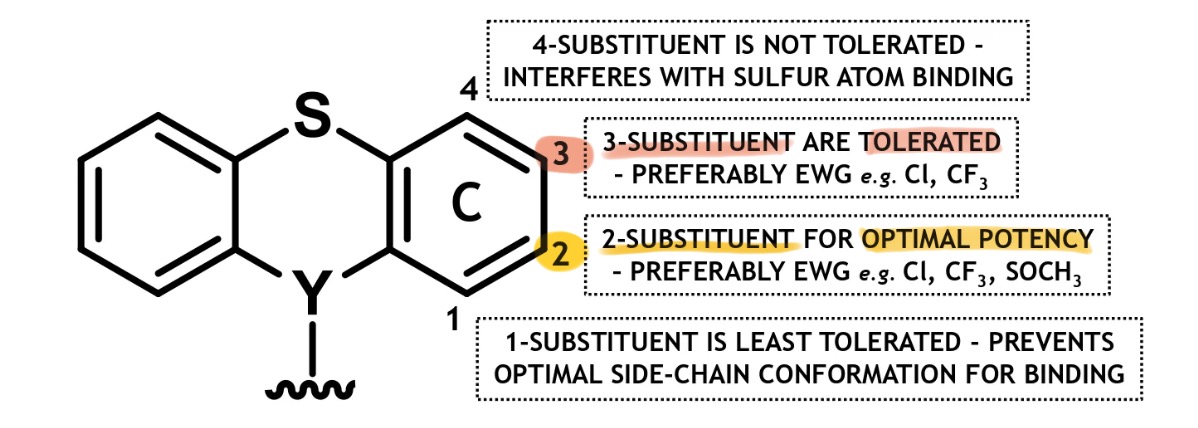
phenothiazines + thioxanthenes tricyclic ring substitution
only v minimal ring substitution on ring C is permitted → <2 ring subs diminishes bioactivity
vast majority of drugs only possess one ring C sub
2-C sub → shld be EWG for optimal dopamine (DA) binding
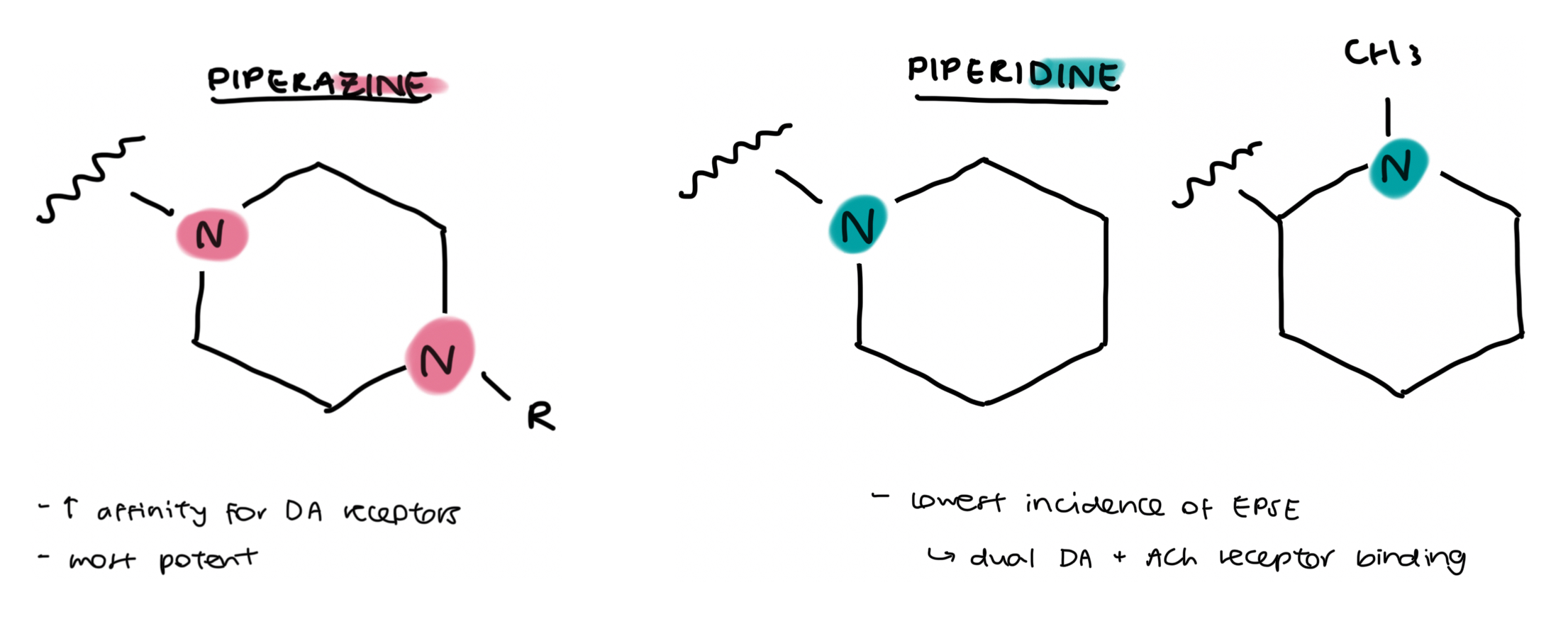
phenothiazines + thioxanthenes terminal amino unit
piperazine based drugs possess the highest affinity for dopamine receptors and are the most potent antipsychotics
piperazine > piperidines > alkylamines
piperazine based drugs also possess the lowest affinities for other receptors (ACh, H1 and a-1) → hence less likely to induce sedation + orthostatic hypotension
piperidine based drugs have lowest incidence of EPSE due to their dual DA and ACh receptor activities
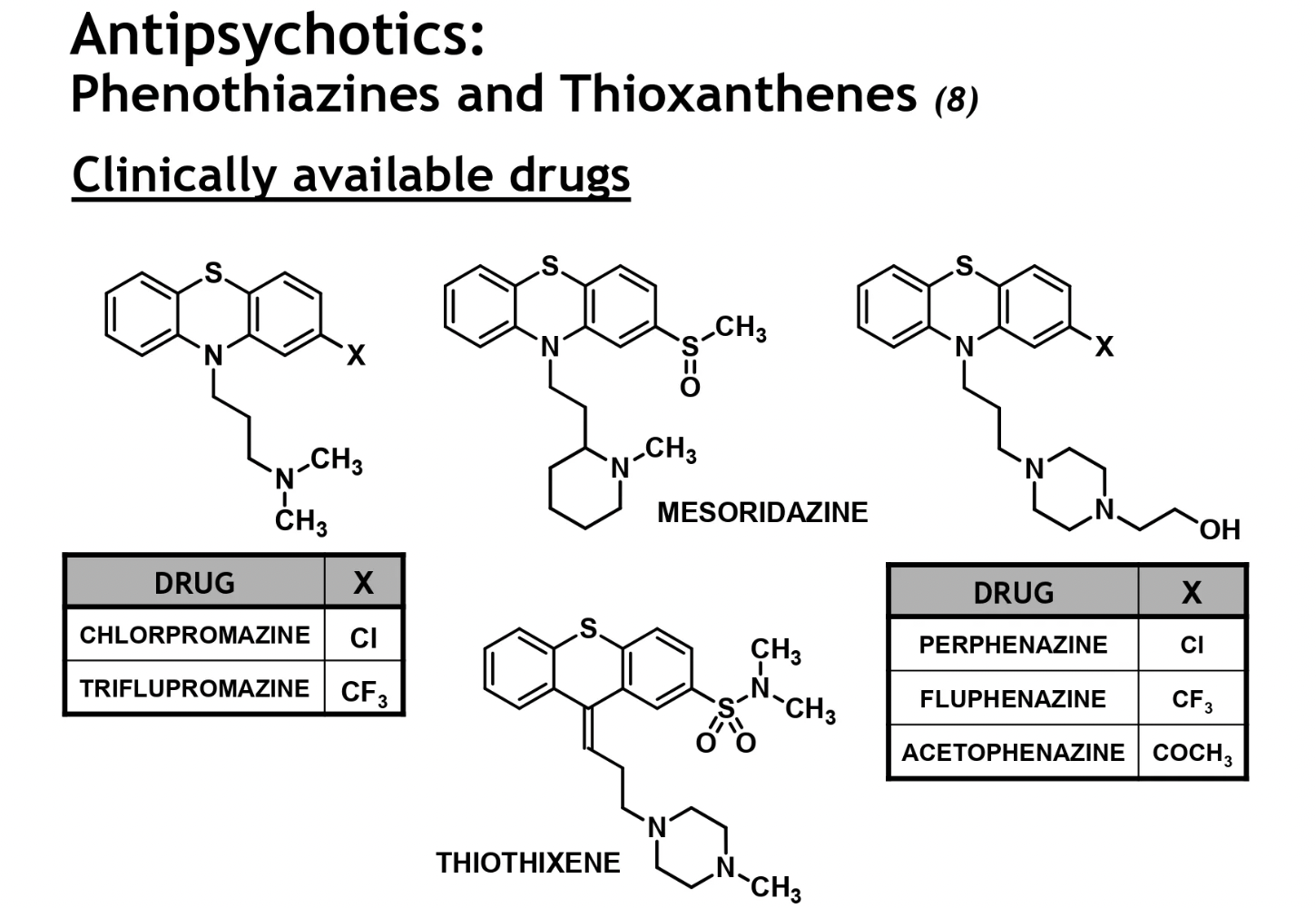
clinically available phenothiazine + thioxanthene antipsychotic drugs
left → alkyl amine
middle → piperidine based drug
right → piperazine based drug (2 N)
chlorpromazine → first antipsychotic
when Cl is replaced w CF3 (trifluoromethyl) → drug potency increases due to EWG effect + increased lipophilicity
same applies to perphenazine (X = Cl) and fluphenazine (X = CF3)
F → highly electronegative → electron withdrawing
halogens also increase potency + lipophilicity
100mg of chlorpromazine = activity of 25mg triflupromazine
triflu more potent as it req a lower dosage in order to induce the same pharmacology
mesoridazine (drug in the middle) → piperidine unit (1 N) will hv less SE’s assoc.
