Basic Science. Anatomy of Lower Limbs (Part 1). 9/15.
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Ilium, sacrum, coccyx
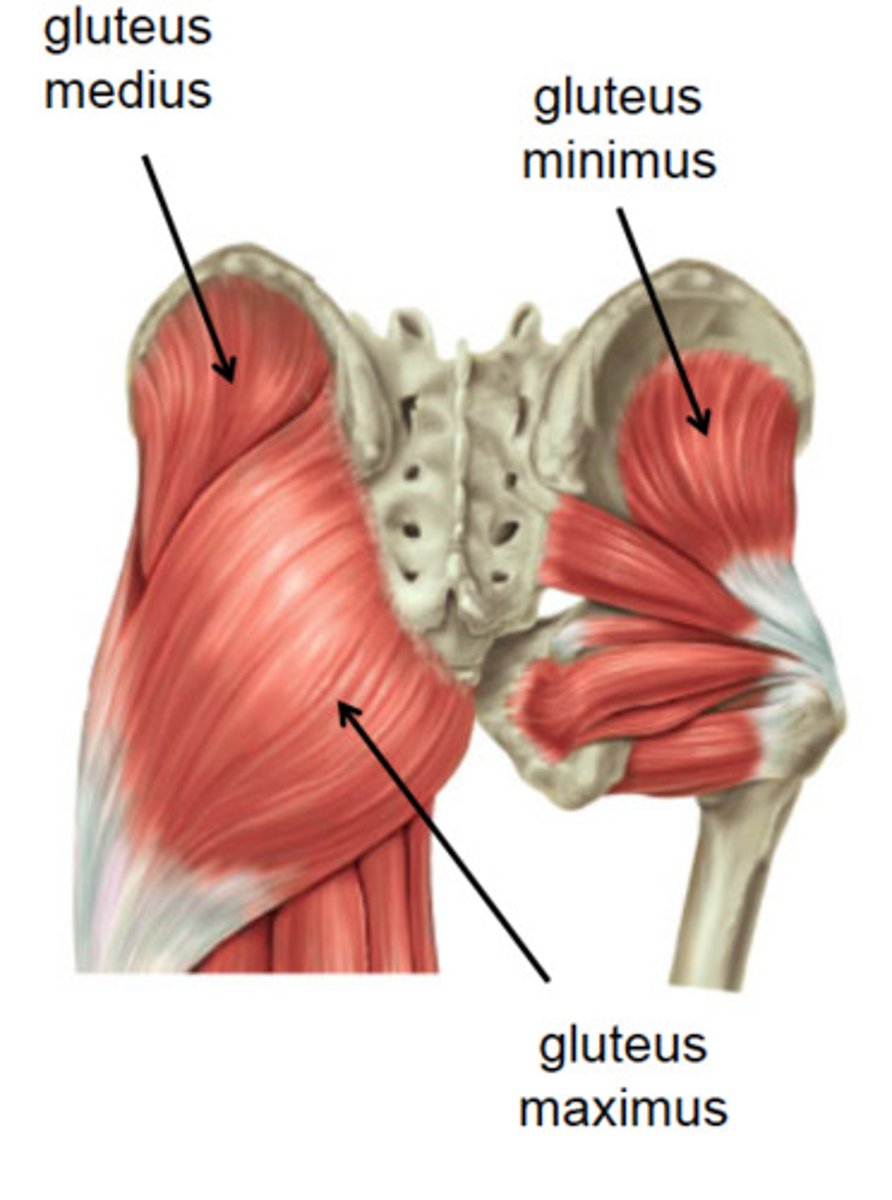
Gluteus maximus attachments? (3)
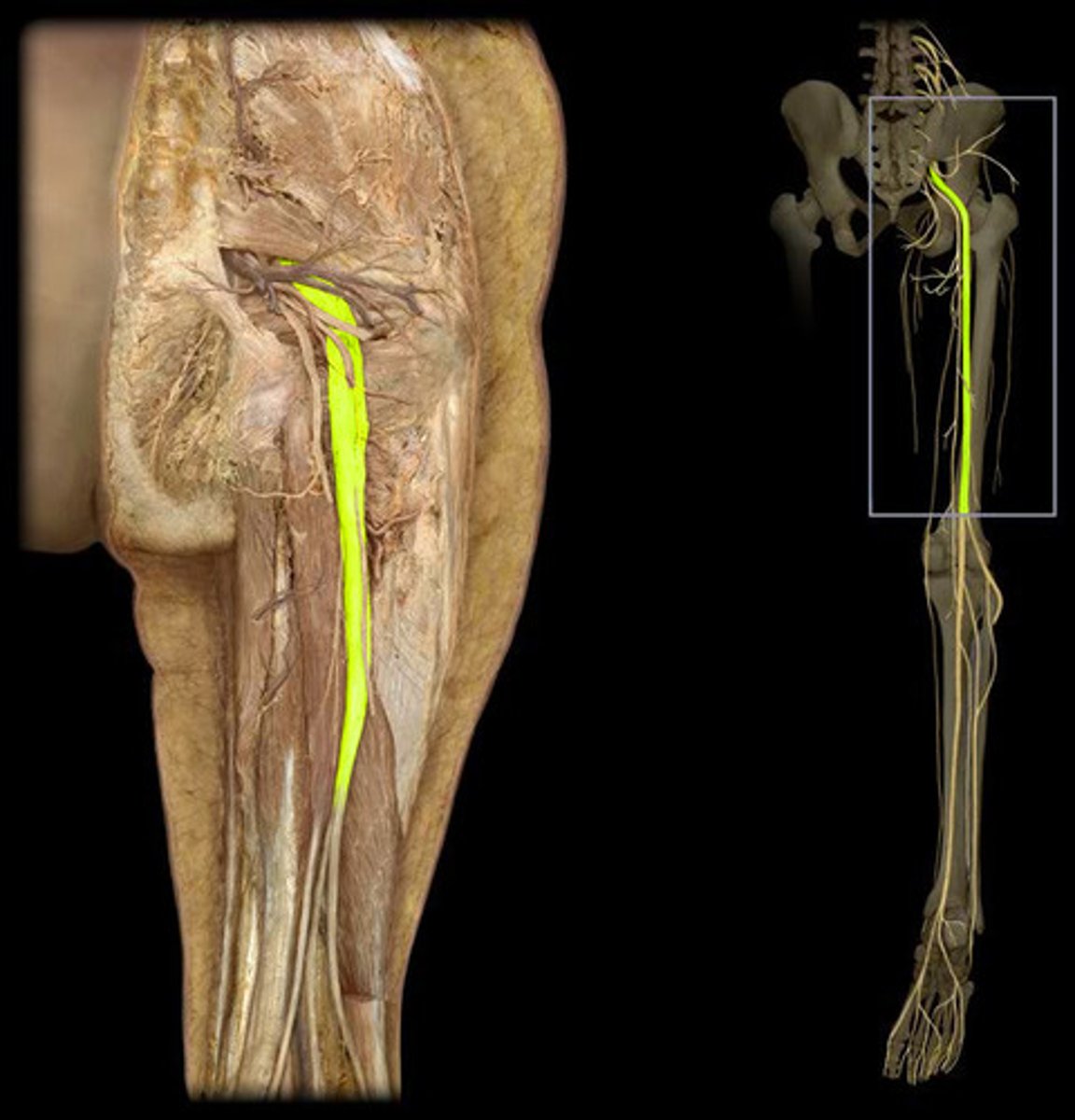
Inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2 roots)
Gluteus maximus innervation
Hip
Lateral
Pelvis
The gluteus maximus actions: extends ____, assists ____ rotation, stablizes ____
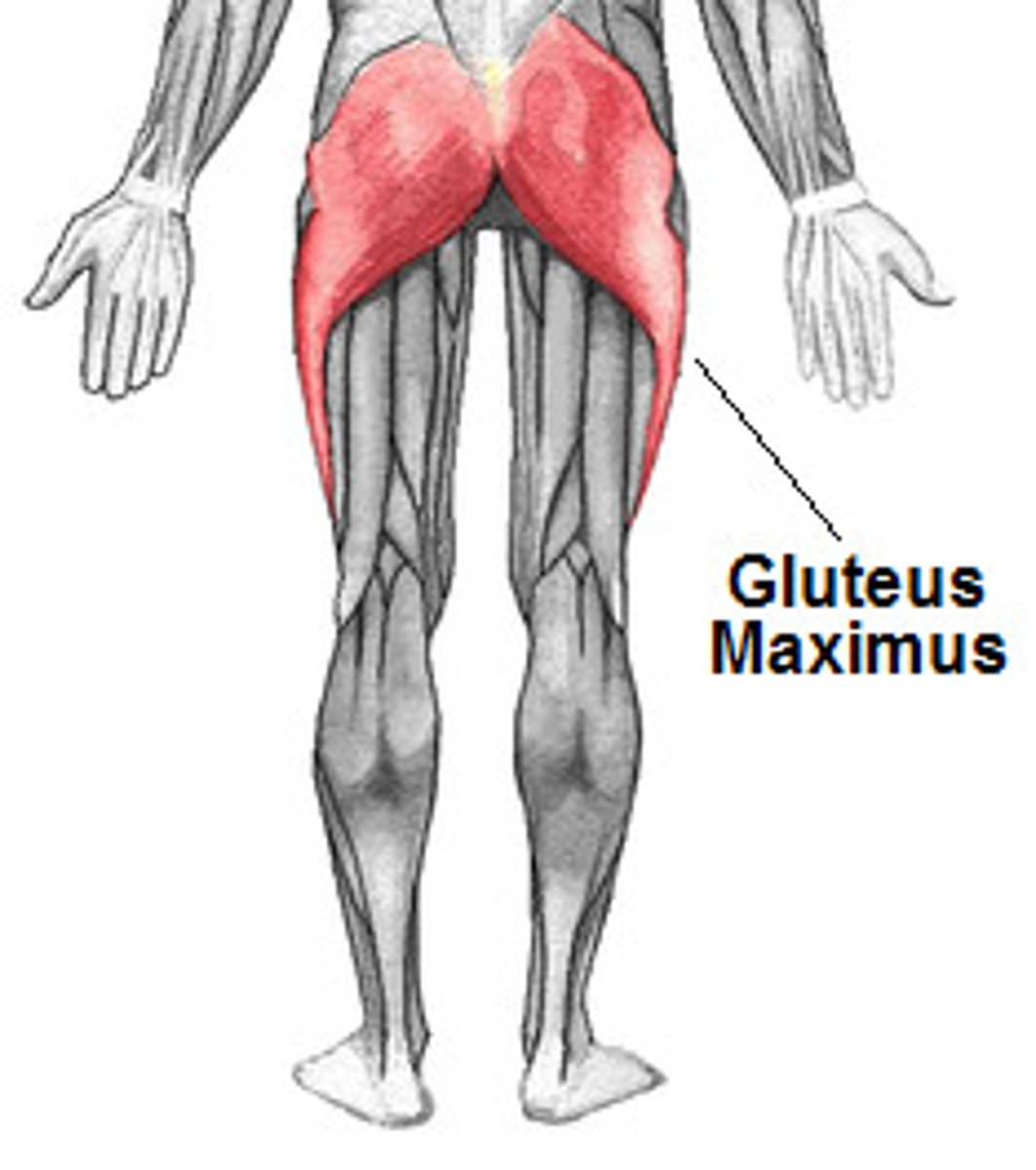
Gluteus maximus
What hip extensor is the most powerful and active during climbing and rising?
Gluteus medius
Anatomy
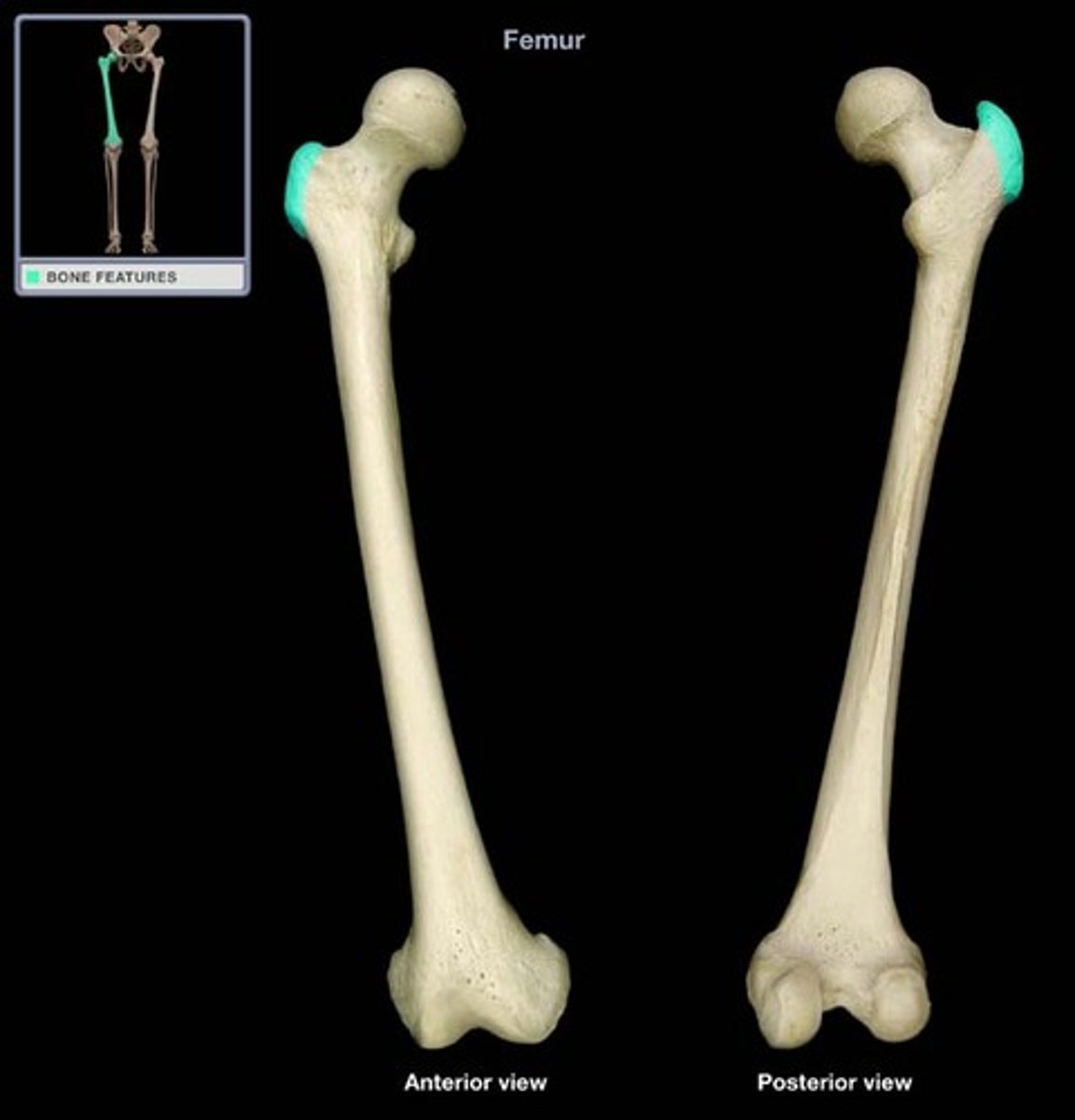
External ilium and greater trochanter of femur
Gluteus medius attachments (origin and insertion)
Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
Gluteus medius, gluteus minus, and tensor fasciae latae innervation
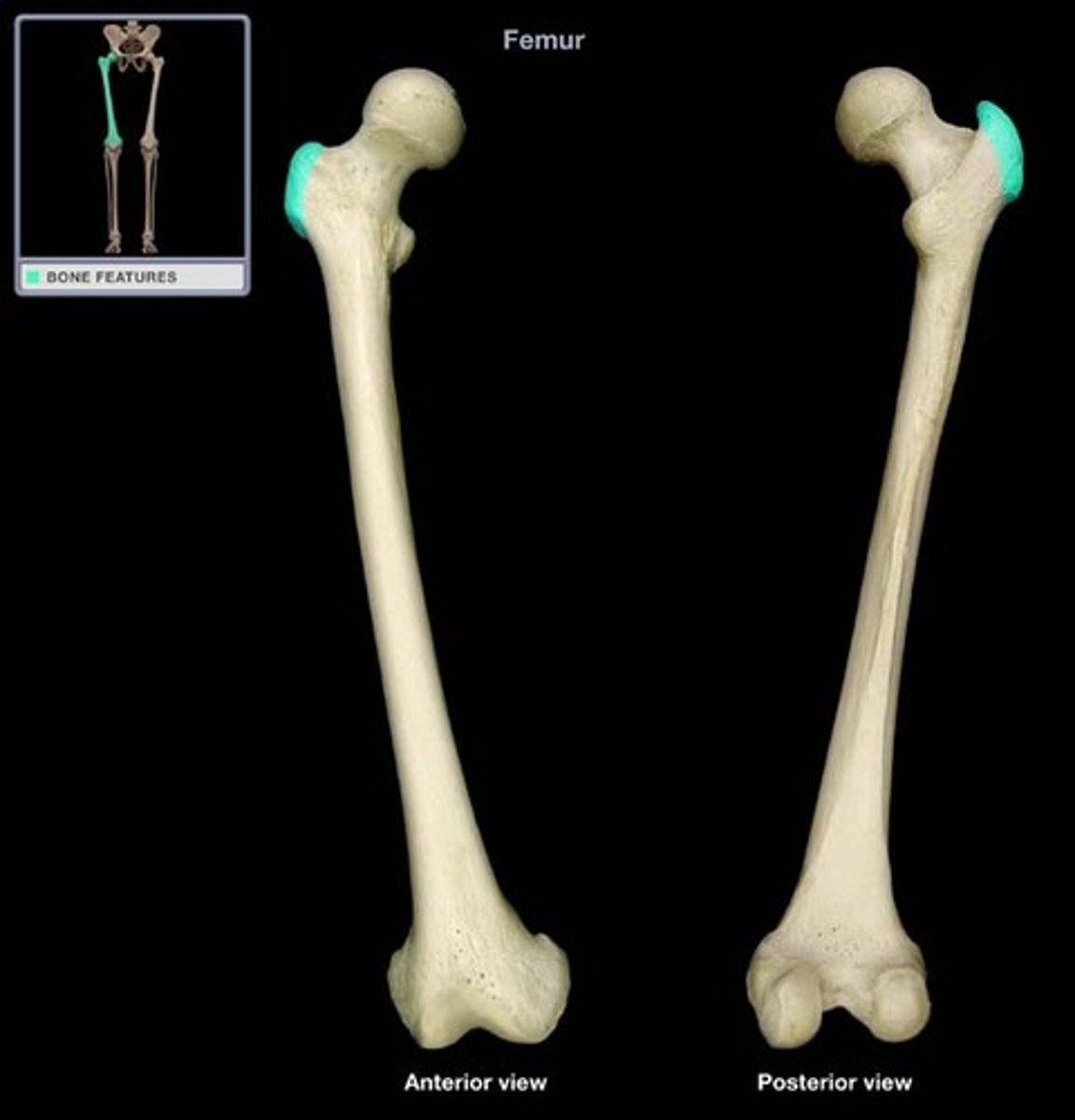
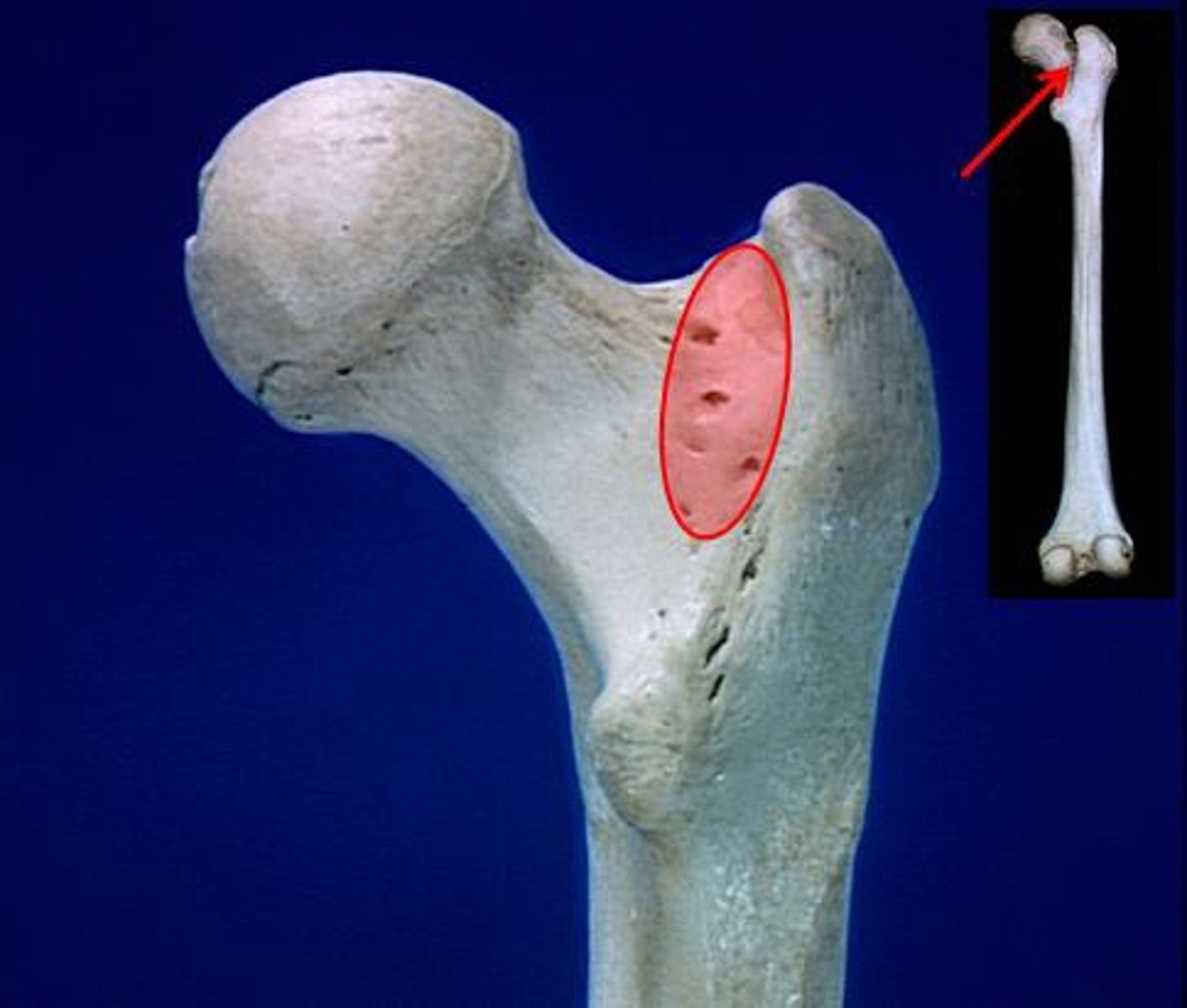
greater trochanter
Femur anatomy
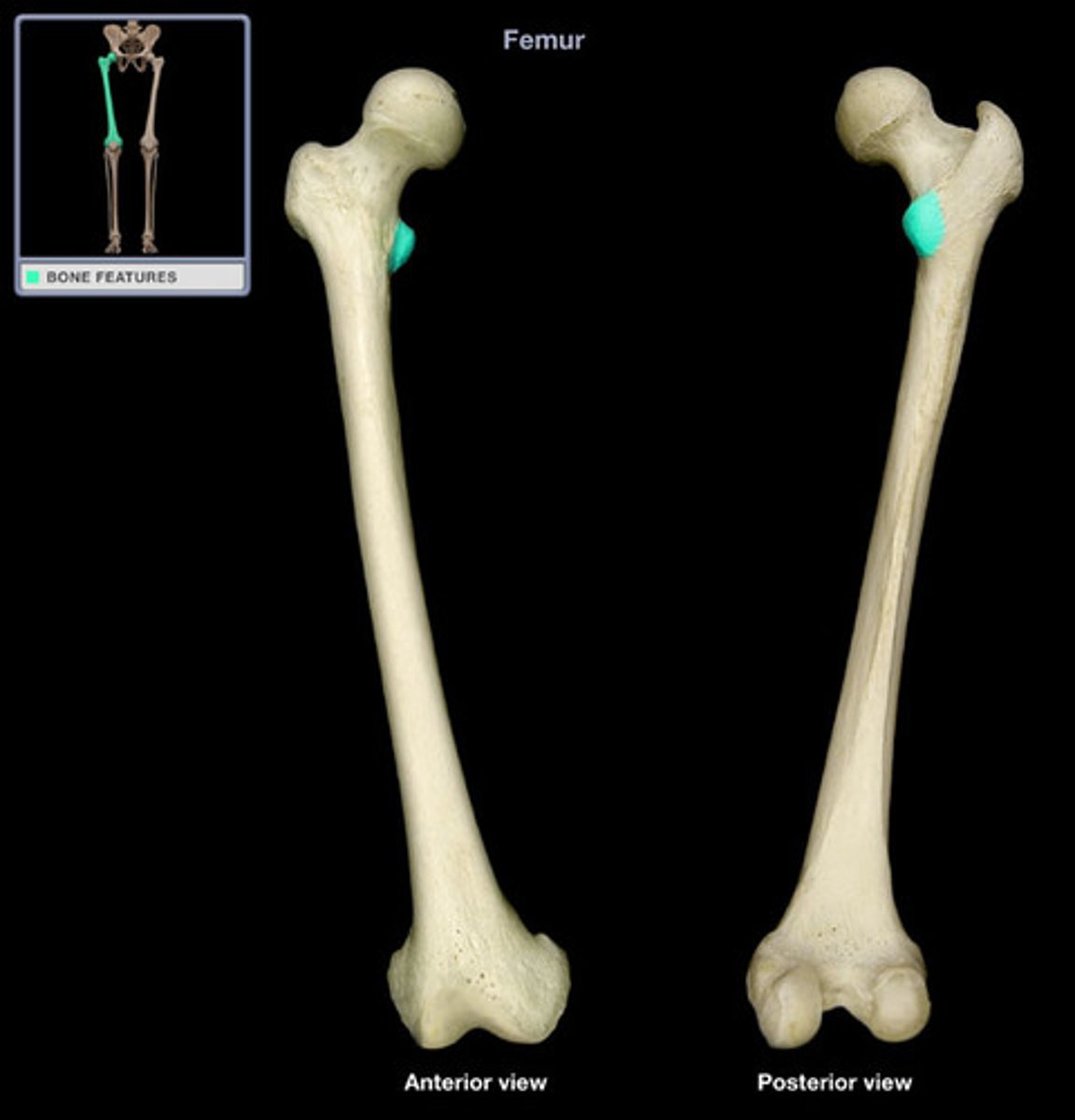
