biology 113 exam 2
1/107
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
histone proteins, ribosome proteins, rna polymerase
evidence that a common lineage between archaeans and eukaryotes
methonagens
produce large amounts of methane
halophile
high salt
acidophile
low ph/high acidity
hyperthermophiles
hot temperatures
spirochetes
free living, internal flagella and spins
chlamydias
steal atp, have to be inside the cell
proteobacteria
oldest cells, samonella, ecoli
cyanobacteria
photosynthesis, most abundant
horizontal gene transfer
direct movement of genes from one organism to another
result of horizontal gene transfer
increase in genetic diversity, endosymbiosis
an example of endosymbiosis
when an entire cell is incorporated into another cell, how mitochondria came to be
thylakoids
folding used to create more usable membrane
magnetosomes
small magnetic crystals that work like a compass to find low oxygen enviornments
gas vesicles
used to control buoyancy
cocci
spheres
bacilli
rods
vibrios
comma shaped
spirochaetes
spiral-shaped flexible
spirilli
spiral shaped rigid
glycocaylx
slimy mucilage made of polysaccharides or protein
uses of glycocalyx
to hold colony together, to evade defenses of any host organisms
peptidoglycan
what bacterial cell walls are constructed of
gram positive cells
purple in color, vulnerable to penicillin, thick peptidoglycan layer
gram negative cells
pink color, resistant to penicillin, has a thin outer envelope
display taxis
movement towards or away from a stimulus
binary fission
produces two genetically identical cells
transformation
cell takes dna from enviornment
conjugation
cells directly swap dna
transduction
dna is injected into the cell
akinetes
found in filamentous cyanobacteria and are produced to survive in the winter
endospores
dormant cells surrounded by a thick protein coat that can survive for a long time
photoautotroph
use energyfrom sunlight to make own organic molecules
chemoautotroph
use energy from inorganic compounds to make organic molecules
photoheterotroph
use energy from sunlight to make atp but take in organic molecules from their environment
chemoorganotroph
must obtain organic molecules for energy and carbon
obligate aerobes
require oxygen
obligate anaerobes
cannot tolerate oxygen
facultative anaerobes
can use oxygen or not
aerotolerant anaerobes
do not use oxygen but can tolerate it
diazotrophs
bacteria capable of fixing nitrogen
symbiotic
living in close proximity with one or more organisms
pathogen
parasitic bacteria that cause disease in the host
protist
eukaryotic organism that does not qualify as an animal, plant or fungi
plankton
protists that swim or float
periphyton
protists that are attached by mucilage to aquatic surfaces
flagellates
move using flagella
ciliates
move using cilia
amoebae
move using pseudopods
supergroup excavata
named from the excavated feeding groove on the side
eugelnozoans
contain a strong flagella and protein strips under their membrane for crawling
kinetoplastids
a cluster of dna found at the base of their flagella
metamonads
parasitic, possess multiple nuclei and highly modified mitochondria
chlorophyta
ancestors of modern land plants, photosynthetic

rhodophyta
red photosynthetic pigments
plastids
photosynthetic organells believed to be the result of endosymbiosis
supergroup alveolata
saclike membranous vesicles
ciliphora
numerous cilia at some point in life cycle
apicomplexa
group of organelles used for invading host cells
dinozoa
possess whirling flagella
supergroup stramenopila
named for small hairs found on their flagella
diatoms
contain silicon-based glassy walls
brown algae
plant like structure, not direct ancestors of land plants
supergroup rhizaria
project thin-hairlike filose pseudopods for feeding
radiolarians
contain radial pseudopods
foraminiferans
contain a hard calcium carbonate shell

supergroup ameobozoa
move using large pseudopods
supergroup opisthokonta
single posterior flagellum found on swimming cells (sperm)
phagotrophic heterotrophs
ingest particles of food
osmotrophic heterotrophs
take in small organic molecules
mixotroph
organism that can be heterotrophic or autotrophic depending on their surroundings
accessory pigments
used to trap light and transfer it to chlorophyll
trichocysts
pointed projectiles
bioluminescence
startles predators
toxins
inhibits animal physiology
zygotic life cycle
species has two mating strains that use gamets to produce a thick walled zygote
sporic life cycle
haploid gametophyte produces gametes and diploid sporophyte produces spores by meiosis
gametic life cycle
all cells except gamets are diploid
cilliate life cycle
have two types of nuclei that swap via conjugation
parasitic life cycle
typicallly use more than one host, in which different life stages occur
nuclearia
the amoeba that fungi originated from
absorptive nutrition
how fungi digest their food, secreate enzymes to digest their food extracellularly and absorb organic molecules
chitin
what fungi cell walls are made up of
mycelium
network of fibers that connect fungi
hyphae
individual fiber that connects fungi
fruiting body
visible reproductive structure that arises from sexual reproduction and produces spores
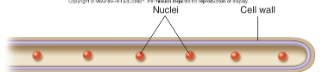
aseptate
cells that comprise of hyphae that are not separated by walls
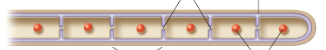
septate
walls that separate nuclei
pros of aseptate
nutrient transport is easier
cons of aseptate
damage affects the entire hyphae
structure and function of hyphae
high surface area allows for more absorbance
spores
microscopic reproductive ways that fungi reproduce
benefits of asexual reproduction in fungi
rapid spread, no mate, no meiosis, no fruitbody
conidia
clusters of asexual spores at the end of hyphae
dikaryotic
gamete cytoplasms fuse but not their nuclei
haploid fungi
majority of fungal life cycle
cryptomycota
single celled fungi found in water and soil
chytridiomycota
have a rigid chitin cell wall, most are decomposers, some are parasites
mucoromycota
aseptate mycelium with distinctive reproductive structure called zygospore
ascomycota
contain unique saclike sporangia on fruiting bodies called asci