Rivers and Flooding
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
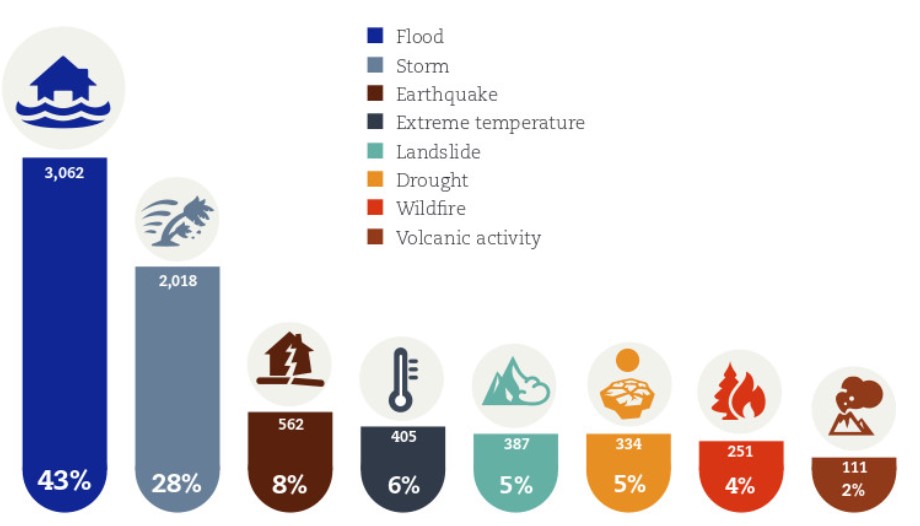
what kind of disasters are the most common and affect most amount of people?
* meteorological
2
New cards
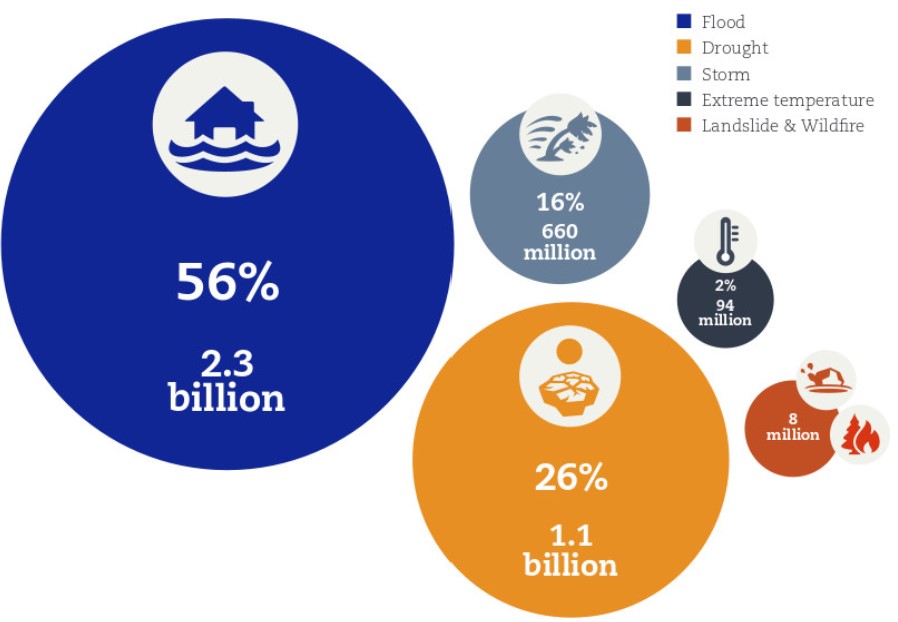
number of people affected by weather-related disasters
3
New cards
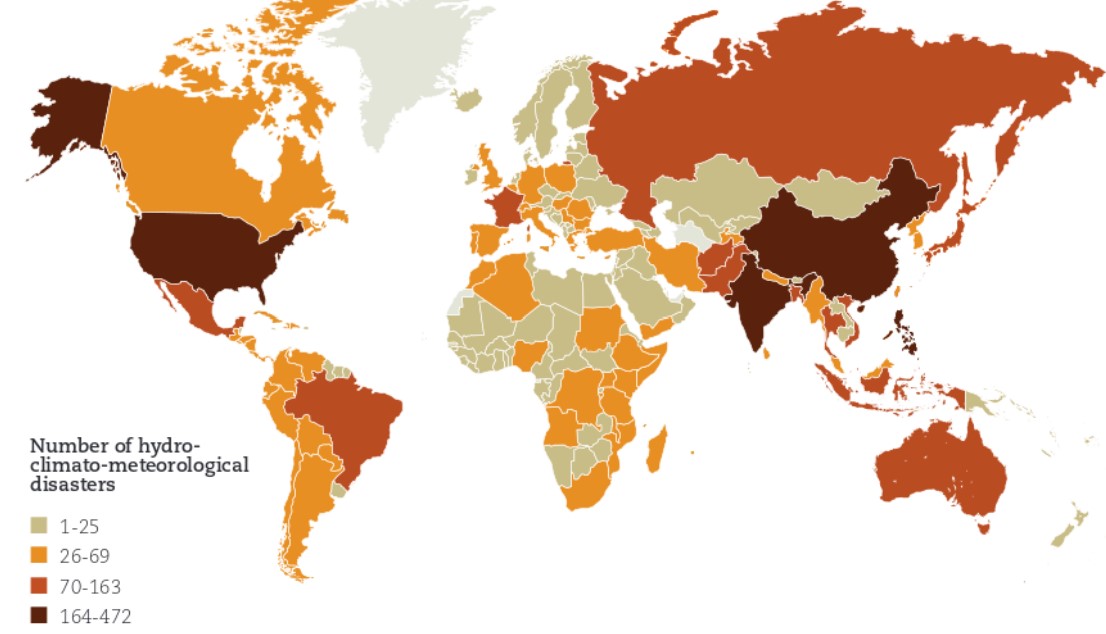
world - number of weather-related diseases reported per country (1995-2015)
4
New cards
what are some weather systems that cause flooding?
* tropical cyclones
* monsoon season
* sever isolated thunderstorms
* atmospheric rivers
* monsoon season
* sever isolated thunderstorms
* atmospheric rivers
5
New cards
what are the 2 types of flooding?
* high intensity & short duration
* lower intensity & long duration
* lower intensity & long duration
6
New cards
what is high intensity & short duration?
* large amount of precipitation falling in a very short time period → flash flood
7
New cards
what is lower intensity & long duration flood?
