IGCSE Biology: Chemicals of Life
Water
Water (H₂O) is used in the body for a number of things. Most organisms are 80% water.
Inside every living organism, metabolic reactions are happening all the time. Metabolic reactions only happen when chemicals are dissolved in water. Hence, water is an important solvent. Without water, cells will dry out, the reactions will stop, and the organism dies.
Water also allows substances like glucose to dissolve in blood plasma. It is also used to dissolve nutrients and enzymes in the alimentary canal for digestion. Water is also used to get rid of waste products.
Carbohydrates
The structure of a carbohydrate is CH₂O - one carbon, two hydrogens, and one oxygen. The formula of a carbohydrate is Cₙ(H₂O)ₙ.
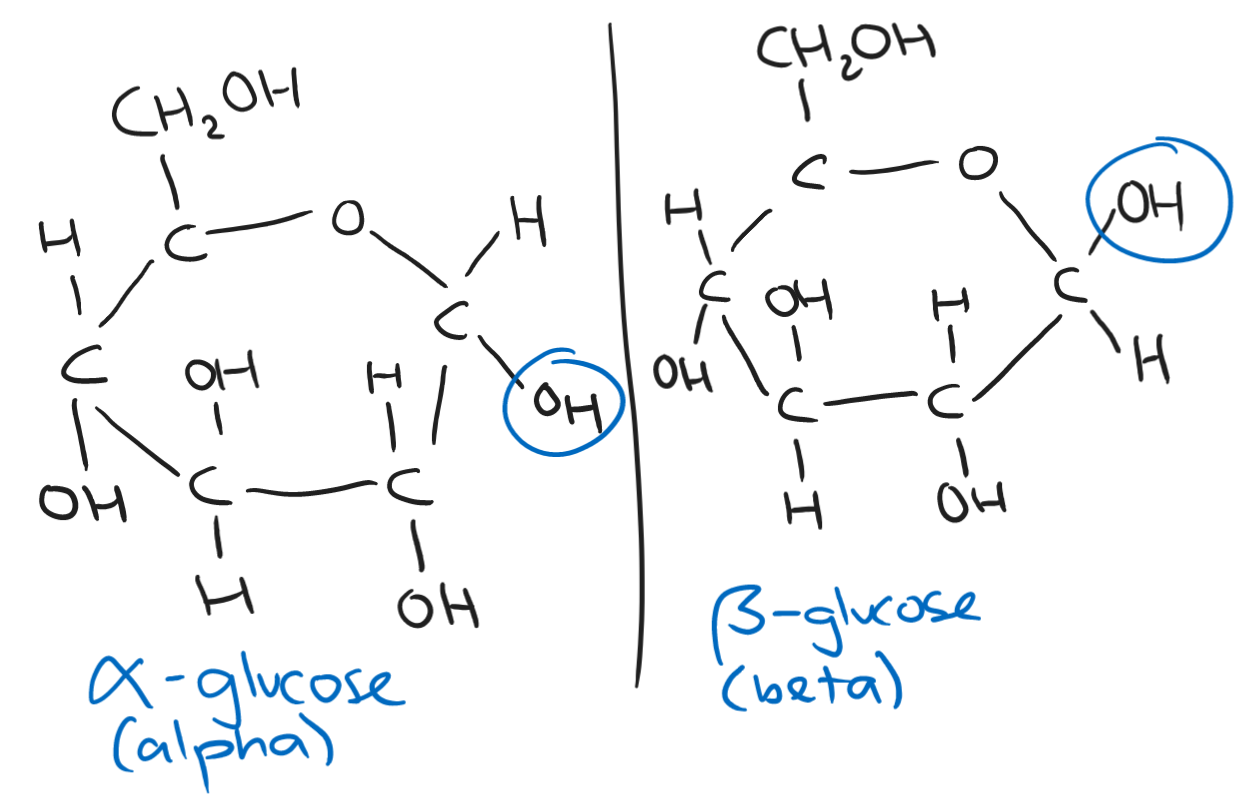
Carbohydrates include starch and sugars. Starch is found in plants while sugars are more diverse.
Sugars - include monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
- monosaccharides: glucose, fructose, galactose
- disaccharides: sucrose, maltose
- polysaccharides: starch, glycogen, cellulose
Carbohydrates are needed for energy.
- 1g = 17 kJ
- energy is required for respiration in cells
- glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is most commonly used
Humans transport glucose in plasma. Plants transport sucrose and change it to glucose when the plant needs it. Humans (and many other animals) store carbohydrates as glycogen. Glycogen is stored in small quantities in the liver and muscles. Plants store carbohydrates as starch.
Cellulose is used for plant cell walls as their crisscrossing fibres are strong and maintain the shape of the cell wall.
Benedict’s test is used to test for the presence of carbohydrates (more specifically, reducing sugars) in a solution.