lesser trochanter
Femur anatomy
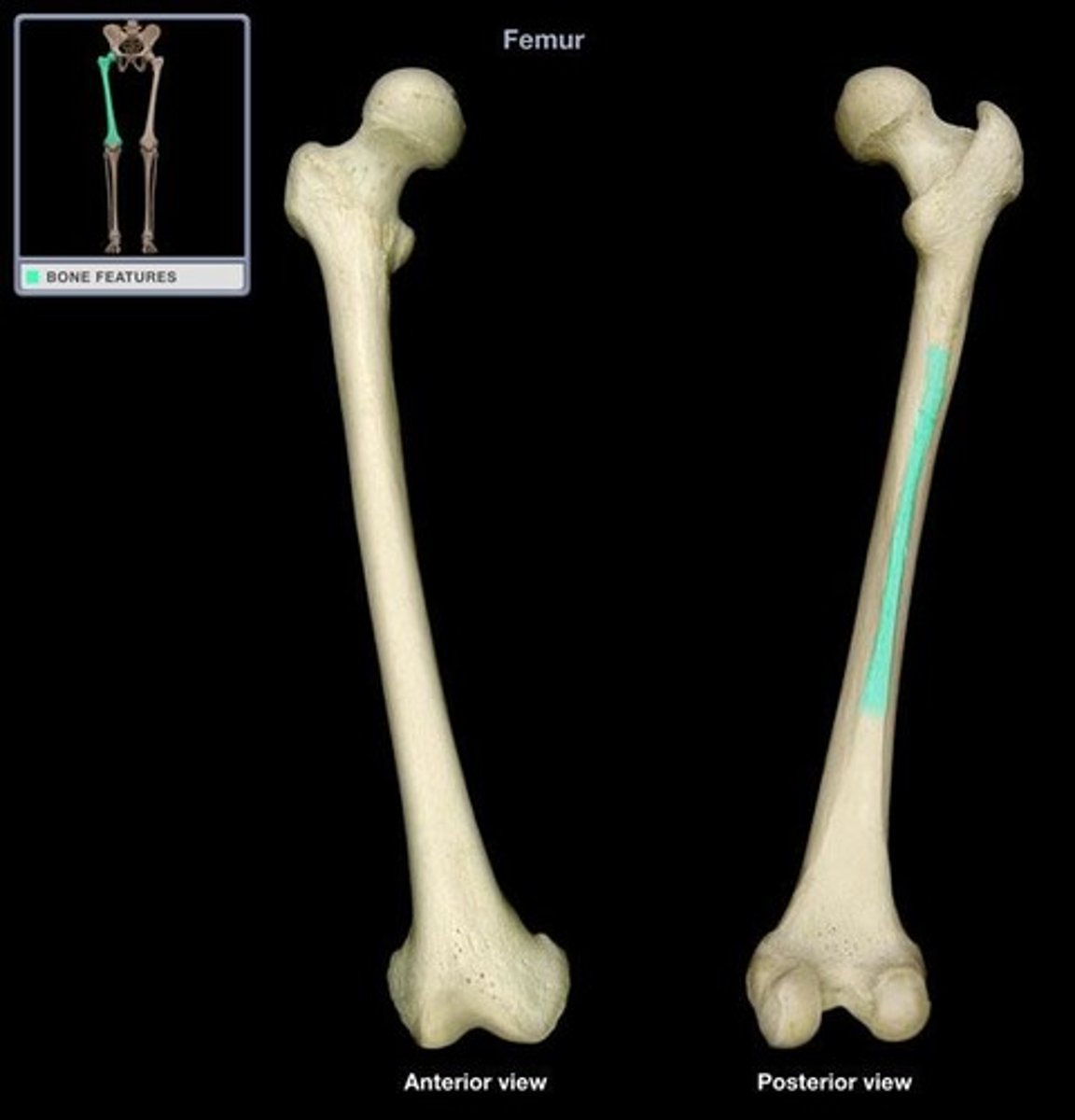
Linea aspera
Anatomy
Abducts hip, stabilizes pelvis during walking
Action of gluteus medius
Trendelenburg gait
Weakness of the gluteus medius produces a hip drop, called?
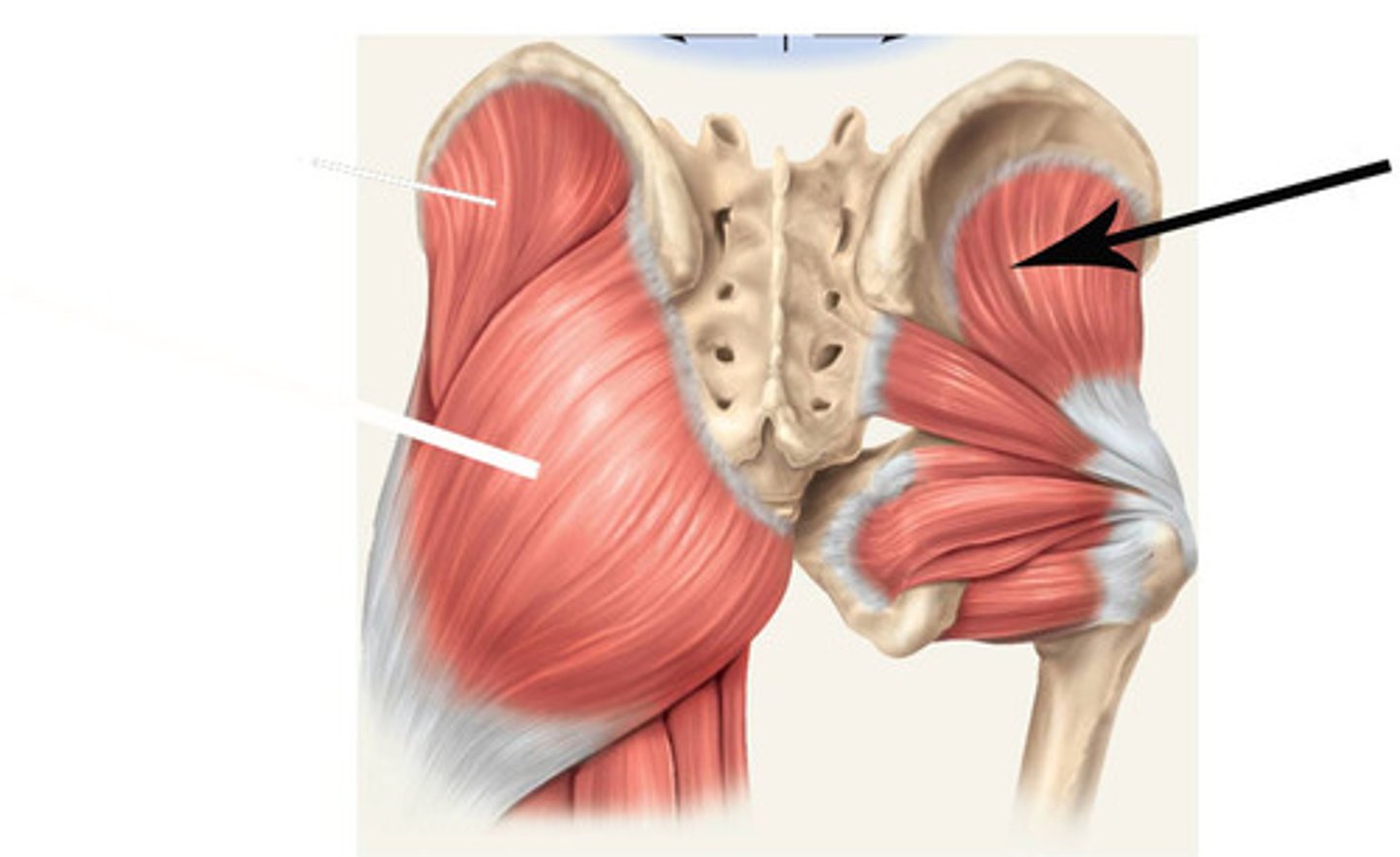
External ilium and greater trochanter
Gluteus minimus attachment (origin and insertion)
Unsteady, waddling
Injury to the gluteus minimus causes what type of gait pattern?
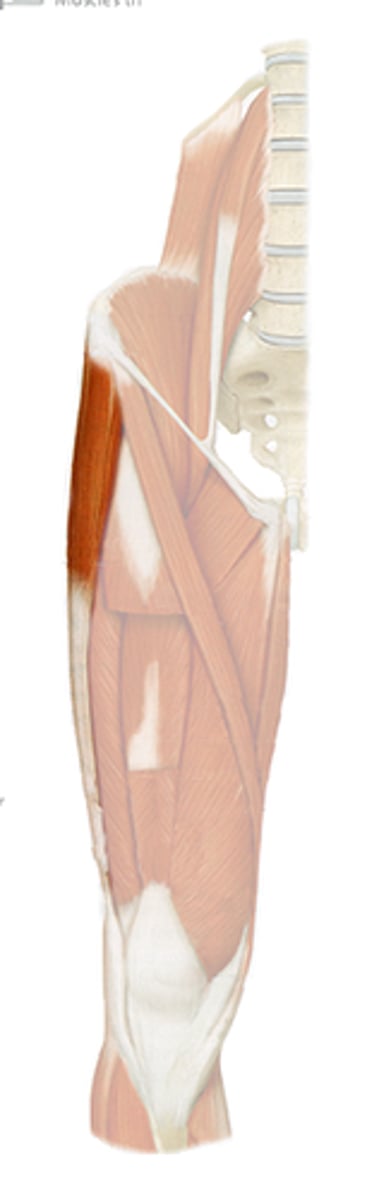
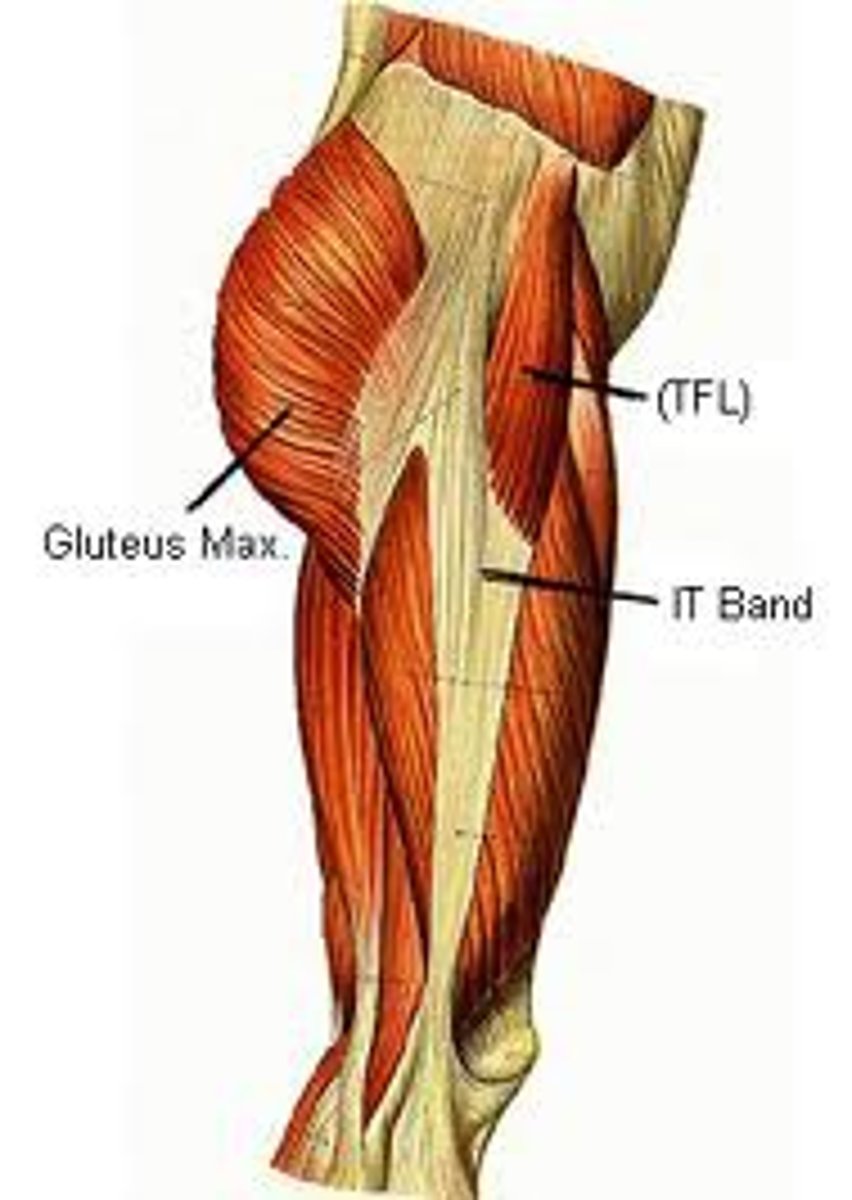
Tensor fasciae latae (TFL)
Anatomy
Anterior iliac crest and iliotibial tract
Tensor fasciae latae attachments (origin and insertion)
Medially rotates
Tensor fasciae latae (TFL) flexes, abducts, and ___ the hip
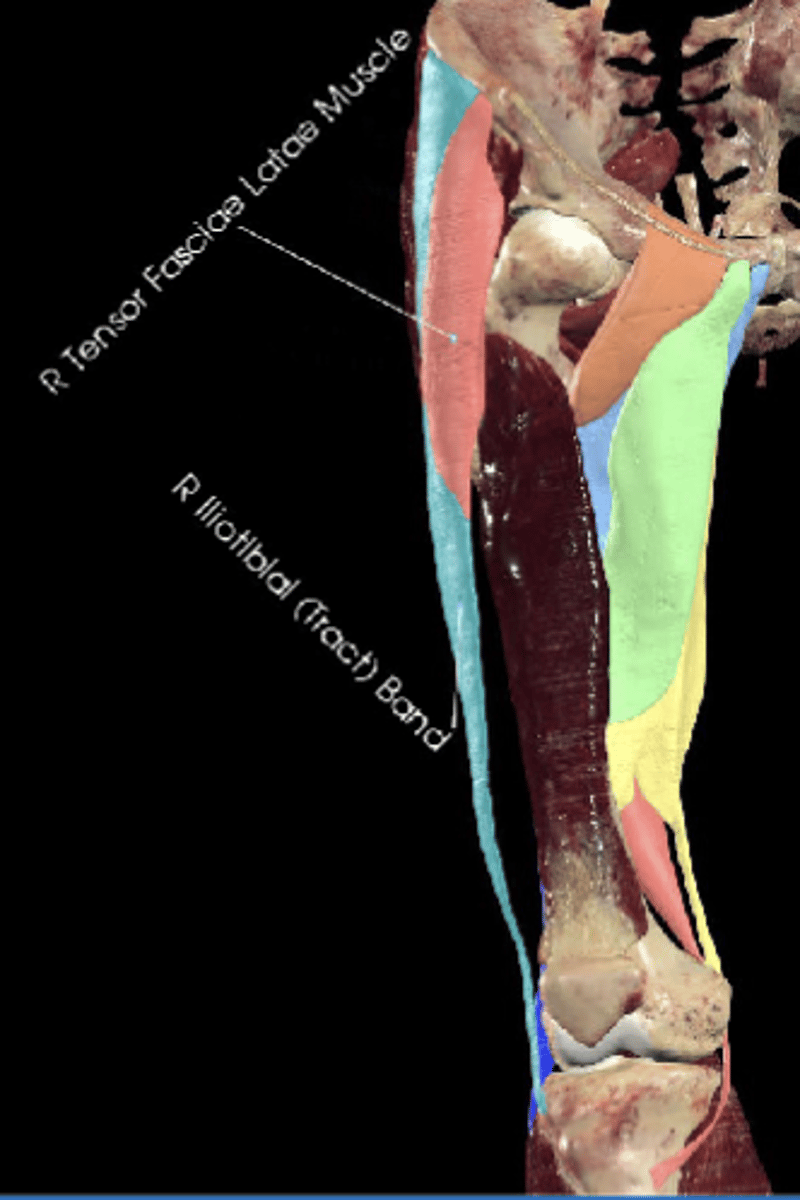
the knee in extension
Tensor fasciae latae tightens the IT band, which stabilizes what?
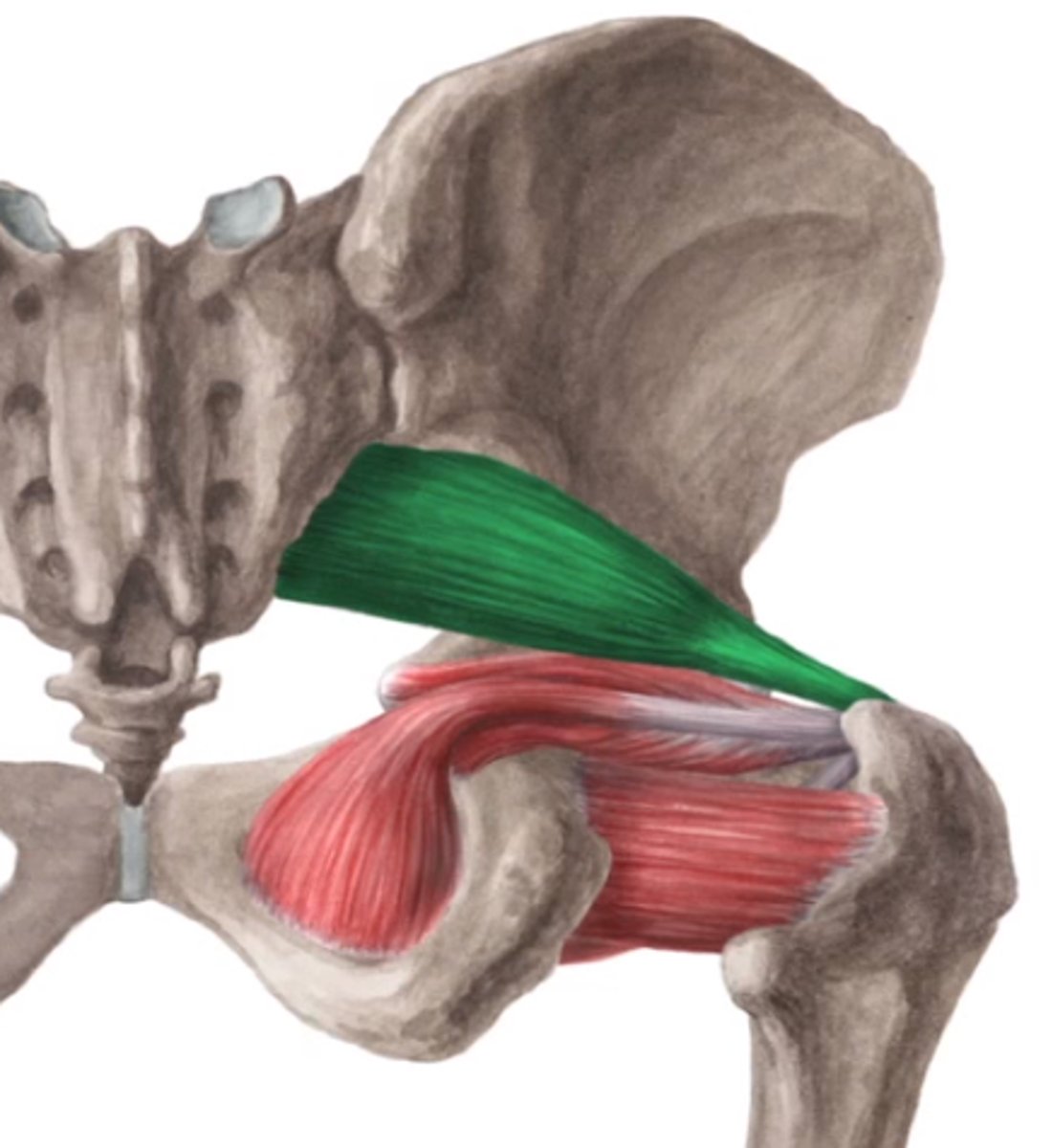
Piriformis, obturator internus, gemelli, quadratus femoris
4 muscles of the deep hip rotators?
