Jackson Algebra Final Review
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Compound Interest Formula
A = Final Amount
P = Initial Amount
r = Interest Rate (decimal form)
n = Number of Times Interest has been Compounded
t = time elapsed
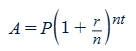
Radioactive Decay Formula
A = Final Amount
P = Initial Amount
t = time elapsed
T = Half Life
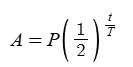
How would you write (10x²)^(3/8) in radical form?
Remember the numerator of the exponent corresponds to the part inside the radical, and the denominator of the radical corresponds to the outside part of the radical.
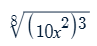
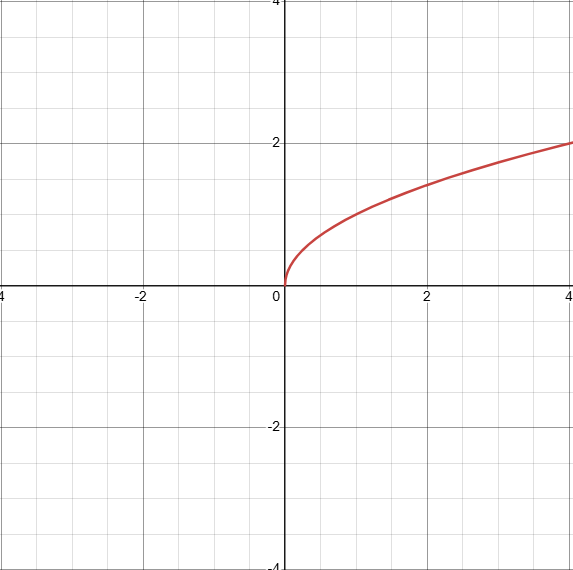
what does the graph of √x look like?
D: [0, inf)
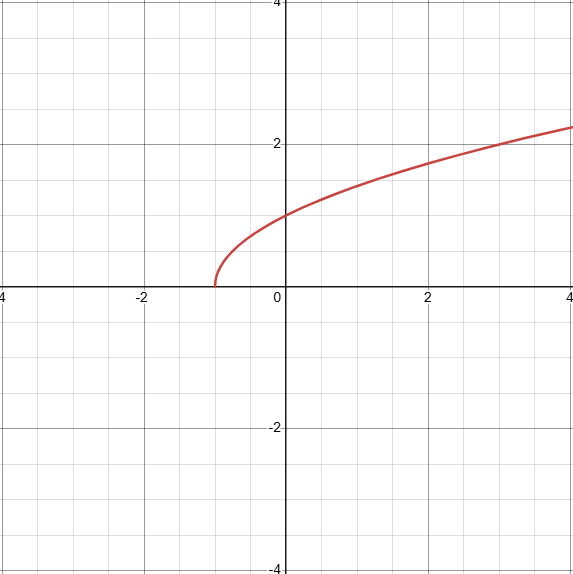
What does the graph of √(x+1) look like? (identify the transformation)
D: [-1, inf)
Shifted to the left by 1 unit, f(x+1)
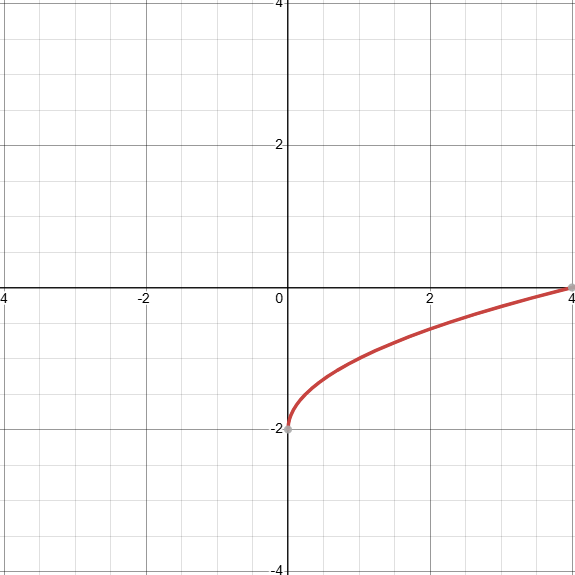
what does the graph of √x - 2 look like? (identify the transformation)
D: [0, inf)
Shifted down 2 units, f(x)-2
how do you rationalize a denominator?
To rationalize a denominator, multiply the numerator and the denominator by a suitable expression that eliminates the radical in the denominator
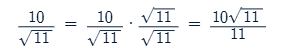
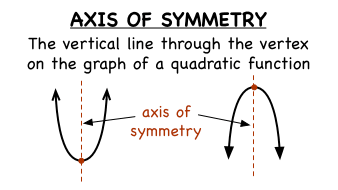
How do you find the axis of symmetry?
