Chapter 6: Computer System and Networks
Computing Devices
- A computing device is a physical artifact that can run a program.
- Some examples include computers, tablets, servers, routers, and smart sensors.
- The device must be able to take inputs, process the inputs, and then calculate results based on those inputs.
- A computer is a computing device, but not all computing devices are computers.
- A computing system is a group of computing devices and programs working together for a common purpose.
- A computer network is a group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data.
Autonomous Systems of the Internet
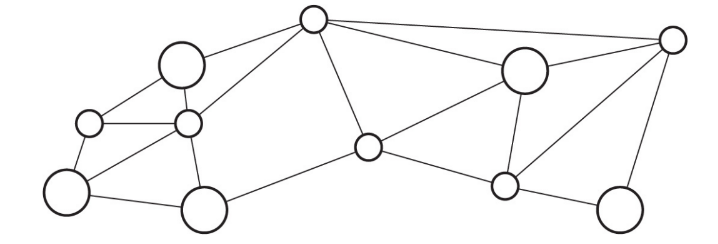
Each circle in the diagram above represents a computer system that is connected to another computer system, forming a computer network.
The larger circles represent systems that have a higher bandwidth capacity measured in bits per second.
The bandwidth of a computer network is the maximum amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time.
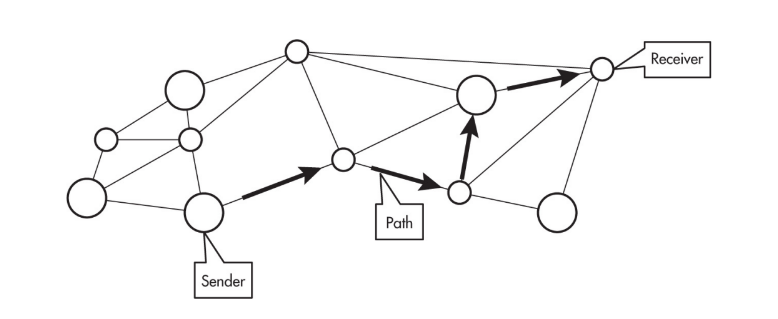
A path between two computing devices on a computer network (a sender and receiver) is a sequence of directly connected computing devices that begins at the sender and ends at the receiver.
Routing is the process of finding a path from sender to receiver.
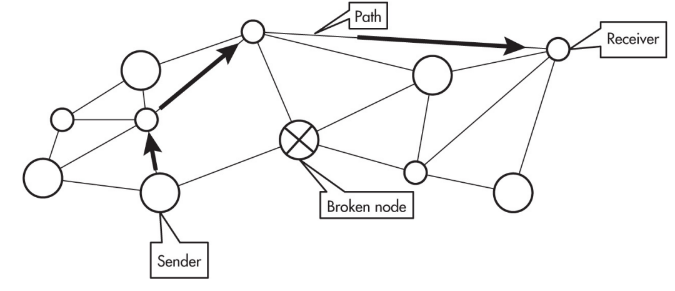
If the path from sender to receiver is broken, the path will be rerouted.
This fault-tolerant nature of the internet makes connections between computing devices more reliable.
Internet Protocol
- Internet protocol (IP) is responsible for addressing and routing your online requests.
- For a device to connect to the internet, it is first assigned an internet protocol address.
Transmission Control Protocol
- Transmission control protocol (TCP) is a protocol that defines how computers send packets of data to each other.
- Data traveling in the internet is broken down into small chunks of data called packets.
User Datagram Protocol
- User datagram protocol (UDP) is a protocol that allows computer applications to send messages without checking for missing packets to save on time needed to retransmit missing packets.
- UDP is not as reliable as TCP, which does resend packets lost when transmitting.
Fault Tolerance
- When a system can support failures and continue to function, it is called fault tolerant.
- This is important because elements can fail at any time, and fault tolerance allows users to continue to use the network.
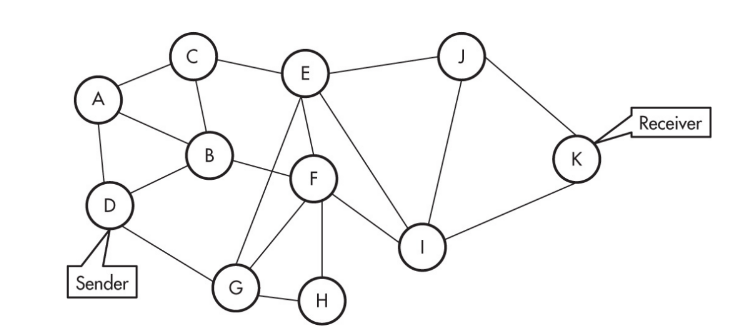
- The process from computer D to computer K in the diagram above is called end-to-end architecture.