- cut or grind a little of the food into small pieces
- add water to dissolve the food in a boiling tube
- add an excess amount of Benedict’s solution to the tube
- heat to 80 degrees Celsius and sit for 4 minutes
If the solution turns from blue to green, yellow, orange, to brick red, reducing sugars are present. If the solution remains blue, the test is negative.
The iodine test is used to test for the presence of starch.
- cut up a small piece of food and put in a test tube
- add a few drops of iodine solution and observe colour change
If the food turns from brown to blue-black, starch is present. If the food remains brown, starch is not present.
Fats
The structure of a fat molecule is made up of four smaller molecules. one glycerol and three fatty acid chains. They contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
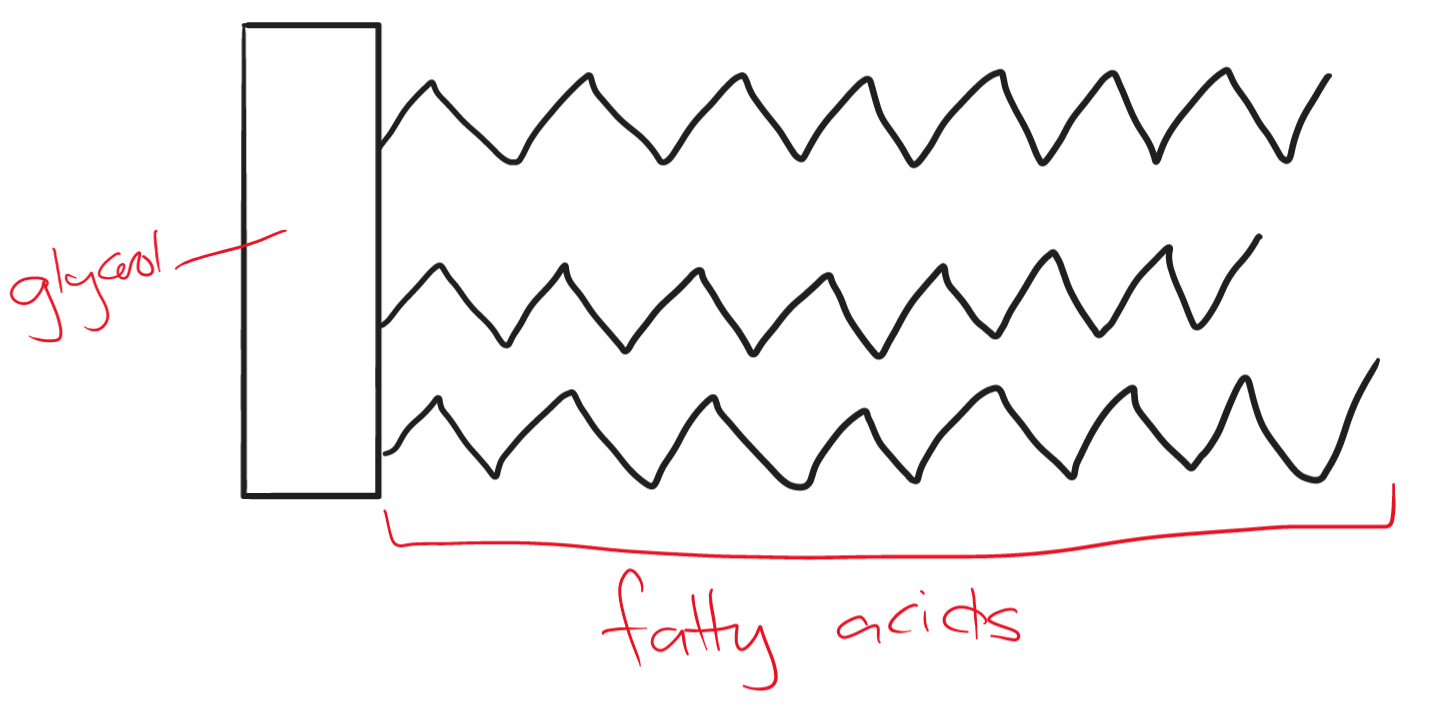
Fats are hydrophobic; they stay separated and cannot dissolve in water. At room temperature, they are known as oils.
Fats store excess energy and are also used for insulation. This layer of cells is known as adipose tissue. Fats are only used as energy when there are no carbohydrates left.
Examples of fats are oil, fatty fish, chocolate, and avocados.
An emulsion test is used to test for the presence of fats in a solution.
- chop or grind a small amount of food and put it in a clean test tube
- put distilled water in another tube
- add pure ethanol to the food and shake thoroughly
- pour a small amount of the liquid from the food test tube into the distilled water
If the solution turns milky-white/cloudy, fats are present. If the solution remains transparent, fats are not present.
Proteins
Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids. Aside from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, proteins also contain nitrogen and small amounts of sulfur.