If a quadratic is given by ax²+bx+c, the axis of symmetry is given by:
x = -b/2a
How do you find the vertex of a quadratic?
First find the axis of symmetry, and plug the x value back into your function to find the corresponding y value.
if a is the axis of symmetry and your function is given by f(x), the ordered pair of the vertex should look like (a, f(a)).
How do you factor a quadratic with a=1?
If a quadratic is given by ax²+bx+c, and a=1, then find two numbers that multiply to give you c and add up to give you b.
How do you factor a quadratic with a≠1?
If a quadratic is given by ax²+bx+c, and a≠1, then multiply a and c together and find two factors that add up to b and use those two factors to turn the problem into a grouping problem.
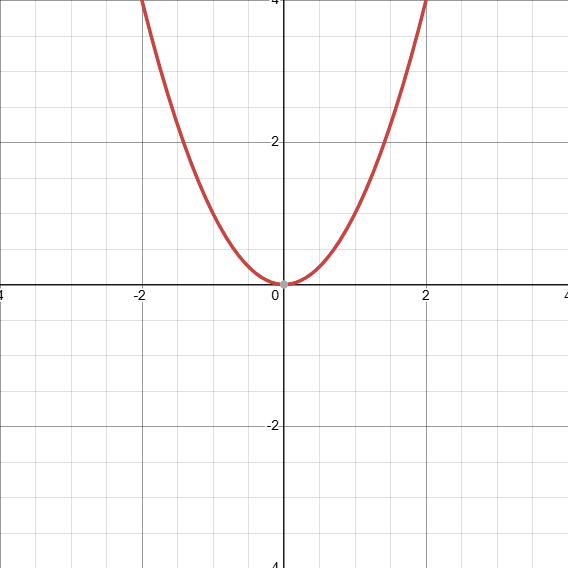
What does the graph of x² look like?
D: (−∞,∞)
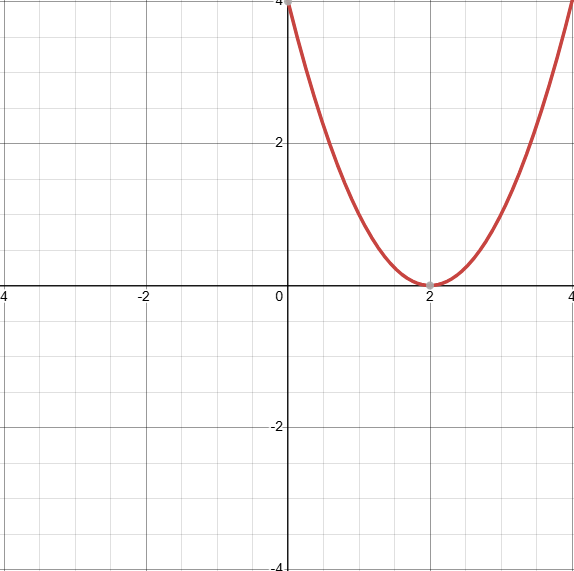
What does the graph of (x-2)² look like? (identify the transformations)
D: (−∞,∞)
Shifted to the right by 2 units, f(x-2)
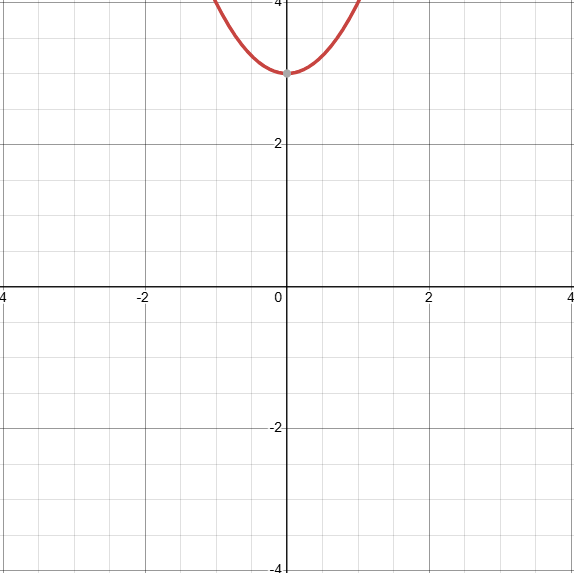
What does the graph of x²+3 look like? (identify the transformations)
D: (−∞,∞)
Shifted up by 3 units, f(x)+3
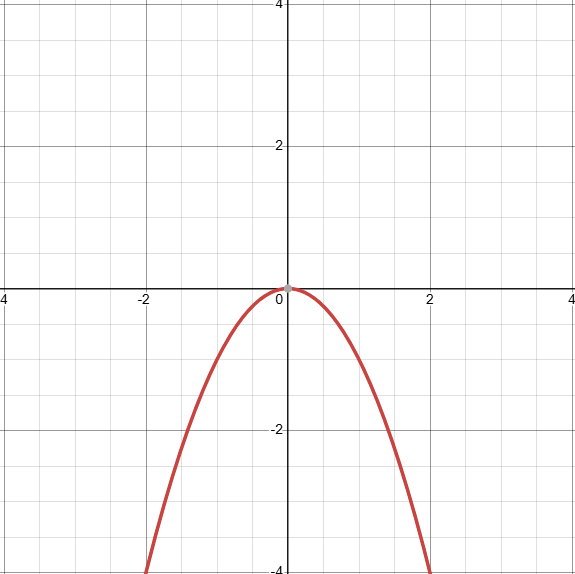
What does the graph of -x² look like? (identify the transformations)
D: (−∞,∞)
Reflection across x-axis, -f(x)