* large amount of precipitation falls steadily over a longer time period → slow-onset flood
* low precipitation, high flooding
* low precipitation, high flooding
8
New cards
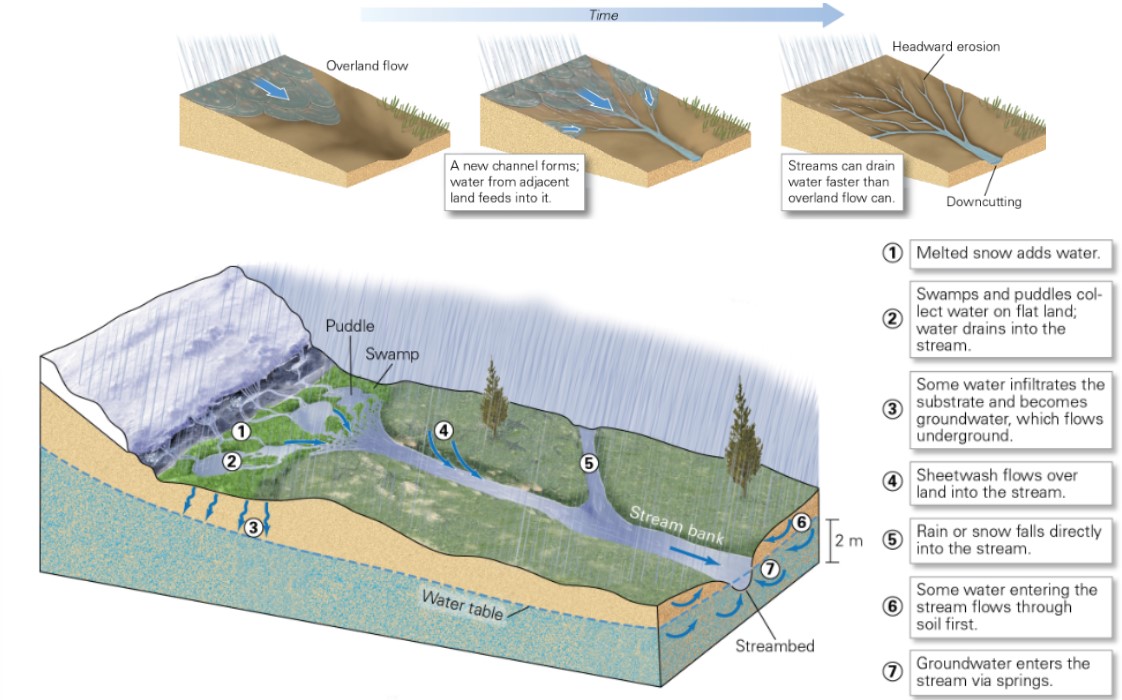
all about streams?
* flows to areas of low elevation → creates channels
* add to groundwater → river
* add to groundwater → river
9
New cards
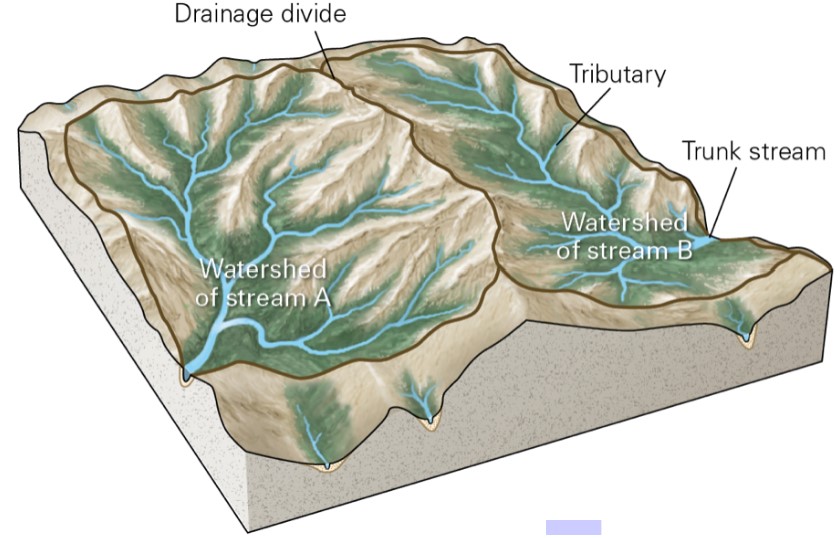
what is a watershed?
* the land area providing water to a specific draining network
10
New cards
what is a draining network?
* an array of streams that drain into the same, larger (trunk) stream
* everything drains into trunk stream
* everything drains into trunk stream
11
New cards
what is the largest watershed in the world?
* amazon river watershed
12
New cards
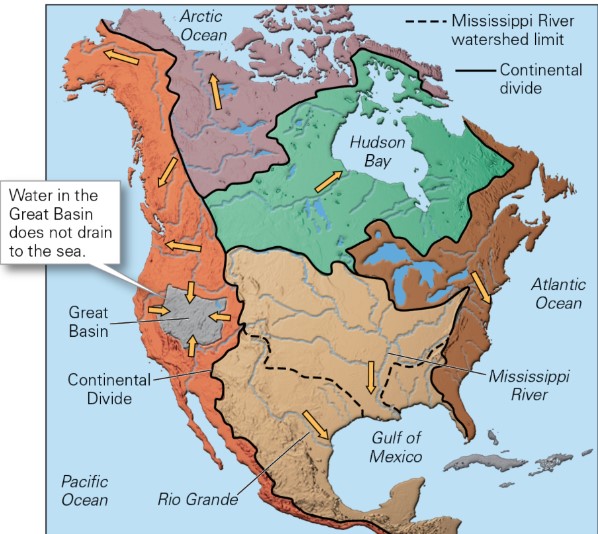
watersheds of North America
13
New cards
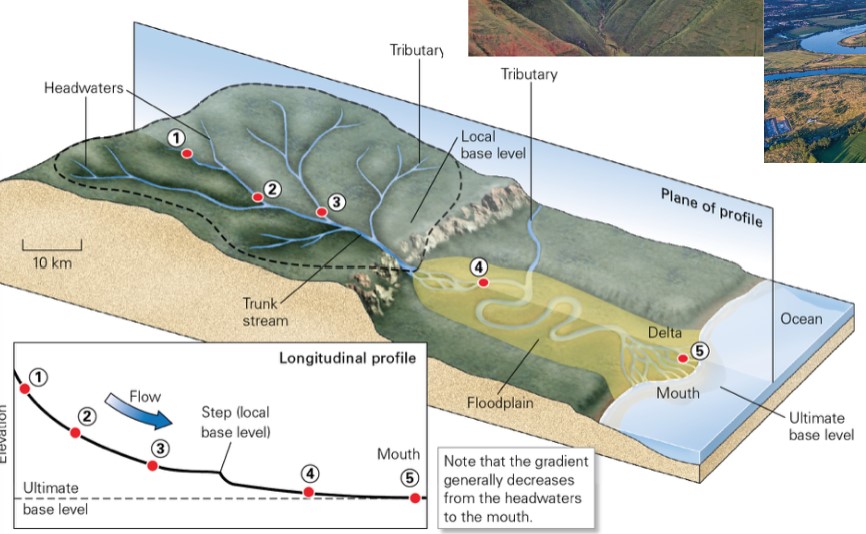
what is a stream gradient?
* slope of the river channel; typically decreases downstream
* headwaters → mountainous areas
* end point of stream → ocean
* headwaters → mountainous areas
* end point of stream → ocean
14
New cards
what is base level?
* an elevation that a stream cannot erode past, controlled by the lvl of the body of water which the stream discharges into
15
New cards
what is bankfull?
* when the water lvl in a river is equal to the height of the banks
* flooding occurs when water rises over bankfull lvls
* rivers do not reach bankfull stage every yr
* on avg → they do not flood
* determining channel bankfull width and depth can approx the bankfull discharge and the capacity of the channel
* flooding occurs when water rises over bankfull lvls
* rivers do not reach bankfull stage every yr
* on avg → they do not flood
* determining channel bankfull width and depth can approx the bankfull discharge and the capacity of the channel
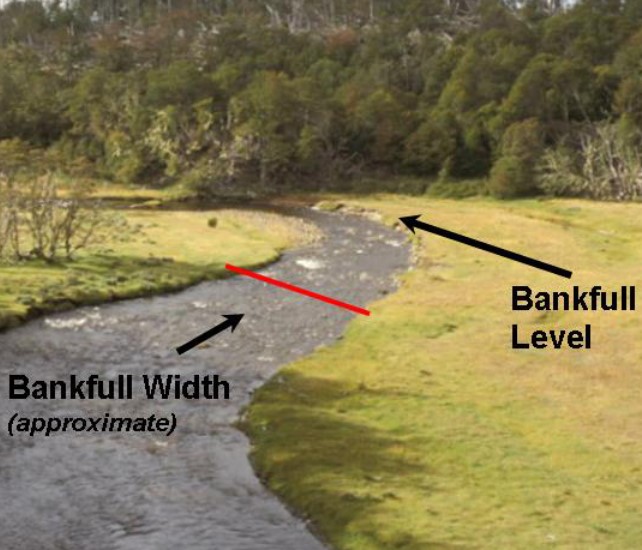
16
New cards
what are floodplains?