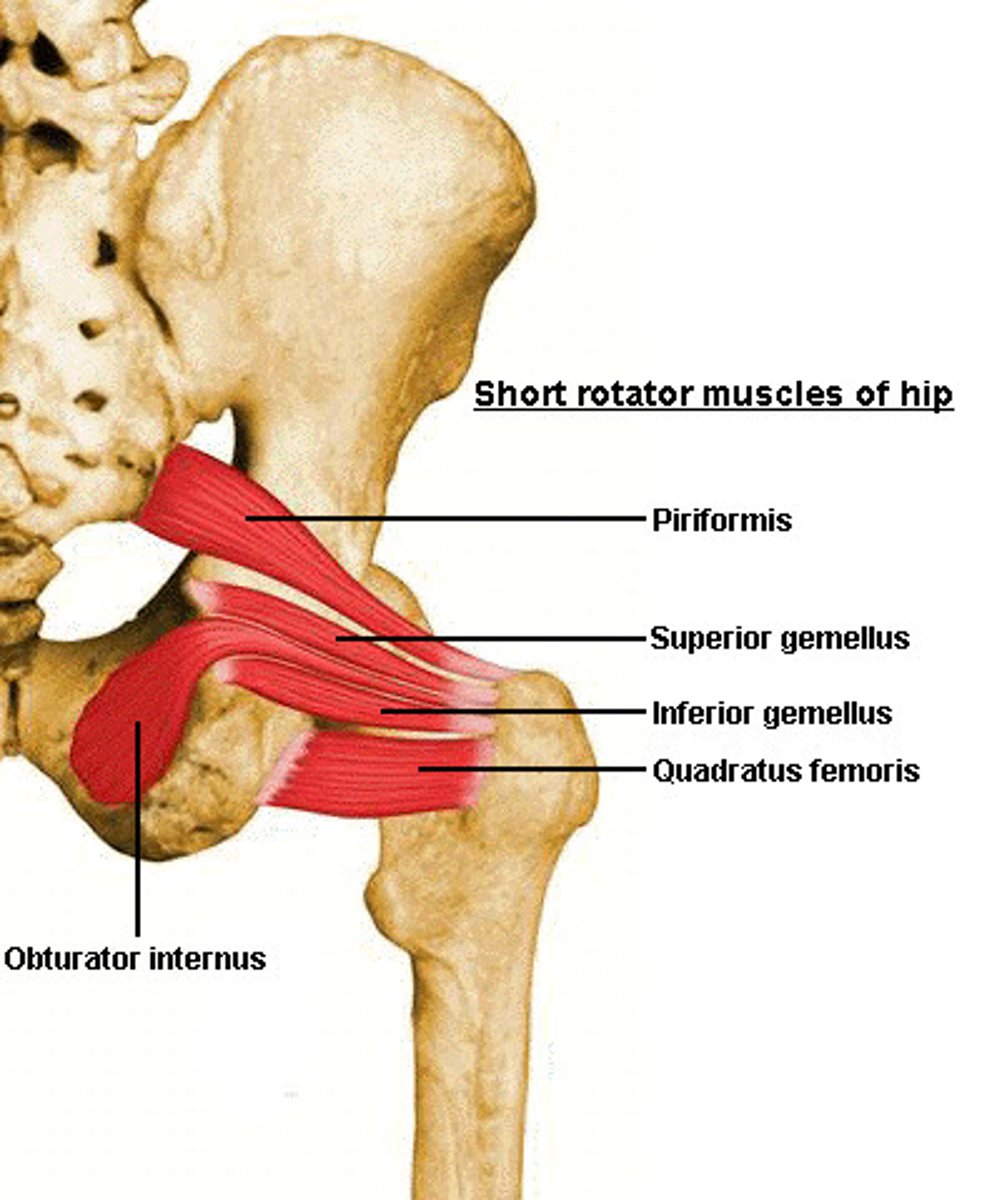
Sacral plexus branches (L4-S2 roots )
Innervation of the deep hip rotators
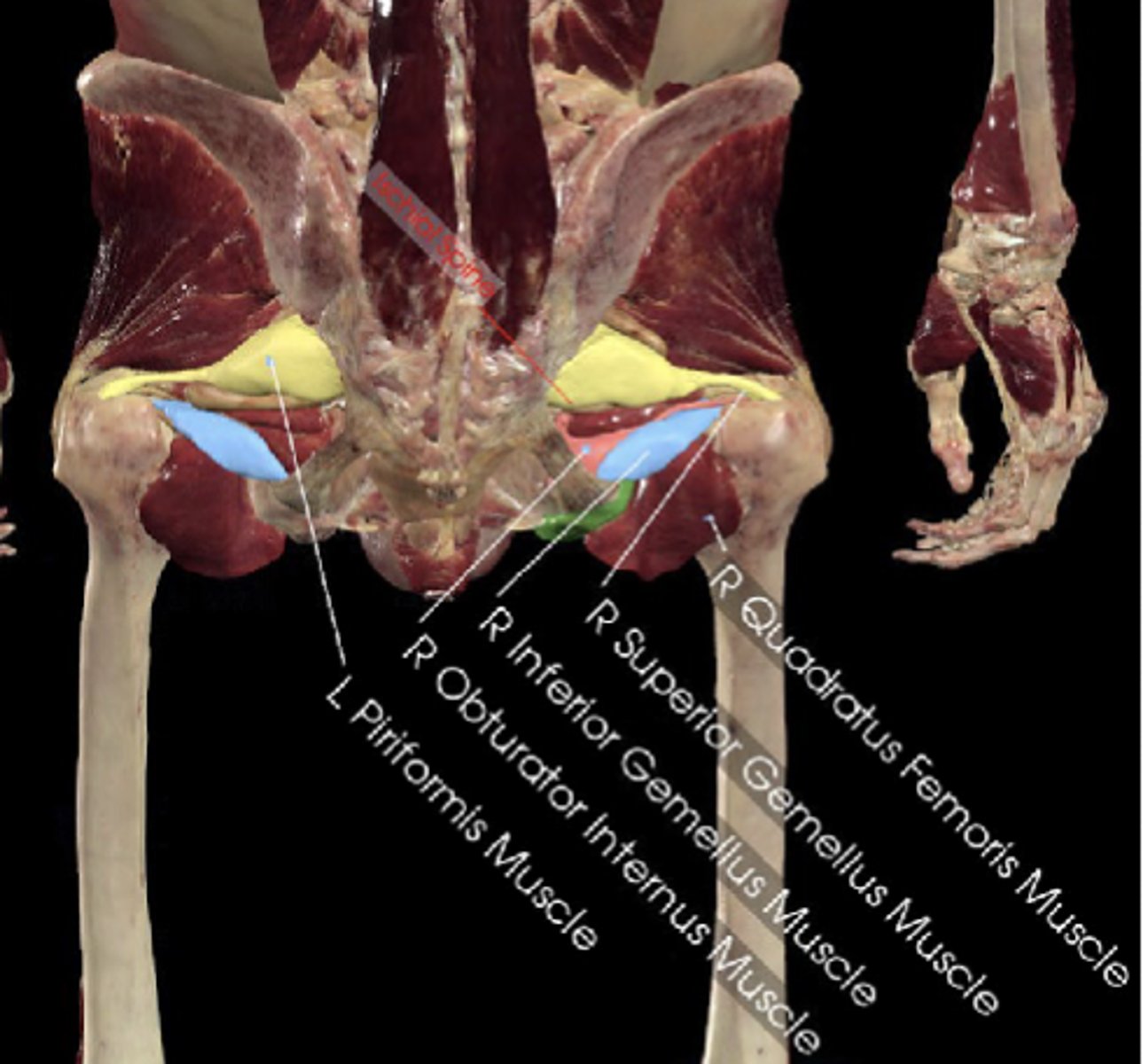
Hip stability in standing
Deep hip rotators laterally rotate and stabilize femoral head which is important for hip ____
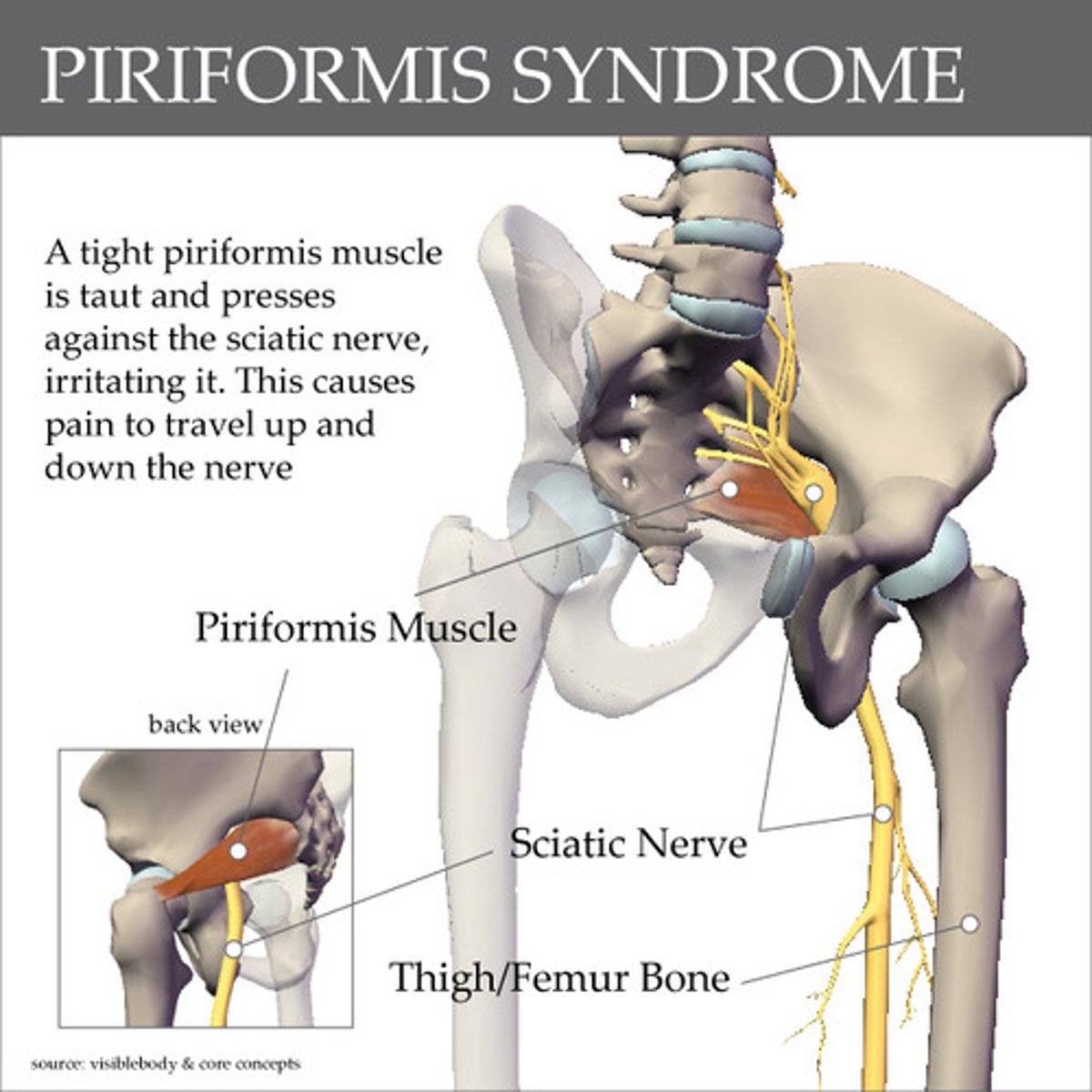
Piriformis
This muscle of the deep hip rotators lies close to the sciatic nerve
Sciatic nerve, causing pain
Piriformis syndrome compresses what nerve?
Ball and socket
What type of join is the hip joint?
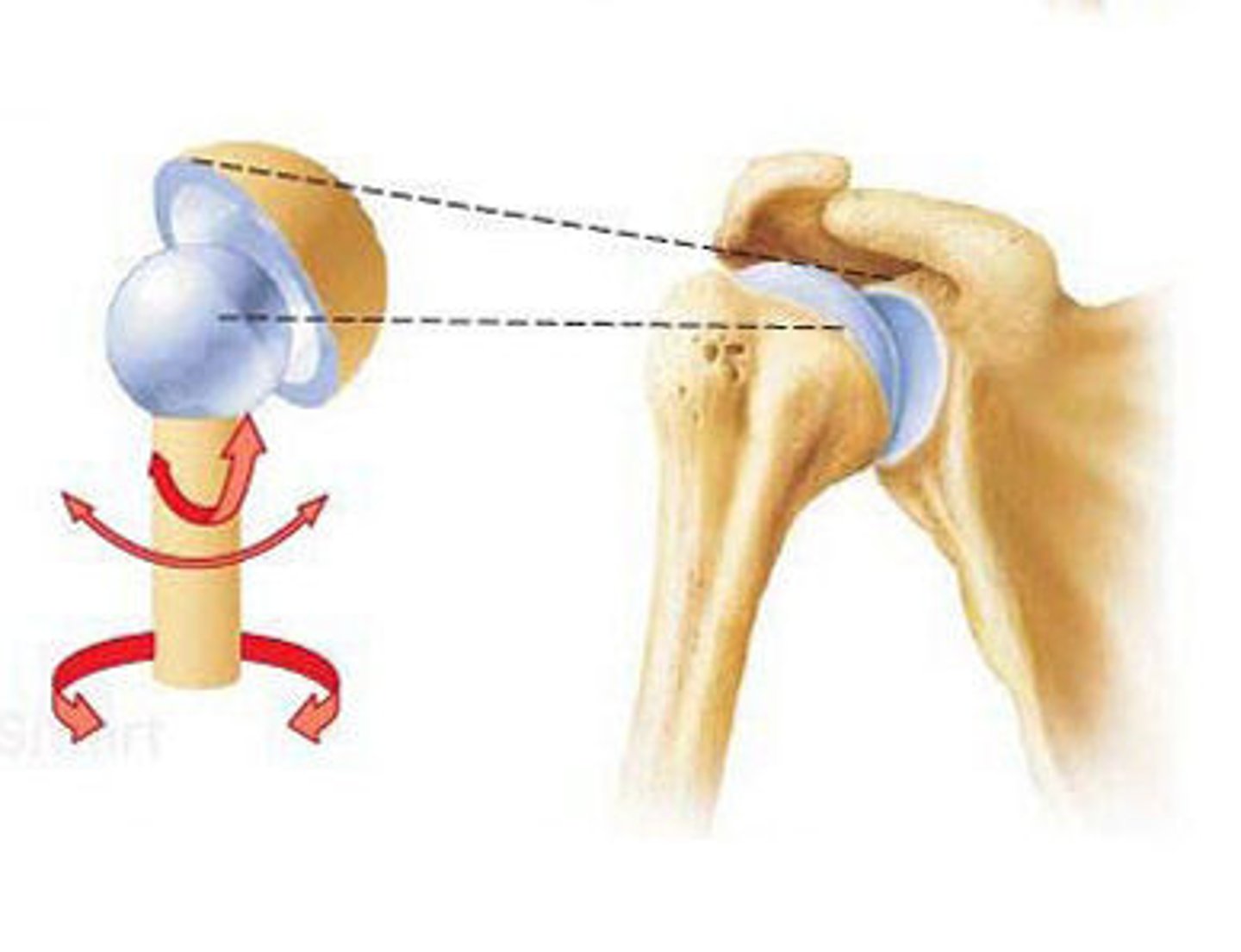
Acetabulum / acetabular labrum
Anatomy shown + femoral head of the femur = ball and socket joint of the hip
Walking, running, climbing; stability with a wide range of motion
The ball-and-socket hip joint supports which activities?
True, since it is weight bearing
T/F: the hip joint is stronger than the shoulder joint
Joint capsule
What attaches around the acetabulum and femoral neck?
