thinking geographically (chapter 1) - APHuman
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
space
the geometric surface of the earth
activity space
an area where activity occurs on a daily basis
spatial
the earth has a spatial surface, when you have objects on it, they are defined by their location and are separated by some amount of distance
place
an area of bounded space of some human importance
when we identify a place, it is important to ask why it matters
sense of place
think of it as knowing where an area of the earth’s spatial surface is important
toponym
when a place becomes recognized, we give them “place-names”, or toponyms
regions
regions are sections of the world, they are a type of place
remember that the three types of regiones (formal, functional, and vernacular) can overlap!
sequent occupancy
the succession of groups and cultural influences throughout a place’s history
remember when you learned about the chinese dynasties? this is very similar!
place-specific
many places have different layers that make up their culture, society, values, economy, etc.
place-specific is the idea that these make up a specific area, and these traits vary depending on a place
scale
the relationship of an object or place to the Earth as a whole. there is map scale and relative scale
map scale
the ratio of distance on a map to distance in the real world in absolute terms
it helps us use small ratios to represent big distances in an area
for example, ursuline is .5 meters away from Houston on a map scale (this is made up btw)
relative scale/scale of analysis
the level at which you group things together for examination (aka level of aggregation)
for example, ursuline might matter to dallas on a map, but not to the US. it is relative
we need relative scale because it helps us compare things accurately and at the same scale
formal regions
an area that has a uniformity (homogenous characteristic) across its entire regional boundary
formal regions - linguistic regions
linguistic regions share a common language
USA and Australia (both speak English, but this is one of the only things that is the same between them)
regional boundaries
these differ based upon the type of region
culture region boundaries have fuzzy borders
political region boundaries are typically well defined
environmental region boundaries are transitional and measurable
bioregions/biomes
large regions of the world that share similar animals and ecostystems, for example, the Sahara Desert
the transition zone between each is known as an ecotone