* broad, flat area next to a stream that becomes either partly or comp. covered during a flood
* it is flat due to past floods (sediment deposition) → good for agriculture
* it is flat due to past floods (sediment deposition) → good for agriculture
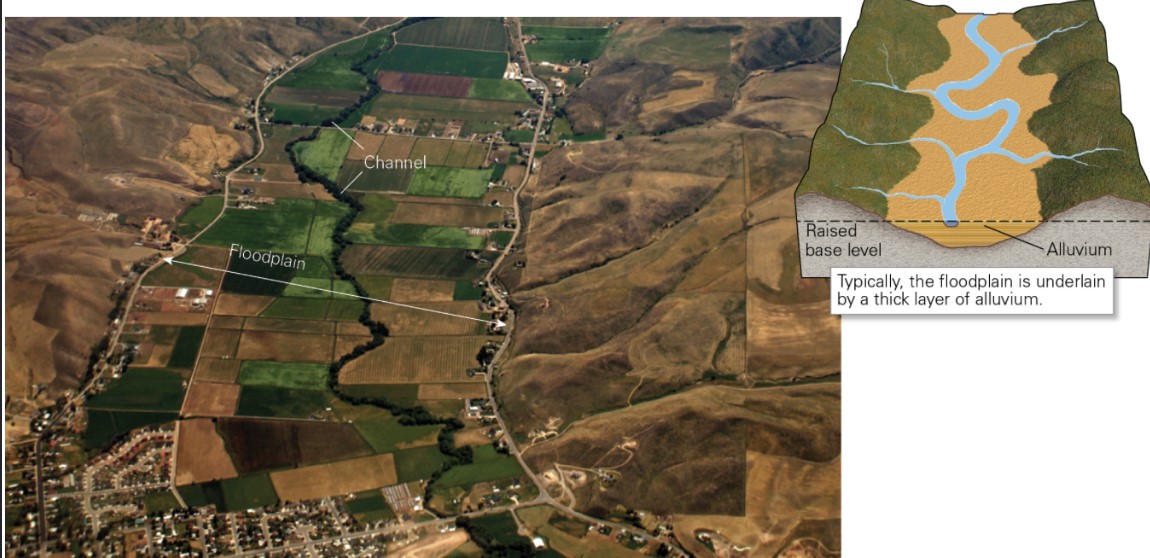
17
New cards
what kind of loads do streams carry?
* dissolved
* suspended
* bed-load
* suspended
* bed-load
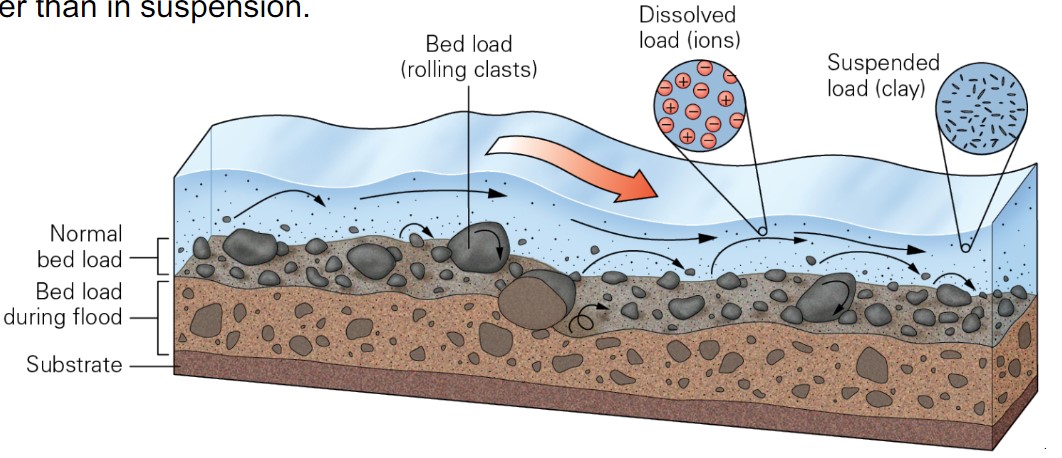
18
New cards
what constitutes as suspended load?
* finer particles, such as clay, silt, and fine sand, carried in suspension
19
New cards
what is bedload?
* heavier sediment in a stream that is moved along the stream bed rather than in suspension
20
New cards
what do fast flowing stream carry?
* larger grain sizes (clasts) than a slower flowing stream
* even boulders
* even boulders
21
New cards
the volume of sediments carried in streams depend on?
* flow volume
* velocity;
* during flood, flow vol + velocity increases, so more sediment is transported
* velocity;
* during flood, flow vol + velocity increases, so more sediment is transported

22
New cards
Natural Levees
* channel geometry is controlled by flow velocities and its associated sediment load carrying capacity
* as a stream spills over its floodplain, it moves from a deep channel with high velocity to a shallow, broad floodplain with a low velocity
* when velocity drops → causes sediments to also fall
* bigger material fall first → right next to channel
* small particles fall a bit farther
* this creates gradient → coarse to fine
* as a stream spills over its floodplain, it moves from a deep channel with high velocity to a shallow, broad floodplain with a low velocity
* when velocity drops → causes sediments to also fall
* bigger material fall first → right next to channel
* small particles fall a bit farther
* this creates gradient → coarse to fine
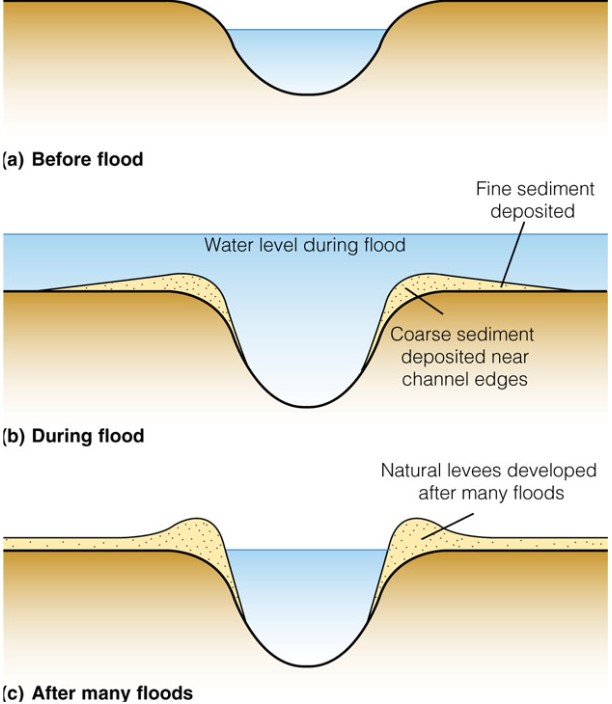
23
New cards
what is an alluvial fan?