Ligament of the head of the femur
Anatomy which carries blood supply to the femoral head
Synovial membrane
Lines the capsule and secretes fluid
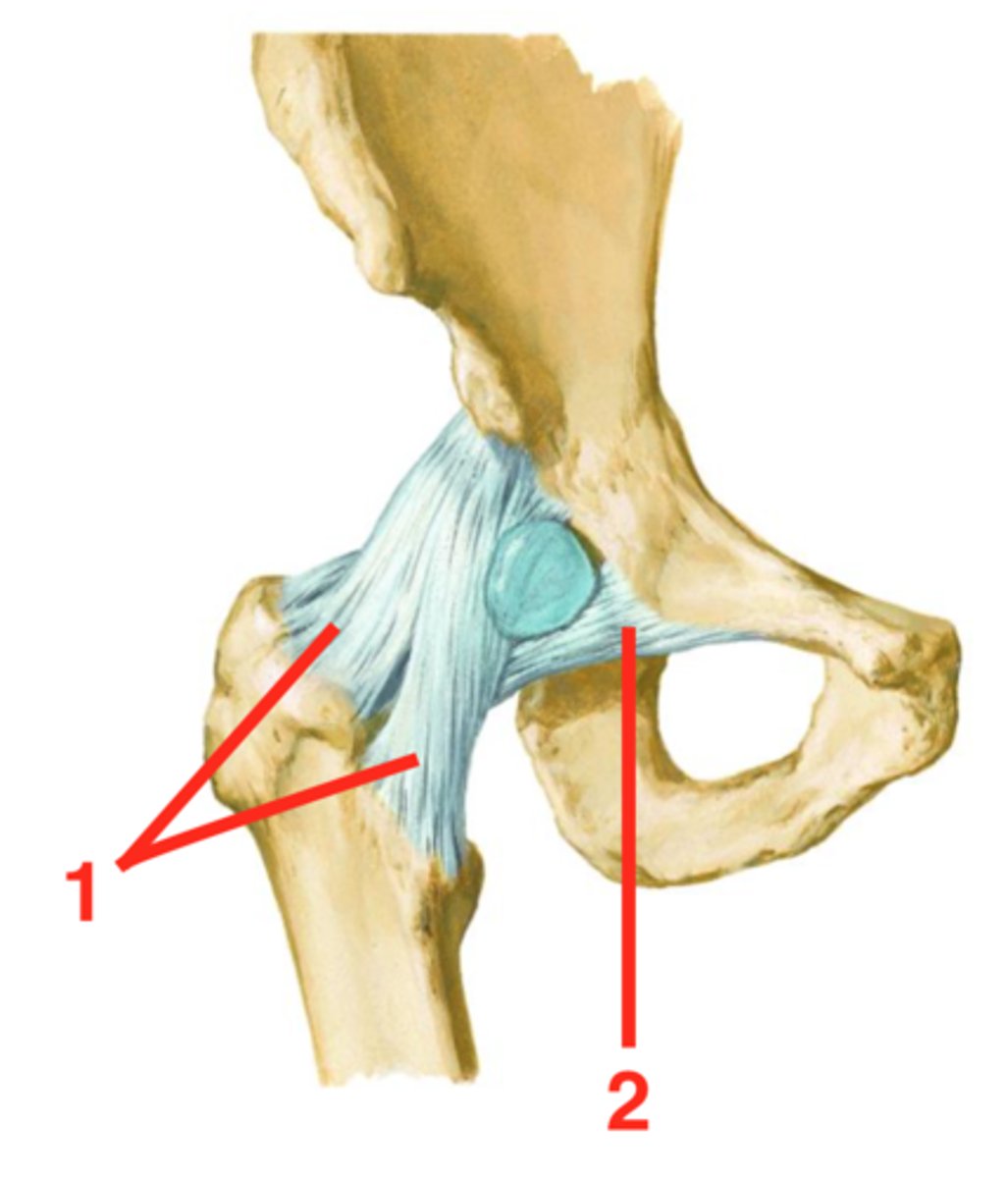
Iliofemoral ligament
Strongest hip ligament which prevents hyperextension of the hip (A)
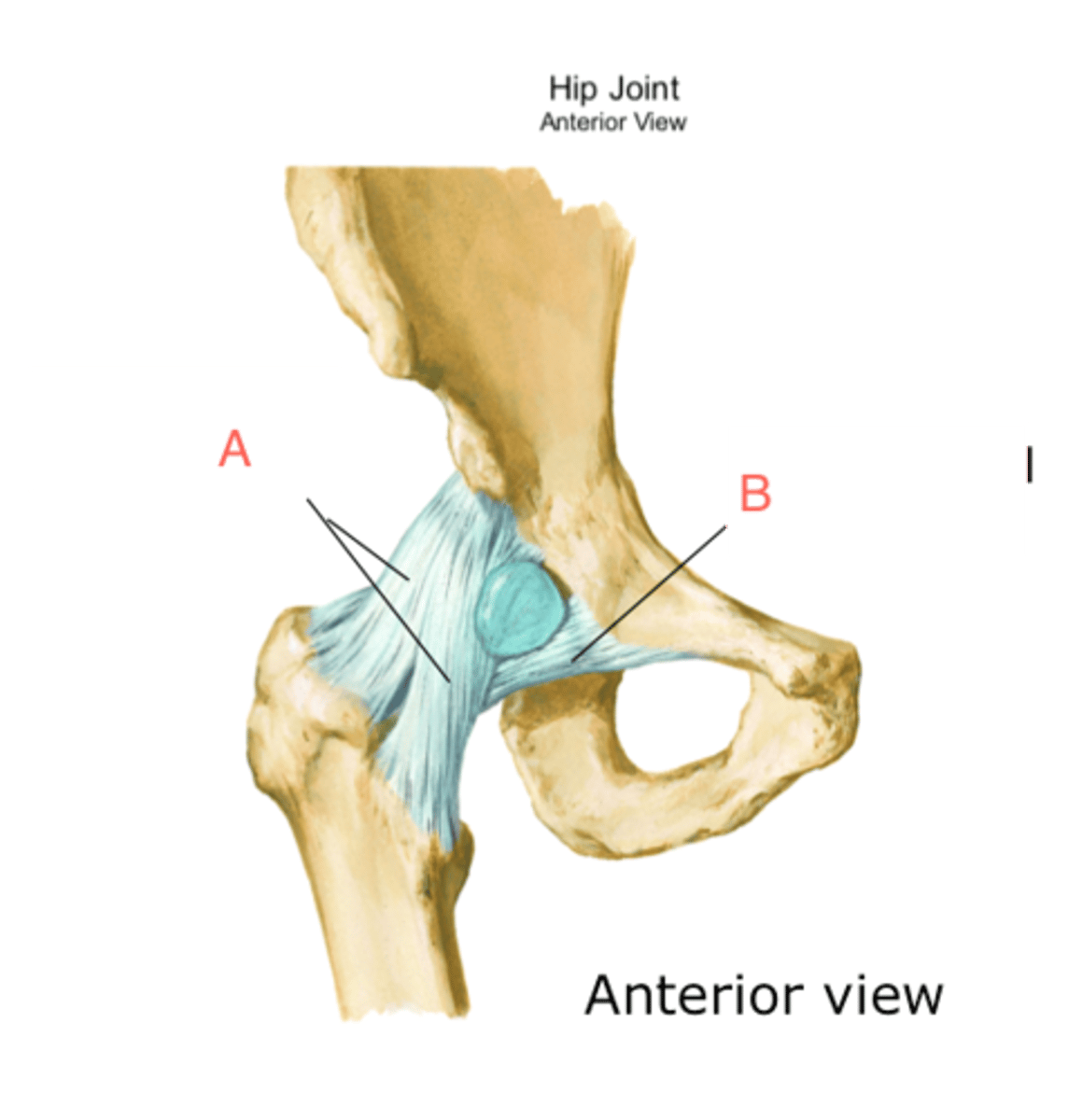
Pubofemoral ligament
Hip ligament which limits excessive abduction (2)
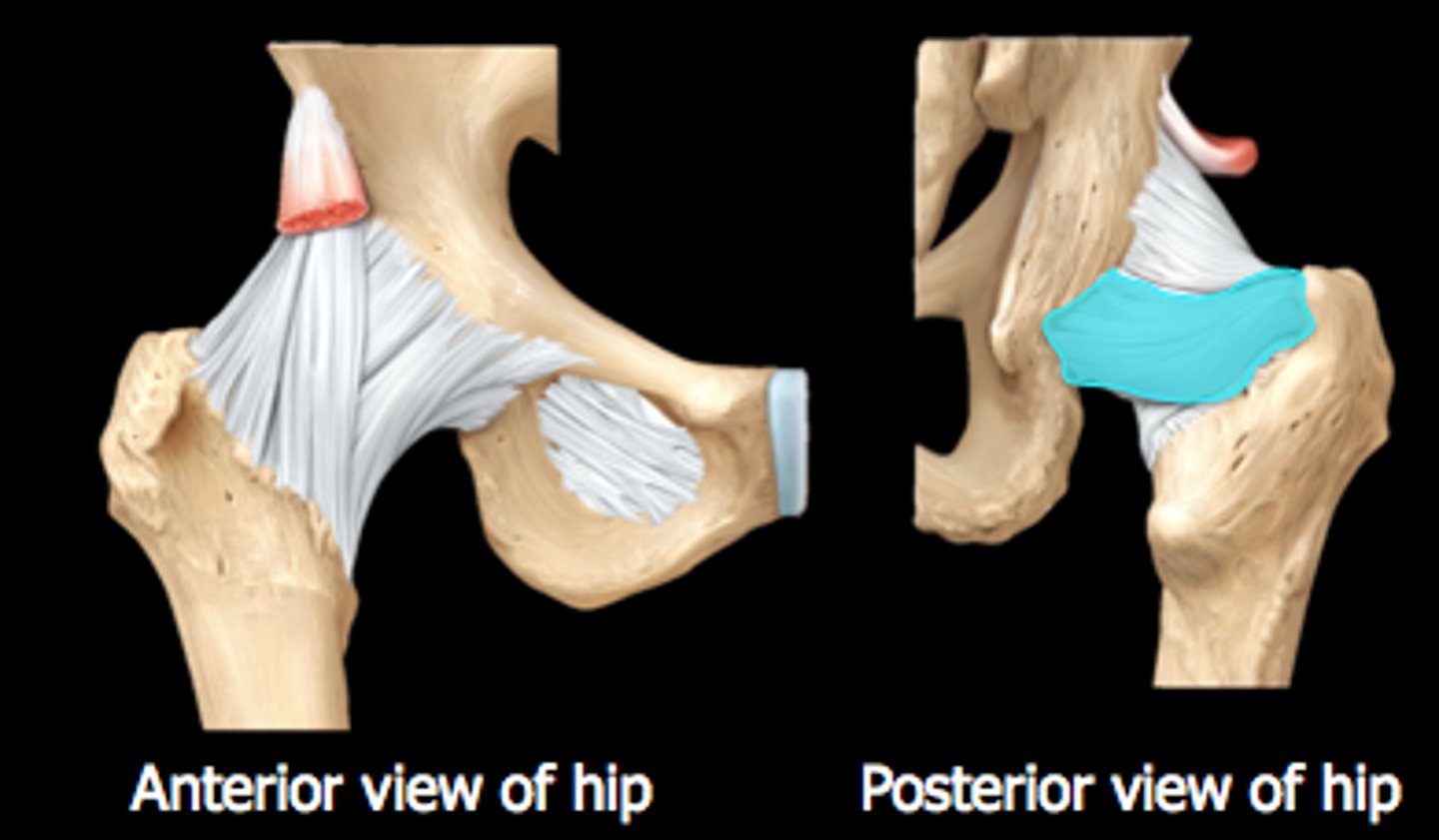
Ischiofemoral ligament
Hip ligament which spirals posteriorly, limits internal rotation (only seen on posterior view)
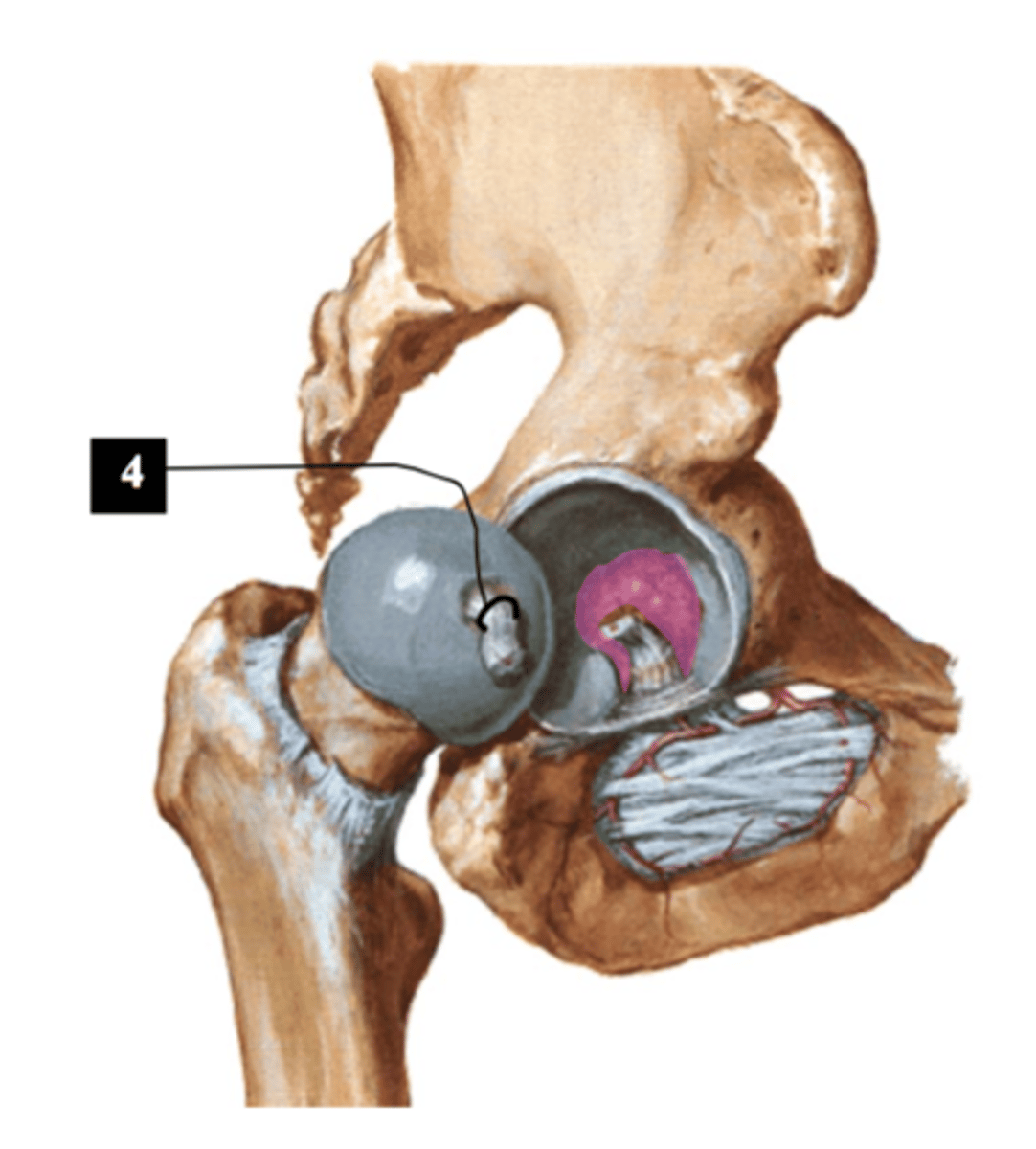
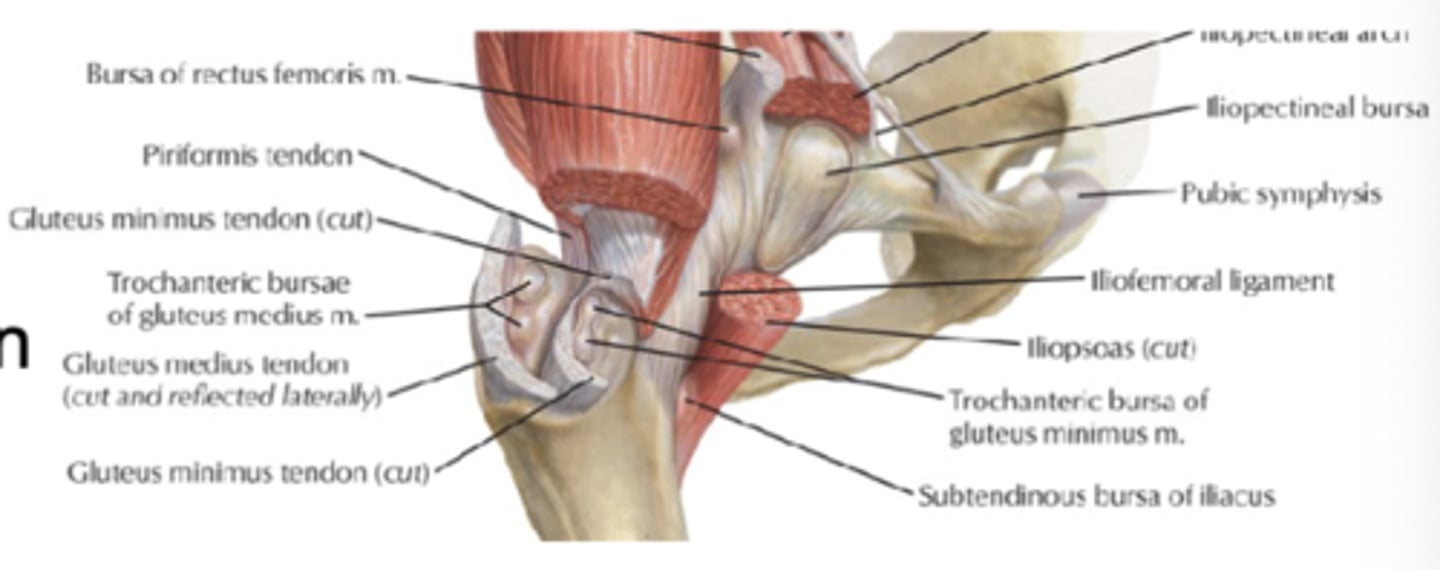
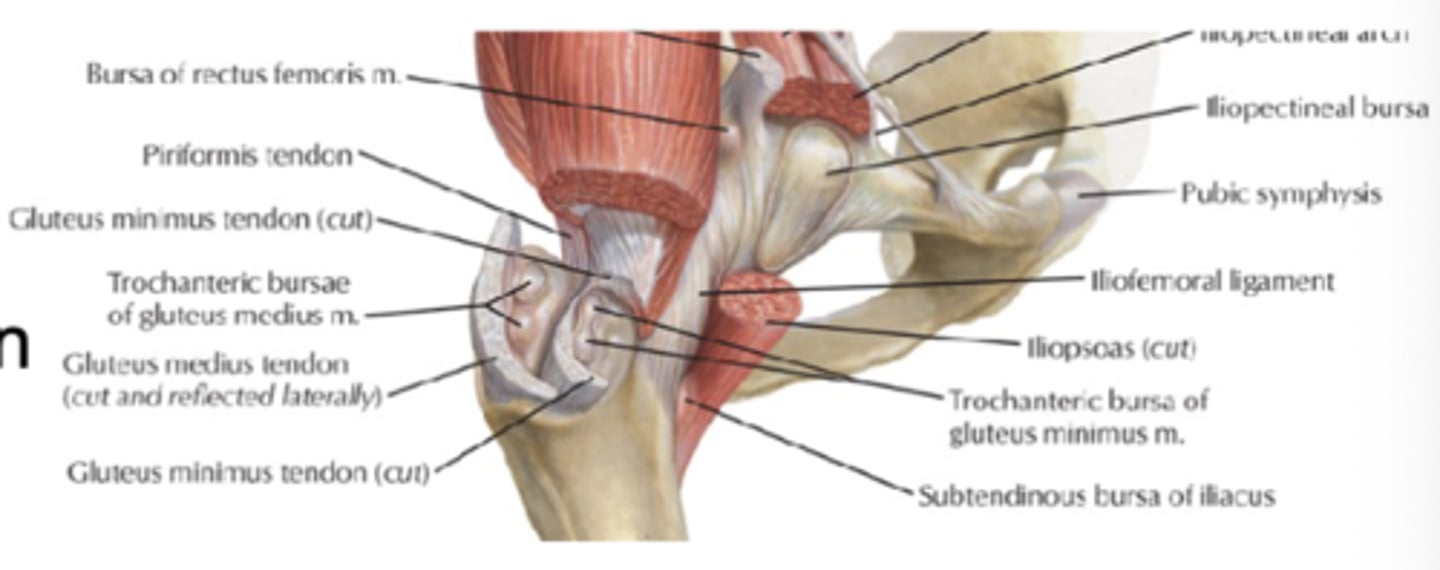
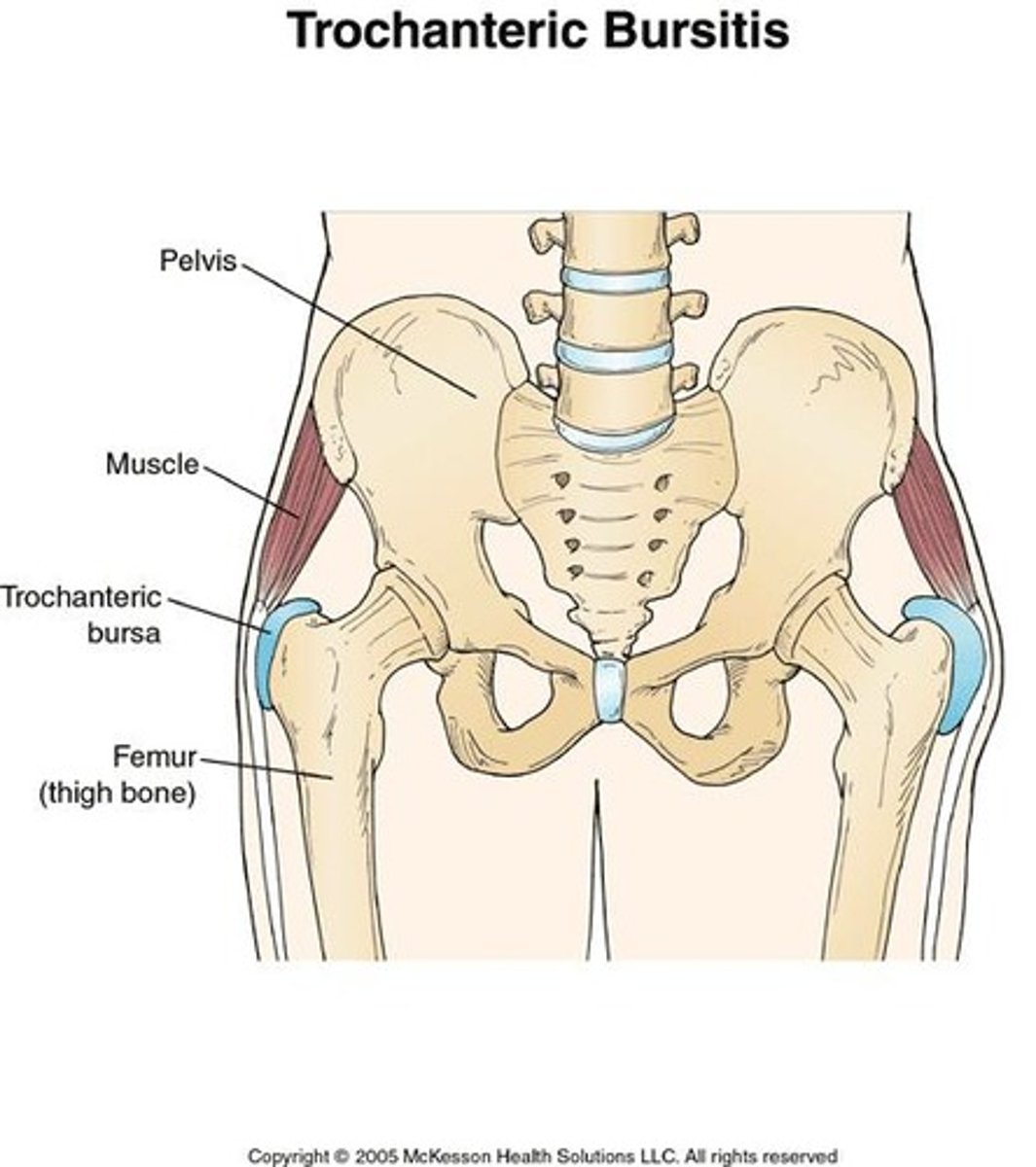
Trochanteric bursa
Bursae (fluid sacs around joints) located between gluteus maximus and greater trochanter
Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy
Ischial bursa/ischiogluteal bursa
Bursae (fluid sacs around joints) located between gluteus maximus and ischial tuberosity
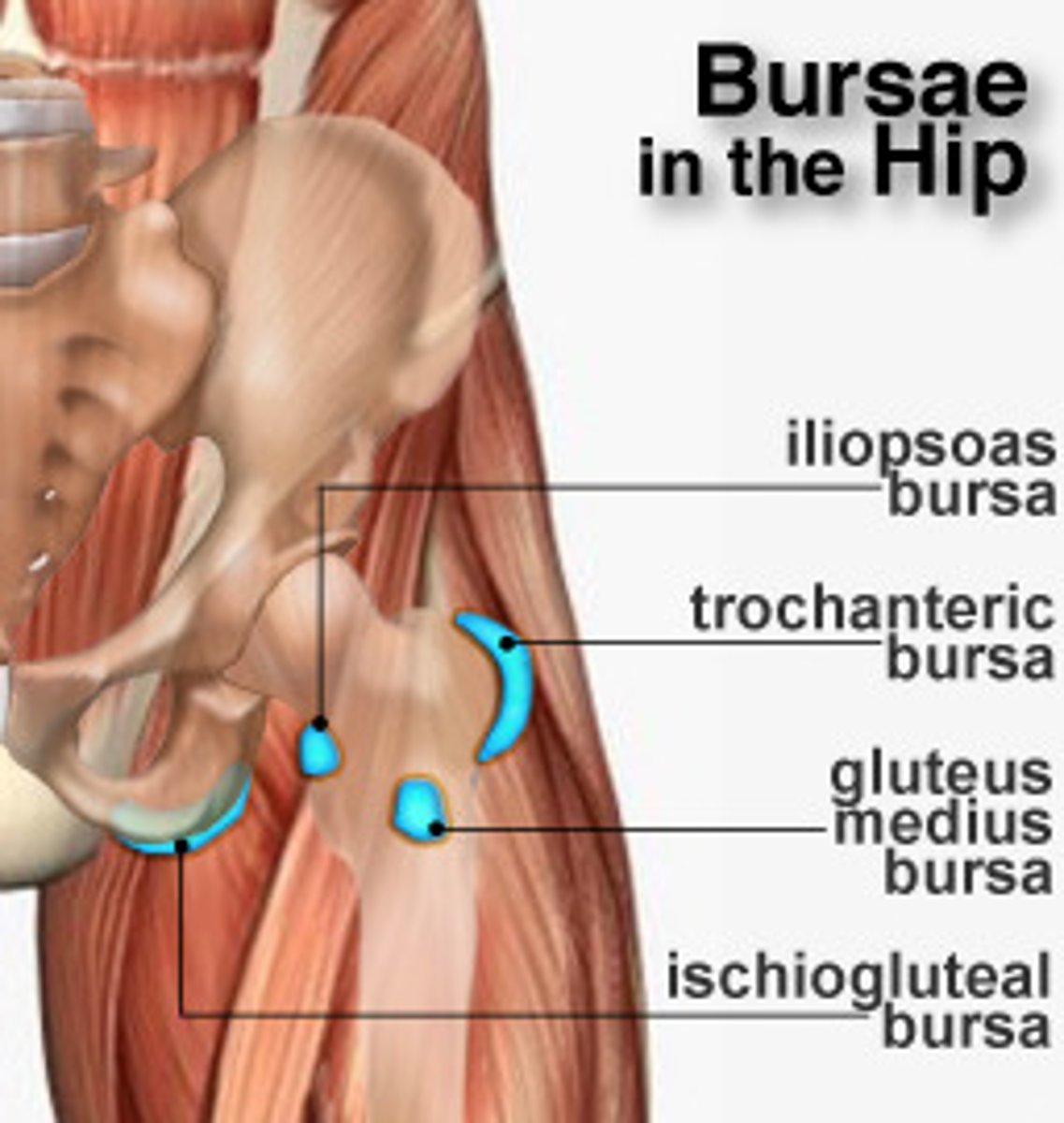
Iliopectinal bursa/iliopsoas bursa
Anatomy which is near the iliosposas tendon and hip joint
Bursitis syndromes
Common in runners and older adults
Inflammation of bursae (fluid sacs around joints) results in ____ which is common in?