- This process involves the breaking down and assembling of the packets at each end.
- What happens to the packets in the middle is hidden from the user in an abstraction.
Difference Between Internet and World Wide Web
- The internet refers to the hardware.
- The World Wide Web, in contrast, refers to the software used on the internet.
Efficiency of Solutions
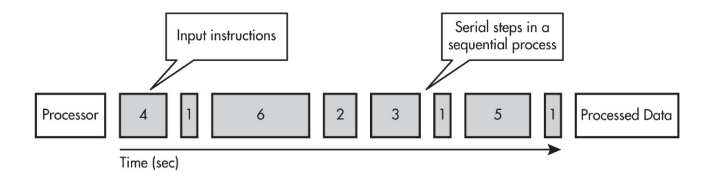
- Sequential computing is a computational model in which operations are performed in order one at a time.
- A sequential solution takes as long as the sum of all of the steps.
- A parallel solution takes at least as long as the longest branch in the program.
Sequential Computing
A problem is broken into discrete instructions.
These instructions are executed one by one by a single computing device having a single central processing unit (CPU).
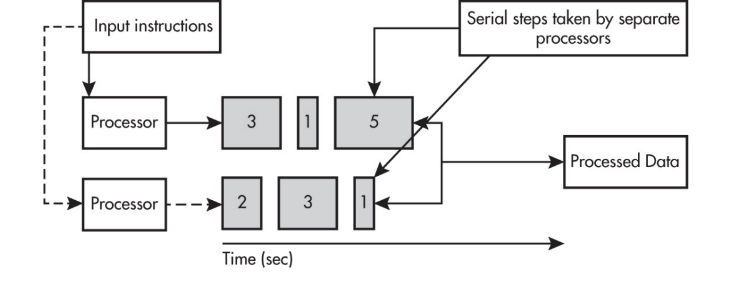
Parallel Computing
- A parallel computing solution takes as long as the longest of the tasks done in parallel.
- A parallel computing solution takes as long as its sequential tasks plus the longest of its parallel tasks.
- Parallel computing can consist of a parallel portion and a sequential portion.
Why Is Parallel Computing Used?
Parallel computing is needed for real-world simulations and modeling.
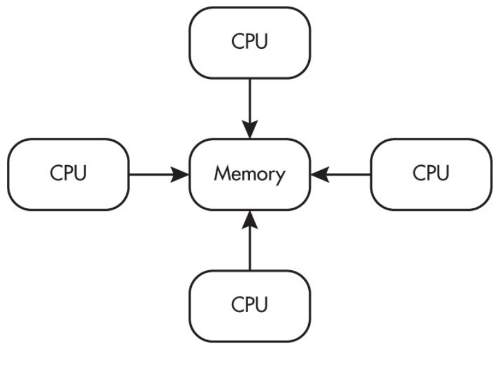
Multiple processors can operate independently but share the same memory resources.
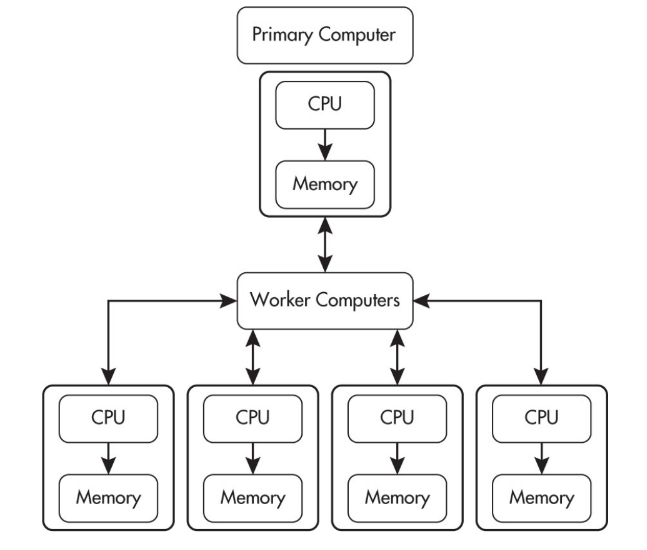
Distributed Computing
Distributed computing allows problems to be solved that could not be solved on a single computer because of either the processing time or storage needs involved.
Parallel computing uses a single computer with multiple processors.
Distributed computing uses multiple computing devices to process those tasks.