Biology Practice
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
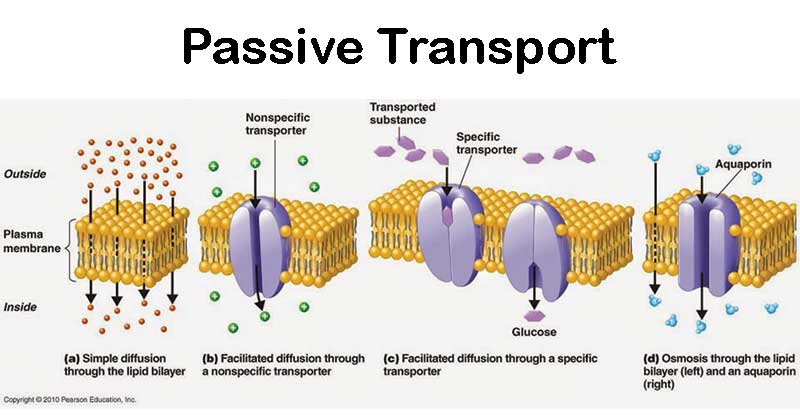
Passive Transport
Movement of ions and other substances across cell membranes without energy. Goes with the gradient.
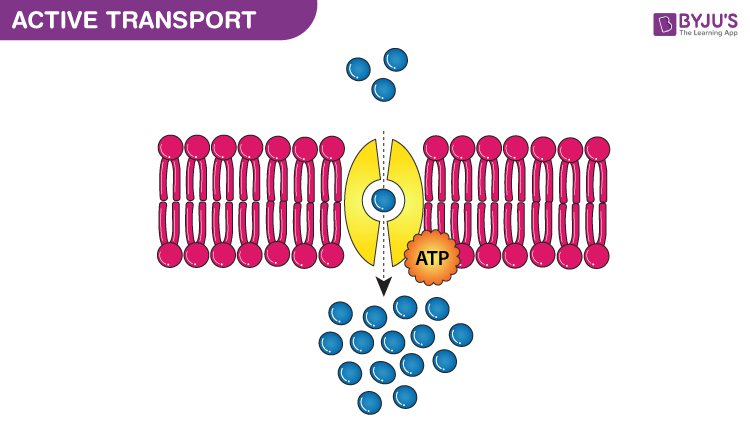
Active Transport
Movement of molecules across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient with energy.
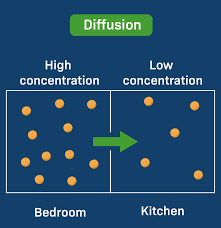
Diffusion
The process of a substance moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration due to random molecular motion.
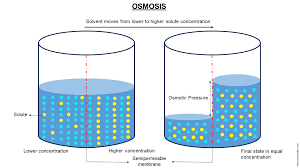
Osmosis
The movement of water molecules from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules, through a cell's partially permeable membrane.
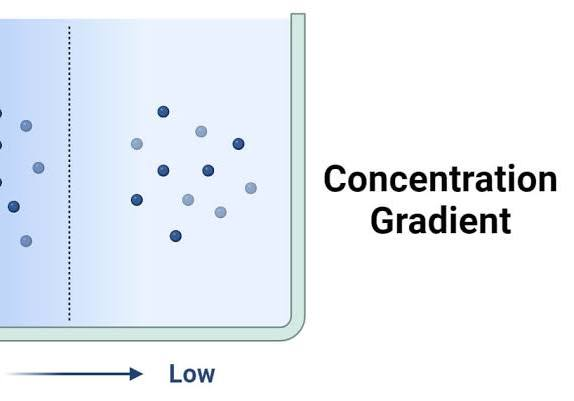
Concentration Gradient
The gradual change in the concentration of a substance over distance, where particles naturally move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
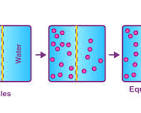
Equilibrium
a state of balance within a system, such as a cell, organism, or ecosystem, where opposing forces or processes are equal, resulting in a stable condition.
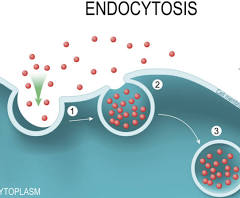
Endocytosis
The process by which cells absorb molecules, particles, or even entire cells from the outside by engulfing them with the cell membrane, which then pinches off to form a vesicle inside the cell.
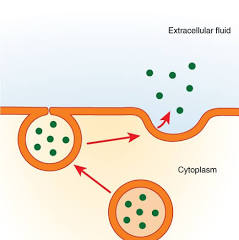
Exocytosis
The process by which cells release substances, such as waste products, hormones, or neurotransmitters, out of the cell by fusing vesicles with the plasma membrane.
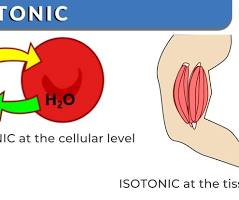
Isotonic
A solution with the same solute concentration as another solution, particularly the fluid inside a cell.
