Plants
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
a metabolic reaction occurring in plants where light energy converts raw materials into carbohydrates- glucose
what is the word equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water ---(with light energy)---> glucose + oxygen
Balanced chemical symbol equation for photosynthesis
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2

How does varying carbon dioxide concentration affect rate of photosynthesis?
Increasing carbon dioxide concentration increases rate of photosynthesis
until above a certain threshold, further increases in carbon dioxide concentration do not increase rate of photosynthesis—> another factor (such as light intensity) is limiting rate of reaction at which the rate plateaus
How does varying light intensity affect rate of photosynthesis?
Increasing light intensity increases rate of photosynthesis
until above a certain point where it doesn’t increase rate of photosynthesis—> another factor (such as CO2 or temperature) is limiting rate of reaction at which the rate plateaus
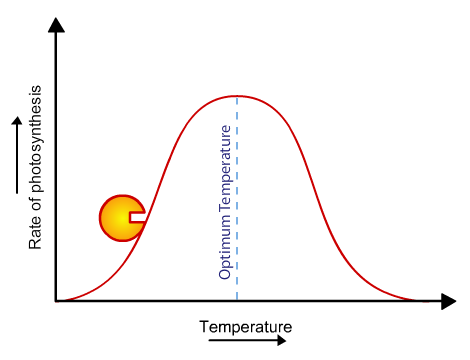
How does varying temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Low temperature:
Rate is low because enzymes have less kinetic energy, —> fewer collisions with substrates.
Optimum temperature (~40 °C):
Rate is highest because enzymes have enough kinetic energy to work at most efficient rate.
High temperature:
Rate decreases sharply because enzymes denature—> active site changes shape so substrates cannot bind
What is the structure of a leaf made of?
waxy cuticle
upper epidermis
palisade mesophyll
spongy mesophyll
lower epidermis
stomata + guard cells
vascular bundles (xylem and phloem)
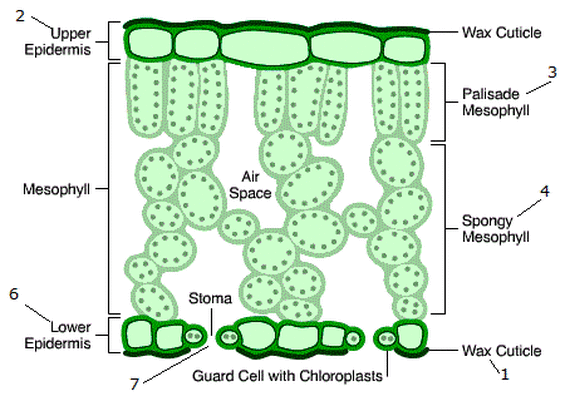
function and adaptation of waxy cuticle
Protective layer on upper and lower sides of the leaf, prevents water loss
function and adaptation of upper epidermis
Thin and transparent to allow light to enter palisade mesophyll layer underneath it
function and adaptation of palisade mesophyll
Column-shaped cells tightly packed with chloroplasts to absorb more light, maximising photosynthesis
function of lower epidermis
Contains guard cells and stomata
function and adaptation of stomata
Where gas exchange takes place: opens during the day, closes during the night
In most plants, more stomata are found on the underside of the leaf to reduce water loss
function and adaptation of guard cells
Absorbs and loses water to open and close the stomata
function and adaptation of vascular bundle (xylem and phloem)
xylem- transport water and dissolved minerals
phloem- Transports sucrose and amino acids
function and adaptation of spongy mesophyll
Contains internal air spaces that increase the SA:V ratio for the diffusion of gases
what mineral ions do plants require?
magnesium
nitrate
why do plants need magnesium ions?
needed to make chlorophyll
why do plants need nitrate ions?
make amino acids
why is oxygen produced in the pondweed (elodea) experiment?
because oxygen is a product of photosynthesis
why is light needed in the pondweed (elodea) experiment?
to make the chemical energy needed to create carbohydrates
—>increasing the light intensity will boost the speed of photosynthesis
describe production of starch test on a leaf
Keep plants in dark for 24-48 hours
Kill the leaf with hot water bath
Remove chlorophyll using ethanol
Rinse leaf and add iodine
Blue-black colour = starch present
Orange-brown = starch not present
why does starch show photosynthesis has occured?
Starch is a product of photosynthesis
Light-exposed leaf areas turn blue-black (starch present)
Covered areas stay yellow-brown (no photosynthesis)
Shows light is needed for photosynthesis and starch production
why is chlorophyll removed in the starch test on a leaf?
because it’s green and would mask blue-black colour change that shows presence of starch when iodine is added
removing chlorophyll makes leaf colourless, so it’s easier to see where starch has been produced
compare the rate of photosynthesis and respiration during daylight
photosynthesis rate > respiration rate
net carbon dioxide in
net oxygen out
compare the rate of photosynthesis and respiration during darkness
rate of photosynthesis < rate of respiration
only respiration occurs- no sunlight
how is the structure of a leaf adapted for gas exchange?
thin which gives short diffusion distance
flat which provides large SA: V ratio
many stomata which allow movement of gases in and out of air spaces by diffusion
why can simple, unicellular organisms rely on diffusion for movement of substances in and out of the cell?
Small
Large SA:V ratio
One cell thick
Works with diffusion over short distance
—> fast enough to supply nutrients and remove waste products
why can’t multicellular organisms rely on diffusion alone?
Large
Small SA:V ratio
Many cells have high demands
why do multicellular organisms need a transport system?
Moves substances quickly over long distances
Supplies all cells with oxygen and nutrients
Removes waste products e.g, CO2
Maintains concentration gradients, allowing diffusion to continue at cells
Eg of transport system in plants
vascular system- xylem and phloem