piperazines (2N) most potent → v small doses for approx equiv dose
piperazines can also terminate w a hydroxy (OH) unit which can be exploited → ester prodrugs can be formed (see next slide)
thiothixene (bottom) → is a thioxanthene, has a double bond instead of the N in the tricyclic ring
100mg chlorpromazine = 5mg thiothixene
thiothixene has a piperazine unit (2N) → v potent
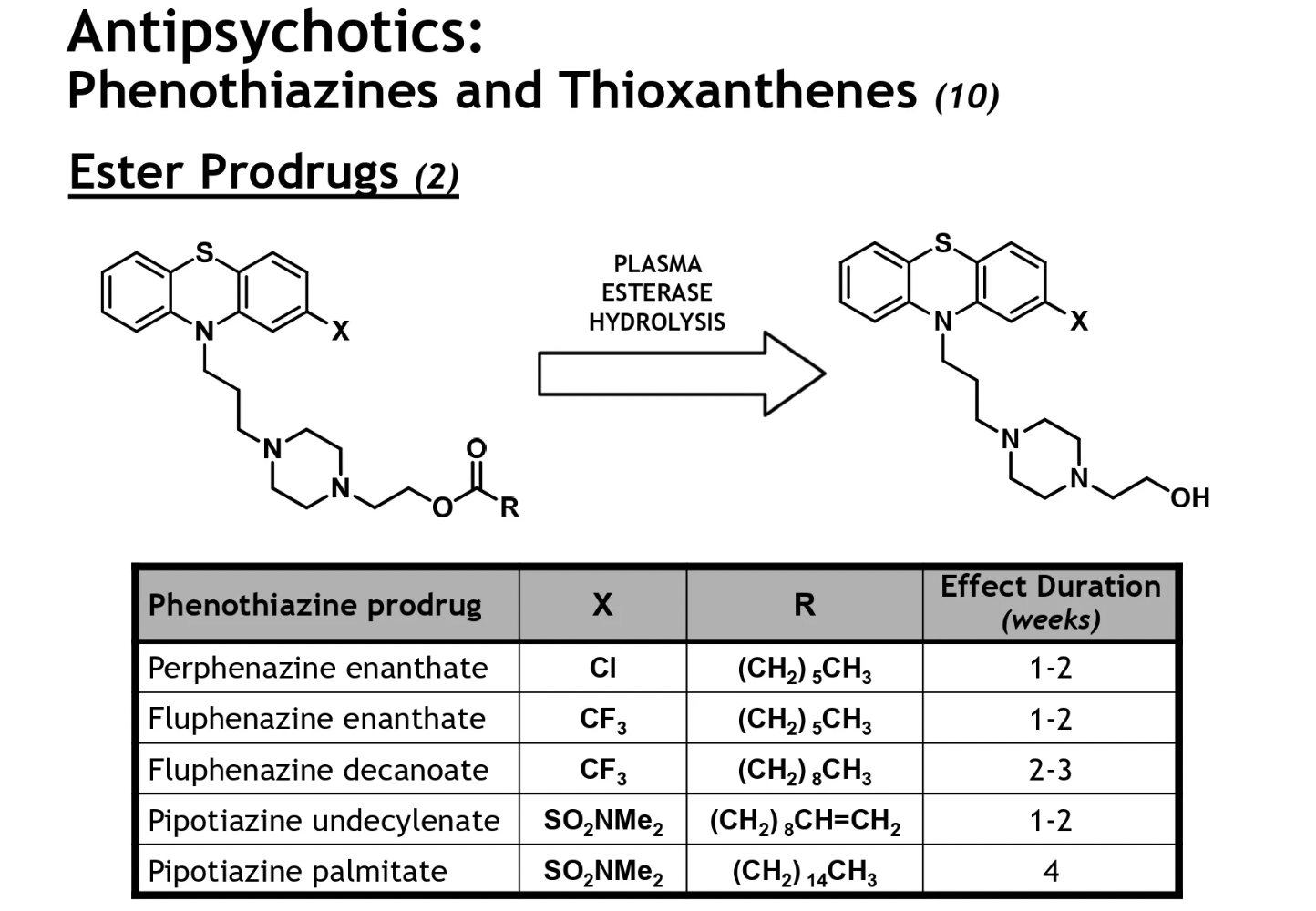
phenothiazine + thioxanthene ester prodrugs
majority of phenothiazine drugs undergo extensive hepatic metabolism to many inactive + active metabolites → therefore bioavail drops significantly
use of highly lipophilic ester prodrugs provides 4-10x more oral bioactivity
HC rich fatty ester units → forms depot/SR forms
IM depot of drug can also improve pt compliance → don’t hv to take meds orally everyday, may be a challenge in some pts
ester prodrugs can also be generated for drugs with a hydroxyl containing alkyl substituent on the terminal amino unit
these func. as long-acting drug forms that undergo slow/sustained bioactivation via plasma esterase hydrolysis