Cell transport
The process of substances moving into and out of a cell through the cell membrane.
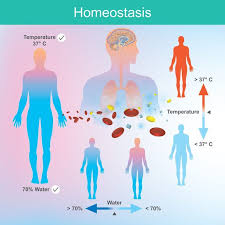
Homeostasis
The process by which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment, like body temperature and blood sugar levels, despite changes in the external environment.
Hypotonic
Has a lower solute concentration than the fluid it is compared to, such as the inside of a cell.
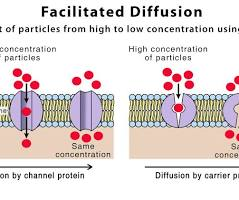
Facilitated diffusion
The passive transport of molecules across a cell membrane with the help of transport proteins, moving from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration without using energy.
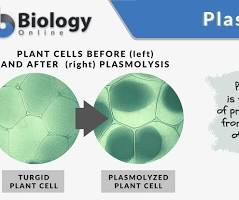
Plasmolysis
The process in which a living cell, particularly a plant cell, loses water and the cytoplasm shrinks away from the cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution.
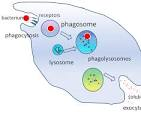
Phagocytosis
The process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf large particles, such as microorganisms and cellular debris, to bring them into the cell.
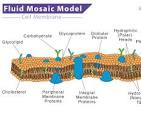
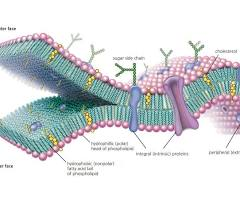
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes the cell membrane as a "mosaic" of components—primarily phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol—that are in constant motion within a two-dimensional "fluid" matrix.
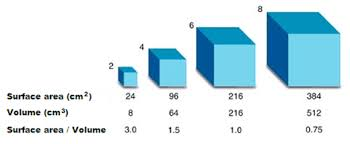
SA: Vol
Surface area to volume ratio
Life
The condition that distinguishes animals and plants from inorganic matter, including the capacity for growth, reproduction, functional activity, and continual change preceding death.