ecotone
transition zone between two biomes
functional/nodal regions
areas with a central place (node) that is the focus or point of origin that expresses some practical purpose. the influence decreases as you move away from the node
central place/node
the center of a functional/nodal region, most often centers of economic exchange
market areas
a type of functional region
the area in which the certain central place is marketed
for example, if you live in Dallas, you are marketed the Dallas Cowboys. as you get farther away, you are marketed OU football
area of influence
the sphere of influence, the amount of distance people will travel for something
attractions that are far spread apart → large area of influence
intervening opportunity
an attraction at a shorter distance that is more important than one farther away
vernacular regions
based on the perception or collective “mental map” of the region’s residents
people identify with this area based on their perception of what it is, not on official boundaries
the “south” is not officially defined as anything, but many people would say certain states (like texas) are a part of it
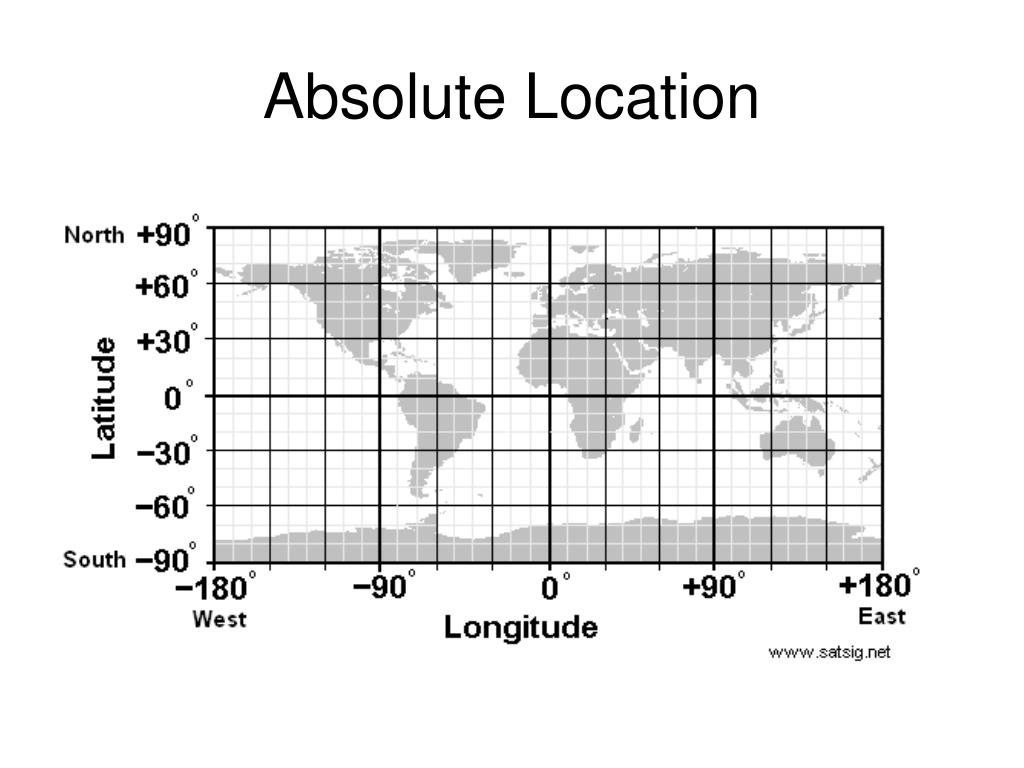
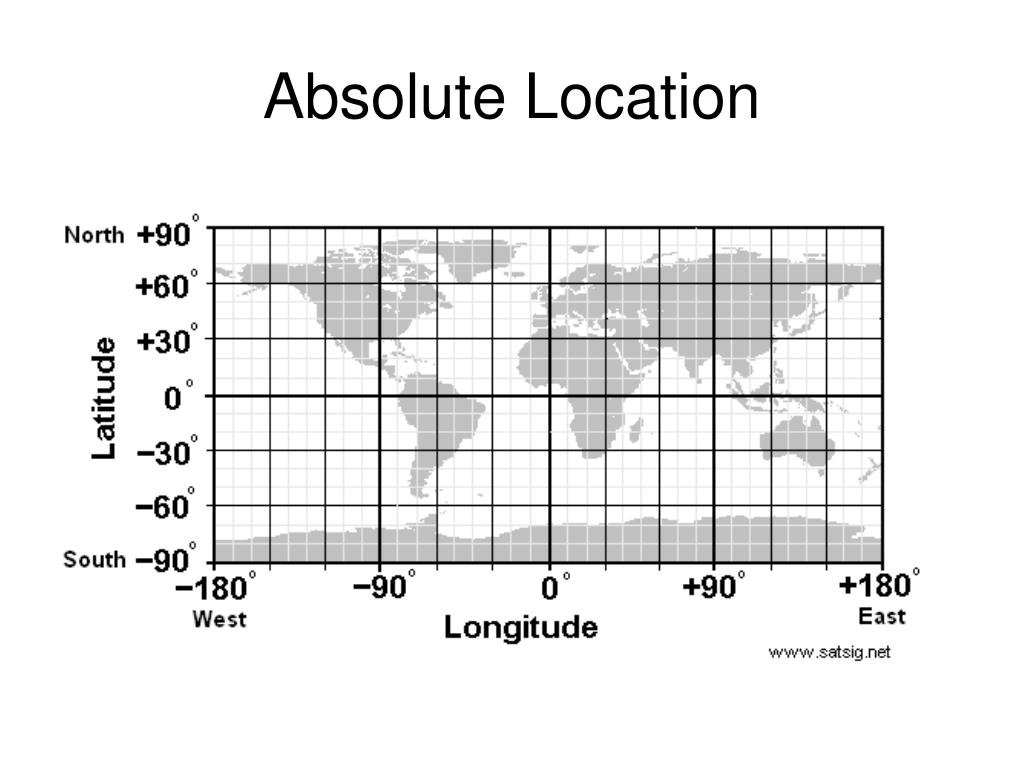
absolute location
define a point or place on the map using coordinates
commonly named using latitude and longitude
relative location
the location of a place compared to a known place or geographical feature
how far some place is from something else
latitude
latter like rungs on a ladder
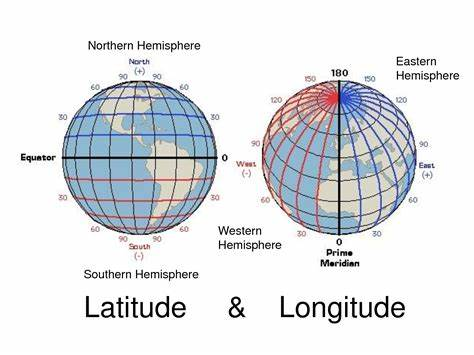
longitude
this long cuz they go down
notation of absolute location
latitude first, then longitude, each with a cardinal direction and separated by a comma. degrees can be divided into smaller minutes, and minutes can be divided into seconds
absolute location of the capitol building is:
38° 53’ 23.2980” N, 77° 0’ 32.6016” W
decimal degrees
way of dividing partial degrees but instead using decimals
instead of using minutes and seconds, you can say 38.98305948 degrees (this is an example) instead
important parts of absolute location
the equator is 0 degrees latitude
north and south poles are 90 degrees latitude
prime meridian is 0 degrees longitude
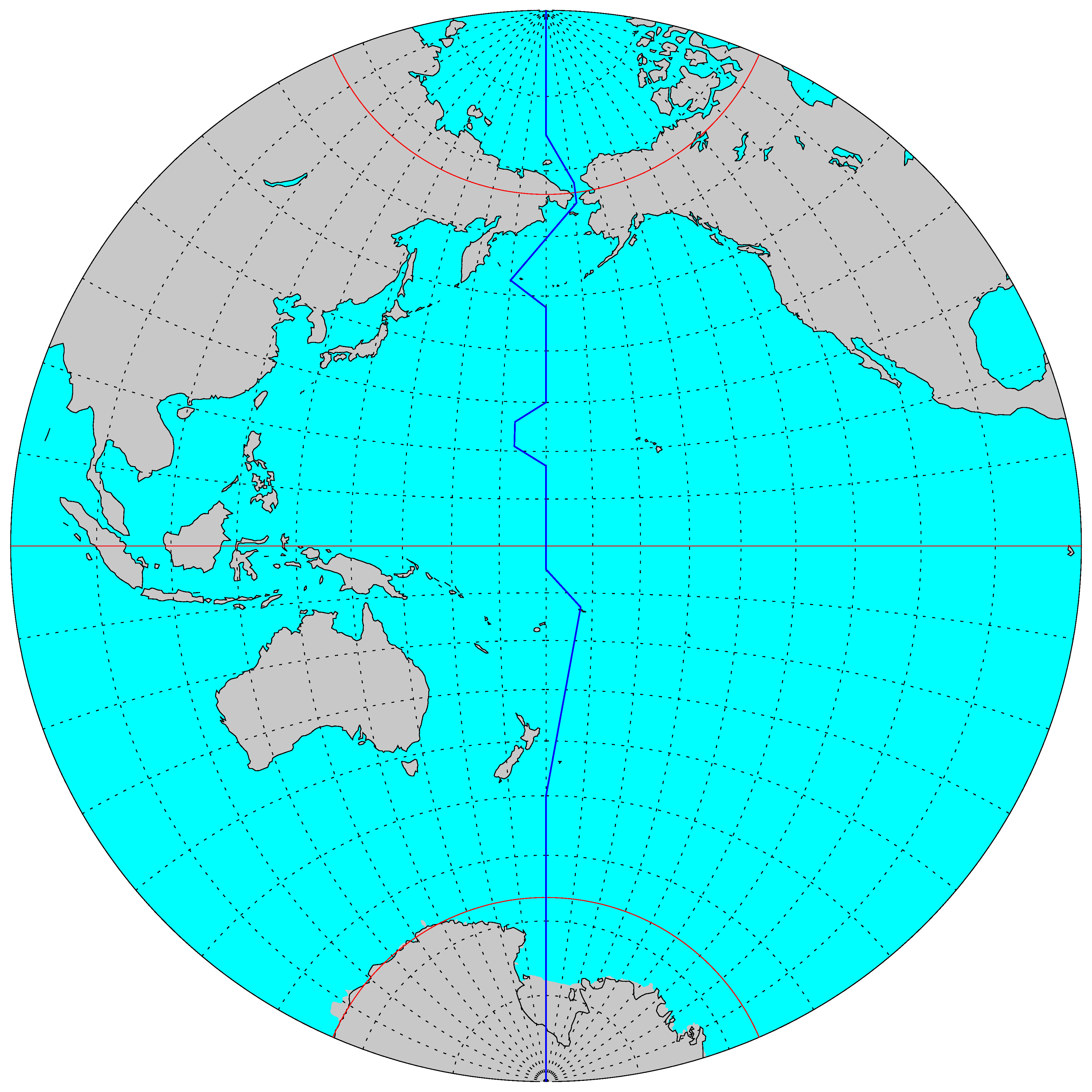
international date line partly makes up 180 degrees longitude (see other side of flashcard)
prime meridian history
the Royal Naval Observatory in London was decided as 0 degrees longitude because the means to accurately calculate longitude at sea was developed by the British Royal Navy
time zones