phenothiazine + thioxanthene ester prodrug examples
COO-R → promoiety unit which over time is hydrolysed to generate the active alc form
increasing the ester chain length (R) → will increase drug duration/depot effect
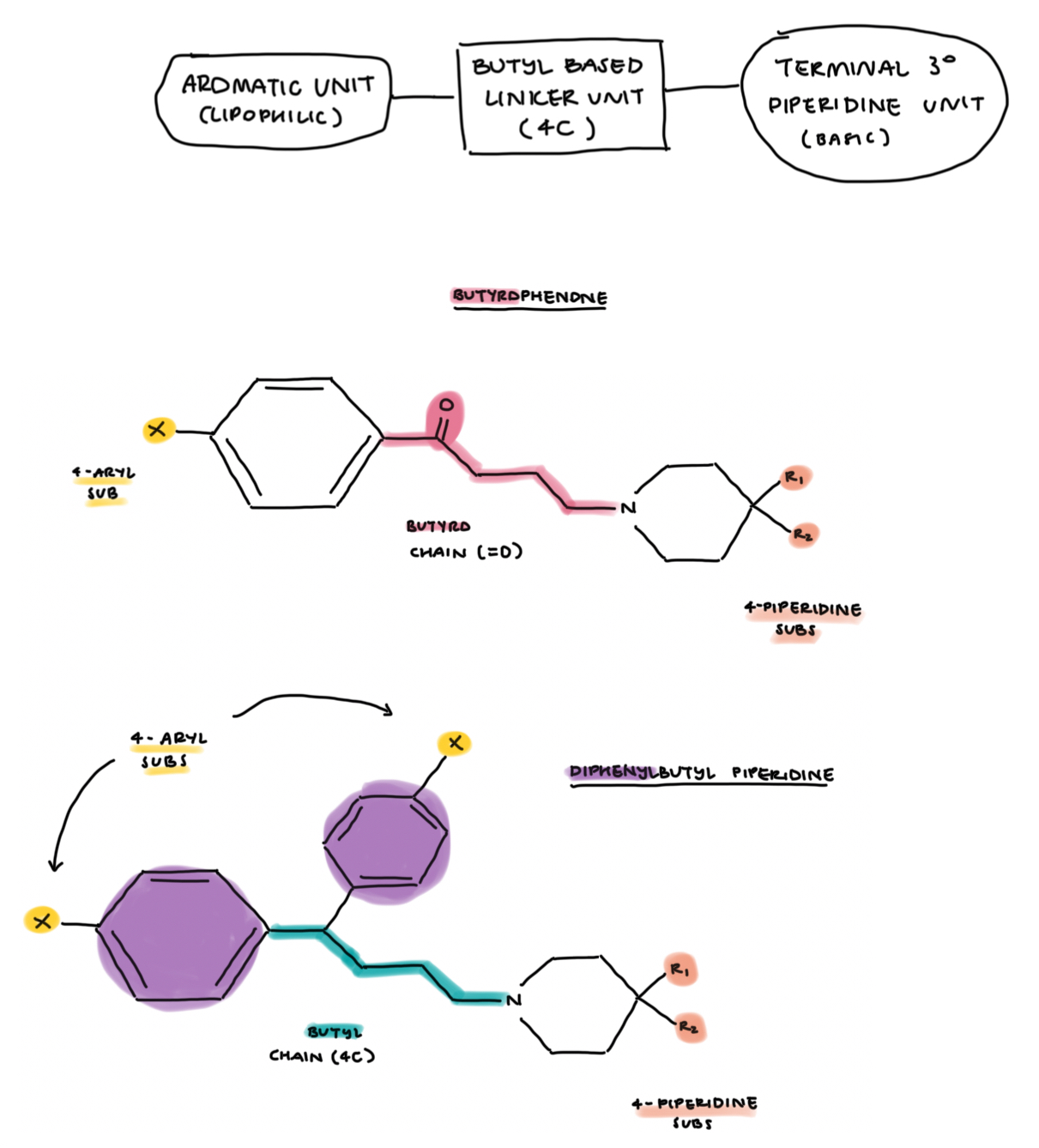
butyrophenones + diphenylbutyl piperidines structure
butyrophenone → keto carbonyl unit (C=O)
diphenylbutyl piperidine → 2 benzene rings
these drugs tend to be more lipophilic → hence more potent than the tricyclics, esp the diphenylbutyl drugs as they have 2 benzene rings
butyrophenones + diphenylbutyl piperidines aromatic + linker units
monosub of the phenyl ring(s) with a para 4-fluoro sub (X=F) results in the most potent compounds
Cl also works but is not as effective
diphenylbutyl piperidines → have an additional benzene ring instead of the keto unit on the 4C linker chain
hence are more lipophilic → greater potency
piperidine unit of butyrophenones + diphenylbutyl piperidines
basic and ionisable amino unit is essential for DA receptor binding and activity
para (4) R1 and R2 positions are most tolerant to substitution
