AP Biology Unit 6
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
operator
region of DNA within the promoter that controls RNA polymerase's access to a set of genes with related functions
operon
a unit of gene regulation and transcription in bacterial DNA that consists of a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes
repressor
a protein that binds to an operator and physically blocks RNA polymerase from binding to a promoter site. is specific to the operator it binds.
regulatory gene
a gene that produces a repressor substance that inhibits an operator
repressible operon
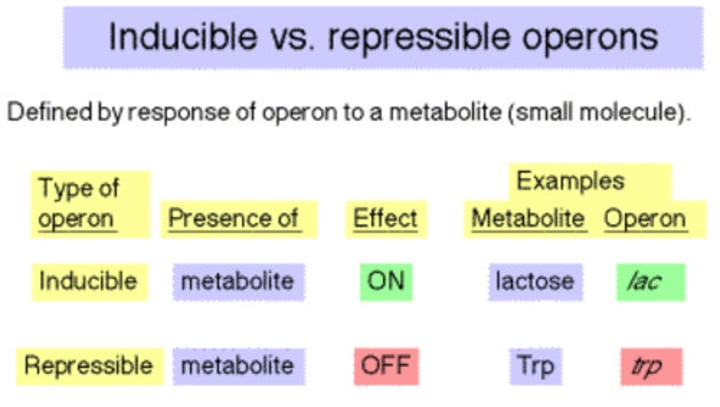
transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited (repressed) when a specific small molecule binds allosterically to a regulatory protein (example tryptophan)
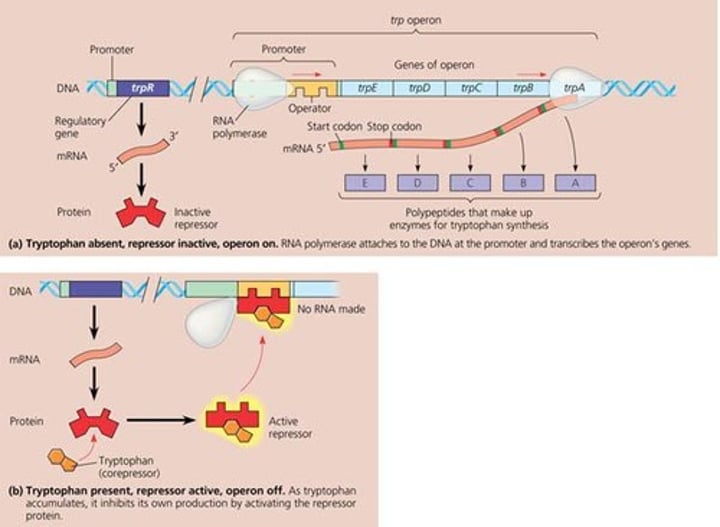
inducible operon
usually off, but can be stimulated (induced) when a specific small molecule interacts with a regulatory protein (example lac operon)
inducer
A specific small molecule that inactivates the repressor in an operon.
activator
A protein that binds to DNA and stimulates transcription of a specific gene.
differential gene expression