they are divided in 15-degree wide longitudinal zones around the world (there are some exceptions, for example, China). this is because 360 degrees/ 24 hrs a day = 15
site vs situation
site is the physical characteristics of a place
situation is how a place is interrelated with other places
two types of distance
distance can be absolute or relative
absolute distance vs relative distance
absolute distance
the distance between two places as measured in linear units such as miles or kilometers
relative distance + distance decay (how they relate)
distance decay (gravity) means that the farther away different places are from a place of origin, the less likely interaction will be with the original place
relative distance is sort of like how close or far two things are in comparison + how it affects their relationship. measures the social/cultural/economic relation
tobler’s law
all places are interrelated, but closer places are more related than farther ones
fricition of distance
when the length of distance becomes a factor that inhibits the interaction between two points
space-time compression
decreased time and relative distance between places is called space-time compression
modes of transportation such as airplanes reduce time and create more interactions b/t places
Internet and technology would be an example!
human environment interaction - key topics
i think we will talk about these in detail but human-environment interaction is the affect that humans have on their environment and vice versa
some key elements are environmental determinism, resource depletion, sustainability, conservation efforts, various economic forces, and globalization
transportation nodes
a type of central place, a node that provides further accessibility to and from central places. markets are often located in these places
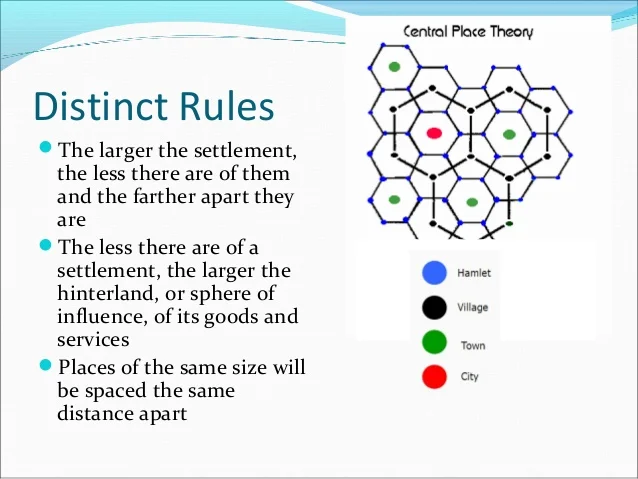
central place theory
developed in the 1930s by German geographer Walter Christaller. his model of the world said that city location and the level of urban economic exchange could be analyzed using central places within hexagonal market areas, which overlapped at different scales
you will take abt this later. ignore for now
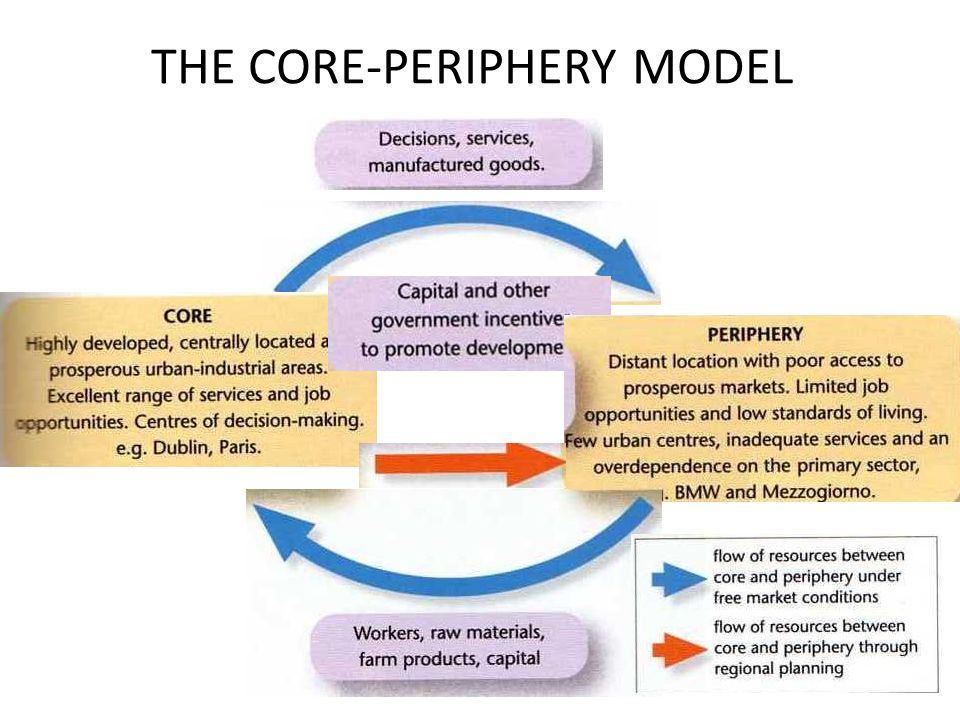
core and periphery
think of a central place as a core of an area. most things happen in relation to the core, there are most opportunities near the core than in the periphery
periphery is an area where there is low development within relationship to its core
cores do not need to be in the center of a region!
