Circuit Devices
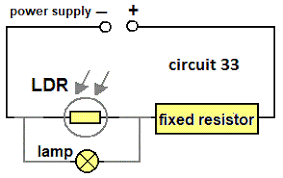
LDR is short for Light Dependence Resistor
- An LDR is a resistor that is dependent on the intensity of light.
- In bright light, the resistance falls
- In darkness, the resistance is highest
- They have lots of applications including automatic night lights, outdoor lighting and burglar detectors
The resistance of a Thermistor depends on Temperature
- A thermistor is a temperature dependent resistor
- In hot conditions, the resistance drops
- In cool conditions, the resistance goes up
- Thermistors make useful temperature detectors, temperature sensors and electronic thermostats
You can use LDRs and Thermistors in Sensing Circuits
- Sensing circuits can be used to turn on or increase the power to components depending on the condition that they are in
- The circuit on the right is a sensing circuit used to control a fan in a room
- The fixed resistor and the fan will always have the same potential difference across them
- The pd of the power supply is shared out between the thermistor and the loop made up of the fixed resistor and the fan according to their resistances-the bigger a component’s resistance, the more of the pd it takes
- As the room gets hotter, the resistance of the thermistor decreases and it takes a smaller share of the pd from the power supply. So the pd across the fixed resistor and the fan rises, making the fan go faster

You can also connect the components across the variable resistor instead.
For examples, if you connect a bulb in parallel to an LDR, the pd across both the LDR and the bulb will be high when it’s dark and the LDR’s resistance is high. The greater the pd across a component, the more energy it gets. So a bulb connected across an LDR would get brighter as the room got darker