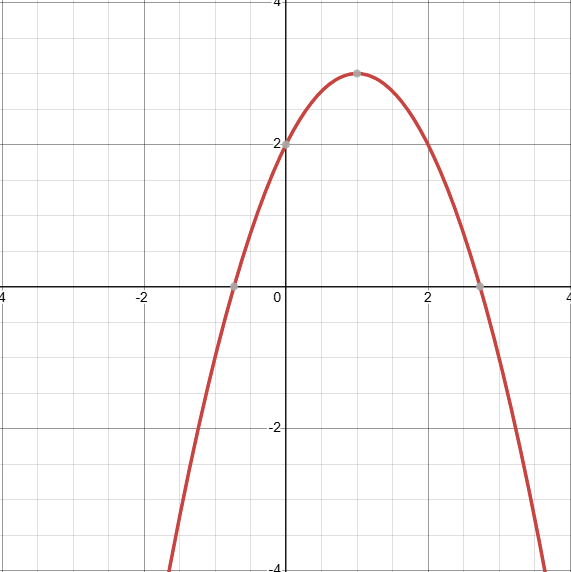
What does the graph of -(x-1)²+3 look like? (identify the transformations)
D: (−∞,∞)
Reflection across x-axis, -f(x)
Shifted to the right by 1 unit, f(x-1)
Shifted up by 3 units, f(x)+3
What is the formula for completing the square when a=1?
if a quadratic is given by ax²+bx+c=0 and a=1, the completing the square formula is given by:
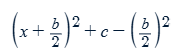
What is the formula for completing the square when a≠1?
If a quadratic is given by ax²+bx+c=0 and a≠1, first normalize the function to the a=1 form by following x²+(b/a)x+(c/a)=0. Then the completing the square formula is given by:
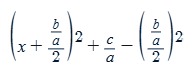
What is the formula for the quadratic equation?
if a quadratic is given by ax²+bx+c, the the quadratic equation is given by:
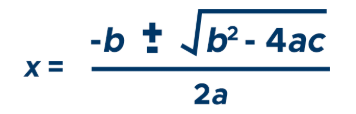
How do you identify the difference between exponential growth and decay in a funciton?
If an exponential function is given by a^x:
if a<1, it is exponential decay
if a>1, it is exponential growth
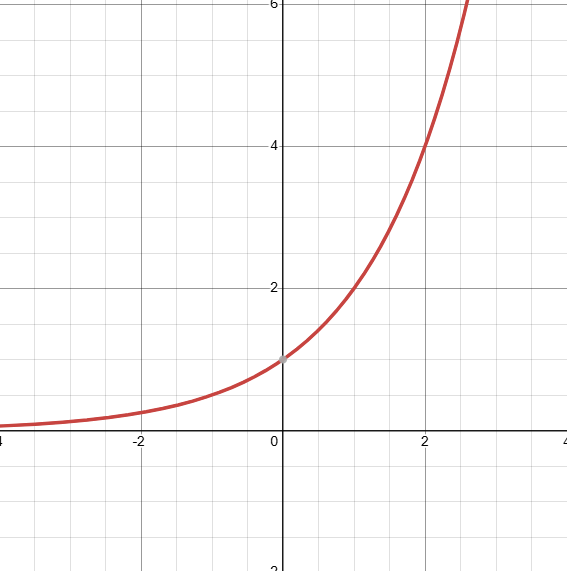
What does a function of exponential growth look like? Where is the horizontal asymptote?
The horizontal asymptote is at y=0
What does a function of exponential decay look like? Where is the horizontal asymptote?
The horizontal asymptote is at y=0