Living
Having life; being alive; not dead.
Cell
The fundamental building block of all living organisms, functioning as the smallest unit that can live independently.
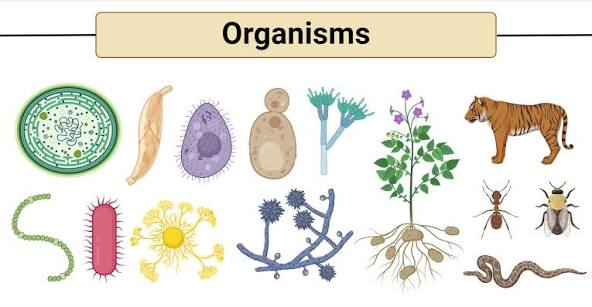
Organism
Any living individual that functions as a whole, possessing organized structure and carrying on the activities of life, such as reproduction, growth, and metabolism.
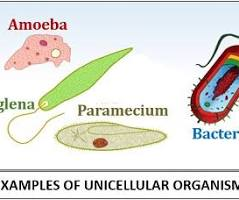
Unicellular
Is a living thing composed of a single cell that performs all essential life functions, such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
Multicellular
An organism made up of more than one cell, where the cells are often specialized to perform different functions.

Non-living
Any object or entity that lacks life, meaning it does not have a cellular structure or perform life processes such as growing, reproducing, respiring, or metabolizing.
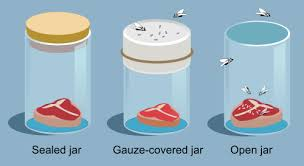
Spontaneous generation
The belief that living things come from non-living things.
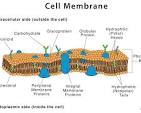
Cell membrane
A semipermeable barrier that surrounds a cell, separating its internal components from the external environment and controlling the passage of substances.
Semi-permeable membrane
A barrier that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through while blocking others

Phospholipids
A type of lipid with a hydrophilic (water-attracting) phosphate head and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) fatty acid tails.
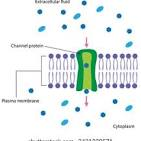
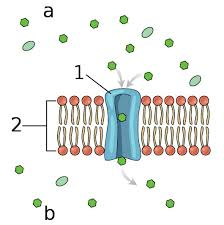
Protein channel
Transmembrane proteins that form hydrophilic tunnels through the cell membrane, allowing specific ions and molecules like water to pass through via passive transport, a process that does not require energy.
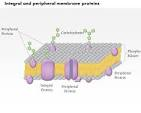
Peripheral Protein
Proteins that are temporarily associated with a cell membrane, either on the exterior or interior surface.
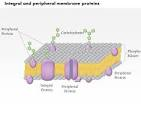
Integral protein
A protein that is permanently embedded within a biological membrane, like the cell membrane
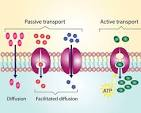
What is allowed through the cell membrane during diffusion?
Small and non-polar molecules
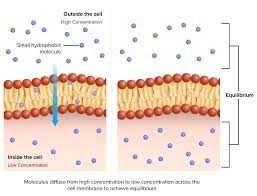
The rate of diffusion can be influenced by a number of factors, Including:
Temperature- Affects kinetic energy of particles in solution
Molecular Size- Larger particles are subjected to greater resistance within a fluid medium
Steepness of Gradient- Rate of diffusion will be greater with a higher concentration gradient
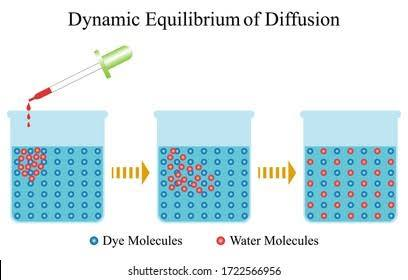
Dynamic Equilibrium
A state where a system remains stable despite continuous, opposing processes occurring at equal rates.
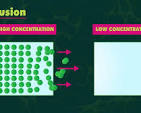
What’s an example(s) of diffusion?
Oxygen entering cells (into lungs)
Carbon Dioxide leaving cells (leaving lungs)
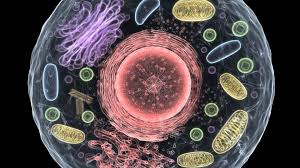
How can substances move in and out of cells?
Simple Diffusion
The Selectively Permeable Cell Membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
Active Transport
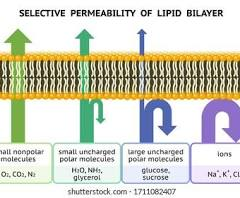
Selectively permeable cell membrane
Controls what enters and exits a cell, allowing certain molecules to pass while blocking others to maintain internal stability (homeostasis).

What happens in a closed system?
Energy enters the system but matter does not leave.

What happens in an open system?
Energy enters the system and matter leaves.

What happens in an isolated system?
Energy does not enter as well as matter does not leave.
What type of system is a cell?
A opened system: Chemical energy (glucose) enters and chemical energy (ATP) leaves.

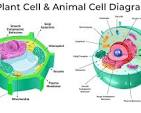
What do only Animal cells have that plant’s don’t?
Lysosomes
Multiple small vacuoles
Cilia/Flagella