CBD
central business district, core of an urban landscape
clusters
when things are grouped together on the Earth’s surface
growth pole
an area of economic development/ central point
agglomeration
used to refer to clustering around a central point/growth pole
random pattern
when there isn’t any reason for where things are distributed
scattered
objects that are normally ordered but appear dispersed ( in patterns)
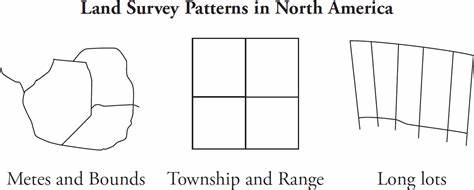
land survey patterns
affect the property lines and political boundaries of states and provinces (where things are divided up)
metes and bounds was a technique used in Europe in old times
after the 1830s, surveyors in US and CA started using the township and range lines, based on lat. and long.
colonial french areas use(d) long-lot patterns
arithmetic density
number of things per square unit of distance
physiologic density
number of people per square unit of arable land (land that is farmed or could be farmed)
agricultural density
number of farmers per square unit of arable land (land that is farmed or could be farmed)
diffusion patterns
there are different ways human phenomena diffuse spatially (spread across the earth)
we study how culture, ideas, or technology spread from a point to other parts
we often call this point a hearth
expansion diffusion
originates in a central place and moves outwards in all directions, the amt it moves does not need to be equal
types of expansion diffusion patterns are heirarchal, contagious, and stimulus
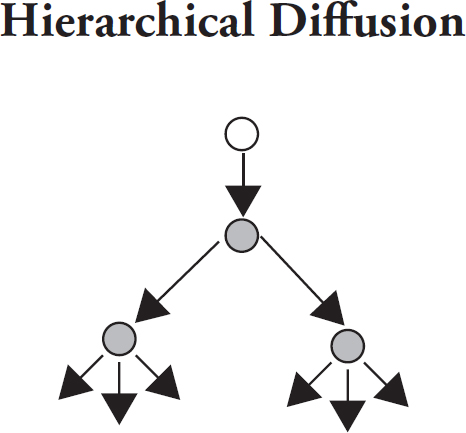
hierarchal diffusion
basically a freaking family tree
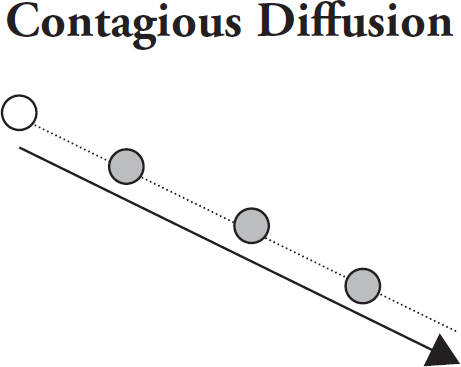
contagious diffusion
point of origin and then moves outward to nearby locations, especially with transportation lines or diseases or news in rural areas
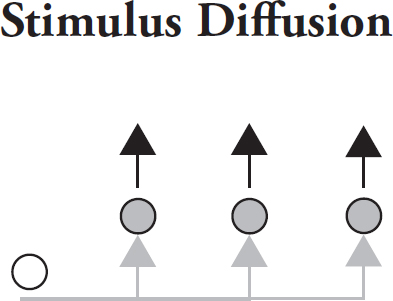
stimulus diffusion
a general or underlying principle diffuses and then stimulates the creation of new products or ideas
for example, vegetarian eating habits (principle) → more vegetarian food in restaurant (product)
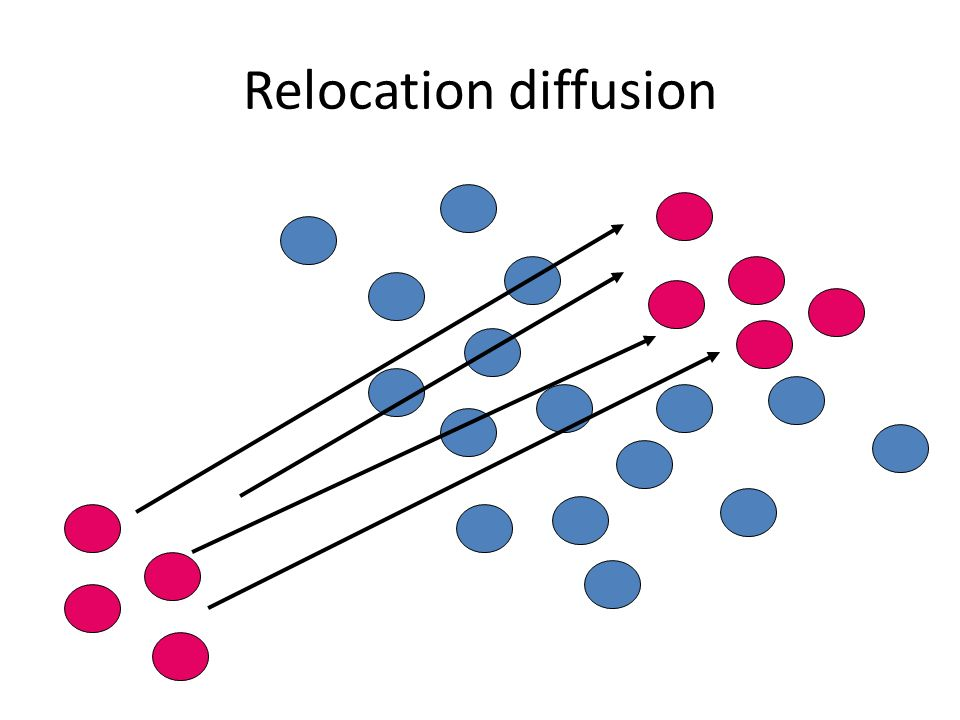
relocation diffusion
pattern begins at a point of origin and then crosses a significant physical barrier (ocean, desert, etc.) and then relocates on the other side
the journey often influences the item being spread
why are maps important
they separate geographers from other groups
they result from spatial analysis (mathematical analysis of 1 or more quantitative geographic patterns)
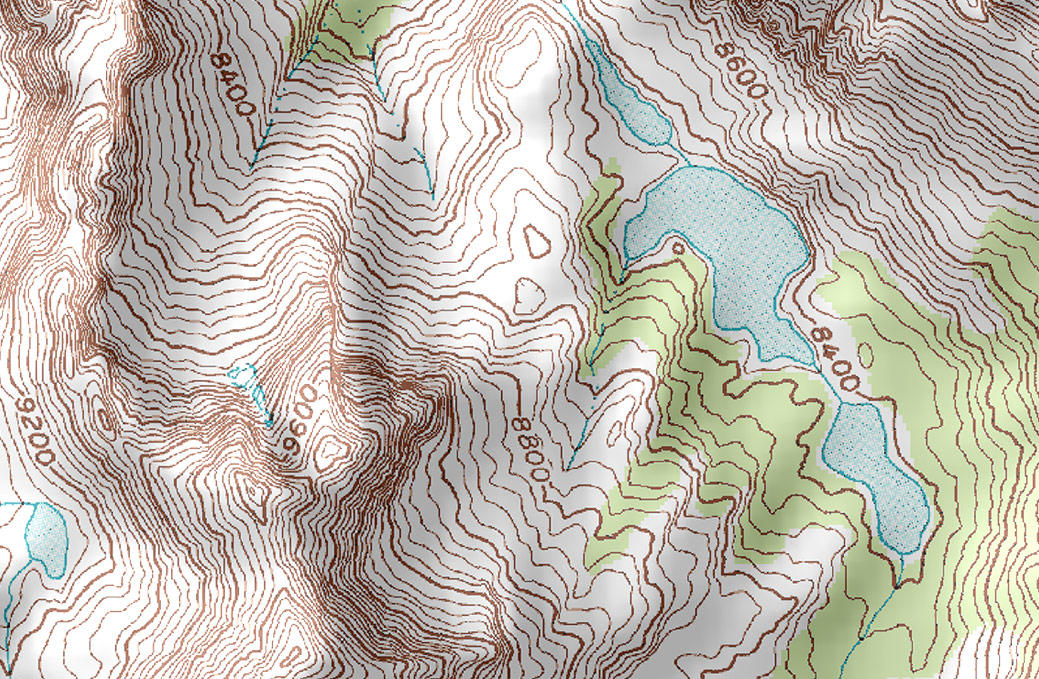
topographic maps
show lines of elevation, urban and vegetations, other natural landscape features