sub at pos 2/3/5/6 → decreases neuroleptic activity
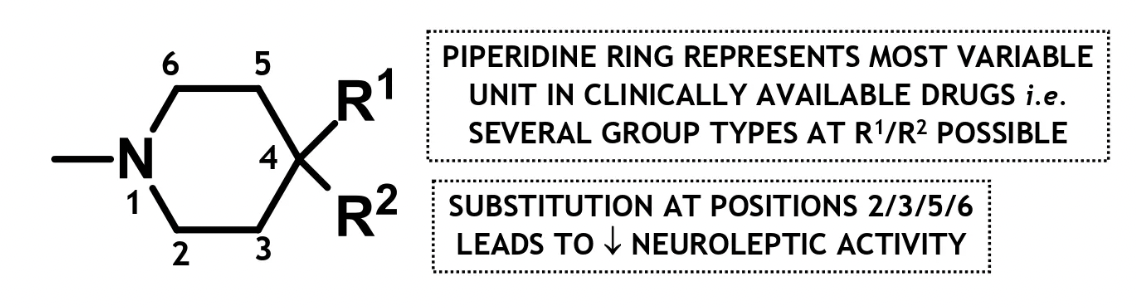
clinically available butyrophenone drugs
butyrophenones + diphenylbutyl piperidines are typically much more potent antipsychotics
pipamperone
OH replaced w 1° amide (CONH) unit
and benzene ring replaced w another piperidine unit → becomes a bis-piperidine
droperidol
short acting sedative and post-op antiemetic
amide (CONH) is closed off to form a ring part of a 2 ring structure→ spirocarbocyclic agent
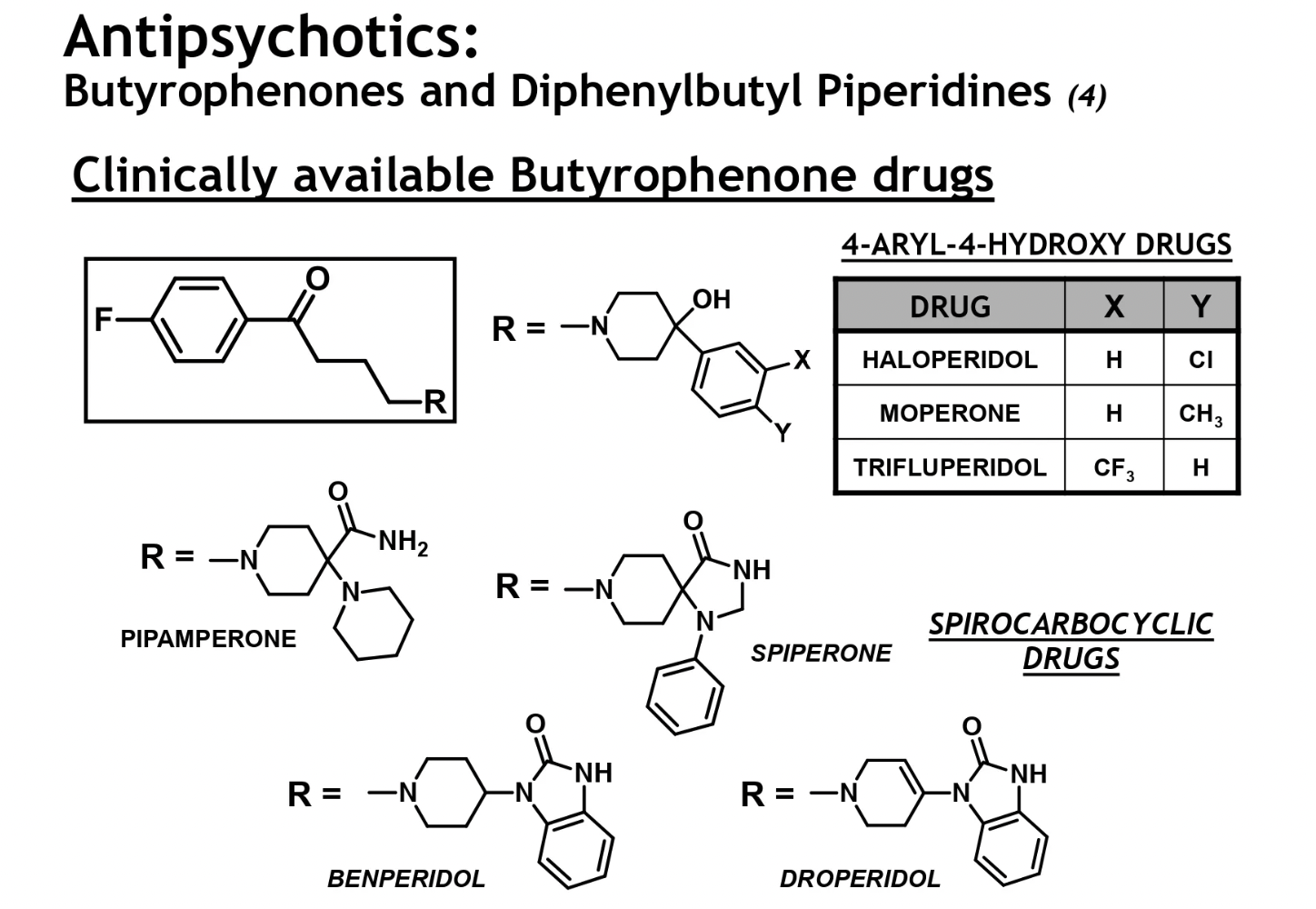
clinically available diphenylbutyl piperidines
diphenylbutyl piperidine drugs → tend to hv greater potency and lipophilicity = increased bioavail + CNS absorption
pimozide (droperidol) → also has the spirocarbocyclic ring system (CONH ring)
2mg is equiv to 100mg chlorpromazine, v high potency
anxiolytics MOA
consist of benzodiazepine drugs used for the Tx of anxiety Sx + disorders
BUT unlike other CNS drugs, anxiolytics are NOT neurotransmitter mimetics → do NOT resemble GABA