* a fan shaped deposit of sand and gravel at the mouth of a mountain canyon, where the stream gradient flattens at the main valley floor
* steep → high velocity
* lower → drop of velocity
* steep → high velocity
* lower → drop of velocity
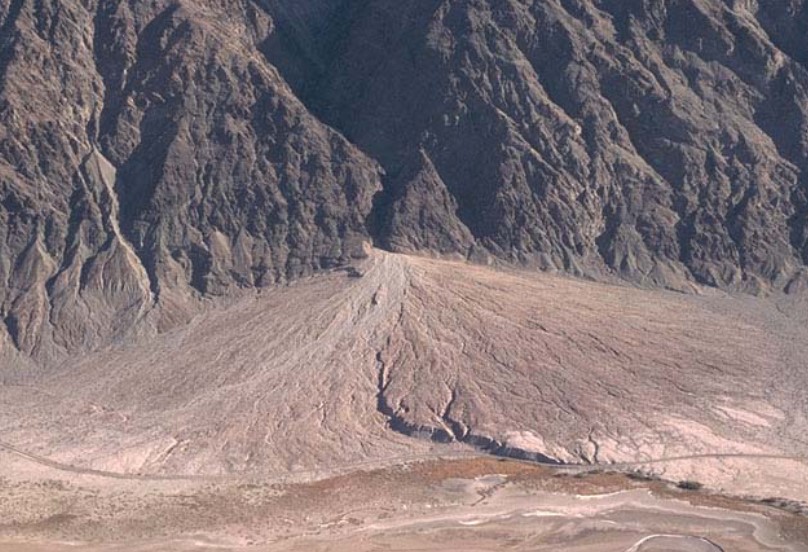

24
New cards
what is a delta?
* accumulation of sediment deposited by a river at its entrance into a basin
* at the bottom, there is sediment deposition
* at the bottom, there is sediment deposition
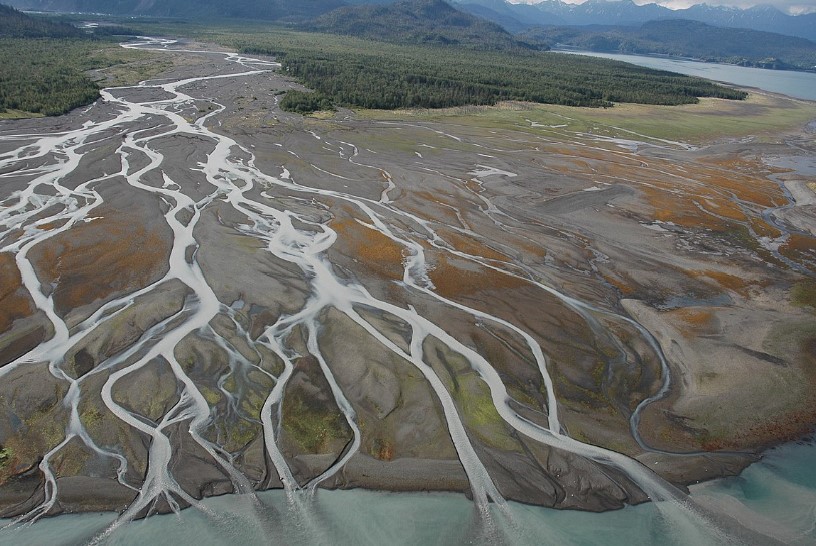

25
New cards
what is a permanent stream?
* flows all yr, below the water table
* recharge
* in temperate climate
* recharge
* in temperate climate
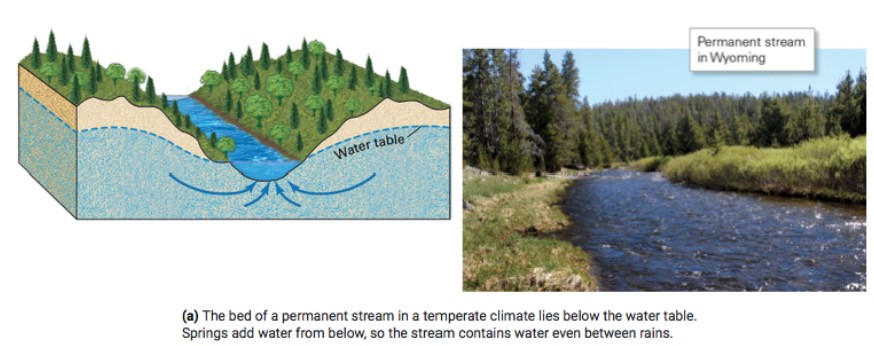
26
New cards
what is an ephemeral stream?
* flows only for part of the year; above the water table
* only flows when water flow is high (precipitation) will dry up
* only flows when water flow is high (precipitation) will dry up
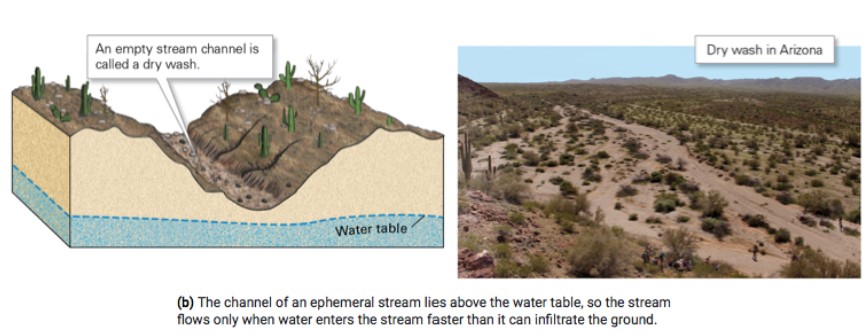
27
New cards
what is a meandering river?
* river with a single channel and high to moderate sinuosity

28
New cards
where do cutbanks form?
* on the outside of meander bends where the water is accelerated along the outside wall and erodes into the bank
29
New cards
where do point bars form?