thematic maps
maps that show one specific topic/subject
chloropleth maps, isolne maps, dot density maps, flow-line maps, cartograms
contour lines
(isotherms) which are temperature lines
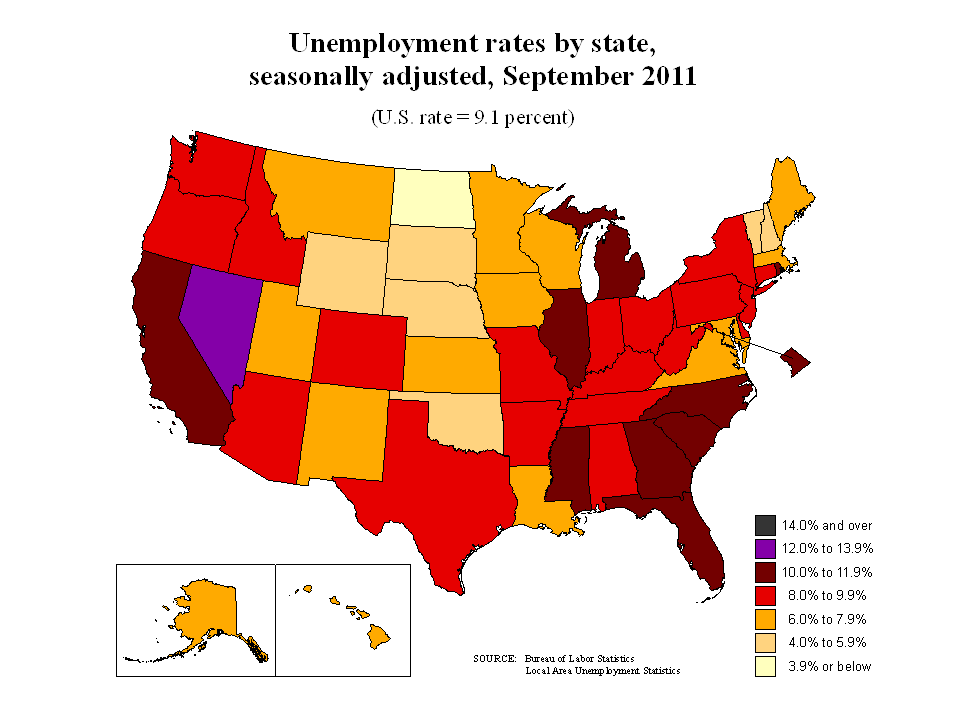
choropleth maps
show geographic variability of a particular theme with color variations
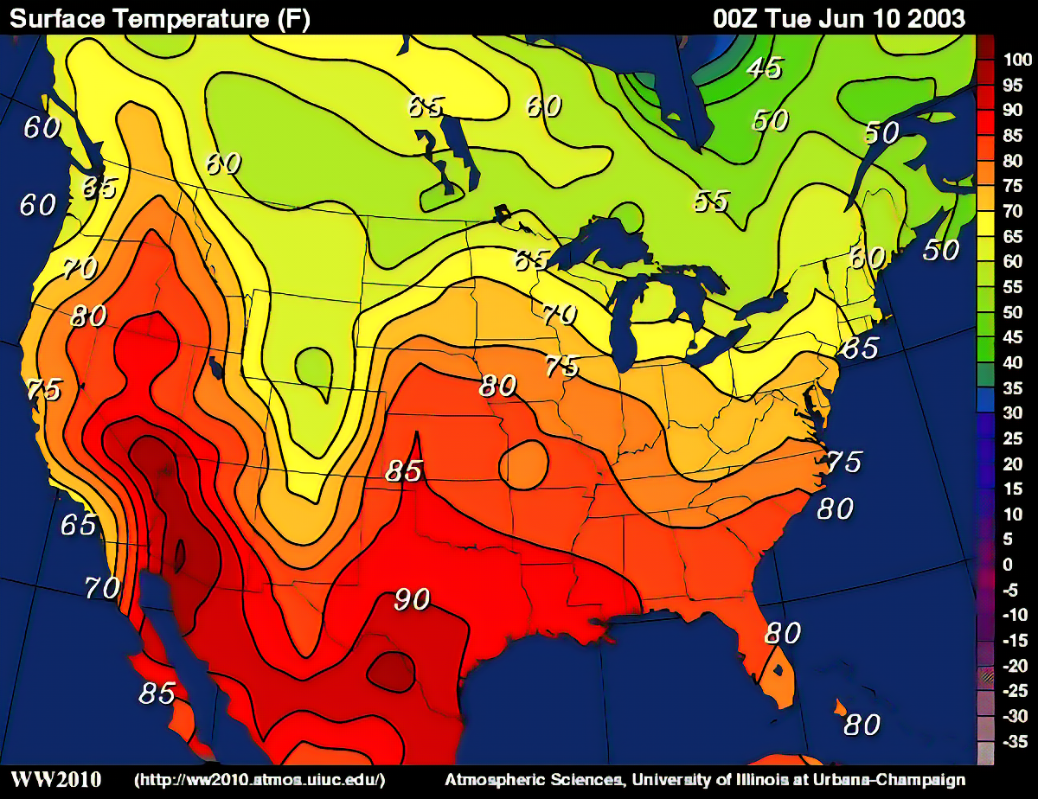
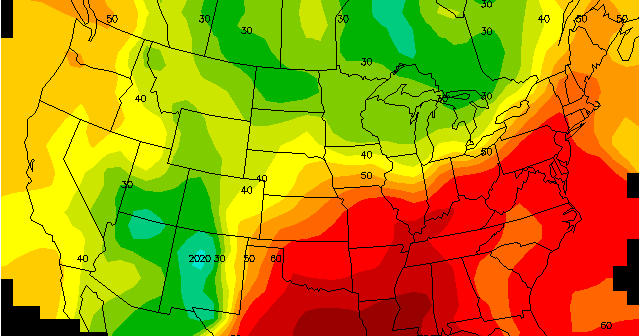
isoline maps
calculate data between points on a variable surface
weather maps are a good example
dot density maps
they use dots to show volume and density of a geographic feature
you will often see a dot represent a larger number
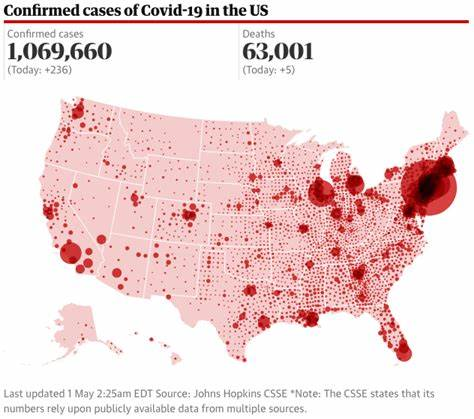
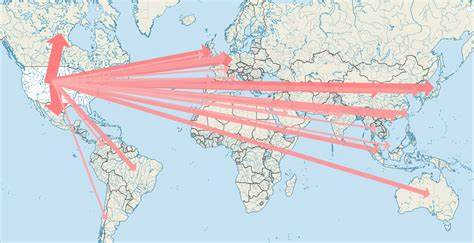
flow-line maps
use lines of varying thickness to show direction and volume of a particular geographic movement pattern
ex: migration patterns
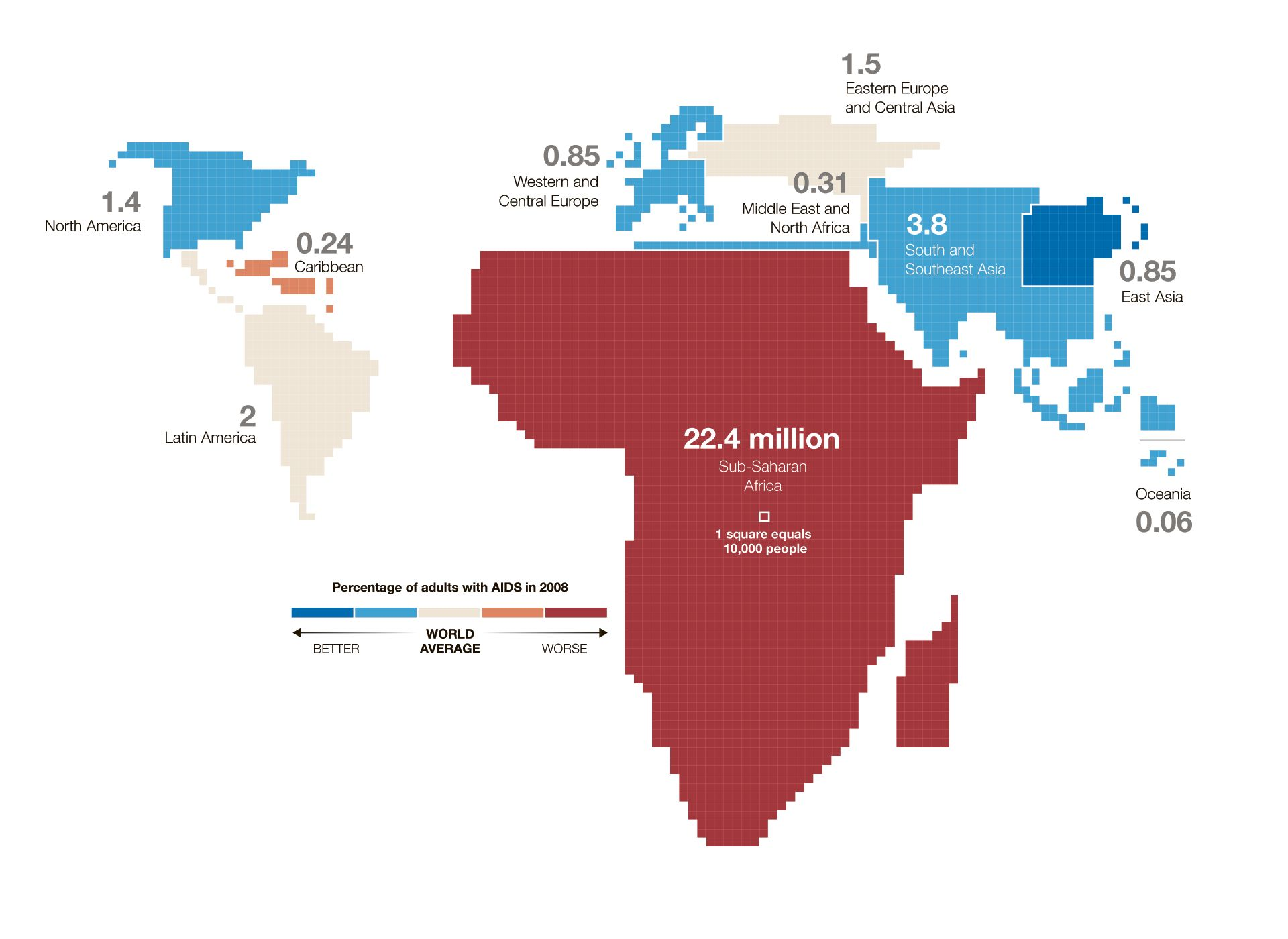
cartograms
use simplified geometries to represent real world places
more abt the data shown than the landscape
ex: subway maps in nyc
mental map
the cognitive image of landscape in the human mind
we have good mental maps abt places that are important to us, and weak mental maps abt anything else
map scale
the “absolute” scale version
linear map scales express distance on the map surface