anxiolytics instead Ix w an extracellular benzodiazepine binding site (BZR) inducing a conformational change in the GABA-a receptor, promoting GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) neurotransmitter binding → encourages flow of Cl across the receptor from one side of the cell to the other
they do not need to resemble GABA as they operate at a diff site within the receptor
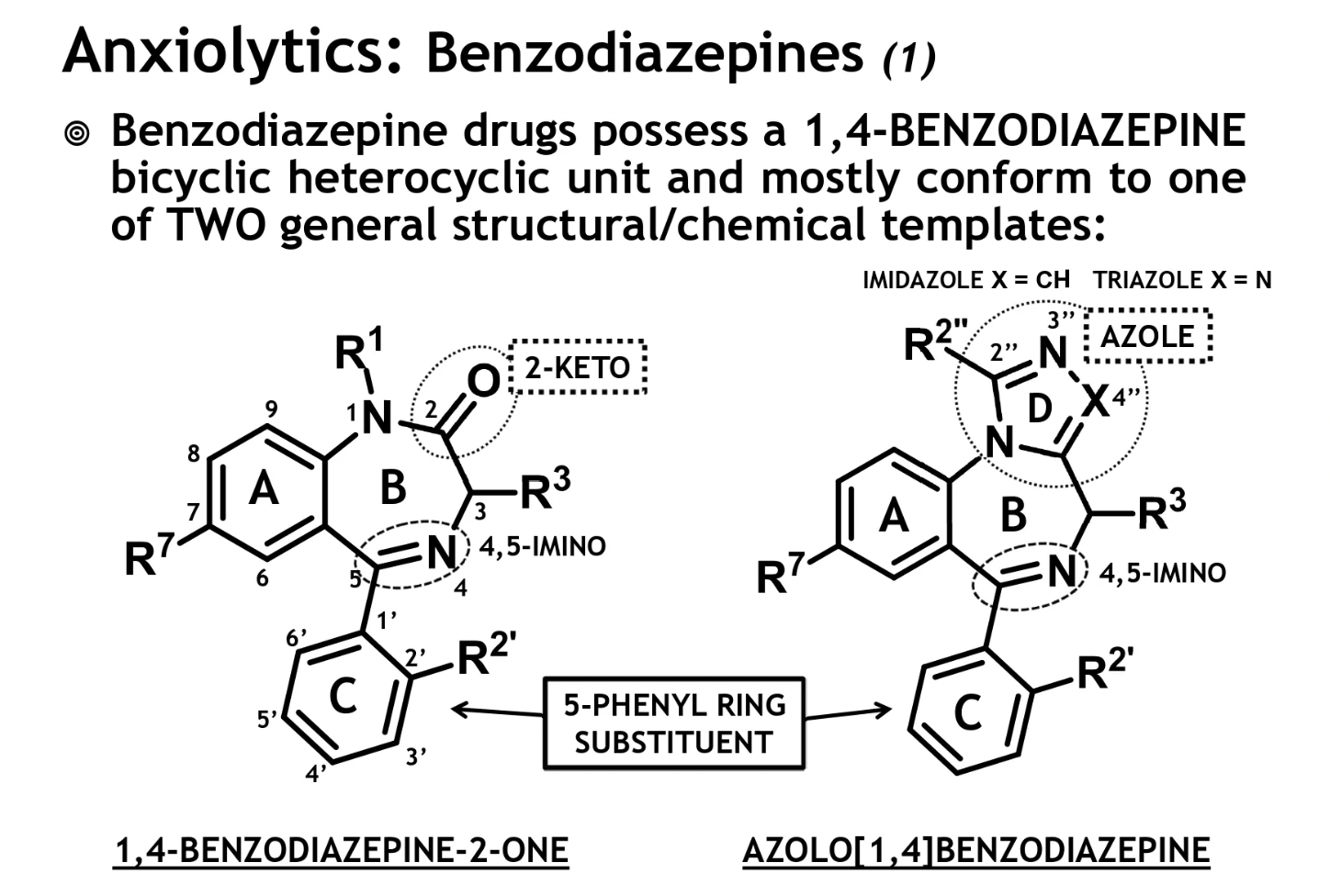
benzodiazepines structure
1,4-benzodiazepine-2-one
has a 2-ketone on the B ring
azolo[1,4]benzodiazepine
has an additional azole ring D, fused to the B ring
![<ul><li><p>1,4-benzodiazepine-2-one</p><ul><li><p>has a 2-ketone on the B ring</p></li></ul></li><li><p>azolo[1,4]benzodiazepine</p><ul><li><p>has an additional azole ring D, fused to the B ring</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/41d0a3c8-38f5-4948-81bb-5964e8793951.jpg)
rings A and C in benzos
both ring A and C are impt for effective binding to the BZR within GABA-a receptor
ring A system, which is typically a benzene ring, Ix via pi-pi aromatic ring stacking w various AA residues within the BZR site
ring A sub at C-7 → usually EWG