The expression of different sets of genes by cells with the same genome.
DNA methylation
addition of methyl group to DNA (usually to Cytosine), associated with decreased transcription (permanent deactivation)
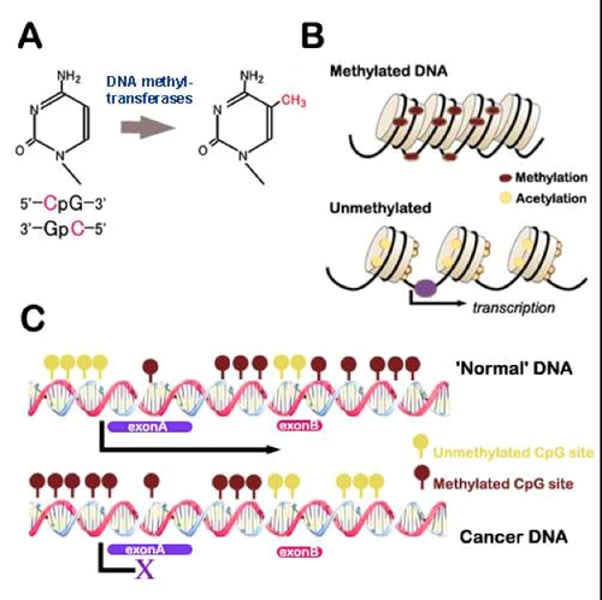
transcription factors
Increase the level of transcription in certain cell types or in response to signals
microRNAs
small single stranded RNA molecules that bind to mRNA and can degrade mRNA or block its translation - miRNAs
epigenetics
the study of changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression rather than alteration of the genetic code itself
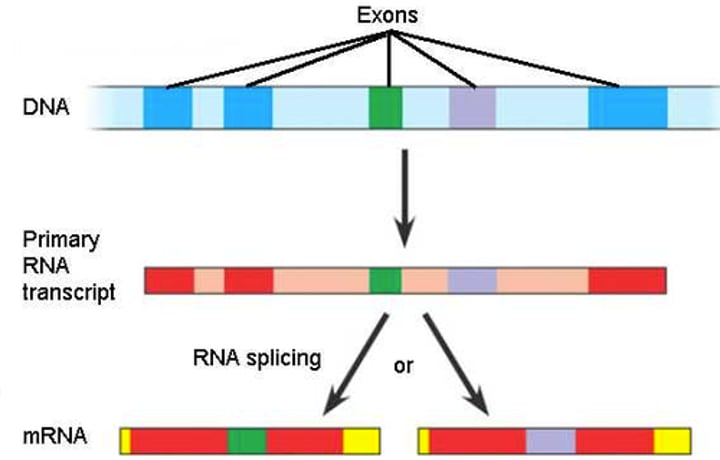
Alternative RNA Splicing
a type of eukaryotic gene regulation at the RNA-processing level in which different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns
Anticodon
a nucleotide triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that base-pairs with a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule
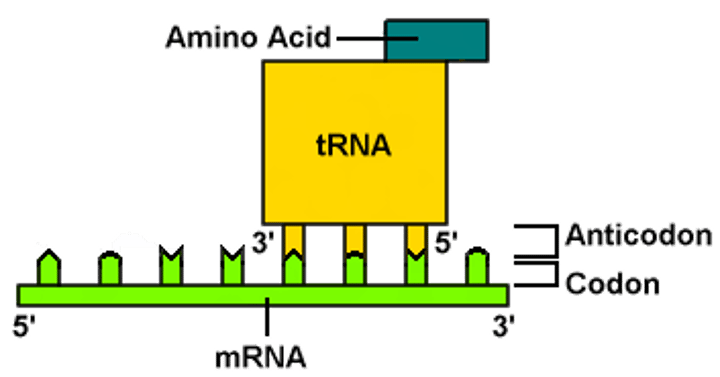
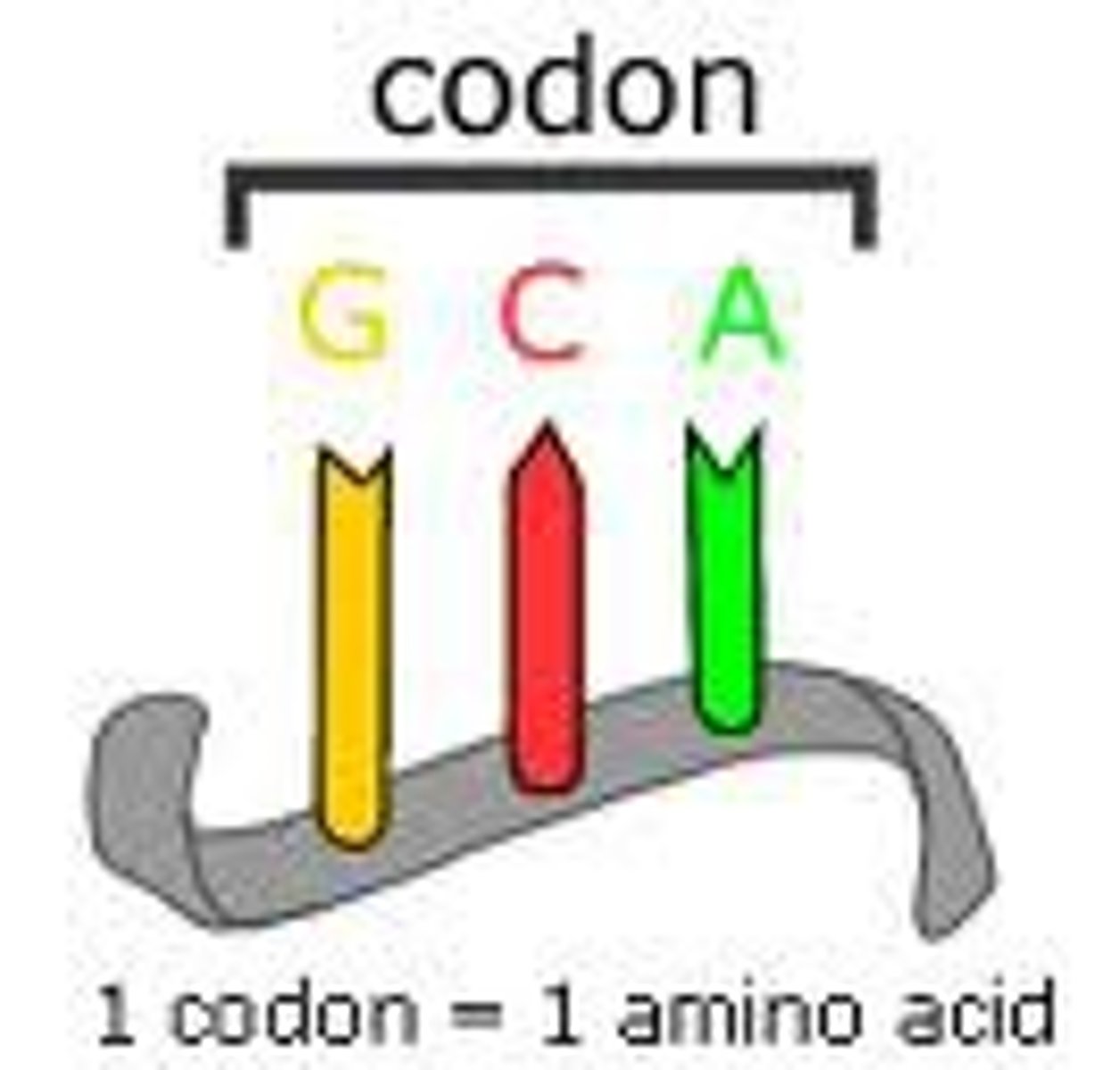
Codon
a three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code
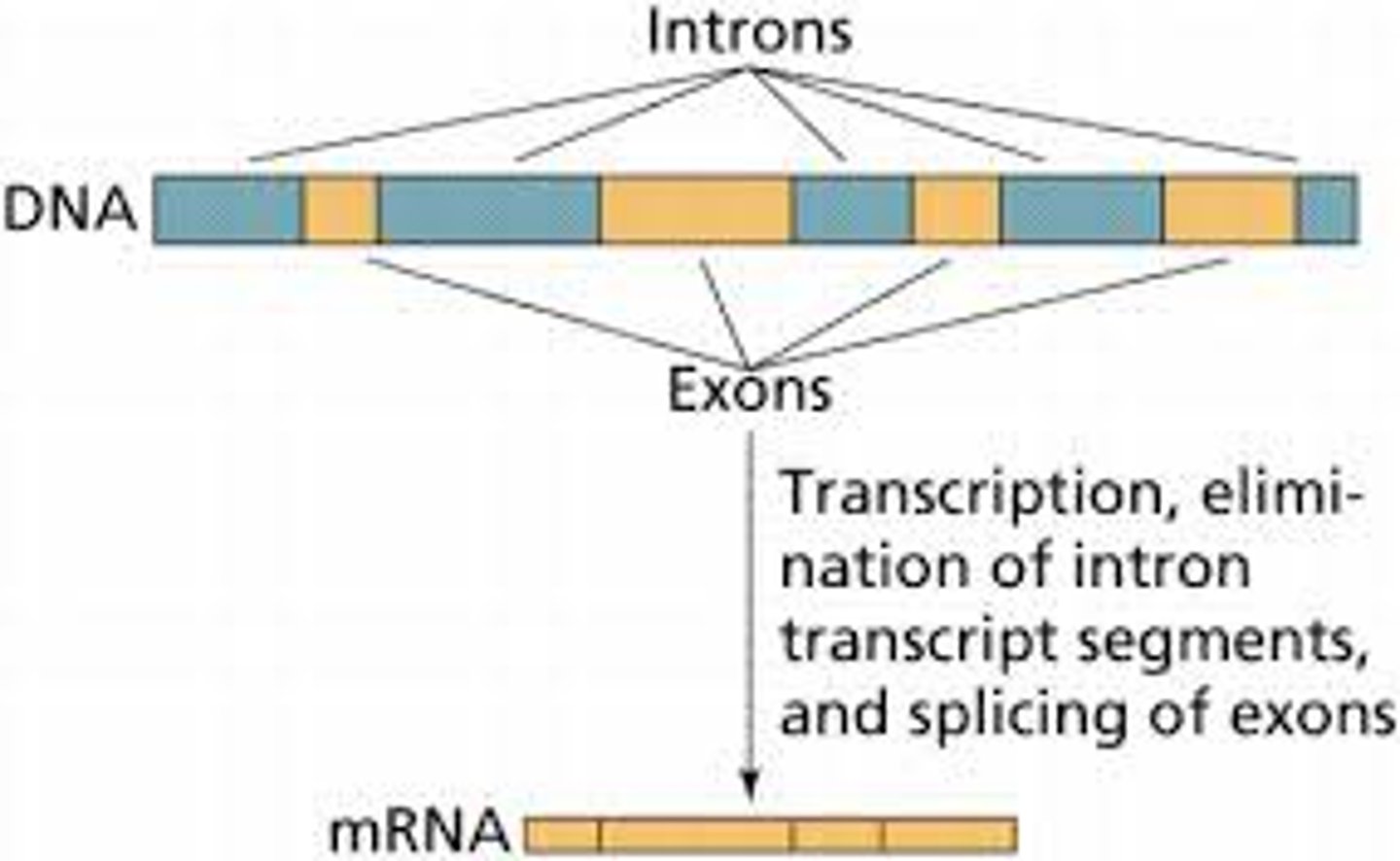
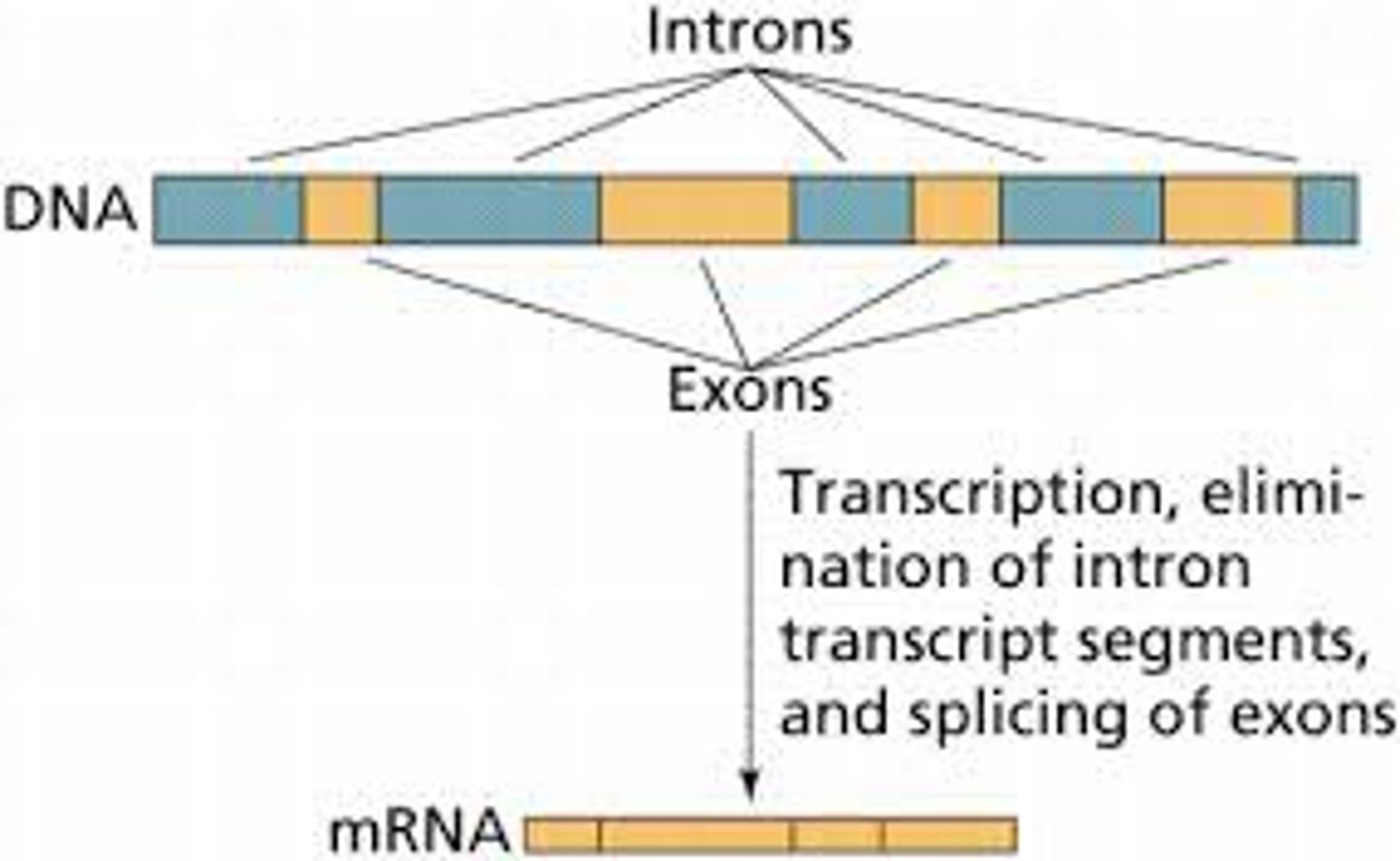
Exon