* as sediment is deposited in the slower water on the inside of the meander bends
30
New cards
meandering river
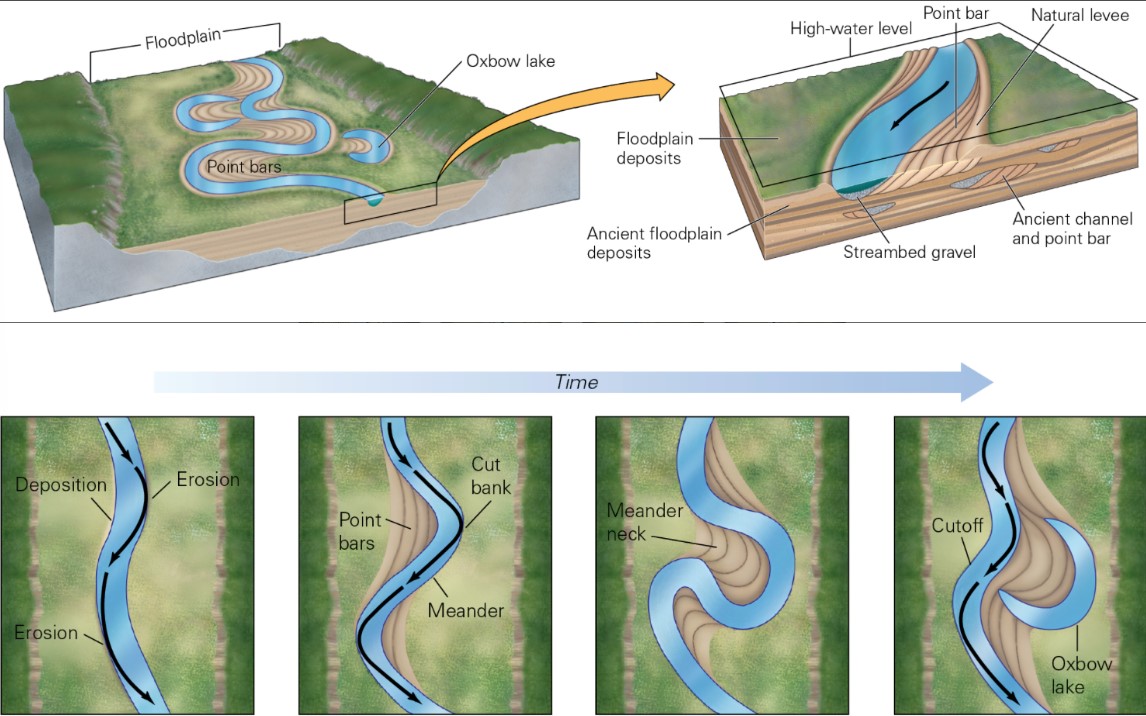
31
New cards
example of meandering rivers
* Mississippi River and Floodplain
* streams change over time bc of flow velocity
* cutbanks are eroded, and pntbars are deposited
* always changing + moving
* streams change over time bc of flow velocity
* cutbanks are eroded, and pntbars are deposited
* always changing + moving
32
New cards
Clark Fork River
* gradually eroded the cutbank until it undercut the house that was originally built 10m back from the river
* issue → land erodes back
* issue → land erodes back
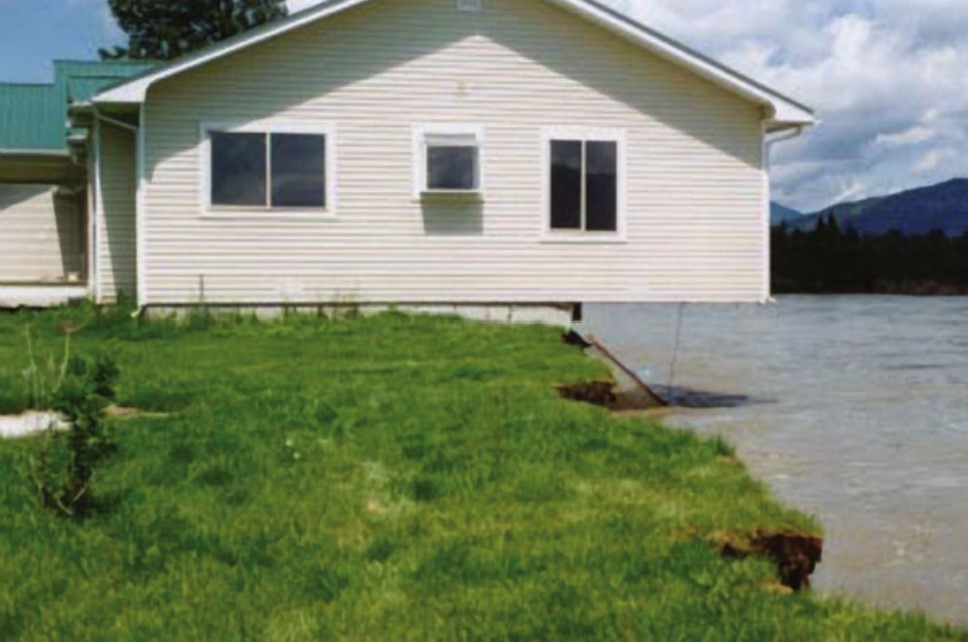

33
New cards
what is a braided river?
* a river characterized by multiple, frequent shifting channels
* common in regions where there is a strong seasonally and monthly variation in stream discharge
* during short periods of high discharge a braided river carries the coarsest sediment
* dev in regions where sediment is readily available
* common in regions where there is a strong seasonally and monthly variation in stream discharge
* during short periods of high discharge a braided river carries the coarsest sediment
* dev in regions where sediment is readily available
34
New cards
bedrock channels
* steep wall → reduce chance of flooding
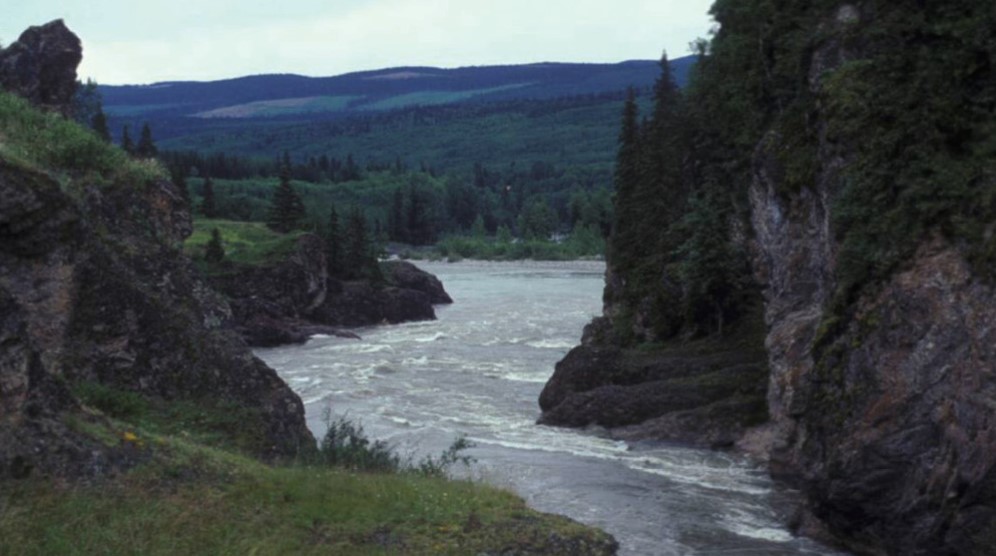

35
New cards
what is discharge (m3/s)?
* measured vol of water flowing past a cross section of a river in a given amount of time
* D = A x v
* D = discharge (m3/s)
* A = cross-sectional area (m2) = width x depth (in m)
* V = velocity (m/s)
* D = A x v
* D = discharge (m3/s)
* A = cross-sectional area (m2) = width x depth (in m)
* V = velocity (m/s)
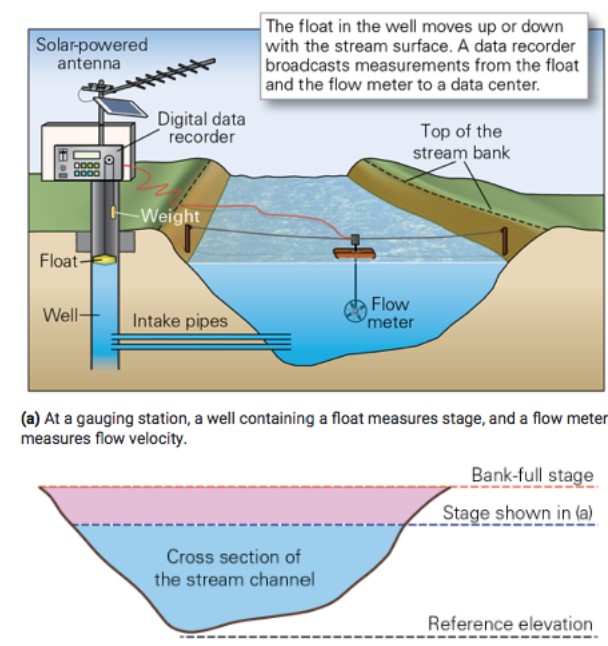
36
New cards
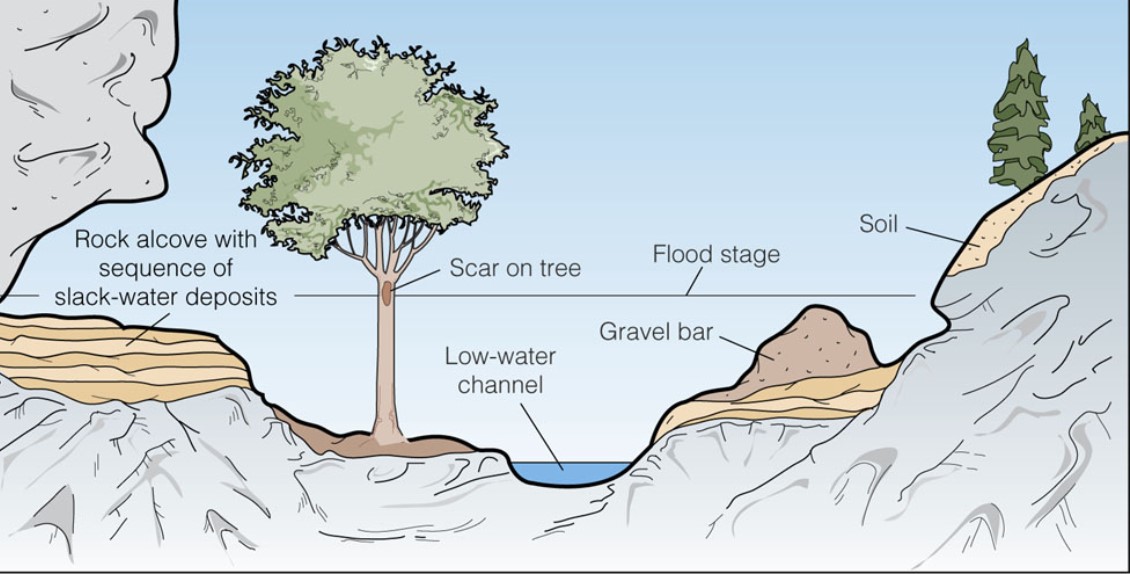
what is flood stage?