Posterior
Which part of the hip is most commonly dislocated?
Avascular necrosis (loss of blood supply to bone)
Femoral neck fractures are common in elderly, increasing risk of?
Abnormal gait
Developmental dysplasia of the hip leads to?
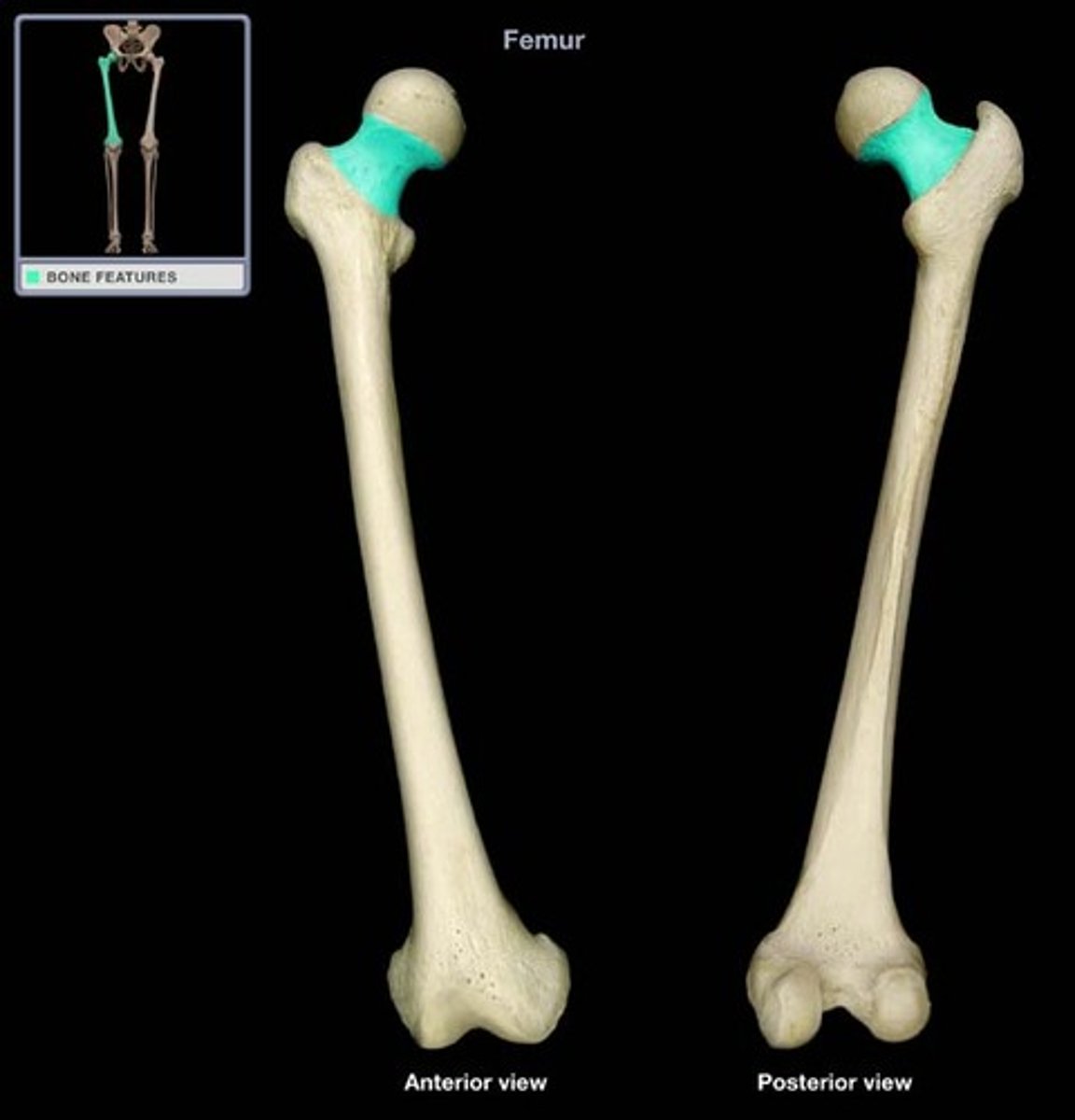
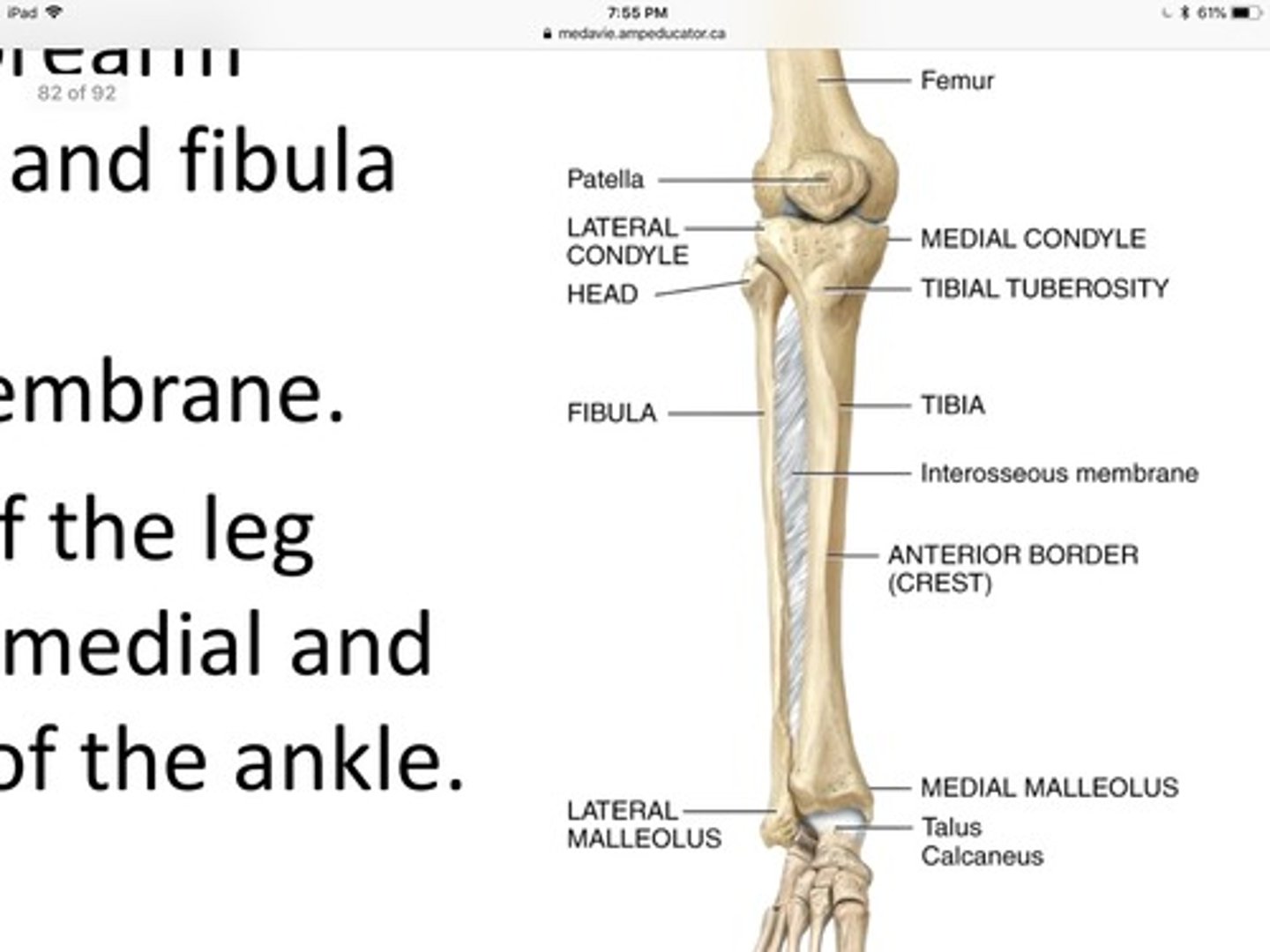
Femur
Longest, strongest bone in the body
Medial epicondyle (knee joint)
Anatomy
Knee joint
The femur, tibia, and patella are connect by the?
Femoral nerve
Which nerve innervates the anterior thigh muscles?
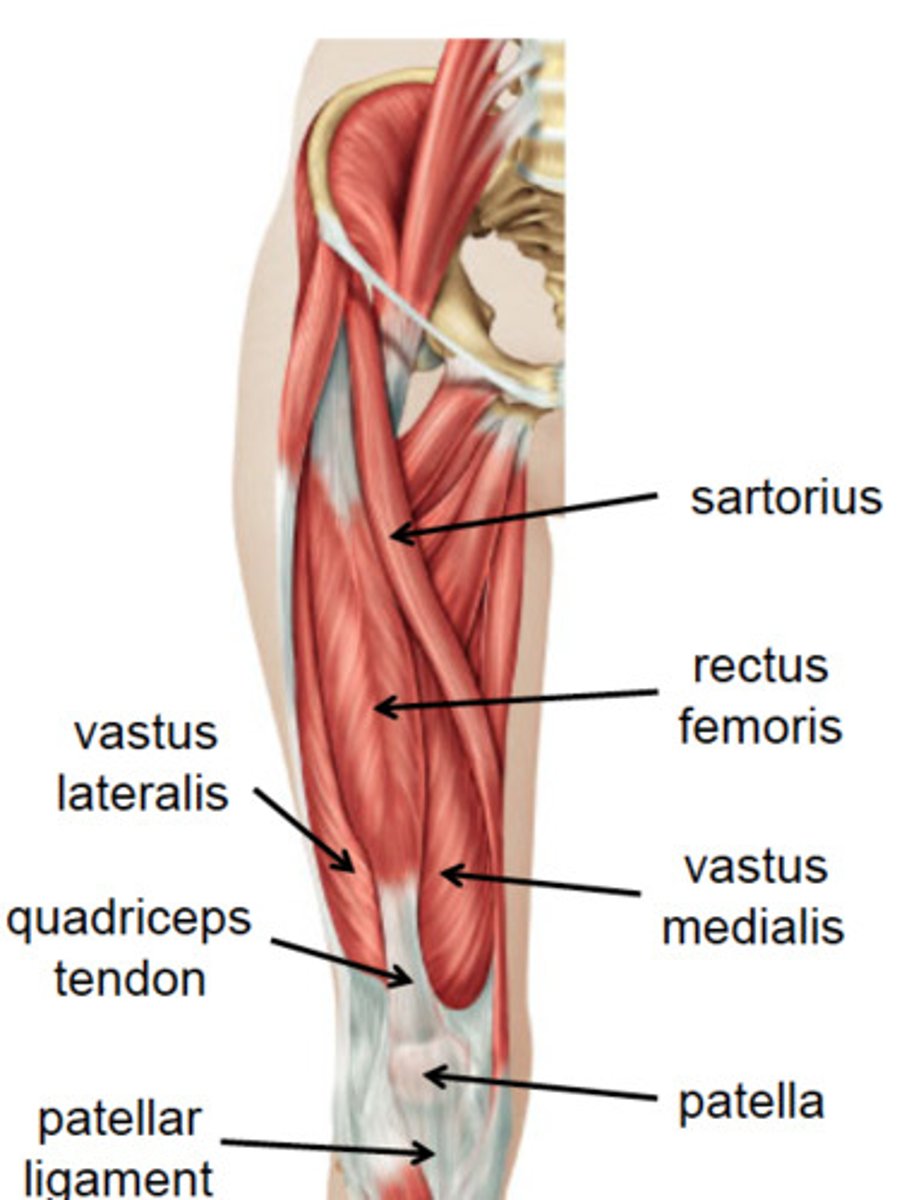
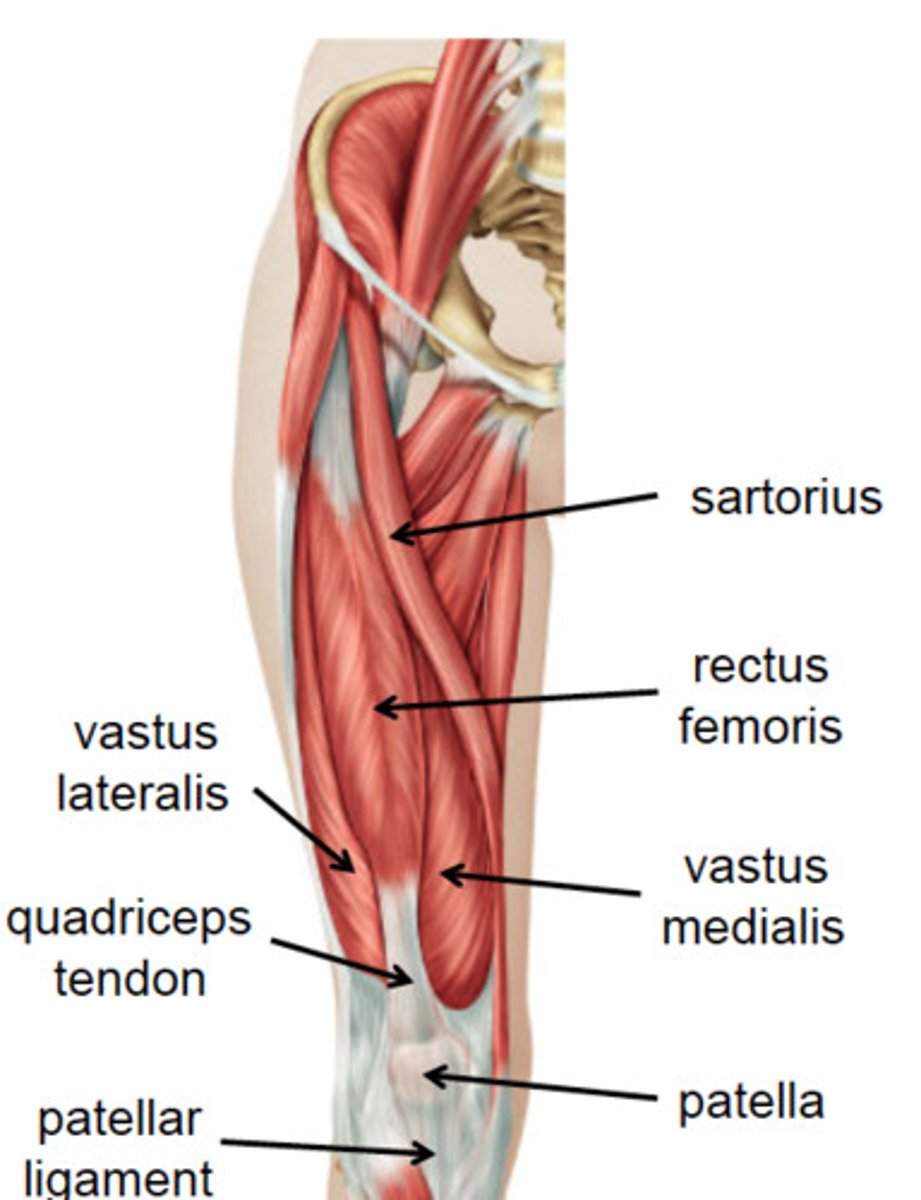
Sartorius
Anterior thigh anatomy
Tailor's muscle
The sartorius is also know as the ___ muscle for cross-legged sitting
Anterior superior iliac spine
Medial tibia (pes anserinus)
Sartorius attachments (origin and insertion)
Flexes hip, flexes knee, laterally rotates thigh
Action of sartorius muscles (3)
Rectus femoris
Anterior thigh anatomy (between the pink and green muscles)
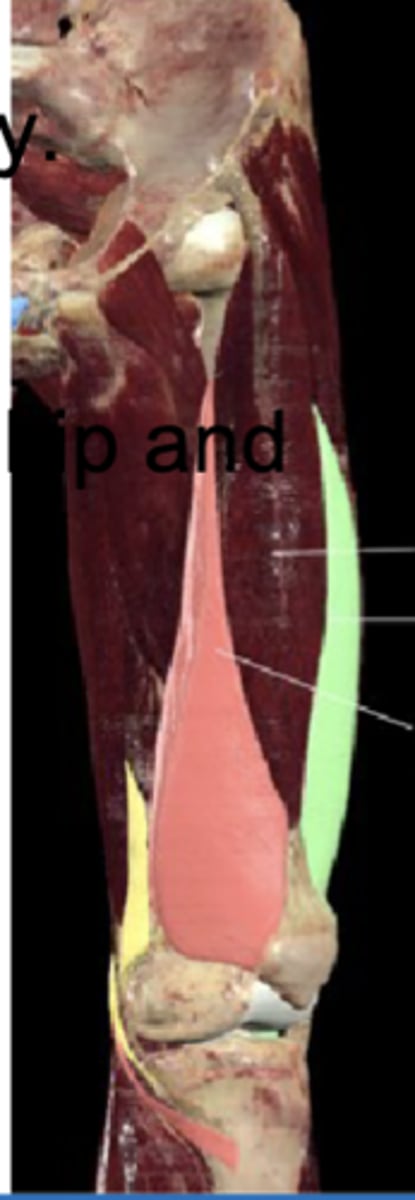
Anterior inferior iliac spine
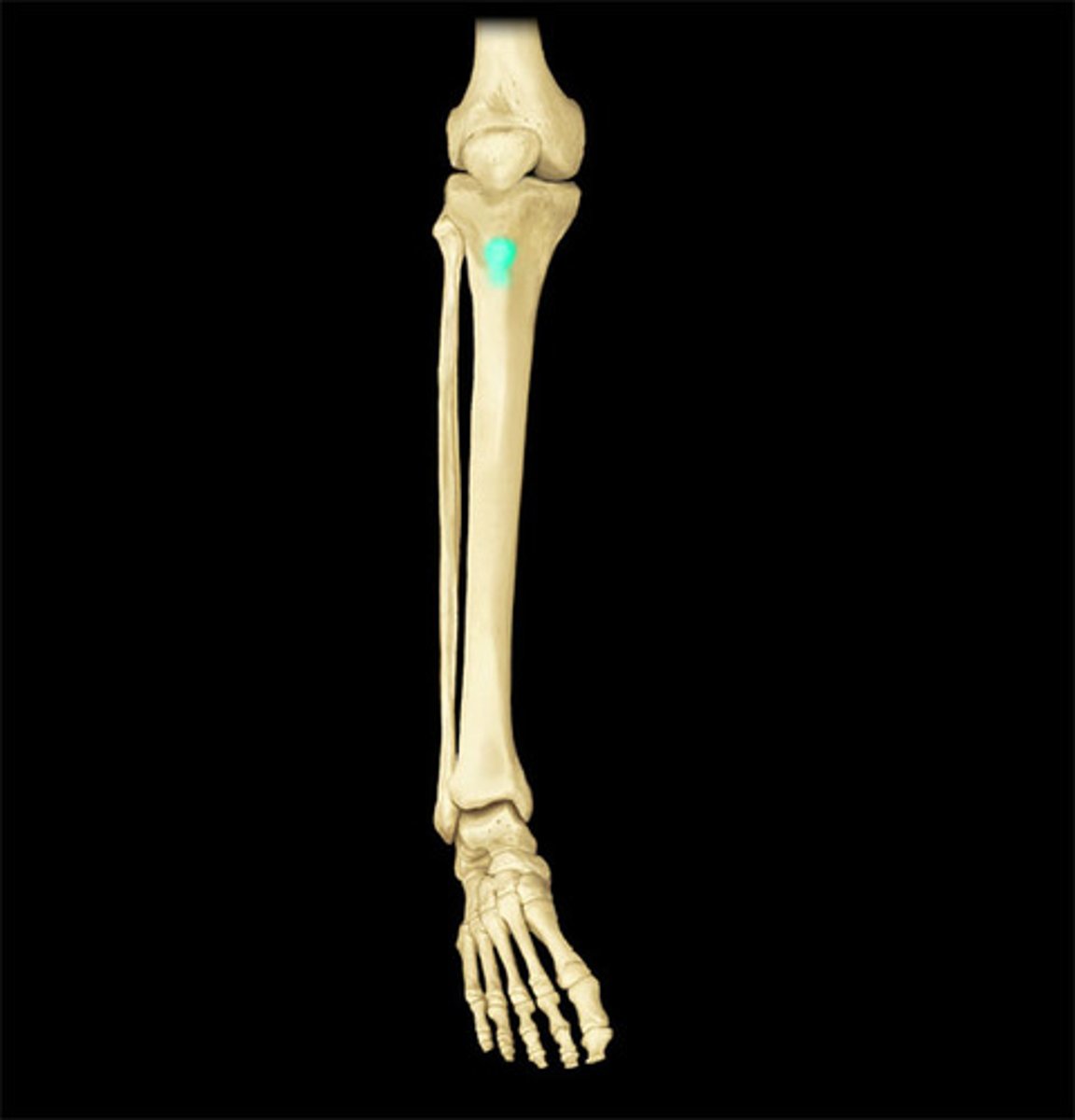
Tibial tuberosity (shown in photo)
Rectus femoris attachments (origin and insertion (photo))
Knee joint (kicking)
Rectus femoris is responsible for hip flexion and extension of?