a sequence within a primary transcript that remains in the RNA after RNA processing; also refers to the region of DNA from which this sequence was transcribed
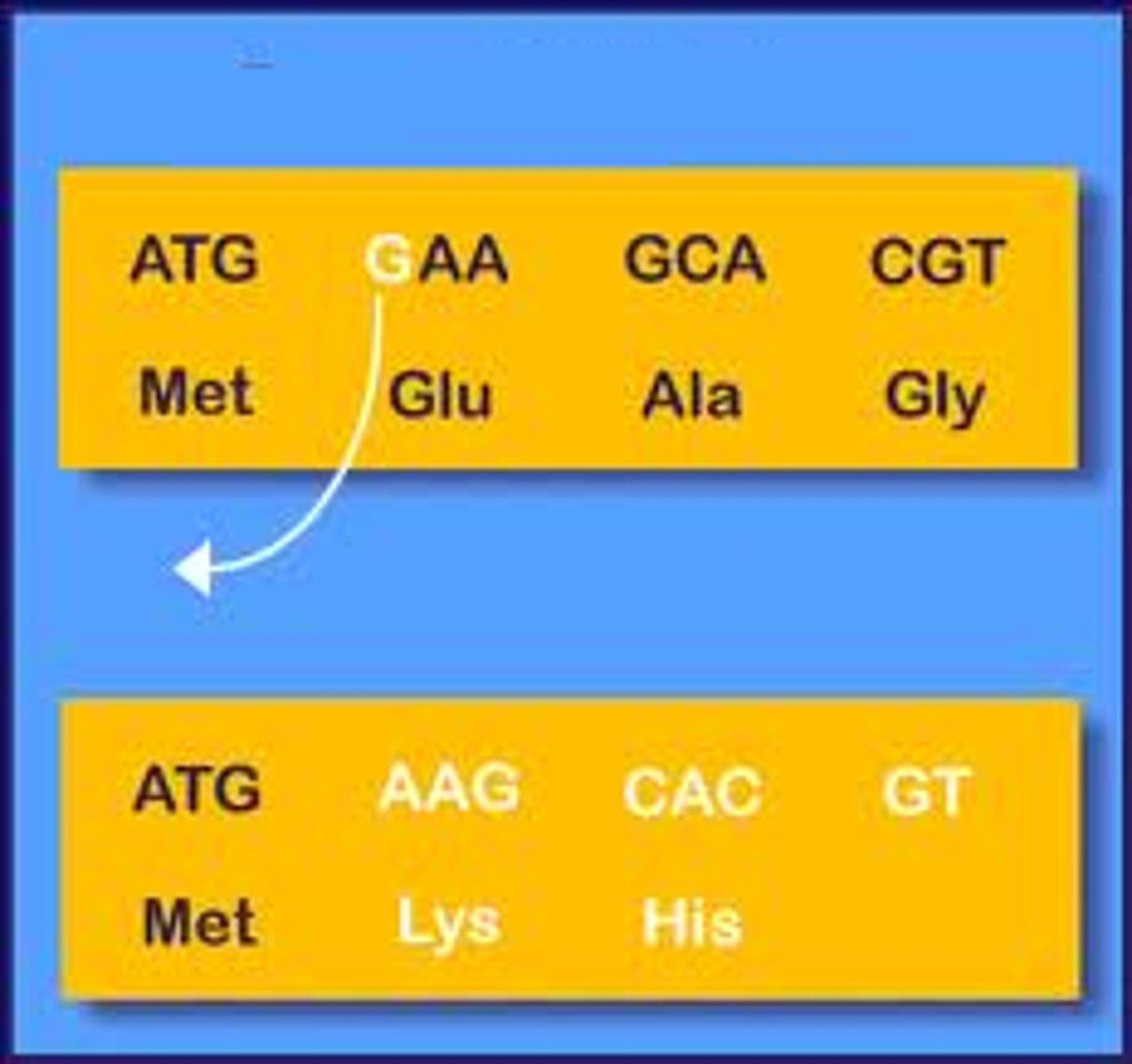
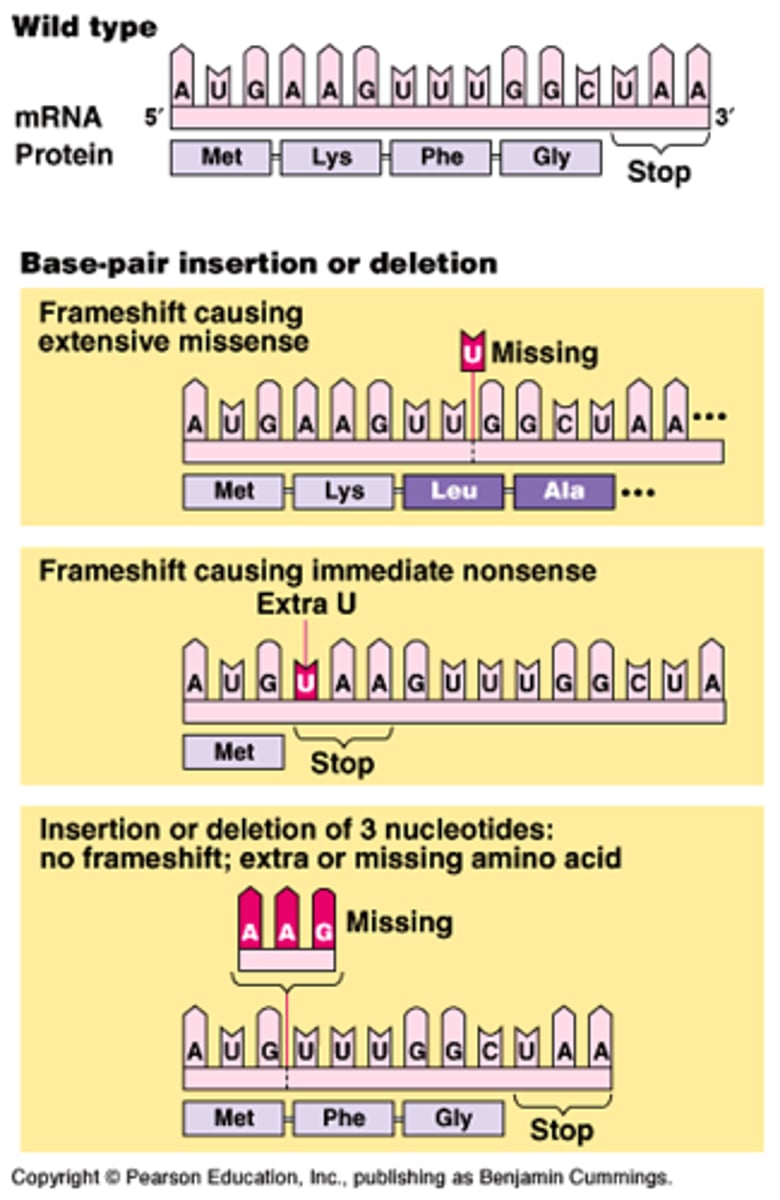
Frameshift Mutation
A mutation occurring when nucleotides are inserted in or deleted from a gene and the number inserted or deleted is not a multiple of three, resulting in the improper grouping of the subsequent nucleotides into codons
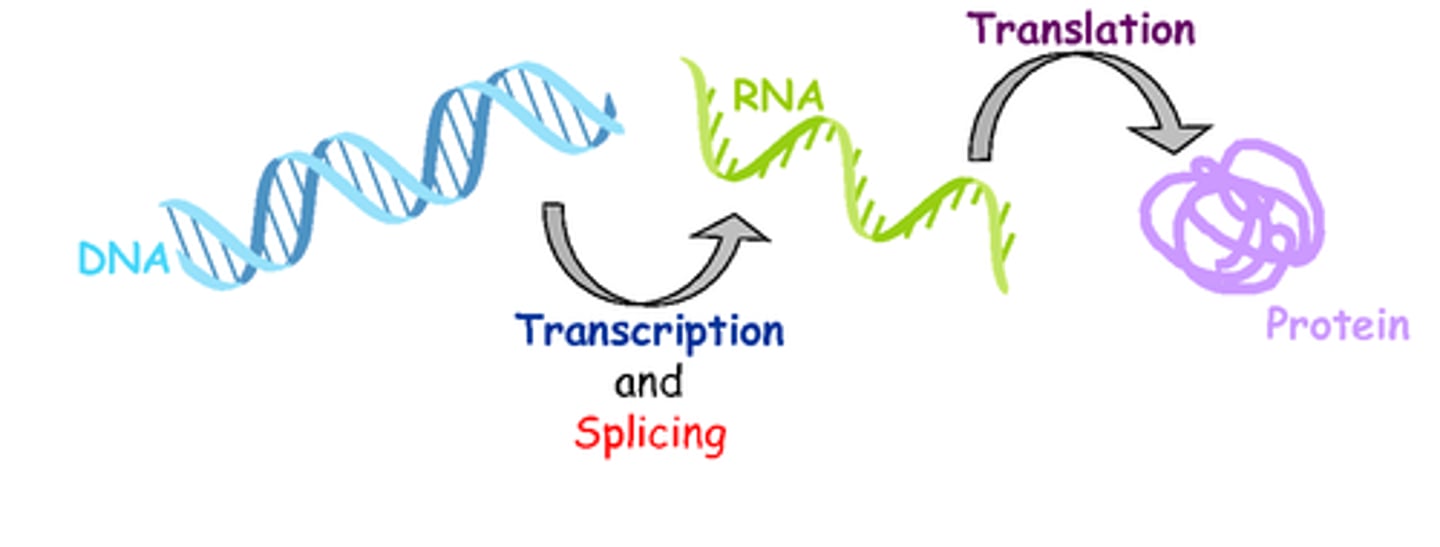
Gene Expression
the process by which information encoded in DNA directs the synthesis of proteins or, in some cases, RNAs that are not translated into proteins and instead function as RNAs
Insertion
a mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene
Intron
a noncoding, intervening sequence within a primary transcript that is removed from the transcript during RNA processing; also refers to the region of DNA from which this sequence was transcribed
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
a type of RNA, synthesized using a DNA template, that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein. (In eukaryotes, the primary RNA transcript must undergo RNA processing to become mRNA.)