* the stage (water lvl) at which a stream rises above its banks in many places and submerges areas outside of the stream channel
* shape + depth is important
* in the top pic → no flooding cuz steep
* e.g., mountains
* bottom → not steep → high water lvl lead to flooding
* e.g., meandering bankfull, then over it → food
* shape + depth is important
* in the top pic → no flooding cuz steep
* e.g., mountains
* bottom → not steep → high water lvl lead to flooding
* e.g., meandering bankfull, then over it → food
37
New cards
what is a hydrograph?
* length of lag time depends on:
* basin area and shape
* spacing of drainage channels
* vegetation cover
* soil permeability and land use
* time delay cuz water has to make way to river
* basin area and shape
* spacing of drainage channels
* vegetation cover
* soil permeability and land use
* time delay cuz water has to make way to river
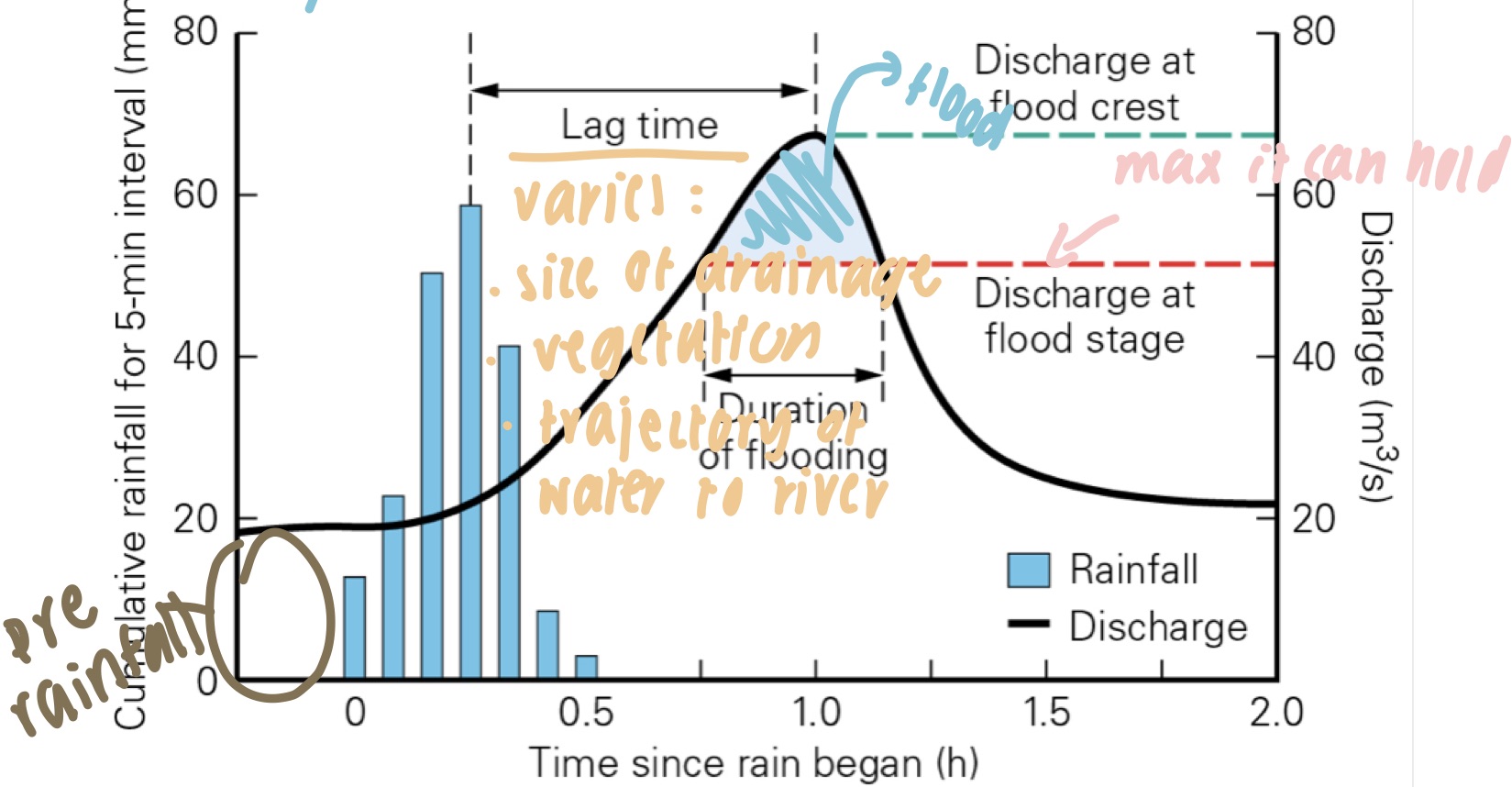
38
New cards
more hydrographs
\
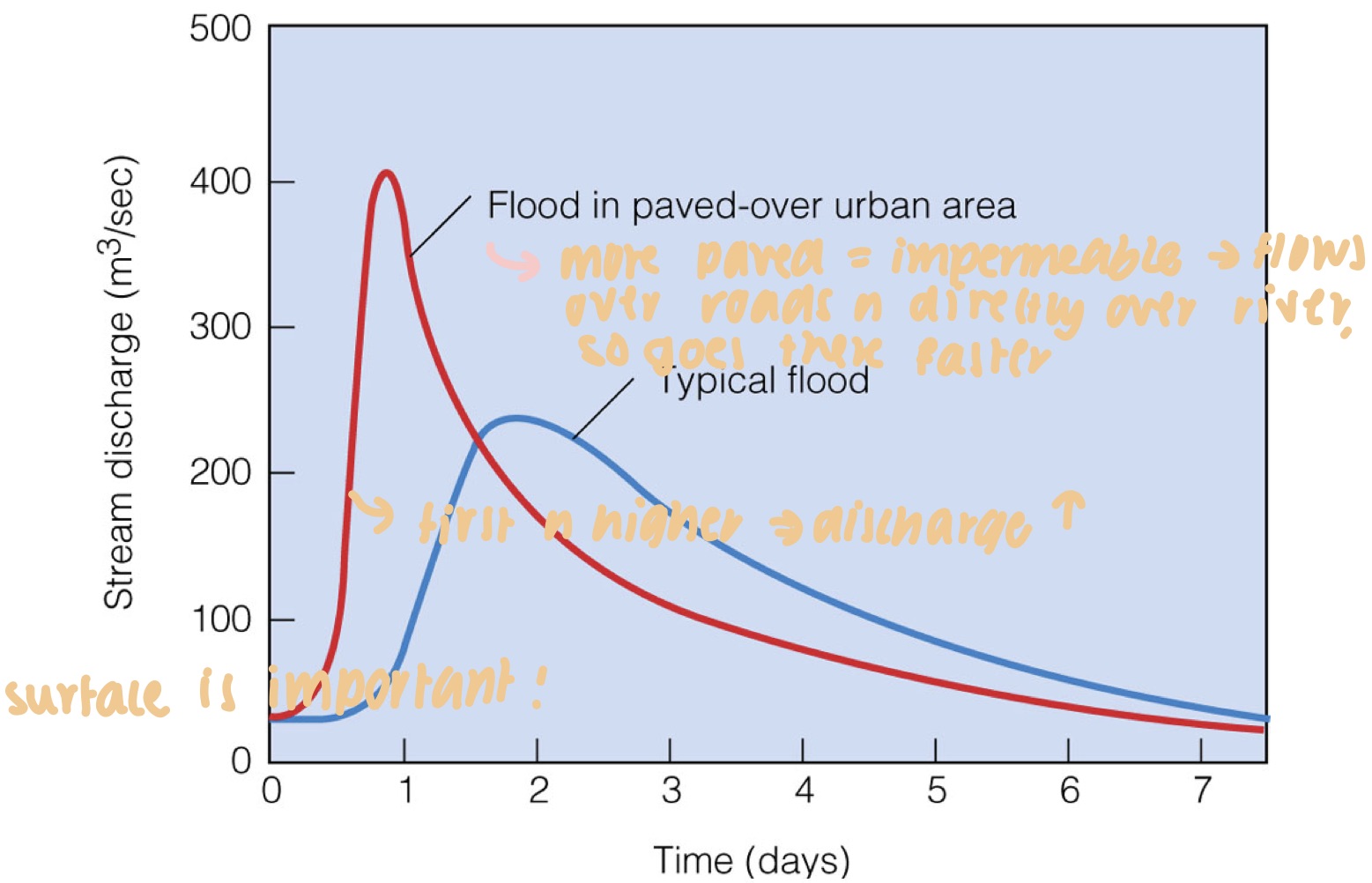
39
New cards
what is a slow-onset flood?
* a flood that devs over a long period (days to weeks) and takes weeks to months to subside (seasonal or regional floods)
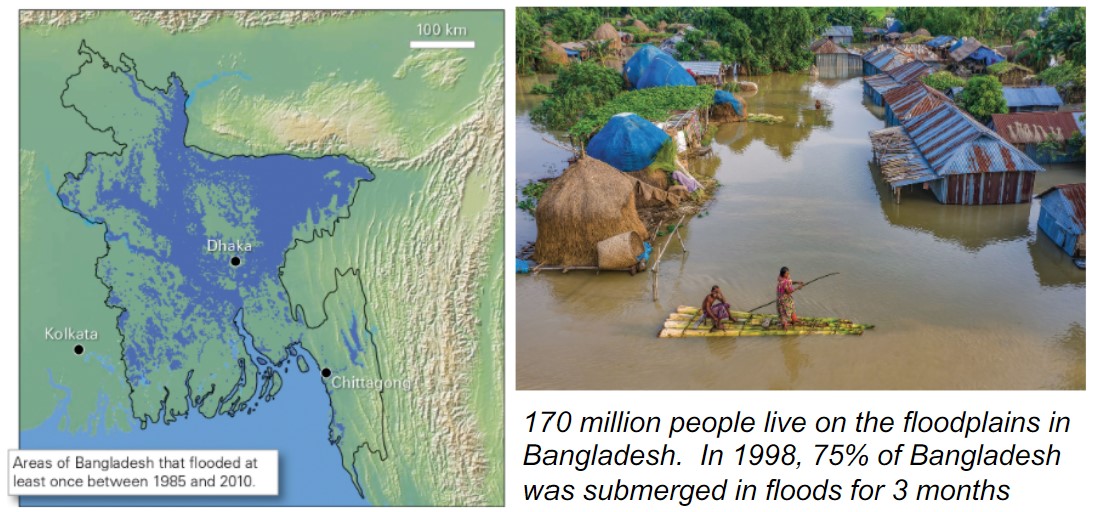
40
New cards
1931 Great China Floods
* flooding of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers
* Flooding persisted for months, affecting crops and causing famine and disease
* Estimated up to 3.7 million people died and 50 million people displaced