Proteins are responsible for growth and repair, creating antibodies, and enzymes.
Because there are twenty (20) different kinds of amino acids, different types will create different shapes of proteins. This is how enzymes and antibodies are made.
The biuret test is used the test for the presence of proteins in a solution.
- put chopped up food in a test tube and add a little water
- add biuret solution OR add potassium hydroxide (sodium hydroxide is a valid alternative)
- if you are adding potassium hydroxide, add two drops of copper sulfate solution
- shake the tube gently and observe colour change
If the solution remains blue, protein is not present. If the solution turns lilac/purple, protein is present.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA is the chemical that makes up our genes and chromosomes. DNA is made up of two long strands each having a series of bases. The bases of DNA are:
- adenine (A)
- cytosine (C)
- guanine (G)
- thymine (T)
The two strands twist together to form a spiral known as the double-helix structure.
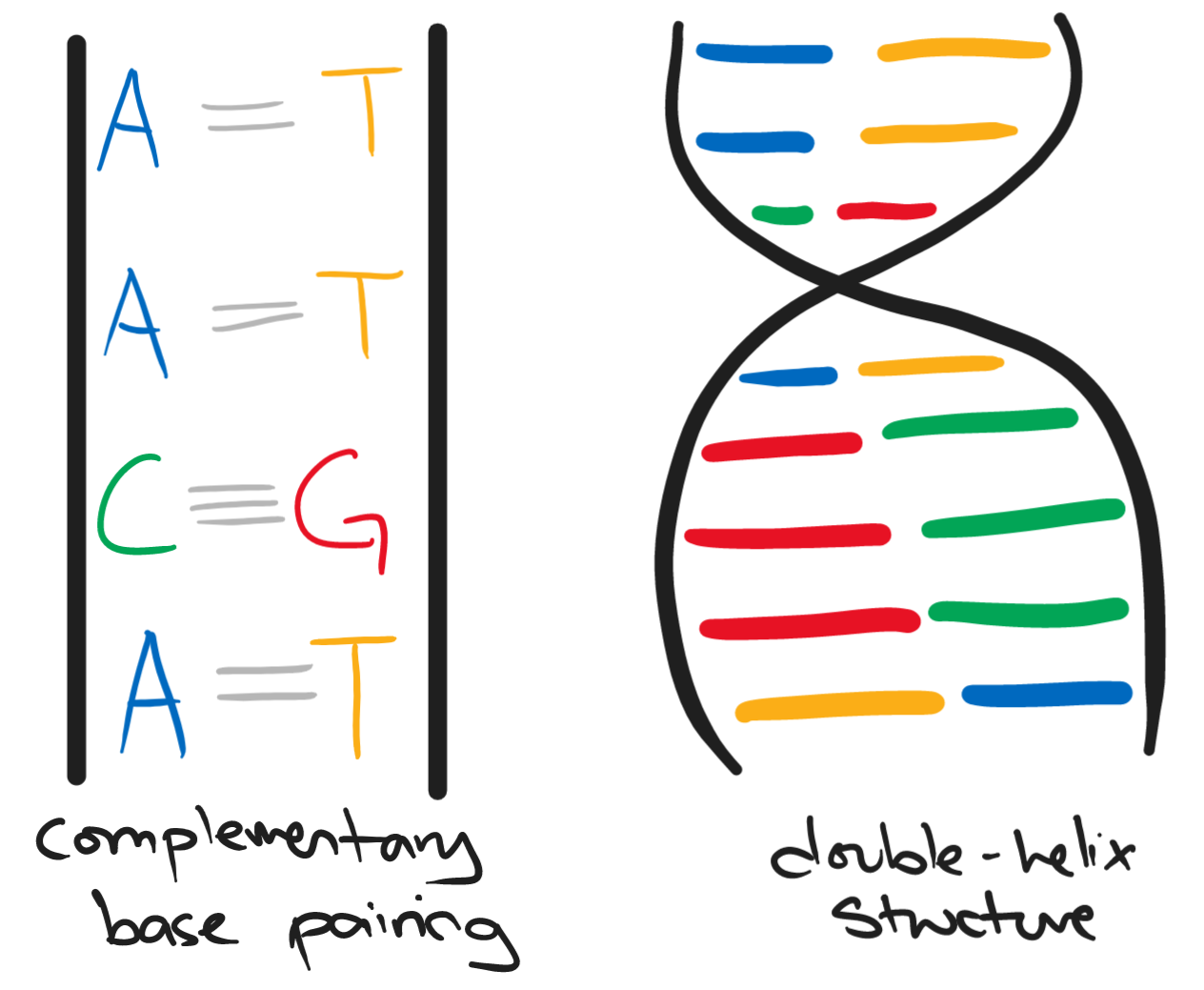
The sequence of bases determines the kinds of proteins in our cells. This then leads to the development of cells, tissues, and organs.