Rates of Reaction
- Rate of a chemical reaction: The amount of reactant used up or product made in a given time.
Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction
Concentration
Increasing concentration of reactants increases rate of reaction
More particles per unit volume, so the collision rate between reacting particles increases
→ The successful collision rate increases, which results in an increased rate of reaction.

Temperature
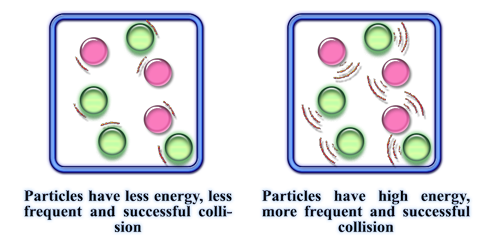
Increasing temperature increases the rate of reaction
The average kinetic energy of particles increase
Particles are moving faster and colliding more ften and so more particles have an energy greater than or equal to the activation energy
- Increased rate of succesful collisions and so increased rate of reaction
Surface Area
Decreasing the particle size (increasing surface area) increases the rate of reaction
This is because there are more reactant particles exposed to collide, so the collision rate increases, therefore the successful collision rate increases, resulting in an increased rate of reaction

Large surface area can be dangerous'
- For example, flour dust and wood dust have large surface areas, and are combustible. A spark from a machine, or a lit match, can cause an explosion. This also applies to gases from mines.
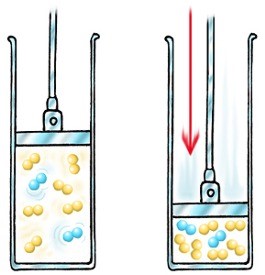
Pressure
Increasing the pressure in a gaseous system increases the rate of reaction
The distance between particles is reduced under pressure
There are more particles per unit volume, so the collision rate increases, therefore the successful collision rate increases, resulting in an increased rate of reaction.
Presence of Catalyst
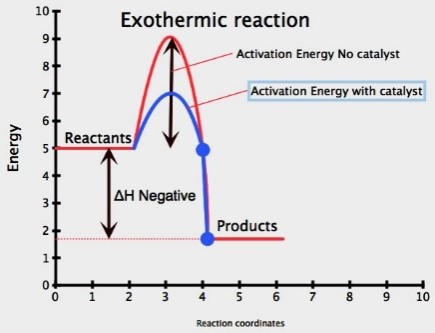
Catalyst: is a substance (usually a transition metal) which speeds up a chemical reaction, but remains unchanged at the end
Adding a catalyst increases the rate of reaction
A catalyst lowers the activation energy for a reaction
More particles will have an energy greater than or equal to the activation energy, therefore successful collision rate increases resulting in increased rate of reaction
Enzymes are protein molecules. They are biological catalysts which speed up reactions but remain chemically unchanged at the end
Enzymes function best at optimum temperature and pH level otherwise they may denature and completely stop functioning
Photochemical Reactions
Light Causing a Chemical Reaction
Photochemical Reaction: reaction which needs light to take place
The higher the light intensity the higher the rate of the reaction.
%%Photosynthesis:%% light provides energy for the reaction and chlorophyll is a dye that absorbs light. carbon dioxide + water → (light + chlorophyll) → glucose + oxygen
Use of silver salts in photography:
- Silver halide salts are used in black and white photography
- AgCl is sensitive to light & breaks down to form metallic silver Ag+ -> Ag
- Appears black
Brighter the light on the film, the faster the reaction & the darker that part of the photograph appears i.e. improves efficiency & accuracy of photos