* Flooding persisted for months, affecting crops and causing famine and disease
* Estimated up to 3.7 million people died and 50 million people displaced
41
New cards
Flooding in BC, November 2021
* Atmospheric river brought heavy rains to southern BC
* Caused mass wasting and severe flooding
* Disrupted major transportations routes
* 600,000 animals perished
* 5 deaths from a mudslide
* Caused mass wasting and severe flooding
* Disrupted major transportations routes
* 600,000 animals perished
* 5 deaths from a mudslide
42
New cards
what is a flash flood?
* a flood that devs within a short time frame (within 6 hrs) of intense rainfall, dam failure, or other cause
* most flash floods occur due to extreme rainfall where the ground cannot absorb the water
* e.g., 2015 flash flood in Joso, Japan
* most flash floods occur due to extreme rainfall where the ground cannot absorb the water
* e.g., 2015 flash flood in Joso, Japan
43
New cards
what are the dangers of flooding?
* floodwater residue contains garbage, sewage, and chemicals
* secondary disasters of cholera and dysentery are common
* submerged homes, businesses, fields
* transportation and communication networks fail
* deaths of animas, and people
* secondary disasters of cholera and dysentery are common
* submerged homes, businesses, fields
* transportation and communication networks fail
* deaths of animas, and people
44
New cards
what is recurrence interval?
* the avg time between floods of a crt discharge
45
New cards
what is annual exceedance probability?