you can find the ratio of the map as well (distance on map to distance irl) ex. 1:4000
large scale map has a ratio that is very large irl, small scale map is the opposite, breaking point to tell the difference is abt 1:250000

equal area projections
attempt to maintain the relative spatial science and the areas on the map, which often distorts actual shapes
lambert projection squished Canada to fit other things
conformal projections
try to maintain the shape of polygons on a map, unfortunately this causes distortion of distance between two parts
mercator projection keeps greenland happy but makes it look bigger than it actually is compared to south america
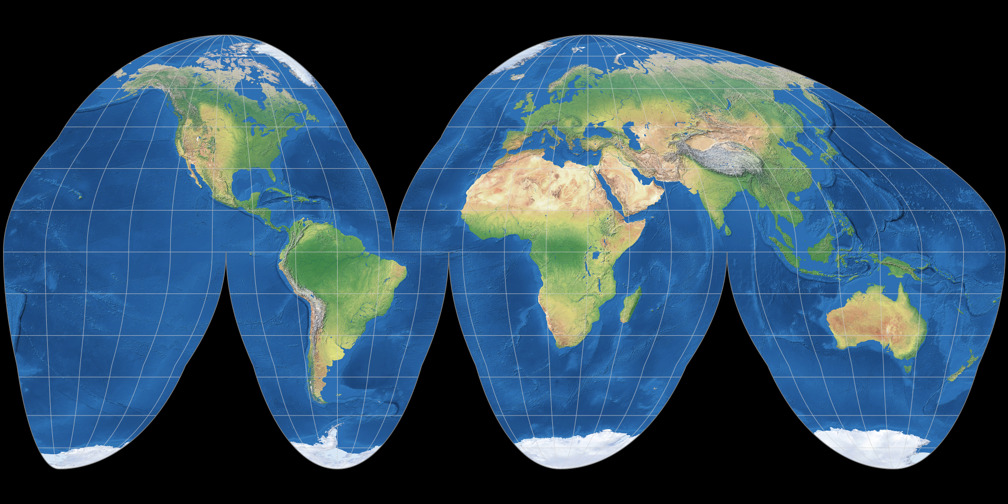
robinson projection + goode’s homolosine projection
goode is on this side of the flashcard
both try to compromise between shape distance and distortion issues
photo → robinson
models
model is an abstract generalization of real-world geographies that share a common pattern
Spatial models attempt to show the commonalities in pattern among similar landscapes
Urban models try to show how different cities have similar spatial relationships and economic or social structures
Demographic transition models are non-spatial models that use population data to construct a general model of the dynamic growth in national scale populations without reference to space