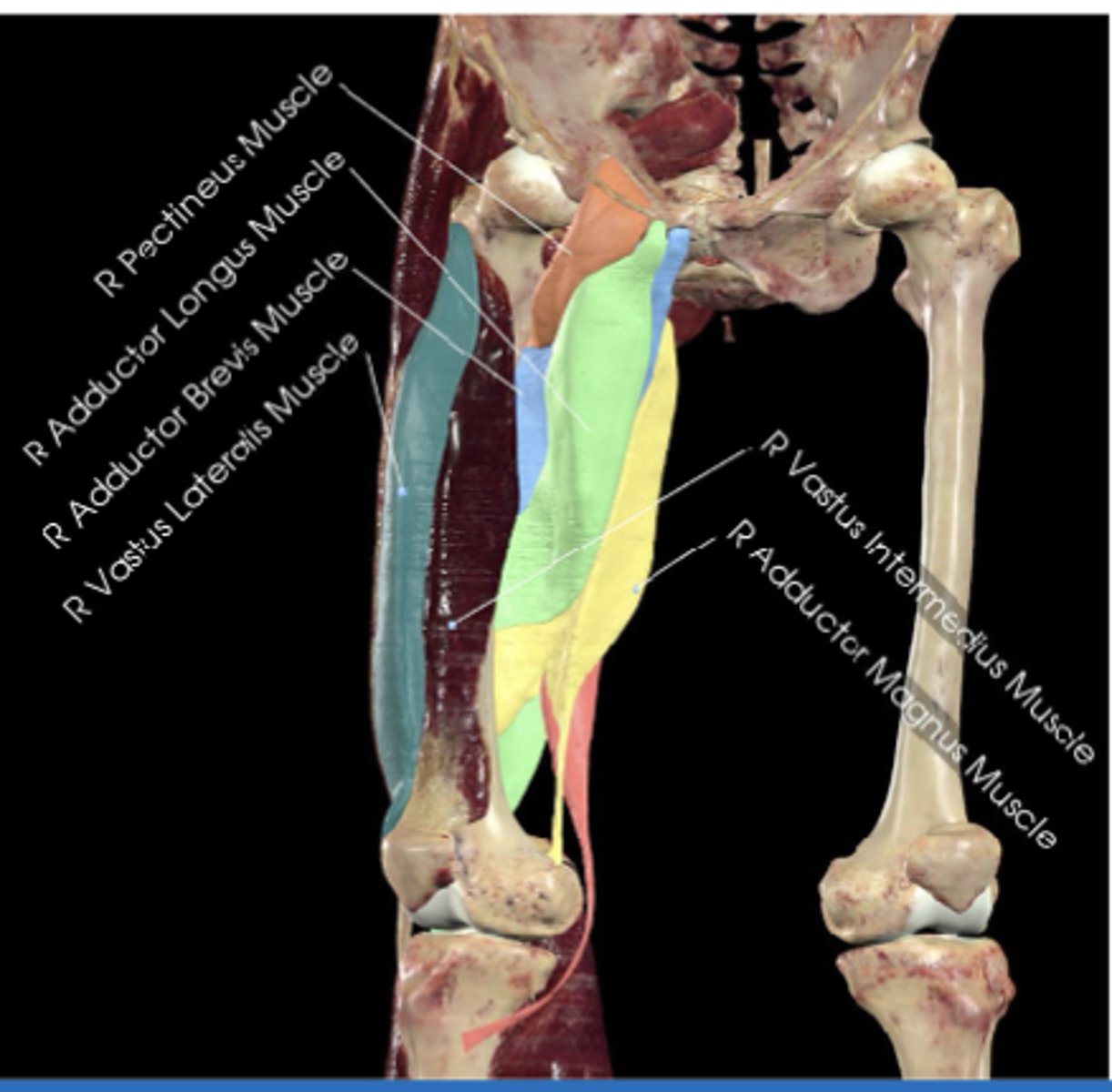
vastus lateralis
Anterior thigh anatomy (green)
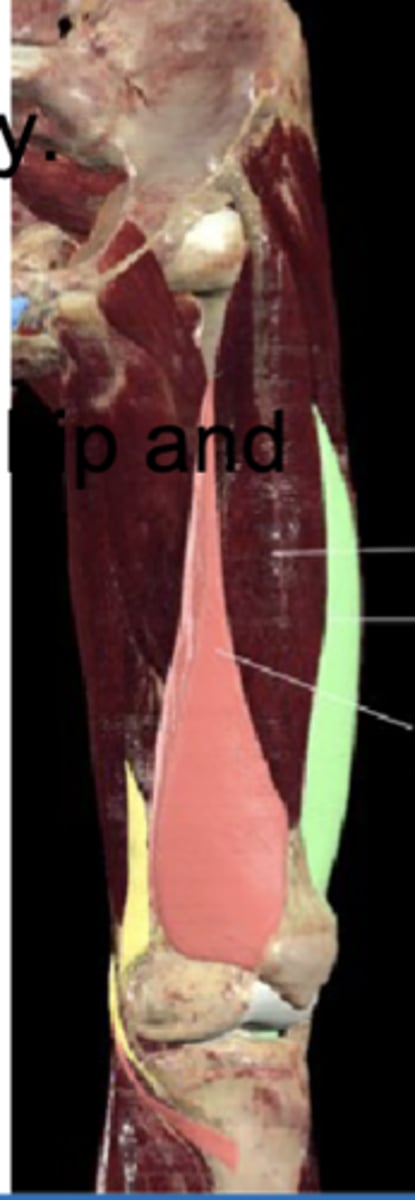
Greater trochanter
Tibial tuberosity
Vastus lateralis attachments (origin and insertion)
Patella
Vastus lateralis extends knee and stabilizes ___ laterally?
Vastus lateralis
Which quadricep muscle is largest?
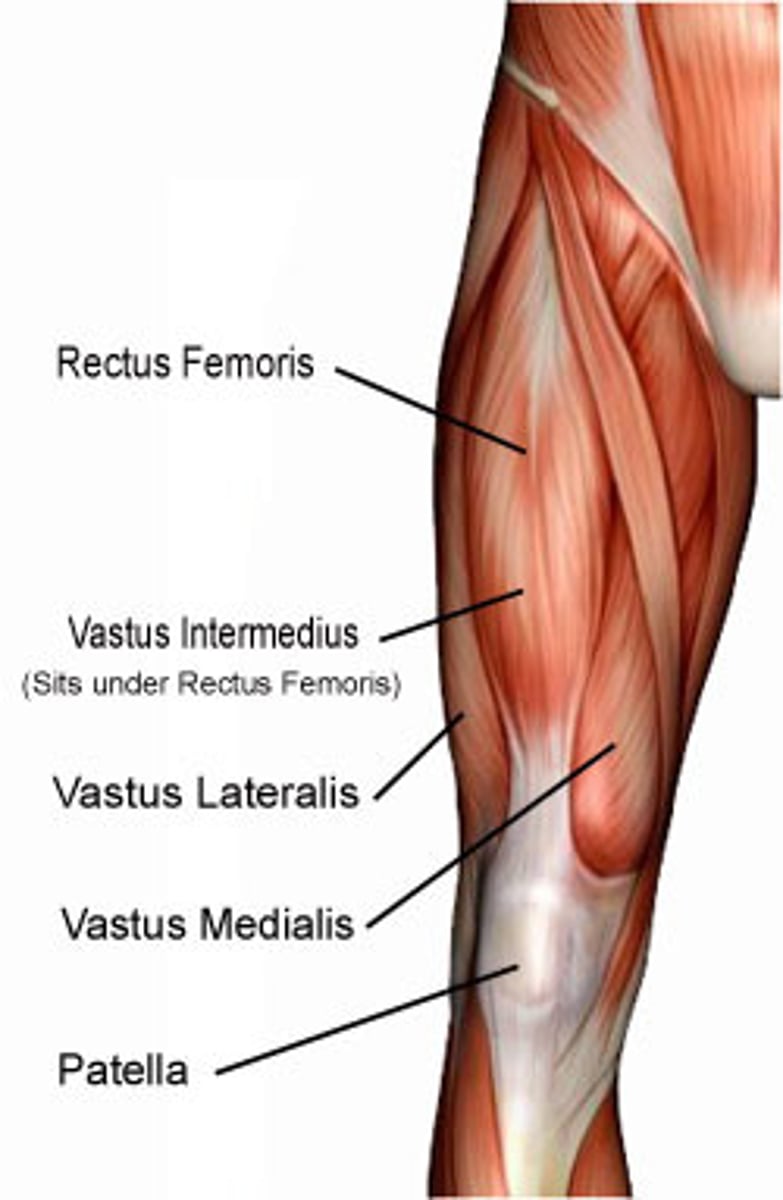
vasus medialis
Anterior thigh anatomy (pink)
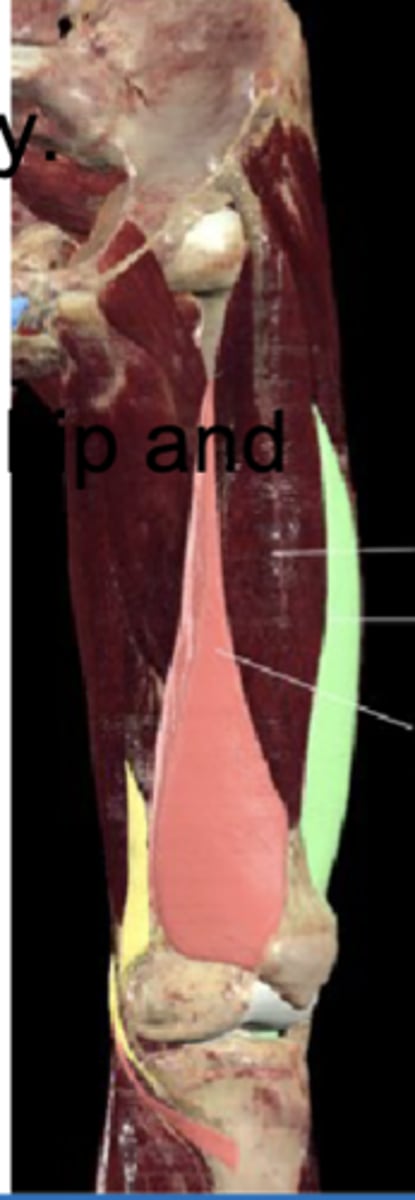
Linea aspera
Tibial tuberosity
Vastus medialis attachments (origin and insertion)
Medially
Action of the vastus medialis includes knee extension and stabilizing the patella ___
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Weakness of the vastus medialis causes ___ syndrome
Vastus lateralis
IM injection for infants
Obturator nerve
Femoral nerve
The medial thigh (except pectineus) is innervated by which nerve? What is the pectineus muscle innervated by?
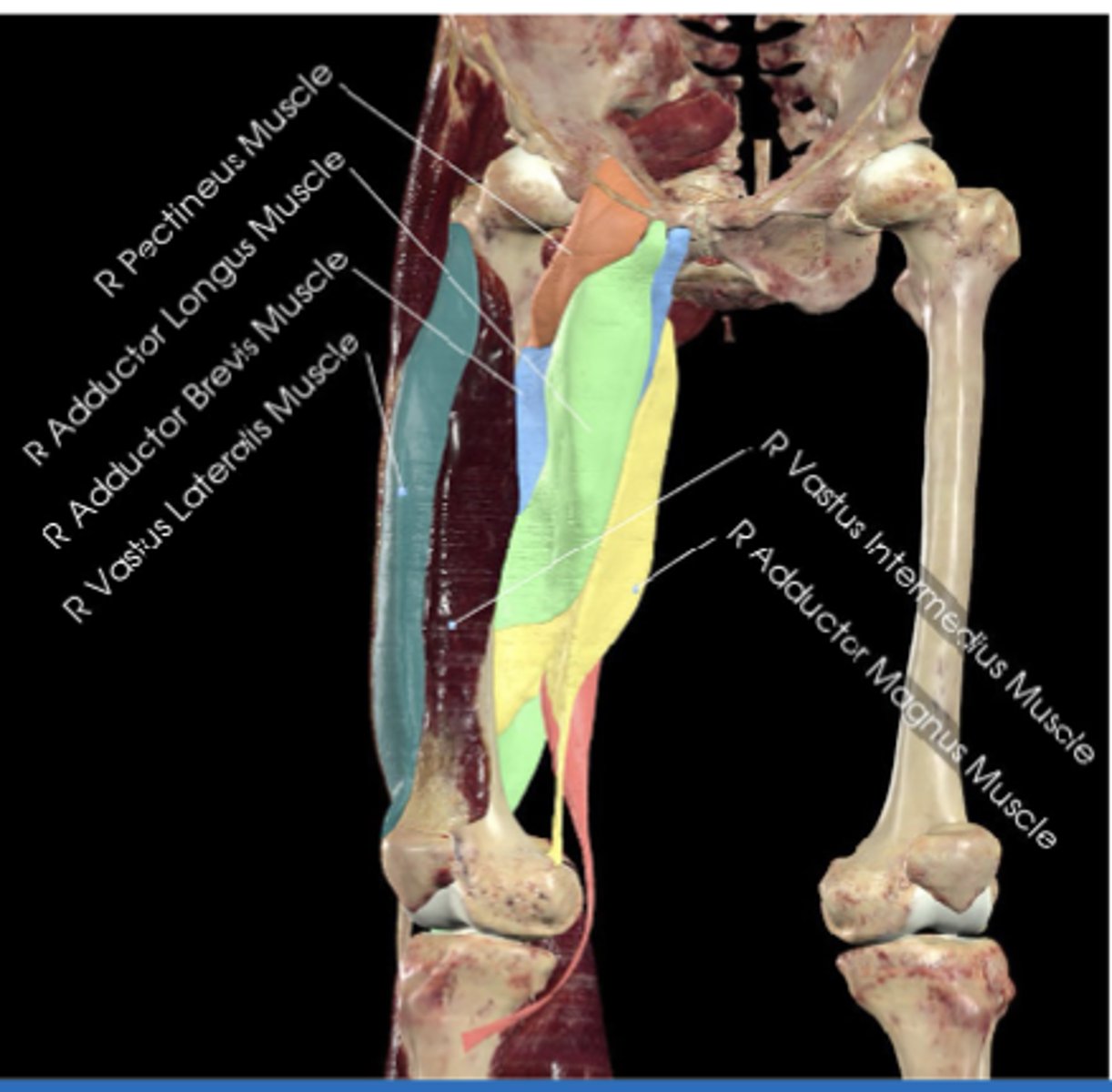
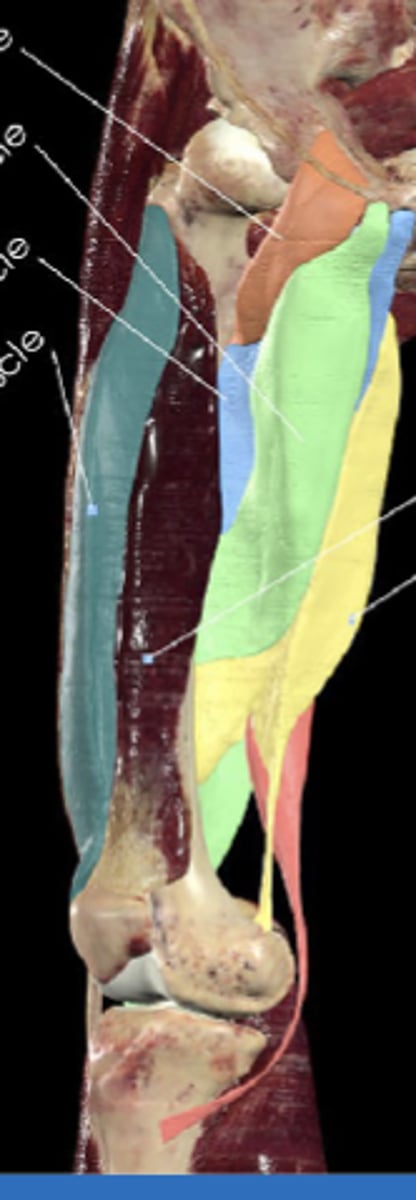
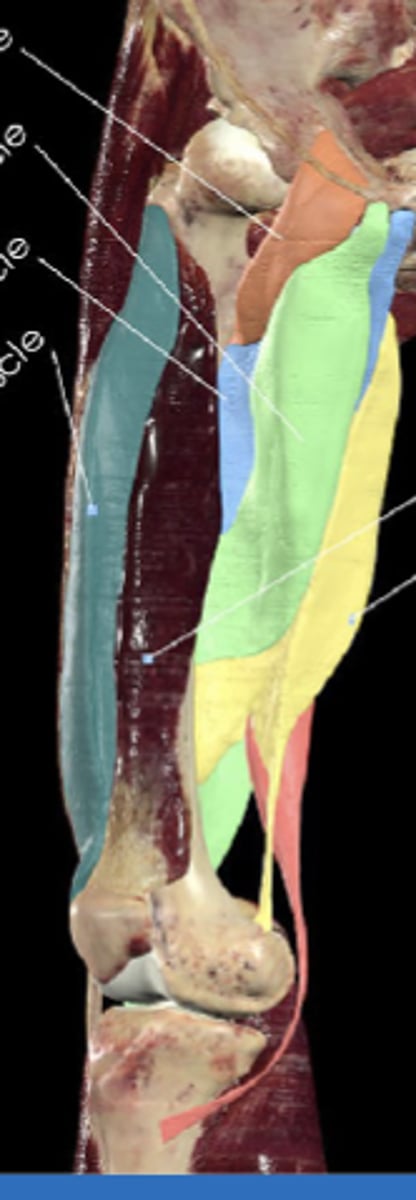
Pectineus muscle
Adducts and flexes thigh at hip joint
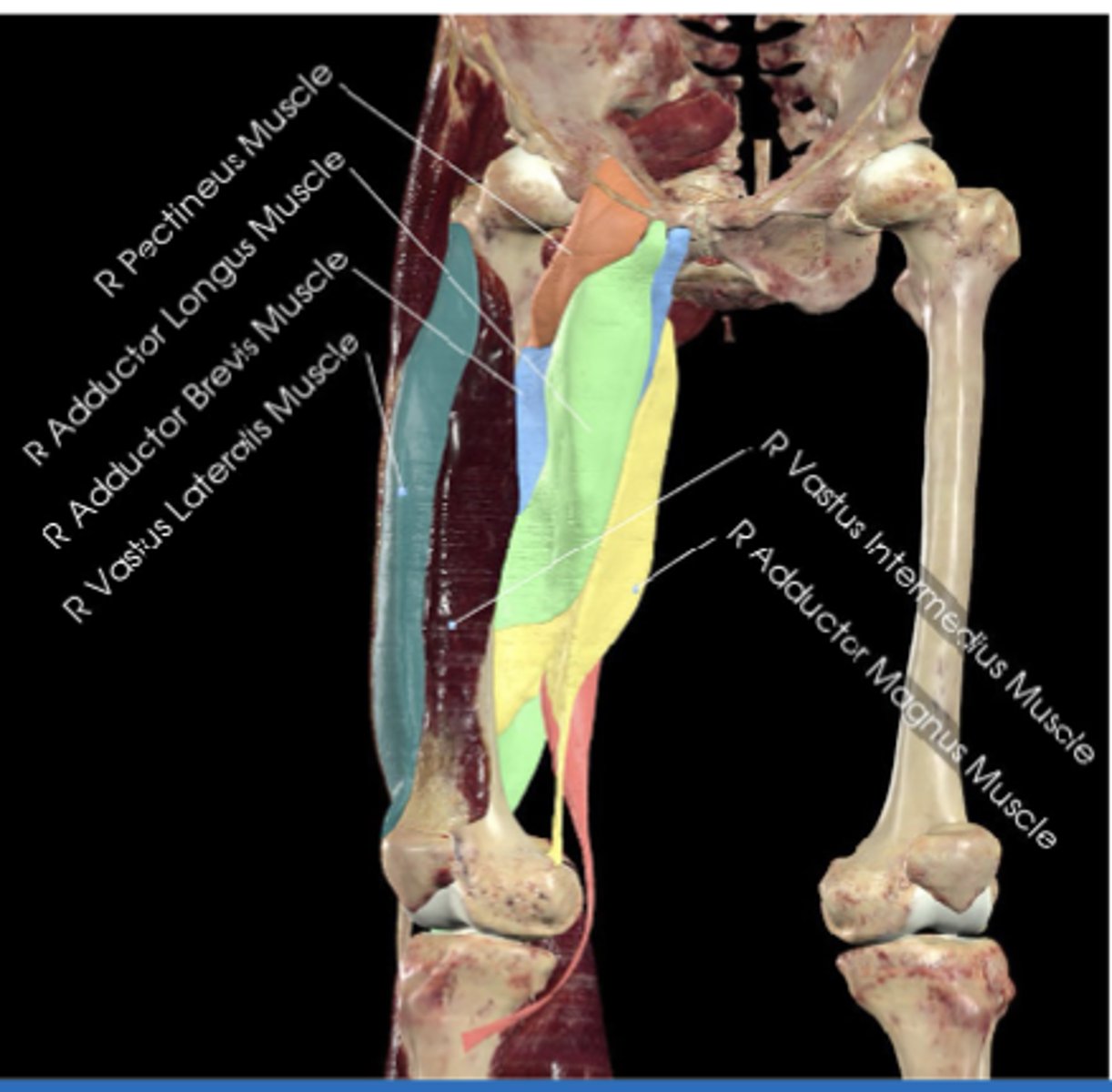
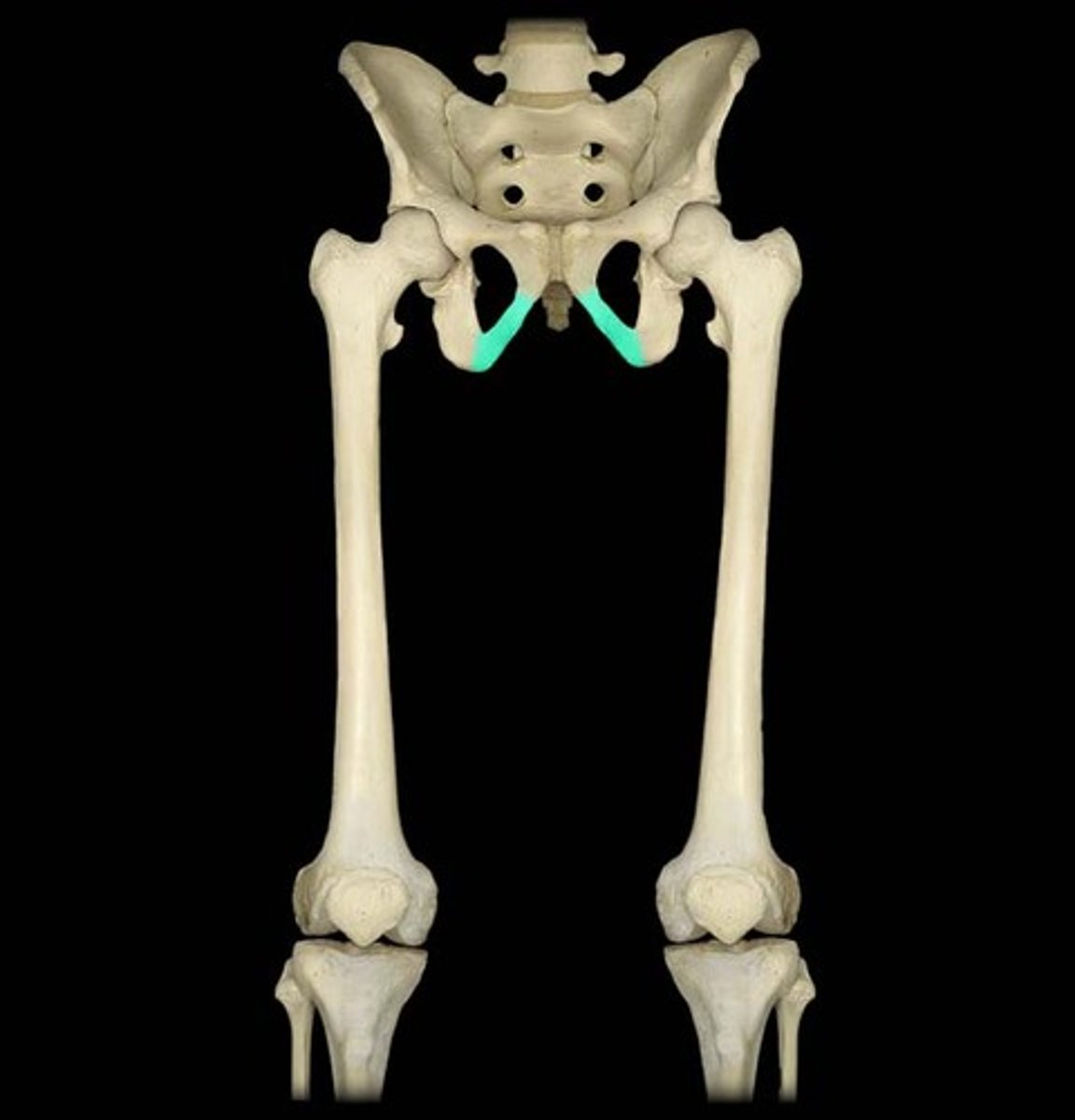
Superior pubic ramus (photo)
Pectineal line of femur
Pectineus muscle attachments (origin (photo) and insertion)
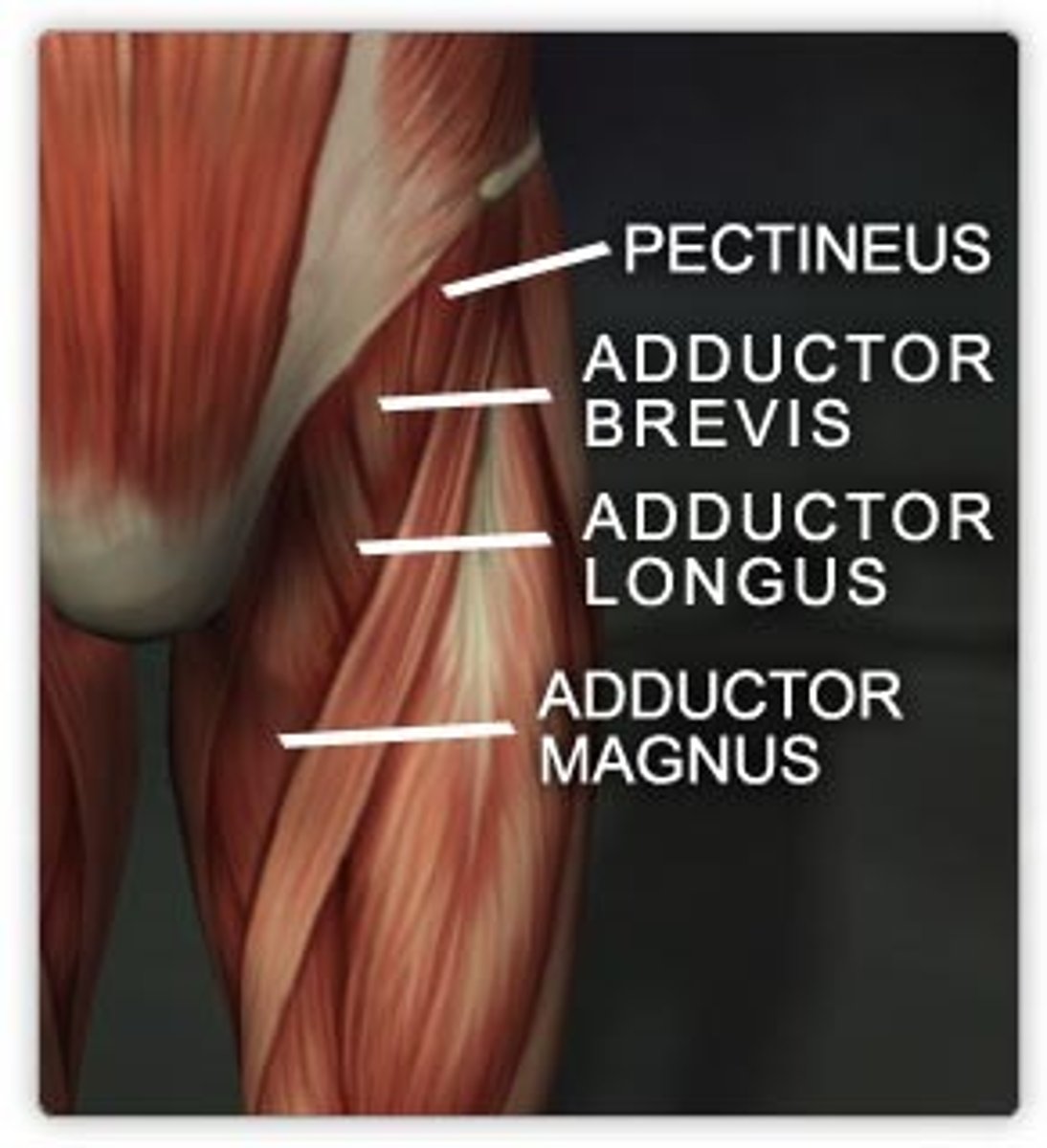
Adductor longus