What do only Plant cells have that animal’s don’t?
Cell Wall
Chloroplasts
Large central vaccule
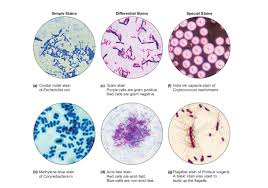
What are the advantages of using stain techniques?
Enhanced visualization of cell shape and size, better differentiation of various structures like nuclei or spores, and the ability to perform rapid and simple analyses for medical and scientific purposes.
How do staining techniques help improve our knowledge of cell structure and function?
Allows scientists to differentiate between various organelles and molecules, thereby linking structure to function.
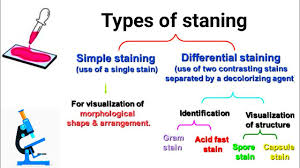
What is the difference between a simple stain and a negative stain?
A simple stain directly colors the bacterial cell, using a positively charged (basic) dye to make the cells visible against a light background. A negative stain uses a negatively charged (acidic) dye to color the background, leaving the bacterial cells unstained and appearing light against a dark background.
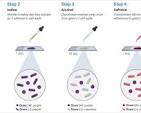
How does gram staining work?
By using a sequence of four reagents—crystal violet, Gram's iodine, a decolorizing agent (alcohol), and a counterstain (safranin)—to differentiate bacteria based on their cell wall structure.
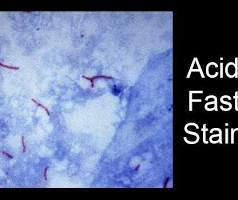
How does acid fast staining work?
By using heat and a strong primary dye to penetrate the waxy, mycolic acid-rich cell walls of acid-fast bacteria, which are then identified by their retention of the red color after a decolorizing step.

Why do we use gram staining and acid-fast staining on bacteria?
To differentiate bacteria based on their cell wall composition.
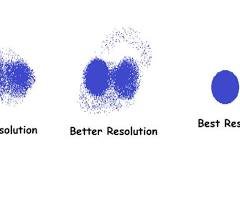
Resolution
The ability to distinguish between two separate points or objects in an image or structure.

Magnification
The process of making an object appear larger than its actual size, though its physical size does not change.
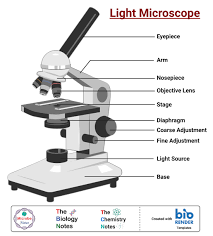
Light Microscope
Small and easy to carry
No vacuum needed
Easy sample preparation
Up to 2000x magnification
Resolution: 200 nm
Specimen can be dead or living
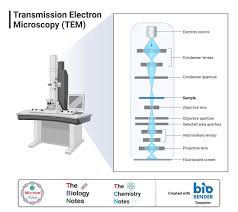
Electron Microscope
Large and installation means it can’t be moved
Vacuum needed
Complicate sample preparation
Over 500,000x magnification
Resolution: 0.5nm
Specimens are dead

What do SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) and TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope) use instead of light to produce images?
Electron gun.

1 m:
1000 mm
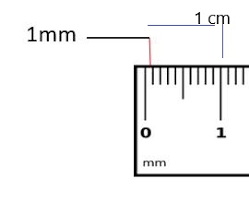
1 mm:
1000 micro meters

1 micro meter:
1000 nm

Magnification formula:
(Ocular lens) x (Objective lens) or image size/actual size
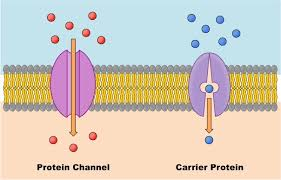
Two types of facilitated diffusion proteins
Channel Protein and Carrier proteins
Channel Protein
A type of transport protein that forms a hydrophilic pore across a cell membrane, allowing for the selective passage of specific ions or small molecules like water.
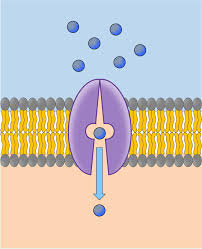
Carrier proteins
Cell membrane proteins that bind to specific molecules or ions and undergo a change in shape to transport them across the membrane.
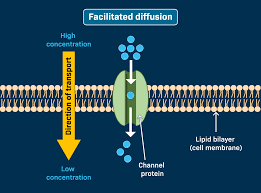
Ion channels role in diffusion
Channel Proteins: These form pores or tunnels across the membrane, allowing specific ions or molecules (such as Na⁺ or K⁺) to flow through. Ion channels are often gated, meaning they can open or close in response to signals like voltage changes.
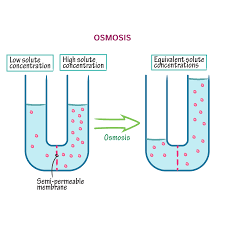
Osmosis is…
The diffusion of water
Passive transport
High water concentration to a Low water concentration or
Low solute to a high solute concentration
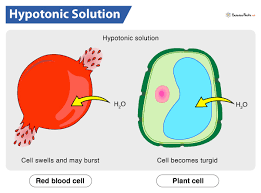
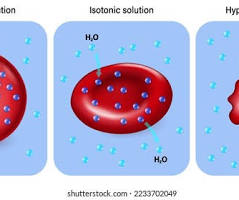
Osmosis in a Hypotonic solution
A cell in a hypotonic solution➡ ️water enters the cell via osmosis and the cell starts to swell (Turgid)
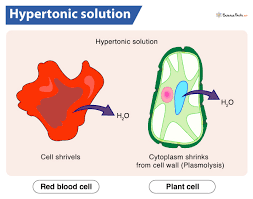
Osmosis in Hypertonic solution
A cell in a hypertonic solution➡ water leaves the cell via osmosis and the cell shrinks (Plasmolyzed or flaccid cell)
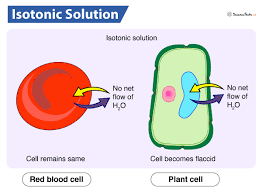
Osmosis in an Isotonic solution
A cell in an isotonic solution➡ there is no concentration difference, so water potential equal and stays the same (Dynamic equilibrium)