improves binding to receptor, improves potency of drug
ring A sub at C-6/8/9 → no go zones, sig. drop in bioactivity
BUT ring C isn’t essential → compounds w/o that phenol ring can still operate at GABA-a receptors
but the presence of the C ring enhances/improves binding and efficacy of drugs
binding occurs thru various hydrophobic Ix
ring C sub at C-2/6 → EWG, improves binding and potency of drug
usually halogens
EDGs instead will diminish potency
ring C sub at C-3/4/5 → no go zones
drug will not work
ring B on benzos
ring B is needed for optimal BZR binding → must contain at least 1 proton accepting group for H bonding to histidine residues
for optimal activity → R1 sub = H, CH3 or small alkyl group
v bulky groups are not well tolerated
R3 sub → small sub is tolerated
R3 = OH increases P2 metabolism to give shorter acting agents
diazepam structure
amide/lactam based drugs
-zepam → lactam unit in drug
R3 = H (i.e. un-subbed)
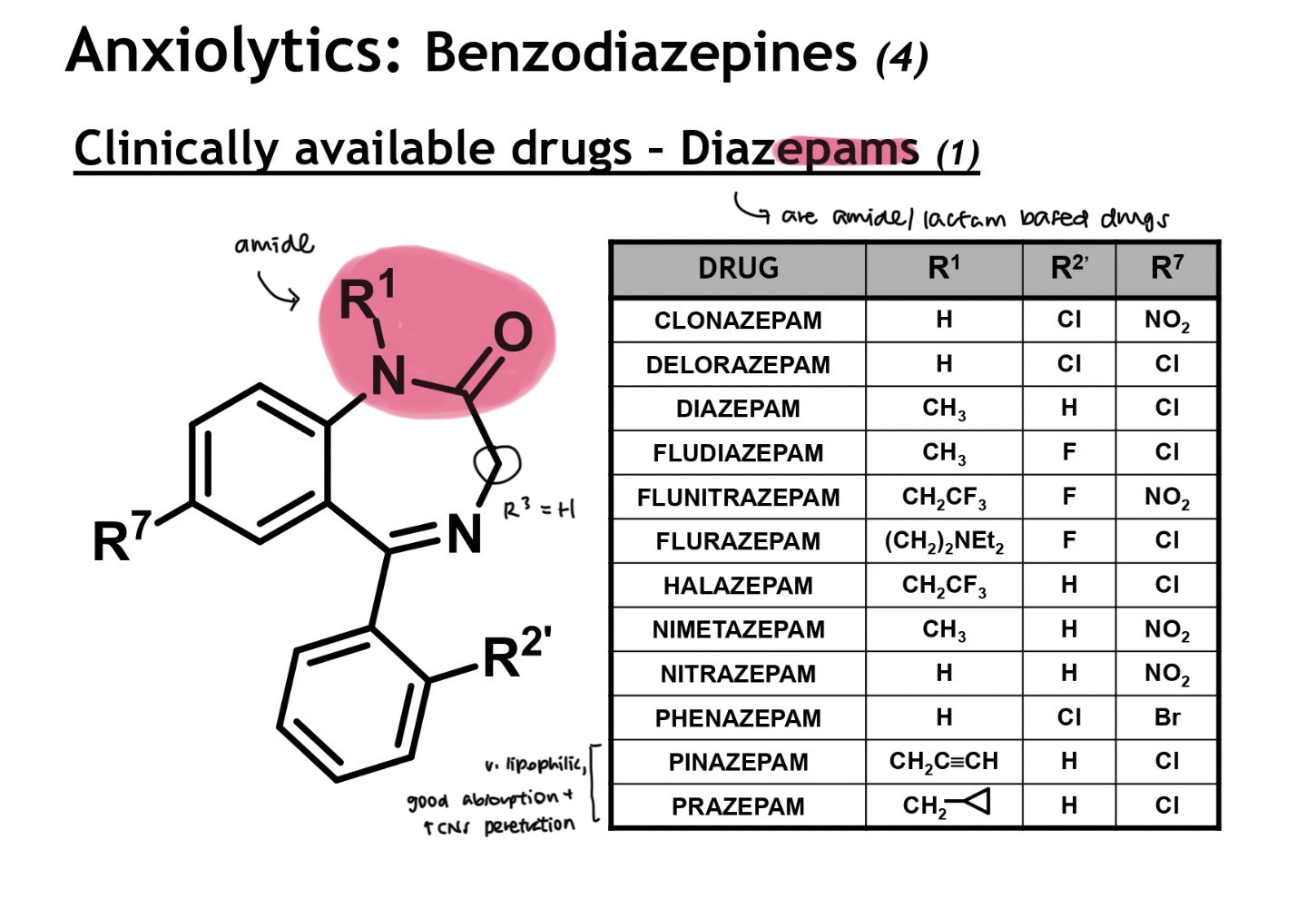
clinically available diazepams
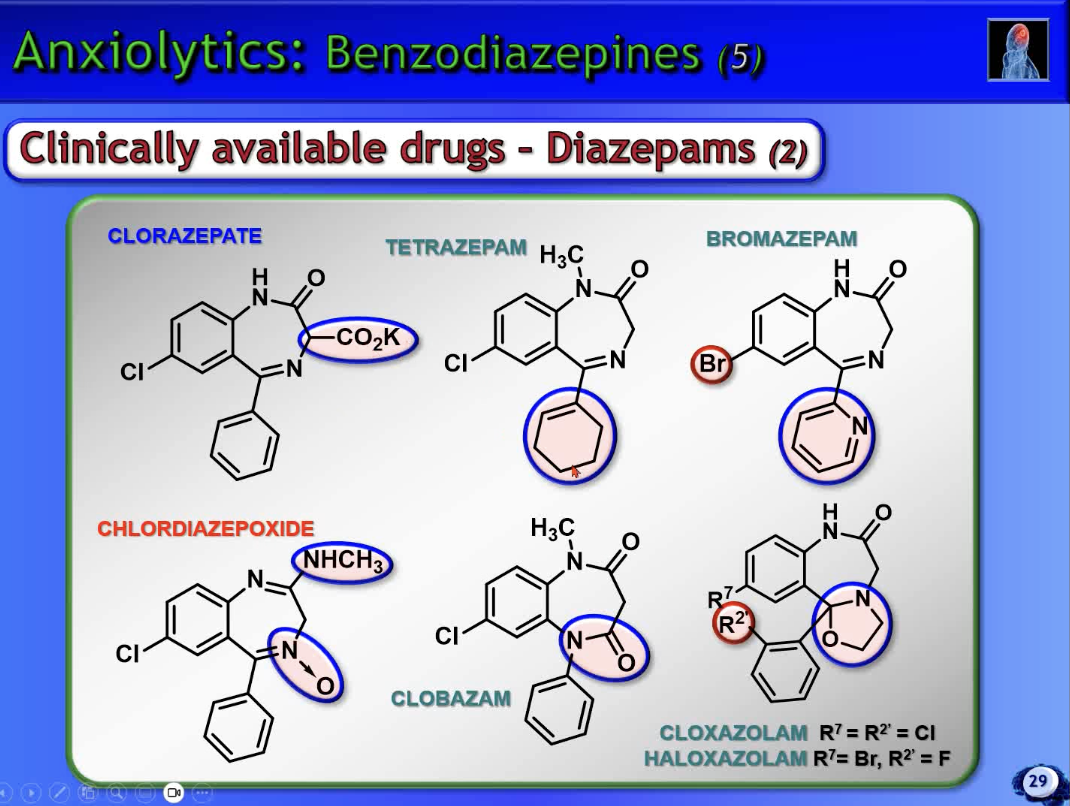
tetrazepam + bromazepam → doesn’t hv a benzene ring