Adducts thigh, assists with medial rotation (green)
Pubic body
Linea aspera of femus
Adductor longus attachments (origin and insertion)
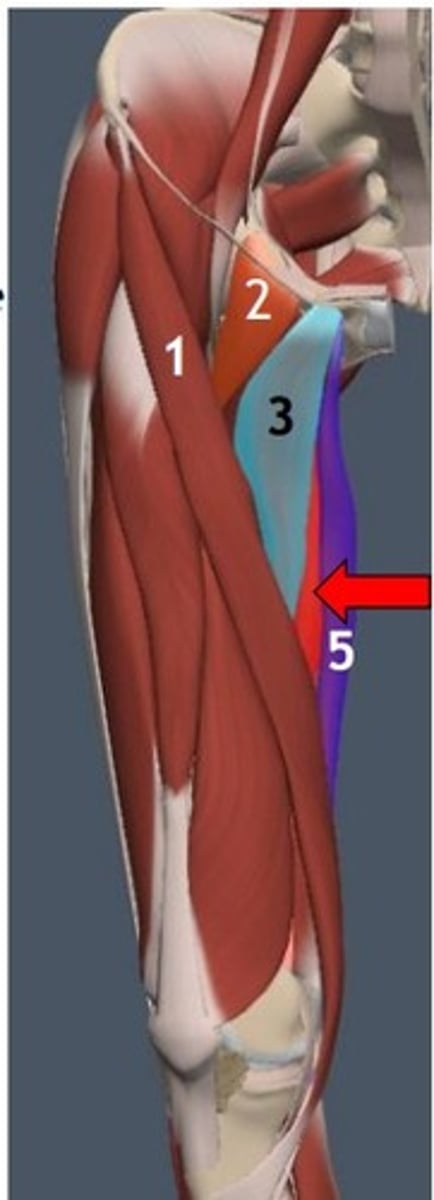
Adductor longus
Thigh muscle commonly strained in sports
Adductor brevis
Adducts thigh, assists flexion at the hip (light blue)
Inferior pubic ramus
Linea aspera of femur
Adductor brevis attachments (origin and insertion)
Groin strain
Injury to the adductor brevis can mimic?
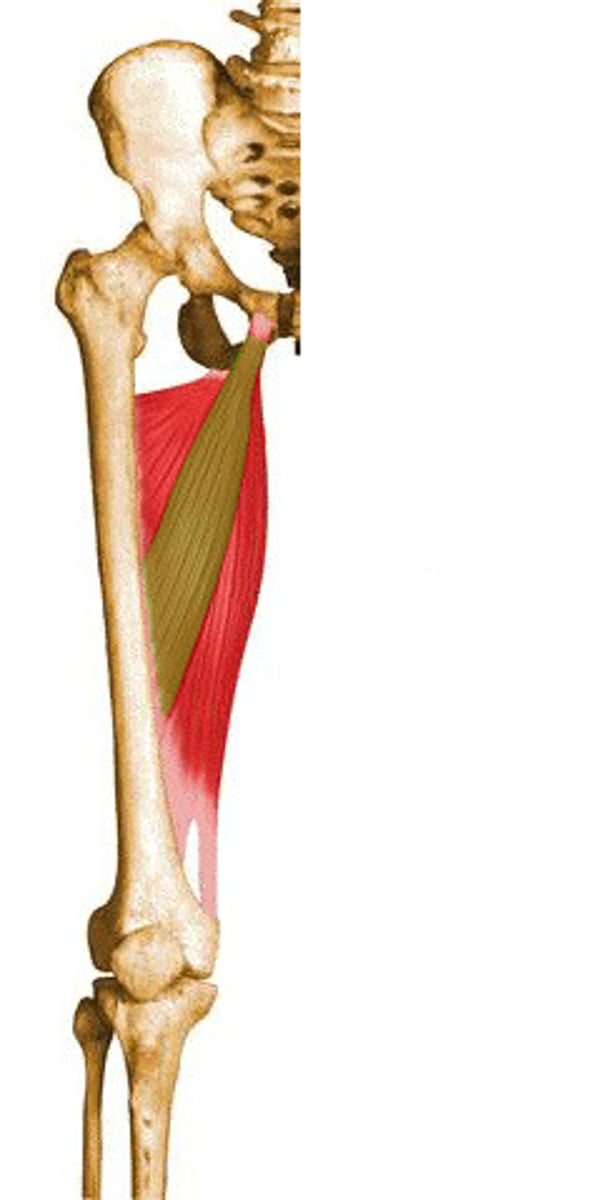
Adductor magnus
Powerful adductor, hamstring portion extends thigh (yellow)
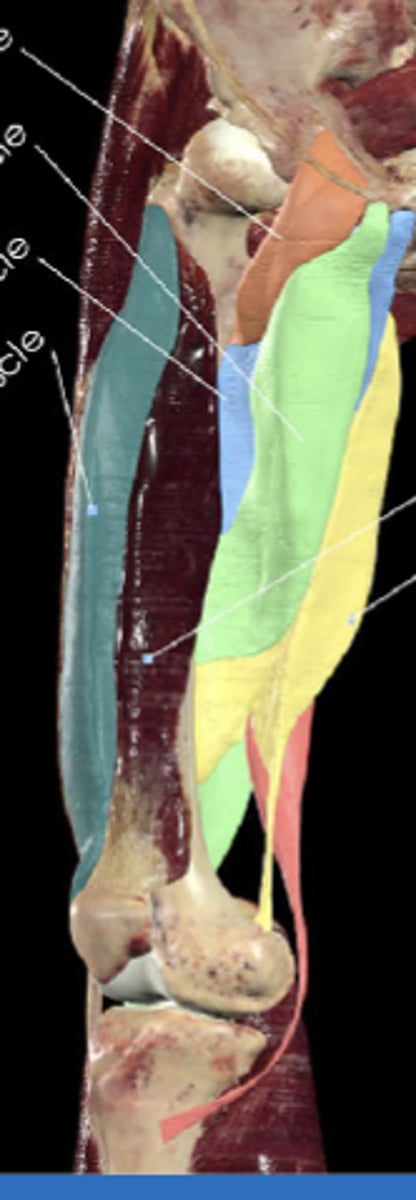
Pubic ramus and ischial tuberosity
Linea aspera
Adductor magnus attachments (origin (2) and insertion)
Adductor hiatus
Adductor magnus is a landmark for?
Gracilis muscle
Adducts thigh, flexes knee, assists medial rotation
Inferior pubic ramus
Medial tibia
Gracilis attachments (origin and insertion)
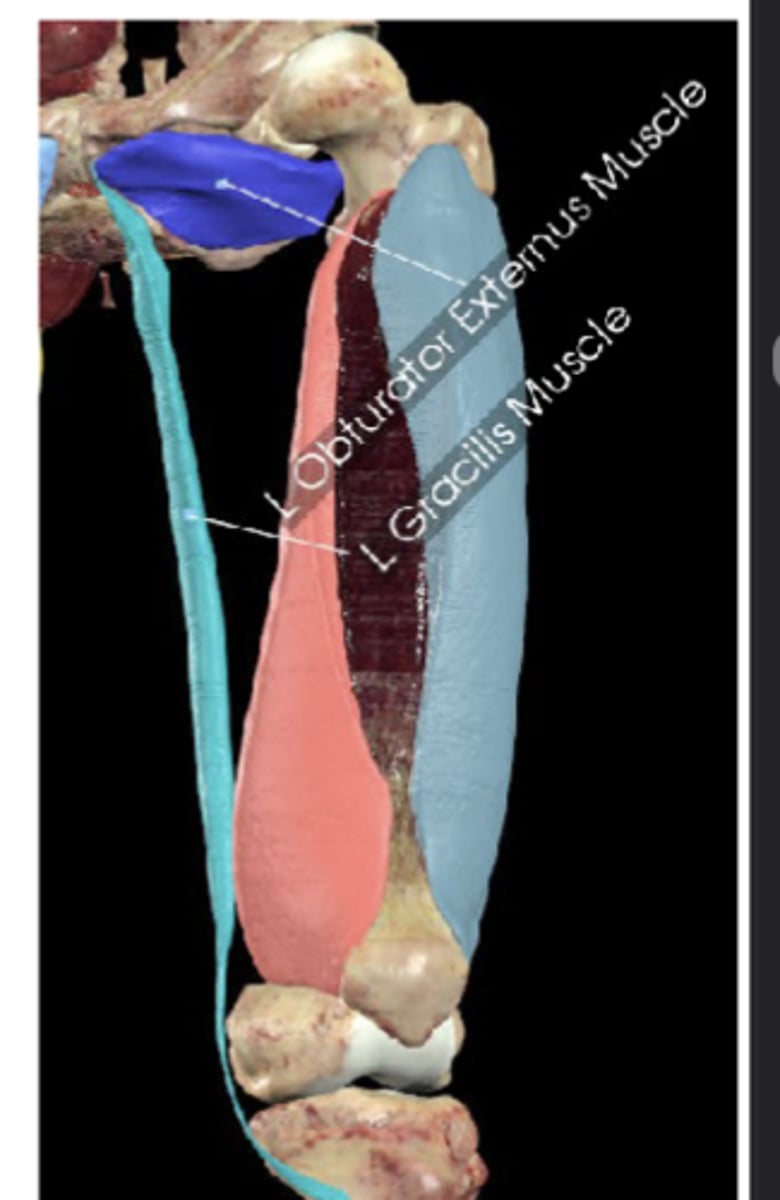
Obturator externus
Laterally rotates thigh, stabilizes femoral head
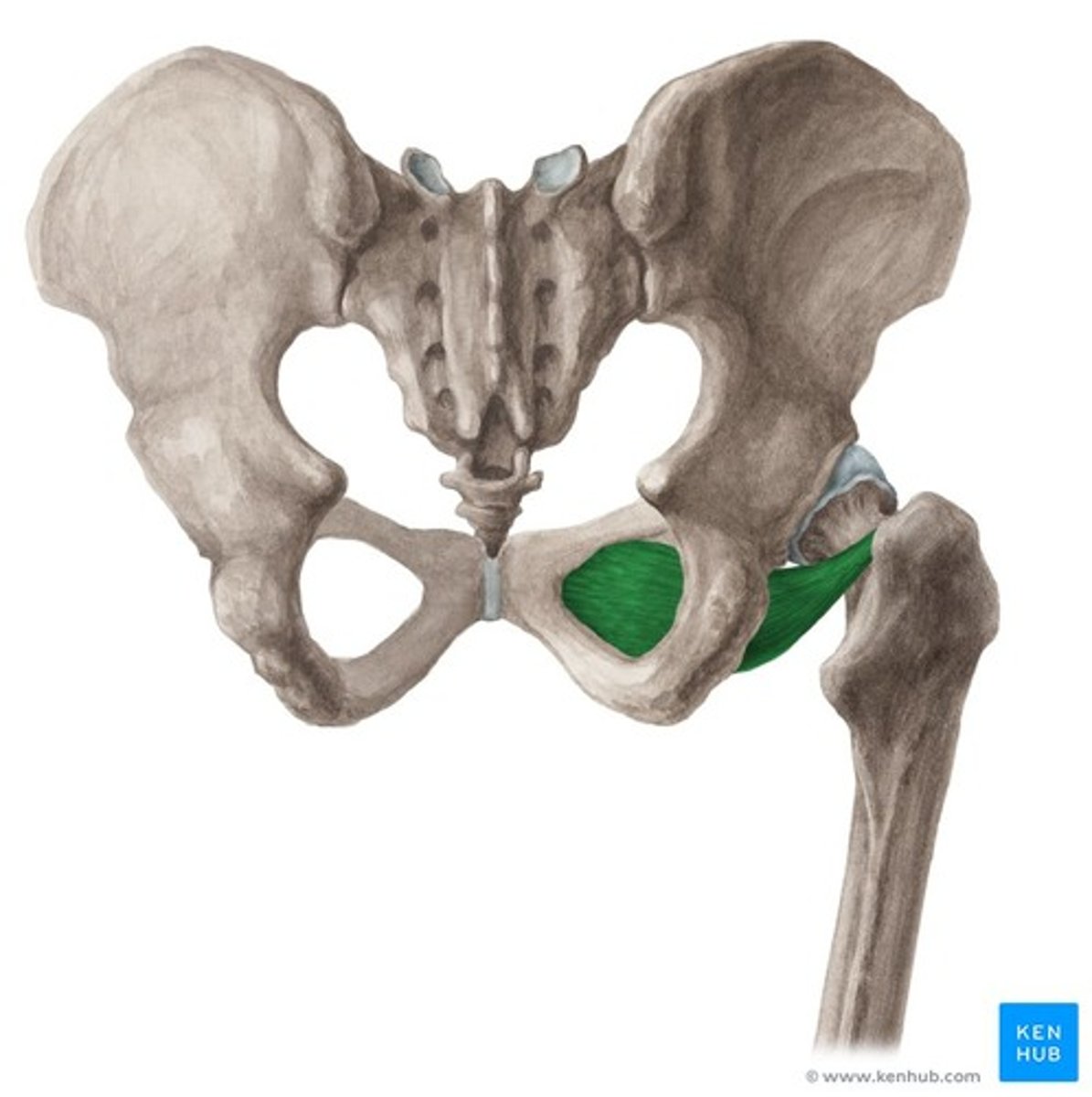
External obturator membrane
Trochanteric fossa of femur (photo)
Obturator externus attachments (origin and insertion (photo))
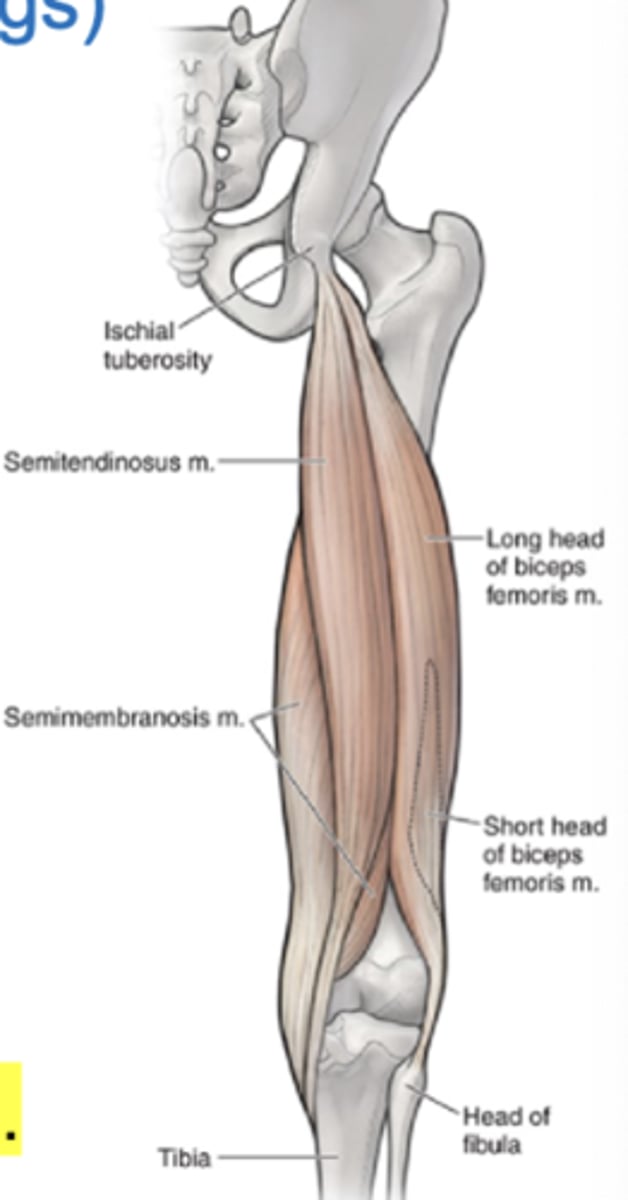
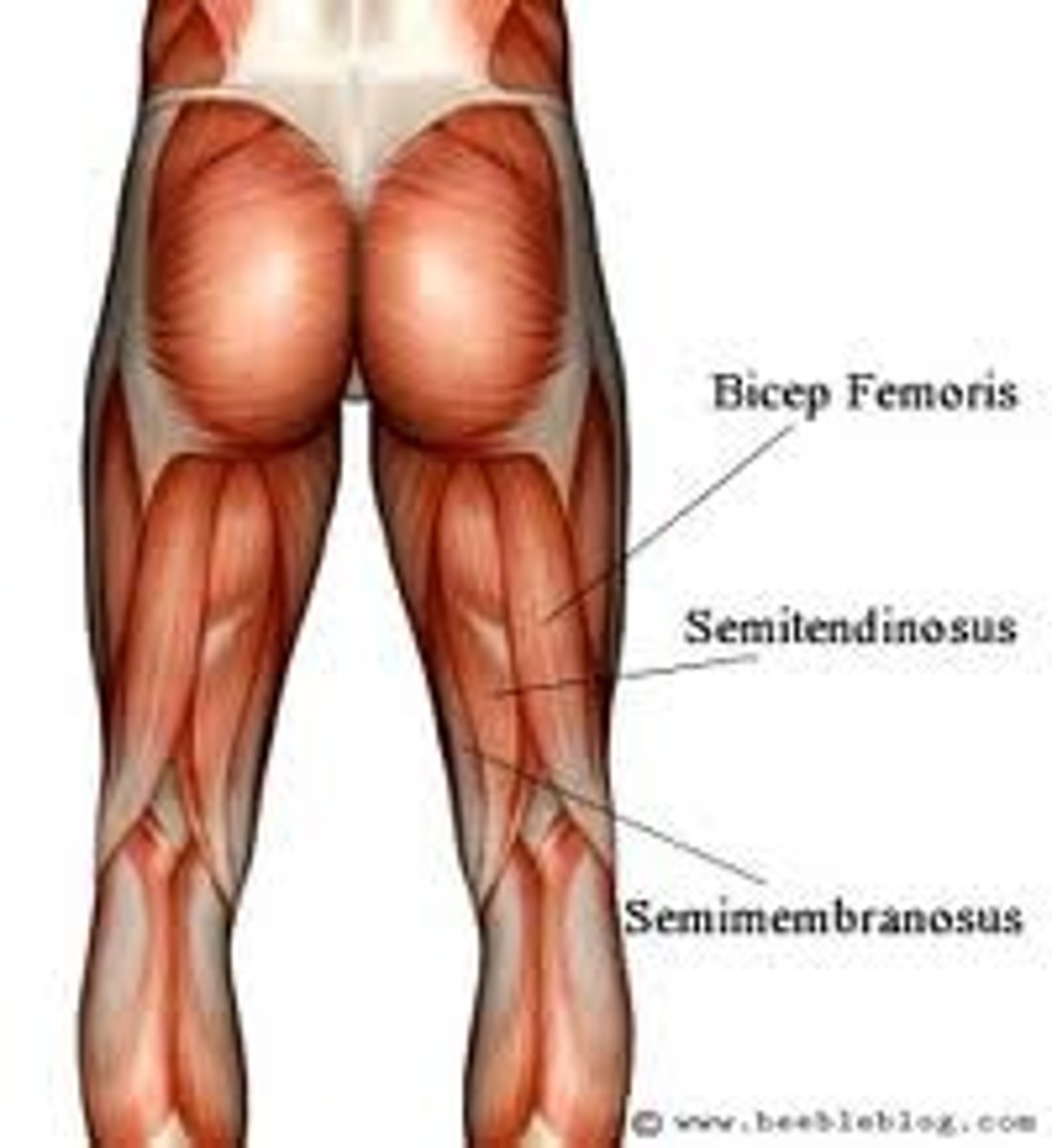
Hamstrings
Another name for posterior thigh muscles
Tibial branch of sciatic nerve