please find some examples lol
why do we use models
to gain understanding of patterns you can’t see on maps and address questions
gravity model
a mathematical model that is used in a number of different types of spatial analysis
used to calculate transportation flow between two points, determine the area of influence of a city’s businesses, and estimate the flow of migrants to a particular place
formula: location 1 pop. x location 2 pop. all divided by distance²
this shows you the gravity (pull) of the relationship between two places
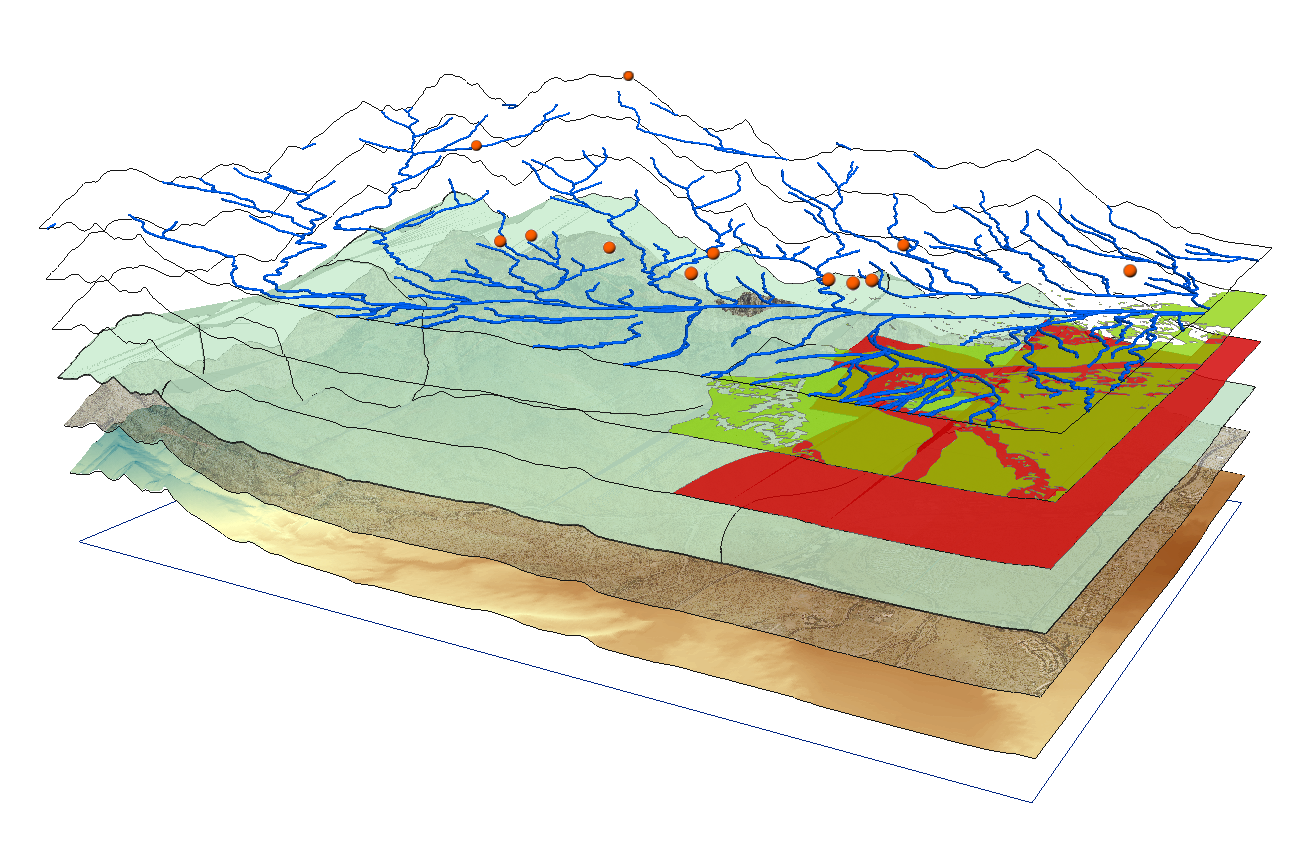
geographic information systems (GIS)
became practical with the onset of the desktop computer in the 1970s
incorporate one or more data layers in a computer program capable of spatial analysis and mapping
each layer can show you a different type of feature
spatial analysis capabilities!!
global positioning system (GPS)
use satellites which emit radio signals
when this signal comes from 3+ Navstar satellites, the signal triangulates a location of where you are
remote sensing
aerial photography (photos taken of the earth from an aircraft) + satellite-based remote sensing (using a computer scanner to record data with light and radar info) make up much of GIS and geographic data today