* the likelihood that a flood of a given discharge or greater will happen in a given yr
* can occur at diff yrs
* can occur at diff yrs
46
New cards
small floods happen often; large events are rare
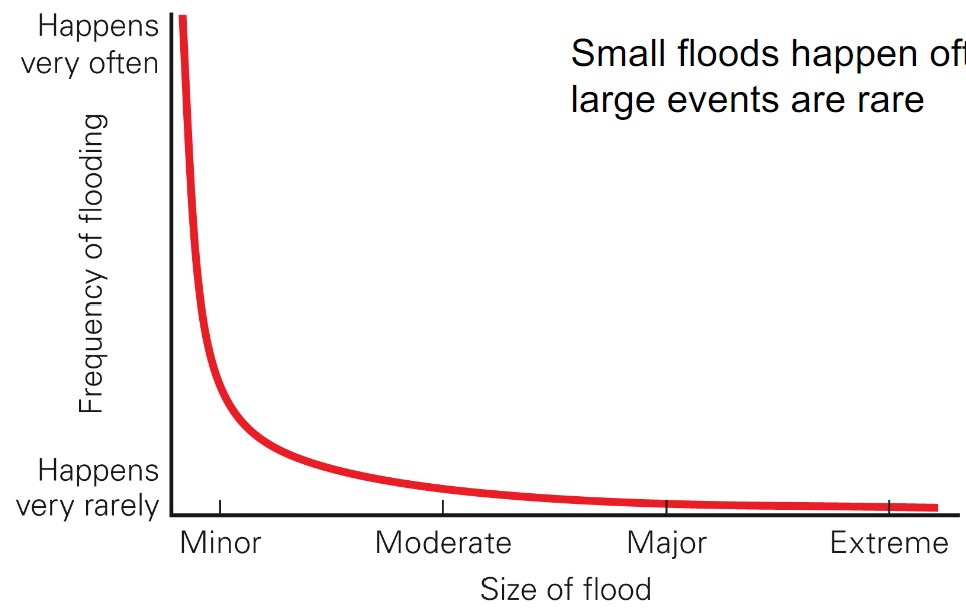
47
New cards
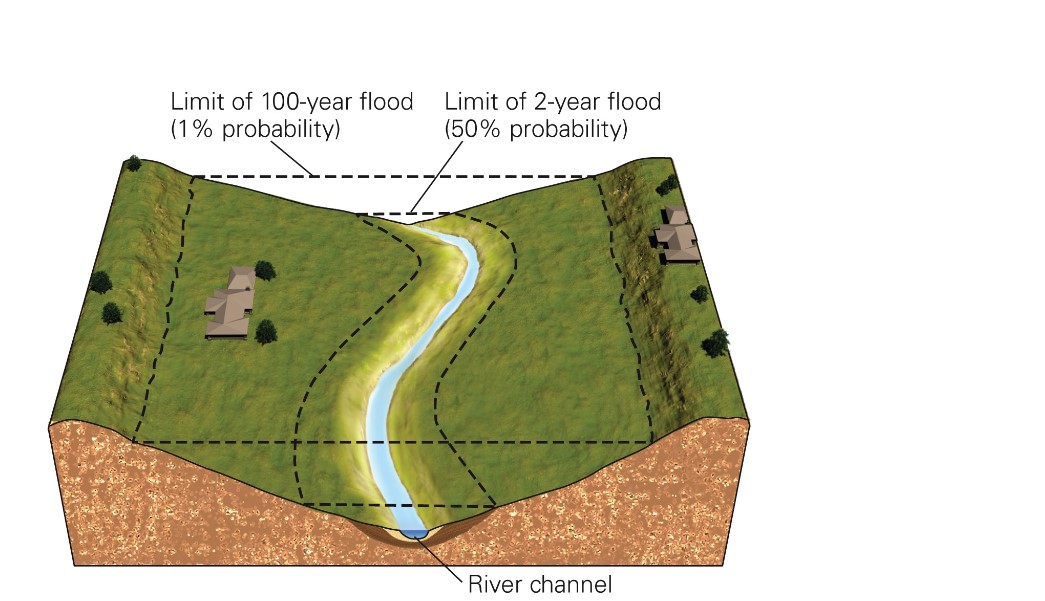
what is an100-yr flood?
* a flood with a reoccurrence interval of 100 yrs
48
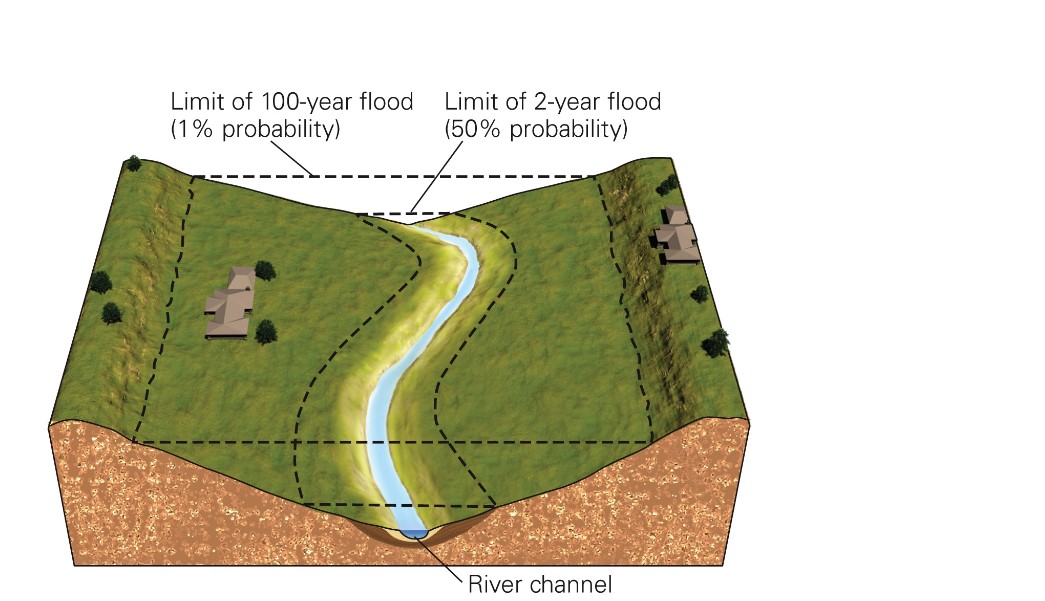
New cards
what is a 100-yr floodplain?
* the area likely to be flooded by a 100-yr flood
49
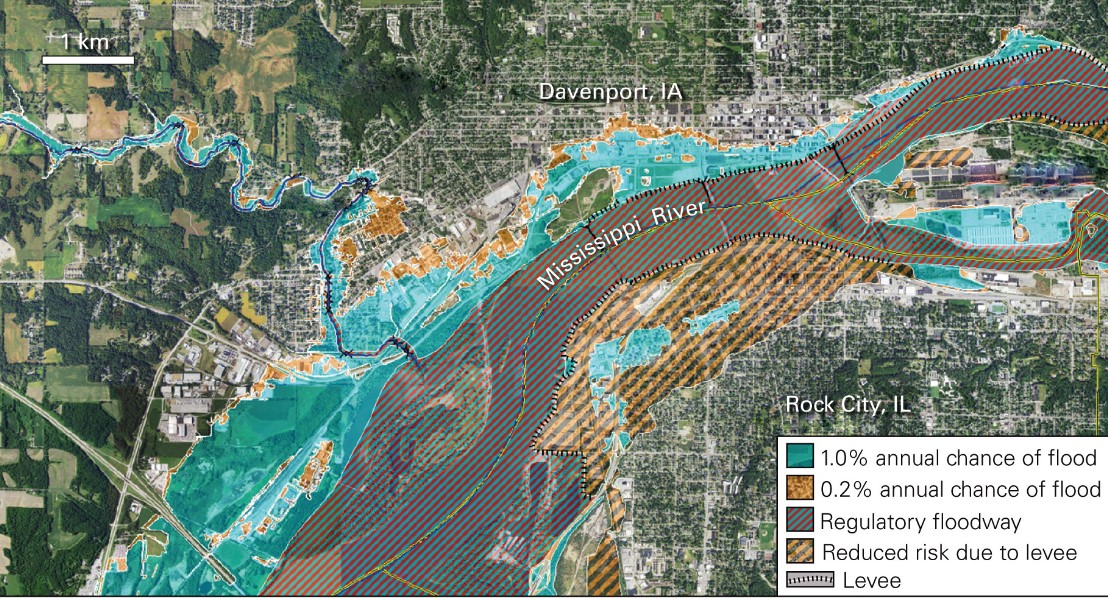
New cards
Flood-Hazard Map
\
50
New cards
what features are used to determine flood lvls?
* paleoflood