Active transport of Na+/K+
Cytoplasmic Na+ binds to the Na+/K+ pump➡ The Na+/K+ pump is phosphorylated by ATP➡ This energy powers the Na+/K+ pump➡ The pump changes its configuration causing Na+ to release➡ Extracellular K+ binds to the pump leading to dephosphorylation➡ The pump changes its configuration, causing K+ to release
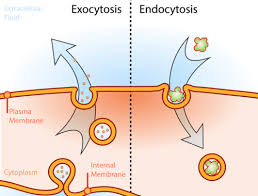
What type of transport is endocytosis and exocytosis?
Active transport.
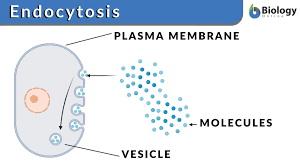
Process of endocytosis
The plasma membrane folds inward (invaginates) forming a cavity that fills with extracellular fluid, dissolved molecules, food particles, foreign matter, pathogens, or other substances. ➡ The plasma membrane folds back on itself until the ends of the in-folded membrane meet. This traps the fluid inside the vesicle. In some cells, long channels also form extending from the membrane deep into the cytoplasm. ➡ The vesicle is pinched off from the membrane as the ends of the in-folded membrane fuse together.
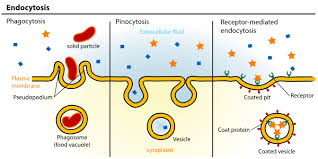
What are the three main types of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Macrophages
Immune cells that find and destroy germs, tumor cells and other things that could harm you.
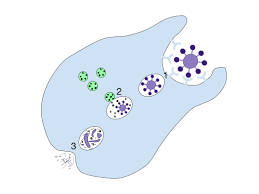
Phagocytosis
The process where a cell engulfs and digests a solid particle, such as a bacterium or a dead cell, to remove it from the body or for nourishment.
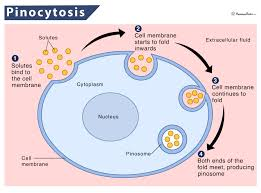
Pinocytosis
The process by which a cell "drinks" by engulfing extracellular fluid and small solutes, forming tiny vesicles to bring them into the cell.
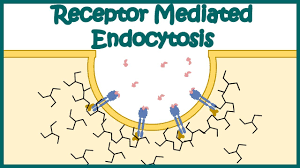
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
A specific type of cellular uptake where cells absorb large molecules (ligands) by having them bind to specific receptors on the cell surface.
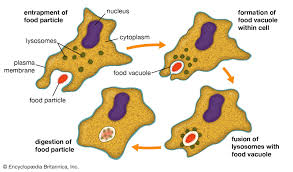
The process of phagocytosis
The virus and the cell needs to come in contact ➡ The virus binds to the cell surface receptors on the macrophage ➡ The macrophage starts to surround the virus and engulf it into the cell ➡ Surrounding becomes educed in a bubble structure called a “phagosomes” within the cytoplasm.
The phagosome fuses with the lysosomes becoming a “phagolysosome”
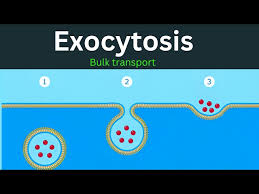
Exocytosis process
A specific type of cellular uptake where cells absorb large molecules (ligands) by having them bind to specific receptors on the cell surface. ➡ The vesicle membrane attaches to the cell membrane.➡ Fusion of the vesicle membrane with the cell membrane releases the vesicle contents outside the cell.
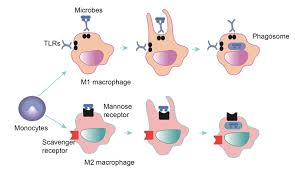
Endocytosis in the human body
Phagocytosis is essential for immune system function, and receptor mediated endocytosis helps to regulate cholesterol levels in the blood.
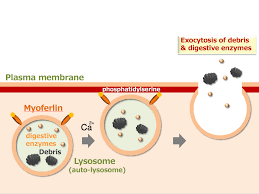
Exocytosis in the human body
Cells in your stomach and pancreas package digestive enzymes into vesicles and release them into the digestive tract through exocytosis.
3 components of cell theory
All living things are made of cells
A cell is the basic unit of life
Cells are made from pre-existing cells

