Fluvio-glacial landforms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
how are fluvioglacial landforms created
meltwater can transport debris flowing under high pressure
meltwater slows and deposits in sorted manner from largest to smallest
which region of valley usually more dominated by f-g
down valley
how can subglacial streams flow upvalley
hydrostatic pressure
what will leave erosive marks
meltwater in contact with bedrock
nye channel
channels that cut downsides into bedrock
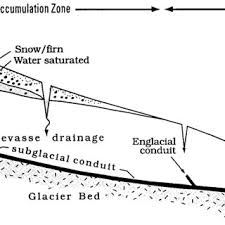
rothlisberger channel
cut upwards into ice itself
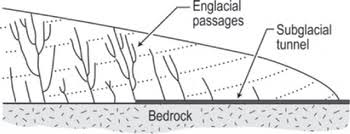
temporal changes to meltwater channels
last very little- only as long as temp high enough for liquid water
however eroded features can last longer
pro glacial lakes
ice melt and creates lake that develops on ice edge
channels created when lake overflows and can define new valleys
diverts rivers formed after deglaciation
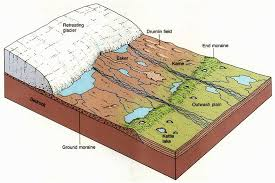
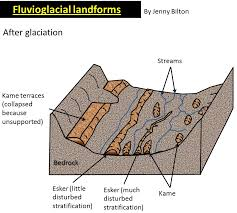
eskers characteristics and formation
long ridges of material running in direction of ice advance
coarse material stratified
made by SUBglacial streams
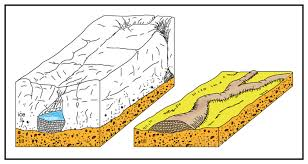
temporal changes to eskers
last medium amount of time
size= difficult to erode but easier than rock composed features
beaded esker
esker ridge combined with other mounds of materials
kames characteristics and formation
meltwater damned by recessional moraine deposits
mounds in fan shape
Kame collapse as ice retreats
temporal changes to kames
last a medium amount of time- eroded and weathered
kame terraces
along glacial valley side and deposits of meltwater streams slowing between ice and valley side
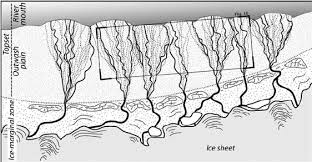
outwash plains c+F
found at front of glacial snout
finer material travels further
deposits layered vertically
temporal changes to outwash plains
last very little time- only sediment so easily eroded/ washed away
even less dominance in alpine regions where only seasonal
braided streams
meltwater streams that cross outwash plains
kettle holes
small depression filled with lakes formed where blocks of ice washed onto plain melt and leave gap in sediments
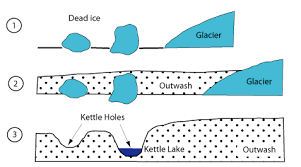
what do kettle holes lead to
peat formation
varves
layering shows year of deposition
seasonal variations in discharge
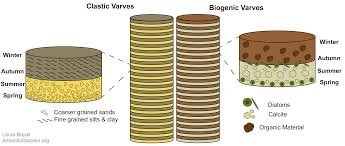
what will show summer discharge in varves and why
coarser material as more meltwater so more energy
what will show winter discharge in varves and why
less meltwater and less energy
how can varves indicate climate change
thickness variations
thicker= more water so higher temps
darker= more organic material so higher temps
7 fluvioglacial features
proglacial lakes
eskers
kames
outwash plains
braided streams
kettle holes
varves
where can these be found in the world x5
finland
alaska
lake district
iceland
japan
where can eskers- be found
finland
where can kames be found
lake district
where can outwash plains and braided streams be found
alaska
where can kettle holes be found
alaska
where can varves be found
japan
typical f-g landscape and why
s iceland
large outwash plain from ice cap
braided streams
sparse vegetation/ population
black sediment from volcanic rock