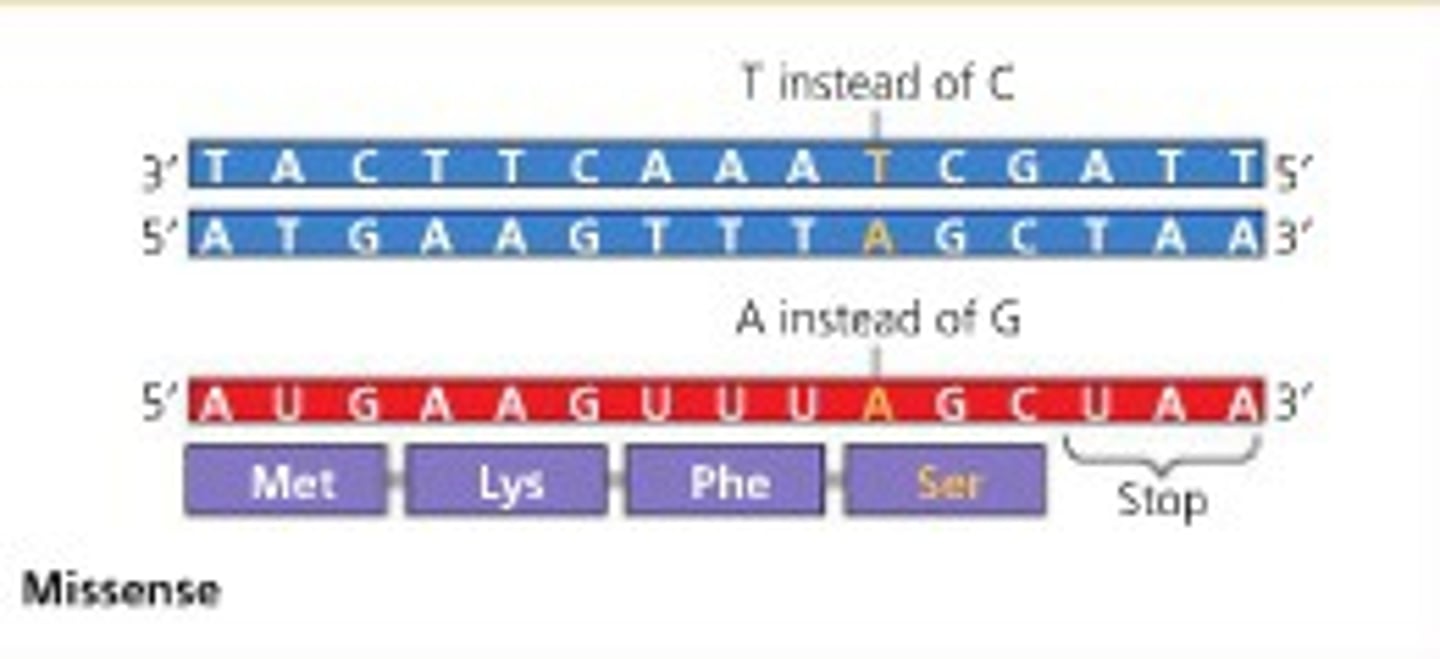
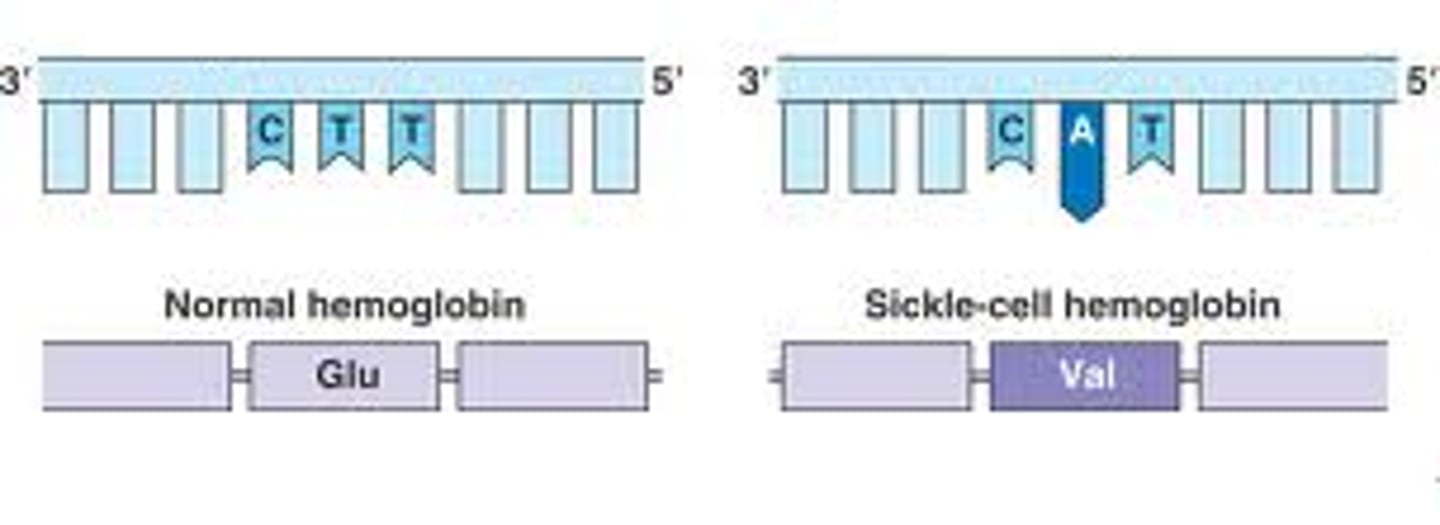
Missense Mutation
a nucleotide-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid
Mutagen
a chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and can cause a mutation (Ex: UV light, tanning bed)
Mutation
a change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA or in the DNA or RNA of a virus
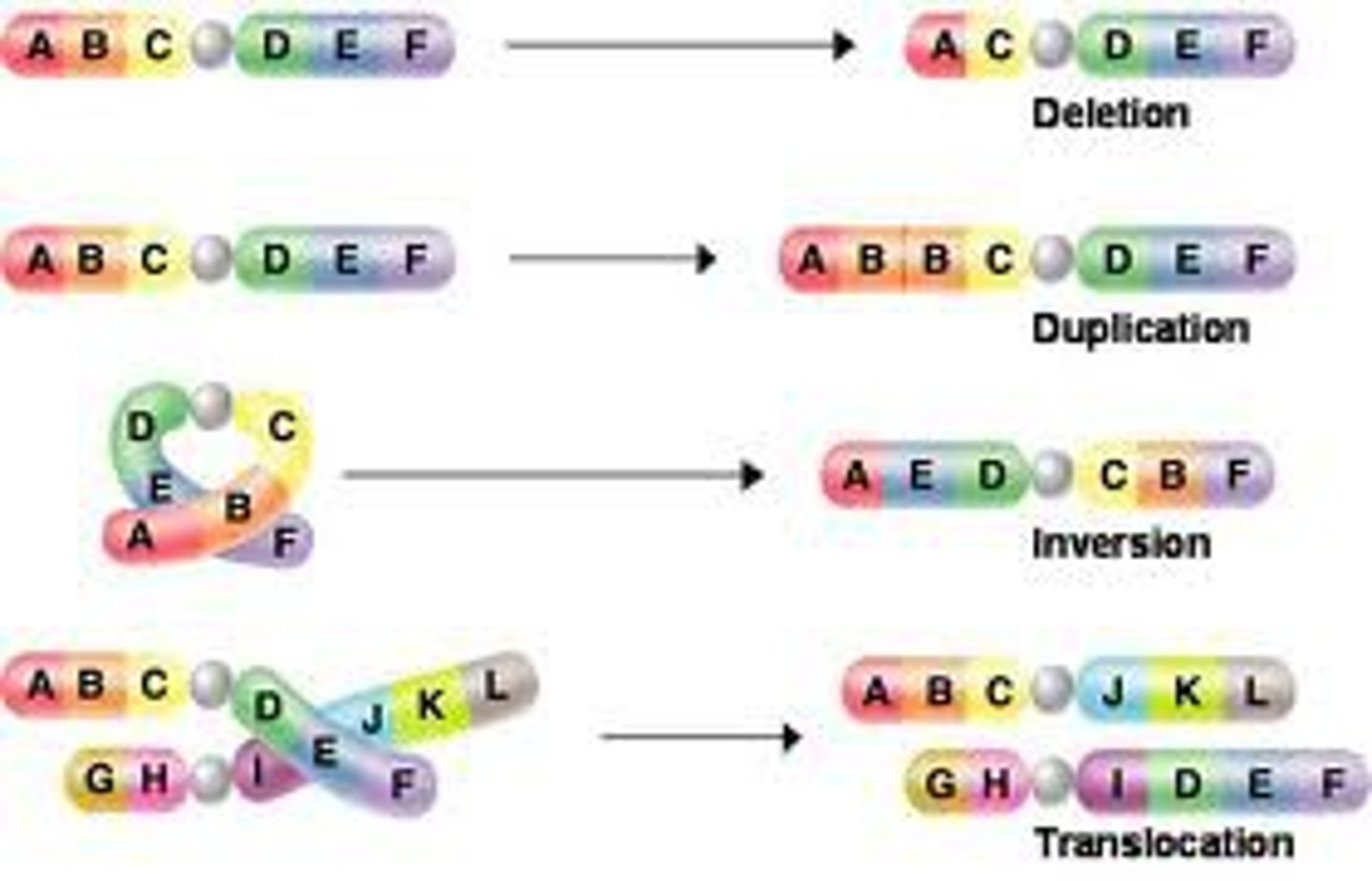
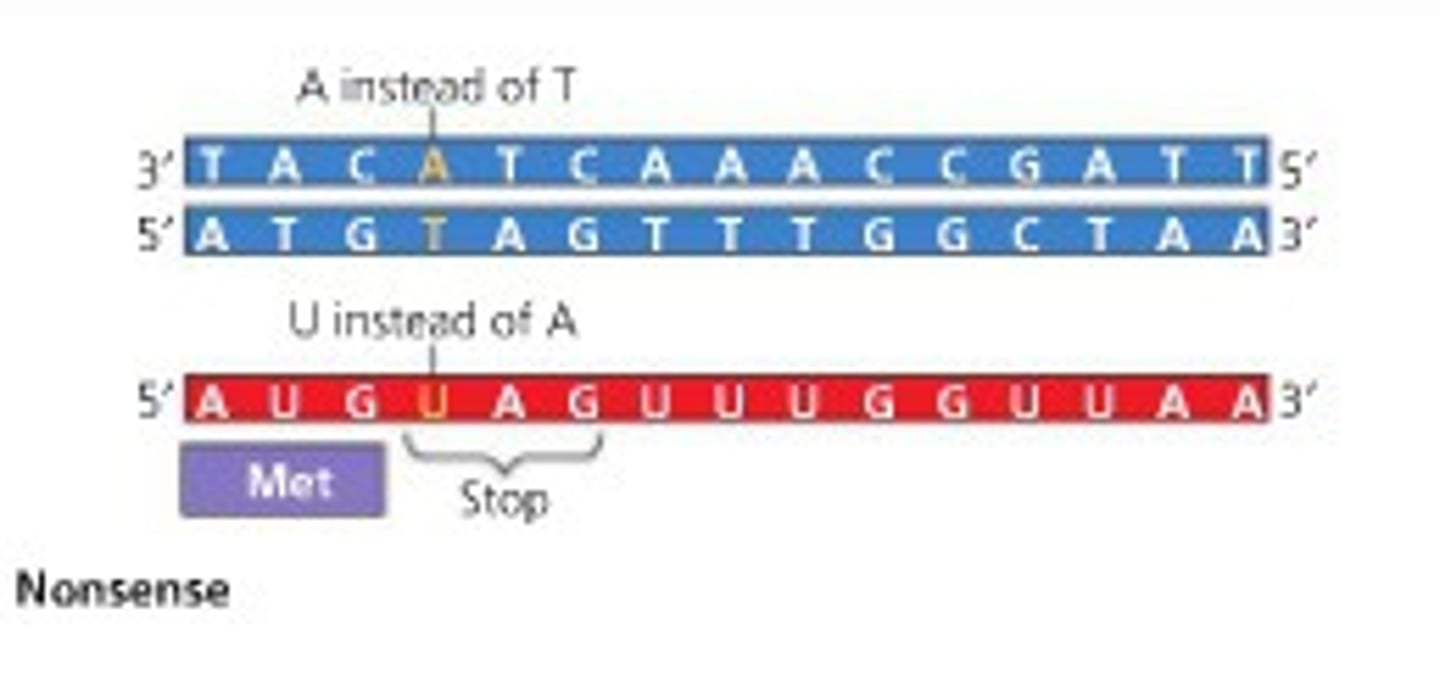
Nonsense Mutation
a mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of the three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein
Substitution
a type of point mutation in which one nucleotide in a DNA strand and its partner in the complementary strand are replaced by another pair of nucleotides
Point Mutation
a change in a single nucleotide pair of a gene
Poly-A Tail
a sequence of 50-250 adenine nucleotides added onto the 3′ end of a pre-mRNA molecule
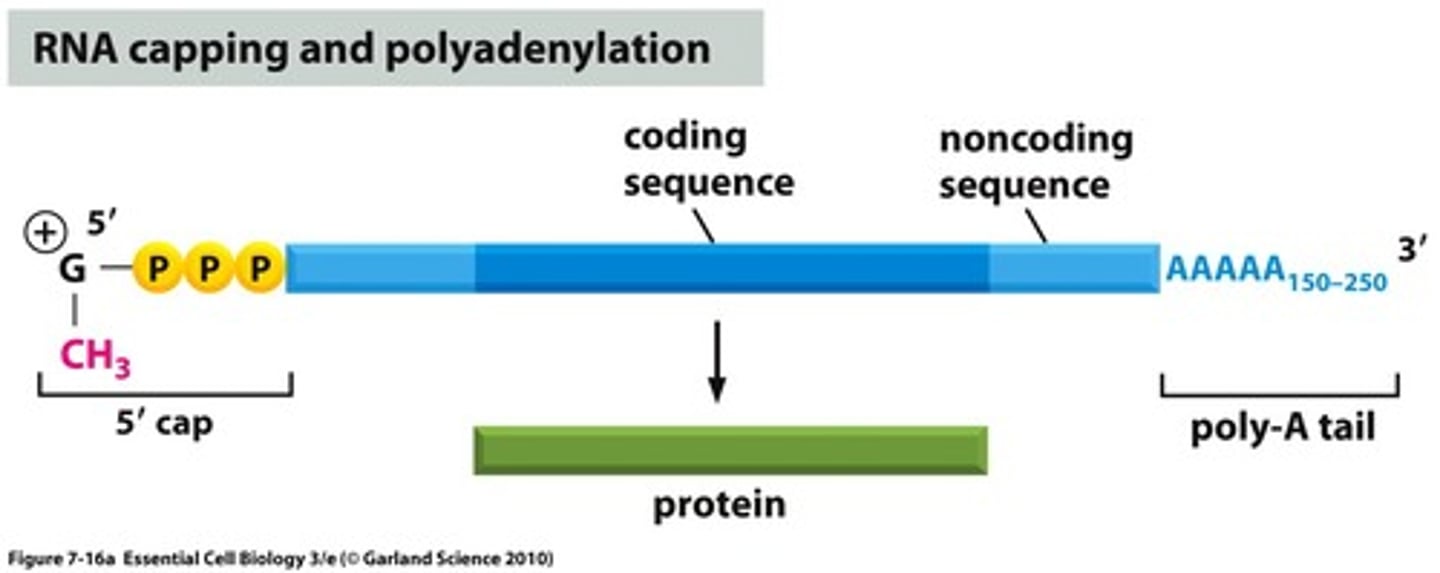
Primary Transcript
an initial RNA transcript from any gene; also called pre-mRNA when transcribed from a protein-coding gene. This is what you get right after the slicing occurs.