bro → also weak basicity, and has a Br instead of Cl/F
clobazam → lactam unit at the top + at the bottom
has a tertiary amine unit
cloxa + haloxa → unusual oxazolidine ring system
clorazepate → CO2K prodrug to improve aq solubility
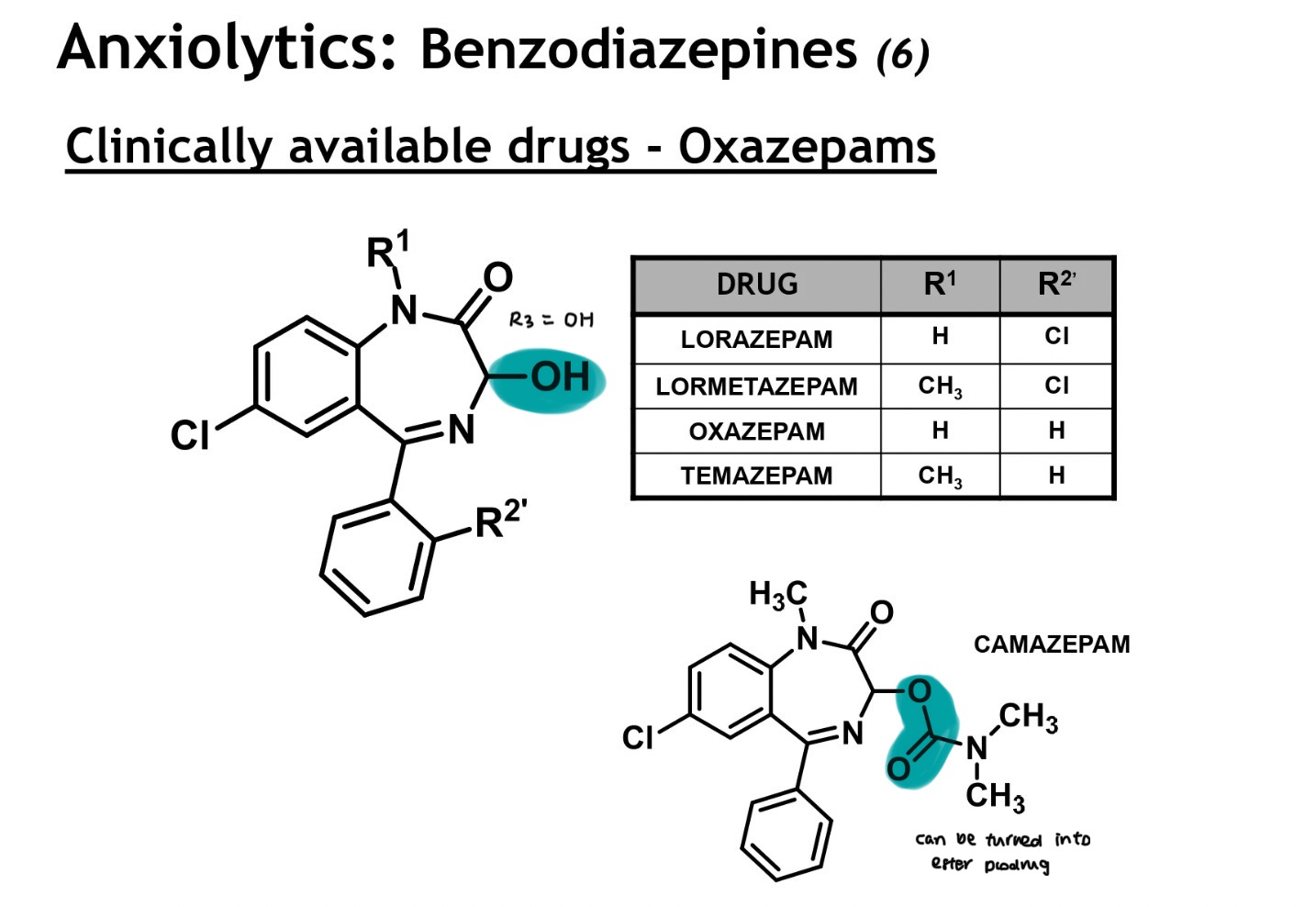
oxazepams structure
related to diazepams, but hv an additional sub in ring B at pos 3
R3 = OH
due to the polar OH unit → less lipophilic drugs, possess a shorter DOA
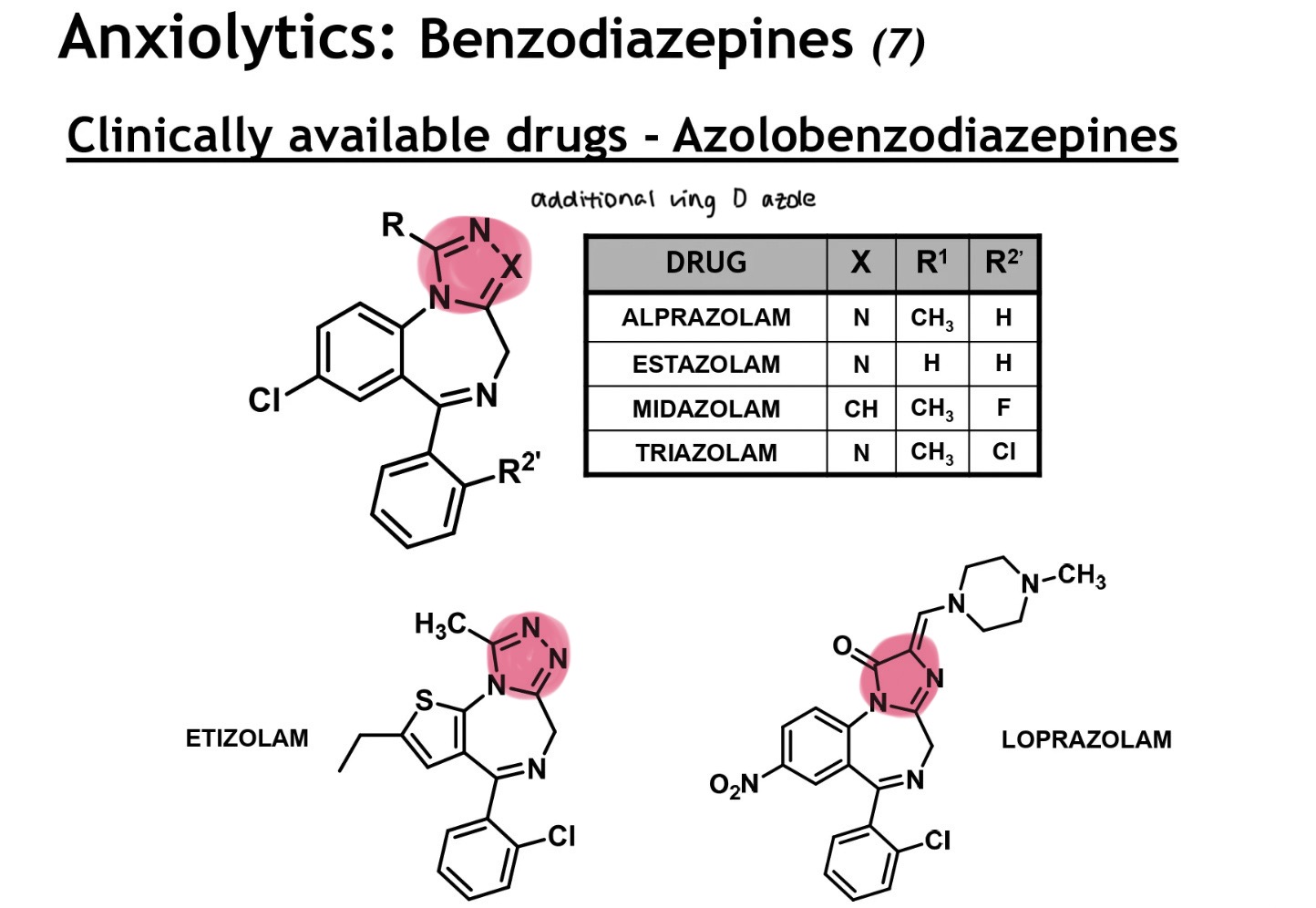
azolobenzodiazepines structure
have an additional ring D → azole
loprazolam → has a fairly large unit extending out from the side of ring D
is a piperazine (2N) based unit that ionises fairly readily and can be converted into HCl salt form for aq delivery
antidepressant MOA
blockade of monoamine neurotransmitter transport/reuptake
inhibit the neuronal reuptake of norepinephrine (NE) and/or serotonin (5-HT) into presynaptic neurones from the synaptic cleft → raising neurotransmitter lvls
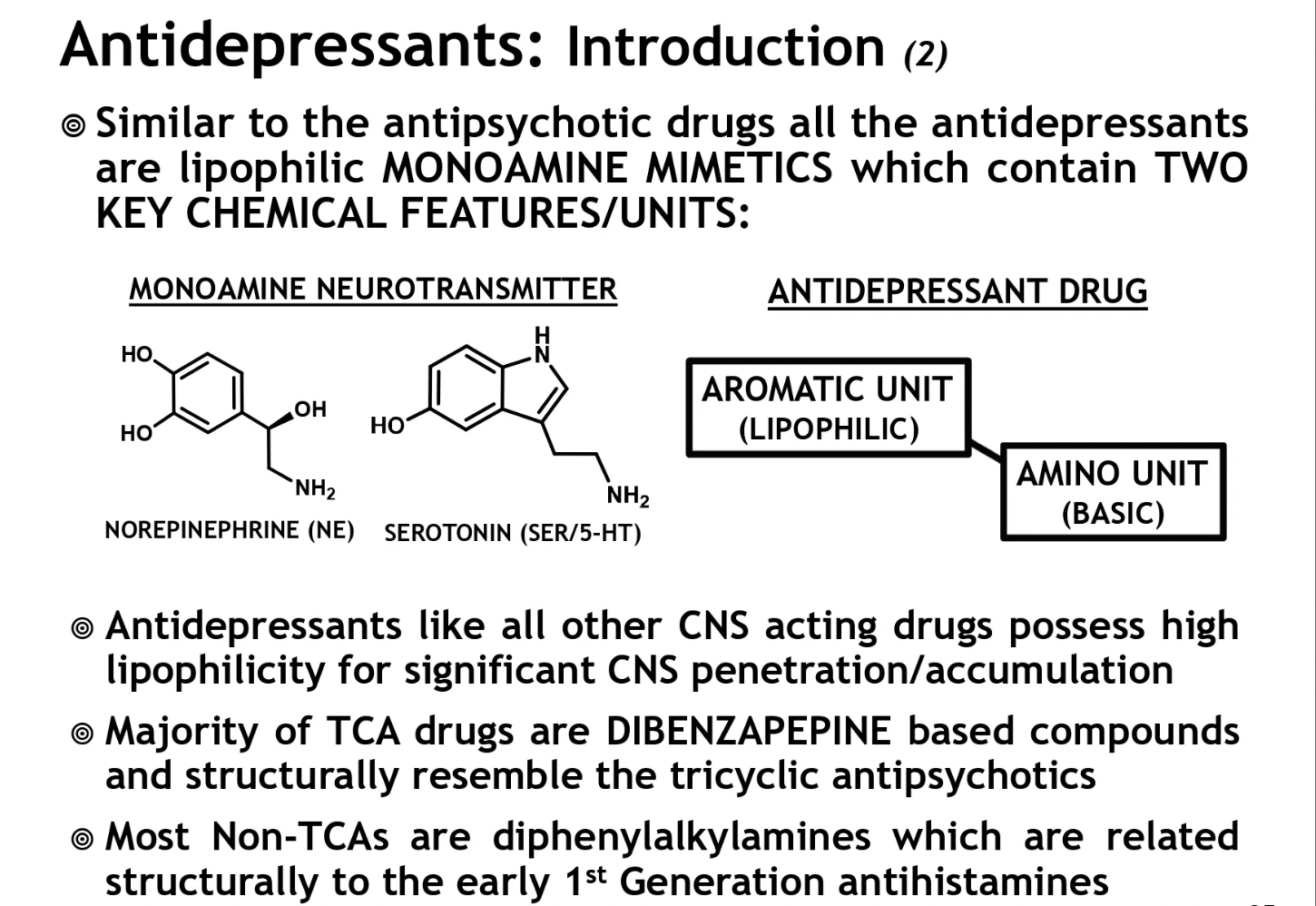
chem structure of antidepressants
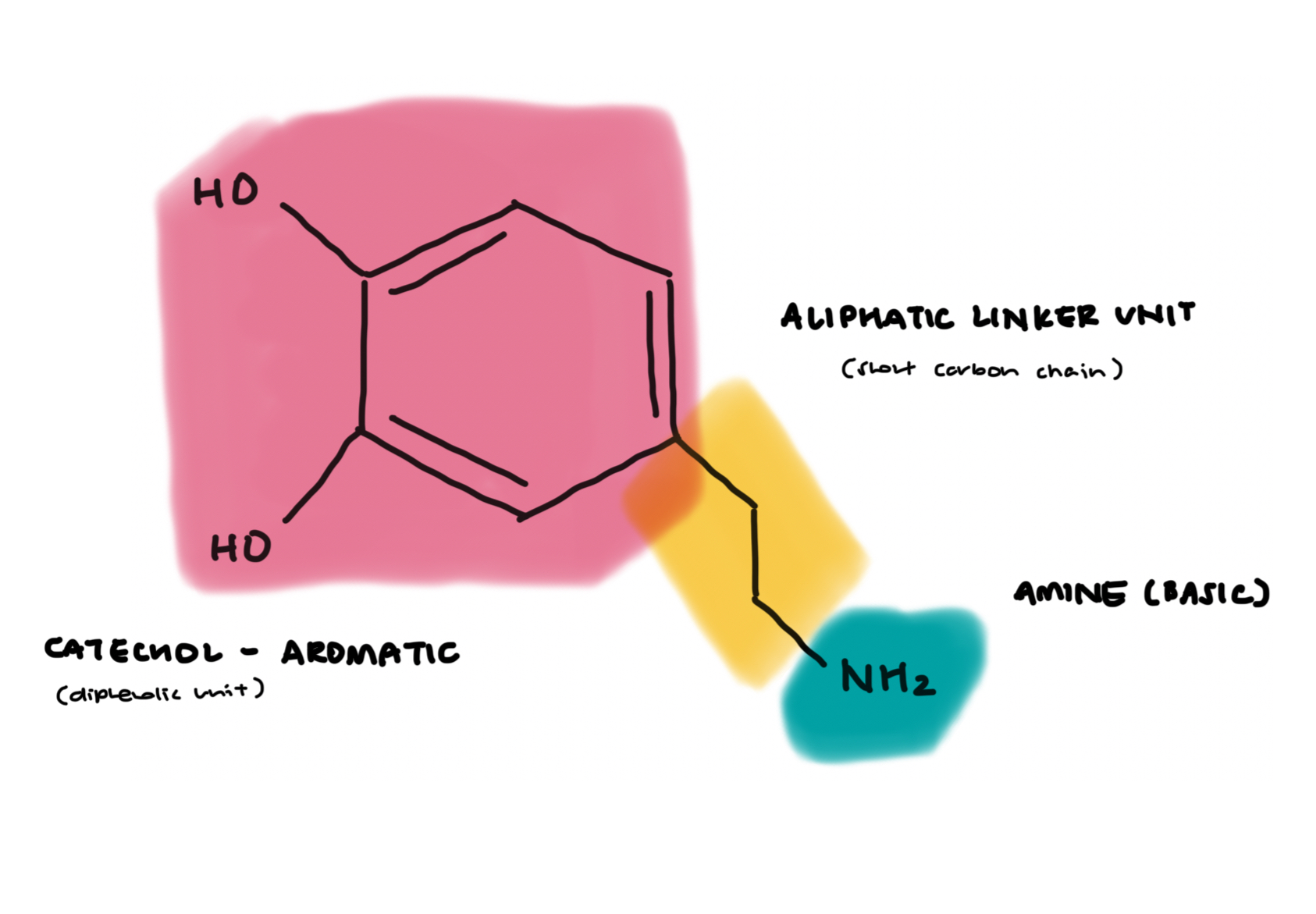