Innervation of the posterior thigh/hamstrings
Hip extension and knee flexion
2 Main functions of the posterior thigh/hamstrings pertaining to the hip and knee
False, very common
T/F: hamstring strains are uncommon in athletes
Biceps femoris
Anatomy
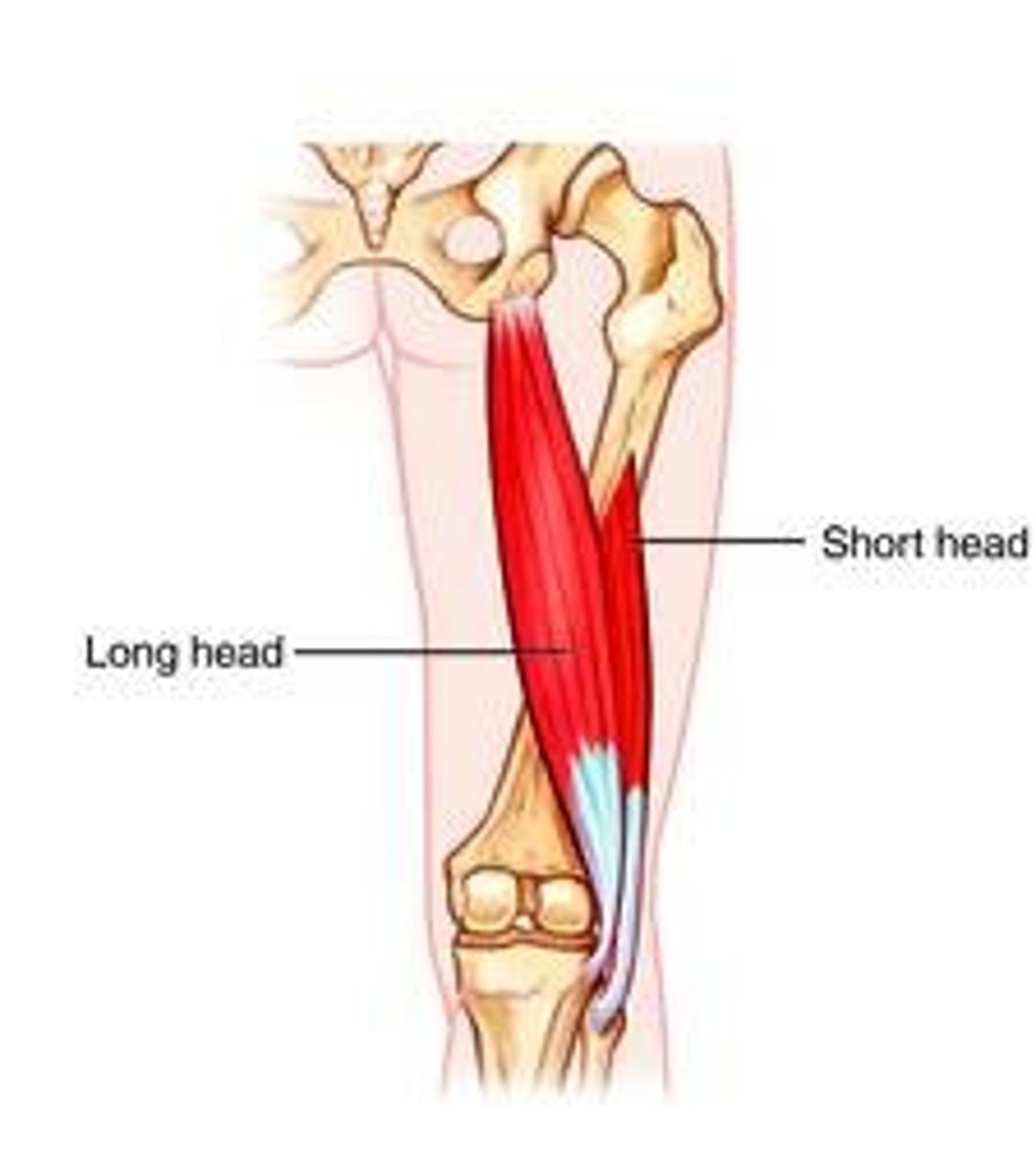
Long head: ischial tuberosity and fibular head
Short head: linea aspera and fibular head
Long head vs. short head of the biceps femoris attachments (origin and insertion)
Knee
Hip
Leg
Biceps femoris flexes ___, extends ___, laterally rotates ___
Tibial nerve
Fibular nerve
Biceps femoris long head vs. short head innervation
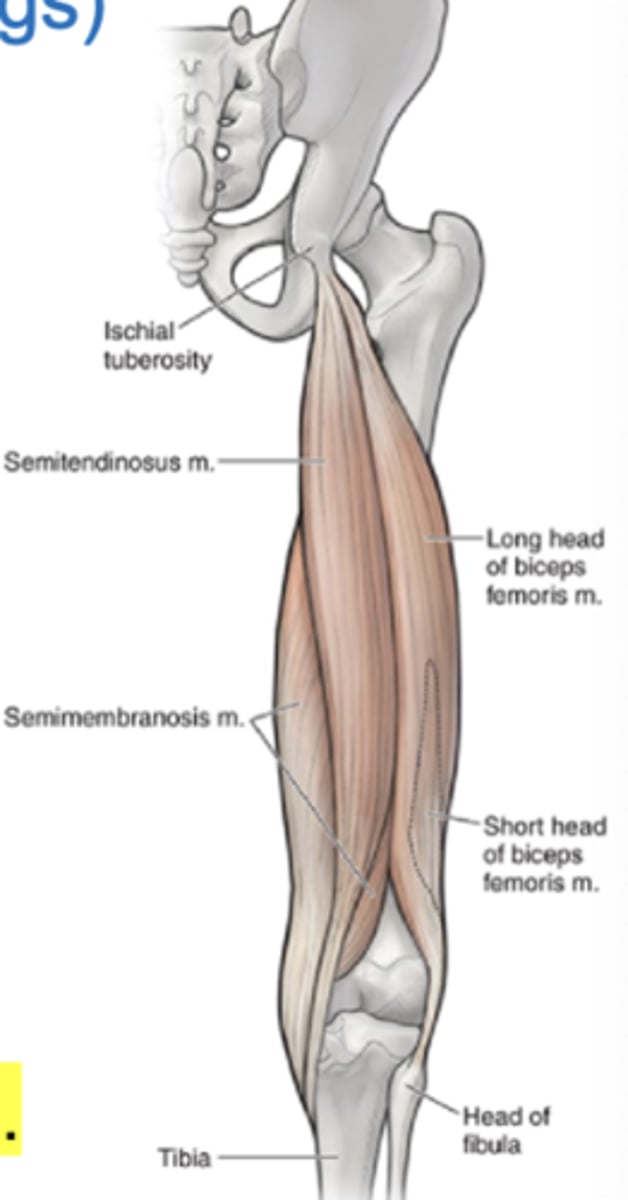
Semitendinosus hamstring muscle
Hamstring muscle that extends hip, flexes knee, medially rotates leg
Semimenbranosus
Injury may mimic medial meniscus pathology
Ischial tuberosity and posterior medial tibial condyle
Attachments (origin and insertion) of semimembranosus
inguinal ligament, satorius (lateral), adductor longus (medial)
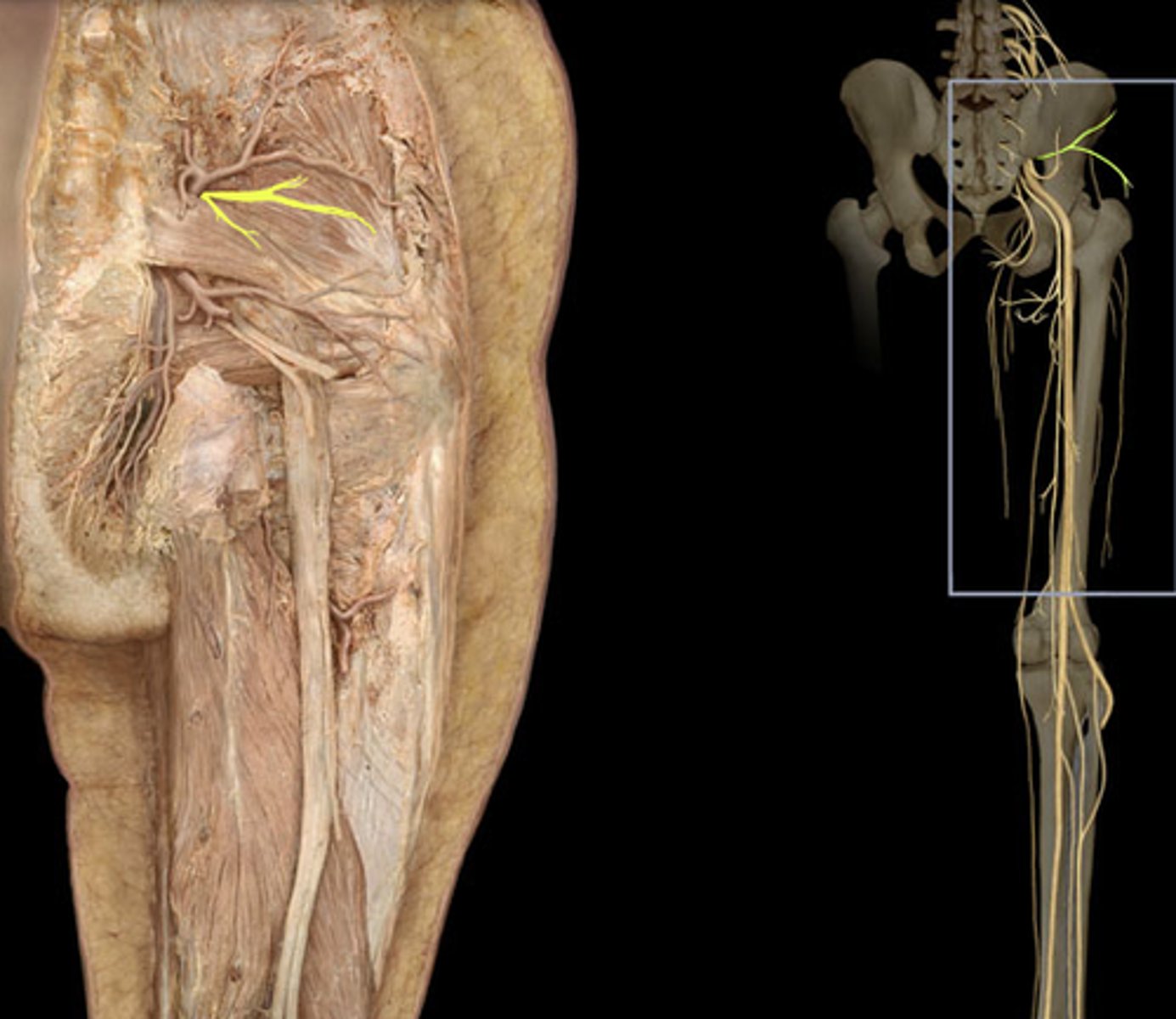
3 borders of the femoral triangle (superior, lateral, medial)
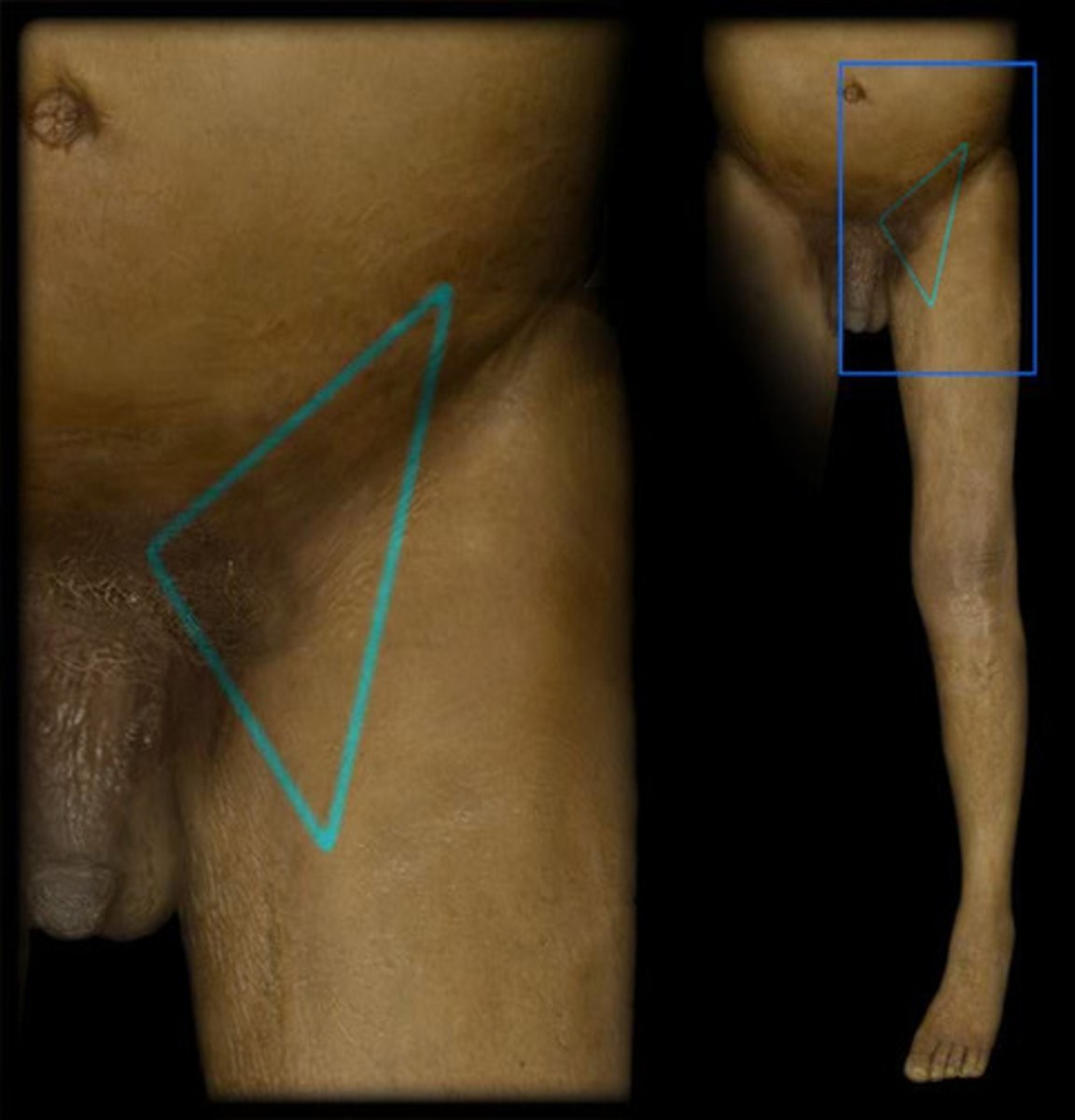
Femoral nerve, artery, vein, lymphatics
The femoral triangle contains which nerve, artery, vein?
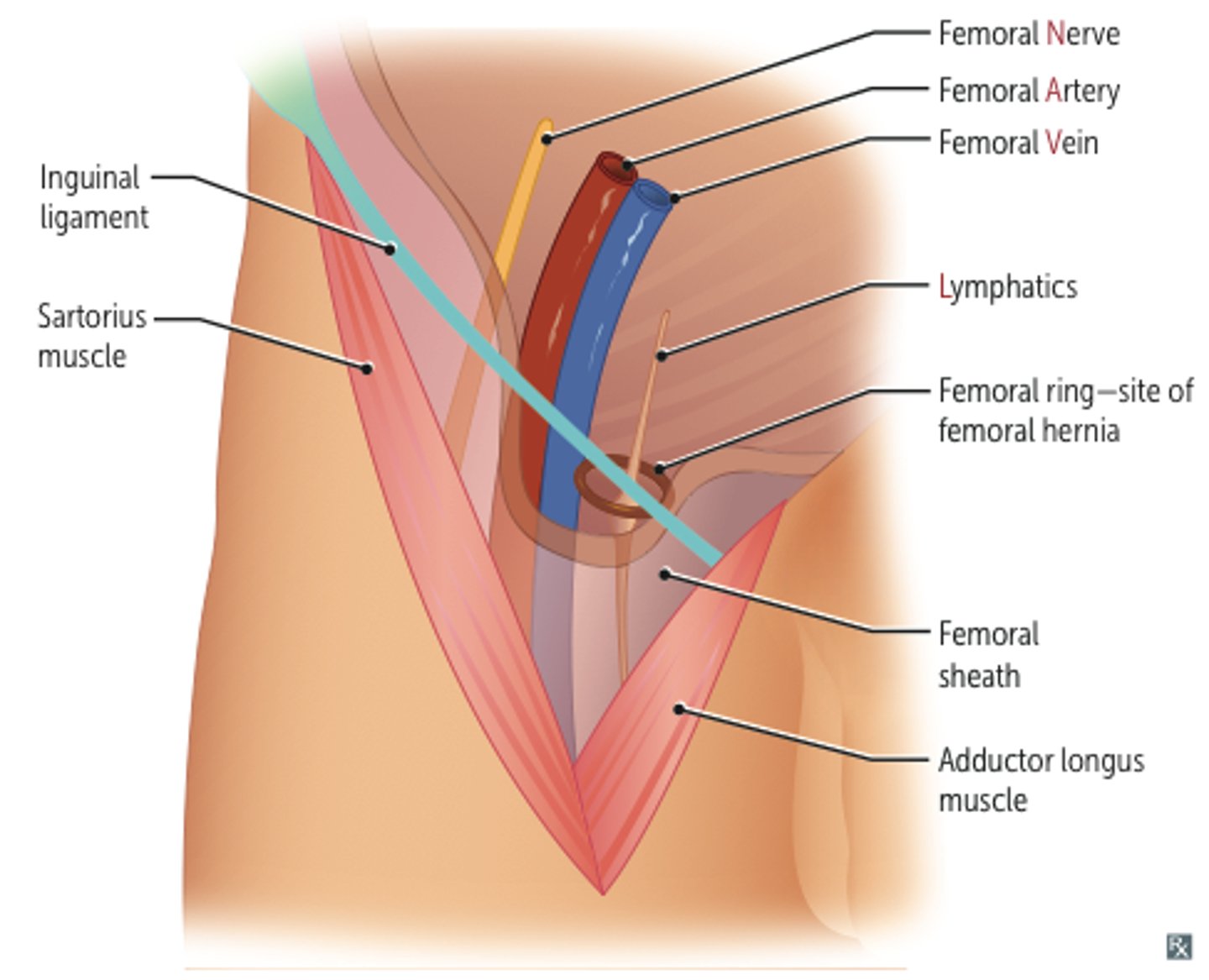
Women
Femoral hernias protrude through the femoral triangle, which is more common in (men, women)