Reading Frame
on an mRNA, the triplet grouping of ribonucleotides used by the translation machinery during polypeptide synthesis
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA molecules that, together with proteins, make up ribosomes; the most abundant type of RNA
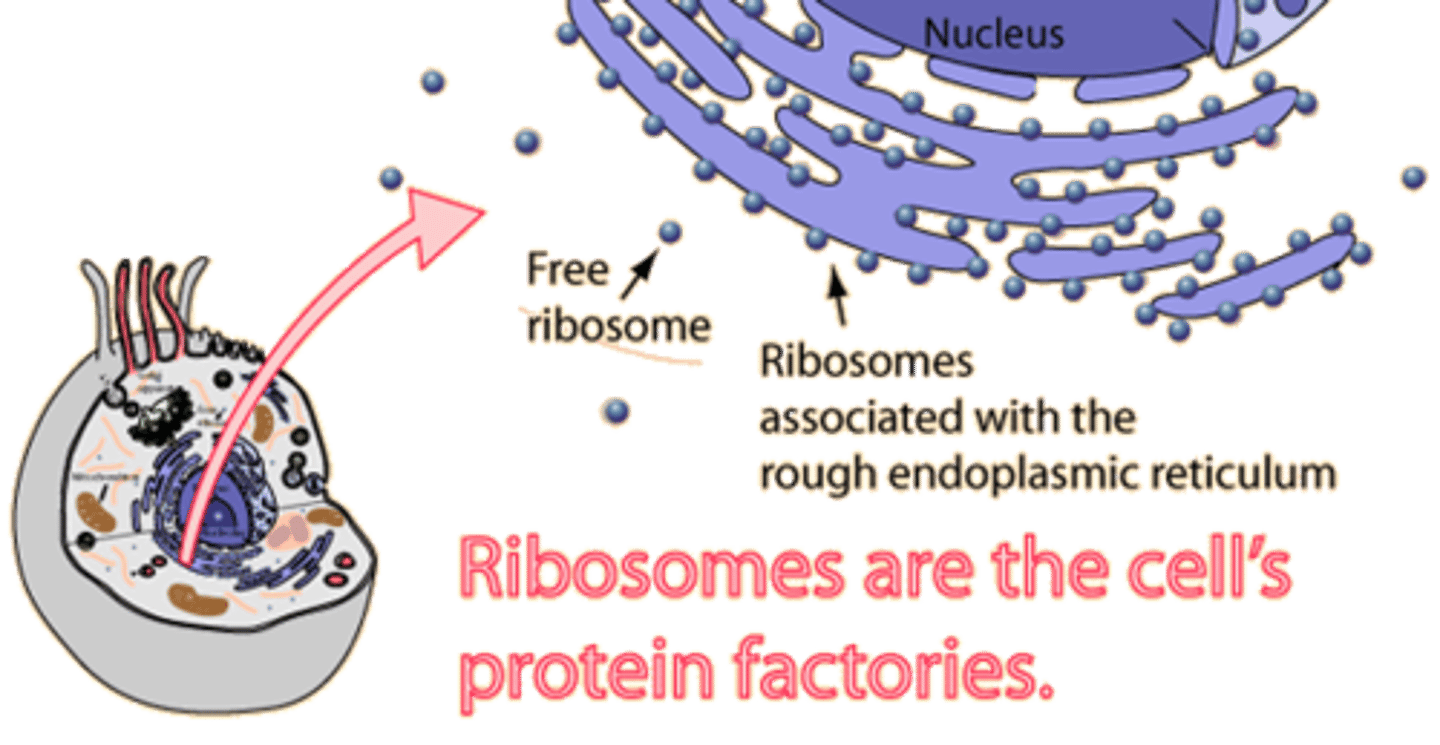
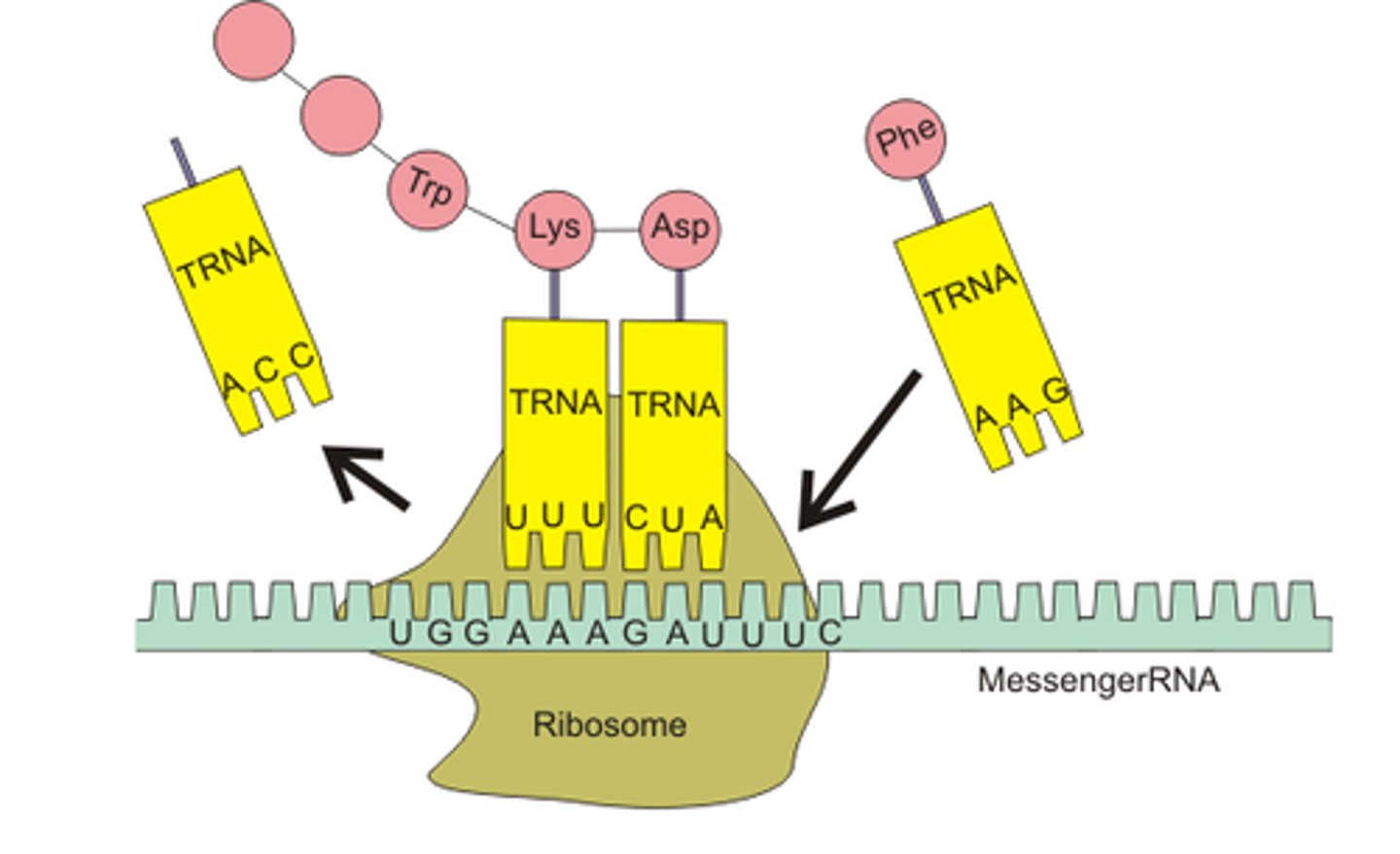
Ribosome
a complex of rRNA and protein molecules that functions as a site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm; consists of a large and a small subunit. In eukaryotic cells, each subunit is assembled in the nucleolus; see also nucleolus
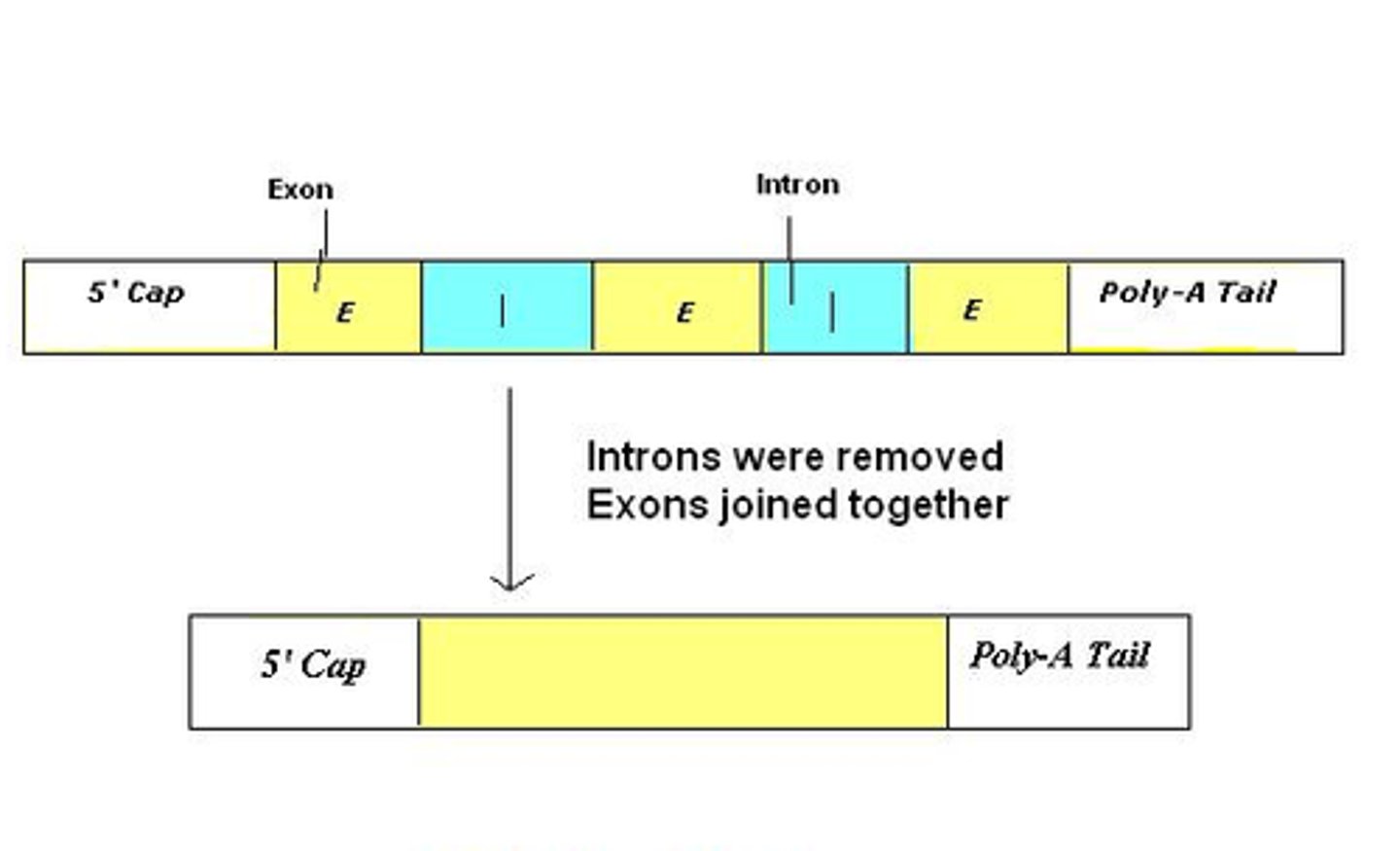
RNA Processing
modification of RNA primary transcripts, including splicing out of introns, joining together of exons, and alteration of the 5′ and 3′ ends
RNA Splicing
after synthesis of a eukaryotic primary RNA transcript, the removal of portions of the transcript (introns) that will not be included in the mRNA and the joining together of the remaining portions (exons)
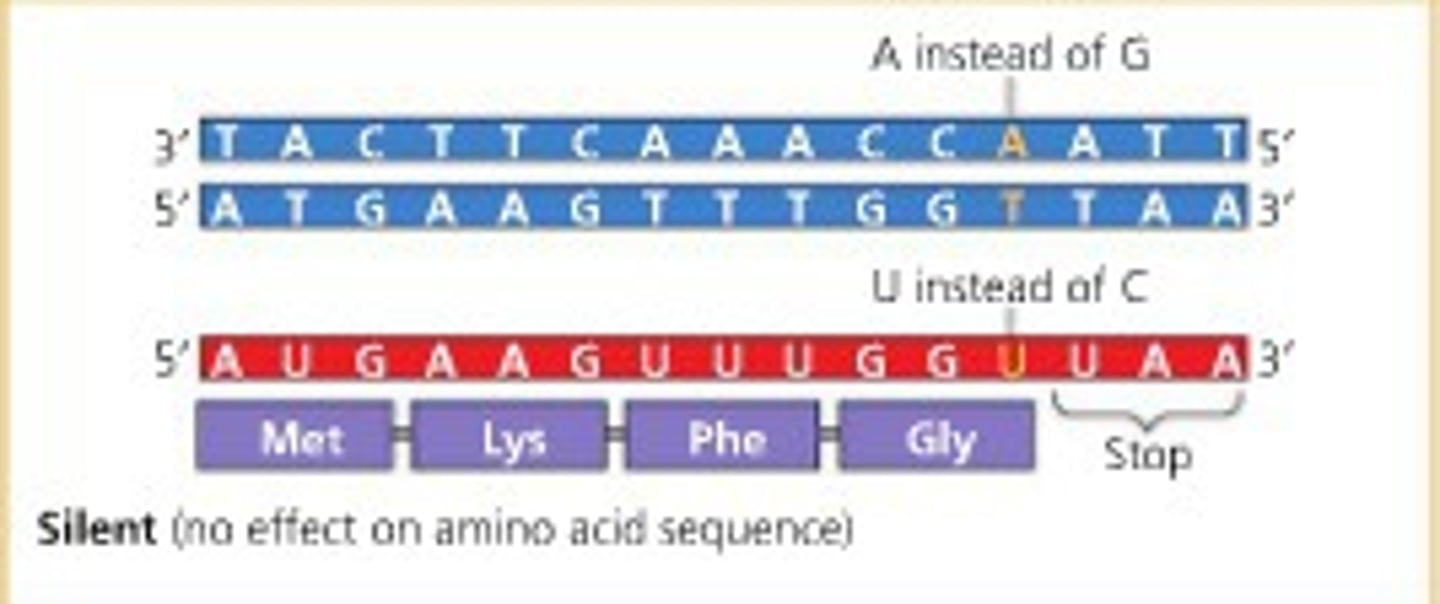