are lipophilic monoamine mimetics that contain 2 key features:
aromatic unit (lipophilic)
amino unit (basic) → 1* amine (-NH2)
like all other CNS acting drugs, possess high lipophilicty for significant CNS penetration/accumulation
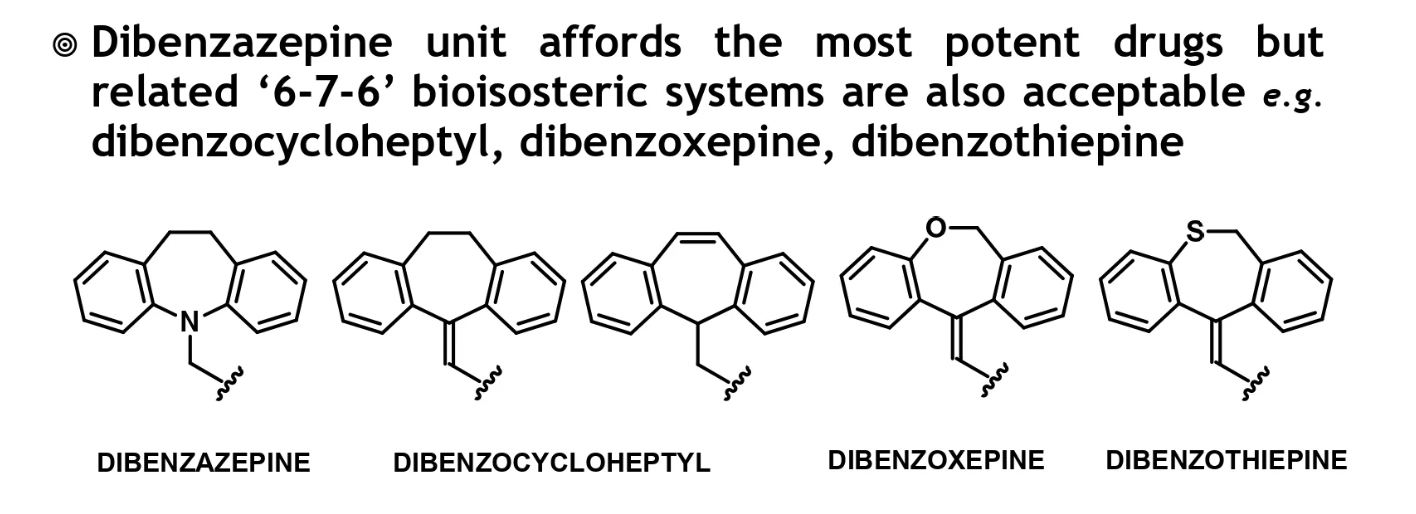
tricyclic antidepressants structure
func. as non-selective norepinephrine (NE) and serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (NSRIs) or selective NE reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
have a lipophilic ‘6-7-6’ tricyclic system and must conform to this chemical template
tricyclic aromatic ring unit (lipophilic)
aliphatic side chain linker unit
mostly fatty 3C
terminal amino unit (basic)
mostly ionisable alkyl 2* or 3* amine
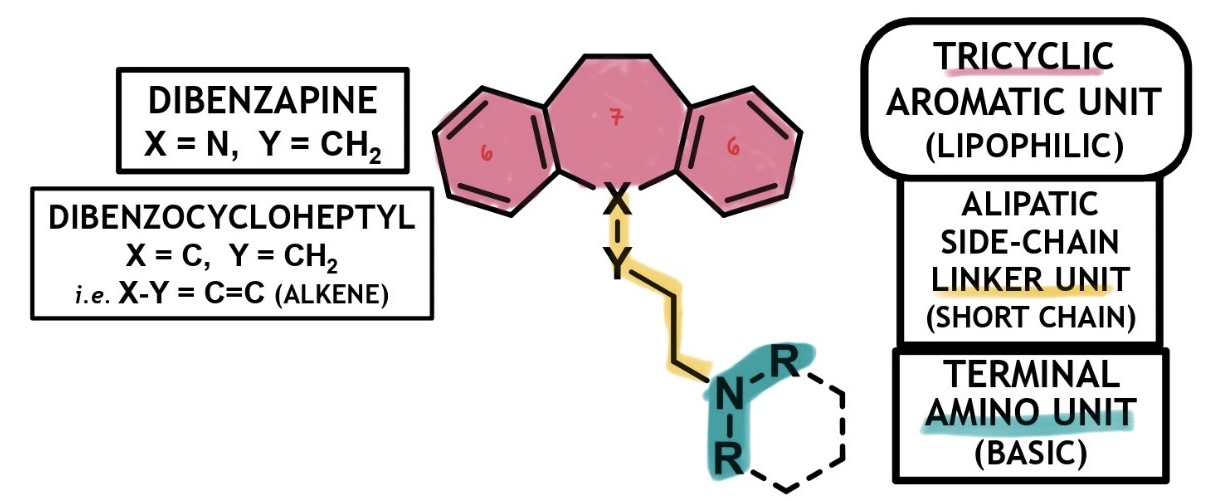
tricyclic ring sub
tricyclic ring dictates drug potency, but possesss little significance w 5-HT and NE activity
ring sub is uncommon but may improve 5-HT affinity selectivity
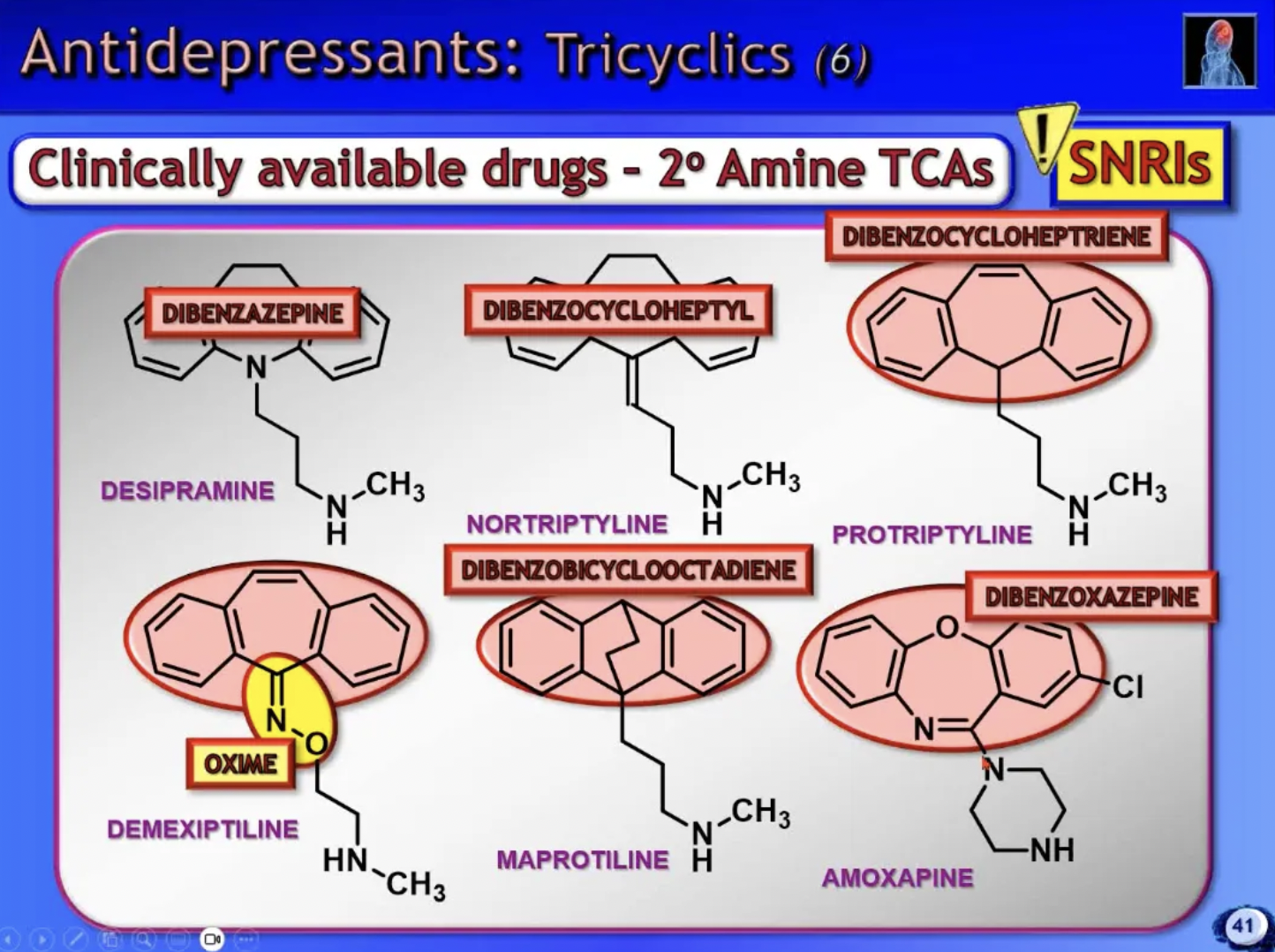
3* amine TCA’s
NSRIs
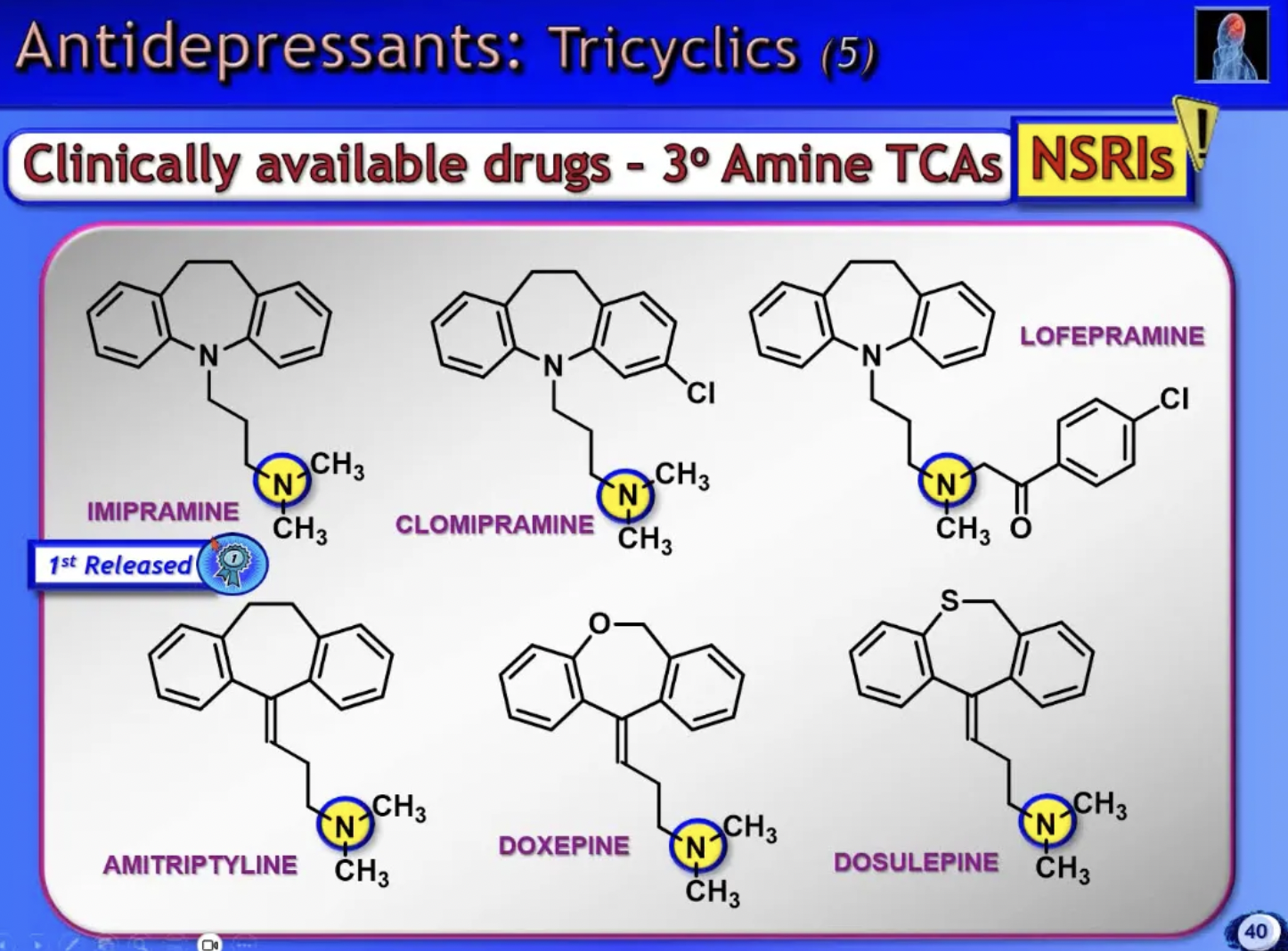
2* amine TCA’s
SNRIs