Francesco Redi
The first person to challenge the theory of spontaneous generation by demonstrating that maggots come from eggs of flies.

Robert Hooke
Used light microscope to look at thin slices of plant tissue (cork). Swatting chambers.

Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
First to see living microscopic organisms (in pond water). Termed these micro-organisms animalcules.

Louis Pasteur
Invented the process of pasteurization. Final person who disproved spontaneous generation.

Robert Brown
Was responsible for discovery of the nucleus of the cell.

Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann
Were German scientists who, in the 1830s, developed the initial form of the cell theory. Observed that all plants are made of cells, extended this to animals, leading to the conclusion that all living organisms are composed of cells. This foundational work proposed that the cell is the basic unit of life for both plants and animals.

Robert Remak
Discovered that all new cells come from pre-existing cells.

The work of Louis Pasteur
Revolutionized medicine and biology through his development of the germ theory of disease, the invention of pasteurization, and the creation of the first vaccines.

Use of microscopes to the development of cell theory
Enabling the discovery of cells and the understanding that they are the fundamental unit of life.

What would happen to this cell?
This cell would die since it would not be able to get enough food or remove enough waste.
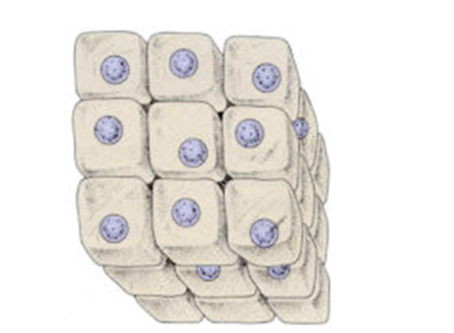
What would happen to this cell?
By multiplying into smaller cells, the overall size is the same but the SA : VOL is much much larger
What could this SA:V ratio signify? 3:1 (highest ratio)
Better able to obtain nutrients (less volume for nutrients to diffuse across)
What could this SA:V ration signify? 2.5:1 (lowest ratio)
Lower ratio most likely to starve
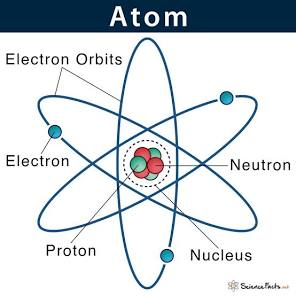
Atom
The smallest unit of a chemical element that retains the properties of that element.
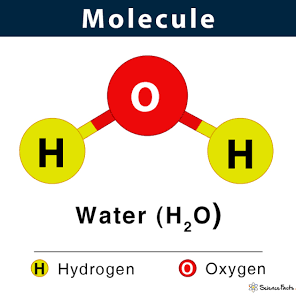
Molecule
A group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Organelle
A subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell.
Tissue
A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
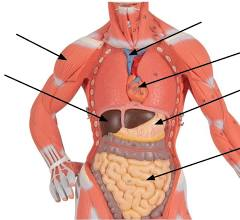
Organ
A specialized structure in a multicellular organism, such as the heart or skin, or to a musical instrument.
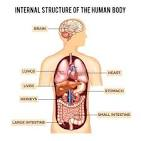
Organ system
A group of organs that work together to perform one or more vital bodily functions, such as digestion, respiration, or circulation.

Population
The study of populations of organisms, specifically how they grow, change in size, and interact with their environment and with other species.

Community
A group of different species' populations that live and interact within a specific area.