Silent Mutation
a nucleotide-pair substitution that has no observable effect on the phenotype; for example, within a gene, a mutation that results in a codon that codes for the same amino acid
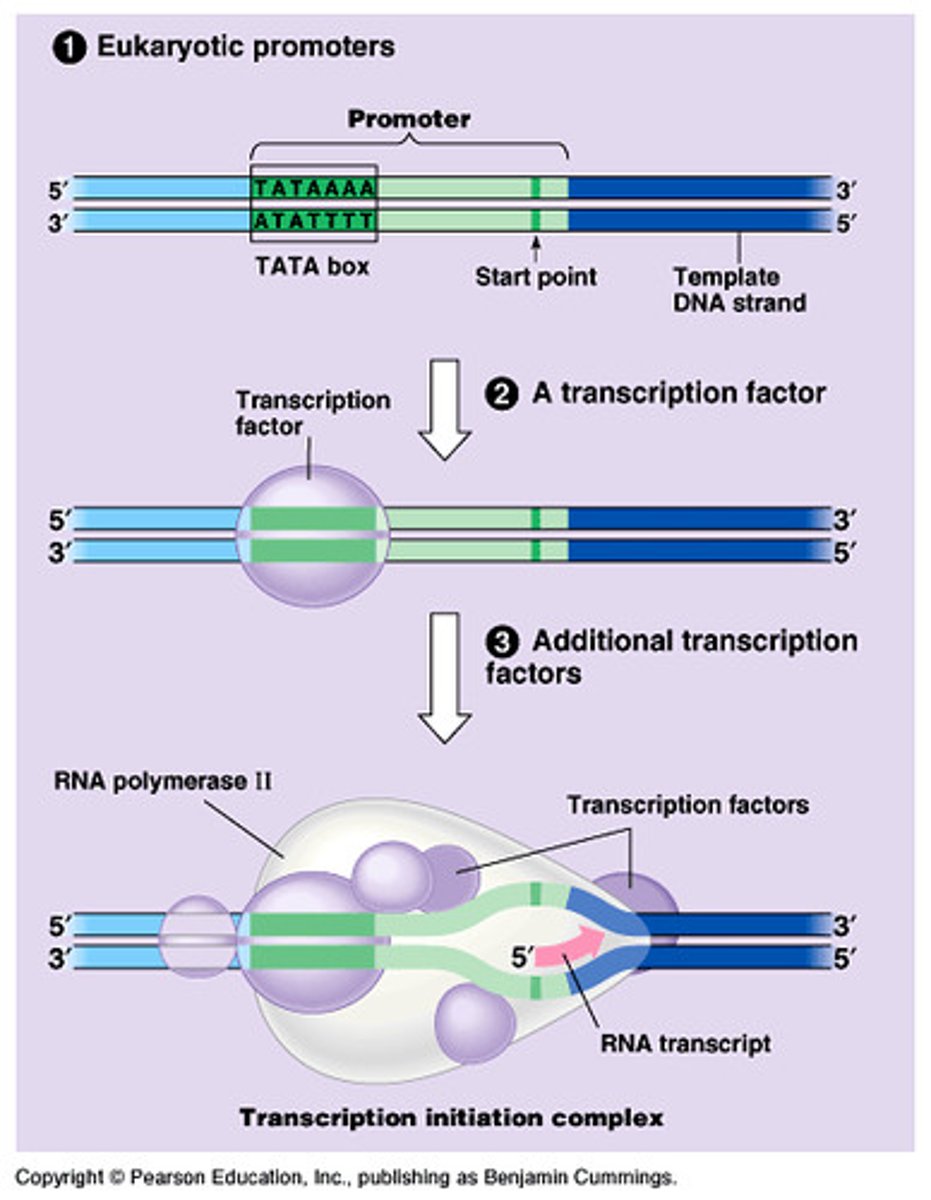
TATA Box
a DNA sequence in eukaryotic promoters crucial in forming the transcription initiation complex
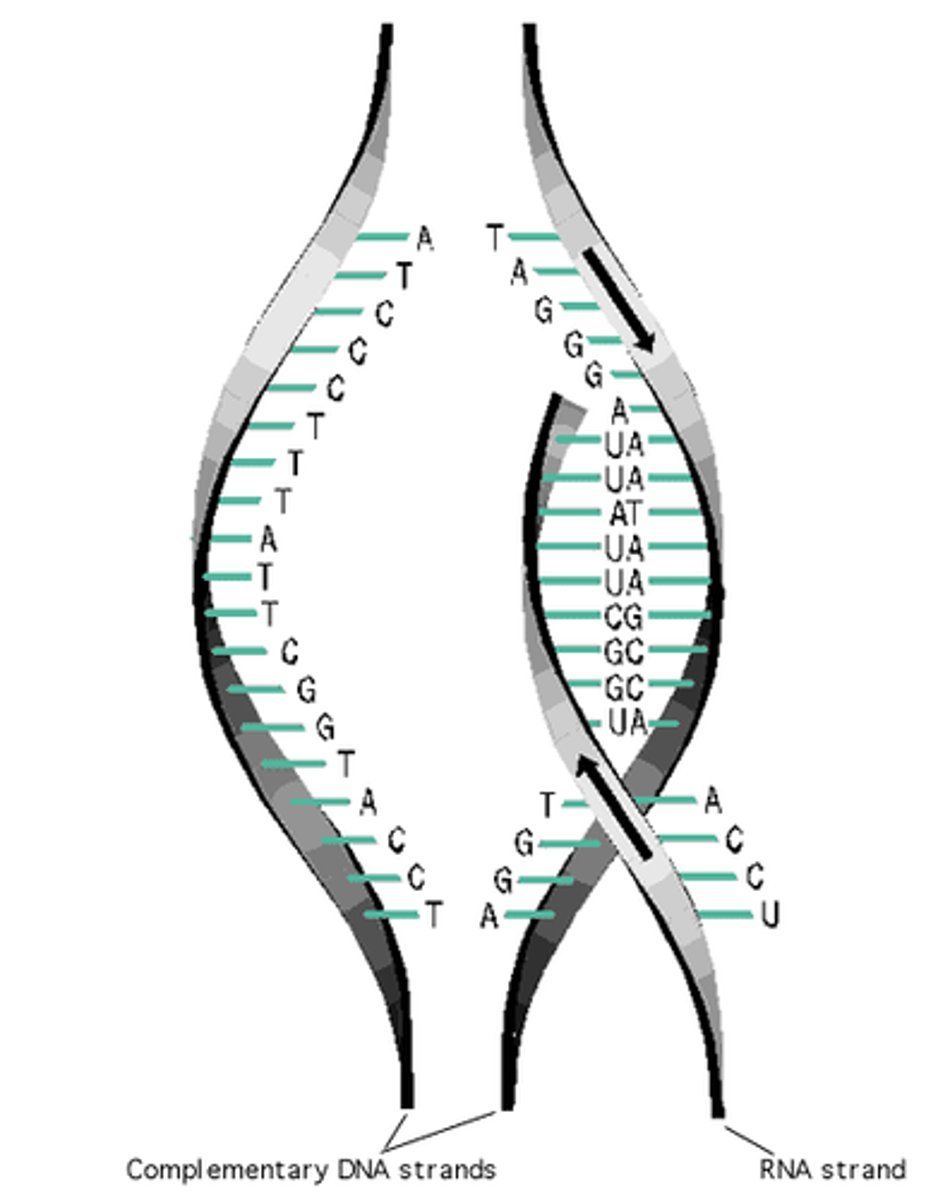
Template Strand
the DNA strand that provides the pattern, or template, for ordering, by complementary base pairing, the sequence of nucleotides in an RNA transcript
Transcription
the synthesis of RNA using a DNA template
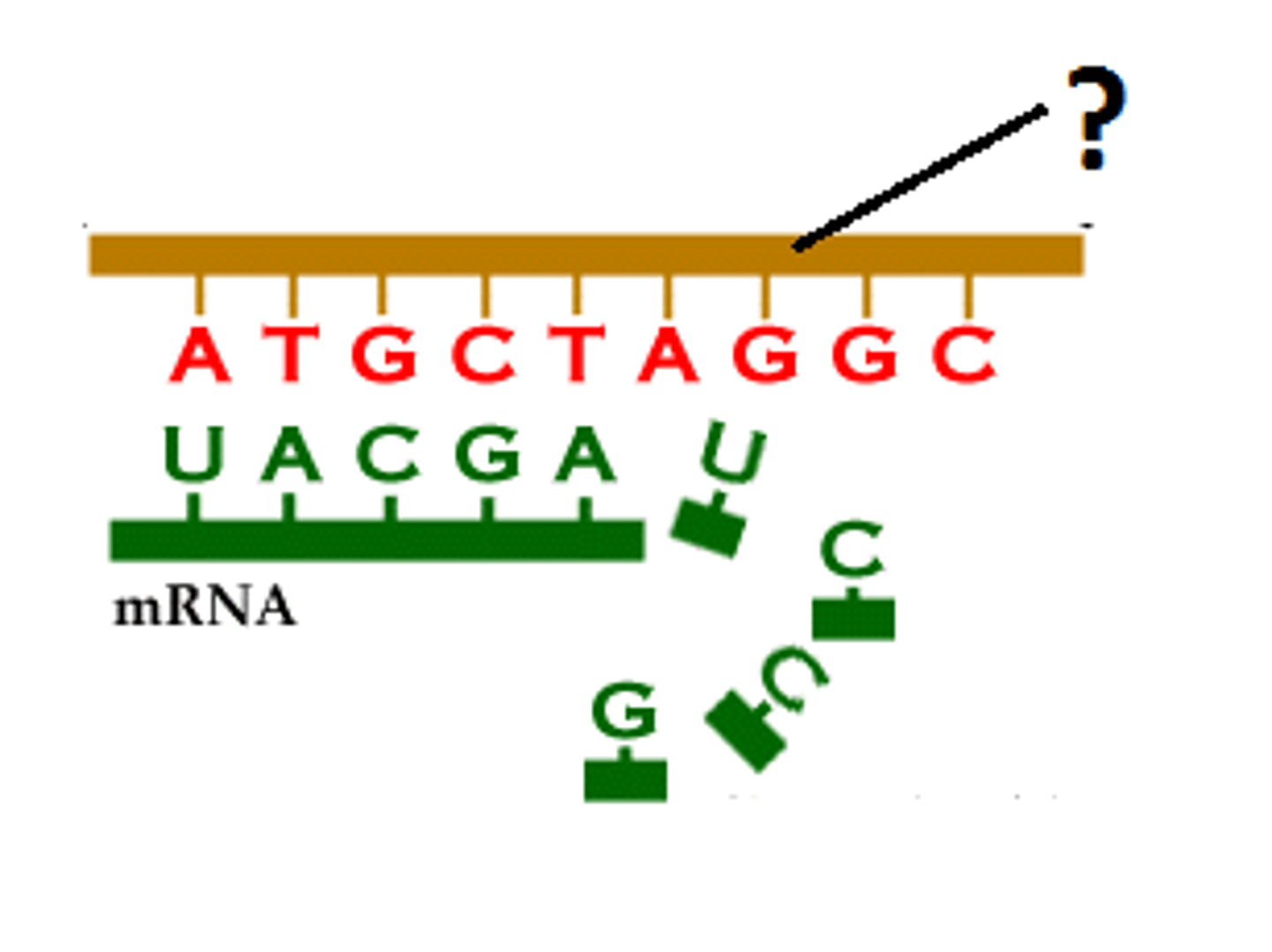
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
an RNA molecule that functions as a translator between nucleic acid and protein languages by carrying specific amino acids to the ribosome, where they recognize the appropriate codons in the mRNA
Translation
The synthesis of a polypeptide using the genetic information encoded in an mRNA molecule; there is a change of "language" from nucleotides to amino acids
Silent mutations
does not change the amino acid sequence of the gene product
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment; DNA glue
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork.
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix at the replication forks, separating the two parental strands and making them available as template strands.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
PCR
(polymerase chain reaction) a method used to rapidly make multiple copies of a specific segment of DNA; can be used to make millions of copies of DNA from a very small amount of DNA
gel electrophoresis
Procedure used to separate and analyze DNA fragments by placing a mixture of DNA fragments at one end of a porous gel and applying an electrical voltage to the gel
DNA sequencing
the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule
bacterial transformation
ability of bacteria to alter their genetic makeup by uptaking foreign DNA from another bacterial cell and incorporating it into their own
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome