DHS IB Biology Option C
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Transects
Method used to ensure that there is no bias in the student selection, it is used to correlate the distribution of a plant or animal species with an abiotic variable
Trophic levels
feeding position in a food chain
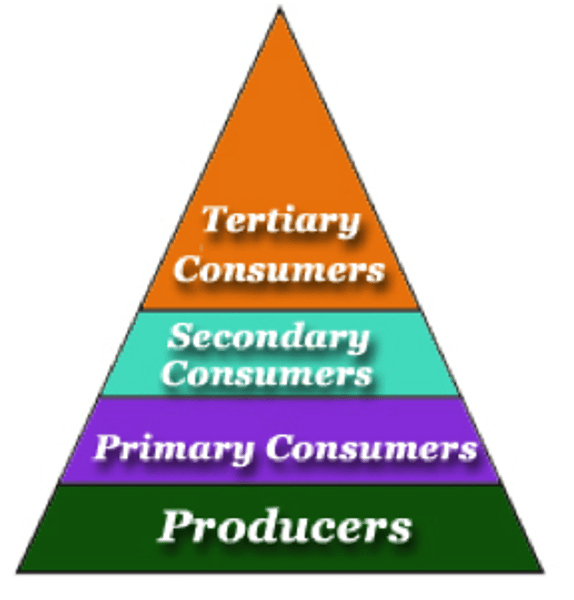
Food webs
all the possible food chains in a community
Food conversion ratios
the quantity of dietary input in grams required to produce a certain quantity of body mass in livestock of fish
Gersmehl nutrient cycle diagram
shows the inter-relationships between nutrient stores and flows between taiga, desert and tropical rainforest
Gross production
total amount of organic matter produced per unit area per unit time by a trophic level in an ecosystem
Closed ecosystem
energy but not matter is exchanged with the surroundings
Alien species
species that are not native to an area and are introduced by humans
Invasive species
have significant effects on the ecosystem where they are released
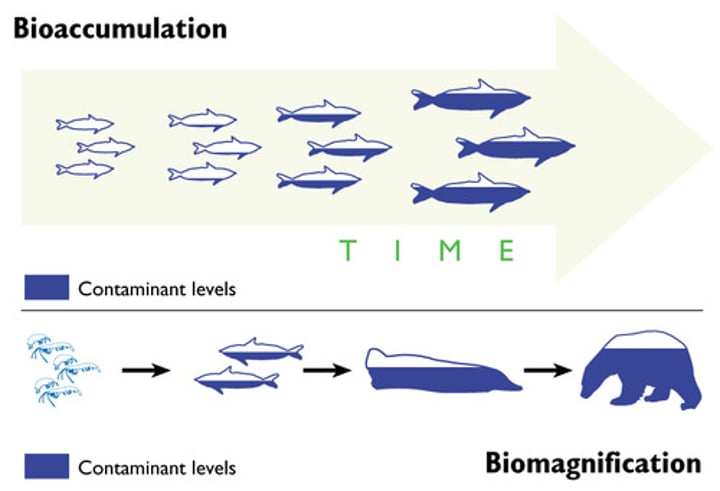
Biomagnification
pollutants become concentrated in the tissues of organisms at a higher trophic level (may be lethal concentration)
Macroplastic
large visible debris including nets, buoys, buckets etc.
Microplastic
physical and chemical degradation of macroplastics, harder to see but are more omnipresent

Components of biodiversity
richness and evenness of ecosystem
Simpson's diversity index
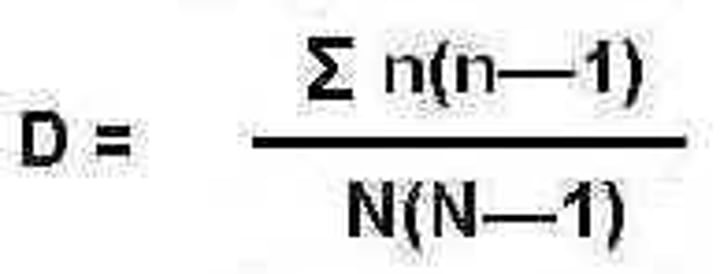
Niche
the unique role a species plays in a community that is linked both to its habitat and its interactions with other species.
Competitive Exclusive Principle
The concept that two species cannot survive indefinitely in the same habitat if their niches are identical.
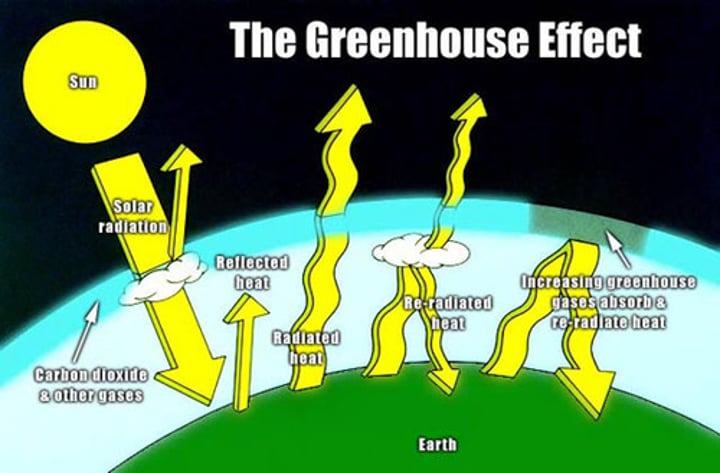
Greenhouse Effect
The warming of Earth due to atmospheric accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and water vapor which absorb reflected infrared radiation and re-radiate some of it back to Earth
Herbivory
the interaction between species where primary consumers feed on producers.

Symbiosis
interspecies interactions that includes mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
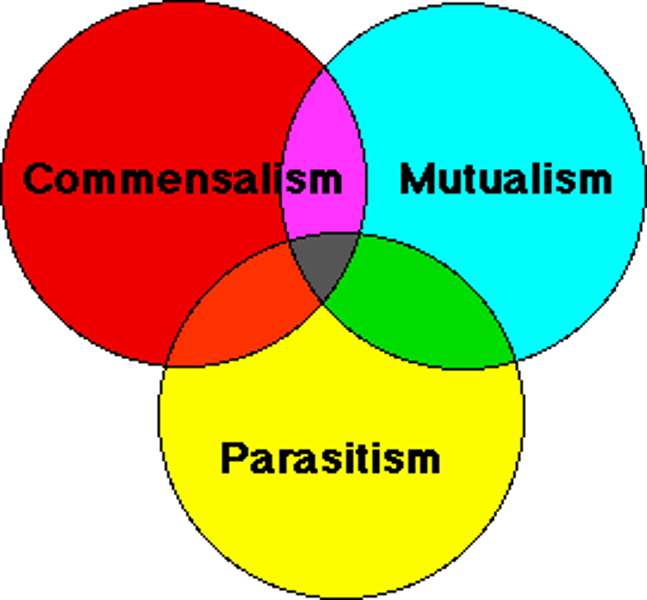
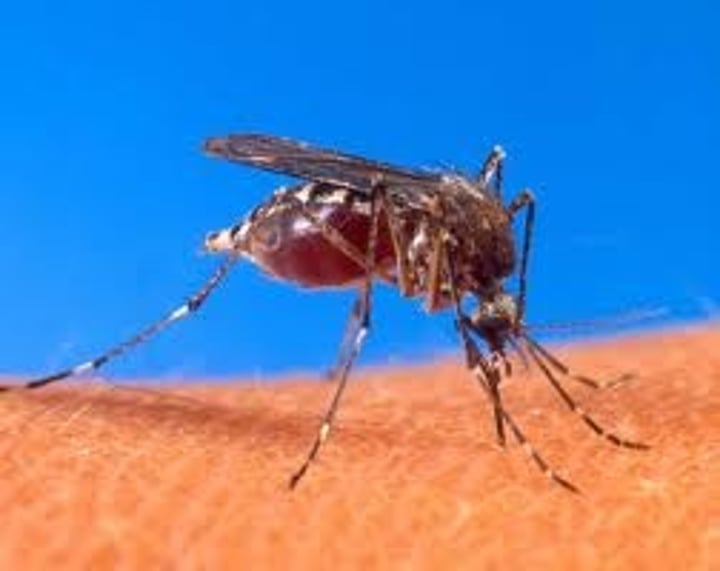
Parasitism
is +/- symbiotic interaction in which one organism (parasite) derives its nourishment from another organism (host) which is harmed in the process.

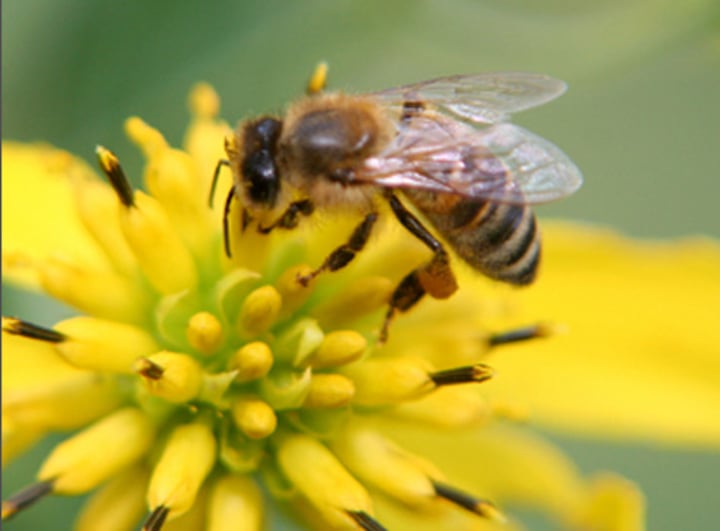
Mutualism
is an inter specific interaction that benefits both species (+/+)

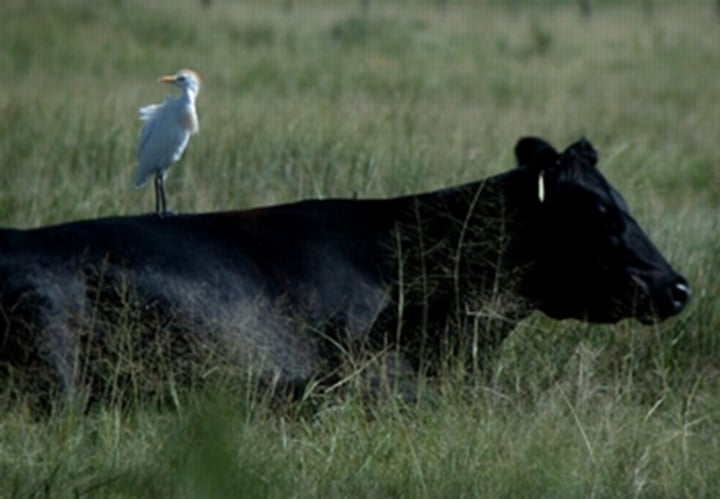
Commensalism
an interaction between species that benefits one of the species but neither harms nor helps the other (+/0)

Keystone Species
species that exist not necessarily in great numbers but inhabit an important ecological niche in the community. Removal of this species can have a great effect on an entire community. Think of the wolves of Yellowstone.

Whittaker Climatograph
shows the relationship between temperature, rainfall and ecosystem type
Limiting Factor
abiotic variable such as pH or salinity that limits the distribution of a species in an ecosystem. Phosphorous is a common limiting factor. Nitrogen can also be a limiting factor, but carnivorous plants living in nitrogen deficient environments supplement their photosynthesis with animal protein.
Resevoir
a supply of water or a key nutrient. The atmosphere is the primary reservoir of nitrogen, and plants are a major reservoir of carbon.
Primary Succession
ecological succession that begins from a soil-less landscape and where no living organism existed before. Example: new volcanic islands
Secondary Succession
succession resulting from disturbed ecosystems with soil still remaining. Example: after a forest fire
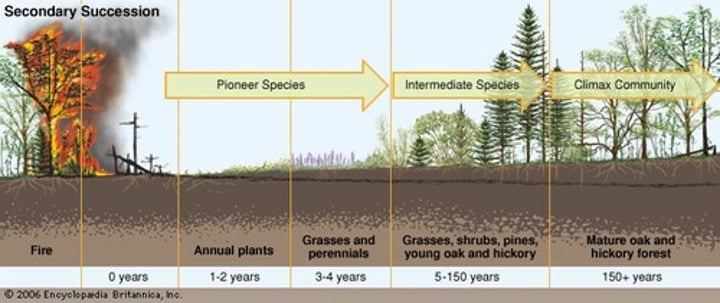
Climax Community
the end result of succession, a stable ecosystem that is no longer undergoing transformation
Pioneer Species
usually lichens/grasses that can tolerate no/poor soils. The first species to colonize an ecological area

Net production
the gross production of an ecosystem minus the production consumed by respiration
Equilibrium
the production of an ecosystem equals one when production is divided by respiration...characteristic of a climax community
Endemic Species
a native species
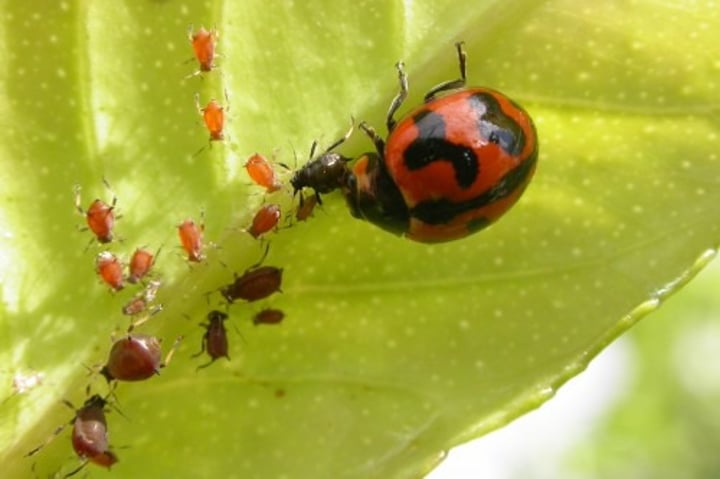
Biological Control
use of an organism to control another organism, usually insects. Goats can be used to eat kudzu, ladybugs can be released to eat aphids, beetles can be released to eat the wooley adelgid that is killing native hemlock trees.

DDT
The insecticide that triggered plummeting birth rates in many birds in top trophic levels, due to the thinning of their eggshells

Methyl Mercury
form of toxic metal that is easily bio accumulated in organisms. Made more available in soils as a result of acid rain.
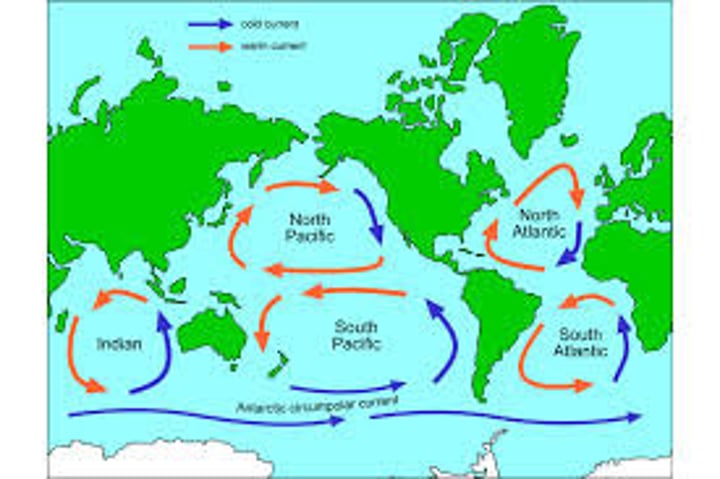
Gyre
one of five global ocean surface areas where circular currents have accumulated large amounts of plastic and other waste
Endangered vs. Threatened Species
Endangered species are at the brink of extinction now. Threatened species are likely to be at the brink in the near future.
Conservation Biology
is the scientific study of nature and of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions.
Fragmentation
A biogeography factor that affects species survival. When humans split an ecosystem in half, making it dangerous for animals to move to key resources like water and food supplies. Roads and power lines and cutting down forests are major causes of fragmentation. Wildlife corridors like ribbons of forests along a stream are often used to restore a pathway for animals.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Indicator Species
organism used to assess the health of an ecosystem, such as crayfish is a Stone Mountain stream.
Biotoc Index
health of an ecosystem as calculated by the presence or absence of indicator species
Ex situ conservation
to remove an organism from its habitat to ensure its survival elsewhere, like pandas in a zoo
In situ conservation
to protect a habitat to ensure an endangered species thrives in its native environment, such as protecting the pandas' native bamboo forest.
Captive Breeding
a specific example of in situ conservation. to move an endangered species to a controlled habitat to breed it so as to ensure its survival